
Medicine and Consumer Goods Supply Management Design to
Reduce Stockout and Days of Inventory in PT. XYZ
Monica Linawati
Master of Management, Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya, Indonesia
Keywords: ABC Analysis, Stockout, Fishbone Diagram, Inventory Management, days of Inventory
Abstract: Stockout and overstock are the trigger factors for increased costs. Overstock will result in a waste in the cost
of savings and a high Days of Inventory (DOI), but if the inventory is low, there will be a potential loss of
opportunity for profit if the actual demand is greater than the estimated inventory and trigger customer
disappointment.This study was an observational (non experimental) study. Medicine and consumer goods
inventory management planning conducted ABC analysis to find out the products that become classes A, B,
and C. Class A products are forecasted using exponential smoothing method for product needs in 2019 and
calculated EOQ and ROP. Interviews were conducted with informants regarding the current inventory
management system. The root cause of the stockout is analyzed using fishbone diagrams. From the results
of fishbone analysis and interviews that have been carried out on informants, it is known that: 1) lack of
communication with marketing; 2) making stock estimates is not according to needs; 3) no planned sales
average; and 4) there is no coordination between the planner, marketing, and warehouse.
1 INTRODUCTION
Good planning needs to be done so that the
inventory level has maximum benefits. Overstock
requires large funding, and conversely the stockout
can have a consequence on customer disappointment
with the company which can have an impact on
customer loss and a decrease in company revenue.
At present competition takes place not only
between companies, but also competition between
supply chains. The company does not only compete
in products and services, but corporate competition
already involves competition in acquiring material
goods from suppliers, competition in obtaining
resources and services in transportation,
warehousing, and finished goods distribution
systems that can reach customer or market access as
wide as broad.
Key activities in SCM include: mapping of
customer needs and unmet demand to determine
sales and production forecasting, fulfilling sales
orders, vendor management, warehousing and
inventory, managing transportation and distribution,
managing accounts payable and receivable, and
managing cash inflows and outflows (Jacobs &
Chase, 2018).
Inventory management is a branch of business
management that focuses on planning and
controlling inventory, which is a critical issue of
logistics management for most companies, both
large, medium and small companies. Logistics is all
about managing inventory, whether moving or
stationary in the warehouse, in the form of finished
products or raw materials. The Bill of Rights from
logistics is "Sending the right product to the right
place, at the right time, the right number and
conditions, and at the right cost (Goldsby &
Martichenko, 2005). Therefore, effective inventory
management is needed to make that happen.
The challenge in managing inventories is to
balance supply and demand. PT. XYZ is a
distributor in Sidoarjo that distributes medicine and
consumer goods. The company has difficulty
adjusting supply to customer demand efficiently,
where there is a high stockout and Days of Inventory
(DOI) in the business. Every time there is a stockout,
then an additional order is submitted, and a long
DOI item will remain in the warehouse until there is
a sales request, there are even products that have
never been sold until they wait to expire to be
730
Linawati, M.
Medicine and Consumer Goods Supply Management Design to Reduce Stockout and Days of Inventory in PT. XYZ.
