
Intelligent MPPT Control of Stationary and Dual‐axis Tracking
Grid‐connected Photovoltaic System
Layachi Zaghba, Messaouda Khennane, Abdelhalim Borni, Amor Fezzani, Idriss Hadj Mahammed
and Abdelhak Bouchakour
Applied Renewable Energy Research Unit, URAER, Renewable Energy Development Center, CDER, 47133, Ghardaïa,
Algeria
Keywords: Neural Network, Boost Converter, MPPT Control, Grid‐connected Photovoltaic System, Dual‐axis
Tracking, Fixed Array.
Abstract: This paper study a performance comparison between 6 kWp dual-axis tracking system and an identical fixed
inclination system on a sunny day (City of Ghardaia in South of Algeria) based on the MPPT approach of
artificial neural networks. The first goal of this work is to extract the maximum power point of the
photovoltaic group. The second objective, a comparison between dual-axis tracking system and an identical
fixed inclination system is conducted. Simulation is carried out in Matlab/Simulink and the results show the
excellent performance, high efficiency, low error, very short response of the neural network approach
compared to a classical method (P&O). Results are reported to show also the effectiveness of the tracking
system of about 25% in energy efficiency, therefore is confirming the economic importance of this type of
system.
1 INTRODUCTION
In literature, several research works focused on
various MPPT control techniques. These commands
are selected based on their needs (complexity, cost,
precision, convergence speed). Hill climbing,
perturbs and observe (P&O) and incremental
conductance are the three most popular methods,
because they have the advantage of easy
implementation. It is based on the disruption of the
system with a constant voltage/duty cycle, and
checks its behavior (Ouchen, 2016; Borni,2017). In
recent years, intelligent controller techniques were
used for the MPPT such as neural network to
overcome these drawbacks (Ouchen, 2016; Borni,
2017).
In this paper, the first part, neural network and
P&O MPPT controllers are applied to control a dual-
axis tracking system and an identical fixed
inclination system. The second part, we present the
results of two-axis tracking and without tracking
(fixed system). In addition a comparison will be
presented the economic utility and the importance of
the dual axis tracking system in terms of generated
power.
2 GLOBAL IRRADIATIONS ON
INCLINED SURFACES
Liu Jordan model based on mathematical equation
was used in order to calculate different components
of solar radiation (Zaghba, 2015; Astudillo, 2015;
Kebour, 2017).
2.1 Direct Solar Radiation
The direct solar radiation estimated on inclined
surface without being diffused by the atmosphere is
given by:
(1)
Where,
and
are respectively the direct
solar radiation measured on horizontal surface and
the tilt factor:
(2)
(3)
Zaghba, L., Khennane, M., Borni, A., Fezzani, A., Mahamed, I. and Bouchakour, A.
Intelligent MPPT Control of Stationary and Dual-axis Tracking Grid-connected Photovoltaic System.
DOI: 10.5220/0009772901990205
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference of Computer Science and Renewable Energies (ICCSRE 2018), pages 199-205
ISBN: 978-989-758-431-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
199

δ: Declination angle, h: height of the sun, ф:
latitude, ω: hour angle and i: tilted angle.
With:
(4)
(5)
(6)
2.2 Diffuse Solar Radiation
The equation of diffuse solar radiation given by Liu
& Jordan model which takes into account the
isotropic part of sky is:
(7)
Where,
is the diffuse solar radiation measured
on horizontal plane.
(8)
B is a constant which reflect the nature of the sky.
2.3 Reflected Solar Radiation
For an inclined plane, the reflected radiation can be
expressed by:
(9)
ρ: Albedo.
The reflected solar component in a horizontal
plane is zero.
2.4 Global Solar Radiation
The total solar radiation measured or estimated on an
inclined plan is given by:
(10)
3 PHOTOVOLTAIC SYSTEM
Figure 1 shows the considered PV system, in the first
stage, the output of the photovoltaic generator is
connected to a boost converter on which the MPPT
control strategy is applied to increases the voltage of
the PV to a suitable level for the DC-AC inverter.
