
Model and Strategy Acceleration of Rural Poverty Alleviation Study
in Jambi Province
Siti Hodijah
1
and Syaparuddin
1
1
Departement of Economic Development, Jambi University, Indonesia
Keywords: Poverty, Rural Poverty, Strategy Acceleration
Abstract: Poverty is a very interesting phenomenon and has always been an issue that is always debated in the midst
of society, technocratic or academic. This study aims to (1) Identify the description of the rural poverty of
Jambi Province, (2) Formulate a model for accelerating rural poverty reduction in Jambi Province and (3)
Designing strategy for accelerating rural poverty reduction in Jambi Province. The data analysis techniques
used in combining qualitative and quantitative descriptive methods. The results showed that the number and
percentage of poor people, most of the districts in Jambi Province tended to increase in 2017 compared to
2010. The districts were Merangin, Batang Hari, Tanjung Jabung Timur, Tanjung Jabung Barat, Bungo and
Tebo. The model of accelerating rural poverty alleviation in Jambi Province which can be formulated is to
encourage poor families to get out of poverty with the main actors being poor families themselves by always
getting attention from the central government, regional government, private sector and universities in the
form of coordination and integration. The main strategy that must be done is to empower the abilities,
talents and skills of poor families and reduce all the limitations that exist in these poor families. The basic
need approach for some poor people still needs to be done.
1 INTRODUCTION
Poverty (Poverty reduction) is an issue that has
always been debated for more than two decades. The
poverty alleviation program is the main measure of
the success of development policies, especially in
the 1970s until the 1980s. Poverty is a long-term
problem ( Ben E. Aigbokhan, 2008 ). Various views
and opinions of economists, especially Development
Economics experts who see that the reduction in
poverty is a central goal for the development of a
country that can be achieved through economic
growth or income distribution. Almost all countries,
especially developing countries, have raised the
issue as the main development policy in the era of
the 1990s ( Hyun H. Son and Nanak Kakwani,
2004).
The failure or lack of success of poverty
alleviation does not only occur in Indonesia, but in
many countries, especially in developing countries,
one of which is Nigeria. One of the failures was
caused by a program that did not focus directly on
poverty and political stability and unstable policies
(Mike I Obadan). Even with the expenditure poverty
criteria of US $ 1 per capita per day, the number of
people living below the poverty line increased from
54.7% in 2004 to 60.9% in 2010 ( Okoroafor,
Michael Onyedikachi and Nwaeze Chinweoke,
2013).
The issue of poverty is still a fundamental
problem and is multidimensional in development in
Indonesia. Being a fundamental problem because
poverty is a problem faced by almost all regions in
Indonesia both in urban and rural areas and is very
difficult to solve. Whereas multidimensional nature
can be seen from two sides, namely the cause and
the alleviation side.In terms of causes, poverty is
caused by a variety of backgrounds, while poverty
alleviation must also be multidimensional.
In various literatures, many have been offered
and have even been implemented in many countries
regarding the model and strategy as well as the
government's approach to poverty reduction
including the basic need approach , the employment
orientation approach , and through economic growth
strategies ( economic growth strategy ), but all of
that has not fully been able to realize one of the great
Hodijah, S. and Syaparuddin, .
Model and Strategy Acceleration of Rural Poverty Alleviation Study in Jambi Province.
DOI: 10.5220/0009506405690576
In Proceedings of the 1st Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science (UNICEES 2018), pages 569-576
ISBN: 978-989-758-432-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
569

ideals in nation building which is free from poverty.
In Indonesia itself, apart from this approach, efforts
have been made to reduce poverty through direct
and indirect or empowerment programs. Various
farming business loans (KUT), people's business
credit (KUR), cash direct assistance (BLT), Raskin,
underdeveloped village Inpres, Home Surgery then
empowerment through PNPM and many other
programs.
Judging from the political will that exists, what
the government has done in alleviating poverty is
sufficient. Especially if the political will is measured
by the disbursement of funds issued by the APBN
(Sukidjo and Ali Muhson, 2010). Similar conditions
also occur in regions including in Jambi Province,
where the tendency for numbers and poverty levels
tends to increase over the past 5 years.
