
The Effect of Tax Avoidance, Real and Accrual Earnings
Management on Cost of Equity
Silvia Dewiyanti
1
and Andi Ulil Amri Burhan
2
1
Department of Accounting, Bina Nusantara University, Jakarta
2
Department of Accounting, ABFI Perbanas, Jakarta
Keywords: Tax Avoidance, Accrual Earnings Management, Real Earnings Management, Cost of Equity
Abstract:
This research aims to examine the effect of tax avoidance, accrual earnings management, and real
earnings management on the cost of equity. The independent variables used in this study are tax
avoidance measured by abnormal book-tax differences (ABTD), earnings accrual management as
measured by performance-adjusted current discretionary accruals (PACDA), and real earnings
management measured by abnormal discretionary expense and abnormal production cost.
Meanwhile, the dependent variable used is the cost of equity as measured by the equity cost
formula. The equity cost formula is obtained by summing the book value per share in period t
plus the earnings per share in the period t+1 then subtracted from the stock price in period t
which is divided by the share price in period t. The population in this study were manufacturing
companies listed on the Indonesia Stock Exchange from 2012 to 2016. Samples were taken using
the purposive sampling method. This study uses panel data regression analysis techniques. The
results showed that tax avoidance had a significantly positive effect on the cost of equity while
accrual earnings management and real earnings management had no effect on the cost of equity.
1 INTRODUCTION
All funding decisions contain risks which are cost
for the company. If funding comes from debt, the
company will bear the cost of debt. Meanwhile, if
funding comes from equity by issuing shares, the
company will bear the cost of equity. Risk
assessment becomes important to determine the cost
of equity, especially for investors. Investors consider
risk to be a cost that must be borne and affect the
expected rate of return on investment in a company.
Investors can see these risks from disclosures or
information contained in financial statements. The
disclosure and quality of information affects the cost
of equity (Botosan, 2006; Botosan & Plumlee, 2002;
Francis et al., 2004; Lambert et al., 2007).
One of the management actions that can
influence the quality of information in financial
statement, which can ultimately affect the cost of
equity, is tax avoidance. Tax avoidance is carried
out in order to reduce the tax or cash burden that the
company must pay to the tax authority. With tax
avoidance, companies will obtain greater cash
availability that can be used in production or
investment activities, thus will increase company
future cash flow. This expected future cash flow will
affect the cost of equity (Lambert et al., 2007).
Hutchens and Rego (2015) shows that tax
avoidance is positively correlated with cost of
equity. Investors regards tax avoidance as a risky
management action that increase uncertainty over
their investment which means increasing the cost of
equity. Meanwhile, Cook et al. (2017) shows that
investors respond differently too the level of tax
avoidance. For companies with low level tax
avoidance, an increase in tax avoidance will reduce
the cost of equity. And for companies with high
level tax avoidance, an increase in tax avoidance
will increase the cost of equity.
Other management actions that can affect the
cost of equity are earnings management. The
management discretion in preparing financial
statements make management freely choose the
accounting method used in financial reporting that
can increase or support the performance of
management. Francis et al. (2004) show that accrual
earnings management had positive impact to cost of
equity. On the other hand, Febrininta and Siregar
1134
Dewiyanti, S. and Burhan, A.
The Effect of Tax Avoidance, Real and Accrual Earnings Management on Cost of Equity.
DOI: 10.5220/0009506111341140
In Proceedings of the 1st Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science (UNICEES 2018), pages 1134-1140
ISBN: 978-989-758-432-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

(2014) show different result that accrual earnings
management does not affect the cost of equity.
Another form of earnings management is real
earnings management. Lambert et al. (2007) shows
that real earnings management can be intended to
cover the actual profits or performance of the
company, so will be distorts the equality of earning,
which are indicators of future cash flow. In line with
this, Kim and Sohn (2013) shows that real earning
management is positively related to the cost of
equity because it increases noises and reduces
investor expectations of future cash flows. Different
results are shown in Meini and Siregar (2014) and
Febrininta and Siregar (2014).
The inconsistency of previous research are the
motivation of this research. This research examine
the effect of tax avoidance, real and accrual earnings
management on cost of equity in Indonesia
manufacturing sector companies. Using data from
2012 until 2016, the result showed that tax
avoidance had a significantly positive effect on the
cost of equity while accrual and real earnings
management had no effect on the cost of equity.