DOI: 10.5220/0009502907300735
In Proceedings of the 1st Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science (UNICEES 2018), pages 730-735
ISBN: 978-989-758-432-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
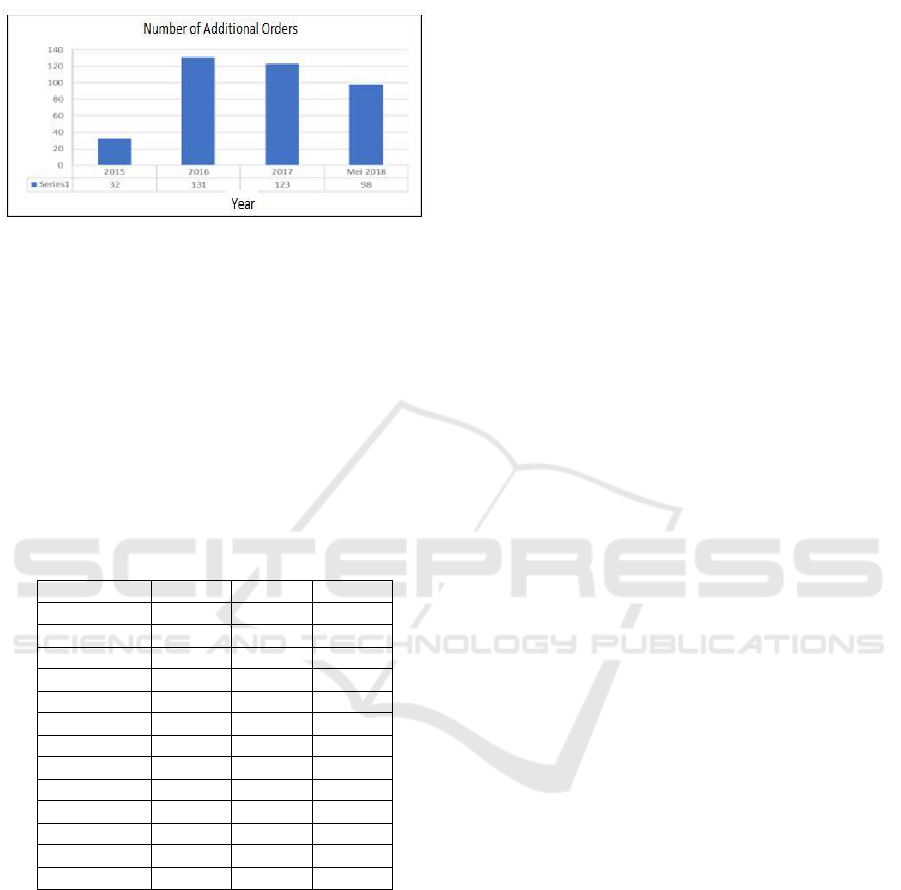
returned to the center. Figure 1 shows the number of
additional orders at PT. XYZ to suppliers.
Figure 1: Additional Orders from 2015 to May 2018
Additional order requests from the data above
are not always fulfilled, so that the stockout event
still occurs and ends in the occurrence of potential
shortages in the company, one of which is the non-
fulfillment of Purchase Order. This can have a
negative impact on the company, where there are
many complaints because the amount of empty stock
does not fit the needs, and can result in the loss of
sales sales due to customer disappointment. The data
in table 1.1 shows the number of Purchase Orders
that are not met every month at PT. XYZ from 2016
to November 2018.
Table 1: Number of Purchase Order Not Fulfilled.
Month
Year
2016
2017
2018
January
NA
627
166
February
NA
689
203
March
NA
685
196
April
NA
555
264
May
NA
438
222
June
282
197
146
July
551
227
253
August
745
275
168
September
706
358
248
October
783
243
217
November
837
185
157
December
607
232
-
Based on the background above, the problem in
this study is to evaluate the current inventory
management system and explore the root causes of
the large number of stockouts and high Days of
Inventory based on fishbone diagram, and design an
optimal inventory management system based on
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) method and ABC
classification at PT. XYZ.
2 METHODOLOGY
This research was conducted in the logistics
department of PT. XYZ in November-December
2018. This study is observational research (non
experimental) by analysis root cause of stockout and
high Days of Inventory using fishbone diagram and
interview to informant, ABC analysis, and
forecasting class A results of ABC analysis.
In-depth interviews were conducted to strengthen
the results of the analysis and dig deeper into the
causes of the large number of stockouts and high
Days of Inventory assisted by fishbone diagrams.
Fishbone diagrams are used to trace the causes so
that they can be expected as managerial aspects and
suggestions to the management of PT. XYZ.
ABC classification divides inventory items into
three groups: high value volumes (A), moderate
volume values (B), and low value volumes (C), with
volume value categories mapped into strategies that
are appropriate for that category. The purpose of
ABC classification is to try to separate the important
from the unimportant, and to establish the
appropriate level of control over each item.
Unit of analysis that will be examined in this
study are sales data, warehouse and corporate
purchasing department. The unit of analysis of a
study can be in the form of individuals, groups,
organizations, objects, regions and certain times in
accordance with the focus of the problem (Kothari,
2004).
The research design used in this study is
descriptive, explaining how the phenomenon of
problems faced in inventory management at PT.
XYZ to be able to answer research questions, and
then provide a design solution.
The data sources used in this study come from
primary data and secondary data. Primary data is
data from the process of observation and direct
interview with the Finance Supervisor and
Marketing Supervisor. Interview questions use a list
of questions assisted with recording devices as
documentation. The search for the high number of
stockouts and Days of Inventory is done using
fishbone diagrams. Secondary data is obtained from
the supporting document study process at PT. XYZ.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Fishbone Analysis
Fishbone analysis is a great tool to go inside and
finding out the root cause of stockout. Based on the
results of observations and interviews, fishbone
analysis are shown in figure 1.
