
The Role of Work Motivation as Moderator in the Relationship
between Training and Job Performance: A Study in Regional
Hospital in West Sumatra Province
Harif Amali Rivai
1
, Hendra Lukito
1
and Atikah Rahmi Fauzi
1
1
Faculty of Economics, Universitas Andalas, Padang -Indonesia
Keywords: Work Motivation, Training, Job Performance
Abstract: This research aimed to exam impact of training on job performance by considering work motivation as
moderating variable. There were four regional hospitals in West Sumatra Province involved in the survey.
The data drawn from 174 nurses who work as permanent worker in regional hospital. The data analysed
using SPSS 2.0. Testing hypotheses was conducted using moderated regression analysis to prove the rolel of
moderating variable. The findings supported that training positively significant influenced on job
performance. Work motivation was found as significant direct determinant of job performance. Further,
effect of training on job performance contingent on work motivation. The study concluded that work
motivation functions as moderating variable in the relationship between training and job performance.
Implications of the research were also discussed in the paper.
1 INTRODUCTION
In today’s uncertain condition of business
environment, any organization should attempt to
strengthen human capital to reach its competitive
advantages. Increasing level of level competition
and technological advance demand business to
manage effectively human resource. It is expected to
proceed organizational superior performance. Job
performance of employees is an essential issue for
any organization and it refers to whether an
employee does his job well or not. Job performance
reflects outcome of employee’s attitude and
behavior in the work place. Therefore employee’s
performance can be key success of organizations.
Managing human resources is the key tool to
improve the level of employees’ job performance.
Understanding factors determining job
performance is important, mainly from employee’s
perspective. Employer might increase subordinate
performance by paying attention on employee’s
motivation and giving opportunity to increase skills
through training and mentoring in the work place.
Lack of motivation might result in decreasing job
performance. In a similar vein, giving opportunity to
attend the training might increase employee’s
commitment which in turn improving job
performance. The role of motivation and training in
health-care industry (i.e. hospitals) seems to be
important to be analyzed due to the consequences of
those variables can be directly assessed by patient
or customer. In the case of lack of nurse’s
motivation, the nurses may not be excellent services
to patient, consequently patient dissatisfaction tend
to increase. Lack of nurse’s training may be
reflected from slowly respond to patient, even to
some extent inappropriate action might happen.
Rivai, H., Lukito, H. and Fauzi, A.
The Role of Work Motivation as Moderator in the Relationship between Training and Job Performance: A Study in Regional Hospital in West Sumatra Province.
DOI: 10.5220/0009501013411348
In Proceedings of the 1st Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science (UNICEES 2018), pages 1341-1348
ISBN: 978-989-758-432-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
1341

Organizations are reluctant to evaluate effect of
training programs due to lack of knowledge to
measure training effectiveness (Broad & Newstroom
1992). Arthur, Bennet & Bell (2003) supported that
training effectiveness can be measured from several
criteria: reaction, learning, and behavior criteria of
training participants. Gordon (1992, p.138) defines
training as “process to enhance employees’ skill,
knowledge and competency necessary to perform
effectively on job”. Training directly develops
individuals, which enhances organizational capacity
(Jacobson, Rubin, & Selden, 2002), and this
capacity, in turn, is linked to organizational
performance (Stavrou, Charalambous, & Spiliotis,
2007). Identified training need is important before
conducting training. By doing training need analysis
is expected to get greater benefit of the training. A
study conducted by Wiley (1997) in health care
industry noted that the managers need to understand
what motivates employees in order to increase
productivity. Relationship among motivation,
employee performance, and intention to quit in
health care industry have paid attention by scholars
(e.g.. Janssen et al., 1999, Levy-Leboyer, 1988,
Tzeng, 2002, Yildiz, 2009). Effort to improve
employee performance is frequently conducted by
setting up training program. Impact of training
programs on job performance might depend on level
of employee motivation. The higher level of
employee motivation, the greater impact of training
on job performance. Dongho (2006) argued that
motivation of employees might be determinant of
success or failure of an organization. Therefore, the
current study attempt to exam impact of training on
nurse’s job performance. The relationship of these
variables by taking into account training as
moderating.
