
Phonology Acquisition through Hijaiyah Learning for Early Age
Children
Alvita Hikmatul Laily
1
, Dwita Dora Virdiana
1
, Rohmani Nur Indah
1
1
Universitas Islam Negeri Maulana Malik Ibrahim Malang, Indonesia
Keywords: Arabic phonology; learning hija`iyah; phonological acquisition
Abstract: Phonological acquisition is experienced by children up to the age of five years. The phonological ability of
each child is different, one variation is the variation of the environment as the input received by children.
On introducing the letters of hija`iyah in Indonesia, children begin to learn to pronounce the sounds of the
symbol in accordance with makhroj and its characteristics. This study aims at examining phonological
acquisition through learning the hija`iyah. The method used is qualitative method combined with
phenomenology approach. The instruments of data collection include observation, interview, and
documentation. Based on the research, the main point that was found is the learning of the letters of
hija`iyah in Indonesia is still on the level of learning phonology, it has not reached the goal of language
acquisition that unconsciously make children acquire Arabic phonology.
1 INTRODUCTION
Learning hija`iyah letters has become essential
among Indonesian children. Since the age of
kindergarten or PAUD, parents have flocked to
invite their children to non-formal institutions such
as the nearest Al-Qur`an Education Park or mosque
and small mosque where the learning of hija'iyah
letters is held. Based on a phenomenon in Gresik,
East Java, Indonesia, Learning Hijaiyah Letters is an
obligation of the children. They go to learn Hijaiyah
letters since early age. Even, when the children was
born, The parents had registered them to the
informal school, namely TPQ Masjid Jami` Gresik.
Because the minimum age to be able join learning
hijaiyah there is 3,5 years old and the time of
waiting is about 3,5 years (Cahyadi, 2017).
There are extraordinary developments in the
reading of the Qur'an. Since the end of 1980, an iqro
method seminar for teachers to recite has the effect
of the emergence of TPQ or TPA. If previously the
number of elementary and junior high school
students who were smart in reading the Qurʻan was
only 10%. With the emergence of this method, the
number of students who could read the Qur'an was
around 30%. Until the early 2000s the number of
elementary and junior high school students who read
the Qur'an was 30%. Those who are smart at reading
the Qur'an are those who have entered the TPQ /
TPA. Meanwhile, students who have never entered
TPQ / TPA until graduating from high school, even
students can never read the Qur'an. It (Supriadi &
Rahmat, 2002) means that learning hija`iyah letters
in the early age of children is important and now, the
parents have realized it.
Even today, in some formal schools, learning
hija`iyah letters which then continue to read Al-
Qur'an, learning has been blended into the school's
main curriculum. Toward the 21
st
century, a new
trend of Islamic education in Indonesia is rising.
Integrated Islamic school. This school has the same
principles and characters of Intregated Islamic
School. One of them is having Al-Qur;an ability.
Until now, there are about 10000 integrated Islamic
schools (Suyatni, 2013).
In the early stages of learning, the child learns to
pronounce the letter hija`iyah interrupted, then
develops on the hija`iyah letter. The most basic thing
in learning hija`iyah letters is that children are able
to pronounce 28 Arabic letters starting at alif (ا) to
ya '(ي) according to the place of exit (makhroj) and
the character of the letter (shifat). In addition, the
letters hijaiyah also play a role in composing words
in Arabic as the Indonesian alphabet has a role in
composing sentences in Indonesian for their
meaning to be understood.
Laily, A., Virdiana, D. and Indah, R.
Phonology Acquisition through Hijaiyah Learning for Early Age Children.
