
Measurement of the Quality of Financial Accounting Information
Systems through Top Management Support and Leadership
Effectiveness
Jufri Darma
1
, Azhar Susanto
2
, Sri Mulyani
2
and Jadi Suprijadi
3
1
Faculty of Economics, Universitas Negeri Medan, Indonesia
2
Faculty of Economics and Business, Universitas Padjadjaran, Indonesia
3
Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences, Universitas Padjadjaran, Indonesia
Keywords: Quality of Financial Accounting Information System, Top Management Support, Effective Leadership
Abstract: Researchers previously conducted research on top management support and leadership and in information
systems. This study aims to examine the influence of top management support and effective leadership on
the quality of financial accounting information system. Surveys are conducted on 270 respondents in 76
ministries and institutions of the Republic of Indonesia. The respondents are the users of financial
accounting information systems. Data is collected by using questionnaires. For data analysis we applied the
SEM-PLS Software. The results indicate that top management support and effective leadership have
significant influence on quality of financial accounting information system.
1 INTRODUCTION
Financial accounting information systems is crucial
to the operation of all organization (Gray &
Bebbington, 2001). Quality of financial accounting
information systems referring to characteristics that
describe the ability of information systems in
processing data to be financial information that
meets user expectations (DeLone & McLean, 1992;
Mandl, 2008: 112; Pham Thi & Helfert, 2009).
Financial accounting information system has quality
characteristics such as: reliability, integration and
accessibility (Bocij et al., 2015, Heidmann, 2008).
The reliability is the ability of financial accounting
information systems function properly and produce
accurate information (Bocij et al, 2015; Baltzan,
2014). Further integration is the integration of
subsystems, information systems with other systems,
and data from various sources (Valacich &
Schneider, 2016; Baltzan, 2014). While the
accessibility is information system can bes accessed
from anywhere and anytime by various users (Bocij
et al., 2015; Avison & Fitzgerald, 2006:).
In fact, accounting information system until now
can’t fully applied to various types of organizations
in Indonesia (Susanto, 2017) such as: universities
(Susanto, 2016 & 2017), higher educations
(Puspitawati, 2016), colleges (Susanto, 2018),
hospital (Fitrios, 2017), financial institutions
(Mulyani et al., 2016; Darma, 2017), government
owned company (Mulyani & Endraria, 2017;
Ladewi et al., 2017), National Zakat Management
Institutions (Nurhayati & Susanto, 2017).
The existing phenomenon that financial
accounting information systems in ministries and
institutions has not been reliable The tax system has
not had good financial accounting information, it is
still manual, so much so that fictitious invoices to
the taxpayer's tax record so it may not be optimal
(Brojonegoro, 2015). The problems in the
administration area of computer application system
are not optimal in supporting the preparation of
financial statements (Azis, 2015). In addition,
financial accounting information systems has not
been integrated. Budget user in ministry and
institution and the Ministry of Finance could not
perform their duties independently and own
themselves but must work together to ensure an
Darma, J., Susanto, A., Mulyani, S. and Suprijadi, J.
Measurement of the Quality of Financial Accounting Information Systems through Top Management Support and Leadership Effectiveness.
DOI: 10.5220/0009502210351042
In Proceedings of the 1st Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science (UNICEES 2018), pages 1035-1042
ISBN: 978-989-758-432-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
1035

orderly budget execution and accountability
(Budiarso, 2014). Besides, financial accounting
information system is easily accessible. Towards the
deadline of SPT reporting on 31 March the server of
Directorate General of Taxes is disturbed because
many people reporting (Utama, 2016).
Management support is important component to
information systems success (Langer, 2008). Top
management support guarantees the availability of
the resources needed by the information system
(Olson, 2004). The availability of human resources,
hardware, software, data and networks is an
information system requirement (Marakas &
O’Brien, 2014). Management support in providing
various resources is needed in the implementation of
information systems (Stair & Reynolds, 2016)
Information systems will succeed optimally if they
get support from top management (Bocij, Greasley
& Hickie, 2015; Olson, 2015; Zaied, 2012; Laudon
& Laudon, 2016)
Top management support in this research are:
providing human resources, providing hardware,
providing software, and providing funds needed to
operate financial accounting information systems
(Bocij, Greasley & Hickie, 2015; Laudon & Laudon,
2016; Palvia & Palvia, 2003; Boonstra, 2013; Dong,
Neufeld & Higgins, 2009;Compean & Higgins,
1995).
