
Employee Performance Model: Analysis of Transformational
Leadership, Organizational Culture, and Innovation: Survey at
Directorate General of Customs and Excise of Indonesia - East Java 1
Regional Office
Mochamad Mulyono
1
, Ma’ruf Akbar
2
and Madhakomala
2
1
Student of Postgraduated Universitas Negeri Jakarta (UNJ) Indonesia
2
Senior Lecturer of Postgraduated Universitas Negeri Jakarta (UNJ) Indonesia
Keywords: Transformational Leadership, Organizational Culture, Innovation and Performance
Abstract: This study aims to analyze the effect of transformational leadership and organizational culture on innovation
and employee performance at the Directorate General of Customs and Excise East Java I. The population of
this study was employees of the East Java Customs Office I with a total of 317. The sample size in this
study was determined through Slovin formula with a 5% margin error, so as to obtain a sample of 177
employees. Quantitative analysis method using path analysis (Path Analysis), followed by partial hypothesis
testing (t test) with alpha 5 percent (0.05). Before further analysis, the requirements test was carried out
through normality and regression linearity. Analysis tools using SPSS version 22.0 for Windows. The
results of the study show that transformational leadership, organizational culture, and innovation affect
performance, transformational leadership and organizational culture influence innovation, and
transformational leadership influences organizational culture.
1 INTRODUCTION
The development of a nation generally relies heavily
on tax revenues, not least in Indonesia. With such
conditions, the government work unit that is given
the task and responsibility of collecting taxes has a
very strategic position. Directorate General of
Customs and Excice, abbreviated as DJBC, which
has a role as state revenue from the import duty,
customs duty and excise tax sectors, and tax
collection in the framework of imports.
The duties, functions and roles of DJBC are very
important and strategic for the Indonesian economy,
especially in supporting the Indonesian economy.
Role as a revenue collector is still the main
performance measure for DJBC because Indonesia
still relies on revenue from the tax sector to finance
the state budget.
Although the role of DJBC is not only as a
collector of state revenue in the import duty, export
duty and excise sector, but the role of revenue
collector is the main role that is used as the Main
Performance Indicator in the performance of DJBC
in general, including in vertical offices, namely
offices area and office of customs and excise
supervision and service. Each year the performance
of the regional offices and the customs and excise
service and supervision office is measured from the
achievement of the targets set.
According to Gibson, Ivancevich and Donnelly
(2004), individual performance is the basis of
organizational performance, which means a decrease
in organizational performance can be caused by a
decrease in the performance of employees, or
conversely employee performance increases will
result in increased organizational performance.
One of the important pillars of institutional
transformation in DJBC is the leadership factor. The
Directorate General of Customs and Excise as a
government agency that has strategic duties and
functions that not only function as revenue collectors
but also function as community protectors, trade
failitation and support to the industry, of course
requires effective leadership to carry out these
functions. The concept of leadership developed in
the phase of institutional transformation is a type or
transformational leadership style. Transformational
Mulyono, M., Akbar, M. and Madhakomala, .
Employee Performance Model: Analysis of Transformational Leadership, Organizational Culture, and Innovation - Survey at Directorate General of Customs and Excise of Indonesia - East
Java 1 Regional Office.
DOI: 10.5220/0009510508810889
In Proceedings of the 1st Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science (UNICEES 2018), pages 881-889
ISBN: 978-989-758-432-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
881

leadership is used as teaching for leadership training
in the Ministry of Finance. Through the
transformational leadership training, it is expected
that leaders or officials in DJBC will be
transformative, which is characterized by the
influence of idealism, inspirational motivation,
intellectual stimuli, and wise individual
considerations can encourage subordinates to show
their best performance. This is in accordance with
the results of research by Jyoti and Bhau (2016) and
Jenewein and Schmitz (2007) which prove that
transformational leadership influences performance.
In addition, another factor that has become an
emphasis in institutional transformation in DJBC is
organizational culture. When the organizational
culture is conducive, reflecting behavior patterns,
assumptions, norms, values, beliefs, and ways of
acting that are believed, felt and carried out and
agreed upon by members of the organization can
also encourage performance improvement. This is in
accordance with the results of Tobing and Syaiful's
research (2016) which prove that organizational
culture influences performance.
In addition, other studies show that innovation in
addition to influencing performance is also
influenced by transformational leadership and
organizational culture. As shown in the research of
Park, Moon and Hyun (2014) and Nusair, Ababneh,
and Bae (2012) that empirically transformational
leadership has a positive and significant effect on
innovation. Then the results of research by Nham,
Pham, and Nguyen (2014), Yeşil and Kaya (2012),
and Daher (2016) show that organizational culture
influences innovation. In addition, organizational
culture besides influencing performance and
innovation is also influenced by transformational
leadership. As shown in the research of Aydogdu
and Asikgil (2011), Al-Sardieh (2012) and Mukhtar
et. al (2016) that transformational leadership
influences organizational culture.