With various models and strategies and
approaches that have been taken, the problem of
poverty is still a development problem that has not
been resolved so far. Thus another model and
strategy is needed which is more appropriate in
alleviating poverty, especially in the Jambi Province
Rural Area.
2 LITERATURE STUDY
Poverty is often seen as an inability to pay minimal
living costs (World Bank, 1990) although some
experts argue that poverty is also a lack of access to
services such as education, health, information, and
lack of public access to development and political
participation. The definition of poverty can also be
viewed in terms of relative and absolute sides: (BPS,
2014)
Relative Poverty Relative poverty is a poor
condition because of the influence of development
policies that have not been able to reach all levels of
society, causing inequality in income distribution.
Minimum standards are prepared based on the living
conditions of a country at a certain time.
Absolute Poverty Absolute poverty is determined
based on the inability to meet minimum basic needs
such as food, clothing, health, housing and education
needed to be able to live and work. Indonesia uses
an absolute definition of poverty that is able to
compare poverty in general and assess the effects of
inter-time poverty reduction policies.
World Bank (2000) as quoted by Jonathan
Haughton and Shahidur R. Khander (2012) defines
poverty as a lack of well-being. One approach used
is to regard welfare as mastery of goods in general,
so that people can be much better if they have
greater resources. The main focus lies in the fact
whether each household or individual has adequate
resources to meet their various needs. Specifically,
poverty is then measured by comparing the income
and consumption of each individual with a set
number of standards where they are considered poor
if their income or consumption is below that
standard.
According to Robert Chambert as quoted by
Achmad Fatony (2011), the essence of poverty is
what is called Depriviation Trap which consists of
five disadvantages that surround the lives of poor
people, namely: poverty itself, physical weakness,
alienation, vulnerability, and , helplesness.
According to Chambers, of the five shortcomings
of these shortcomings, the most needed attention is
vulnerability and powerlessness. Vulnerability can
be seen from the inability of poor families to provide
something to deal with emergency situations such as
the arrival of natural disasters, rising fuel prices or
diseases that suddenly afflict families (subsistence,
according to James Scott). This vulnerability often
leads to poverty rockets or "driving wheels of
poverty" which causes poor families to have to sell
the most valuable assets for consumption needs so
that the family becomes increasingly into the valley
of poverty . Helplessness is considered the most
significant factor in encouraging the process of
poverty or impoverishment, because the process of
exploitation is in this line in all its forms. Although
the substance of powerlessness often appears in the
form of exploitation, namely extortion by a stronger
group
Furthermore, World Bank (2008) as quoted by
Made Kerta Adhi, I Ketut Ardana and I Made
Maduriana , (2016), distinguishes poverty into three,
namely absolute poverty, relative poverty, and
cultural poverty. Someone belongs to the absolute
poor if the income is below the poverty line, no
enough to meet minimum living needs, bothb food,
clothing, health, boards and education. While
poverty relative poverty is an inner poverty level has
to do with an absolute poverty line ratio or the
proportion of income distribution (welfare) that is
lame or uneven. Oscar Lewis stated, cultural poverty
emerged as a result of the values or culture adopted
by poor people, namely lazy, easy to give up on fate,
lack work ethic and so on. kcultural emiskinan a
domino effect from the shackles of structural
poverty sits on society too long, or indirectly shows
the link between structural poverty and cultural
poverty that makes society apathetic,surrender, and
view if something happens is fate In measuring
poverty rates, there are several approaches, first the
Economic approach Poverty from the economic side
is measured through the income approach. Second .
Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) approach . The
World Bank defines the international poverty line as
US $ 1 and US $ 2 per day in 1993 as measured by
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
570

the purchasing power parity approach . Purchasing
power parity is defined as a method used to measure
how much a currency can buy the same number of
goods or services in international measurements
because the prices of goods and services in several
countries are different. While US $ 2 poverty
measurement is intended for countries that are in the
category of having middle income , such as East
Asia and Latin America. This conversion number is
calculated based on the price and quantity in each
country collected in a survey which is usually
carried out every five years.