Several previous research results show the effect
of top management support on information systems.
Support from top management is essential for
effective implementation of information systems
(Thong, Sing Yap & Raman, 1996). Top
management support is positively related to the
effectiveness of information systems (Seliem, et al,
2003). Top management support relates directly or
indirectly to the performance of information systems
(Ragunathan, et.al, 2004). Top management support
is significantly related to the quality of information
systems (Husein, et.al, 2007). Top management
support influences the use of management
accounting information systems (Gil & Hartman,
2007). The level of management support is related to
the level of quality of information systems (Medina
& Chaparro). Top management support has the most
powerful influence on information systems
(Rouibah, et.al, 2009). Management support very
helpful to improve the quality of information
systems (Zaied, 2012). Top management support is a
key factor for the success of information systems
(Chen, Zhao & Wang, 2012). One of the factors
consistently found to influence the success of
information systems is top management support
(Petter, DeLone & McLean, 2013). Top
management support has a strong effect on the
operation of information systems (Khan, Lederer &
Mirchandani, 2013). Top management support has
an effect on information systems (Al-Mamary,
Shamsudin & Aziati, 2014). Support from top
management is an important point for the success of
corporate information systems (Shao, Feng & Hu
(2015).
Leadership is key component in realizing the
government's financial accounting information
system of quality, so it takes the role of a leader who
can give an example (Budiarso, 2014). Leadership is
an important aspect to success of financial
accounting information system (Ward & Peppard,
2003). Leadership style is one of the features that
affect the financial accounting information system of
an organization (Laudon & Laudon, 2016).
The influence of leader on individual subordinate
i.e., leader improves: quality of subordinate life,
subordinate confidence, subordinate skills, and
development of subordinates (Yukl, 2013). The
influence of leaders in groups, i.e., leaders improve:
team work, group commitment, confidence of group
members in achieving goals, problem solving by
groups, and decision making by groups (Yukl,
2013). The influence of leader to organization i.e.,
leader help to: resolve disputes constructively,
efficiency of organizational activities, resource
accumulation, and organizational readiness in the
face of change (Yulk, 2013).
Previous research shows the influence of
leadership on information system. Stone (1994)
proves that leadership style is a significant factor in
influencing the successful application of information
systems. Thite (2000) found evidence that
transactional leadership effectiveness leads to a
successful level of information systems projects. Shi
(2007) proves that the leadership of information
systems have a positive impact on the performance
of information systems. Cho, Park & Michel (2011)
proves that transformational leadership is positively
associated with the success of information system
users. Fitriati & Mulyani (2015) found evidence that
leadership influences the success of accounting
information systems. Carolina (2015) found
evidence that transformational leadership has a
significant effect on accounting information
systems. Rapina (2015) also found evidence that
transformational leadership influences the successful
implementation of accounting information systems.
Mulyani & Endraria (2017) found evidence that
leadership style have significant effect on the
implemetantion enterprise resource planning system.
Fitrios (2017) found evidence that leadership
behavior significantly influences to accounting
information systems. Nurhayati & Susanto (2017)
found evidence that transformational leadership has
significant influence on success of accounting
information systems
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
1036

This study aims to examine effect of top
management support and the effective leadership on
the quality of financial accounting information
systems in ministries and institutions of the Republic
of Indonesia.
Based on the above statement and the results of
previous research, the hypothesis in this study is :
1. Top management support significantly influence
on the quality of financial accounting
information system
2. effective leadership significantly influence on the
quality of financial accounting information
system
2 METHODOLOGY
This study uses descriptive and verification method.
