A Some of Paddy Cleaning Machine on Activity Free Float in
Activity- on –Arrow and Node Networks: Part II
S. Bangphan
1
and P.Bangphan
1
1
Department of Industrial Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Rajamangala University of Technology Lanna
Keywords: Some paddy cleaning machine, activity, project management, activity on arrow (AOA) and activities on the
node (AON), total float, free float
Abstract: This research presents important guidelines for implementing the implementation process. Advantages and
disadvantages of the project implementation. Considering the project as a network, we use CPM techniques
to try to find the critical path of the network, and suggest the best way to supply and manufacture certain
machines. Under these constraints, critical paths that include certain project activities. Means the longest path
(Depending on the duration) of the project and any delays that will occur on this path will lead to delays in
the project. Therefore, critical path analysis is done using the PERT / CPM module. In the project schedule,
the total floats and free floats of activity show agility in scheduling. Activity time without affecting subsequent
activities.
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 Total Float
Total float is what many of us are aware of, and is
commonly referred to as a float. Total float is the
amount of time an activity can be delayed without
delaying the project completion date. On a critical
path, the total float is zero. Total float is often known
as the slack. (https://pmstudycircle.com)
This research can calculate the total float by
subtracting the Early Start date of an activity from its
Late Start date (Late Start date – Early Start date), or
Early Finish date from its Late Finish date (Late
Finish date – Early Finish date).
(https://pmstudycircle.com)
1.2 Free Float
Now we come to free float. This is going to be a bit
different and might be new to you. Free float is the
amount of time an activity can be delayed without
delaying the Early Start of its successor activity.
We can calculate the free float by subtracting the
Early Finish date of the activity from the Early Start
date of next activity (ES of next Activity – EF of
current Activity).
Keep in mind that if two activities are converging
to a single activity, only one of these two activities
may have free float.
(https://pmstudycircle.com)
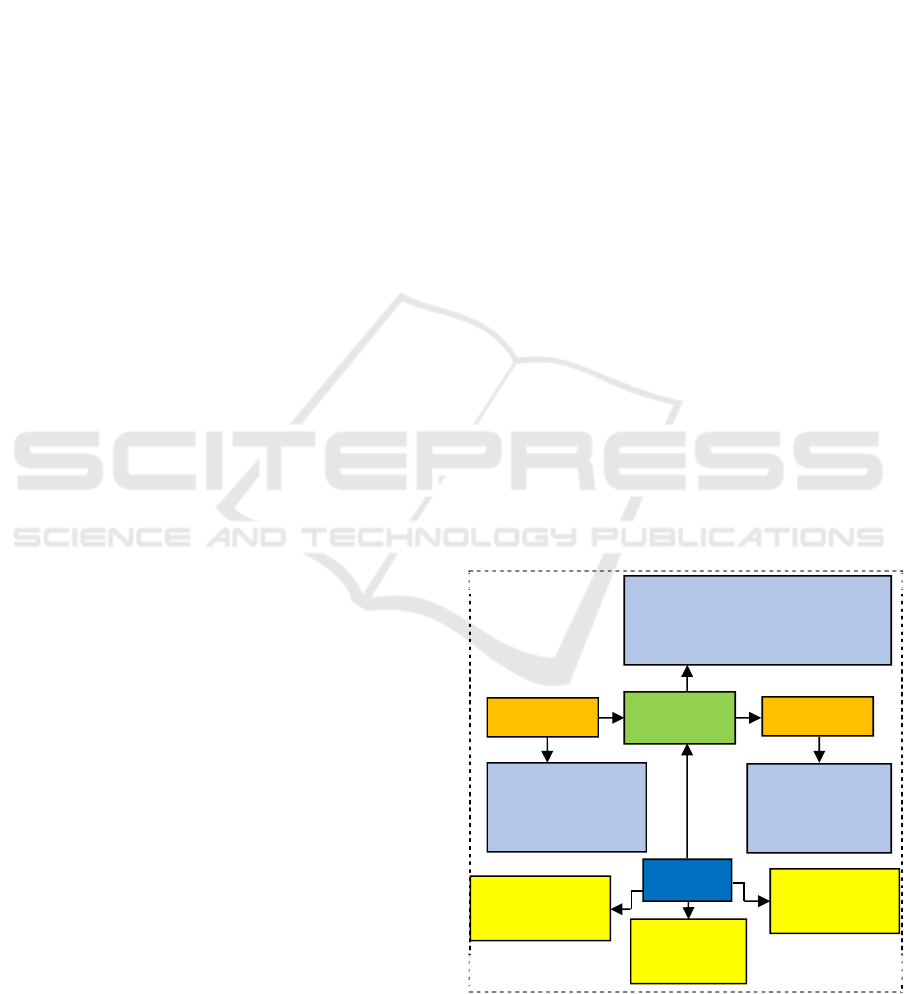
The Figure 1 below shown activity of network
analysis.
