The Role of International Trade to Economic Growth: The Case of
Indonesia
Hendri Tanjung
1
and Abrista Devi
1
1
Universitas Ibn Khaldun Bogor, Jl. KH. Soleh Iskandar,Bogor, Indonesia
Keywords: Export, Import, Economic Growth
Abstract: This study is aimed to identify the effect of export and import toward economic growth in Indonesia. Using
the monthly data from the year 1999 to 2017 and Vector Autoregression analysis, it is found that Gross
Domestik Product (GDP) will response negatively in short term and positively stable in the long term in period
of 15 due to the shocked of export. Furthermore, GDP will response positively in short term and positively
stable in the long term in period of 20 due to the shocked of import. There is no significant effect export to
GDP as well as import to GDP in the short term and long term. Therefore, there is no effect of international
trade (export and import) to economic growth for Indonesia.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the earliest 2018, several government policies
shocked Indonesian related to the food material
import. This policy remain unrest to the society
because Indonesia is popular with Agrarian and rich
with natural resources country but in fact still
importing for some food materials. Nowadays,
Indonesia still suffers from the lack of rice stock;
therefore the inflation rise due to the rice price
increased. Despite of rice, the inflation also might
happen to other food materials such as brown sugar,
salt industry, etc. Indonesia is not only importing food
materials, but also importing other products such as
gas and oil. Plethora public news highlight that
Indonesia also import labor from China. Supporting
this latter assertion of BPS year 2017, China was
dominated export and import activity in Indonesia.
Notwithstanding, Indonesia balance of trade
conditions were surplus at US$ 1.76 billion, export
were at US$ 14.54 billion and import were at US$
12.78 billion. The supernumerary of trade balance is
occurred due to the number of import were greatly
decreased compared to the number of export.
Economic sector is the most important sector to
measure the welfare of a country. We can consider
that a country is in a prosperity condition through the
number of its economic growth. Basically, if the
economic growth experience positive direction,
therefore we can say that the country is welfare, and
otherwise. There are many determinant factors
affected to the level of country’s prosperity
measurement, for example, inflation, politic situation,
etc. Be advised that papers in a technically unsuitable
form will be returned for retyping. After returned the
manuscript must be appropriately modified.
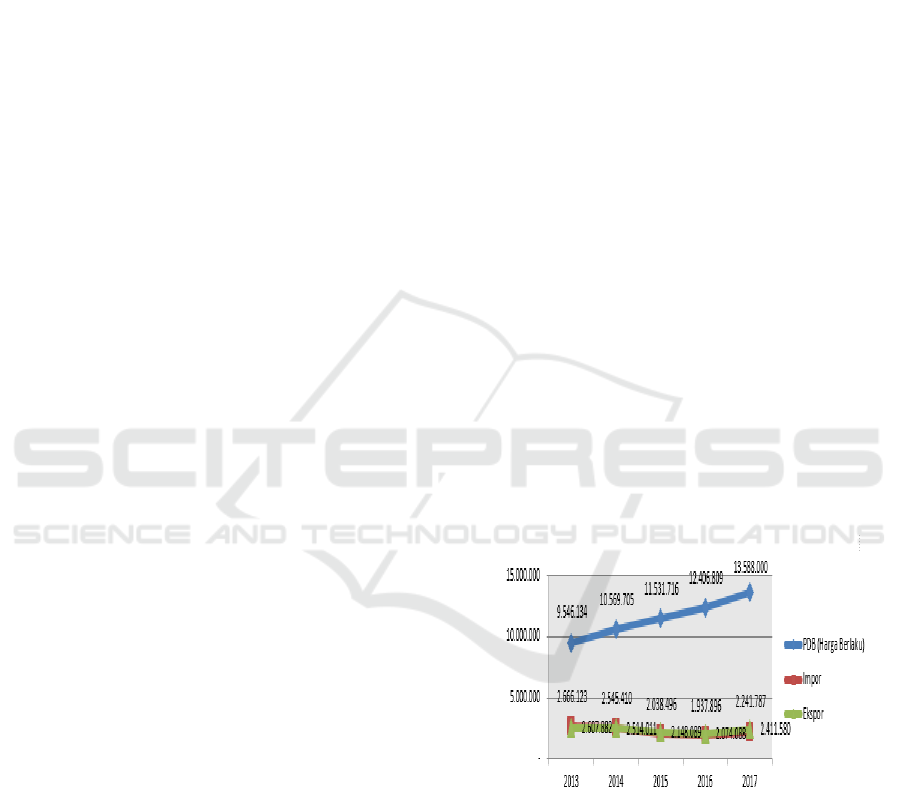
Graph 1: The GDP, Import, and Export Trend by the year
2013-2017 (IDR billion) Source: Statistic Center (2017)
The graph 1 depicts of Indonesia economic
growth trend which is reflected by GDP (Gross
Domestic Product), import and export value by the
year 2013 - 2017. According to the number of
economic growth which is represented by GDP,
Indonesia experienced a good economic growth
where GDP positively increased over time. However,
the growth of product and services produced
disproportionate with the movement of export and
2166
Tanjung, H. and Devi, A.