2 THEORICAL FRAMEWORK
Performance
According to Catherine (2009) performance can be
interpreted from two perspectives, namely
performance as behavior and results. Performance as
a behavior, among others, is defined by Rotundo and
Sackett in Catherine (2009) as follows, job
performance typically conceptualized as actions and
behaviors that are under the control of the individual
that contributes to the goals of the organization.
Performance is usually conceptualized as actions
and behaviors that are under the control of
individuals who contribute to organizational goals.
Brumbrach as quoted by Armstrong (2009) states
that performance means both behaviors and results.
Behavior emanates from the performer and
transform performance from abstraction to action.
Not just the instruments for results, but also the
results of their own right - the product of mental and
physical effort, applied to tasks - and can be judged
apart from results.
According to Wibowo (2009) performance is the
result of work or work performance. Yuniarsih and
Suwatno (2008) also suggest that performance is a
real achievement that is displayed by someone after
the person in charge performs their duties and roles
in the organization. While Sutrisno (2011) argues
that employee performance is an achievement that is
obtained by someone in carrying out a task.
Transformational Leadership
Every organization needs leadership. This urgency is
related to the strategic position of leadership for the
dynamics and survival of the organization. One
leadership style that is very popular today is
transformational leadership. According to Kinicki
and Kreitner (2008) the transformational leadership
model generates significant organizational changes
because this form of leadership emphasizes a higher
level of intrinsic motivation, trust, commitment and
loyalty from subordinates.
For Bateman and Snell (2015) in
transformational leadership, leaders who motivate
people to transcend their personal interests for the
good of the group. The same was stated by
Ivancevich et. al (2014) that transformational leaders
are able to influence others by using charisma,
paying attention, to followers, and stimulating
others. Transformational leaders are able to
influence others by using charisma, paying attention
to followers, and stimulating others.
According to Bass, transformational leadership
can be interpreted as Transformational leadership
describing such leaders as change agents that are
elicit and transform followers ’beliefs, attitudes and
motivations. These leaders provide vision and
develop emotional relationships with their followers,
increase the latter's consciousness and higher goals,
above their own interests (Cavazotte, Flávia.,
Moreno, Valter., And Bernardo, Jane., 2013). Bass
further explained in different literature that
transformational leadership is transformational
leadership emphasizes charisma, individualized
consideration, and intellectual stimulation
(Champoux, Joseph E., 2011).
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
882
Organizational culture
Culture consists of unwritten rules and represents the
emotional side of the organization. Everyone who
participates in culture but culture generally
processes are not realized by everyone.
Organizations are aware of culture when they try to
implement new and different strategies or programs
that are contrary to fundamental cultural norms and
values. According to Daft, and Schneider that
organizational culture provides cohesiveness and
coherence inside the organization and resembles it to
"glue" which brings and holds people together. This
understanding implies that organizational culture
provides coherence and coherence within the
organization and equates it with the "glue" that
brings and unites people (Zeyada, Mustafa., 2018).
Luthan (2011) defines organizational culture as
Who is probably most closely associated with the
study of organizational culture, defining it as a basis
for assumptions that are discovered, discovered, and
developed by a group of people. adaptation and
internal integration that has worked well enough to
be considered valuable and therefore to be taught to
new members as well as to perceive, think and feel
in relation to those problems.
Schein as quoted by McShane and Von Glinow
(2015) states that organizational culture consists of
three main elements. First, artifacts, which consist of
stories / legends, rituals / ceremonies, organizational
language, and physical structure. Second, shared
values, including realized trust and evaluation of
what is good and bad, right or wrong. Third, shared
assumptions, consisting of unconsciousness (pre-
existing perceptions or beliefs), and ideal mental
models. This means that the organizational culture
must at least include artifacts, shared values, and
shared assumptions. From this it appears that
organizational culture is very thick element of
togetherness.
Innovation
According to Ireland, Hoskisson and Hitt (2011),
innovation is the process of creating a commercial
product from invention. On the other hand Montalvo
argues that innovation is a well-recognised
determinant of growth in firms, regions and in the
economy as a whole, although explaining why (and
how) firms innovate remains a challenge for
academics and practitioners alike (Lenihan, Helena.,
and McGuirk, Helen, 2014).
According to Kreitner and Knicky that
Innovation creation of new things that are used by
consumers. Innovation is to create new things based
on desire users. So it also according to scemerhorn.