2 HEORICAL FRAMEWORK
2.1 The Relation between Tax Avoidance and
Cost of Equity
Frank et al. (2009) revealed that tax avoidance is
related to the aggressiveness of financial reporting,
while Balakrishnan et al. (2018) revealed that tax
avoidance increases the obscurity of the company’s
information environment. Tax avoidance can reduce
the quality of financial statement information.
Lambert et al. (2007) shows that when the quality of
information is low, information held by investor to
assess future cash flow is less accurate. As a result,
investor assume there is uncertainty about the
company’s future cash flows. Future cash flows are
indicators of investment returns in the form of
dividends so that the uncertainty of future cash flow
will increase uncertainty in return on investment or
increase the cost of equity. This is confirmed by
Cook et al. (2017) and Hutchens and Rego (2015)
that for companies with high levels of tax avoidance,
an increase in tax avoidance will increase the cost of
equity. Based on previous research, the first
hypothesis in this research is:
H1 : Tax avoidance has a positive effect on the
cost of equity.
2.2 The Relation between Accrual Earnings
Management and Cost of Equity
Low accrual earnings quality can be caused by
accrual quality in financial reporting (Geraldina,
2013). Aggressive accrual earning management
contains discretional accrual elements such as
discretion in the selection of accounting method and
estimates in determining the useful life on an asset
loaded with uncertainty. This will have an impact on
the quality of accruals in financial reporting so that
the quality of earnings reported in financial
statement is doubtful. Profits reported in financial
statements do not reflect actual company profits. As
a result, investors do not have accurate information
in predicting the company’s future cash flow.
Francis et al. (2004) shows that accrual quality
has a positive effect on cost of equity. This is
confirmed by the research of Kim and Sohn (2013)
and Meini and Siregar (2014) which provide
empirical evidence that accrual earnings
management has a positive effect on the cost of
equity.
Investors consider there are risks or uncertainties
in the company’s future cash flow. Thus, investors
consider accrual earnings management to be risky so
that the information presented in financial
statements also contains risks. As a results, investors
want a higher rate of return in the presence of these
risks or in other words, the cost of equity increases.
Based on previous research, the second hypothesis
in this research is
H2 : Accrual earnings management has a
positive effect on the cost of equity.
2.3 The Relation between Real Earnings
Management and Cost of Equity
Real earnings management is an action that aims to
change reported earnings in a certain direction
achieved by changing the time or structure of
operations, investments, or funding that have
suboptimal business consequences (Zang, 2011).
According to Kim and Sohn (2013), manager are
more likely to do real earnings management than
accrual earnings management. In real earnings
management, management can change the time and
scale of real activities such as production, sales,
investment, and funding throughout the accounting
period. These real earnings management actions
include sales manipulation, reduce discretionary, and
excessive production (Roychowdhury, 2006).
Real earnings management can generate
abnormal profits, so they do not reflect actual profits
or real company performance. Real earnings
management can distort the quality of reported
The Effect of Tax Avoidance, Real and Accrual Earnings Management on Cost of Equity
1135

earnings which is an indicator of future cash flow.
Investors want a higher rate of return for companies
whose income is susceptible to interference (noisier)
and lower than expected levels of future cash flow
(Lambert et al., 2007).
In line with this, real earnings management is
positively related to the cost of equity because it
increases noise to company profits and reduces
investor expectations of future cash flow which are
indicators of investment returns. Kim and Sohn
(2013) shows empirical evidence that real earnings
management is positively correlated with the cost of
equity. Thus, investors demand a higher risk
premium for this activity by increasing the cost of
equity. Based on previous research, the third
hypothesis in this study is
H3 : Real earnings management has a positive
effect on cost of equity
3 RESEARCH METHOD
This research uses descriptive quantitative methods.
Thus, it carried out by processing data and
conducting analysis to obtain a conclusion on
existing data. This conclusion is in the form of
relationship between the independent variable and
the dependent variable.
This research using all manufacturing
companies, covering the basic industrial sector and
chemicals, various industries, and consumer goods
industries, listed on the Indonesia Stock Exchange
for period of 2012-2016. To get the desired sample,
this research using purposive sampling method, with
the following criteria :
1. Manufacturing sector company
2. Listed on Indonesia Stock Exchange before 1
Januari 2012
3. Use the rupiah currency in financial reporting
4. Has complete financial reports elements for the
period 2011 – 2015
The operationalization of this research variable
consists of one dependent variable, three
independent variables, and three control variables
which will be explained as follows:
1. Cost of equity
The measurement of the cost of equity in this
research used the modified Ohlson Model Approach.