The Role of International Trade to Economic Growth: The Case of Indonesia.
DOI: 10.5220/0009940421662174
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Recent Innovations (ICRI 2018), pages 2166-2174
ISBN: 978-989-758-458-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

import activity in Indonesia. As shown in graph 1,
export and import activity from the year 2013 to 2017
were fluctuated and tend to decreased. Specifically,
export and import experienced decreased from the
year 2014 to 2016 and start to increase in 2017.
Trade reformation has an important role to
determine the policy direction of a country. Every
country, both advanced countries and developed
countries have a very uniqueness natural resource and
tend to differ among another. This means that every
country has potency to create product with their own
comparative advantage, such as raw material, labor,
and other costs to produce the specific product
(Adeleye, Adeteye & Adewuyi, 2015). Therefore, the
existence of trading system is greatly important, not
only rely on intern trading, but also expand to the
international scale.
Import-export activity provides much benefit to
the involved-country. Export is one of foreign
exchange source that are greatly required by the open-
country or region as well as Indonesia, because a wide
export to various countries will increase the number
of production and promote the economic growth, so
it is expected to greatly contributing toward economic
stability (Rivai, 2006). Meanwhile, through import, a
country is able to fulfill their intern need that probably
cannot be produced internally or use the comparative
advantage pattern so the exceed cost of product and
services will be cheaper.
Export and import activity can support the
economic growth of a country (Roshan, 2007;
Velnampy & Achchuthan, 2013). Hye (2012) argues
in his research in China that export will lead to
economic growth of a country as well as economic
growth will lead to export. Besides, import also will
lead to economic growth as well as economic growth
will lead to import (exports-led growth, growth-led
exports, imports-led growth, and growth-led
imports). Meanwhile, plethora empirical research
revealed that despite of export, import also led to
economic growth. Hasim & Masih (2014) also
addresses the issue of import activity, where import
has an important role to stimulate the overall
economic performance of a country. The effect of
import toward economic growth may be difference
with the effect of export toward economic growth.
“The transfer of technology from developed to
developing countries through imports may serve as an
important source of economic growth. Imports can be
a channel for long run economic growth because it
provides domestic firms access to foreign technology
and knowledge.” (Hasim & Masih, 2014).
Through import, country will have opportunities
in technology and knowledge exchange among
countries, so it also will lead to the economic growth
in the long term. Supporting this latter assertion of
Mazumdar (2001) that import will led to economic
growth (import-led-growth (ILG). The source of
western knowledge also has important role toward the
growth of productivity of a country through their
technology innovations scuh as computer, machine,
and tools. So, it is fairly to conclude that import
influences the economic growth through import
competitiveness. “Imports can affect the productivity
growth through its effect on domestic innovation
through import competition. An increase in import
penetration will exposes the domestic firms to foreign
competition. Import are important to productivity
growth because the domestic producers will respond
to the technological competitive pressure from
foreign competition.”(Hasim & Masih, 2014).
As well-discussed in the previous paragraph,
export and import activity is being an important factor
which is contributing to the economic growth of a
country. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) indicator
represents the economic growth consist of 17
economic sector categories based on industry sector.