DOI: 10.5220/0009916029072912
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Recent Innovations (ICRI 2018), pages 2907-2912
ISBN: 978-989-758-458-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
2907

There are various kinds of terms in makhraj and
shifatul surat (Dahlan, 2003; Arwani, 2012 ) namely:
Jahr, namely the retention of the breath caused
by a strong touch between the two breathing
organs when pronouncing the letter, the letters
are: ء ب ج د ذ ر ز ض ط ظ ع غ ق ل م ن و ي
Isti'la ', in the pronunciation of the letters occurs
the removal of most of the tongue, for example ق
ض ط ظ غ
Ithbaq, when pronouncing the letter the base of
the tongue is raised towards the soft palate, the
letters are: ظ ط ض ص
Ishmat, the letters on the ismat are rather heavy
when spoken and cannot be pronounced quickly,
the letters of grace are the same as the example
of the letter ithbaq
Syiddah, when the pronunciation of the letters
there is a temporary detention of sound on the
makhraj then it is released simultaneously with
the air, namely: ط
Midway, when you recite the middle letter, there
is a simplification of sound, namely ر ع ل م
ن
Shafir, the addition of sounds similar to whistling
sounds, namely: ص س ز
Qalqalah, the letter qalqalah when you read
sukun there is a kind of vibration that sounds
strong, the letters are: ط د رد ب
Layin, the pronunciation of the letters is easy and
rather longitudinal, namely ي و
Inhiraf, which is the transfer of a letter to another
letter after leaving the makhraj. There are 2
letters, namely: ل ر
Takrir, the tip of the tongue vibrates when
passing letters, there is only one letter, namely: ر
Tafasysyi, when pronouncing the letters of air
distribution in the mouth, namely: ش
Istithalah, extending the sound on the letter,
namely: ض
Khafa, that is the loss of some letters when
pronouncing them, the letters are 3, namely: ه و ي
Gunnah, which is the sound that comes out of the
nasal cavity in the form of echoes that are in the
tidings of the م and ن letters
The first language acquisition at the age of
children is the stage where children get language
sound rules based on the input they receive as a
process from the simplest to the most complex stage,
then it will continue to be stored in its memory as a
language stimuli (Indah, 2008). The acquisition of
this language, then evolved from the original child
experienced phonological acquisition then
developed into morphological acquisition, syntactic
acquisition, and the last is semantic acquisition
(Indah, 2017).
In language, the phonological word consists of
Fon and Logi, Fon means sound, while Logi means
Science. In the study of the field of science,
phonology can be interpreted as a science in the field
of Linguistic studies that study, discuss, and discuss
and analyze the kinds of sounds of language derived
from the human sensory instruments, namely oral
(Chaer, 2009).
Syllable or syllable is a unit consisting of several
sequences of sounds which are indicated by the
loudest sound unit, which is in front of it, behind it,
or in front of and behind it, this peak of loudness
which is usually called a vowel sound, which can be
interpreted as sound produced from the oral cavity
without any obstacles (a, i, u, e, o).
Phonology consists of two parts, phonetics, and
phonemes (Rafiek, 2014). Phonetics is a branch of
phonology that discusses the sounds of language
without regard to the origin of the word, whether or
not the sounds can distinguish meaning (words).
Phonetics learns about how the sounds of the
language are produced by human utensils, such as
the position of the lips and tongue in uttering a
sound and sound waves.
Phonemes are a branch of phonological studies
that discusses the sounds of language by focusing on
the function of letters as distinguishing meanings
(words), such as the example in words (tun) and
(run), the sounds "t" and "l" cause the two words to
have different meaning. The smallest unit of sound
which is the object of study of phonetics is called
phon (sound of language). While phonemes are the
smallest sound units that are used as objects of
phonemic study.
The study uses the Clark & Clark phonology
acquisition theory (1977) which says that mastery of
the child phonetic segment uses hypothesis testing
theory or discovery procedure. Children will try to
use various hypotheses to say the correct sound
(Indah, 2017). As when he will say the word "baru".
At first, he could only say "lu", then "halu", only
then could you say "balu" and later on
“baru”. A child will be able to speak better when he
is able to master many new segments and is able to
correct himself when an error occurs. This situation
can certainly occur when there is a "model", namely
the exposure he gets from what is exemplified by the
adults around him (Indah, 2017). The phonetic
acquisition will further support the next phases of
language acquisition (Nurjamiaty, 2015).
