
Technical Assessment of a Photovoltaic Panel and a Wind Domestic
Turbine Systems in Morocco
A. Serbouti , M. Rattal, A. Boulal, E. Oualim and Az. Mouhsen
Laboratory of Radiation - Matter & Instrumentation, University Hassan First
Faculty of Science and Technology Settat, Morocco
Keywords: Photovoltaics, Wind Power, Optimization, Sensitivity Analysis, TRNSYS
Abstract: This paper presents a general methodology of optimizing the energy performance of a photovoltaic panel in
five different cities in Morocco, by varying its slope and azimuth. A domestic wind turbine is also studied in
Casablanca. For the same capacity, simulations in TRNSYS software prove that photovoltaic panels have a
better yield than the domestic wind turbines. These wind generators can be coupled with the photovoltaic
system in order to lessen the intermittence of the photovoltaic production at night and during short cloudy
days.
1 INTRODUCTION
Morocco benefits from a remarkable potential in
renewable energies thanks to its suitable
geographical position. In fact, our national rate of
sunshine is the ninth best in the world: Morocco’s
710,000-km2 lands profit from a range of 2800 and
3400 hours of sunshine per year. The Moroccan
Agency For Solar Energy (MASEN) evaluates the
Moroccan technical potential of solar energy to
20,000 MW. However, the actual installed capacity
is only estimated to 180 MW in 2016 (MASEN,
2018).
Among the various available technical
solutions to exploit the energy of the sun,
photovoltaic technologies make it possible to
convert the sunlight into electricity, and global
efficiencies are typically around 14-16% for
polycrystalline modules.
Many Moroccan authors studied the
performance of PV installations; K. Attari and al.
presented an evaluation of a grid-connected
photovoltaic (PV) system installed on the roof of a
government building located in Tangier,
Morocco(Attari, 2016). D. Lahjouji and al.
optimized the tilt angle for maximum solar energy
collection in Ifrane, Morocco (Lahjouji, 2013).
In the framework of the study, a PV system is
modelled in TRNSYS transient simulation program
using a PV panel (Type 94) and a typical
meteorological year (TMY2) conditions (with
Meteonorm software data). The panel performance
is studied and optimized in five different cities in
Morocco: Casablanca, Fez, Tangier, Ouarzazate and
Marrakech, using genetic algorithms. These cities
are located in five different climatic zones according
to the Moroccan thermal regulation for buildings
(ADEREE, 2015).
The global installed capacity of wind turbines
was about 318,1 GW by the end of 2013. Morocco
has launched, on June 28, 2010 an ambitious wind
energy program, aiming to grow the wind plants to
2000 MW by 2020. The commissioning of the first
wind farm in Morocco took place in 2000
(Abdelkhalek Torres Farm in Tetouan, 50.4 MW)
(ATLAS ADEREE, 2018). Many other wind energy
generation projects were completed since then:
Amougdoul in Essaouira (60 MW), Tangier wind
farm (140 MW), Houma (50 MW)…
Mohamed Oukili and al. performed a
comparative Study of the Moroccan Power Grid
Reliability in Presence of Photovoltaic and Wind
Generation. They conclude that wind and solar
power sources to be used in order to save fossil fuel
and increase the total energy generation in Morocco
(Oukili, 2013).
Serbouti, A., Rattal, M., Boulal, A., Oualim, E. and Mouhsen, A.
Technical Assessment of a Photovoltaic Panel and a Wind Domestic Turbine Systems in Morocco.
DOI: 10.5220/0009774902110217
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference of Computer Science and Renewable Energies (ICCSRE 2018), pages 211-217
ISBN: 978-989-758-431-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
211
Consequently, the second chapter of this article
will shed the light on the study of a domestic wind
turbine, with a capacity of 1Kw in Casablanca, using
the type 90 of TRNSYS and the weather data (wind
and direction speed) collected by Meteonorm in a
weather station located in Casablanca.
