
Board of Director and Earnings Management in Islamic Bank
Virasty Fitri and Dodik Siswantoro
Faculty of Economics and Business, Universitas Indonesia, Jakarta - Indonesia
Keywords: Earnings Management, Islamic Banks, Board of Director.
Abstract: The purpose of this paper is to test and prove empirically the influence of the characteristics of the board of
directors on earnings management. The characteristics of the board of directors used in this study are
Islamic education background, size, number of independent directors and the financial background of
members of the board of directors. The research sample is Islamic banks in Indonesia during 2013-2017.
Data is taken from annual reports which can be accessed on the Islamic bank website. The proxy used to
measure the amount of earnings management uses Discretionary Loans Loss Provision (DLLP). The results
of this study indicate no significant results. The characteristics of the board of directors have no influence
on the practice of earnings management in Islamic banks.
1 INTRODUCTION
The phenomenon of earnings management is a
common thing in companies and banks, and even
Islamic-based banks also take part in the practice
(Quttainah et al. 2013). Viewed from an Islamic
perspective, earnings management is not in
accordance with Islamic teachings because there are
efforts to deceive the company's financial condition
to investors, which will harm investors (Obid and
Demikha, 2011). One effective way to reduce
earnings management practices is by governance
mechanisms (Jensen and Meckling, 1976). One part
of the governance mechanism is the existence of a
board of directors that acts as a link between
interests between shareholders and company
management and ensures compliance with
accounting principles (Dechow et al. 1996;
McMullen and Raghunandan, 1996), preventing
fraud in financial statements (Beasley, 1996) and
limiting earnings management practices that are
likely to occur in companies (Klein, 2002; Xie et al.,
2003). One dimension in the board of directors is a
board of directors who have an Islamic education
background considering that earnings management
practices are contrary to Islamic principles (Mersni
and Ben Othman, 2015; Quttainah et al. 2013;
Hamdi and Zarai, 2012; Ben Othman and Mersni,
2014). The size of the board of directors also plays a
role in reducing earnings management practices (Xie
et al. 2003; Quttainah et al. 2013; Mersni and Ben
Othman, 2015). Likewise the existence of
independent directors can reduce the practice of
earnings management (Liu, 2012; Taktak and
Mbarki, 2014). The board of directors with an
accounting education background are expected to
reduce earnings management practices with their
capabilities (Dechow et al., 1996; Klein, 2002;
DeFond and Jiambalvo, 1993; Naser and
Pandlebury, 1997).
The purpose of this paper is to test and prove
empirically the characteristics of the board of
directors for earnings management. Since earnings
management behavior is not in accordance with
Islamic teachings, the board of directors are
expected to play an important role in reducing
earnings management practices.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
There are many studies on the practice of earnings
management in Islamic banks that are reviewed from
the aspect of governance. Members of the board of
directors who are members of AAOIFI play a role in
reducing the practice of earnings management
(Mersni and Ben Othman, 2015; Quttainah et al.
2013; Hamdi and Zarai, 2012). But other studies
show the opposite results (Kolsi and Grassa, 2016).
Thus, the first hypothesis is:
H1: There is a negative relationship between the
board of directors who have an Islamic religious
Fitri, V. and Siswantoro, D.
Board of Director and Earnings Management in Islamic Bank.
DOI: 10.5220/0009507511631166
In Proceedings of the 1st Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science (UNICEES 2018), pages 1163-1166
ISBN: 978-989-758-432-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
1163

education background and earnings management
practices.
Large board size can reduce the practice of
earnings management (Quttainah et al. 2013). But
there are also studies that argue the opposite
(Beasley, 1996; Dechow et al. 1996; Loderer and
Peyer, 2002). So, the second hypothesis is:
H2: There is a negative relationship between
board size and earnings management practices in
Islamic banks.
The existence of independent directors can
reduce earnings management practices (Quttainah et
al. 2013). However, some studies have argued
otherwise (Liu, 2012; Taktak and Mbarki, 2014). So,
the third hypothesis is:
H3: There is a negative relationship between the
independent board of directors and earnings
management practices.
Members of the board of directors with a
financial background can reduce earnings
management practices using their abilities (Naser
and Pandlebury, 1997). However, other studies have
argued otherwise (Kolsi and Grassa, 2016; Xie et al.
2002). Then the fourth hypothesis is:
H4: There is a negative relationship between the
board of directors and the financial background and
practice of earnings management.
3 RESEARCH METHOD
The research method used is a quantitative empirical
study. In this study, researchers will conduct panel
regression statistical testing of the influence of the
characteristics of the board of directors on earnings
management in Islamic banks in Indonesia. The
object of this research is Islamic banks in Indonesia
in 2013-2017. The research instrument used was
documentation. Research uses quantitative data
sourced from secondary data, namely annual reports
that can be accessed on the website of Islamic banks.