The stages in the process of acquiring language
in a child are interesting. Therefore, linguistic
experts are interested in researching about the
acquisition of these languages. So from the past until
ICRI 2018 - International Conference Recent Innovation
2908

now there have been many researchers about
language acquisition. This study of language
acquisition is one way to find out how the human
brain works.
According to Chomsky (in Dardjowidjoyo, 2000)
humans have what is called faculties of the mind that
is a kind of intellectual (abstract) plot in their brain.
Among these plots is intended for language
acquisition. When the baby is bitter to the world, he
has the provision to grow the language. The
language acquisition device (LAD). The device
receives input in the form of sentences from people
around it. Then Input from the environment is
accepted and filtered by language acquisition tools.
So, the child will filter all entries in the language
acquisition tool in the form of hypotheses. Language
acquisition includes syntactic, semantic, and
phonological acquisition. The language component
is acquired or developed together. But in its
assessment the linguistic component must be done
separately (Eviyanti, 2008).
In acquiring phonology, each individual has: (1)
variations in performance arising based on heredity
in different forms of choice or different types of
learning. Thus, determining differences between
children; (2) environmental variations caused by
differences in input for different children; (3)
linguistic variations that arise from the number of
different choices. On language acquisition tools that
provide acquisition, especially types of structures,
the types of individual variations in phonological
acquisition are influenced by these three variations
(Ingram, 1987).
There are several studies that discuss the
acquisition of child phonology, including discussing
about the acquisition of phonology of children
consisting of obtaining a minimal consonant and
vocal pair and different phonemes of the child's
language distribution in each child according to their
abilities (Rafiek, 2014). There are also findings
about several factors that influence the ability of
children to recognize hija`iyah letters, including: (1)
environmental factors, namely the family
environment and social abilities of each child and
(2) psychological factors namely children's interest
and motivation. In teaching hija`iyah letters the
teacher uses two methods, including: (1)
musyafahah method or tongue fighting and (2)
'ardhul qira'ah or reading deposits (Iqromah, 2018).
The research focuses on the study of phonological
acquisition through learning hija'iyah letters in early
childhood.
This research is deemed necessary because there
are still not many who have conducted studies on
phonological acquisition through learning hija`iyah
letters. In fact, the phenomenon of reciting at the age
of a child seems to have helped many children to
recite sounds that eventually form language.
2 METHOD
This study uses a phonology approach to
language acquisition and qualitative comparison
methods. The phenomenology approach aims to find
the meaning contained in a phenomenon or
phenomenon that occurs in society (Raco, 2010).
The study aimed to capture the meaning of language
acquisition in the phenomenon of learning hija'iyah
letters of kindergarten children.
This research was carried out on early childhood
in two TPQ in Jombang Regency namely TPQ
Hidayatu Qur`an Tambakberas and TPQ Nurul
Qur`an Ploso, Indonesia. These children are
classified between children who often go to the
Koran and who rarely recite the Koran. Then a few
words are provided which are a collection of words
from the phoneme distribution for them to say. The
techniques used in data retrieval are through
observation, interviews and documentation.
Observations on the phonological abilities of
kindergarten-aged children at TPQ were conducted,
interviews with teachers and parents, and
documentation in the form of video recordings,
photographs, and recording of children's
phonological abilities. Video recording is done using
a mobile camera then analyzed comprehensively
with other data sources and described through
writing.
The data analysis in this study goes through the
following stages: (1) collecting sounds in
Indonesian; (2) group them into vowel phoneme
distributions, diphthong phoneme distributions, and
consonant phoneme distributions; (3) observing the
object of research in pronouncing these words; (4)
analyze the data obtained based on these
observations supported by information obtained
during the interview; and (5) conclude the results of
data analysis.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
There are three types of phoneme distributions,
namely: (1) distribution of vocal phonemes; (2)
distribution of diphthong phonemes; (3) the
distribution of consonant phonemes. This
distribution was chosen because it felt more
Phonology Acquisition through Hijaiyah Learning for Early Age Children
2909

appropriate to the phonological abilities of children
in kindergarten age.