2 THEORICAL FRAMEWORK
The Relation between Training and Job
Performance
The study conducted by Mia et al (2009) showed
there is relationship between training and
performance of teachers, then the training increased
their productivity. Training is believed to enhance
employee’s commitment which in turn might
increase performance. Therefore most companies
need to allocate training budget in order to increase
company performance (Tarawneh, 2009). In other
studies by Ghannam et al (2010) about relationship
between training and employee performance in
Palestine insurance. The training can enhance the
performance. Giving opportunity to students will
strengthen employee’s commitment.
Training and development of employee refers to
a systematic process of learning and development to
upgrade the effectiveness of a single worker, a
group, or an organization (Aguinis & Kraiger,
2008). Performance self-efficacy develops from
trainees’ beliefs about their abilities. This belief
system leads trainees to realize that they can use
learned skills on the job and, thereby, improve their
job performance. In addition, self-efficacy increases
trainees’ confidence in their ability to overcome the
obstacles that they face during skills transfer and to
use their new skills at work in order to perform
better. Research that conduct by Becker (1975)
defined General training is delivered to all employee
in order to improve performance. In contrast,
specific training is provided for specific purpose,
specific requirement, and selected participants.
Training relates to work-life balance programs might
enhance performance by attracting and retaining
high quality employees, by reducing the extent to
which work life conflicts interfere with work.
(Greenhaus and Parasuraman, 1999; Lobel and
Kossek, 1996; Lobel 1999).
H1 : Training is positively influence job
performance
The Relation between Work Motivation and Job
Performance
Motivation can be considered as a variable
contribute to enhance performance of employee.
Motivation to perform a job can be viewed as
intrinsic and extrinsic motivation. A study conducted
by Deci and Ryan (2000) noted that intrinsic
motivation brings positive effect in order to increase
creativity. Relationships among motivation and
other variables have been demonstrated in previous
studies, for instance associates with creativity (Deci
& Ryan, 2000), job satisfaction and well-being
(Ilardi, Leone, Kasser, & Ryan, 1993; Shirom,
Westman, & Melamed, 1999), organizational
citizenship behavior (Bolino, 1999), and affective
commitment (Eby, Freeman, Rush, & Lance, 1999).
Employee might intrinsically be motivated thought
they encounter obstacles and challenges (Utman,
1997). Feedback from manager is needed to enhance
employee development through learning program.
The program can be perceived as support of
organization towards employee. Motivation is a
short of inner energy that drive individual behaviour.
Motivation is a driver of causal behaviour that make
individual to take action (Chaudhary & Sharma,
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
1342
2012). According to Said et al (2015) employee
motivation is related to willingness individuals to
fulfil their needs. This concept refers to Maslow’s
hierarchy of needs. This need will lead the
individual to perform batter in their career in the
simple they can perform in their job performance.
Performance can be on their customers, salary or
others. Chaudhary and Sharma (2012) argued that
employee with high motivation tend to have higher
productivity than low motivation. Motivation might
be linked to satisfaction which makes them happy, it
will result in enhancing productivity. A highly
motivated employee attempts to demonstrate good
responsibility for their jobs. Employee with good job
performance will result in increasing value to the
organization. The issues about employee motivation
frequently associates with perceived job satisfaction
and employee well-being (Bogdanova &
Naunivska,2008).
A motivated person demonstrates his or her
strong effort to achieve organization goals with the
best way (Owusu,2012). Employee with high level
motivation shown the best fit individuals by
resulting in good outcomes (i.e. performance) which
in turn achieving organizational goals. Motivated
workers are likely to affect increasing job
performance. Therefore, attempts to increase job
performance can be taken into account by increasing
employee motivation. The the hypotheses can be
proposed:
H2 : Motivation is positively influence job
performance
Work Motivation as Moderator
Training is defined as the organized activity aimed
at imparting information or instructions to improve
the recipient’s performance. (Saeed et al, 2012).
Training can be said as effort to improve level of
knowledge or skill by giving opportunity to
employee to participate. Employees motivations are
increased when the organization empower them.
When they are empowered, then they did well.
Kreitner (1995) describes the psychological way that
gives the purpose and direction to behaviour.