GDP value is representing the growth of society’s
economic activity who work and also the total
number of value added (product) which are produced
from various number of job employment. According
to the discussion above, the objectives of this study is
aimed to identify the effect of export and import
toward economic growth in Indonesia.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Boediono (1999) defines economic growth theory as
an explanation of factors which are affecting the
increasing of income per-capita in the long term. He
also argues that economic growth as an explanation
of enhancement factors among others, then the
growth process occurred. Economic growth theory is
divided into two groups: (1) classical theories,
involve the growth theory of Adam Smith, David
Richard, and Arthur Lewis. The difference between
Lewis theory and other classical theories was found
that Lewis emphasizes to the economic dualism
aspect, where the existence of modern sector and
traditional sector. Each sector has its own specific
economic characteristic. (2) Specific theories,
involve 4 (four) sub groups, namely:
a. Growth theory of Neo Classic, initiated by
Robert Solow and Trevor Swan theory
b. Optimum growth theory. This theory is
intended to seek the most optimum of
The Role of International Trade to Economic Growth: The Case of Indonesia
2167

economic growth path involve Dalil Emas
theory and Jalan Raya theory
c. Growth theory escorted by money. This is a
development theory of neo classical theory,
but by the additional of money as the wealth
property. The basic theory comes from James
Tobin masterpiece.
Nowadays, the definition of economic growth has
an extended discussion, another main issue explored
in detain in Prof. Simon Kusnets, where Jhingan
(2005) analyzes that economic growth is defined as
the increasing of country’s capability to serve a large
number of economic product variations to their
society in the long-term. This growth of this potency
is tailored to the technology development,
organization adjustment, and the ideology
requirement. This definition is divided into 3 (three)
component; (1) economic growth of a country is seen
from the persistently increasing of commodity stock;
(2) advanced technology is being a factor of
economic development where determine the growth
level of ability to serve a large number of economic
product variations to their society; (3) the using of
technology widely and efficiently is required the
adjustment of organization and ideology, so the
innovations that are generated by knowledge can be
utilized effectively.
Plethora academic research found that economic
growth affects toward international trading activity
and whereas the international trading (export and
import activity) can led to the economic growth
(Won, 2008; Shahbaz & Rahman, 2014). One of the
economic groth indicator is GDP. In the several of
academic reserarch, GDP is widely used as proxy
represents the economicy growth (Adeleye, Adeteye
& Adewuyi, 2015; Akanni, 2007; Vohra, 2001).
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the market value of
overall product and service, which are produced by a
country in a period of time (Kravis, Heston &
Summers, 1982). GDP is also used to calculate the
national income. GDP means the overall value of
product and service which are produced by a country
in the specific period (normally in a year).
Internationl trading involve export adn import
activity where the exchange of product and service
among countries is occured. Export is an activity
where a country sells their commodity (both product
and service) outside the coutry by utilizing the
approved-payment system between seller (exporter)
and buyer (importer). Meanwhile, import is the
purchasing activity of commodity from the outside
countries to the domestic (Seyoum, 2009).
Please remember that all the papers must be in
English and without orthographic errors. Do not add
any text to the headers (do not set running heads) and
footers, not even page numbers, because text will be
added electronically. For a best viewing experience
the used font must be Times New Roman, on a
Macintosh use the font named times, except on
special occasions, such as program code (Section
2.3.7).
3 RESEARCH METHOD
This study is conducting timeseries secondary data
which is obtained from Statistic centre (BPS/Badan
Pusat Statistik) and published in their official website
(www.bps.go.id). Data is obtained from the monthly
data from the year 1999 to 2017.
Table 1: Operational Variable Explanations
NO Variable Operational
Explanations
Source
of Data
1 GDP
(Gross
Domestic
Product)
Current price will
be used as proxy of
GDP due to more
representattive of
the real price
Statistic
Centre
2 Export Monthly export
value
Statistic
Centre
3 Import Monthly import
value
Statistic
Centre
To have better understanding of the data usability in
this research, following explanation will be
discussed:
1. GDP (Gross Domestic Product): current price is
used as proxy of GDP due to more representative
of the real price (real time). Current price is
selected rather than nominal price due to
diminisshing of inflation effect, therefore, the
value of economic growth will represent the real
condition. Monthly GDP data is obtained using
interpolation method (quadratic match sum
method) over quartile GDP with Eviews 9.