Third . Multidimensional Poverty Index
(Multidimensional Poverty Index - MPI) definition
of poverty is growing and not just judged by the
monetarists. The United Nation Development
Program (UNDP) develops the definition of poverty
from various aspects by developing a
multidimensional poverty index. The
multidimensional poverty index identifies the
inability of a person to fulfill their basic needs based
on three dimensions, namely health, education, and
living standards. These dimensions are further
reduced to 10 indicators, namely nutrition, child
mortality, school duration, school enrollment rates,
cooking fuel, type of toilet, water, electricity, type of
floor, and ownership of assets. The
multidimensional poverty index calculation can be
calculated from micro data sourced from household
surveys. The MPI methodology can be modified to
produce a multidimensional national poverty
measure that reflects culture, economy, climate, and
other local factors. International MPI is designed as
an analytical tool to compare acute poverty between
countries.
The results of Mahmood Messkoub's ( 2008)
study in Mena Arab countries (Arab and North
Africa), found that economic growth and job
creation were not good enough in reducing poverty
in MENA Arab countries mainly due to the low
growth rate of employment opportunities, due to the
low skill possessed by workers. Poverty in Nigeria is
a long-term problem. Judging from the incidence
and dimensions of poverty, there has been an
increase in poverty in urban areas from 17.2% in
1980 increased to 58.2% in 1996, but fell back to
43.2% in 2004. On the other hand, rural poverty
increased from 28.3% in 1980, increased 69.3% in
1996 and decreased slightly in 2004 to 63.3%.
economic growth does not help much to reduce
poverty. From the education dimension it shows that
poverty is concentrated in the community with basic
education ( Ben E. Aigbokhan, 2008 ).More than
90% of the poor in Rwanda live in rural areas, most
of the income sources of poor households come
from wages working in the agricultural sector. As
many as 91% of poor households are below the
poverty line. Poor households that depend on a
combination of working in the agricultural sector
and as a laborer not more than 82% (Minestry of
Finance and Economic Planning, 2007).
3 RESEARCH RESULT AND
ANALYSIS
3.1. Overview Poverty in Jambi
In general, the number of poor people in Jambi
Province and in the municipal districts in Jambi
Province in the last decade (2010-2017) tended to
fluctuate, with the highest number of poor people
being in 2015 with a total population of 300,710
people. According to regencies / cities, the highest
number of poor people in 2010 was in Jambi City,
namely 52.6 thousand people, West Tanjung Jabung
Regency 31 thousand people and Merangin District
27.3 thousand people. Whereas in 2017 the highest
number of poor people was found in Jambi City,
namely 52.08 thousand people, West Tanjung
Jabung Regency 36.33 thousand people and
Merangin District 35.48 thousand people. Most of
the regencies in the province have a poor population
in 2017 compared to 2010, only Kerinci Regency,
Sungai Penuh City and Jambi City have experienced
a decline, although not much.
Similar to the number of poor people, the
majority of districts in Jambi Province, the
percentage of poor people tends to increase in 2017
compared to 2010. The districts are Merangin,
Batang Hari, Tanjung Jabung Timur, Tanjung
Jabung Barat, Bungo and Tebo. Referring to the data
an interesting thing that can be studied is that in
2011 was a good period where the percentage of
poor people both Jambi Province and district / city
decreased, in 2012 the percentage of poor people in
Jambi Province and regencies / cities experienced an
increase . In other words, 2012 was a turning point
in the decline in development achievements in
poverty alleviation. This condition occurs more due
to the decline in people's purchasing power caused
by the decline in prices of plantation and agricultural
commodities.
Aside from the number and level of poverty, the
other problem picture of poverty is the depth of
poverty (Poverty Gap Index) that is one of the
indicators used to measure the level or average
expenditure gap that occurs in each population, with
a measurement standard limited by the poverty line.
Districts with more than one poverty depth index
during the period 2010-2017 are Sarolangun District,
Model and Strategy Acceleration of Rural Poverty Alleviation Study in Jambi Province
571
Tanjung Jabung Timur, Tanjung Jabung Barat and
Batang Hari. When associated with poverty levels,
districts with high levels of poverty have a greater
poverty depth index compared to districts / cities
with low poverty rates.