Medicine and Consumer Goods Supply Management Design to Reduce Stockout and Days of Inventory in PT. XYZ
731

Figure 1: Fishbone analysis
In this research, the main problems of PT. XYZ
is a high stockout and Days of Inventory. Overstock
requires large funding, and conversely the stockout
can have a consequence on customer disappointment
with the company which can have an impact on
customer loss and a decrease in company revenue.
PT. XYZ is a pharmaceutical distributor, with
supply chain services consisting of inventory
management, ordering, inventory storage, shipping,
order acceptance, information systems, and all other
processes so that activities can run smoothly. Second
fishbone analysis alongside the Why-Why analysis
will reveal the reasons.
3.1.1 System Problems
Having a computerized system and using it properly
is one of the supporting factors in the inventory
management system. PT. XYZ revealed that one of
the causes of goods vacancies was due to the
unavailability of a system for inventory control, so it
was still manual by conducting one-on-one checks
by the personnel on duty. Another reason is to
upgrade to a more call system that requires high
costs, therefore PT. XYZ has not been able to catch
up in the technology field and lags behind in
competition with other distributors.
3.1.2 Process Problems
The process of inventory management management
of PT. XYZ revealed a number of problems, namely
because of the large amount of inventory that must
be managed, but done manually causing frequent
stockouts and overstocks. Estimated stock
requirements are made more than demand and vice
versa, this is due to the absence of sales plans. Poor
execution of this process also stems from causes
such as the wrong ordering system and high costs.
PT. XYZ also has many suppliers and high lead
times, which can also worsen the frequent
occurrence of stockout cases.
3.1.3 Procedure Problems
Every company must have a procedure in carrying
out an activity so that it runs correctly and
accordingly. Ordering procedure at PT. XYZ must
be done through the Center distribution of PT. XYZ
first, so that the lead time becomes longer, because
there are several factories whose locations are the
same as PT. XYZ, but must be sent to the Center of
PT. XYZ first in Jakarta. There are also many
routine allocations every month from the distribution
center, and this affects the amount of inventory.
If the current stock is low, but the demand is
greater then it creates additional orders, and impacts
on the vacuum of goods, and vice versa, if the
current stock is still sufficient due to small demand,
but coupled with routine allocations, the stock will
accumulate and make days of inventory long.
PT. XYZ also has a routine activity called
'closing day', which is the pursuit of turnover so that
it can be reached, every end date of the month,
before changing tomorrow (already changing
months). The phenomenon that is often faced is to
close the turnover, suddenly there is a surge in
demand, where the existing stock is insufficient, so
there is a 'goib' item, where the stock can increase
first, but new items will be sent that day.
3.1.4 Human Resource Problems
Human resources must be well motivated and
directed according to the company's vision and
mission. Human resources at PT. XYZ is enough for
now, but the lack of skills in inventory management
is something that has a negative impact on the
company's process flow. The company is still
manual in checking the stock so that more time is
needed in reviewing the number of available stocks.
The lack of time to review this stock is also one
of the obstacles. In determining the estimation of
stock requirements based on information from
informants, there is no coordination and
communication between the planner, warehouse, and
marketing. The planner also has no reciprocal
relationship with the supplier, so he does not know
whether the order that has been made has been
received, the stock at the supplier is there/ not, and
whether it has been sent/ not. After the goods
vacuum occurs, then PT. XYZ pursues suppliers.
3.1.5 Product Problems and Prices
Based on information from informants, so far the
inventory management system at PT. XYZ has never
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
732

been classified based on ABC analysis. The budget
allocation for drug supplies is not too calculated, so
there is a lot of empty stock and then making
additional orders, which can actually increase the
cost for the company. The existence of a 'retail last
bite' program also sometimes causes the number of
orders to jump suddenly to suppliers and causes
excess stock and warehouse capacity to overload /
insufficient.
3.2 Solutions From Fishbone Analysis
There are several reasons of stockout in PT. XYZ.
Here are some solutions to help PT. XYZ for
improving their supply management.