2 STUDY AND OPTIMIZATION
OF THE ENERGY
PERFORMANCE OF A PV
PANEL
2.1 Weather Data
Meteonorm7 software generates the weather data
used in this paper.
Meteonorm is a complete, worldwide
climatological database. The software enables data
generation of hourly values for any place in the
world (Meteonorm, 2018). The user can synthesize
these data in an output file compatible with
TRNSYS software.
For Casablanca, Tangier, Fez, Ouarzazate and
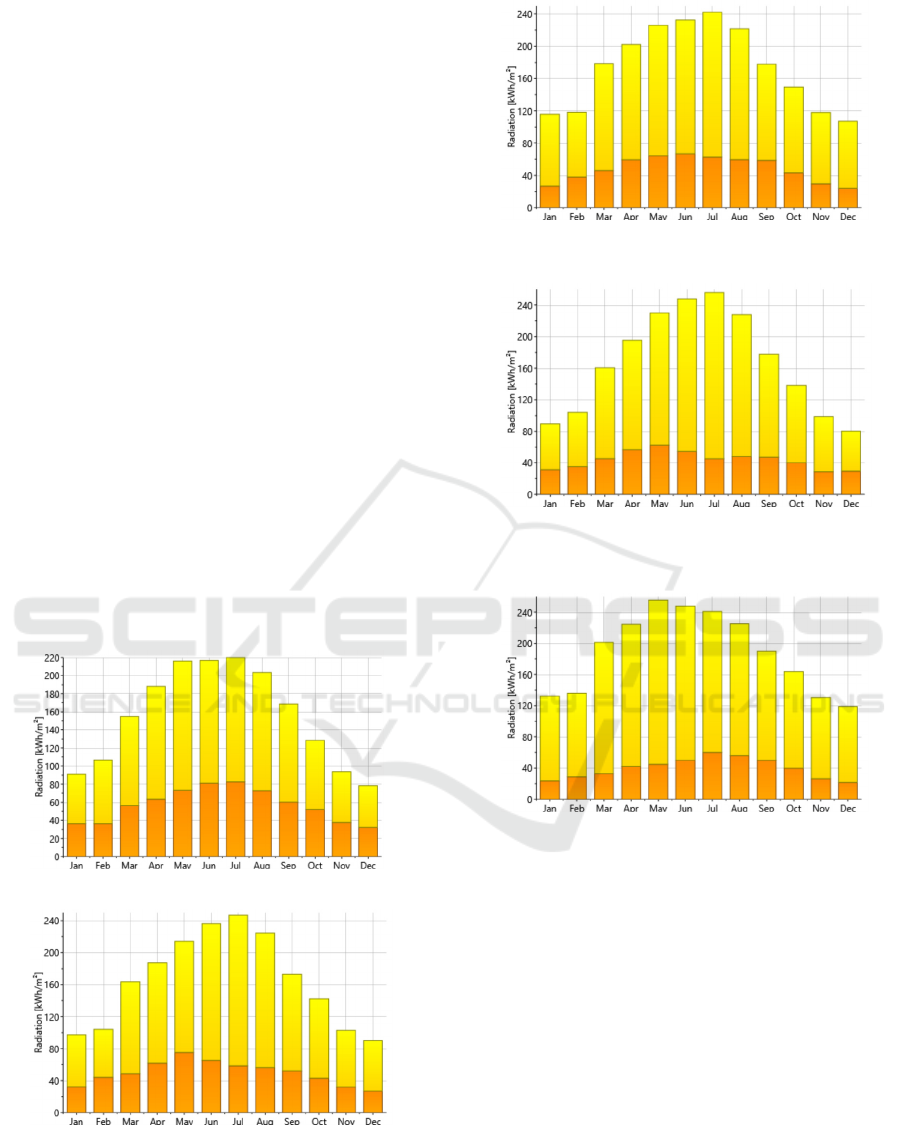
Marrakech, radiation data cover respectively the
period 1991-2010. Figures 1 to 5 show the global
and diffuse radiations evolution in the five cities.