The problem of poverty lies not only in the
number and percentage of the poor, but also the
problem of poverty severity (Poverty Severity Index
). The poverty severity index is an index that
provides information about the description of the
distribution of spending among the poor. The higher
the index value, the higher the inequality of
expenditure among the poor.
The poverty severity index in the district / city of
Jambi Province in 2010 was all less than 0.5. Sungai
Penuh City and Merangin Regency have the smallest
poverty severity indexes of 0.11 and 0.13
respectively, while the largest are Tanjung Jabung
Barat (0.67) and Jambi City (0.49). While for 2017
the smallest poverty severity index was Sungai
Penuh City and Muaro Jambi respectively 0.03 and
0.07, while the largest were Tanjung Jabung Timur
District (1.05) and Sarolangun District (0.69).
3 .2. Characteristics of Poor Households
3 .2.1. Age
The influence of this age can be attributed to
experience and maturity of thinking and acting in
dealing with every problem and problem in family
life and in society in general. The description of the
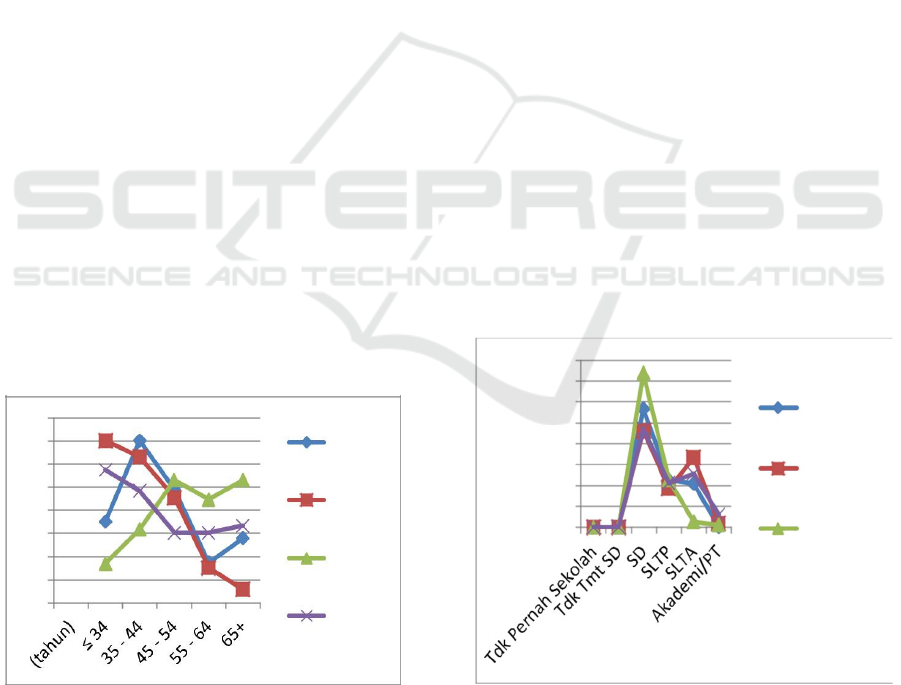
age distribution of respondents is presented in Figure
1. Based on figure 1, it can be described that the
highest number of poor household heads are at the
age of 35-44, which is 26.70.
Figure 1: Age Distribution of Poor Rural Household
Heads in Jambi Province in 2018.
3.2.2. Education
Education plays a very important role in shaping
one's mindset and pattern of action. The higher a
person's education, the better the pattern and pattern
of the pattern, including its ability to analyze an
issue. In the context of poverty alleviation, education
is considered a breaker in the poverty chain. It can
be informed that most of the education levels of poor
household heads of respondents are elementary
schools (East Jabung Tanjaung, Tanjung Jabung
Barat and Batang Hari) and SLTP (Sarolangun
District).
According to the Regency, Tanjung Jabung
Timur Regency has the highest number of
elementary school graduates (56.60%), junior high
school (22.64%) and senior high school (20.75%)
and there is no academy or university education.