3.2.1 Solution to System Problems
To overcome system problems, PT. XYZ can
upgrade the system so that it has a program as a
'reminder' of what stock is left, and when is the right
time to reorder. So the system does not only function
as a note taker and see what the final stock is, then it
is checked manually, but it can also be used as a
reminder of the remaining existing stock. The
electronic system will be able to solve the problem
of shortages and excess stock, and also the wrong
ordering process.
3.2.2 Solution to Process Problems
To reduce and resolve process problems, PT. XYZ
can supply contracts with suppliers, so there are
clear agreement terms and commitments that must
be fulfilled between PT. XYZ and suppliers. The
supply of the contract can determine the lead time
agreement that must be maintained, so that long lead
time problems can be prevented by ordering earlier.
With an earlier booking, the stock will arrive on
time and there will be no stockout and backordering.
Backordering can trigger customer disappointment
and potential loss of sales / sales.
Estimates of fewer stock requirements than
demand can be prevented by coordinating in
advance between warehouses, marketing, and
planning, so that better forecast results are obtained,
not just on intuition. Another method that can be
used is using the forecast method selection that is in
accordance with the pattern of PT. XYZ.
3.2.3 Solution to the Procedure Problem
Procedure problems are the main key
problem in management. The wrong initial
procedure will make the whole series not smooth,
and need to be resolved immediately. The procedure
where the goods must go through the central
distributor first, even though it should be closer if
from the factory directly to PT. XYZ should only be
done administratively, so that the achievement of
lead time is shorter and the cost estimation is lower,
because there does not have to be a factory cost to
the central distributor PT. XYZ first, then the
Distribution Center sends to PT. XYZ. Also, there is
no safety stock at PT. XYZ. So when the stock is out
of stock, then planner make an additional orders, so
in this study provides a design of inventory
management for the management of PT. XYZ for
optimal inventory.
3.2.4 Solution to Human Resource Problems
Human resource is the blood of business life
and it is very important to motivate and maintain it
so they are on the right track. To solve employee
problems, PT. XYZ can conduct comprehensive
training in the right way. Good comunication and
coordination between the marketing, warehouse, and
purchasing also need to be done to determine about
each other's responsibilities. Every time planner will
make a purchase plan there should be good
communication and coordination so that there is a
clear estimation of sales requirements in the amount
and how much stock is currently in the warehouse.
3.2.5 Solution to Product Problems and Prices
Based on information from informants, PT.
XYZ has never done inventory classification based
on ABC analysis. ABC analysis can be used to
classify which products are more important and have
a greater investment value so that they do not sit
quietly in a warehouse and make a high Days of
Inventory.
PT. XYZ also has many products that check it
manually, so that proper forecasting is needed so
that stockouts don't occur frequently. Better
forecasting means lower safety stocks and higher
levels of availability. It also means a reduced
exposure to excess and obsolete stock risk (a large
contributor to holding cost of stock).
3.2.6 Solution to Supplier Problems
PT. XYZ there should be a supply contract with the
supplier, so that there are clear agreements regarding
lead time, supplier response, and other agreements.
A close relationship with supplier is crucial. When
supplier lead times are reduced below the required
lead time, it’ll help remove the requirement to hold
Medicine and Consumer Goods Supply Management Design to Reduce Stockout and Days of Inventory in PT. XYZ
733

much stock, especially consumables. Cutting lead
times in half will reduce safety stocks by about 30%
for the same availability.
Unreliable supply is one of the reasons for
holding safety stocks. If delivery is guaranteed on
the due date then safety stock can be reduced what's
needed to cover common-cause variability. A good
start is sharing demand, forecast and stock positions
with suppliers. When there’s heightened
transparency of information throughout the supply
chain it’ll improve reliability and mitigate
Bullwhip/Forrester effects.
3.3 Inventory Level as an Effort To Minimize
Stockout
In minimizing stockout cases, we need control over
demand. the control applied by the company is to
use inventory level. Inventory level is a safety stock
that must be on that day to anticipate a surge in
demand the next day. Inventory or level stock is
used as an effort to anticipate high demand so
companies don't have to worry about shortages of
stock.
The stock level for suppliers is needed as an
effort to optimize the order purchase costs related to
minimum orders applied by suppliers.
Considerations in installing stock levels to suppliers
include lead time, condition of goods, quality, and
others.