In addition, information is collected that supports
research through books, online access media
(internet), and published information such as
journals, theses, and dissertations relevant to
research. The initial sample used in the study
amounted to 11 Islamic banks in Indonesia.
However, there is one Islamic bank that does not
have an annual report in 2014. Thus, the final
sample is 10 Islamic banks in Indonesia for 5 years,
namely 2013-2017.
The dependent variable in this study is earnings
management. Measurement of earnings management
To examine the relationship between the
characteristics of the board of directors and earnings
management in Islamic banks, following the
approach taken by Ben Othman and Mersni (2014)
and Mersni and Ben Othman (2015). This study uses
a two-stage approach. In the first stage, using
specific accruals to measure earnings management
in Islamic banks. More specifically, using majority
accruals in the banking sector, LLP. The proxy is
divided into two components, namely discretionary
and non-discretionary. Here's the form of the model
equation:
Non-discretionary components that are part of
LLP are the portion of accruals arising from changes
in the bank's business conditions. Because this
cannot be directly observed, it is estimated to use
variables that reflect the level of losses in the loan
portfolio. Just like Ben Othman and Mersni (2014),
the Non Discretionary LLP (NDLLP) component
was measured using a series of variables including
the initial balance of Non Performing Loans (NPL),
changes in NPL and changes in total loans. So, the
model equation is as follows:
......................................................................................1
Then, using the estimated coefficient from equation
we can calculate the non-
discretionary component of LLP, namely NDLLP:
…………………………………………………………2
Finally, the discretionary component of LLP can be
calculated through the difference between toral LLP
and NDLLP estimates. So the estimation of the
equation is as follows:
……………………………………….......3
then the equation uses the dependent variable and
independent based on the hypothesis as follows:
…………………….........4
Where:
a.
Discretionary loan loss provision
for loans, investment, murabaha,
musyarakah and mudharabah to bank I in
year t
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
1164
b. Percentage of board
members who have Islamic education
background in bank i in year
c.
The size of the board of directors
in bank I in year t, expressed as the number of
board members in the bank i in year
d. Percentage of number of
external directors on the board of directors in
bank i in year t
e.
Percentage of number of board
members who have an financial background at
bank i in year t
f.
: The size of the company is proxied by
the logarithm of natural total assets in bank i in
year
g.
: ROA is obtained from net income
divided by total assets in bank i in year
h.
: CAR is determined by the formula for
capital divided by risk weighted assets bank i in
year t.
4 ANALYSIS
Descriptive Statistic
Table 1: Statistic Descriptive.
Table 1 provides the descriptive statistics for the
variables used in those estimation during the period
2013 to 2017. The mean of DLLP, measured as the
residual value from equation (1), was 441190.1 with
a minimum 11046.05 and maximum 6667881. The
average board of directors who have an Islamic
education background is 0.11 with a maximum of 1
and a minimum of 0. The average board of directors
size is 3.7 with a maximum of 6 and a minimum of
2. While the average percentage of independent
directors is 69% with a minimum of 50 % and 100%
maximum. Board of directors who have a financial
background have an average of 95% with a
minimum of 60% and a maximum of 100%.
Panel regression analysis
Table 2: Panel Regression.
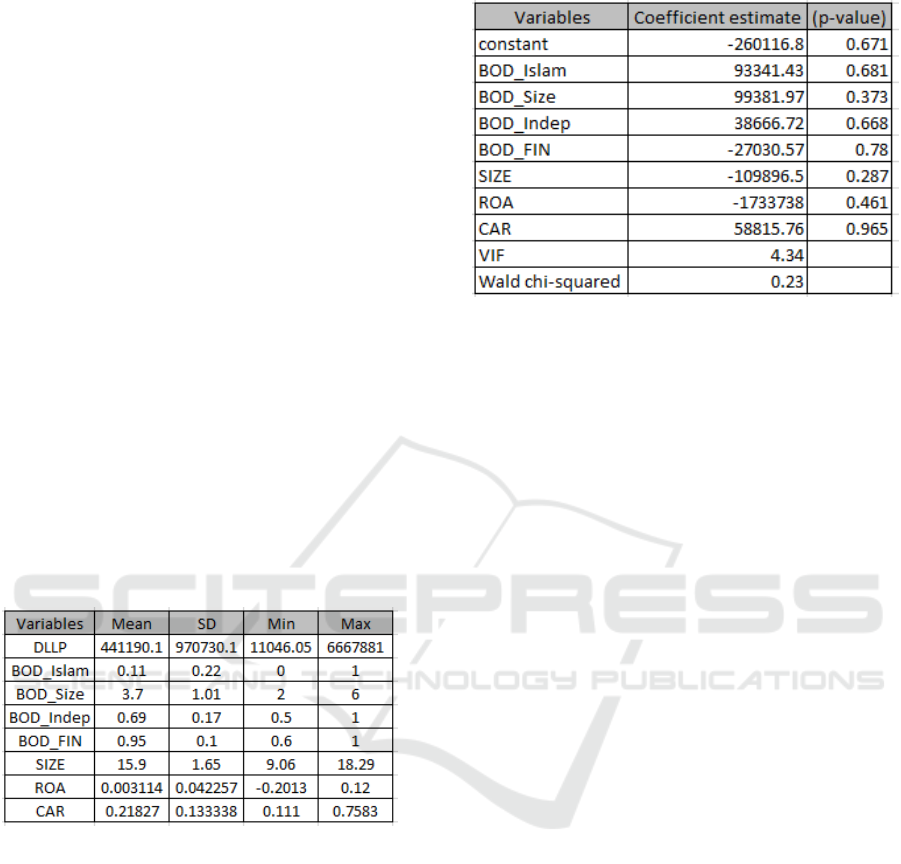
Based on regression results, there are no
significant variables on earnings management.