The cost of equity is calculated based on the
discount rate used by investors to evaluate the future
cash flow (Dechow & Dichev, 2002).
r = (B
t
+ X
t+1
– P
t
) /P
t
where,
r : cost of equity
B
t
: Book value per share period t
P
t
: Stock price period t
X
t+1
: Earnings per share
1. Tax Avoidance
The measurement of tax avoidance in this
research using Tang and Firth (2011) approach
for measuring book tax differences (BTD).
BTDit = β0 + β1ΔINVit + β2ΔREVit +
β3NOLit + β4TLUit + εit
where,
BTD
it
: pretax income – current tax
expense/tax
rate
ΔINV
it
: investment changes in gross PPE and
intangible assets
ΔREV
it
: changes of revenue
NOL
it
: Net Operating Loses
TLU
it
: Total compensation for Loss
ε
it
: company residual value
All the above variables are scaled with total
assets in year t
2. Accrual Earnings Management
Jaggi et al. (2009) use performance-adjusted
discretionary accruals (PACDA) to measure
accrual earnings management, because it can
better capture accrual earnings management
and management usually has the most
discretion in current accrual activities.
PACDA is calculated by the following steps :
a. Calculating the total current accrual
estimated every year
TCA
it
/ A
it-1
= α0 (1/ A
it-1
) + α1 (ΔREV
it
/ A
it-
1
) + α2 (ROA
it-1
) + ε
it
b. Using the coefficients generated from
previous calculations to predict current
accruals (expected current accrual/ECA)
ECA
it
/ A
t-1
= α0 (1/ A
it-1
) + α1 {(ΔREV
it
-
ΔAR
it
) /A
t-1
)} + α2 (ROA
it-1
)
c. Determine PACDA
PACDA = (TCA
it
/ A
it-1
) – (ECA
it
/ A
t-1
)
Where,
TCA : total current accruals, from net income
before extraordinary items and terminated
operations plus depreciation and amortization
minus cash flows from operating activities
ΔREV : changes in net revenue
ΔAR : changes in account receivables
ROA : Returnof Assets
ECA : Expected current accrual
A : Net assets
ε
it
: residual value
3. Real Earnings Management
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
1136
This research using the model from Cohen and
Zarowin (2010) to measure real earning
management
REM = (- R_DISX) + R_PROD
From these equation, Cohen and Zarowin (2010)
multiply R_DISX with negative 1 to make the
relationship unidirectional. Meanwhile, R_PROD is
not multiplied by negative 1 because the higher
production cost indicate that overproduction reduces
the COGS. Thus, the greater REM, the greater
manipulation of discretionary expense and
production cost to increase company profits.
4. Control Variables
This research using Size, Book-to-Market Ratio
(BM), and Leverage as control variable
5. Real Earnings Management
This research using the model from Cohen and
Zarowin (2010) to measure real earning
management
REM = (- R_DISX) + R_PROD
From these equation, Cohen and Zarowin (2010)
multiply R_DISX with negative 1 to make the
relationship unidirectional. Meanwhile, R_PROD is
not multiplied by negative 1 because the higher
production cost indicate that overproduction reduces
the COGS. Thus, the greater REM, the greater
manipulation of discretionary expense and
production cost to increase company profits.
6. Control Variables
This research using Size, Book-to-Market Ratio
(BM), and Leverage as control variable.