"Innovation is the process of creating new ideas and
putting them into practice. Schermerhorn (2010) also
said, "innovation is the process of taking a new idea
and putting it into practice." Innovation is the
process of taking new ideas and putting them into
practice. . Along with this, Certo and Certo (2009)
stated that "innovation is the process of applying
new ideas for improvement of organizational
processes, products, or services."
In addition, Ahmed and Shepherd (2010) say,
innovation is a source of advancement and
development. Further explained, innovation as
creation (invention): the focus is on resources
(people, time and money) to invent or develop a new
product, service, new way of doing things, a new
way of thinking about things. While Schumpeter
defines innovation as innovation is described as the
engine of growth and carrying out new combinations
of productive means. "creative destruction. While
Roper et al., mentions while firms rely on diverse
sources of knowledge including horizontal,
backward, forward and in-house linkages for
innovation (Lenihan and McGuirk, 2014).
Then Robbins and Coulter (2016) signal creative
innovation ideas and turning them into useful
products or work methods. This understanding can
be interpreted that innovation takes creative ideas
and turns them into useful products or new work
methods.
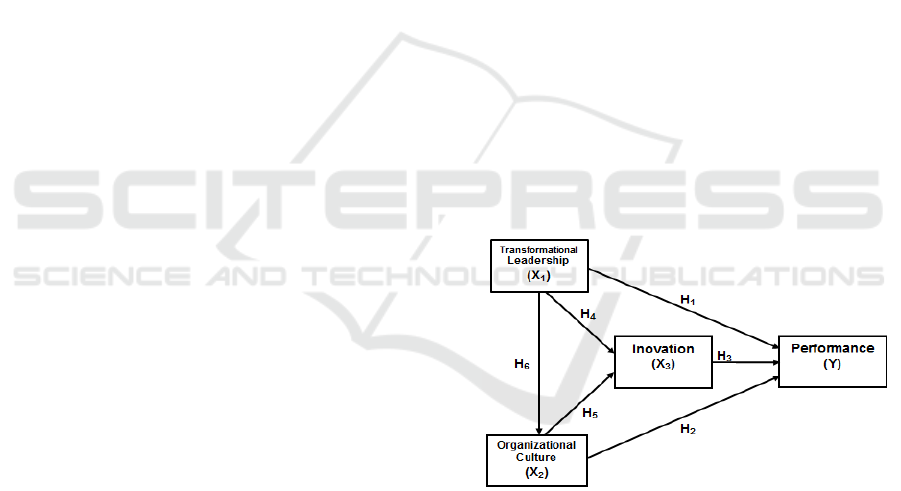
Conceptual Framework
The research framework can be described in Figure
1, as follows:
Figure 1: Conceptual Framework
The research hypothesis are :
1. Transformational leadership influences
performance.
2. Organizational culture influences performance.
3. Innovation affects performance.
4. Transformational leadership influences
innovation.
5. Organizational culture influences innovation.
6. Transformational leadership influences
organizational culture.
Employee Performance Model: Analysis of Transformational Leadership, Organizational Culture, and Innovation - Survey at Directorate
General of Customs and Excise of Indonesia - East Java 1 Regional Office
883
3 RESEARCH METHOD
The unit of analysis of this study was employees of
the East Java Customs Office I, with a sample of 177
respondents. The research approach used in this
study is a quantitative approach using Path Analysis.
This analysis is a development of the regression
equation, which is one option in order to study the
dependence of a number of variables in the model.
This analysis is a good method to explain if there is
a large set of data to analyze and look for a causal
relationship. Path analysis is one of the analytical
tools developed by (Dillon and Goldstein in Ali, H
and Limakrisna, N, 2013). Wright developed a
method to find out the direct and indirect effects of a
variable, where there are variables that exogenous
variables and endogenous variables.
The path diagram above consists of three sub-
structures with three equations, where X1 and X2
are exogenous variables (exogenous) which are
variables that have no explicit cause, this variable
functions as an independent variable / cause for the
following sequence variables Y and Z as
endogenous variables (endogenous). Before the
analysis, a questionnaire instrument test was carried
out with validity and reliability testing, and a
requirement test was carried out through normality
and linearity tests.
4 ANALYSIS
Before stepping into testing hypotheses, it must first
go through calculation analysis requirements.
Testing the analysis requirements used consisted of
two types, namely the normality test, and the
linearity test.
From the results of the Liliefors, it shows that there
is no Lcount value greater than Ltable, so it can be
concluded that the estimated error originates from a
population that is normally distributed. While the
test of regression significance and linearity shows
that the F-count value is greater than Ftable, so it can
be concluded that all regression equations are linear.