Figure 1: Network analysis.
Activity
Analysis
Results
-Relationships
-Duration
-Resource
-ES, EF, LS, LF, FF, TF
- Project Duration
-Critical Path / AOA, AON
-Reduce cost
-Reduce time
-Productivity
Float
Activity
Begin event
Activity
Duration
Activity
End Event
62
Bangphan, S. and Bangphan, P.
A Some of Paddy Cleaning Machine on Activity Free Float in Activity- on –Arrow and Node Networks: Part II.
DOI: 10.5220/0009771100620066
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference of Computer Science and Renewable Energies (ICCSRE 2018), pages 62-66
ISBN: 978-989-758-431-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
1.3 Part I Research
Part I research has been conducted in the field of
planning, management and project control. The
project is a rice paddy cleaner of the project using a
network of activities (S. Bangphan, 2018).
This research has been funded by the University
for the Organic Business of 7 types of Organic Brown
Rice. The Network Analysis (CPM / PERT) has been
conducted and has provided the following answers:
• What are the important activities or tasks in the
project that could delay all projects if they are not
completed on time?
• Does the project meet deadlines or do not exceed
deadlines?
• If the project has to be completed earlier than
planned, what is the best way to do this in the least
possible way? (S. Bangphan, 2018)
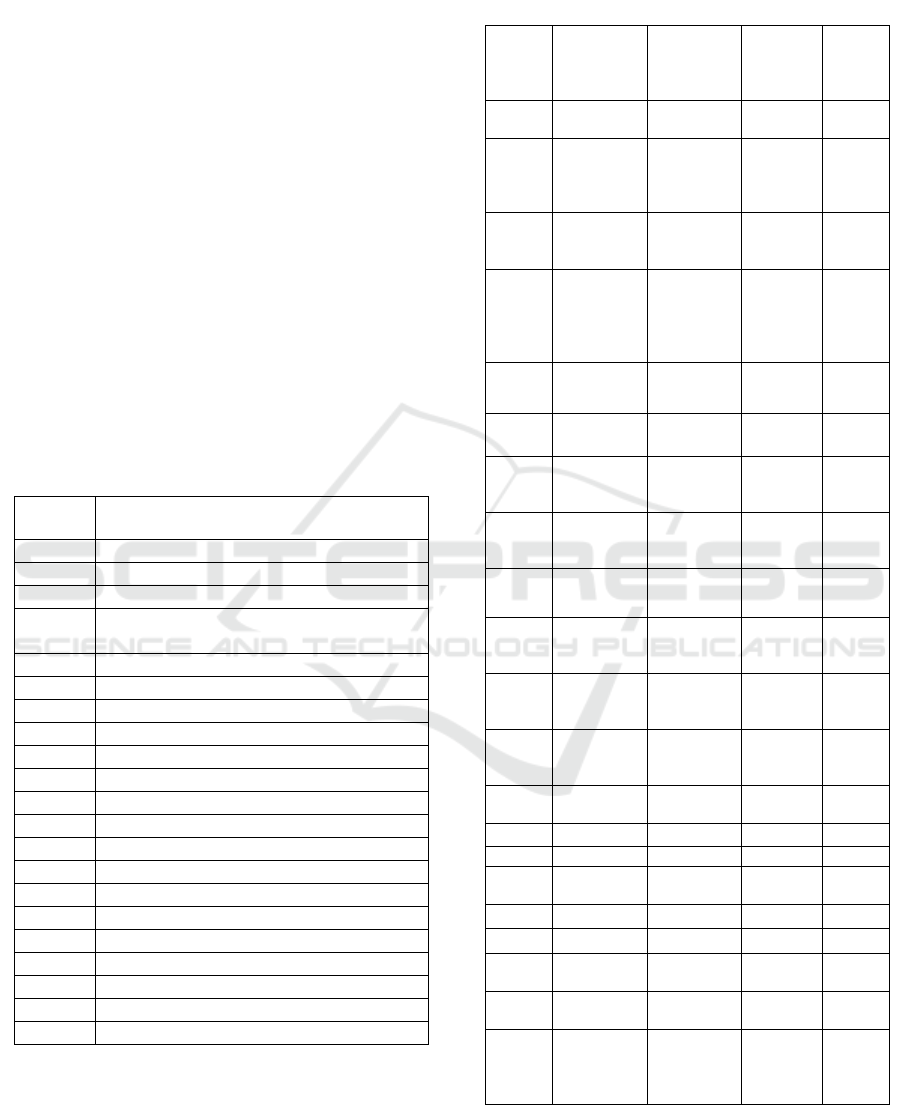
• Table 1 shows the work breakdown structure and
Table 2 shows the details of the paddy cleaner.