Training can be directly to link with job
performance because it is likely to enhance the
knowledge towards the job. It also increases the
efficiency of work and contributes to the success of
organization. Importance of training cannot be
neglected in any organization worldwide. By
participating in training employees become more
efficient in their jobs and they are likely to give
better results. Deficiencies and discrepancies are
identified first and with the help of training
programs employees become able to do work well.
By introducing more training programs in the
organization employees perceive organization
providing opportunity to increase knowledge and
skill. Training affects the performance positively
only when organization found appropriate personnel.
It is a set of energetic forces that originate inside the
persons to initiate behavior and to determine the
direction, intensity, form and duration. Motivation is
the willingness to exert high levels of effort to reach
organizational goals, conditioned by the effort's
ability to satisfy some individual need. Motivation
has a significant importance on the performance of
employees. But if the right person for the right job is
not selected then motivation will be having no effect
or zero effect on employee’s job performance.
The studies by Roos and Van Eeden (2013) and
Soliha et al (2014) have been considered motivation
as a moderating variable to explain whether
motivation can strengthen relationship between
training and job performance. Then, the hypothesis
can be proposed:
H3 : The relationship between training and job
performance is positively moderated by work
motivation
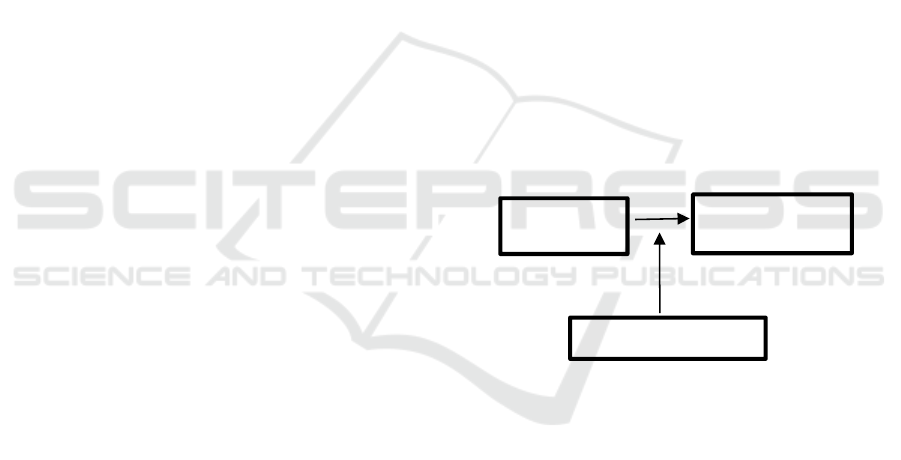
Figure 1: Theorical Framework
3 RESEARCH METHOD
The design of this study uses a quantitative approach
to the type of survey research. The survey was
conducted in Regional Hospitals in West Sumatra
Province. There were four hospitals involved in the
this research with total number of respondents is 174
nurses. The data was analysed by using SPSS 20
includes analysis of the respondent’s characteristic.
Measurement variable of training consisted of 15
items of 5 point likert scale which was adapted from
Khanfar (2014). Job performance as dependent
variable was measured using 22 items with 5 point
likert scale. The instrument was adapted from Al-
Homayan, Samsuddin and Islam (2013). Work
T
ra
i
n
i
ng
J
o
b
Performance
W
or
k
M
ot
i
vat
i
on
The Role of Work Motivation as Moderator in the Relationship between Training and Job Performance: A Study in Regional Hospital in
West Sumatra Province
1343

Motivation as moderator variable instrument was
adapted from Negarandeh & Ghasemi (2015)
consists of 17 items. All research instruments using
5 point Likert Scale (1= strongly disagree, 2=
disagree, 3= neutral, 4= agree, and 5= strongly
agree). Checking for data entry also was conducted
before data enters in subsequent analysis.
4 ANALYSIS
Testing the hypotheses was conducted by using
moderated regression analysis. It began from
checking for data entry. The reliability of each
construct was assessed using cronbach alpha. Hair et
al. (1998) suggested that usual lower limit for
Cronbach alpha is .70, but in exploratory research
this limit may decrease to .60). The constructs of
training, work motivation, and job performance
demonstrated good reliability. The psychometric
properties of variables are reported in Table 1.