The population in this study are all users of financial
accounting information system consisting of head of
finance bureau, head of finance department,
accounting department head and data entry staff in
86 units Reporting & Accounting in Ministry and
Institution of Republic of Indonesia. The sampling
technique used is simple random sampling to
obtained 270 respondents. The instrument that is
used for the collection data is questionnaire. The
questionnaires using Likert scale on five choices of
responses ranging from strongly disagree (1) and
strongly agree (5)
The questionnaire includes two variables
namely: top management support (TMS), leadership
effectiveness (LE) and quality of financial
accounting information system (QoFAIS). TMS
consists of four dimensions namely providing of
human resources (TMS1), hardware (TMS2),
software (TMS3), and fund (TMS4) as needed. The
dimensions of providing of human resources as
needed consists two indicators ie the suitability of
the data entry personnel (TMS11) and technical
(TMS12) to needs. Further, the dimensions of
providing of hardware as needed consists two
indicators i.e., the suitability of computer hardware
(TMS21) and communications network hardware
(TMS22) to needs. Furthermore, the dimensions of
providing of software as needed consists two
indicators ie the suitability of the operation systems
software (TMS31) and application software
(TMS32) to needs. While the providing of fund as
needed consists three indicators ie suitability of the
budget amount for: maintenance and replacement
hardware (TMS41), software (TMS42), and training
of data entry personnel (TMS43) to needs.
LE consists of three dimensions namely
influence of leader on individual subordinate (LE1),
influence of leader on group (LE2) and influence of
leader on organization (LE3). LE1 consists four
indicator i.e., leader improves the quality of
subordinate life (LE11), leader build subordinate
confidence (LE12), leader improve subordinate
skills (LE13), and leader contribute to the
development of subordinates (LE14). LE2 consists
five indicators i.e., leader enhance teamwork
(LE21), leader increase group commitment (LE22),
leader increase members group confidence in
achieving goals (LE23), leader improve problem
solving by group (LE24), and leader improve
decision making by group (LE25). LE3 consists four
indicators i.e., leader help to resolve disputes
constructively (LE31), leader contribute to the
efficiency of organizational activities (LE32), leader
contribute to resource accumulation (LE33), and
leader contribute to organizational readiness in the
face of change (LE34).
QoFAIS consists of three dimensions namely
reliability of financial accounting information
system (QoFAIS1), integration of financial
accountig information system (QoFAIS2) and
accessibility of finnancial accounting information
system (QoFAIS3). QoFAIS1consists two indicators
i.e. ability of financial accounting information
system function properly (QoFAIS11) and ability of
financial accounting information system to produce
accurate information (QoFAIS12). QoFAIS2
consists three indicators i.e., the integration
subsystem in the financial accounting information
system (QoFAIS21), integration financial of
accounting information system with other
information systems (QoFAIS22) and integration of
data from various sources (QoFAIS23). QoFAIS3
consists two indicators i.e., the ability ability of
financial accounting information system accessed
anytime by user (QoFAIS31) and the ability of
financial accounting information system accessed
from various place by user(QoFAIS32).
All causal relationships between indicators and
constructs in this study used a reflective
measurement model. The data analysis we applied
the variance based structural equation modeling
