
The Impact of the Pitch Angle on the Power of the AEOLOS V300
and AEOLOS V600 Wind Turbines
Zitouni Zineb, Mounir Hamid, El Marjani Abdellatif and Rabie El Alaoui
EMISys Research Team, Engineering 3S Research Center, Mohammadia School of
Engineers,University Mohammed V in Rabat, Rabat, Morocco
Keywords: VAWT, MATLAB, Variable Pitch Angle, Power Output, Wind speed, AEOLOS-V300W,
AEOLOS- V600W
Abstract: Nowadays wind power has become a promising source for electricity generation because wind power is
clean and efficient. The aim of this paper is to study the effect of the variable pitch angle on the
performance of the vertical axis wind turbines. The study concerns two type Darrieus wind turbines;
AEOLOS-V 300W and AEOLOS-V600 W. The results show that the pitch angle has a significant effect on
the output power. The turbines with a variable pitch angle can produce a maximum output power in low
wind speed compared to classic turbines, with an increase of 30% on the power coefficient.
1 INTRODUCTION
Wind energy is very essential as one of the
cleanest energy sources, it can help to reduce the
need for fossil fuels, and the wind turbines are the
most efficient tools to explore this clean energy (S.
Brusca, 2015) (Taher, 2015) (M. Predescu, 2009)
(Arti Tirkey, 2014) (M. Zheng, 2015). Several
configurations were developed in the latest years and
two types of the VAWTs namely Darrieus and
Savonius has been noticed (W. Roynarin, 2004). The
vertical axis wind turbines type Darrieus have grown
interest to produce electricity, even in urban areas.
This type of turbines presents several advantages
over the horizontal axis wind turbines (HAWT) such
as; a low noise, omnidirectional, able to catch the
wind from all directions, uses less material, can be
mounted at ground level, running with low wind
speed. Despite the low performance of these
turbines, they are more suitable for urban areas (M.
Ghasemian, 2017).
Many researchers have proposed different
optimization techniques to improve the performance
of vertical axis wind turbines, such as the effect of
the pitch angle control. Figure 1 shows several
variations of the pitch angle. M. Elkhoury et al (M.
Elkhoury, 2015) carried out the effect of variable
pitch angle on the performance of the micro vertical
axis wind turbine, the results have shown that the
power coefficient increases significantly with the
variable-pitch mechanism below TSR=1.5. A.
Rezaeiha et al (A. Rezaeiha, 2017), found that a
small negative pitch angle
β=-2° increases the power
coefficient by 6.6% compared with β=0° . G.
Abdalrahman et al (Abdalrahman, 2017) found that
the wind energy produced by H-type VAWT with
the variable pitch control increases by 25%
compared to the fixed pitch VAWT cases. M. El-
Samanoudy et al (M. El-Samanoudy, 2010)
concluded that for a pitch angle equal to 10°, the
maximum values of Cp ,Ct and
have been
obtained.
Figure 1: Geometric model of the pitch angle (A.
Rezaeiha, 2017)
Zineb, Z., Hamid, M., Abdellatif, E. and El Alaoui, R.
The Impact of the Pitch Angle on the Power of the AEOLOS V300 and AEOLOS V600 Wind Turbines.
DOI: 10.5220/0009773002490253
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference of Computer Science and Renewable Energies (ICCSRE 2018), pages 249-253
ISBN: 978-989-758-431-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
249

Q. Li et al (Q. Li, 2016), found that the Performance
of the test wind turbine depends of the blade pitch
angles and for a blade pitch angle of 6°, the power
coefficient takes a maximum value. Young-Tae Lee
et al (Young-Tae Lee, 2015), investigated the effect
of the pitch angle on 500 W Darrieus-type vertical-
axis wind turbine, and found that when the pitch
angle reaches -2° with a helical angle of 0, the
Darrieus-type VAWT showed maximum power.
In this work we aim to study the effect of the variable
pitch angle on the performance of the vertical axis
wind turbines in term to output power and the
maximal wind speed, furthermore two types of
turbines AEOLOS-V300W and AEOLOS-V-600 W
have been examined.