Tanjung Jabung Barat Regency has the highest
number of elementary school graduates (46.19%),
senior high school (33.30%), junior high school
(18.71%) and academics or tertiary education with
1.75%. Batang Hari Regency has elementary
(73.86%), junior high school (22.72%) and high
school (2.72%) and academy or tertiary education
with 1.14%. Whereas in Sarolangun District, there
were elementary school education (46.96%), high
school (25.75%) and junior high school (21.21%)
and Academy or Higher Education as much as
6.06%. In general, the education level of the heads
Of poor households is of low primary and secondary
education. The details are East Tanjung Jabung
District 79.24%, Tanjung Jabung Barat 64.90%,
Batang Hari 95.52% and Sarolangun 68.11%.
Figure 2: Distribution of the Education Level of
Poor Rural Household Families in Jambi Province in
2018.
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
572

3 .2.3. Work and Working Hours
In general, poor families depend their lives mainly
on the primary sector namely agriculture, plantations
and fisheries or forestry compared to other sectors .
S ost respondents living in the field of business
sector and the primary sector, especially agriculture
and fisheries. Viewed by regency, Tanjung Jabung
Timur Regency is the main occupation of poor
families dominant in the agricultural sector (56.14%)
and fisheries (19.29%), West Tanjung Jabung
Regency in the fisheries sector (52.40%) and trade
(21.68 %). Batang Hari Regency in the agricultural
sector (31.82%) and fisheries (30.68%). Then
Sarolangun District 54.54% worked in the
agricultural sector, trade (13.65%) and processing
industries, especially CPO and Rubber processing
(13.65%)
Based on information as obtained by almost no
poor people who have side jobs. Thus it can be
concluded that the lives of poor households rely on
the main work or main work of agriculture, fisheries
and trade (trade with very little capital).
Judging from j am workweek heads of poor
households in the province of Jambi between 14 to
more than 55 hours per week. Referring to the BPS
criteria as stated earlier, it can be concluded that
Sarolangun and Tanjung Jabung Barat Regencies
working hours of family heads 35 hours and above
(full working) reached 77.26% and 81.86%
respectively. Whereas Tanjung Jabung Timur and
Batang Hari districts with working hours of family
heads 35 hours and above are 63.28% and 30.67%
respectively. The head of the household included in
the usual under employment category (working
hours 14-34 hours) is mostly in Batang Hari
Regency (64.77%) and Tanjung Jabung Timur
(32.14%) while belonging to the category of critical
unemployment only in Batang Hari Regency and
Tanjung Jabung Timur 4.54% and 3.57%
respectively. The relative number of poor household
heads working normally (working above 35 hours
per week), but still in the poor category indicates:
1. Not always long working hours can create /
generate more income.
2. The heads of poor households generally work in
the traditional agricultural, plantation and
fisheries sectors
3. The head of a poor household works more on
relying on the power of his strength rather than
skill or skill.
4. With long working hours, even with low
income, poor families can survive.
3.2.4. Structure and Education of
Household Members
The results of the study showed that the structure of
family members of poor households in the Rural
Province of Jambi was generally the core family.
There are only 1.28% in the West Tanjung Jabung
Regency and 0.33% in the Batang Hari Regency in
the broad sense. This condition is very reasonable,
considering that poor families have limitations,
making it difficult for them to invite or
accommodate other people to live with them.
Viewed from the burden of dependents, one
family head has a burden of between two and three
people and three to four people. Tanjung Jabung
Timur and Batang Hari Regencies have a burden of
2-3 people per family and Tanjung Jabung Barat
Regency and Sarolangun have a burden of 3-4
people.
In general, the education level of the family
members of poor households in each district is
relatively different. In Batang Hari Regency it is
more concentrated in elementary school (52.84%)
and junior high school graduates (26.42%), in
Tanjung Jabung Barat and Tanjung Jabung Timur
Regencies concentrated in senior secondary
education with 45.93% and 49.03% respectively.
One more interesting thing happened in Sarolangun
District, where 34.81% of poor family members
were educated in Higher Education and 33.03% had
high school education. This illustrates that the
fighting capacity of poor families to get out of
poverty through education is very high compared to
other districts.