Table 1: Work breakdown structure (W.B.S.) of paddy
cleaning machine.
Activity
code
Activity description
A Frame
B Install wheel base with wheel flange
C Install bearing sets and shaft
D
Install shaft combine with bearing
and pulleys
E Assembly kit one
F Hopper
G Control hopper sets
H Shaft support sets
I Flow controller
J Assembly kit two
K Sieve cleaning sets
L Made shaft of sieve cleaning
M Crankshaft
N Belts
O pulleys
P Assembly kit three
Q Top plate
R Down plate
S Adjust of belts
T Assembly kit four
U all assembly kit and adjust
Table 2: Description of activities paddy cleaning machine
(S. Bangphan, 2018).
Act
code
Activity
description
Immediate
predecessor
Estimate
d
duration
(Day)
Norma
l cost
(Dollar
)
A Frame - 5
115
B
Install
wheel base
with wheel
flange A 3
55
C
Install
bearing sets
and shaft A 2
125
D
Install shaft
combine
with
bearing
and pulleys A 2
135
E
Assembly
kit one B,C,D 3
120
F Hopper E 3
85
G
Control
hopper sets E 2
65
H
Shaft
support sets E 3
35
I
Flow
controller E 2
30
J
Assembly
kit two F,G,H,I 4
85
K
Sieve
cleaning
sets J 2
140
L
Made shaft
of sieve
cleaning J 3
110
M Crankshaft J 3
80
N Belts J 2
100
O pulleys J 2 120
P
Assembly
kit three K,L,M,N,O 3
135
Q Top plate P 1
120
R Down plate P 1
120
S
Adjust of
belts P 2
135
T
Assembly
kit four Q,R,S 4
100
U
all
assembly
kit and
adjust T 5
110
A Some of Paddy Cleaning Machine on Activity Free Float in Activity- on –Arrow and Node Networks: Part II
63
2 MATERIALS AND METHOD
Consider the activity of the project using the
replacement of the AOA network, as shown in Figure
2. This is how the PERT / CPM identifies the critical
path. Each activity with a zero slack center is on an
critical path through the project network, such that
delays along this path will cause the project to delay.
Thus, the critical path is (S. Bangphan, 2018)
The starting and finishing times of each activity
without delay occurring anywhere in the project are
called the earliest start time and the earliest finish
time of activity. This time there are symbols (Scaat,
2009), (Surapong, 2013).
ES = earliest start time for a particular activity,
EF = earliest finish time for a particular activity,
D = (estimated) duration of the activity
Where
EF = ES + D (1)
The latest finish time has the corresponding
definition with respect to finishing the activity. In
symbols,
LS = latest start time for a particular activity,
LF = latest finish time for a particular activity,
Where
LS = LF - D (2)
The slack or total float for an activity is the
difference between its latest finish time and its
earliest finish time. In symbols,
Slack = LF – EF (3)
(Since LF - EF = LS - ES, either difference actually
can be used to calculate slack.)
ABEFJLMPSTU
= 5333433245 = 31 days
Project network has an important path and no plan
in the duplicate diagram. The corresponding AOA
and AON network displays are shown in Figures 2
and 3. The free and floating totals for some activities
are summarized in Table 3.