2 METHODOLOGY
2.1 Description of the Studied Turbines
AEOLOS-V blades use the aerodynamic design
which limits the maximum rotating speed to 360
rpm even if the wind speed is 30m/s or 40m/s. It is
safer and more reliable than traditional vertical axis
wind turbines. It could start up with 1.5m/s and has
the power output in 2.5m/s to the inverter. This is
more efficient than vertical wind turbines with a
3.5m/s or even 4.5m/s start up wind speed. The
technical characteristics of the adopted wind
turbines provided by the company of AEOLOS
Wind turbine have been presented in Figure 2,
Figure 3 and Table 1 (AEOLOS WIND TURBINE,
2013).
Figure 2: AEOLOS-V300W Power curve
2.2 Effect of the Pitch Angle
2.2.1 Angle of Attack
The angle of attack is expressed as (Mazharul ,
2008) (Travis, 2011) (S. Lain, 2010):
-1
sin( )
tan
cos( )
f
(1)
Where λ is the tip speed ratio and θ is the azimuth
angle.
For the turbines with variable pitch angle, the angle
of attack became:
-1
sin( ) sin( )
tan
cos( ) cos( )
v
(2)
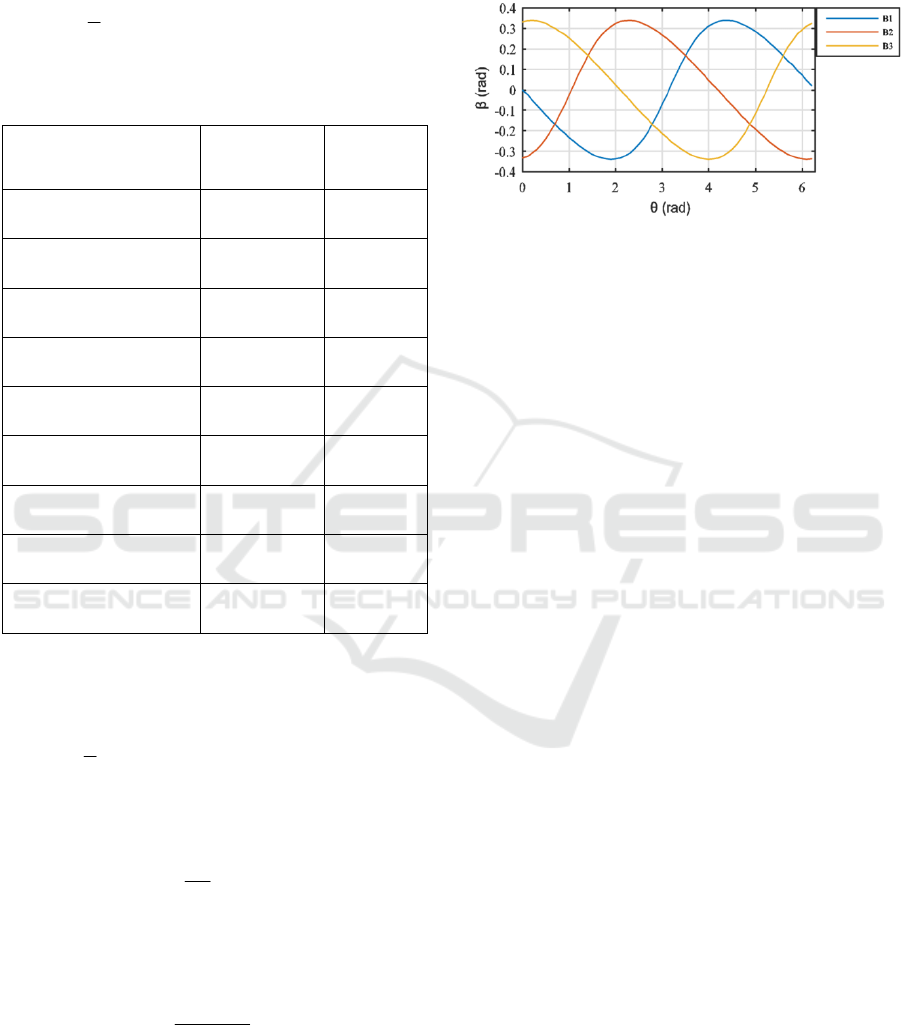
Where β is the sinusoidal pitch angle, it depends on
the position angle and it varies between -19° and
19°, shown on Figure 5.