3.2.5. Residence
Judging from the status of home ownership, most of
the respondents live in their own homes between
69.0% and 95.45%. Tanjung Jabung Timur
Regency, the majority of poor families occupy their
own homes (73.80%) and parents' (22.61%).While
in Tanjung Jabung Barat Regency owned by
themselves (69.0%) and rent (19.88%), Batang Hari
Regency belongs to itself (95.45%) and belongs to
parents (4.54%). Sarolangun Regency occupies the
most part of the house itself (87.87%), owned by
parents and each rent is 6.06%. The data shows that
there is still a need for assistance policies for the
construction of poor family homes in all sample
regions, especially in the East Tanjung Jabung and
Tanjung Jabung Barat Regencies. These
considerations are due to the relatively large number
of poor families who do not have their own homes.
Model and Strategy Acceleration of Rural Poverty Alleviation Study in Jambi Province
573

3.2.6. Source of Information
The main source of information for rural poor
households in Jambi Province is PLN with the
number of households between 94.74% and 100%.
According to the regency, the main source of
information for poor family households in each
district other than East Tanjung Jabung Regency is
PLN which reaches 100%. Especially for East
Tanjung Jabung Regency there are still 5.26% of
poor families using Kerosene Lamps.
3.2.7. Source of Clean Water
The source of clean water used by poor households
is mostly dug wells or Drill wells with up to 59.09%
to 99.41% of poor sample households. Source of
clean water comes from dug wells or bore wells in
Tanjung Jabung Barat District (99.41%), Most rivers
in Tanjung Jabung Timur (22.61%), Most Rainwater
in East Tanjung Jabung (5.95%) and most PDAMs
in Sarolangun Regency ( 49.90%).
3.2.8 . Income and Assets
In general, the monthly income of the heads of poor
households is between Rp.500,000 and
Rp.2,000,000. Only 7.92% up to 18.18% of the
income of the household heads of poor households is
less than Rp.500,000 and 10.0% to 13.63% of the
income of the heads of poor households is more than
Rp.2,000,000.
3.2.9 . Household expenditure patterns
Theoretically expenditure follows income, meaning
that the greater one's income, the greater the
expenditure. On the other hand, the smaller the
income of a person or family, the greater the share of
income that is used for food or food expenditure.
Viewed from the distribution of expenditure of poor
households, most of them are concentrated in food
expenditure between 83.00% and 95.65%, while
non-food expenditure is between 4.34% to 17.00%.
This proves that the largest expenditure of poor
families is concentrated in food expenditure and at
the same time records the low capacity of poor
families to finance non-food expenditure.
3.2.1 0 . Asset ownership
The inability of poor families to have assets,
especially productive assets, is allegedly one of the
causes of the poverty of a household from an
economic perspective. The absence or lack of
ownership of productive assets makes it difficult for
poor families to get out of poverty. The results
showed that of the 391 respondents, poor households
that had assets were 69.00% to 95.45%. According
to the districts of poor households that have the most
assets in Batang Hari Regency (95.45%), then
Sarolangun District (87.87%), Tanjung Jabung
Timur (73.80%) and Tanjung Jabung Barat District
(69.00%).
3.2.1 1 . Health and Medical Complaints
There is a positive correlation between the level of
income and the degree of public health, the higher
the income of a family the higher the degree of
health, and vice versa. Poor families are usually very
vulnerable to health problems. Based on the results
of the study, generally complaints about the health
of rural poor households in Jambi Province are
cough, heat and colds, especially in Batang Hari and
Tanjung Jabung Barat Regencies. The main health
complaints of poor households in Tanjung Jabung
Timur and Tanjung Jabung Barat Districts, Batang
Hari and Sarolangun are Batuk and Panas.
Meanwhile, when viewed from facilities or
facilities for treatment of families of poor
households in rural areas, Jambi Province is
generally treated at Puskesmas with respondents
reaching 61.81% to 93.18%. According to the
regency, the highest number of treatment for
families of poor households in East Tanjung Jabung
Regency is Puskesmas (61.81%), health and
traditional labor practices respectively 7.27. In
Tanjung Jabung Barat District, there are Puskesmas
(68.23%), doctor practices (12.35%), health
personnel practices (8.23%) and hospitals (5.88%).