2. Export and Import: the data which is used to
represent the value of import and export is the
total number of monthly export and import by the
year 1999-2017 and can be obtained from the
official website of statistic centre
(www.bps.go.id)
The equation model that is constructed in this
model to identify the export and import contribution
toward economic growth as follows:
ICRI 2018 - International Conference Recent Innovation
2168
LnGDPt = α + βj ∑ LnEkspt-j + γj ∑ LnImpt-j
+ μ1t......(3.1)
j =1 j=1 j=1
Where:
LnExp : Natural Logarithm transformation of export
LnImp : Natural Logarithm transformation of import
LnGDP : Natural Logarithm transformation of GDP
The research problem of this study will be analyzed
by employing Vector Auto-regression econometric
technique. VAR simply describes the causality
relationship among variables in a system, by adding
intercept. Ascarya (2009) argues that this method was
developed by Sims in the year 1980 respectively.
Sims (1980) assumed that all variables are
endogenous (determined in the model), therefore this
method is named by e-theoretic model (without
theoretical based). If the used data is stationer in the
first difference, then VAR model will be combined by
the correction model so we called as Vector Error
Correction Model (VECM). Impulse response
function analysis will be conducted to identify the
response of endogenous variables toward the shock of
other variables in the model. Variance
decomposititon analysis also will be conducted to
explain the variability of endogenous variables
(Tanjung & Devi, 2013). The entire data of this study
is transformed to the natural logarithm form (LN
form). The software employs in this study is
Microsoft Excel and Eviews 9.
VAR method provides the convenience to use
and also minimizes the lack to determine the
endogenous and exogenous variables. There are
several benefit provided by VAR (Gujarati, 2003):
1. Easy to estimate, Ordinary Least Square (OLS)
method can be applied to each different equation
separately.
2. Better estimation of forecasting rather than
complexity simultaneous equation model.
3. Impulse Response Function (IRF) provides the
response from dependent variable in the VAR
system toward shock of error term.
4. Variance Decomposition provides information
regarding to the importance of each error term to
influence all variables in VAR.
The step of research using VAR analysis will be
explained as follows
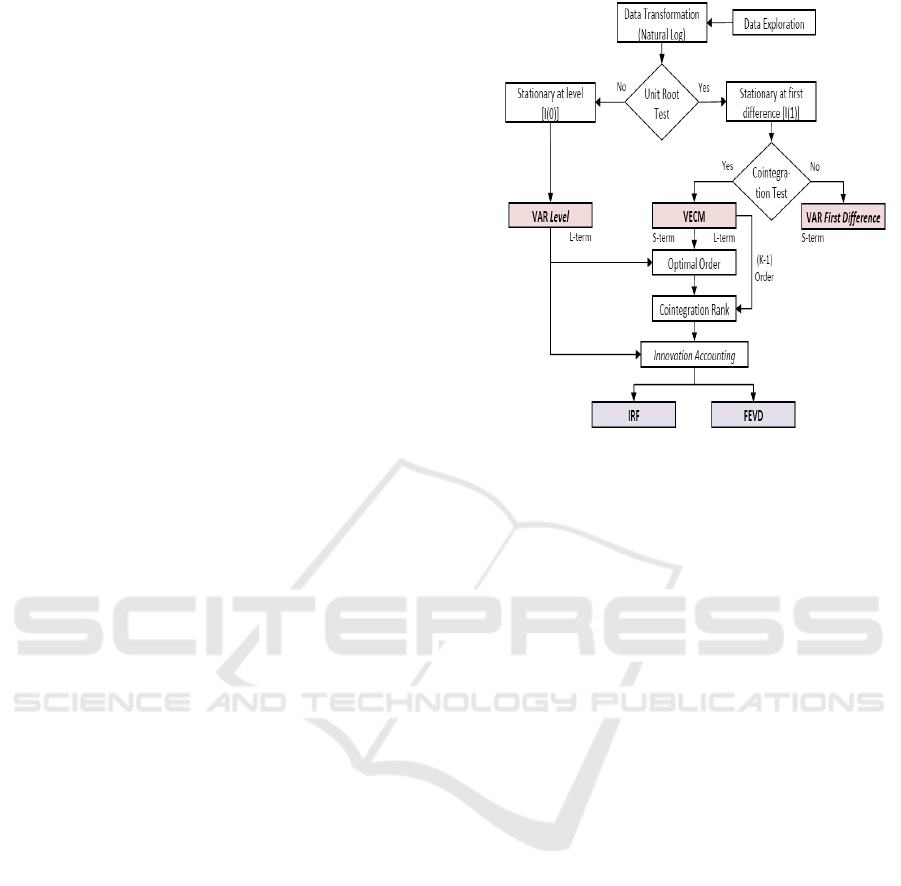
Figure 1: VAR Step of Research
Source: Ascarya, et al. (2008
Figure 1 describes the steps of research where
provides different information comply with the
characteristic of result. If data is stationer in VAR
level, this means that the data contains long-term
information. While, if data is non-stationer in VAR
level, unit-root test has to be conducted in first
difference level. In this step, data contains
information specific only for short-term. However, in
order to obtain the result which is containing long-
term information, co-integration test must be
conducted. Supposing that co-integration is occurred,
therefore, it can be proceed to the next step, so called
as Vector Error Correction Model (VECM). In this
level, information produced trough VECM consist of
short term and long term.
On the assumption that the data has been obtained