Table 1 The Psychometric Properties of Variables
Variable 1 2 3
Cron
bach Mean SD
Training
(1)
-
.
811
3.94 .46
Work
Motivati
on (2)
.46
8**
- .
785
3.85 .59
Job
Perform
ance (3)
.35
3**
.442* -
886
3.72 .64
Further, this research is also aimed to exam the
impact of moderating variable (i..e. work
motivation) between training and job performance. It
is purported to asses the interaction effect of
moderating variable.
Table 2: F-test for overall model
R R-
Square
F Significan
t
.332 .164 5.088 0.01
F Test aims to know the impact of independent
variables (include moderating variable) in overall
toward dependent variable. The result indicates that
overall independent variables have impact on
dependent variable.
Table 3: Regression Analysis
Variable
a
Job Performance
Model 1 Model 2 Model 3
Step 1: Training
(T)
.116** .124* .174**
Step 2: Main
Effect of Work
Motivation
(WM)
.225** .155*
Step 3:
Interaction
Training x
Work
Motivation
(T*WM)
.311**
Overall F 1.156 2.334** 5.088**
R ² .021 .065 .164
F Change 1.178** 2.754**
R ² Change .044 .099
Note: N = 174. Entries are standardized regression
coefficients.
a
Variables are standardize.
* p ≤ .05. ** p ≤ .01
In order to test the interaction effects of training
and work motivation, regression analysis was
conducted with three steps (Table 3). Multiplicative
terms for the standardized independent variables
were created, as suggested by Cohen and Cohen
(1983). Then, the standardized independent variables
were included into the equation in three steps. Step
1, regression equations were computed by entering
independent variable in the regression analysis, then
step 2, it was followed by moderator variable.
Finally, interaction effect of independent variable
and moderator variable was computed in step 3 (see
table 2). In the step 2, regression showed the
incremental variance accounted for by interaction
effect of training and work motivation was
significant forjob performance ( ∆ F=2.754, p ≤
.01). The results supported that job performance
significantly influenced on work motivation.
Training are found significantly influence on job
performance. The finding also supports that work
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
1344

motivation significantly moderates relationship
between training and job performance.
5 RESULTS
In this research, there are 200 questionnaires
distributed in the hospitals, however there were 174
returned questionnaires. There were173
questionnaires are proceeding in to the next process
(respond rate 86,5 %). The summary of
respondent’s characteristics was in the Table 4.
Table 4: Respondents Characteristic
Characteristics Result
Gender Female (85,5%)
Education Background Diploma III (53,8%)
Age >35 (38,7%)
Marital Status Married (83,8%)
Employment Status Civil Servant (65,3%)
Working Experience 6-10 years (31,8%)
Income/Month 2.000.000-4.000.000
(42,2%)
Ever Taken Training
or Not
Taken (95,4%)
Training Match or Not Match (97,1%)
Numbers of Training <3 times (44,5%)
Type of Training Skill for Nurses
(69,4%)
Benefit of Training Useful (60,1%)
6 DISCUSSION
The Effect of Training on Job Performance
Testing of the hypothesis found that training has
positive relationship to job performance. Impact of
training can improve employee’s performance
towards the job. This research indicated that training
increases the job performance. Training also aims to
increase the professional knowledge to accomplish
the jobs. The training is purported to improve
behavioral aspects of employee to increase
effectiveness working with groups or teams (Abu
Snenah and Al Farisy, 2003, p. 201).
Training is needed to increase employee
performance. In the case of health-care industry
(e.g. hospital), role of training is crucial to improve
nurse’s skill. The finding noted that the nurses who
have obtained the training would feel the training
was match with their current job and it could
increase their ability. It can be concluded that the
more frequent nurses get training, the more they get
new skills and get developed. Lack of training of
nurse might result in low level competency which in
turn affects the performance. The nurses in a
hospital does not stay in one unit. They often rotate
to other units in the hospital. For example in
emergency unit, not all nurses that rotate can get this
position except nurses that have been trained in
emergency training. To some extent only nurses
with high skill can get particular unit (e.g. operation
room) because the position needs specific skills and
high risk for the patient. Employee training and
development refers to a systematic process of
learning and development to upgrade the
effectiveness of a single worker, a group, or an
organization (Aguinis & Kraiger, 2009). The result
of current study consistent with study conducted by
Mia et al (2009). Their study in the context
educational industry noted that impact of training
able to improve teacher’s performance and
productivity. Ghannam et al (2010) also supported
effect of training and job performance is exist. The
employees obtained training would also demonstrate
higher level the organizational commitment.