method.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
Demography of Respondent: Based on the answers
of the respondents on questions relating to gender,
age, education level, and educational background.
The gender of male dominated respondents as much
as 154 respondents or 57.04%, based on age of
respondents dominated age between 30-39 years that
is as much as 118 respondents or 43.70%, based on
education level most respondents are bachelor that
Measurement of the Quality of Financial Accounting Information Systems through Top Management Support and Leadership Effectiveness
1037
is as much as 155 respondents or 57.41%, and based
on the educational background of most respondents
background accounting that is as much as 158
respondents or 58.52%
Assessment of Measurement Model: The reflective
measurement model is considered to meet validity if
the extracted average variance (AVE) is higher than
0.5 and the outer load indicator on the construct
must be higher than all the cross loads with the other
constructs. The reflective measurement model is
considered reliable if the composite reliability and
outer load indicator is higher than 0.708 (Hair,
et.al.,2014). The of evaluation first order on outer
model, we found that the outer loading of all items
used to measure each dimension of top management
support, leadership effectiveness and quality of
financial accounting information systems is above
0.7. Average variance extracted above 0.5 it’s
concluded that the reflective measurement model is
valid. Likewise, composite reliability and all
indicator outer loading higher than 0.708, it’s
concluded that the reflective measurement model is
reliable (see Table 1)
Table 1: Result of Validity and reliability Test
Variabel Indicator
Composite
Reliability
(CR)
Average
Variance
Extracted
(AVE)
Top
Management
Support
(TMS
TMS 0,929 0.596
TMS1 0,919 0,850
TMS2 0,955 0,914
TMS3
0,973 0,948
TMS4
0,915 0,784
Leadership
Effectiveness
(LE)
LE
0,871 0,501
LE1
0,836 0,603
LE2
0,803 0,741
LE3
0,844 0,758
Quality of
Financial
Accounting
Information
System
(QoFAIS)
QoFAIS
0,946 0,580
QoFAIS1
0,854 0,720
QoFAIS2
0,934 0,578
QoFAIS3
0,926 0,732
Descriptive Statistics: Two hundred seventy
questionnaires from user of financial accounting
information systems at 76 Ministries and Institutions
of Republic of Indonesia (78.49%) were returned
and completed. Inter-quartile range (IQR) was used
to categorize the respondents’ responses (Cooper &
Schindler, 2014). The category of respondents’
responses are : an mean score : 1,00-1,99 (poor),
2,00-2,99 (less), 3,00-3,99 (sufficient) and 4.00-5,00
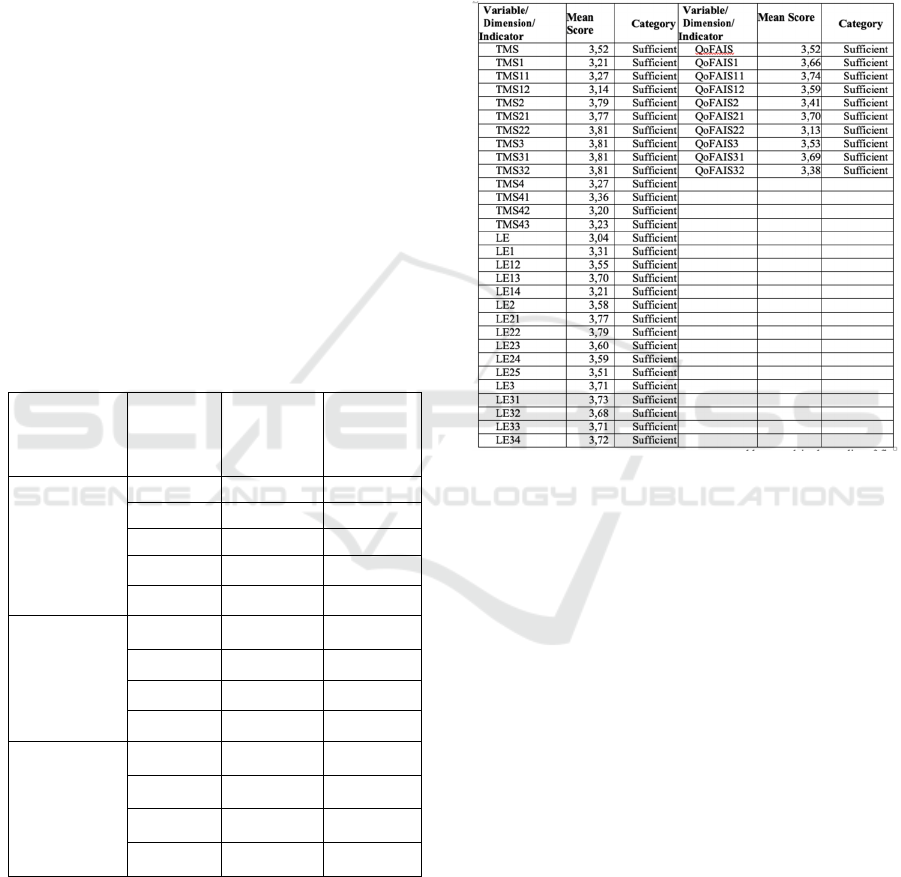
(good). Descriptive statistics show that all
dimensions and indicators have mean scores
between 3.04 - 3.79 or below 4 so that the categories
are “sufficient” (see Table 2)
Table 2: Descriptive Statistics
Hypothesis Testing: The hypothesis to be tested in
this study are:
Ho1: Top management support have not significant
influence on the quality of financial accounting
information systems.
Ha1: Top management support have significant
influence on the quality of financial accounting
information systems.
Ho1 is accepted if significance level <5%. Based
on result of the analysis we found the significance
level is 0,039 (see Table 3). This means that Ho1 is
rejected or in other words top management support
have significant influence on quality of financial
accounting information system. Path coefficient
between top management and quality of financial
accounting information systems is 0.128, coefficient
determination (R2) is 0,016. this means that top
management able to explain the quality of financial
accounting information system equal to 1,6%,
Ho2: Effective leadership have not significant
influence on the quality of financial accounting
information systems.