Figure 1: Global (yellow) & Diffuse (orange)
radiations in Casablanca;
Figure 2: Global (yellow) & Diffuse (orange)
radiations in Fez;
Figure 3: Global (yellow) & Diffuse (orange)
radiations in Marrakech;
Figure 4: Global (yellow) & Diffuse (orange)
radiations in Tangier;
Figure 5: Global (yellow) & Diffuse (orange)
radiations in Ouarzazate;
These cities and Morocco in general, benefit
from a very important global radiation (255 kWh/m²
per month at its highest in Ouarzazate). Morocco is
then an attractive country for investing in solar
technologies.
2.2 TRNSYS Model and Initial
Results
In our case study, we chose a photovoltaic panel
produced locally in Skhirat, Morocco by PV
Industry, subsidiary company of Jet Energy and
specialized in Photovoltaics.
ICCSRE 2018 - International Conference of Computer Science and Renewable Energies
212
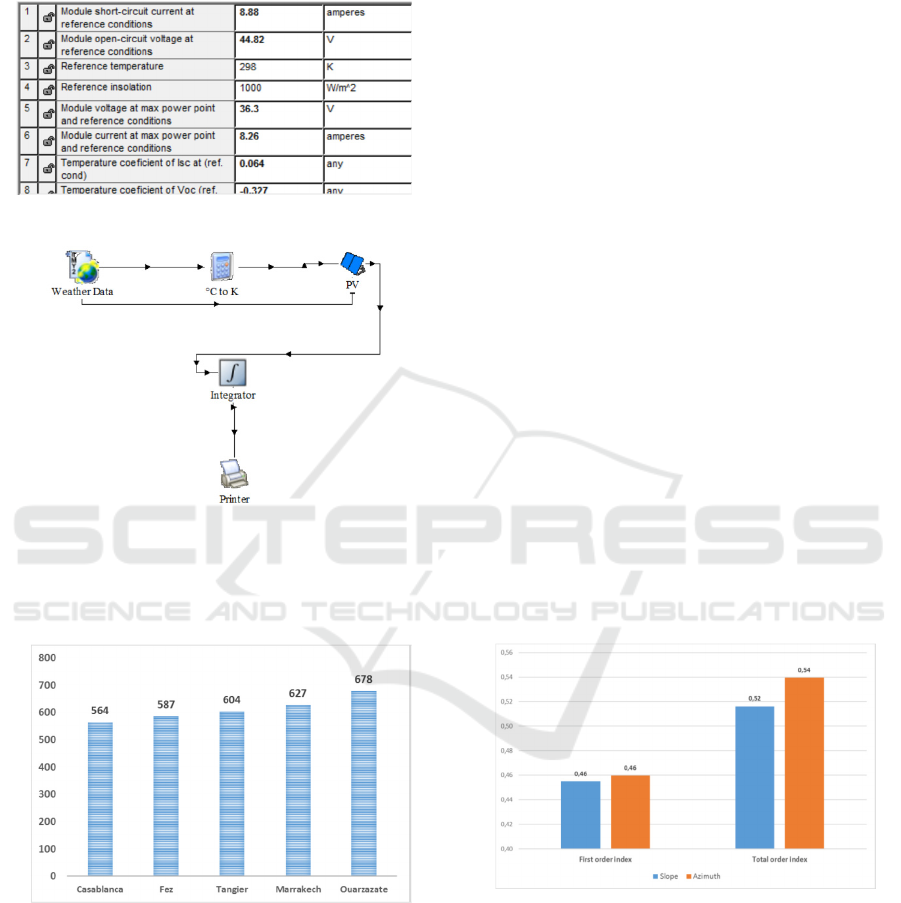
These panels have a surface of 1,94m² (1,952 x
0,992 m²) and a 300Wc per-unit power. The
TRNSYS model is showed in the figure 7.
Figure 6: PV Industry 300Wc polycrystalline module
parameters in TRNSYS
Figure 7: TRNSYS model
We will study the performance of a single
photovoltaic panel in the five cities, with an initial
slope and azimuth of 0° (horizontal panel, south-
faced). The results are presented in the figure 8.