4 NALYSIS AND RESULTS
4.1 Descriptive Statistics
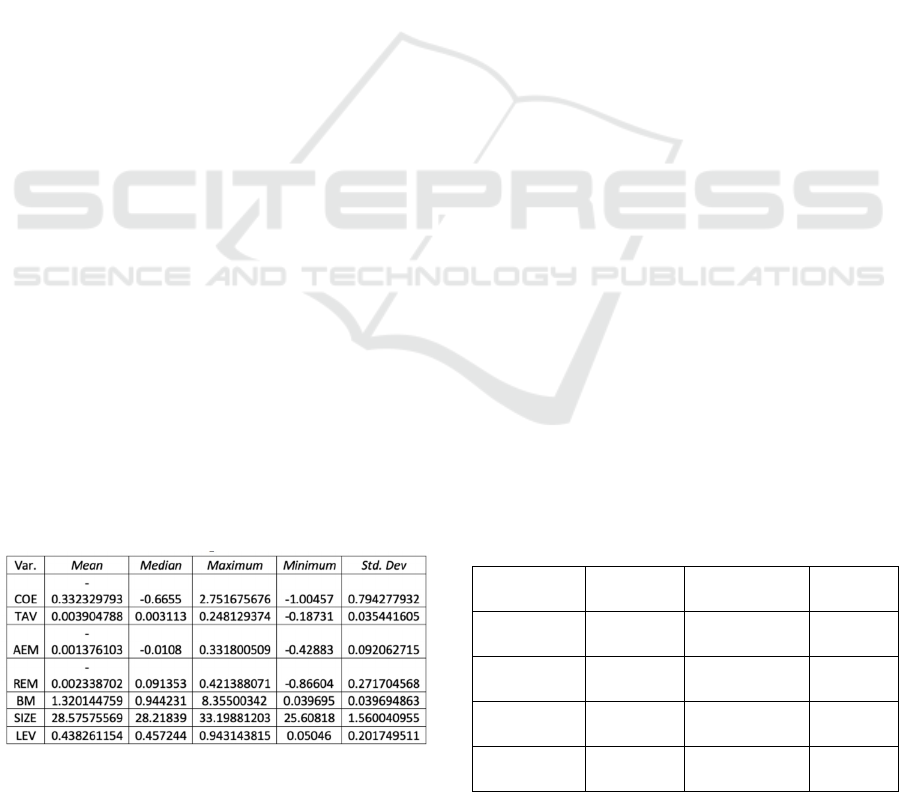
Table1: Descriptive Statistics
Cost of equity are the minimum rate of return
that an investor expects for his investment in a
company. The higher the value of the cost of equity,
the higher the minimum rate of return expected by
investors on their investment in the company’s
shares, and vice versa. The negative number on the
average cost of equity in the table 1 shows that the
average investor loses their investment during period
of 2012 – 2016. Meanwhile, the highest of the cost
of equity indicates investors get a profit on their
investment in the company’s shares.
The negative value of tax avoidance shows that
the average accounting profit before corporate tax is
smaller than the company’s taxable income.
However, the negative average value does not mean
that the average tax avoidance is negative at every
year. This is interesting to observe especially for the
tax authorities in assessing corporate tax avoidance,
especially in the period when tax avoidance is
positive. However, it does not rule out the possibility
of companies making tax evasion in the period when
tax evasion in the period when tax avoidance is
negative.
Accrual earnings management is an intervention
in financial reporting so that it can increase or
decrease accounting profit, by changing the
accounting method or estimation used when
presenting transaction in financial statements. The
negative average accrual earnings management
indicates, in average, management does not conduct
earnings management, or in other words,
management does not increase accounting profit
through accrual activity.
Real earnings management is an act of changing
accounting profits through real activities with sales
manipulation, decreasing discretionary expenses,
and excessive production. The negative average
value of real earnings management indicates that, in
average, management does not carry out real
earnings management through decreasing expenses
and not overproducing.
4.2 Hypothesis Result
Tabel 2: Determination coefficient result
R-squared 0,427938
Mean
dependent var -0,0579
Adjusted R-
squared 0,416971
S.D.
dependent var 0,27696
S.E. of
regression 0,211477
Sum squared
resid 13,99811
F-statistic 39,02384
Durbin-
Watson stat 1,575138
Prob(F-
statistic) 0,003
The Effect of Tax Avoidance, Real and Accrual Earnings Management on Cost of Equity
1137

Adjusted R-squared value of 0.4169, shows that
the variation in the value of cost of equity can be
explained by the independent variable and the
control variable in the regression model of 41.40%.
The remaining 58.30% is explained by other factors
outside the research model.
The probability value of F statistic is below the
0.05 significance level, meaning that the
independent variables affect the dependent variable.
Tabel 3: T test result
Variable Coefficient
Std.
Error
t-
Statistic Prob.
TAV 0,468314 0,1890 2,47740 0,0138*
AEM -0,13334 0,1102
-
1,20955 0,2274
REM 0,079118 0,1084 0,72925 0,4664
BM 0,271431 0,0305 8,87609 0,0000
SIZE -0,15928 0,0135 -11,746 0,0000
LEV 0,385968 0,2456 1,57103 0,1172
C 3,689984 0,3024 12,1989 0,0000
The effect of Tax Avoidance on Cost of Equity
The results in table 3 showed that tax avoidance had
a positive and significant effect (below the 0.05
significance value) on the cost of equity. Thus, it can
be concluded that the first hypothesis (H1) which
states "tax avoidance has a positive effect on the cost
of equity" can be accepted.