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
1038

Ha2: Effective leadership have significant influence
on the quality of financial accounting information
systems.
Ho is accepted if significance level <5%. Based on
result of the analysis we found the significant level
is 0,777(see Table 3). This means that Ho2 is
rejected or in other words effective leadership have
significant influence on quality of financial
accounting information system. Path coefficient
between effective leadership and quality of financial
accounting information systems is 0.777, coefficient
determination (R2) is 0.603 this means that effective
leadership able to explain the quality of financial
accounting information system equal to 60,3%
Table 3: Result of Data Analysis
No
Variable
Path
Coefficiet
P
Value
Significant
1
QFAIS TMS 0,128 0,039
2
LE 0,777 0,000
The results of testing the hypothesis about the
influence of top management support on the quality
of financial accounting information systems indicate
that the path coefficient value is
0.128 with a significance of 0.39 so it can be
decided that H0 is rejected, so it can be concluded
that top management support has a positive effect on
the quality of financial accounting information
systems. The results of this study provide empirical
evidence that the better the top management support,
the more appropriate human resources, hardware,
software and existing funds with needs, the more it
will improve the quality of financial accounting
information systems. In other words, the quality of
the financial accounting information system will
increase if the support of top management is getting
better.
The results of this study are in line with the
statements of several experts. Management support
will lead to improved system quality (Zaied, 2012).
The success of the application of information
systems is due to the high support of top
management (Laudon & Laudon, 2016: 590). Top
management support has often proven to be an
important factor for the success of information
systems (Olson, 2015: 11).
Top management support, namely top
management guarantees the availability of resources
needed by information systems (Olson, 2004: 13).
Top management support for the quality of the
financial accounting information system in the
ministries and institutions of the Republic of
Indonesia is realized in the form of providing
various resources that are in accordance with the
operational requirements of the financial accounting
information system.
The quality of financial accounting information
systems in ministries and institutions depends on the
suitability of various existing resources with needs
such as: human resources (personnel), hardware,
software and funds. This is in line with the
statements of several experts. Information systems
depend on human resources, hardware, software, and
networks (Marakas & O’Brien 2014: 28). Resources
needed in the implementation of accounting
information systems include: enthusiastic resources,
hardware, software and funds. Management support
ensures that information systems receive sufficient
funds and resources for their success (Laudon &
Laudon, 2016: 591). Furthermore, top management
support related to resources is the provision of funds
needed for hardware, software and others (Dong,
Neufeld & Higgins, 2009).
Empirical evidence about the influence of top
management support on the quality of financial
accounting information systems in ministries and
institutions, in line with the results of previous
studies conducted by: Thong, Sing Yap & Raman
(1996), Seliem, et al. (2003), Ragunathan, et al.
(2004), Husein, et al. (2007), Gil & Hartman (2007),
Medina & Chaparro (2008), Rouibah, Hamdy & Al-
Enezi (2009), Zaied (2012), Chen, Zhao & Wang
(2012), Petter, DeLone & McLean (2013 ), Khan,
Lederer & Mirchandani (2013), Al Mamary,
Shamsudin & Nor Aziati (2014), and Shao, Feng &
Hu (2015).
Furthermore, the results of testing the hypothesis
about the effect of leadership effectiveness on the
quality of financial accounting information systems
indicate that the path coefficient value is 0.777 with
a significance of 0.000 so that it can be concluded
that leadership effectiveness has a positive effect on
the quality of financial accounting information
systems. The results of this study provide empirical
evidence that the more effective leaders in
influencing subordinate individuals, groups and
organizations will lead to increased quality of
financial accounting information systems. In other
words, the quality of financial accounting
information systems will increase if leadership
becomes more effective.
The results of this study are in line with the
statements of several experts. Leadership is an
important aspect in achieving success in financial
accounting information systems (Ward & Peppard,
2003: 369). The same thing, leadership is one
Measurement of the Quality of Financial Accounting Information Systems through Top Management Support and Leadership Effectiveness
1039

feature that influences financial accounting
information systems (Laudon & Laudon, 2016: 116).