2.1 Float Calculations
In the Arrow activity network, the computer
calculates the data for both events at the end of the
arrow and the activity itself (arrows). As a result, a
variety of data sets are available to determine:
Free Float: This means all floats that can handle
the activity without affecting the float of the activity.
It can be calculated by subtracting the discount of the
main activity from the total float of the activity.
FF
i
j
= TF
i
j
– (slack of event j) (4)
The float is the maximum time that this activity
can cause a delay in completion before an activity
becomes an important activity, that is, the delay of the
project.
Free float indicates the value at which the
problem activity can be delayed beyond the
beginning, without affecting the fastest start.
2.2 Part II Research
Second Research, It is a study of floating time sums.
And free floating time. The research is part one. Is a
critical path.
.
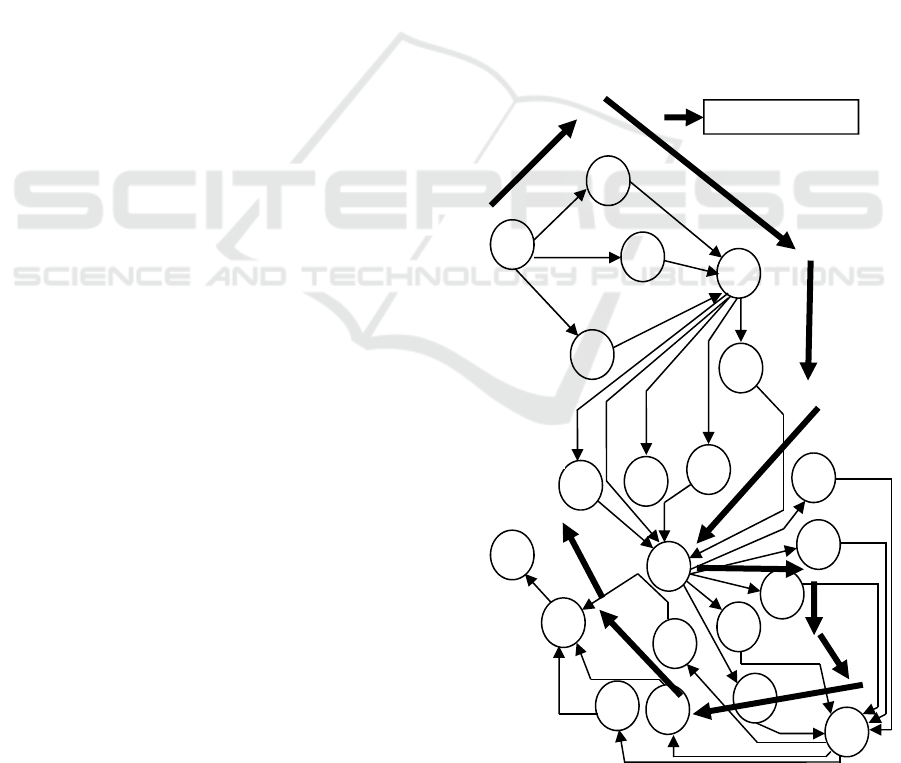
Figure 2: Network diagram for activities paddy cleaning
machine (S. Bangphan, 2018).
A
5
B
C
D
F
E
2
2
3
3
2
G
3
H
3
I
2
4
J
N
2
L
2
K
3
M
3
O
2
P
3
R
2
S
1
Q
1
U
4
T
5
Critical Path
ICCSRE 2018 - International Conference of Computer Science and Renewable Energies
64

Figure 3: Diagram Node for constructs of paddy cleaning
machine (S. Bangphan, 2018).
3 IMPLEMENTATION AND
RESULTS
Consider sample projects with AOA networks.
Shown in Figure 2. The project network has an
important path and no plans in the duplicate diagram.
The corresponding AON network representation is
shown in Figure 2. The use of (3), (4) free float for
some activities summarizes the final column in Table
3.
Table 3: Summary of free floats for some activities of the
activity network of project (S. Bangphan, 2018).