Furthermore, the Batang Hari District Health Center
was 93.18% and the hospital was 4.54%. Then
Sarolangun District has 64.51% Puskesmas, 16.12%
doctors and hospitals practice 6.45%.
3.3. Strategy and Model for Accelerating Poverty
Reduction
Based on information obtained from respondents,
poverty in Rural Jambi Province caused by:
1. Lack of capital
2. Lack of capital to buy fertilizer
3. Lack of business fields
4. Low education
5. Lack of knowledge
6. Lack of information
7. HR is unable to compete
8. Lack of skill
9. Age factor
10. Lack of knowledge about entrepreneurship
11. Lazy to work
12. Descent
13. Lack of government assistance and attention
14. Non-permanent income
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
574
15. Rubber prices continue to decline
16. Lack of public transportation customers
17. Low purchasing power
18. High prices of basic goods while low income
19. Small business opportunity
Based on the previous problems, which are the
main causes of poverty in the Jambi Province, the
strategy that can be done is to find a solution from
the source of the problem. In other words the model
that can be done is based on or based on the self of
the poor himself. All respondents are eager to get
out of poverty, meaning that there has been an
encouragement from within themselves to change
their destiny.
Job creation, capital assistance , improvement of
poor family education, improvement of knowledge
and skills through training, guidance, vocational
training centers so that their human resources can
increase and have competitiveness, provide access to
and information services as wide as possible both
employment opportunities, assistance government,
training and others, developing entrepreneurial
capabilities, encouraging work culture, increasing
people's purchasing power, and enforcing inflation.
Some of the efforts expected by poor households to
get out of poverty are through business:
a. Tanjung Timur Regency
1. Trade
2. Business credit
3. Online business
4. Area nut business
5. Raising native chickens
6. Raising chickens pot o ng
7. Open a grocery store
8. Farming
9. Open a cafe business
10. Open a breakfast business
11. Raising catfish
12. Trade results own fish catch
13. Fishing business
14. Fish cultivation
15. Recycle items and sell them
16. Make shrimp crackers
17. Open a restaurant
18. Trade fish
b. West Tanjab Regency
1. Trade
2. Trade fish
3. Fish container
4. Fish processing business
5. Opening a UMKM business
6. Candied business
7. Has pompong and fishing gear
8. Cracking business
9. Food shop business
10. T u kang Enterprises sewing
11. Business for washing cars and motorbikes
12. Areca shop
13. Buying and selling coconuts
c. District Batanghari
1. Food shop business
2. T u kang Enterprises sewing
3. Open a selling kiosk
4. Fish cages
5. Gardening
6. farming
7. Open a chicken farm
8. Trade
d. Sarolangun Regency
1. Trade
2. Open a restaurant
3. Open a shop
4. Raising S fire
5. Raising goats
6. Raising chickens
7. Raising quails
8. Fruit gardening
9. Selling on the market
10. Open a workshop business
11. Open chili land
12. Wood furniture business
13. Open your own rubber land
14. Open your own palm land
15.