Then strong effective leadership is needed in order
to achieve successful implementation of financial
accounting information systems (Stair & Reynold,
2016: 399)
Empirical evidence about the effect of leadership
effectiveness on the quality of financial accounting
information systems in the accounting and reporting
section of the ministries and institutions of the
Republic of Indonesia is in line with the results of
previous studies such as: Stone (1994), Thite (2000),
Shi (2007), Cho, Park & Michel (2011), Azmi
Fitriati & Mulyani (2015), Carolina (2015) and
Rapina (2015).
4 CONCLUSION
This study aims to measure the quality of financial
accounting information systems that are influenced
by top management support and effective leadership.
The results of this study show evidence that top
management support and leadership effectiveness
influence the quality of financial accounting
information systems. It can be concluded that this
model can be used to measure the quality of
financial information systems..
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The researcher would like to thank the ministers and
heads of the Republic of Indonesia's institutions and
all respondents who have supported this research.
REFERENCES
Al-Mamary, Y.H., Shamsuddin, A., and Nor Aziati, A.H.
(2014). Key factors enhancing acceptance of
management information systems in Yemeni
companies. Journal of Business and Management
Research, 5 (2014) 108-111.
Avison, D. And Fitzgerald, G. (2006). Information
Systems Development – Methodologies. Techniques
and Tools. Fourth Edition. New York: The McGraw-
Hill
Azis, H.A. (2015).
http://nasional.kontan.co.id/news/keuangan-
pemerintah-masih-bermasalah. Azis, H.A. 2016.
http://ekbis.sindonews.com/read/1114372/33/bpk-
ungkap-6-masalah-laporan-keuangan-pemerintah-
2015-1465191938
Baltzan, P. (2014). Business Driven Information System.
Fourth Edition. New York: The McGraw- Hill
Bocij, P., Greasley, A. and Hickie, S. (2015). Business
Information Systems Technology, Development and
Management for the E-Business. Fifth edition.
London: Pearson Education Limited
Brojonegoro, B. (2015)
http://bisniskeuangan.kompas.com/read/2015/07/14/11
2059526/Menkeu.Banyak.Faktur.Fiktif.Penerimaan.N
egara.Tergerus
Budiarso, T. (2014).
http://www.kemendagri.go.id/article/2014/02/27/imple
mentasi-sistem-keuangan-pemerintah.
Carolina, Y. 2015. How to Attain Accounting Information
Systems Quality? (Empirical Evidence from
Manufacturing Company in Bandung – Indonesia).
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences.
Vol. 9 (9) pp.87-94.
Chen, X.C., Zhao, Z. and Wang, Y.F. (2012). The Effects
of Top Management Support on Information System
Success: Manufacturing Industry Cases. Applied
Mechanics and Materials Vols 157-158 (2012) pp 344-
348.
https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.157-
158.344
Cho, J., Park, I. and Michel, J.W. (2011). How does
leadership affect information systems success? The
role of transformational leadership. Information &
Management 48: 270–277.
Cooper, D.R. and Schindler, P.S. (2014). Business
Research Methods. Twelfth Edition. New York:
McGraw-Hill Education.
Darma, J. (2017). How the Clarity of Business Vision
Affect the Quality of Business Intelligence Systems
and It’s Impact on the Quality of decision Making
(Evidence from North Sumatera- Indonesia). Journal
of Engineering and Applied Sciensce. 12 (9): 2461-
2466
DeLone, W.H. and McLean, E.R. (1992). Information
System Success: The Quest for The Independent
Variable. Information System research. 3 (1): 60-95
Dong, L., Neufeld, D. and Higgins, C. (2009).Top
management support of enterprise systems
implementations. Journal of Information Technology
24, pp.55–80. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1057/jit.2008.21
Fitriati, A. dan Mulyani, S. (2015). Factors That Affect
Accountinng Information System Success and It’s
Implication on Accounting Information Quality. Asian
Journal of Information Technology 14 (5). Pp.154-
161. DOI: 10.3923/ajit.2015.154.161
Fitrios, R. 2017. Leadership Behavior and Accounting
Information System ( An Empirical Study at the
Hospitals in Riau Province-Indonesia. Journal of
Engineering and Applied Sciences. 12 (22): 6062-
6068.