2.2.2 Output Power
Figure 3: AEOLOS-V600W Power curve
Figure 4: AEOLOS-V turbine
The mechanical power output is expressed as
(Mazharul , 2008) (Travis, 2011) (S. Lain, 2010):
ICCSRE 2018 - International Conference of Computer Science and Renewable Energies
250
.PT
(3)
Where
ω
is the rotational velocity and T the total
torque, the expression founded is :
22 2
1
12cos()
2
ff
PrNSkV
(4)
Table 1: Technical characteristics of the AEOLOS-V
turbines
Geometry and
operating conditions
AEOLOS-
V-300W
AEOLOS
-V-600W
Number of blades[-] 3 3
Chord [m] 0.3 0.3
Rotor Height [m] 1.6 2
Rotor Width [m] 1.2 1.6
Rated Power[W] 300 600
Max Output Power
[W]
400 800
Tip Speed ratio[-] 3 3
Rated wind speed
[m/s]
10 10
Max wind speed
[m/s]
11 13
For the turbines with variable pitch angle, the power
output became:
22 2
1
12cos()
2
vV
PrNSkV
(5)
With the tip speed ratio
is expressed as (Mazharul,
2008) (Travis, 2011) (S. Lain, 2010):
r
V
(6)
The wind turbine rotor is characterized by its power
coefficient
p
C
:
3
0.5
P
P
C
SV
(7)
Where β is the sinusoidal pitch angle, N is the
number of blades, V is the axial flow velocity
through the rotor, θ is the angle azimuth angle of the
blades, ω is the rotational velocity, r is the radius of
the turbine, ρ is the air density, S is the swept area of
the rotor and k is the Wake Decay Constant.
Figure 5: The variation of the sinusoidal pitch angle of the
tree blades
3 RESULTS
This section illustrates the MATLAB simulation
results.
Figure 6 presents the validation curve of the output
power produced by AEOLOS-V 300W and
AEOLOS-V 600W with the wind speed. The tested
blade pitch angle is sinusoidal and vary between -
0.34 rad and 0.34 rad corresponding to -19° and
19°shown on figure 5.
As seen in figure 6, for the turbines equipped with a
variable pitch control, AEOLOS-V300W produces a
maximal output power (400W) in 8.5m/s instead of
13m/s while AEOLOS-V600W produced a maximal
output power (800W) in 10 m/s instead of 13m/s,
compared with the turbines with fixed pitch angle.
Table 2 shows a comparison of wind speed
corresponding to the maximal output power for both
turbines with variable pitch angle and fixed pitch
angle.
In term of wind speed, the turbines produce the same
power but in low wind speed compared with fixed
pitch angle, consequently the turbines don’t need a
height wind speed to achieve their maximal power
output.
The variation of the pitch angle between -19° and
The Impact of the Pitch Angle on the Power of the AEOLOS V300 and AEOLOS V600 Wind Turbines
251

19°, affects the power coefficient, and it increases by
30% compared with the fixed pitch angle. Table 3
presents the comparison of the improvement of the
Cp in this study with other researches.
As results the variable pitch angle has a satisfactory
effect on the vertical axis wind turbines, it increases
the power output by 30% compared with fixed pitch
angle. And the turbines equipped with the
mechanism of variable pitch angle reach their
maximal output power in low wind speed compared
with basic turbines.
Table 2: The wind speed corresponding on the maximal
output power for the variable and fixed pitch angle
Maximal wind speed
Fixed pitch
angle
Variable pitch
angle
AEOLOS-
V 300W
11m/s
8.5m/s
AEOLOS-
V 600W
13m/s
10m/s
4 CONCLUSION
This survey has been interested in the study of the
effect of the variable pitch angle on the vertical axis
wind turbines. The comparison has been carried out
in MATLAB and took in consideration AEOLOSV-
300W and AEOLOSV-600W wind turbines.