The second stage is applied and DC-AC converter
connected to a grid through à filter.
Figure 1: Grid connected PV system.
3.1 Photovoltaic Module
For this work, the 6 kWp PV generator contains 20
series modules and 5 parallel modules. Each one
presents the following characteristics: Nominal peak
power: 60 W, Nominal voltage: 17.1 V, Nominal
current: 3.5 A.
Table 1: Electrical characteristics of 6 kwp photovoltaic
arrays.
Parameter
Value
Maximum Power
P
PV
6000W
Voltage at Pmax
V
MPP
342 V
Current at Pmax
I
MPP
17.5A
Open Circuit Voltage
Voc
422V
Short Circuit Current
Isc
19 A
ICCSRE 2018 - International Conference of Computer Science and Renewable Energies
200

3.2 Boost Converter
The schematic diagram of DC-DC boost converter
connected to photovoltaic generator to a resistive
load is shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2: DC-DC Boost converter.
The state-space averaged model of the boost
converter can be written as (Zaghba
1
, 2017;
Zaghba
2
, 2017):
(11)
Where u is the duty cycle, V
pv
is the input voltage
to the boost converter, I
L
is the inductor current, C is
the capacitance, R
L
is the load resistance and V
dc
is
the DC link output. The equation (11) can be written
as:
Where
(12)
3.3 P&O MPPT Method
Figure 3 shows the flowchart of the P&O method,
current and voltage are required to determine the
power of the PV at each moment where the evolution
of power is calculated and analyzed after each
voltage disturbance (Ouchen, 2016; Borni, 2017).
Figure 3: Flowchart of Perturb and observe MPPT.
3.4 Artificial Neural Network MPPT
The ANN is used as an intelligent control MPPT
approach of the Boost converter; the simpler
architecture contains three layers as shown in Fig. 4.
The input layer receives the extern data (temperature
and irradiation). The second layer, hidden layer,
contains several hidden neurons which receive data
from the input layer and send them to the third layer,
output layer (output voltage).
The relationship between the inputs and output
formulated as (Mellit, 2013):
(13)
Where x Neural inputs, Wi: Neuronal network
weights, y the output of the system.
The training of the network was provided by
back propagation process using the Levenberg-
Marquardt algorithm. After the learning of the
network we have taken the adjusted weights and we
used them with feed-forward equations into a
Simulink file "embedded function" to control the PV
system with the values of D provided automatically.
Back propagation algorithm used to update the
weights and biases and to minimize a mean squared-
error performance index given as (Mellit, 2013):
(14)
Where:
the i- th desired output of the system.
The update of Wi is done according to the following
rule (Mellit, 2013):
(15)
We build a very rich database, which has a lot of
information that will be used to learn and test the
neural network on different levels of irradiation and
temperature. For this phase, the following table has
been realized:
Table 1: RNA training table.
T(C°)
G
(W/m²)
10
15
25
40
55
70
200
310.8
308.3
305
292.7
292.3
277.8
300
323.2
319.5
314.5
304.7
306.1
287.6
400
327.9
327.2
321.7
314.5
314.8
299.6
500
336.2
333.3
327.5
321
320.6
306.1
600
340.6
336.9
333.3
326.4
326.1
310.8
700
343.9
340.6
335.9
330.8
329.3
315.5
800
347.1
345.3
339.5
333.7
333.7
319.9
900
349.7
347.8
342.8
336.2
336.6
323.2
1000
352.6
350.4
350
339.9
339.5
326.4
Intelligent MPPT Control of Stationary and Dual-axis Tracking Grid-connected Photovoltaic System
201

The following Matlab code creates a feed-
forward neural network:
P= [Temperature Data; Irradiation Data];
T= [Optimal voltage data];
net=newff(minmax(P),[40,3,1],
{'tansig','tansig','purelin'},'traingd');
net.trainParam.epochs=1000;
net.trainParam.goal=1e-3;
net.trainParam.show=50 ;
net.trainParam.lr=0.05;
[net,tr]=train(net,P,T);
a=sim(net,P)
gensim(net)
The conception of the MPPT control proposed
shown in Fig.3.