Gil, D.N. and Hartmann, F. (2007). Management
accounting systems, top management team
heterogeneity and strategic change. Accounting,
Organizations and Society 32. Pp. 735–756.
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
1040

http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S036
1-3682(06)00078-X
Gray, R and Bebbington, J. (2001). Accounting for the
environment. Second Edition. London: SAGE
Publications Ltd.
Hair Jr., J.F., Hult, G.T.M., Ringle, G.M. & Sarsted, M.
(2014). A Primer Partial Least Squares Structural
Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM), Los Angeles: Sage
Publications, Inc
Heidmann, M. (2008). The Role of Management
Accounting Systems in Strategic Sensemaking.
Germany: Deutscher Universitats-Verlag Wiesbaden
Husein, R., Abdul Karim, N.S., Mohamed, N., & Ahlan,
A.R. (2007). The Influence Organizational Factors on
Information Systems Success in E-Government
Agencies in Malaysia. The Electronic Journal on
Information System in Developing Countries 29, 1, 1-
17. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1681-
4835.2007.tb00195.x
Khan, S.A., Lederer, A.L., and Dinesh A. Mirchandani.
(2013). Top Management Support, Collective
Mindfulness, and Information Systems Performance.
Journal of International Technology and Information
Management. Volume 22, Number 1 pp.95-122.
http://scholarworks.lib.csusb.edu/jitim/vol22/iss1/6
Laudon, K.C., and Laudon, J.P.( 2016). Management
Information System: Managing the Digital Firm,
Fourteenth Edition, London: Pearson Education
Limited
Ladewi, Y., Susanto, A., Mulyani, S. & Suharman, H.
(2017). Effect of Organizational Commitment on the
Quality of Accounting Information Systems and their
Impact on the Quality of Accounting Information.
Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences, 12
(24):7649-7655
Langer, A.M. (2008). Analysis and Design of Information
Systems. Third Edition. London: Springer-Verlag
Limited
Mandl, T. (2008). Automatic Quality Assessment for
Internet Pages. Munoz, C.C., Moraga, A., and Piattini,
M.(eds.). Handbook of Research on Web Information
Systems Quality. New York: Information science
reference.
Marakas, G.M. & O’Brien, J.A. (2014). Introduction To
Information Systems. International Edition. New
York: The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Medina, M.Q. and Chaparro, J.P. (2008). The Impact Of
The Human Element In The Information Systems
Quality For Decision Making And User Satisfaction.
Journal of Computer Information Systems. Winter
pp:44-52.
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/088744
17.2008.11646008
Mulyani, S., Darma, J. & Sukmadilaga, C. (2016). The
Effect of Clarity of Business Vision and Top
Management Support on the Quality of Business
Intelligence Systems: Evidence from Indonesia. Asian
Journal of Information Technology 15 (16): 2958-
2964
Mulyani, S., Hasan, R. & Anugrah, P. (2016). The Critical
Factors for the Use of Information Systems and its
Impact on the Organizational Performance.
International Journal Management, 10 (4): 552-560.
Mulyani, S. & Endraria. (2017).The Empirical Testing for
the Effect of Organizational Commitment and
Leadership Style on the Implementation Success of
Enterprises Resource Planning Systems and Its
Implications onn the Quality of Accounting
Information. Journal of Engineering and Applied
Sciences. 12 (20): 5196-5204.
Nurhayati, N & Susanto, A. (2017). The Influence of
Transformational Leadership on the Success of
Accounting Information Systems Implementation
(Survey on National Zakat Management Institution of
West Java). Journal of Engineering And Applied
Sciences. 12. (17): 4534-4539
Olson, D.L. (2004). Information System Project
Management. Second Edition. New York. The
McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Olson, D.L. (2015). Information System Project
Manajemen. New York: Business Expert LLC.
Petter, S., DeLone, W. and McLean, E.R. (2013).
Information System Success: The Quest for the
Independent Variables. Journal of Management
Information Systems/ Spring Vol 29, No.4, pp.7-61.
DOI: 10.2753/MIS0742-1222290401
Pham Thi, T.T. and Helfert, M. (2009). An Information
System Quality Framework Based on Information
System Architectures. Barry; C., Conboy, K., Lang,
M., Wojtkowski, G., and Wojtkowski, W. (Editors).