Figure 8: Energy output in kWh in the five cities
In the following paragraph, we will use a
sensitivity analysis approach to determine which of
the two studied parameters (slope and azimuth) has
the most influence on the energy performance. Then,
we will optimize it by studying them in their
variation intervals.
2.3 Sensitivity Analysis
Systems simulated on dynamic thermal simulation
(DTS) tools present many input parameters. In order
to optimize a chosen output of these tools according
to the combinations made up of input parameters,
sensitivity analysis allows the identification of the
parameter or set of parameters that have the greatest
influence on the model output, and thus not to study
the parameters which have a low influence on the
model (École Chercheur Mexico, 2010). Sensitivity
analysis helps determining how a digital model
answers variations intervening on its inputs (Looss,
2011).
Sobol sensitivity analysis determines the
contribution of each input parameter and their
interactions to the overall model output variance.
The sensitivity of the output compared to the
parameters is given by various orders indices of
sensitivity.
Among these indices, the total order index allows
to study both the effect of the parameter alone and
the effects of its interaction with all the other
parameters on the variation of the output.
We developed algorithms on the OpenSource
programming language Python, in order to adapt our
case study to the algorithms of the SALIB library
(Sensitivity Analysis Library) available on GITHUB
(Herman, 2017).
The studied parameters are:
• Slope (from 0 horizontal to 90° vertical);
• Azimuth (from 0 south to 360° south);
Figure 9: Sensitivity analysis first and total indexes
We notice that the two parameters have almost
the same first order index (same influence when
varying one parameter and fixing the other).
The total index of the azimuth is although higher
than the total index of the collector slope. The panel
azimuth has then a slightly higher influence on the
energy yield than the panel slope.
The second order index shows also that there is a
high interaction between these two parameters.
Technical Assessment of a Photovoltaic Panel and a Wind Domestic Turbine Systems in Morocco
213
2.4 Optimization using MOBO
Software
In this paragraph, we carry out a coupling of the
TRNSYS software with MOBO (Multi-Objective
Building Optimization tool) optimization tool,
developed by the Technical Research Centre of
Finland (Palonen, 2013).
To perform the optimizations, we will use the
genetic algorithms GA (in specific the non-
dominated sorting genetic algorithm NSGA-II),
coupled to the Hooke-Jeeves algorithm (Deb, 2001).
GA reflect the process of natural selection where the
fittest individuals are selected for reproduction in