To answer the objectives in this study, the main
structure in the research model was broken down
into three sub-structures, as follows :
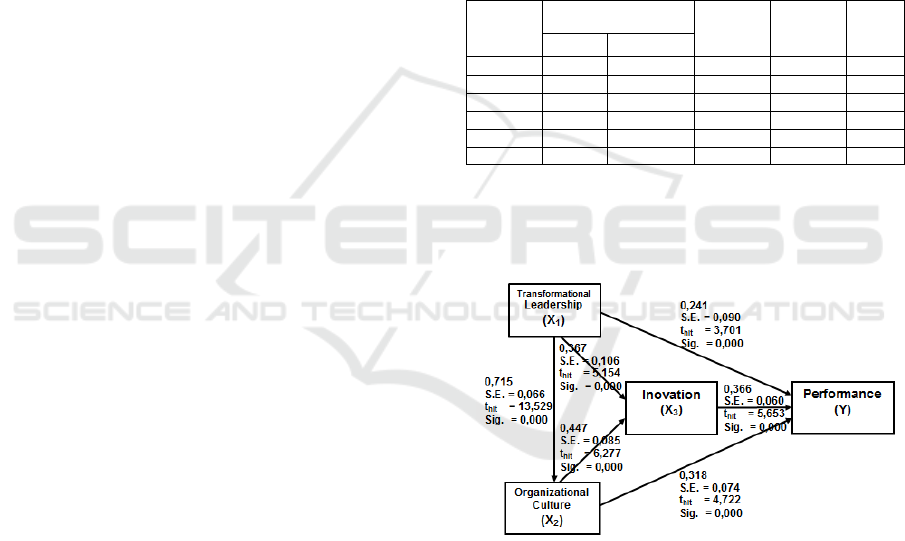
1). Y = 0,241.X1 + 0,318.X2 + 0,366.X3 + 0,31.
2). X3 = 0,367.X1 + 0,447.X2 + 0,43.
3). X2 = 0,715.X1 + 0,49.
Where to answer goals 1, 2, and 3 with the first sub-
structure, to answer the objectives 4 and 5 by using
the second sub-structure, and to answer goal 6 using
the third sub-structure.
The value of cooficient of determination (R2)
shows 0,69. This means that transformational
leadership, organizational culture and innovation
contribute to performance as big as 69%. Based on
the results of the analysis of determination there are
still many factors that influence performance, such
as the researchs had been conducted by Aima, H., &
Ali, H. (2017), Ansori, A., & Ali, H. (2017),
Riyanto, S., Sutrisno, A., & Ali, H (2017) and Ali H.
& Syailendra, Y. (2013), therefore further research
is needed.
The following is the SPSS output of the three
structures summarized in the following table.
Table 1: SPSS Output Three Sub Structures
Model
Unstandardized
Coefficients
Beta t Sig.
BStd.Error
X1
–
Y .334 .090 .241 3.701 .000
X2
–
Y .352 .074 .318 4.722 .000
X3
–
Y .338 .060 .366 5.653 .000
X1
–
X3 .549 .106 .367 5.154 .000
X2
–
X3 .535 .085 .447 6.277 .000
X1
–
X2 .894 .066 .715 13.529 .000
Path Analysis Results
The output results above are included in the
structural equation image as follows:
Figure 2: Hypothetic Model along with Path
Coefficient Value
The results of the influence analysis between
variables are as follows:
1. Effect of Transformational Leadership (X1)
on Performance (Y).
Based on the calculation results obtained the path
coefficient of the direct effect of transformational
leadership (X1) on performance (Y) is P41 = 0.241.
The path coefficient value shows that the direct
effect of transformational leadership (X1) on
performance (Y) is 0.241. The path coefficients
obtained are positive, so that the effect is directly
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
884

proportional, meaning that the higher or better the
level of transformational leadership will improve
performance. The value of tcount obtained is 3.701,
while the value of ttable for dk = 177 at = 0.05 is
1.653. tcount > ttable, then Ho is rejected and H1 is
accepted. This means that transformational
leadership has a positive and significant direct effect
on performance.
2. Effect of Organizational Culture (X2) on
Performance (Y).
From the calculation shows the path coefficient of
the influence of organizational culture (X2) on
performance (Y) is P42 = 0.318. The path
coefficient value shows that the direct effect of the
variable organizational culture (X2) on performance
(Y) is 0.318. Positive path coefficients prove that
improving organizational culture will lead to
improved performance. While the value of tcount
obtained is 4.722, and the value of ttable for dk =
177 at = 0.05 is 1.653. tcount > ttable which
means Ho is rejected and H1 is accepted. This
means that organizational culture has a positive and
significant direct effect on performance.