Continuing the bamboo business
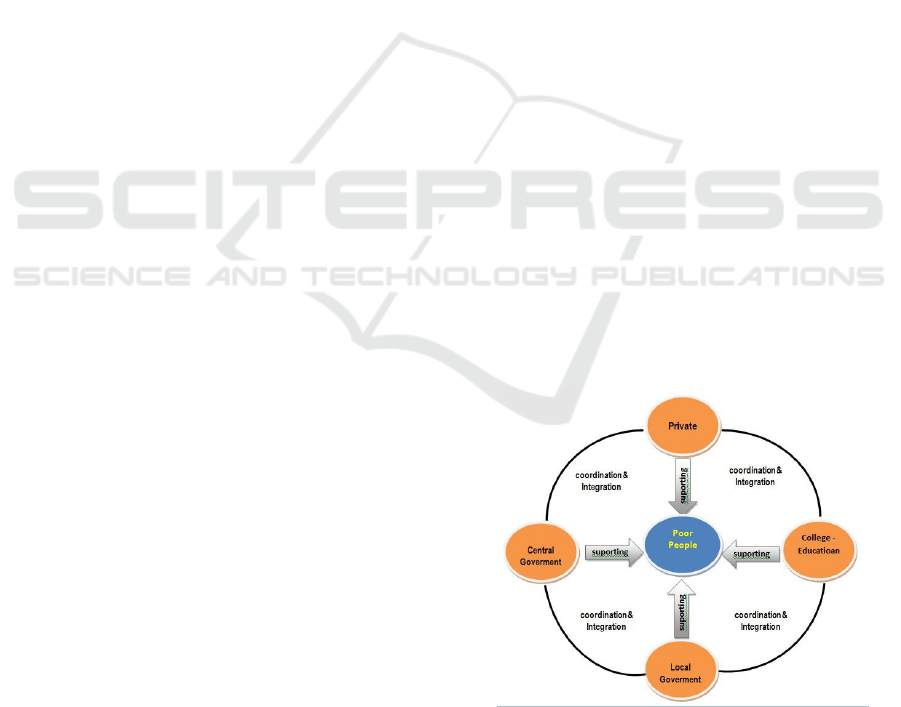
Figure 3: Model of Accelerating Rural Poverty
Reduction Jambi Province
Model and Strategy Acceleration of Rural Poverty Alleviation Study in Jambi Province
575

4 CONCLUSION AND
SUGGESTION
4.1. Conclusion
1. Most districts in Jambi Province, the percentage
and number of poor people tend to increase in
2017 compared to 2010.
2. The model of accelerating rural poverty
alleviation in Jambi Province which can be
formulated is to encourage poor families to get
out of poverty with the main actors being poor
families themselves by always getting attention
from the central government, regional
government, private sector and universities in the
form of coordination and integration.
3. The main strategy that must be done is to
empower the abilities, talents and skills of poor
families and reduce all the limitations that exist
in these poor families.
4.2. Suggestion
1. The basic need approach for some poor people
still needs to be done
2. Job creation, improvement of skills and
knowledge and opening access to and
information as widely as possible for poor
families in various aspects becomes very
important.
3. The poverty alleviation base is the poor and
makes it a subject.
REFERENCES
Achmad Fatony, (2011). Poverty Alleviation Policy Based
on Participatory Poverty Assessment: The Case of
Yogyakarta. Journal of Socioconseptia volume 16
number 02. 2011
BPS, (2014). National Poverty Profile and Analysis.
Ben E. Aigbokhan, (2008). Growth, Inequality and
Poverty in Nigeria. ACGS / MPAMS Discussion
Paper No.3. Prepared for United Nations Economic
Commission for Africa (UNECA) Addis Ababa,
Ethiopia February, 2008. Economic Commission for
Africa.
Haughton Jonathan and Khander Shahidur R, (2012).
Guidelines on Poverty and Inequality: Handbook on
Poverty and Inequlaity. Salemba Empat. Jakarta
Hyun H. Son and Nanak Kakwani, (2004). Economic
Growth and Poverty Reduction: Initial
Conditions Matter United Nations Development Program.
Working Paper Number 02 August 2004.
Made Kerta Adhi, I Ketut Ardana, I Made Maduriana ,
(2016). Actors Causing Cultural Poverty and Local
Wisdom-Based Eradication Models: A Study of the
Poor in the Kintamani Mountains, Bali . Journal of
Bali Studies Vol. 06, No. 02,
October 2016. Mahmood Messkoub, (2008). Economic
Growth,
Employment and Poverty in the Middle East and North
Africa. Workin Paper No. 460. Institute of Social
Studies.
Mike I Obadan. Poverty Reduction in Nigeria: The Way
Forward. CBN Economic review Volume 39 No. 4.
Minestry of Finance and Economic Planning, (2007). The
Republic of Rwanda: Economic Development and
Poverty Reduction Strategy. 2008-2012.
Okoroafor, Michael Onyedikachi and Nwaeze Chinweoke,
(2013). Poverty And Economic Growth In Nigeria
1990–2011. The Macrotheme Review 2 (6), SI-IMT,
2013.
Sukidjo and Ali Muhson, (2010). Model of Empowerment
of Poverty Alleviation Based on Local Institutions
and Business Development in the Special Province
of Yogyakarta. Yogyakarta State University.
Yogyakarta
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
576