3.1 Distribution of Vocal Phonemes
The distribution of vowel phonemes is as shown
in table 1.
Table 1. Vowel distributions
vowel initial middle final
/ a / air
(water)
rasa
(taste)
kita
(we)
/ a / atas
(at the top)
kata
(word)
luka (injury)
/ i / ikan
(fish)
lihat
(see)
tani (farming)
/ i / indah
(beautiful)
sikat
(brush)
kami (we)
/ u / usil
(annoying)
lupa
(forget)
palu (hammer)
/ u / udah
(already)
rumah
(home)
ratu (queen)
/ e / erat
(strictly)
benar
(correct)
pare
(vegetable that
taste bitter)
/ e / enak
(delicious)
lelah
(exhausted)
sate (satay)
/ o / obat
(medicine)
robot
(robot)
ayo (come on)
/ o / obor
(torch)
kotor
(dirty)
opo (what)
3.2 Diphtong Phoneme Distribution
Phoneme distribution of diphthongs can be seen
in table 2.
Table 2 Diphtong distribution
diphtong initial final
/ai/ air (water) pantai (beach)
/ai/ sungai (river)
/au/ aurora pulau (island)
/au/ hijau (green)
/oi/ amboi (amazing)
/oi/ ikan koi (koi fish)
3.3 Consonant Phoneme Distribution
Phoneme distribution of consonants can be seen
in table 3.
Table 3 Consonant distribution
conso
nant
initial middle final
/ b / bawah
(bottom)
robot kebab
/ b / bentuk
(form)
ubah (change) sebab
(because)
/ c / cantik
(pretty)
kucing (cat) jelek
(bad)
/ c / cari
(find)
kecil (small) -
/ d / depan padat (solid) -
conso
nant
initial middle final
(in front
of)
/ d / dari
(from)
roda (wheel) -
/ f / forum sofa (couch) aktif
(active)
/ f / film limfa (limph pasif
(passive)
/ g / goyang
(move)
ragam (various) kemenag
(religious
ministry)
/ g / gaya
(style)
raga (body) -
/ h / harus
(must)
lihat (see) bawah
(bottom)
/ h / hasil
(result)
bahan
(material)
sawah
(ricefield
)
/ j / jangan
(don’t)
tajam (sharp) bajaj
(tradition
al
vehicle)
/ j / jadi
(done)
haji (hajj) unej
(jember
univ)
/ k / kucing
(cat)
ikan (fish) cantik
(pretty)
/ k / kuda
(horse)
tukar (change) bentuk
(form)
/ l / lupa
(forget)
palu (hammer) usil