Information Systems Development. Challenges in
Practice, Theory and Education. Volume 2. New York:
Springer Science+Business Media, LLC.
Puspitawati, L. (2016). The Analysis Of Effectiveness
Measurement In Accounting Information Systems
Through Competence Factor Of Information System
User (Research on Higher Education in Bandung).
IJABER. 14 (1): 313-339
Ragunathan, B.S., Apigian, C.H., Ragu-Nathan, T.S. and
Tu, Q. (2004). A Path Analytic Study of The Effect of
Top Management Support for Information System
Performance. Omega. International Journal of
Management Science, 32, pp: 459-471.
https://kundoc.com/pdf-a-path-analytic-study-of-the-
effect-of-top-management-support-for-information-
sy.html
Rapina. (2015). Factors that Affect Accounting
Information Systems and Accounting Information
(Survey on Local Bank in Bandung-Indonesia).
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences.
Vol. 9 (9) pp.78-86
Rouibah, K., Hamdy, H.I., and Al-Enezi, M.Z. (2009).
Effect of Management Support, Training, and User
Involvement on System Usage and Satisfaction in
Kuwait. Industrial Management and Data Systems.
Vol. 109. No.3. pp.338-356.
Seliem, A.A.M., Ashour, A.S., Khalil, O.E.M and Millar,
S.J. (2003). The Relationship of Some Organizational
Factors to Information Systems Effectiveness: A
Measurement of the Quality of Financial Accounting Information Systems through Top Management Support and Leadership Effectiveness
1041

Contingency Analysis of Egyptian Data. Journal of
Global Information Management. 11 (1) pp.40-71,
Jan-Mar. DOI: 10.4018/jgim.2003010103
Shao, Z., Feng, Y. and Hu, Q. (2015). Effectiveness of top
management support in enterprise systems success: a
contingency perspective of fit between leadership style
and system life-cycle. European Journal of
Information Systems (2015), pp.1–23. DOI:
10.1057/ejis.2015.6
Shi, Z..( 2007). An Empirical Test of IS Leadership as The
Driving Force in Improving IS Performance. Journal
of Information, Information Technology, and
Organizations. 2: 61- 77
Stair, R.M., and Reynolds, G.W. (2016). Fundamentals of
Information Systems. Eighth Edition. USA: Cengage
Learning.
Stone, R.D. (1994). Leadership and Information System
Management: A Literature Review. Computer in
Human Behavior.Vol.10. No.4 pp:559-568
Susanto, A. (2016). The Empirical Testing How the
Quality of Accounting Information Systems Affected
by Organizational Culture. Research at Universities in
Bandung. Asian Journal of Information Technology.
15 (6): 1098-1105.
Susanto, A. (2017). How the Quality of Accounting
Information System Impact on Accounting
Information Quality (research on Higher Education in
Bandung. Journal of Engineering and Applied
Sciences. 12 (14): 3672-3677.
Susanto, A. (2018). How Internal Control and
Organizational Structure Impact on Accounting
Information System. Journal Engineering and Applied
Sciences, 13 (8):1935-1941
Thite, M. (2000). Leadership Styles in Information
Technology Projects. International Journal of Project
Management. 18: 235-241
Thong, J.Y.L., Sing Yap, C. and Raman, K.S. (1996). Top
Management Support, External Expertise and
Information Systems Implementation in Small
Businesses. Information Systems Research. Vol 7. No.
2 Juni. Pp.248-267.
Utama, M.S. (2016).
http://www.beritakepo.com/2016/03/situs-djp-sulit-
diakses-e-filing-spt.html Valacich, J. and Schneider,
C. 2016. Information Systems Today Managing in the
Digital World, Seventh Edition, England: Pearson
Education, Limited
Valacich, J. and Schneider, C. (2016). Information
Systems Today Managing in the Digital World,
Seventh Edition, England: Pearson Eduction Limited
Ward, J. and Peppard, J.. (2003). Strategic Planning for
Information Systems. Third Edition. England: John
Wiley & Sons
Yukl, G. (2013). Leadership in Organization. Eighth
Edition. England: Pearson Education Limited..
Zaied, A.N.H. (2012). An Integrated Success Model for
Evaluating Information System in Public Sectors.
Journal of Emerging Trends in Computing and
Information Sciences. Vol. 3 No.6 July. page: 814-825
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
1042