order to produce offspring of the next generation
(Dubrow, 2010). The Hooke-Jeeves algorithms
perform modified iterations of Hooke and Jeeves
until no further progress is forthcoming.
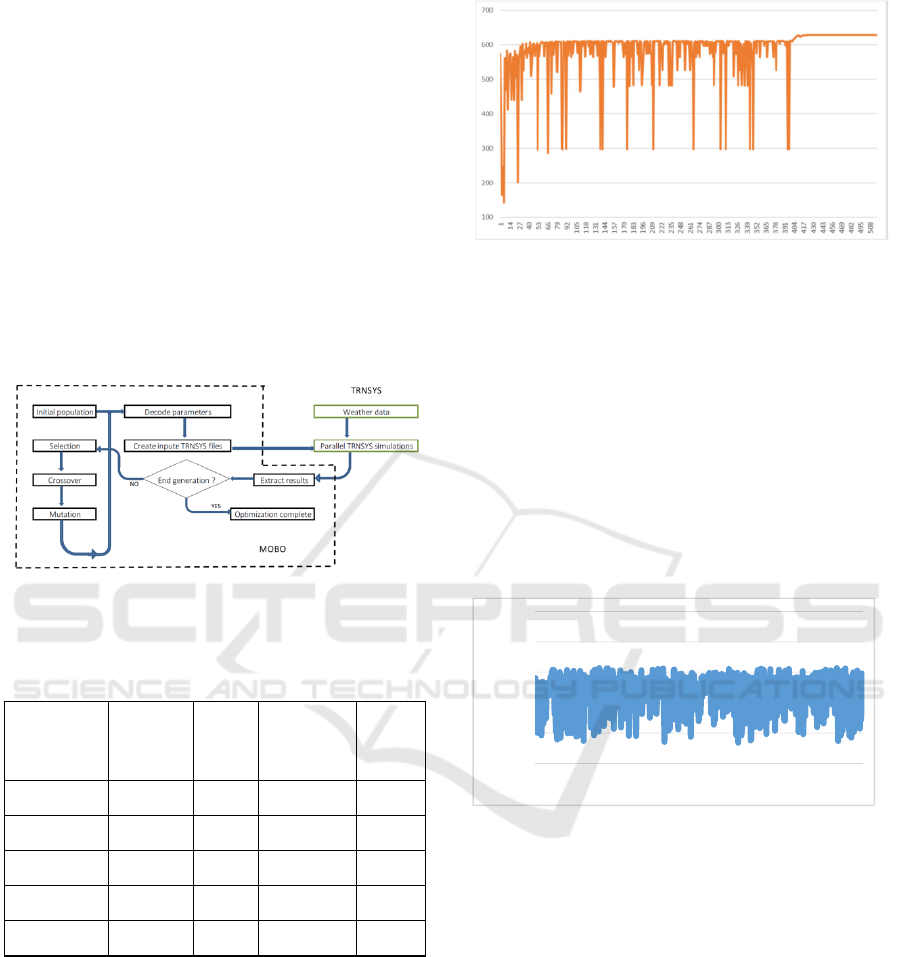
Figure 10: Coupling TRNSYS / MOBO GA
The table below shows the optimization results
in the five cities.
Table 1 - Optimization results
City
Azimuth
(°)
Slope
(°)
Optimized
Yield
(kWh)
Initial
Yield
(kWh)
Casablanca 0 29,52 629 564
Fez 0 31,21 663 587
Tangier 0 31,97 690 604
Marrakech 358,4 30,32 704 627
Ouarzazate 0,05 30,81 765 678
We notice that in the five cities, the optimal
orientation of the panel is south (0°), and the optimal
slope is around 30°.
By optimizing these two parameters, we gain
around 12% of the annual electricity production.
Fig. 11: Optimization process (510 simulations) of the
energy yield inCasablanca
2.5 Comparison with Random
Search Algorithm
The random search algorithm randomly varies the
values of the two parameters within their intervals of
variation, until reaching the number of simulations
specified by the user.
With 500 simulations, the optimal combination
is:
- Yield : 627 kWh;
- Azimuth : 355°;
- Slope : 29.55°;
Figure 12: Random search algorithm
We notice that the random search algorithm
permits having a good approximation of the optimal
value (627 kWh instead of 629 kWh), although the
NSGA-II algorithm is more efficient.
2.6 Effect of the Temperature on the
Yield
We studied below the effect of variation of the
temperature (from -5°C to 45°C) on the electrical
output of the most efficient hour of the year. The
figure 13 shows the results obtained with the random
search algorithm.
We notice that the yield is decreasing while
increasing the ambient temperature. The optimal
operating temperature is 5°C.
0
1000
1
35
69
103
137
171
205
239
273
307
341
375
409
443
477
ICCSRE 2018 - International Conference of Computer Science and Renewable Energies
214
The PV panel is losing around 8% of its
efficiency when passing from 5 to 45°C.
Figure 13: Effect of the temperature on the electrical
yield of 1 hour (in Watt)
3 DOMESTIC WIND TURBINE
STUDY
Solar energy is generally not enough alone to supply
the needed energy, especially during the night and in
the short gray days of winter. Moreover, according
to local weather statistics, wind speed increases in
winter, so that solar energy and wind energy can
complement each other. In addition, small wind
turbines have a rather simple manufacturing
technology and require less land area (Elnaggar,
2017).
For these considerations, we will study in this
section a domestic wind turbine installation in
Casablanca.
3.1 Weather Station
The weather station used in this study is located in
Casablanca, its coordinates are 33,6°N / -7,7°E, 55m.