Figure 4: Topology of the ANN network for MPPT
control.
3.5 Grid Side Power Control
The objective of the inverter control is to
synchronize the phase’s frequency between the grid
and the PV, and to regulate the DC link voltage to a
constant value. Fig.1 shows the connection between
the inverter and the grid.
The voltage of three-phase power grid given by
the following equations (Boudaraia, 2016):
(16)
: The peak value of voltage in power grid, : The
angular frequency of power grid.
By applying Kirchhof’s laws, we can write the
voltage equation:
(17)
Applying Park transformation, we obtain:
(18)
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
The study was conducted in Ghardaia, Algeria
located at 32.48° North and 03.67° East. This site is
characterized by hot and dry climate in the summer
with an average temperature of 38°C. The solar
radiation on the region is very high; the horizontal
solar radiation is very important, in summer, it can
reach 1040 Wh/m². The wind is dry and hot with an
average speed between one and 2.5 m/s
(Boukhelkhala ,2016). Simulation studies have been
carried out in Matlab/Simulink environment to
verify the proposed artificial neural network method
for a sunny day (Ghardaia site).
Figure 5: Variations of irradiance over time in a sunny day
(Ghardaia site).
ICCSRE 2018 - International Conference of Computer Science and Renewable Energies
202

Figure 6: Output current of the PV (Fixed array and dual
axis tracking array).
Figure 7: Output voltage of the PV in a sunny day (Fixed
array and dual axis tracking array).
Figure 8: Output power of the PV (Fixed array and dual
axis tracking array).
Figure 9.a: AC three phase’s grid currents using P&O
MPPT controller (fixed array).
Figure 9.b: AC three phase’s grid currents using P&O
MPPT controller (dual axis tracking).
Figure 10.a: AC three phase’s grid currents using neural
network MPPT approach (fixed array).
0 5 10 15 20 25
-5
0
5
10
15
20
Time of day
Current (A)
Neural Network(Fixed array)
P&O (Fixed array)
Neural Network (Dual axis tracking array)
P&O (Dual axis tracking array)
8 9 10 11 12
8
10
12
14
16
Sunset
Noon
Sunrise
0 5 10 15 20 25
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
Time of day
Current (A)
7 8 9
50
100
150
200
Neural Network(Fixed array)
P&O (Fixed array)
Neural Network (Dual axis tracking array)
P&O (Dual axis tracking array)
Sunrise
Sunset
Noon
0 5 10 15 20 25
-1000
0
1000
2000
3000
4000
5000
6000
7000
Time of day
Power (W)
Neural Network(Fixed array)
P&O (Fixed array)
Neural Network (Dual axis tracking array)
P&O (Dual axis tracking array)
7 8 9
0
1000
2000
Sunset
Sunrise
Noon
0 5 10 15 20 25
-40
-30
-20
-10
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
Time of day