Employees motivations are increase when the
organization able to empower them.
The Effect of Work Motivation on Job
Performance
An examination relationship between work
motivation and job performance found that work
motivation significantly influenced on job
performance. Motivation is internal power that
energize worker to behave. According to Chaudhary
& Sharma (2012), motivation is internal energy that
drive workers to take action. Work motivation is the
process that includes individual’s intensity, direction
and persistence of effort in order to achieve the goal.
Workers can be intrinsically motivated by
demonstrating persistence when encountering
obstacles and challenges (Utman, 1997), and they
will devote greatertime and attention to accomplish
jobs (Deci & Ryan, 2000; Hackman & Oldham,
1980). It should enhance his or her job skills.
Employee with high motivation tend utilize
feedback from supervisor to improve learning and
future development. It can argue that motivation
determines how much efforts of the nurses to
increase their job performance which in turn lead to
a successful service of a hospital.
The Role of Work Motivation as Moderator in the Relationship between Training and Job Performance: A Study in Regional Hospital in
West Sumatra Province
1345

The current finding strengthen that employees
with high level of motivation lead to better job
performance. Chaudhary and Sharma (2012) argued
that the higher level of employee motivation, the
more productive the workers. The situation might be
linked to feeling satisfisfaction and happy of the
workers. The current finding noted there is direct
effect of employee motivation on job performance.
It is in line with study conducted by Chaudhary and
Sharma (2012) that argued employees with high
level motivation frequently attempts to accomplish
every aspect in their duties. Increasing job
performances would lead to higher productivity of
organizations.
Work Motivation as Moderator between training
and job performance
The result of testing hypotheses supported the role
of work motivation can be moderator between
training and job performance. The effects of training
on employee’s job performance demonstrated that
training able to increase job performance.
Nevertheless, the impact might contingent on level
of work motivation. The greater level of employee
work motivation would lead to higher job
performance. Employees with low level work
motivation would lead to increase job performance,
however the impact will be greater when the
employee have higher level of work motivation. It
also increases the efficiency of work and contributes
to the success of organization. Importance of
training cannot be neglected in any organization
worldwide. Training is efforts to enhance employee
skill and knowledge in order to improve
productivity. The recent finding notes that work
motivation functions as strenghtening effect of
training on job performance. The motivation is
needed to increase job performance of nurses who
obtained the training. Effect of training on job
performance contingents on work motivation.
Worker with high level motivation will demonstrate
stronger effect of training on job performance than
worker with low level motivation. Training helps
nurses to understand their duties and responsibilities
while improving technical and managerial skills.
The hospital also send a message that the
organization values progress, both in organizational
achievements as well in the careers of its people,
especially nurses. This can be the way of the
hospital to appreciate nurses. By this way the nurses
feel their hard-work is appreciated by the hospital.
Nurses who have obtained training can effectively
do their job and increase their job performance. By
giving training for the nurses, they will get ready
things on track to increase work quality and
incomes.
7 CONCLUSIONS
This research is a quantitative research using
primary and secondary source of data to exam the
role of work motivation as a moderator between
training and job performance. The surveys were
aimed to nurses in regional hospital in West Sumatra
Province. The result indicates that training positively
impacted on job performance. It is happened
because most of the nurses already taken training.