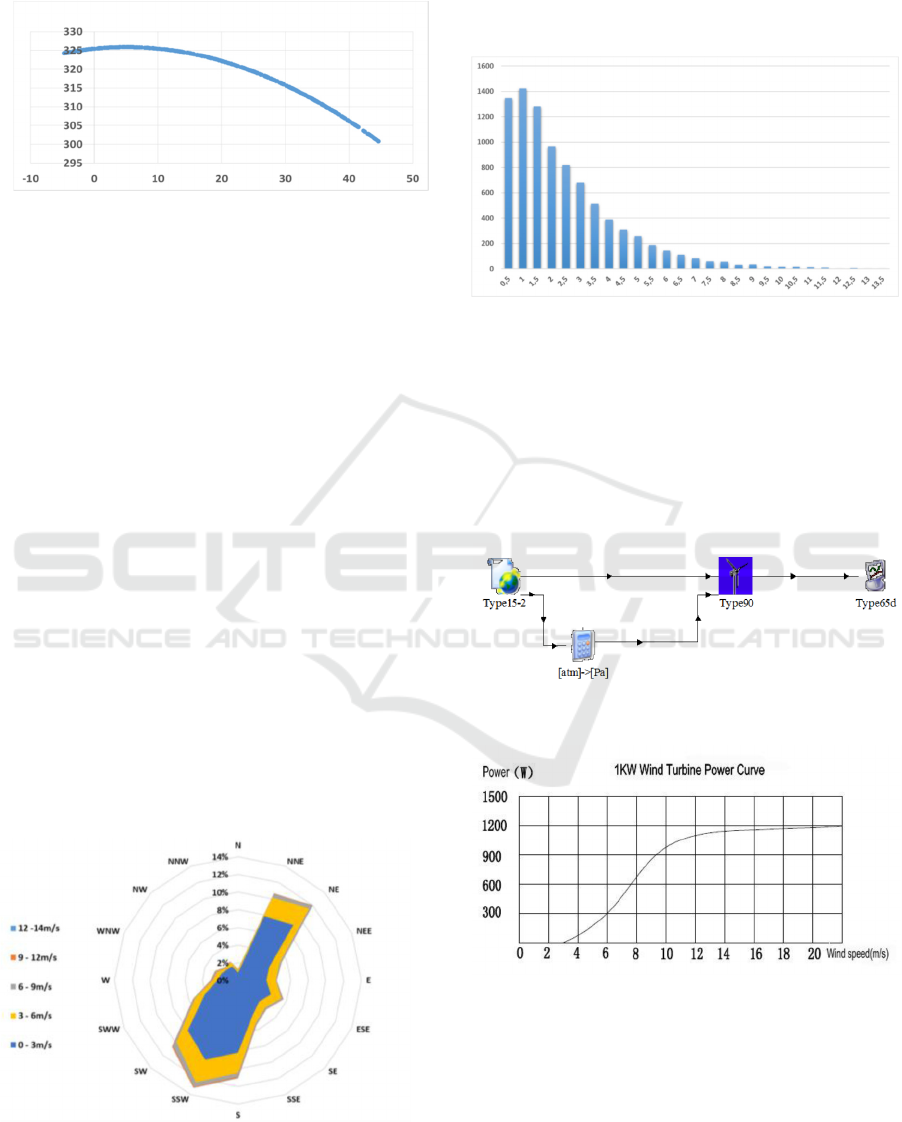
Figure 14 below shows the wind rose and the wind
speed evolution in Casablanca.
Figure 14: Wind rose in Casablanca
Then, the preponderant wind directions in
Casablanca are NNE, NE, SW, SSW and South.
In the figure 15, Y-axis shows the sum of hours per
year (for a total of 8760 hours per year) and X-axis
refers to the wind speed in m/s.
Figure 15: Wind speed distribution in Casablanca
3.2 Domestic Wind Device and
TRNSYS Model Weather Station
In this paragraph, we will study the
performance of a 1kW wind Turbine (HUMMER
1kW wind generator). The TRNSYS model and
thecharacteristics of the generator are detailed below
(HUMMER, 2018).