(annoyin
g)
/ l / lava sulap (magic) kapal
(ship)
/ m / mata
(eyes)
zaman (era) ragam
(various)
/ m / makan
(eat)
cuma (just) seram
(terrifyin
g)
/ n / nasi
(rice)
benar (correct) teman
(friend)
/ n / nama
(name)
panah (arrow) akan
(would
be)
/ p / palu
(hammer)
lupa (forget) asap
(smoke)
/ p / pada (of) rupa (form) usap
(wipe)
/ q / quran - -
/ r / rasa
(taste)
harus (must) bayar
(pay)
/ r / rupa
(form)
keruh (murky) sabar
(patient)
/ s / sate
(satay)
rasa (taste) atas (at
the top)
/ s / sabar
(patient)
pasir (sand) harus
(must)
/ t / tani
(farming)
sate (satay) robot
/ t / tikar
(mat)
batu (stone) lalat
(flies)
/ v / vas lava -
/ v / venus diva -
/ w / waktu bawah (bottom) -
ICRI 2018 - International Conference Recent Innovation
2910
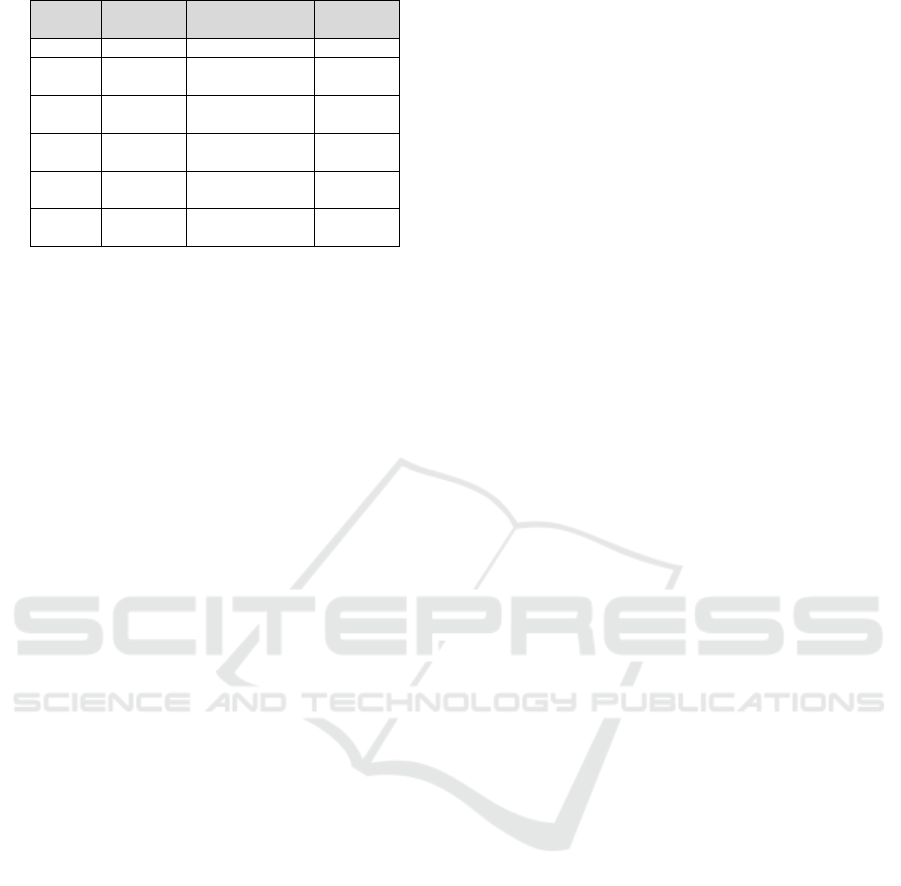
conso
nant
initial middle final
(time)
/ w / warna
(color)
awas (beware) -
/ y / yang
(which)
bayar (pay) Roy
/ y / yaitu
(namely)
dayung (row)
/ z / zaman
(era)
bazar -
/ z / zakat
(zakah)
lezat (delicious) -
Based on observations to the objects in two TPQ
in Jombang, Indonesia, there are two kinds of
phonological acquisitions found: (1) the children are
able to recite all phonology presented in various
phoneme distributions; (2) only some still cannot
pronounce the phoneme distribution of the letter "r".
Of these two types, children who are able to recite
all phonology presented are kindergarten children of
grade A, both on the group who are diligent in
recitation and those who rarely attend the TPQ. The
later are those who have reached the age of 5 years
or less. While those who still cannot recite the "r"
consonant phoneme distribution are those who also
frequently recite, but their age is still 4 years or 4
and a half years. They change the consonant "r" to
"l". The word robot becomes lobot. The similar
finding is also shown in antoher research on
preschool children (Wulandari, 2018; Faldy, 2018).