3.4 Inventory Optimization Using ABC Analysis
The researcher obtained data on the recording of
demand and purchase prices in the period January-
November 2018 totaling 469 products. A total of
469 products are grouped based on ABC analysis of
investment value. According to the results of the
interview, PT. XYZ has never done ABC analysis to
help in product inventory management systems.
Drug products and consumer goods are grouped
based on the cumulative percentage of investment
value. Products with a cumulative percentage of up
to 70% are group A, 70-90% are group B, and 90-
100% are group C.
Table 2: Result of ABC Analysis
Class
Investment
Perce
Total
Perce
Amount (IDR)
ntage
Produ
ct
ntage
A
31,483,513,143.00
70,4%
51
10,9%
B
8,751,119,247.00
19,6%
78
16,6%
C
4,467,926,887.00
10,0%
34
0
72,5%
Total
44,702,559,277.00
100%
46
9
100%
From the calculation of ABC analysis, the value
of investment is obtained by the results of group A
with an investment amounting to 70.4% of the total
investment consisting of 51 products which is equal
to 10.9% of the total product. Group B investment
amounted to 19.6% of the total investment and
consisted of 78 products which amounted to 16.6%
of the total product. Group C with a minimum
investment of 10.0% of the total investment,
consisting of 340 medicinal products and consumer
goods, which amounted to 72.5% of total products.
3.5 Dynamic Inventory Approach To Minimize
Days on Inventory
High Days of Inventory is a result of overstock that
cannot be controlled and a waste with a considerable
amount of expenditure. Until now, eliminating the
risk of overstock up to 100% is not possible, given
the fluctuating customer demand can cause the
Purchase Order issued by the customer to be much
smaller than the forecasting that the company had
previously done.
For close suppliers, companies are still easier to
make delays or order cancellations. different from
outside island suppliers, considering the lead time is
very long, which is one to two weeks, so the goods
still come to the company without further processing
due to the absence of requests again. based on this,
the risk of a stockout will always be there and
difficult to eliminate.
After conducting an analysis to find the root
cause of the case of high stockout and Days of
Inventory, then a proposed improvement is
formulated which can be an alternative action that
can be taken in reducing the occurrence of this
stockout case. Approach to dynamic inventory by
considering uncertainty in demand can be
considered to be applied in minimizing high
stockouts and Days of Inventory.
This policy is characterized by the parameters of
the reorder point and number of orders. The ordering
point is the same as the total forecasting and the
maximum number of forecasting uncertainties
during the + 1 period lead time for a service level
cycle target. While the safety stock equals the
maximum number of forecasting uncertainties
during the protection interval. The point of reorder
and the number of orders can be determined by the
following equation:
EOQ =
√
2 (%
ℎ
/100 )
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
734

3.6 Limit Analysis
This study is limited to internal logistics inventory
management PT. XYZ in November - December
2018, does not reach the external supply chain
network. Research focus on the categories of all
products distributed. Historical data used is in the
period January to November 2018.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Stockout is never a pleasant incident for the
company, it is even less so for those responsible for
it. Retailer company as PT. XYZ suffer huge losses
every year because of empty shelves and potency of
disappointed customers. Damaged reputation and
customer loyalty, decreased impact of promotions,
and higher costs for re-ordering all again.
The fishbone diagram and analysis was very
innovative and efficient way of resolving key issues
of the organizations. This research reveals that the
root causes of frequent stockouts at PT. XYZ is (1)
lack of communication and coordination between
planner, marketing, and warehouse, (2) no sales
plan, and (3) estimation of stock requirements that
are less than demand and vice versa (planning does
not match reality) .
This research also provides some solutions for
resolving those problems. If PT. XYZ can apply
supply management design and undertake those they
can get rid of the ongoing problems of stockout and
strive forward for optimal inventory level.
REFERENCES
Goldsby, Dr. Thomas, Robert Martichenko. (2005). Lean
Six Sigma Logistics Strategic Development to
Operational Success. USA: J. Ross Publishing, Inc.
Jacobs, Robert F & Richard B. Chase. (2018). Operations
and Supply Chain Management fifteenth edition.
New York: McGraw Hill Education International
Edition.
Kothari, C.R. (2004). Research Methodology, Methods
and Techniques, Second Revised Edition. New
Delhi: New Age International Publishers.
Medicine and Consumer Goods Supply Management Design to Reduce Stockout and Days of Inventory in PT. XYZ
735