Islamic education background has a positive but not
significant effect. this result is not in accordance
with previous research. So, this result is not in
accordance with hypothesis 1. So is the variable size
of the board of director. The regression results show
a positive but not significant relationship. This result
is in accordance with the Taktak and Mbarki (2014).
Thus, hypothesis 2 is rejected. The number of
independent directors has no significant effect on
earnings management. The regression results show a
positive but not significant relationship. This result
is in accordance with Mersni and Ben Othman's
(2015) study. Thus, hypothesis 3 is rejected. The
number of members of the board of directors with a
financial background also has no significant
influence on earnings management. Regression
results show a negative but not significant
relationship. Thus, hypothesis 4 is rejected.
This insignificant result can be caused by a small
number of samples. It is necessary to do a similar
study with more sample sizes. In addition, state
conditions also play a role in these insignificant
results. As is known, the growth of Islamic banks in
Indonesia is something new, unlike other Islamic
countries. So, the case of earnings management in
Islamic banks is still considered normal. Possible
perspectives that influence the actions of the board
of directors in dealing with earnings management
behavior. It is expected that the results of this study
can make the board of directors more aware of
earnings management behavior.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of the study, the characteristics
of the board of directors did not play a significant
role in reducing the practice of earnings
Board of Director and Earnings Management in Islamic Bank
1165

management in Islamic banks. However, these
results cannot be generalized because the number of
samples is small and carried out in only one country.
Hopefully, further research can include more
samples with various countries.
REFERENCES
Beasley, M. S. (1996), "An Empirical Analysis of the
Relation between the Board of Director Composition
and Financial Statement Fraud", The Accounting
Review, vol. 71, no. 4, pp. 443-465
Ben Othman, H. & Mersni, H. (2014), "The use of
discretionary loan loss provisions by Islamic banks
and conventional banks in the Middle East region: A
comparative study", Studies in Economics and
Finance, vol. 31, no. 1, pp. 106-128.
DeFond, M. L., & Jiambalvo, J. (1993). Factors related to
auditor‐client disagreements over income‐increasing
accounting methods. Contemporary Accounting
Research, 9(2), 415-431.
Hamdi, F. M., & Zarai, M. A. (2012). Earnings
management to avoid earnings decreases and losses:
empirical evidence from Islamic banking industry.
Research Journal of Finance and Accounting, 3(3),
88-107.
Jensen, M. C., & Meckling, W. H. (1976). Theory of the
firm: Managerial behavior, agency costs and
ownership structure. Journal of financial economics,
3(4), 305-360.
Klein, A. (2002). Audit committee, board of director
characteristics, and earnings management. Journal of
accounting and economics, 33(3), 375-400.
Kolsi, M. C., & Grassa, R. (2017). Did corporate
governance mechanisms affect earnings management?
Further evidence from GCC Islamic banks.
International Journal of Islamic and Middle Eastern
Finance and Management, 10(1), 2-23.
Liu, B. (2012). Sentiment analysis and opinion mining.
Synthesis lectures on human language technologies,
5(1), 1-167.
Loderer, C., & Peyer, U. (2002). Board overlap, seat
accumulation and share prices. European Financial
Management, 8(2), 165-192.
McMullen, D.A., Raghunandan, K. & Rama, D.V. (1996),
"Internal Control Reports and Financial Reporting
Problems", Accounting Horizons, vol. 10, no. 4, pp.
67.
Naser, K., & Pendlebury, M. (1997). The influence of
Islam on bank financial reporting. International
Journal of Commerce and Management, 7(2), 56-83
Xie, B., Davidson, W.N. & DaDalt, P.J. (2003), "Earnings
management and corporate governance: the role of the
board and the audit committee", Journal of Corporate
Finance, vol. 9, no. 3, pp. 295-316.
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
1166