trough previously determined sources, stationary test
is implied toward the data. Stationary test is intended
to identify whether the variables used stationer or
non-stationer. This means that the employed time
series data will be stationer only if the data is not
containing unit root where mean, variance, and
covariance are constantly over the time. Contrarily,
time series data will be non-stationer if containing
unit root, where mean, variance, and covariance are
variables over the time. The implementation of unit
root test is the most popular test to identify the
stasionerity of the entire data. In order to make easier,
author will determine the kind of test that utilizd to
test unit root, namely Augmented Dickey-Fuller
(ADF) which has been developed by Dickey Fuller.
The Role of International Trade to Economic Growth: The Case of Indonesia
2169
Gujarati (2003) argues that after conducting ADF
test toward, lag determination shoul be done for the
next step of reseach. insufficient lag will induce to the
inability of regression residual to perform white noise
processes, so the model has no ability to estimate the
actual error properly. In consequence, γ and error
standard is not estimated properly and if the inserted
lag is too much, so it will affect to the reduction of
ability to reject H0, because the extravagant of
additional parameter will reduce degrees of freedom.
Optimum lag might be determined by setting lag
value that can be obtained from LR (squential
modified LR test statistict), FPE (Final Prediction
Error), AIC (Akaike Information Criterian), SC
(Schwarz Information Criterion), and HQ (Hannan-
Quinn Information Criterion).
Assuming that stationerity phenomenon were at
first difference or I (1) level, so the test must be
undertaken to seek the existence of co-integration. In
essence, co-integration concept is intended to seek
long-term equilibrium among observed variables. In
several cases, we might find where the data is non-
stationer, but in other cases they will have a linier
connection, therefore the data will become stationer.
This condition is called as co-integrated data.
Besides, co-integration tests also conducted by
following Johansen procedure. Johansen test focus on
trace statistic and max eigen statistic value to
determine the co-integration. Trace statistic and max
eigen statistic value which are exceed of its critical
value indicates the existence of co-integration in the
model used.
VECM is a form of restricted Vector
Autoregression. This additional restriction must be
applied due to the existence of non-stationer form of
data but has co-integration. Formerly, VECM utilize
co-integration restriction information in its
specification. Therefore, VECM is often called as
VAR design for series nonstasioner but has co-
integration relationship. In the analysis, VAR has a
specific instrument that has a special function to
explain the interaction among variables in the model.
The referred instruments involve Impulse Response
Function (IRF) and Forecast Error Variance
Decompisitions (FEVD), or generally called as
Variance Decompisition (VD). IRF is an application
of vector moving average has the aim to identify the
length of shock from one variable toward another
variables. Meanwhile, VD in VAR has a function to
analyze to what extend the shock from one variable
affect to other variables.