The above results have shown that the variable pitch
angle is an essential parameter, it influences
positively the performance of the vertical axis wind
turbines. In fact, for turbines with variable pitch
angle their maximal output power has been reached
in low wind speed compared with fixed pitch angle,
with a 30 % increase in the Cp factor.
Table 3: The comparison of the improvement of the Cp
with other studies
Pitch angles
(degree)
Cp
increased
by
Rezaeiha 2017 -2 6.6%
G. Abdalrahman
2017
-6,-4, 0, 4, 6 25%
M. El-
Samanoudy 2010
10° 19%
Present study
-19< β <19
30%
REFERENCES
S.Brusca, R. Lanzafame, M. Messina “Design and
Performance of a Straight-Bladed Darrieus Wind
Turbine” 2015
Taher G. Abu-El-Yazied, Ahmad M. Ali, Mahdi S. Al-
Ajmi, Islam M. Hassan, “Effect of Number of Blades
and Blade Chord Length on the Performance of
Darrieus Wind Turbine” 2015
M.Predescu, A.Bejinariu, O.Mitroi, A. Nedelcu,
“Influence of the Number of Blades on the Mechanical
Power Curve of Wind Turbines” 2009
Arti Tirkey, Yamini Sarthi, Khemraj Patel, Ritesh Sharma,
Prakash Kumar Sen, “Study on the effect of blade
profile, number of blade, Reynolds number, aspect
ratio on the performance of vertical axis wind turbine”
2014
Maosheng Zheng, Yusheng Li, Yangyang Tian, Jun Hu,
Yuan Zhao, Lijun Yu, “Effect of blade installation
ICCSRE 2018 - International Conference of Computer Science and Renewable Energies
252

angle on power efficiency of resistance type VAWT
by CFD study” 2015
Wirachai Roynarin, Ph.D. Thesis “OPTIMISATION OF
VERTICAL AXIS WIND TURBINES” 2004.
Masoud Ghasemian, Z. Najafian Ashrafi, Ahmad
Sedaghat, “A review on computational fluid dynamic
simulation techniques for Darrieus vertical axis wind
turbines” 2017
M.Elkhoury, T. Kiwata, E. Aoun “Experimental and
numerical investigation of a three-dimensional
vertical-axis wind turbine with variable-pitch”2015
A.Rezaeiha, I. Kalkman, B. Blocken,“Effect of pitch angle
on power performance and aerodynamics of a vertical
axis wind turbine”2017
G. Abdalrahman, W. Melek, F. Lien “Pitch angle control
for a small-scale Darrieus vertical axis wind turbine
with straight blades (H-Type VAWT)” 2017
M. El-Samanoudy, A.A.E. Ghorab, Sh.Z. Youssef, “Effect
of some design parameters on the performance of a
Giromill vertical axis wind turbine” 2010
Q . Li , T. Maeda , Y. Kamada , J. Murata ,M. Yamamoto ,
T. Ogasawara, Ke. Shimizu, T. Kogaki “Study on
power performance for straight-bladed vertical axis
wind turbine by field and wind tunnel test” 2016
Young-Tae Lee, Hee-Chang Lim “Numerical study of the
aerodynamic performance of a 500 W Darrieus-type
vertical-axis wind turbine” 2015
AEOLOS WIND TURBINE, AEOLOS Eolienne
domestique,
EditionInternet,[Enligne],2013.[http://www.windturbi
nestar.com/products.html]
Mazharul Islam, David S.-K. Ting, Amir Fartaj
“Aerodynamic models for Darrieus-type straight-
bladed vertical axis wind turbines” 2008
Travis J. Carrigan, Brian H. Dennis, Zhen X. Han, and Bo
P. Wang, “Aerodynamic Shape Optimization of a
Vertical-Axis Wind Turbine Using Differential
Evolution” 2011
S.Lain, C. Osorio, “Simulation and evaluation of a
straight-bladed Darrieus-type cross flow marine
turbine” 2010
The Impact of the Pitch Angle on the Power of the AEOLOS V300 and AEOLOS V600 Wind Turbines
253