This is in accordance with the view that the
acquisition of mother tongue will occur in a normal
child up to about 5 years of age (Indah, 2017). Clark
and Clark (1977) also argued that the process of
language acquisition of a child at the age of
approximately 5 years was able to resemble adult
language both in terms of phonology, word form,
sentence, and discourse organization
(Sukartiningsih, 2010; Maharany, 2016).
However, based on the phenomenon that shows
no difference in phonological acquisition of children
who are diligent in recitation and who rarely recite,
it can be concluded that learning hija`iyah letters of
children or commonly known as recitation activities
can not be categorized as environmental factors that
influence the acquisition of child phonology. As
Krashen's theory states that language acquisition is a
process that occurs naturally where a child has
learned a language without him knowing. Whereas
language learning has the opposite meaning, namely
language is learned consciously (Herlina, 2016). In
this case it can be seen that the learning of the letter
hija`iyah which is actually the first stage of the
acquisition of second language phonology namely
Arabic is still at the level of purpose to be able to
read the Qur'an correctly. Whereas according to
Ingram (1970) each individual or child is different in
obtaining phonology (Nasution, 2013). Among these
variations are: (1) performance variations based on
learning type abilities; (2) environmental variations,
because the input received by children varies; (3)
linguistic variations namely differences in language
acquisition devices (Herlina, 2016; Setiyadi, 2013).
4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the division of the structure of
children's language in terms of aspects phonological
acquisition, the phoneme distributions of children's
language are as follows:
1) Distribution of children's language vocals which
includes / a /, / i /, / u /, / e /, / o / takes place in all
positions. It is similar to the finding of other study
on children aged below five (Yuliawan, 2016).
2) Child language diphthong distribution which
includes / ai /, / au /, and / oi /. / ai / and / au / at the
beginning and end. Whereas / oi / place only at the
end
3) The consonant distribution includes / b /, / c /, / d
/, / f /, / g /, / h /, / j /, / k /, / l /, / m /, / n /, / p /, / q /,
/ r /, / s /, / t /, / v /, / w /, / y /, / z /. Consonant / b /, /
f /, / g /, / h /, / j /, / k /, / l /, / m /, / n /, / p /, / r /, / s /,
/ t /, / y / occupies all positions. Whereas consonant /
c /, / d /, / v /, / w /, / z / occupies the initial and
middle positions and / q / occupies the initial
position. This is also supported by the finding in the
context of preschool children (Eviyanti, 2008).
From the research on phonological acquisition of
kindergarten children in two TPQ in Jombang,
Indonesia, it shows that kindergarten children
around 5 years of age who often and rarely recite are
able to recite all phoneme distributions presented.
While kindergarten children who are less than 4
years old and often go to the Koran still cannot
pronounce the "r" consonant distribution. based on
this, it can be concluded that learning hija'iyah
letters in Indonesia is still at the level of
phonological learning, not reaching the level of
phonological acquisition.
As the implication, the result of this study can be
an evaluation for teachers who teach hija`iyah letters
to make the learning process of hija'iyah as a means
to support children’s phonological acquistion
complemented by habituation as articulation training
(Chiang, 2003) and exposure for optimum result of
acquisition. The researcher also suggested to the
next researchers to be able to examine the
phonology acquisition through learning hija'iyah
Phonology Acquisition through Hijaiyah Learning for Early Age Children
2911

letters with larger and more diverse samples so that
more accurate data can be obtained.
REFERENCES
Arwani, M. U. (2012). Yanbu`a : Latihan Makhraj dan
Sifat Huruf. Kudus: Pondok Tahfidz Yanbu`ul Qur`an
Kudus. 35-36
Cahyadi, C. (2017, August 27). Ortu Sudah Daftarkan
Anak meski Belum Punya Nama. Jawa Post.
Chaer, Abdul. (2009).Fonologi bahasa Indonesia.Jakarta :
Rineka Cipta.