Figure 16: TRNSYS model.
Figure 17: HUMMER 1kW Power / wind speed curve.
3.3. Results
The figure 18 shows the hourly wind power
generation in Casablanca (in Watts).
Technical Assessment of a Photovoltaic Panel and a Wind Domestic Turbine Systems in Morocco
215
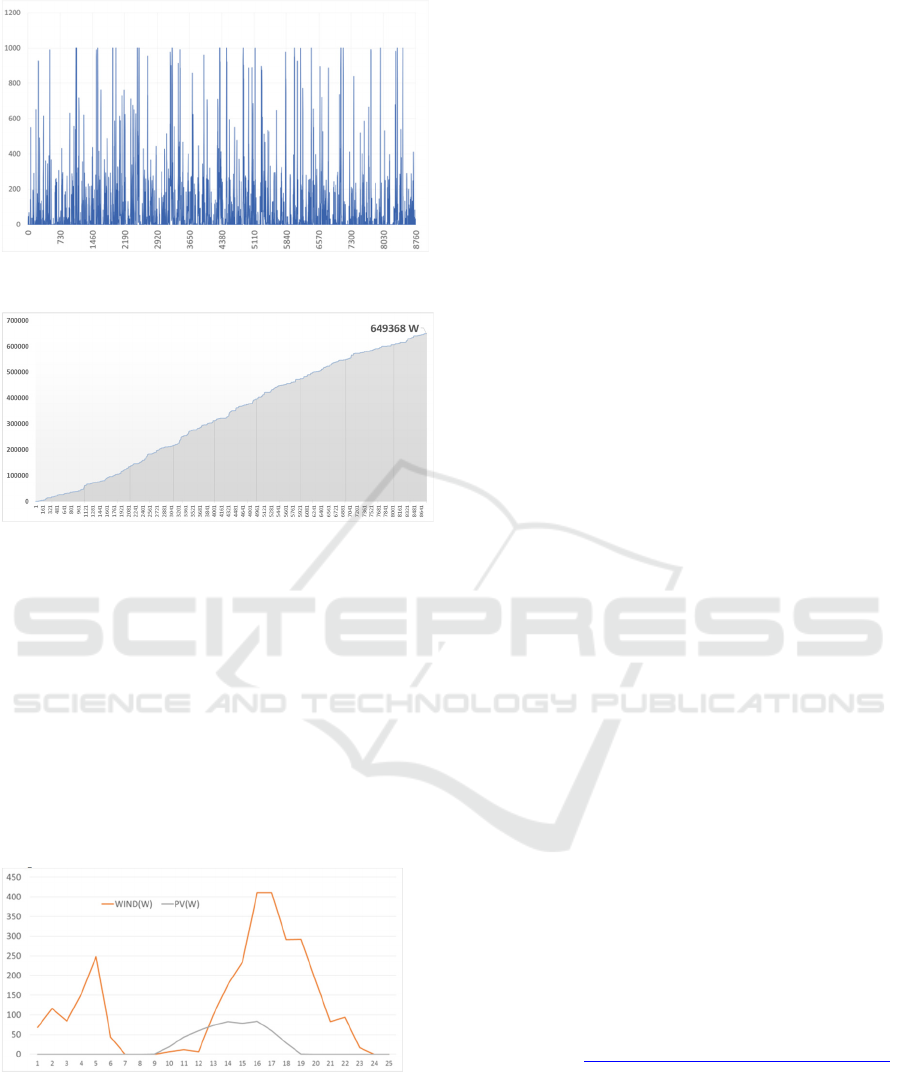
Figure 18: Hourly cumulative power generation (8760
hours per year)
Figure 19: Hourly power generation (8760 hours per year)
The annual electrical production is then
around 650 kWh, for the 1kW domestic wind
turbine, while a single photovoltaic panel may
produce the same yield as showed above.