The training able to improve the nurses’ skills which
directly affected on their job performance. Further,
the result indicated that work motivation positively
influenced on job performance. Many factors
contribute to work motivation of nurses included
basic salary. The result indicated that the effect of
training on job performance will depend on the level
of employee’s motivation. It can be argued that work
motivation is needed to enhance job performance of
nurses after they get training. In general, work
motivation and training significantly impact on
enhancing job performance of nurses. The research
provides several implications for improvement of
better understanding job performance of nurses. To
increase job performance of nurses the hospital have
to increase the frequency of training, especially for
nurses. In order to make the training become
effective, the management have to allocate budget
for employees that will be trained or to held a
training in the hospital. There are some implications
of this research regarding effort to improve
performance. First, conducting training needs
analysis to find the need of training. Choosing
candidate that will be trained also have impact that
will make training become effective, candidate that
will be trained have to match with her/his abilities.
Second, the need of the training that suitable with
job and abilities of each trainee. Lastly, the hospital
have to evaluate the nurses after they get trained. By
evaluating the training programs, the hospital
management could measure whether the training
effective or not and also to evaluate the performance
of nurses after getting training.
Work motivation have direct influence on job
performance, meanwhile work motivation as
moderating variable did not have influence on job
performance. Work motivation of nurses can be
influenced by source of motivation where it is
internal and external. Intrinsic motivation such as
opportunity for growth, responsibility, achievement
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
1346

and recognition. Extrinsic motivation such as job
security, salary, working conditions and company
benefits. Both intrinsic and extrinsic motivation can
be controlled by hospital, for example like create a
comfortable workplace for nurses, giving
compliance when the nurses achieve something and
fully responsible to their job, increase their salary,
create more opportunity to promote them self to
higher position in hospital and giving reward for
nurses that have high achievement
REFERENCES
Aguinis, H. & Kraiger, K. (2008). Benefit of Training and
Development for Individual and Teams,
Organizations and Society. Annual Review of
Psychology 60 (1): 451-474
Al-Homayan et al. (2013). Impacts of Job Performance
Level of Nurses in Public Sector Hospitals.
American Journal of Applied Sciences. 10 (9):
1115-1123, 2013
Arthur, W., Bennett, W., Edens, P.S., & Bell, S.T. (2003),
Effectiveness of training in organizations: a meta-
analysis of design and evaluation features. Journal
of Applied Psychology, Vol. 88 No.2, pp.234-45.
Bogdanova, A., Enfors, H., & Naumovska, S. (2008).
Work environment stressors-The link between
employees’ well-being and job performance?
Bachelor dissertation, Jönköping University.
Becker. (1975). Does Training Generally Work? The
Returns to In-Company Training: Industrial and
labor Relation Review, Vol. 54, No. 3. Cornell
University.
Bolino, M. C. (1999). Citizenship behavior and impression
management: Good soldiers or good actors?
Academy of Management Review, 24, 82-98
Broad, L.M. and Newstrom, W.J. (1992). Transfer of
Training. New York.
Chaudhary.N., & Sharma. B (2012). Impact of Employee
Motivation on Performance (Productivity). In
Private Organization. International Journal of
Business Trends and Technology, Vol 2, Issue 4-
2012.
Dongho, K. (2006). Employee motivation: Just ask your
employees. Seoul Journal of Business, Vol. 12,
No. 1, pp. 19-35.
Eby, L. T., Freeman, D. M., Rush, M. C., & Lance, C. E.
(1999). Motivational bases of affective
organizational commitment: a partial test of an
integrative theoretical model. Journal of
Occupational and Organizational Psychology, 72,
463–483.
Ghannam. (2010). The impact of training on the
performance of employees in the insurance sector
of the Palestinian. Unpublished research, An-
Najah University, Nablus, Palestine.
Gordon, B. (1992). Are Canadian firams under investing
in training? Canadian Business Economics, Vol 1,
No 1, 25–33.
Greenhaus, J.H., & Parasuraman, S. (1999). Research on
work, family and gender: current status and future
directions. In G.N. Powell (Ed.). Handbook of
gender and work. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Hackman, J. R., & Oldham, G. R. (1980). Work redesign.
Reading, MA: Addison- Wesley.
Hair, Josep F. Anderson, Tatham, (1998). Multivariate
Data Analysis With Readings, 3rd Edition. New
York: Mcmilan Publishing Company.
Ilardi, B. C., Leone, D., Kasser, R., & Ryan, R. M.