3. Effect of Innovation (X3) on Performance (Y)
Based on the calculation of the path coefficient for
the direct effect of innovation on performance (P43)
coefficient = 0.366. The path coefficient value
shows that the direct effect of the innovation
variable (X3) on performance (Y) is 0.366. The
obtained path coefficient is positive, which shows
the understanding that increasing innovation will be
followed by increased performance. The tcount
obtained is 5.653 and the t-value for dk = 177 at =
0.05 is 1.653. The tcount > ttable carries the
meaning that Ho is rejected and H1 is accepted. This
means that innovation has a positive and significant
direct effect on performance.
4. Effect of Transformational Leadership (X1)
on Innovation (X3).
Calculation of the path coefficient for the direct
effect of transformational leadership (X1) on
innovation (X3) is P31 coefficient = 0.367. The path
coefficient value shows that the direct effect of
transformational leadership (X1) on innovation (X3)
is 0.367. The path coefficient obtained is positive,
which shows the understanding that increasing
transformational leadership will be followed by
increased innovation. While the tcount obtained is
5.154 and the t-value for dk = 177 at = 0.05 is
1.653.
5. Effect of Organizational Culture (X2) on
Innovation (X3).
Based on the calculation of the path coefficient
shows the path coefficient direct effect of
organizational culture on innovation (P32) = 0.447.
The path coefficient value shows that the direct
effect of the variable organizational culture (X2) on
innovation (X3) is 0.447. The path coefficient
obtained is positive, which means that the increase
in organizational culture will be followed by an
increase in innovation. While the value of tcount
obtained is 6.277, and the value of t¬ for dk = 177 at
= 0.05 is 1.653. tcount > ttable, so H0 is rejected
and H1 is accepted. This implies that organizational
culture has a positive and significant direct effect on
innovation.
6. Effect of Transformational Leadership on
Organizational Culture
Based on the calculation of the path coefficient of
the influence of transformational leadership on
organizational culture (P21) the value = 0.715 was
obtained. The path coefficient value shows that the
direct effect of transformational leadership (X1) on
organizational culture (X2) is 0.715. The path
coefficient is positive which means that the
improvement of transformational leadership will
have an impact on improving organizational culture.
The tcount obtained is 13,529, and the t-value for dk
= 177 at 177 = 0.05 is 1,653. tcount > ttable which
means Ho is rejected and H1 is accepted. This
implies that transformational leadership has a
positive and significant direct effect on
organizational culture.
5 DISCUSSION
From the results of the interpretation of the data
above, it can be discussed that:
1. Effect of Transformational Leadership on
Performance
The results of this study indicate that
transformational leadership has a positive and
significant direct effect on performance. This finding
is understandable because in the dynamics of
organizational life, including government
organizations, transformational leadership has an
important and vital role in encouraging employee
performance improvement, including goods
inspection staff at the Kantor Wilayah Direktorat
Jenderal Bea dan Cukai Jawa Timur I. Research
results of Gooty et al (2009 ) and Biswas (2012) also
Employee Performance Model: Analysis of Transformational Leadership, Organizational Culture, and Innovation - Survey at Directorate
General of Customs and Excise of Indonesia - East Java 1 Regional Office
885

show that transformational leadership has a positive
effect on performance. This means that the results of
this study support and confirm the results of
previous studies that transformational leadership has
a positive effect on performance with the location
and object of research on goods inspectors in
government organizations, especially the Kantor
Wilayah Direktorat Jenderal Bea dan Cukai Jawa
Timur I.
2. Effect of Organizational Culture on
Performance
The results of this study have shown that
organizational culture has a positive and significant
direct effect on performance. This emphasizes the
meaning that organizational culture has a vital role
for the advancement of organizational members
(employees) and organizations, including
government organizations, especially the Kantor
Wilayah Bea Cukai Jawa Timur I. The results of
this study show the same results as the research
conducted by Nikpour (2017 ) which shows that
organizational culture influences performance, with
research settings on employees examining
government organizations, especially the Kantor
Wilayah Bea Cukai Jawa Timur I. However,
compared to these previous studies, the results of
this study have differences in the scope of
performance variables. In the Nikpour study the
scope is an organization, while in this study the
scope is individual. In this research perspective,
individual performance is predisposed to
organizational performance, as constrained by
Gibson et al (2009) that individual performance is
the basis of organizational performance.