This positive relationship means that the greater
the tax avoidance by the company, the more the cost
of equity that must be borne by the investor. The
results of this study are in line with the results of the
Hutchens and Rego (2015) who also revealed in his
research that corporate risk (tax avoidance proxy)
has a positive effect on the cost of equity. This is
confirmed by Cook et al. (2017) that for companies
with high levels of tax avoidance, an increase in tax
avoidance will increase the cost of equity.
The effect of Accrual Earnings Management on
Cost of Equity
The results in table 3 showed that accrual earnings
management did not affect the cost of equity. Thus,
H2 which states "accrual earnings management has a
positive effect on the cost of equity unacceptable.
This negative relationship means that the greater the
accrual earnings management carried out by the
company, the smaller the cost of equity. The results
of this study are in line with the results of Reizky
Ifonie (2012) who conducted research on the effect
of information asymmetry and earnings management
on the cost of equity capital. The results of his
research show that earnings management has no
significant effect on the cost of equity. Reizky Ifonie
(2012) said the results were due to investors
evaluating at this time, while issuers or companies
issued new ordinary shares to cover their operational
and investment debts so the company was less
attractive to investors. In addition, investors consider
other things in investing in a company.
The results of this study prove that the greater
the profit management performed by the company,
the smaller the cost of equity. Accrual earnings
management actions do not affect investors.
Investors consider accrual earnings management
actions to be non-risky so that the information
presented in financial statements is in accordance
with reality. Another guess is the type of mutual
fund investor as one of the biggest types of investors
who invest in bonds. In mutual fund products, total
risk can be minimized and spread so that these
investors become less concerned with accrual
earnings management by the company. In addition,
it is suspected that the inability of creditors or bond
investors to detect the existence of management
profit actions made by the company because the
method of detecting both types of earnings
management (accruals and real) is fairly
sophisticated.
The Effect of Real Earnings Management on Cost
of Equity
The results of the study show that real earnings
management does not affect the cost of equity. Thus,
the third hypothesis (H3) which states that "real
earnings management has a positive effect on the
cost of equity" cannot be accepted. This negative
relationship means that the greater the real earnings
management by the company, the lower the cost of
equity. The results of this study indicate that
management does not carry out real earnings
management through manipulation of discretionary
expenses and excessive production.
The probability level that is above 0.05 is in line
with the average real earnings management which is
negative, which means that the average
manufacturing company in Indonesia in the study
period did not carry out real earnings management.
Manipulation of discretionary burden is carried out
by reducing the burden of research and
development, advertising, sales, administration and
general. This reduction will increase profit for the
year. This occurs when these expenses do not
directly lead to profits and income. This decrease
will also increase the cash flow for the period if the
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
1138

company issues the burden in the form of cash.
However, this risks lower cash flows in the coming
period. Decreasing the burden of discretion causes
abnormal discretionary expenses. Managers also
carry out real earnings management through
manipulation of production by increasing production
more than is needed to increase revenue. When a
company produces more units, the fixed cost per unit
will be lower. This strategy can reduce cost of goods
sold and increase operating profit margins.
Excessive production will produce abnormal
production costs (abnormal production cost). The
combination of abnormal discretionary costs and
abnormal production costs will cover actual profits
or company performance.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Tax is one of the significant components of
corporate profits. In Indonesia, the tax rate that
applies to companies is 25% or a quarter of company
profits. This large tax burden has made the company
make efforts to reduce the tax burden that must be
paid to the tax authorities by tax evasion which
clearly violates the law and with tax avoidance. Tax
avoidance is still in the realm of the legal framework
of tax law by utilizing loopholes in tax law carried
out in order to reduce the tax burden that must be
paid to the tax authorities.
The company's actions to increase company
value are in line with what investors expect. With
the value of the company increasing, company
management hopes to get compensation for the
achievements they have achieved. However, tax
avoidance measures carry risks, which means that
there are additional risks that must be borne by
investors which can harm investors. tax avoidance
can reduce the quality of financial statements. As a
result, investors assume there is uncertainty about
the company's future cash flows. Disrupted future
cash flows will increase the cost of equity. This is in
accordance with the results of the study.
Earnings management is an opportunistic act of
management to increase or decrease accounting
profits with the intention of gaining personal gain.
Earnings management is done to cover actual
earnings or company performance so that it distorts
the quality of earnings reported in the financial
statements. The management discretion in preparing
financial statements makes management freely
choose the accounting method used in financial
reporting that can increase or support the
performance of management. Accrual earnings
management is achieved by changing the accounting
method or estimation used when presenting
transactions in financial statements. Aggressive
accrual earnings management contains discretional
accrual elements such as discretion in the selection
of accounting methods and estimates that are loaded
with uncertainties that will impact accrual quality in
financial reporting.