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
In order to obtain the valid data, we need to analyze
several pre-tests before conducting VAR/VECM
analysis. The pre-test that is conducting in this study
involve root test analysis, stability test, lag optimum
test, and co-integration test. If the overall data has
fulfilled the series-test as required, then the model can
be analyzed. Following discussion provide the result
information of GDP model.
4.1 Unit Root Test
Unit root test were used to identify the stationary of
variables by using Augmented Dickey Fuller (ADF)
with 5% sinificant level. If t-ADF value is smaller
than McKinnon critical test value, we can conclude
that the data is stasioner or not consisting unit root
any longer. In this test, all varibles in equation will be
tested. The result of export, import, and GDP
variables stationary test will be described trough
following table:
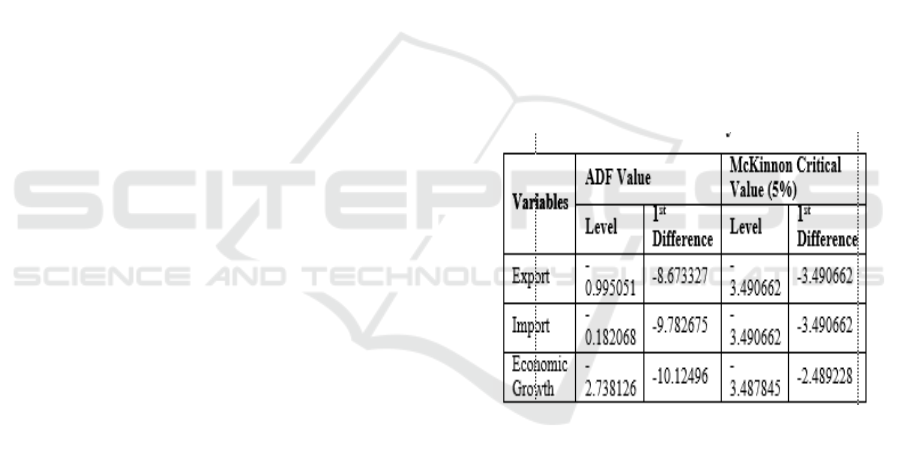
Table 2: Augmented Dickey Fuller Test Summary
Table 2 depicts that three mentioned variables,
namely export, import, and economic growth are not
stationary in level, but all variables are stationary in
first difference (1
st
difference) for both ADF value
and McKinnon critical value. According to this
situation, the variables can be analyzed to the next
level.
4.2 Stability Test and Optimum Lag
Stability test results show that GDP model is stable
up to 9 (nine) maximum lag.
ICRI 2018 - International Conference Recent Innovation
2170
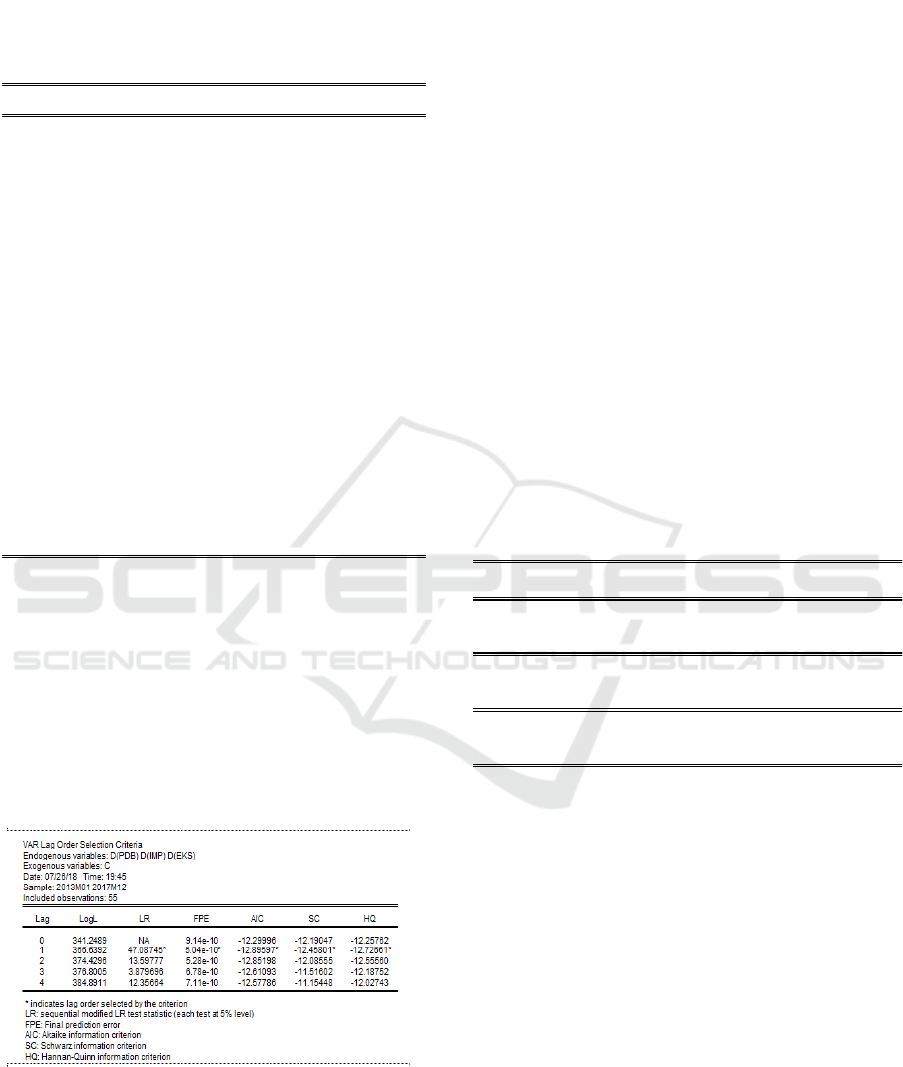
Table 3: Stability Test Lag Specification
According to the stability test, we can conclude
that VAR estimation that is used to analyze IRF and
VD is stable. Stability test results show that GDP
model is stable up to 9 (nine) maximum lag due to the
number of modulus value <1 or closer to 1, accounted
for 0.986964. Therefore, the conclusion is that the
data condition to all variables are stable
Table 4: Optimum Lag Criterion
Optimum lag test is important to remove auto-
correalation in VAR system. Therefore, by using