3. Effect of Innovation on Performance
The results of this study also show that innovation
has a positive and significant direct effect on
performance. This finding is easy to understand,
because innovation has now become a necessity and
has become part of modern organizations, including
government organizations, especially the Kantor
Wilayah Direktorat Jenderal Bea dan Cukai Jawa
Timur I. The results of research by Marques and
Ferreira (2009), and Omri (2015), provide support
for this research. And the research of Tantayanubutr
and Panjakajornsak (2017) also shows that
innovation influences business performance. This
means that the results of this study support and
confirm the results of previous studies that
innovation has a positive effect on performance with
research settings on employees examining
government organizations, especially the Kantor
Wilayah Direktorat Jenderal Bea dan Cukai Jawa
Timur I.
4. Effect of Transformational Leadership on
Innovation.
The results of this study also show that
transformational leadership influences innovation.
This finding is also understandable.
Transformational leadership is a person's ability to
influence, motivate, manage activities and
interactions between individuals, and enable others
to build a vision and confidence so that they can
contribute to the achievement of organizational
goals, through the influence of idealism,
inspirational motivation, intellectual stimuli, and
individual considerations. The results of Park's
research, Moon and Hyun (2014) and Nusair,
Ababneh, and Bae (2012) also show that leadership
influences innovative behavior. This means that the
results of this study support and confirm the results
of previous studies that transformational leadership
has a positive effect on employee innovation with
research settings on employees examining
government organizations, especially the Direktorat
Jenderal Bea dan Cukai.
5. Effect of Organizational Culture on
Innovation
The results of this study also show that
organizational culture has a positive and significant
direct effect on innovation. This finding shows the
vitality of organizational culture for employee
innovations, including employees of auditors at the
Kantor Wilayah Direktorat Jenderal Bea dan Cukai
Jawa Timur I. Results of research by Nham, Pham,
and Nguyen (2014), Yeşil and Kaya (2012), and
Daher (2016) also prove that the organizational
culture is related to innovation. This means that the
results of this study support and confirm the results
of previous studies that organizational culture has a
positive effect on innovation with research settings
on employees examining government organizations,
especially the Direktorat Jenderal Bea dan Cukai.
6. Effect of Transformational Leadership on
Organizational Culture
The results of this study also show that
transformational leadership has a positive and
significant effect on the culture of organization. This
condition confirms the meaning that
transformational leadership is not only important for
improving employee performance and innovation,
but also vital for building organizational culture. The
results of Aydogdu and Asikgil (2011) and Al-
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
886

Sardieh (2012) research also prove that
transformational leadership has an influence on
organizational culture. Thus, the results of this study
support and confirm the results of previous studies
that transformational leadership has a positive effect
on organizational culture with research settings on
employees examining government organizations,
especially the Direktorat Jenderal Bea dan Cukai.
6 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results and discussion, the conclusions
of this study are:
1. Transformational leadership has a positive and
significant direct effect on performance. This
finding shows that the improvement of
transformational leadership at the leadership
level in the work area of the Kantor Wilayah
Bea Cukai Jawa Timur I, can improve the
performance of goods inspection staff in the
Kantor Wilayah Bea Cukai Jawa Timur I.
2. Organizational culture has a positive and
significant direct effect on performance. This
finding shows that the improvement of
organizational culture in the work environment
at the Kantor Wilayah Bea Cukai Jawa Timur I
can improve the performance of goods
inspection staff in the Kantor Wilayah Bea
Cukai Jawa Timur I.
3. Innovation has a positive and significant direct
effect on performance. This finding shows that
improvements in innovation in the work
environment of the Kantor Wilayah Bea Cukai
Jawa Timur I can improve the performance of
goods inspectors at the Kantor Wilayah Bea
Cukai Jawa Timur I.
4. Transformational leadership has a positive and
very significant direct effect on innovation. This
finding shows that the improvement of
transformational leadership at the leadership
level in the work area of the Kantor Wilayah
Bea Cukai Jawa Timur I can increase the
innovation of goods inspectors at the Regional
Office of the Directorate General of Customs
and Excise at the Kantor Wilayah Bea Cukai
Jawa Timur I.
5. Organizational culture has a positive and very
significant direct effect on innovation. This
finding shows that the improvement of
organizational culture in the Kantor Wilayah
Bea Cukai Jawa Timur I can increase the
innovation of goods inspectors in the Kantor
Wilayah Bea Cukai Jawa Timur I.
6. Transformational leadership has a positive and
very significant direct effect on organizational
culture. This finding shows that the
improvement of transformational leadership at
the leadership level in the working area of the
Kantor Wilayah Bea Cukai Jawa Timur I can
create organizational culture conducivity in the
Kantor Wilayah Bea Cukai Jawa Timur I.
REFERENCES
Ahmed, Pervaiz K., dan Shepherd, Charles D. (2010).