The results of this study prove that accrual
earnings management actions do not affect investors.
Investors consider accrual earnings management
actions to be non-risky so that the information
presented in financial statements is in accordance
with reality.
Management opportunistic behavior in earnings
management is not only done through the selection
of estimates and accounting methods (accrual
earnings management), but also with the real
activities of companies by changing the structure of
operations, investments, or funding that have
suboptimal business consequences (real earnings
management). The results of the study show that real
earnings management does not affect the cost of
equity. Technological advances and the ease with
which investors can capture information on the
market make management rethink the management
of earnings
REFERENCES
Balakrishnan, K., Blouin, J., & Guay, W. (2018). Tax
Aggressiveness and Corporate Transparency. The
Accounting Review.
Botosan, C. A. (2006). Disclosure and the cost of capital:
what do we know? Accounting and Business
Research, 36(sup1), 31-40.
Botosan, C. A., & Plumlee, M. A. (2002). A re‐
examination of disclosure level and the expected cost
of equity capital. Journal of accounting research,
40(1), 21-40.
Cohen, D. A., & Zarowin, P. (2010). Accrual-based and
real earnings management activities around seasoned
equity offerings. Journal of Accounting and
Economics, 50(1), 2-19.
Cook, K. A., Moser, W. J., & Omer, T. C. (2017). Tax
avoidance and ex ante cost of capital. Journal of
Business Finance & Accounting, 44(7-8), 1109-1136.
Dechow, P. M., & Dichev, I. D. (2002). The quality of
accruals and earnings: The role of accrual estimation
errors. The Accounting Review, 77(s-1), 35-59.
Febrininta, C. N., & Siregar, S. V. (2014). Manajemen
Laba Akrual, Manajemen Laba Riil, dan Biaya Modal.
Jurnal Akuntansi Multiparadigma, 5(1), 365-379.
The Effect of Tax Avoidance, Real and Accrual Earnings Management on Cost of Equity
1139

Francis, J., LaFond, R., Olsson, P. M., & Schipper, K.
(2004). Costs of equity and earnings attributes. The
Accounting Review, 79(4), 967-1010.
Frank, M. M., Lynch, L. J., & Rego, S. O. (2009). Tax
reporting aggressiveness and its relation to aggressive
financial reporting. The Accounting Review, 84(2),
467-496.
Geraldina, I. (2013). Preferensi Manajemen Laba Akrual
Atau Manajemen Laba Riil Dalam Aktivitas Tax
Shelter. Jurnal Akuntansi Dan Keuangan Indonesia,
10(2), 206-224.
Hutchens, M., & Rego, S. (2015). Does greater tax risk
lead to increased firm risk?
Jaggi, B., Leung, S., & Gul, F. (2009). Family control,
board independence and earnings management:
Evidence based on Hong Kong firms. Journal of
Accounting and Public Policy, 28(4), 281-300.
Kim, J.-B., & Sohn, B. C. (2013). Real earnings
management and cost of capital. Journal of
Accounting and Public Policy, 32(6), 518-543.
Lambert, R., Leuz, C., & Verrecchia, R. E. (2007).
Accounting information, disclosure, and the cost of
capital. Journal of accounting research, 45(2), 385-
420.
Meini, Z., & Siregar, S. V. (2014). The effect of accrual
earnings management and real earnings management
on earnings persistence and cost of equity. Journal of
Economics, Business & Accountancy Ventura, 17(2),
269-280.
Reizky Ifonie, R. (2012). Pengaruh Asimetri Informasi
Dan Manajemen Laba Terhadap Cost of Equity
Capital Padaperusahaan Real Estate Yang Terdaftar Di
Bursa Efek Indonesia. Jurnal Ilmiah Mahasiswa
Akuntansi, 1(1), 103-107.
Roychowdhury, S. (2006). Earnings management through
real activities manipulation. Journal of Accounting and
Economics, 42(3), 335-370.
Tang, T., & Firth, M. (2011). Can book–tax differences
capture earnings management and tax management?
Empirical evidence from China. The International
Journal of Accounting, 46(2), 175-204.
Zang, A. Y. (2011). Evidence on the trade-off between
real activities manipulation and accrual-based earnings
management. The Accounting Review, 87(2), 675-
703.
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
1140