Act
Predecessor
s Duration ES EF LS LF SL
FF
A 0 5 0 5 0 5 0
0
B A 3 5 8 5 8 0
0
C A 2 5 7 6 8 1
1
D A 2 5 7 6 8 1
1
E B,C,D 3 8 11 8 11 0
0
F E 3 11 14 11 14 0
0
G E 2 11 13 12 14 1
1
H E 2 11 13 12 14 1
1
I E 2 11 13 12 14 1
1
J F,G,H,I 4 14 18 14 18 0
0
K J 2 18 20 19 21 1
1
L J 3 18 21 18 21 0
0
M J 3 18 21 18 21 0
0
N J 2 18 20 19 21 1
1
O J 2 18 20 19 21 1
1
P K,L,M,N,O 3 21 24 21 24 0
0
Q P 1 24 25 25 26 1
1
R P 1 24 25 25 26 1
0
S p 2 24 26 24 26 0
0
T Q,R,S 4 26 30 26 30 0
0
U T 5 30 35 30 35 0
0
Explanation: Consider activity B. The slack of head
event 5 is 8 – 8 = 0. Therefore, free float = 0 – 0 = 0.
Likewise slack of tail event A is 0 – 0 = 0. Therefore
independent float = 0.
Critical Path: ABEFJLMPSTU
5333433245= 31 days.
The data analysis in Table 3 can be seen as the
date of completion of the activity U. The last activity
of the project should be 35 days, which is equal to the
time it takes to complete the project.
5 B 8
0
5 3 8
Description
Critical path
11 I 13
1
12 2 14
Description
0 A 5
0
0 5 5
Description
5 C 7
1
6 2 8
Description
5 D 7
1
6 2 8
Description
8 E 11
0
8 3 11
Description
11 F 14
0
11 3 14
Description
11 G 13
1
12 2 14
Description
11 H 13
1
12 2 14
Description
14 J 18
0
14 4 18
Description
18 L 21
0
18 3 21
Description
18 M 21
0
18 3 21
Description
18 K 20
1
19 2 21
Description
18 O 20
1
19 2 21
Descript
18 N 20
1
19 2 21
Description
21 P 24
0
21 3 24
Description
24 S 26
0
24 2 26
Description
24 Q 25
1
25 1 26
Description
24 R 25
1
25 1 26
Description
30 U 35
0
30 5 35
Description
26 T 30
0
26 4 30
Description
A Some of Paddy Cleaning Machine on Activity Free Float in Activity- on –Arrow and Node Networks: Part II
65

3.1 Calculated Project Float
Team research requires a 44-day end date. Project
Float is the total length of time a project can be
delayed without delaying the project.
44 days – 35 days = 9 days.
The float may be deleted on a date determined by
the research team prior to the time specified in the
project schedule. Crashed projects need to be
removed or tracked quickly. Crashing is a technique
used to shorten the duration of a project by assigning
additional resources to the task and reducing the time
required for those tasks and details of the components
for the construction paddy cleaning.
4 CONCLUSIONS
This research presents a free float for AOA and AON
diagrams that assign activity to a specific column in a
network diagram, a schedule under a dependency
structure, by examining a selected group or activity
for each change.
May result or improve all the time estimated by
the PERT / CPM method to summarize the paddy
machine production project for 44 days. After
accelerating all the activities that constitute the
critical path, the total project completion time will be
35 days.
The results show that PERT / CPM techniques can
lead to improved time and cost of paddy mill
production projects and application to other industry
and university projects. Increasing number of projects
implemented and leading to increased
competitiveness.
The float of the project shows a decrease in
construction time of 9 days, because it can easily
handle data exchange and sequence planning.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Financial support “RMUTL Research grants for
agricultural research, such as cutting and packaging,
cold storage, processing and packaging. Research and
development of economic crops. Project Code AG2-
180307163528-60”: Rajamangala University of
Technology Lanna, Chiang Mai is gratefully
acknowledged.
.
REFERENCES
https://pmstudycircle.com/2013/03/total-float- versus-
free-float.
S, Bangphan., P, Bangphan., and S, Phanphet., 2018.
Application of production process for paddy cleaning
machine by using pert & cpm techniques
:case study, The 2018 International Conference
of Computer Science and Renewable Energies,
Ouarzazate, Morocco, 22-24 November 2018.
Scaat., [Internet]., 2009. [cited 2013 July 12]
www.scaat.in.th/Bachelor/new/1_2552/010.
Surapong Bangphan., 2013. Project Management
Engineering, teaching materials, translation and
collection, Chiangmai.
ICCSRE 2018 - International Conference of Computer Science and Renewable Energies
66