Innovation Management: Context, Strategies, Systems
and Processes. Essex: Pearson Education Limited
Armstrong, Michael. (2009). A Handbook of Human
Resource Management Practice. London: Kogan Page.
Aima, H., & Ali, H. (2017). Model of Employee
Performance: Competence Analysis and Motivation
(Case Study at PT. Bank Bukopin, Tbk Center). Quest
Journals Journal of Research in Business and
Management, ISSN (Online), 2347-3002.
Ali, H., & Syailendra, Y. (2013). Pengaruh Tunjangan
Profesi Guru Dan Kompetensi Guru Tehadap Kinerja
Guru Pada Guru Sma Negeri 1 Muara Bungo. Jurnal
Ilmiah Universitas Batanghari Jambi Vol, 13(2).
Al-Sardieh, Eid Muhareb Eid. (2012). Transformational
Leadership and Organizational Culture in Small-Scale
Industries in the Governorate of Mafraq, European
Journal of Economics, Finance and Administrative
Sciences, ISSN 1450-2275, Issue 45.
Ali, H., & Limakrisna, N., (2013), Research Methodology,
Practical Guide to Business Problem Solving
Preparation of Theses and Dissertation, ISBN: 978-
602-280-044-6, Deepublish Yogyakarta, Indonesia.
Ansori, A., & Ali, H. (2017). Analisis Pengaruh
Kompetensi dan Promosi terhadap Kinerja Pegawai
Negeri Sipil pada Sekretariat Daerah Kabupaten
Bungo. Jurnal Ilmiah Universitas Batanghari Jambi,
15(1), 50-60.
Aydogdu, Sinem dan Baris Asikgil. (2011). The Effect of
Transformational Leadership Behavior on
Organizational Culture: An Application in
Pharmaceutical Industry, International Review of
Management and Marketing, Vol. 1, No. 4, 2011, pp.
65-73.
Bateman, Thomas S., and Snell, Scott A. (2015).
Management, 11th edition. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Biswas, Soumendu. (2012). “Impact of Psychological
Climate and Transformational Leadership on
Employee Performance,” The Indian Journal of
Industrial Relations, Vol. 48, No. 1.
Catherine, Johnson Emily. (2009). A Multi Level
Investigation of Overall Jop Performance Ratings.
Partkway: ProQuest LLC.
Cavazotte, Flávia., Moreno, Valter., and Bernardo, Jane.
(2013). “Transformational Leaders and Work
Performance: The Mediating Roles of Identification
Employee Performance Model: Analysis of Transformational Leadership, Organizational Culture, and Innovation - Survey at Directorate
General of Customs and Excise of Indonesia - East Java 1 Regional Office
887

and Self-efficacy,” BAR, Rio de Janeiro, Vol. 10,
No.4.
Certo, Samuel C., and Certo, S. Trevis. (2009). Modern
Management: Concepts And Skills, 11th Edition. New
Jersey: Pearson Education, Inc.
Champoux, Joseph E. (2011). Organizational Behavior:
Integrating Individuals, Groups, and Organizations,
Fourth Edition. New York: West Publishing
Company.
Daher, Nick. (2016). “The Relationships Between
Organizational Culture and Organizational
Innovation,” International Journal of Business and
Public Administration, Volume 13, Number 2, Winter.
Gibson, J.L., Ivancevich, J.M., and Donnelly, J.H. (2004).
Organisasi dan Manajemen: Perilaku, Struktur,
Proses. Jakarta: Erlangga.
Gibson, James L., Donnelly, James H Jr., Ivancevich, John
M., dan Konopaske, Robert. (2009). Organizations:
Behavior, Structure, Processes (New York: McGraw
Hill Education.
Gooty, J., et. al. (2009). “In the eyes of the beholder:
transformational leadership, positive psychological
capital, and performance,” Journal of Leadership and
Organizational Studies, Volume 15 Number 4.
Ireland, R. Duane., Hoskisson, Robert E., and Hitt,
Michael A. (2011). The Management of Strategy:
Concept and Cases (Mason, OH: South Western,
Cengage Learning, 2011)
Ivancevich, John M., Kanopaske, Robert., and Matteson,
Michael T. (2014). Organizational Behavior and
Management, 10th edition. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Jenewein, Wolfgang and Schmitz, Christian. (2007).
“Creating a high performance team through
transformational leadership: the case of Alinghi.”
Business Case Journal, Vol. 14, No. 2.
Jyoti, Jeevan and Bhau, Sonia. (2016). “Transformational
Leadership and Job Performance: A study of Higher
Education.” Journal of Services Research, Volume 15,
Number 2.