Chiang, Pi-Yu (2003) Bilingual children’s phonological
awareness: the effect of articulation training Nordlyd
31(3), 532-544
Dardjowidjoyo, S. (2000). Echa: Kisah Pemerolehan
Bahasa Anak Indonesia. Jakarta: Grasindo. 19
Dahlan, N. Al-Barry, Y., Al-Ulya Sofyan Ya’qub, (2003)
Kamus Induk Istilah Ilmiah Seri Intelektual, Surabaya:
Target Press
Eviyanti, Evi (2008) Pemerolehan fonologi pada anak
umur 2;3. Bahas, 69(1), 20-30.
Faldy (2018) Pemerolehan bahasa (analisis pemerolehan
fonologi (vokoid dan kontoid) pada anak 24 bulan)
IDEAS 6(1), 78-89
Herlina. (2016).Pemerolehan fonologi pada anak usia dua
tahun dua bulan (studi kualitatif pemerolehan fonologi
pada Aisyah). Jurnal Pendidikan Usia Dini 10(2),
295-314.
Indah, Rohmani Nur (2008). Proses Pemerolehan Bahasa
: dari Kemampuan hingga Kekurangmampuan
Berbahasa.
Indah, Rohmani Nur. (2017). Gangguan Berbahasa:
Kajian Pengantar. Malang: UIN Maliki Press.
Ingram, D. (1987). Individual Variation and Its
Relevanceto a theory of Phonological Acqisition.
Journal of Child Language, 420.
Iqromah, Fitri. (2018) Identifikasi kemampuan anak dalam
mengenal huruf hijaiyah di TK sekecamatan
Samigaluh Kulon Progo. Jurnal Pendidikan Anak Usia
Dini 1(7), 11-24.
Maharany, Andi Firdha. (2016) Gejala fonologis bahasa
indonesia pada anak usia 3-4 tahun di PAUD Permata
Hati kota Kendari Bastra 1(2), 1-21
Nasution, Julidar. (2013) Phonological acquisition of
children aged 2-4 years (a case study about change of
sounds or phonemes). Lantern 2(3), 24-40
Nurjamiaty (2015) Pemerolehan bahasa anak usia tiga
tahun berdasarkan tontonan kesukaannya ditinjau
dari kontruksi semantik Edukasi Kultura 1(2), 42-62
Raco, J.R. (2010) Metode Penelitian Kualitatif: Jenis,
Karakter, dan Keunggulannya. Jakarta: Grasindo.
Rafiek, Muhamad & Rusma Noortyani. (2014)
Pemerolehan fonologi anak di tiga PAUD Kecamatan
Banjarmasin Utara Banjarmasin: Universitas
Lambung Mangkurat.
Setiyadi, Alif Cahya & Muhammad Syamsun Salim
(2013). Pemerolehan bahasa kedua menurut Stephen
Krashen. Jurnal Ta`dib 8(2), 265-280.
Sukartiningsih, Wahyu. (2010) Kontruksi semantis kata
pada perkembangan bahasa Indonesia anak, Bahasa
dan Seni 38
(2), 205-216.
Supriadi, U., & Rahmat, M. (2002). Percepatan
Keterampilan Membaca al-Qur`an di Sekolah Melali
Metode bil-hikmah. Jurnal Penelitian Pendidikan No.
2, October .
Suyatni. (2013). Sekolah Islam Terpadu; Filsafat, Ideologi,
dan Tren Baru Pendidikan Islam di Indonesia. Jurnal
Pendidikan Islam Vol. II No. 2 , 355.
Wulandari, Desy Indah (2018) Pemerolehan bahasa
Indonesia anak usia 3-5 tahun di PAUD Lestari desa
Blimbing kecamatan Paciran kabupaten Lamongan
Lingua Franca: Jurnal Bahasa, Sastra, dan
Pengajarannya. 2(1):74-83
Yuliawan (2016) Pemerolehan bahasa Indonesia pada
anak usia 2-5 tahun di perumahan Air Dingin
Marpoyan Pekanbaru Riau GERAM 4(3), 91-99
ICRI 2018 - International Conference Recent Innovation
2912