Three phases grid current , Iabc (A)
0 5 10 15 20 25
-40
-30
-20
-10
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
Time of day
Three phases grid current , Iabc (A)
Ia
Ib
Ic
Ia
Ib
Ic
11 11.5 12 12.5 13
-20
0
20
11 11.5 12 12.5 13
-20
0
20
Dual axis tracking array
Fixed array
0 5 10 15 20 25
-40
-30
-20
-10
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
Time of day
Three phases grid current , Iabc (A)
0 5 10 15 20 25
-40
-30
-20
-10
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
Time of day
Three phases grid current , Iabc (A)
Ia
Ib
Ic
Ia
Ib
Ic
11 11.5 12 12.5 13
-20
0
20
11 11.5 12 12.5 13
-20
0
20
Dual axis tracking array
Fixed array
0 5 10 15 20 25
-20
-10
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
Time of Day
Three phases grid current, Iabc (A)
10 10.1 10.2
-20
0
20
0 5 10 15 20 25
-20
-10
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
Time of day
Three phases grid current, Iabc (A)
10 10.1 10.2
-20
0
20
Ia
Ib
Ic
Ia
Ib
Ic
Fixed array
Dual axis tracking array
Intelligent MPPT Control of Stationary and Dual-axis Tracking Grid-connected Photovoltaic System
203
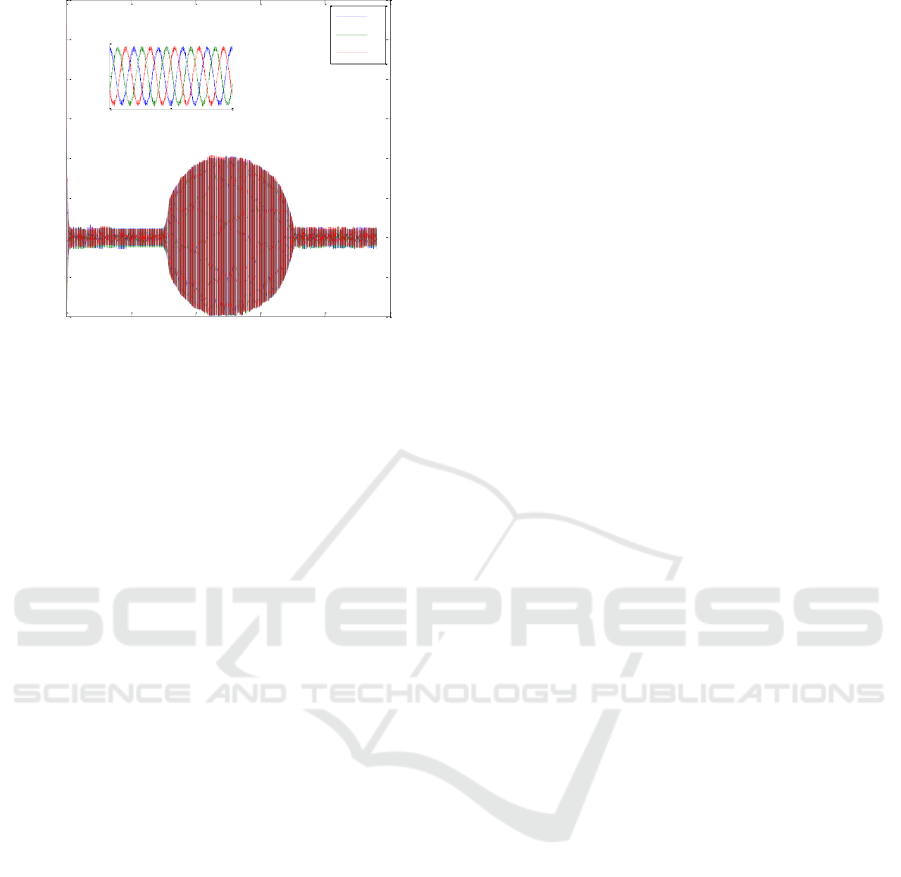
Fig. 10.b: AC three phase’s grid currents using neural
network MPPT approach (dual axis tracking).
Fig. 6, Fig. 7 and Fig. 8 show the waveforms of
the output voltage, current, and power of the PV
respectively. Here we can see that both P&O and
neural network approach were successfully able to
track the maximum power point for a PV panel at
any given irradiation. The neural network –based
MPPT algorithm can quickly and accurately find the
maximum power of each type (fixed and tracking
array) and the system achieved a true sense of the
maximum power output. The P & O algorithm
strongly depends on the initial conditions and it
presents oscillations around the optimal value. This
algorithm is bad behavior following a sudden change
in irradiation .The results show that neural network
optimization technique given better results compared
to P&O. As shown, for south facing fixed surface
solar power varies over the day, peaking at the solar
noon where tracking system has flatter hourly
energy production profile. As shown, the value of
the solar energy produced by the fixed system
approaches that of the two-axis system between 11
am and 14 pm, but it moves away during the hours
of the sunrise and the hours of the end of the
afternoon.
We can see also that the power production of a
PV system is directly related to the amount of solar
irradiance incident on the array. On average,
tracking systems yield a higher average normalized
power output under sunny conditions when
compared to stationary systems since they are
always oriented nearly perpendicular to direct beam
radiation.