(1993). Employee and supervisor ratings of
motivation: Main effects and discrepancies
associated with job satisfaction and adjustment in
a factory settiournal of Applied Social Psychology,
23, 1789-1805.
Jacobson, W., Rubin, E., & Selden, S. (2002). Examining
training in large municipalities: Linking individual
and organizational training needs. Public
Personnel Management, 31(4), 485-506.
Janssen PPM., De Jonge J., Bakker AB. (1999). Specific
determinants of intrinsic work motivation,
burnout, and turnover intentions: a study among
nurses. Journal of Advanced Nursing,
296(6):1360-9.
Khanfar, S. M. (2015). Training and its Important in the
Efficiency of Employees' Performance in Five –
Star Hotels in Jordan. Journal of Business Studies
Quarterly, Vol 6, No 2.
Kreitner, R. (1995). Management (6th ed.). Boston:
Houghton Mifflin Company.
Lobel, S.A.(1999). Impacts of diversity and work-life
initiatives in organizations. In G.N. Powell (Ed.).
Handbook of gender and work, pp: 453-476,
Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Lobel S.A., and Kossek, E.E. (1995). Human resource
strategies to support diversity in work and personal
lifestyles: beyond the “family friendly”
organizations. In E.E. Kossek, & S.A. Lobel (Eds.)
Managing diversity: Human resource strategies
for transforming the workplace, pp. 221-
243.Cambridge, MA: Blackwell.
Levy-Leboyer, C. (1988). Looking at work motivation
from a wider angle. Br J Guid Couns, 16, 242-249.
Mia et al. (2009). Measuring the impact of training on the
performance of workers an Empirical Study of the
Directorate of Education in Al Buraimi
Governorate in the Sultanate of Oman. Economic
Sciences, Legal, 31(1).
Negarandeh, R. et all. (2015) Motivating Factors among
Iranian nurses. Iranian Journal of Nursing and
Midwifery Research, Vol 20, No 4, pp 436-441.
Owusu, T. (2012). Effects of motivation on employee
performance: A case study of Ghana commercial
bank, Kumasi zone. Doctoral dissertation, Kwame
Nkrumah University of Science and Technology.
Roos, W. & Van Eeden (2013). The Relationship Between
Employee Motivation, Job Satisfaction and
The Role of Work Motivation as Moderator in the Relationship between Training and Job Performance: A Study in Regional Hospital in
West Sumatra Province
1347

Corporate Culture, SA Journal of Industrial
Psychology, 34 (1), 54-63.
Shirom A., Westman M., & Melamed S. (1999). The
Effects of Pay Systems on Blue-Collar
Employees’ Emotional Distress : The Mediating
Effects of Obective and Subjective Work
Monotony. Human Relations. Vol . 52.
Soliha, E., Dharmmesta, B. S., Purwanto, B.M.
&Syahlani, S.P. (2014). Message Framing, Source
Credibility, and Consumer Risk Perception with
Motivation as Moderating Variable in Functional
Food Advertisements, American International
Journal of Contemporary Research. Vol 4, No 1,
pp. 193-208.
Stavrou, E. T., Charalambous, C., & Spiliotis, S. (2007).
Human resource management and performance: A
neural network analysis. European Journal of
Operational Research, Vol 181, Issue 1, pp. 453-
467
Tarawneh, T. (2009). The obligation to apply the stages of
training and its impact in the field of performance
of employees. Arab Journal of Security Studies
and Training, Vol 26, No 51.
Tzeng, H.M., (2002) The influence of nurses’ working
motivation and job satisfaction on intention to quit
: an emplirical investigation in Taiwan.
International Journal of Nursing Studies, Vol 38,
No 8, pp. 867–878
Wiley, C. (1997). What motivates employees according to
over 40 years of motivation surveys. International
Journal of Manpower, Vol. 18, No. 3, pp. 263-
280.
Bogdanova, A., Enfors, H., & Naumovska, S. (2008).
Work environment stressors-The link between
employees’ well-being and job performance?
(Bachelor dissertation, Jönköping University,
2008).
Becker. (1975). Does Training Generally Work? The
Returns to In-Company Training: Industrial and
labor Relation Review. Vol. 54, No. 3, Cornell
University.
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
1348