We deduce then that for the same capacity,
photovoltaic panels have a better annual electric
yield than the domestic wind turbines in Casablanca.
However, these domestic wind turbines can be
coupled with a photovoltaic installation, in order to
lessen the intermittence of the photovoltaic
production at night and during short cloudy days
(Figure 20).
Figure 20: PV and wind yield in the 31th of December
4 CONCLUSIONS
The sunlight harvesting and the photovoltaic
applications are interesting in Morocco, due to the
important global radiations received by its surface.
In the scope of this work, we studied the energy
performance of a PV panel manufactured locally in
Skhirat by PV Industry. The electric output was
optimized following the intervals of variation of the
panel slope and azimuth. It was proved that a south-
facing panel, with a slope of around 30° gives the
best annual energy yield. A sensitivity analysis
performed in the city of Casablanca, shows that the
azimuth influences more the annual yield than the
slope of the panel.
Furthermore, Meteonorm collected weather
data in the Meteonorm station of Casablanca (wind
speed and direction) were used to study a domestic
wind farm of 1kW. The simulation gives an annual
production of around 650 kWh, which is almost the
production of a single-unit photovoltaic panel. For
the same capacity, photovoltaic panels have than a
better yield then the domestic wind turbines in
Casablanca. These two technologies can be coupled
in order to lessen the intermittence of the
photovoltaic production at night and during cloudy
days.
REFERENCES
Kamal Attari, Ali El Yaakoubi, Adel Asselman,
Performance analysis and investigation of a grid-
connected photovoltaic installation in
Morocco,Energy Reports Volume 2, November 2016,
Pages 261-266
Driss Lahjouji, Hassane Darhmaoui, Tilt angle
optimization for maximum solar energy collection -
Case study for Ifrane, Morocco, 2013 International
Renewable and Sustainable Energy Conference
(IRSEC)
Mohamed Oukili, Smail Zouggar, Mohamed Seddik,
Taoufik Ouchbel,François Vallée, Mohamed El
Hafiani, Comparative Study of the Moroccan Power
Grid Reliability in Presence of Photovoltaic and Wind
Generation, Smart Grid and Renewable Energy, 2013,
4, 366-377 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/sgre.2013.44043
MASEN OU LE DÉVELOPPEMENT
RENOUVELABLE, Moroccan Agency For Solar
Energy
Agence Nationale pour le développement des Energies
Renouvelables et de l’efficacité énergétique
(ADEREE), Règlement thermique de construction au
Maroc (RTCM), 2015
ICCSRE 2018 - International Conference of Computer Science and Renewable Energies
216

Agence Nationale pour le Développement des Energies
Renouvelables et de l’Efficacité Energétique - ATLAS
ÉOLIEN GLOBAL NUMÉRIQUE DU MAROC
Meteonorm Software
Looss, Revue sur l’analyse de sensibilité globale de
modèles numériques, 2011
École Chercheur Mexico – Analyse de sensibilité: mesure
de l’importance des facteurs par décomposition de la
variance 9 Juin 2010
J. Herman, W. Usher - SALib Documentation – October
2017
MattiPalonen, Mohamed Hamdy, AlaHasan - MOBO A
NEW SOFTWARE FOR MULTI-OBJECTIVE
BUILDING PERFORMANCE OPTIMIZATION -
Technical Research Centre of Finland, Espoo, Finland
– 2013
Deb, K. Multi-Objective Optimization using evolutionary
algorithms; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester,UK, 2001
Tuhus-Dubrow D, Krarti M. Genetic-algorithm based
approach to optimize building envelope design for
residential buildings. Build Environ 2010; 45:1574–81
Mohamed Elnaggar, EzzaldeenEdwan and Matthias Ritter
2 Wind Energy Potential of Gaza Using Small Wind
Turbines: A Feasibility Study, Department of
Engineering, Palestine Technical College, 18 August
2017
HUMMER 1kW wind generator technical datasheet
Technical Assessment of a Photovoltaic Panel and a Wind Domestic Turbine Systems in Morocco
217