In addition, this paper demonstrates the
importance and efficiency of dual tracking system.
The results indicate that the solar tracking system
generated more energy about 25% compared to the
power generated by identical fixed solar panels.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The neural network based MPPT control has clearly
demonstrated its utility and the effectiveness in
tracking the maximum power point of two identical
photovoltaic systems, the first is equipped with a
solar tracker while the second is without a tracker
and shows an excellent performance, high efficiency,
low error, very short response time, high dynamics
for both inverter and MPPT compared to classical
MPPT control.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This project was financially supported by the
Directorate General for Scientific Research and
Technological Development - Algerian Ministry of
Higher Education and Scientific Research.
REFERENCES
Ouchen, S., Abdeddaim, S., Betka, A., Menadi, A.,
Experimental validation of sliding mode-predictive
direct power control of a grid connected photovoltaic
system, feeding a nonlinear load, Solar Energy 137
(2016) 328–336.
Borni, A., Bouarroudj, N., Bouchakour, A. and Zaghba,
L., P&O-PI and fuzzy-PI MPPT Controllers and their
time domain optimization using PSO and GA for grid-
connected photovoltaic system: a comparative study
,Int. J. Power Electronics, Vol. 8, No. 4, 2017.
Zaghba, L., Terki, N., Borni, A., Bouchakour, A., Benbitour
Née Khennane Messaouda, Adaptive intelligent MPPT
controller comparison of Photovoltaic system under
different weather Conditions of ghardaia site (south of
Algeria), Journal of Electrical Engineering, Volume 15 /
2015 - Edition: 3.
Astudillo, D. P., Bachour, D., 2015. Variability of
measured global horizontal irradiation throughout
Qatar. Sol. Energy 119, 169–178.
Kebour, O., Arab, A. H., Abdelkader Hamid, Kamel
Abdeladim, Contribution to the analysis of a stand-
alone photovoltaic system in a desert environment,
Solar Energy 151 (2017) 68–81.
Zaghba
1
, L., Khennane, M., Terki, N., Borni, A.,
Bouchakour A., Fezzani, A., Hadj Mahamed, I., and
Oudjana, S. H., The effect of seasonal variation on the
performances of grid connected photovoltaic system in
southern of Algeria, AIP Conference Proceedings,
0 5 10 15 20 25
-20
-10
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
Time of Day
Three phases grid current, Iabc (A)
10 10.1 10.2
-20
0
20
0 5 10 15 20 25
-20
-10
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
Time of day
Three phases grid current, Iabc (A)
10 10.1 10.2
-20
0
20
Ia
Ib
Ic
Ia
Ib
Ic
Fixed array
Dual axis tracking array
ICCSRE 2018 - International Conference of Computer Science and Renewable Energies
204

1814, 020005 (2017);
https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4976224.
Zaghba
2
, L., Borni, A., Khennane, M., Terki, N., Fezzani,
A., Bouchakour, A., Hadj Mahamed, I., Oudjana S. H.,
Experimental typical meteorological years to study
energy performance of a PV grid-connected system,
Energy procedia, Volume 119, July 2017, Pages 297-
307.
Mellit, A., Sa_glam, S., Kalogirou, S. A., Artificial neural
network-based model for estimating the produced
power of a photovoltaic module, Renewable Energy,
60 (2013) 71e78.
Boudaraia, K.; Mahmoudi, H.; El Azzaoui, M., Modeling
and Control of Three Phases Grid Connected
Photovoltaic System, Renewable and Sustainable
Energy Conference (IRSEC), 2016 International, DOI:
10.1109/IRSEC.2016.7984004.
Boukhelkhala, I., Bourbiab, F., Thermal Comfort
Conditions in Outdoor Urban Spaces: Hot Dry Climate
-Ghardaia- Algeria, Procedia Engineering, 169 (2016)
207 – 215.
Intelligent MPPT Control of Stationary and Dual-axis Tracking Grid-connected Photovoltaic System
205