Kinicki, Angelo., and Kreitner, Robert. (2008).
Organizational Behavior. New York: McGraw-Hill
Irwin.
Lenihan, Helena., and McGuirk, Helen. (2014).
“Measuring and Estimating the Impact of Innovative
Human Capital on Firm Performance: Is There A Role
for Public Policy?,” Paper presented at the Regional
Studies Association (RSA) European Conference,
Izmir, Turkey.
Luthan, Fred. (2011). Organizational Behavior: An
Evidence-Based Approach, 12 th Edition. New York:
McGraw Hill-Irwin.
Marques, Carla Susana., and Ferreira, João. (2009). “SME
Innovative Capacity, Competitive Advantage and
Performance in a ‘Traditional’ Industrial Region of
Portugal”, Journal of Technology Management
Innovation, Volume 4, Issue 4
McShane, Steven L.,& Mary Ann Von Glinow. (2015).
Organizational Behavior.New York: McGraw-Hill
Companies, Inc.
Mukhtar., Risnita., Muspawi, Mohamad., dan Ali, Hapzi.
(2016). “Influence of Transformational Leadership and
Culture Organization toward Chairman Innovation of
Stai: The College of Islamic Religion of Private in
Jambi Province,” International Journal of Business and
Commerce, Vol. 6, No. 02.
Nham, Phong Tuan., Pham, Huong Giang., and Nguyen,
Nhan. (2014). The Impact of Organizational Culture
on Innovation Acitivities - The Case of X Corporation
in Vietnam,” Journal of Global Management Research.
Nikpour, Amin. (2017). “The Impact of Organizational
Culture on Organizational Performance: The
Mediating Role of Employee’s Organizational
Commitment,” International Journal of Organizational
Leadership, Vol. 6.
Nusair, Naim., Ababneh, Raed., and Bae, Yun Kyung.
(2012). “The Impact of Transformational Leadership
Style on Innovation as Perceived by Public Employees
in Jordan,” International Journal of Commerce and
Management, Vol. 22, No. 3.
Omri, Waleed. (2015). ”Innovative Behavior and Venture
Performance of SMEs: The Moderating Effect of
Environmental Dynamism,” European Journal of
Innovation Management, Vol. 18, Iss: 2.
Park, Gi-Ryun., Moon, Gye-Wan., & Hyun, Sung-Eun.
(2014). “An Impact of Self-leadership on Innovative
Behaviour in Sports Educators and Understanding of
Advanced Research,” The SIJ Transactions on
Industrial, Financial & Business Management (IFBM),
Vol. 2, No. 3.
Robbins, Stephen P., dan Coulter, Mary. (2016).
Management, 13th Edition. Essex: Pearson Education
Limited.
Riyanto, S., Sutrisno, A., & Ali, H. (2017). The Impact of
Working Motivation and Working Environment on
Employees Performance in Indonesia Stock Exchange.
International Review of Management and Marketing,
7(3), 342-348.
Schermerhorn, John R. (2010). Introduction to
Management, 10th Edition. Hoboken: John Wiley &
Sons
Sutrisno, Edy. (2011). Budaya Organisasi. Jakarta:
Kencana Prenada Media Group.
Tantayanubutr, Monika., and Panjakajornsak, Vinai.
(2017). “Impact of Green Innovation on the
Sustainable Performance of Thai Food Industry,” BEH
Business and Economic Horizons, Vol. 13, Issue 2.
Tobing, Diana Sulianti K. and Syaiful, Muh. (2016). “The
Influence of Transformational Leadership and
Organizational Culture on Work Motivation and
Employee Performance at The State Property Service
Office and Auction in East Java Province,”
International Journal of Business and Commerce, Vol.
5, No. 6.
Wibowo. (2009). Manajemen Kinerja. Edisi Kedua.
Jakarta: Penerbit RajaGrafindo Persada.
Yeşil, Salih and Kaya, Ahmet. (2012). “The Role of
Organisational Culture on Innovation Capability: An
Empirical Study.” International Journal of Information
Technology and Business Management, Vol. 6 No.1.
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
888

Yuniarsih, Tjutju dan Suwatno. (2008). Manajemen
Sumber Daya Manusia Teori, Aplikasi dan Isu
Penelitian. Bandung: CV Alfabeta.
Zeyada, Mustafa. (2018). “Organizational Culture and its
Impact on Organizational Citizenship Behavior,”
International Journal of Academic Research in
Business & Social Sciences, Vol 8, No. 3.
Employee Performance Model: Analysis of Transformational Leadership, Organizational Culture, and Innovation - Survey at Directorate
General of Customs and Excise of Indonesia - East Java 1 Regional Office
889