optimum lag, it will prevent the reappeared of
autocorrelation problem. Lag optimum determination
employs in this study referred to the shortest lag by
using Akaike Information Criterion (AIC). Pursuant
to GDP model, the lag optimum was at lag 1, so the
model can be analyzed to the next level. Similarly,
referred to other criteria such as LR FPE and HQ,
optimum lag was at lag 1. So, the final conclusion is
GDP model can be analyzed to the next step.
4.3 Granger Causality Test
Granger causality test is used to identify whether two
variables have causality relationship or parallel
relationship. Similarly, whether one variable
significantly has causality relationship to other
variables, this due to every single variable has an
opportunity to be endogenous variables or exogenous
variables. Bivariate causality test in this model
employs VAR pair-wise Granger causality test with
5% significant level. The Granger causality test result
is shown trough the following table.
Table 5: Optimum Lag Criterion
Granger causality test concludes that export
variables statistically insignificant affect to the GDP
(0.1426 > 0.05 this means that hypothesis 0 is
accepted, where there is no influence), similarly,
GDP also statistically insignificant affect to the
export (0.2631 > 0.05 this means that hypothesis 0 is
accepted, where there is no influence). Therefore, we
can conclude that there is no any causality to both
variables export and GDP.
Import variables statistically insignificant affect
to the GDP (0.1067 > 0.05 this means that hypothesis
0 is accepted, where there is no influence), similarly,
GDP also statistically insignificant affect to the
import (0.2692 > 0.05 this means that hypothesis 0 is
accepted, where there is no influence). Therefore, we
can conclude that there is no any causality to both
variables import and GDP.
Roots of Characteristic Polynomial
Endogenous variables: D(PDB) D(IMP) D(EKS)
Exogenous variables: C
Lag specification: 1 9
Date: 07/26/18 Tim e: 19:42
Root Modulus
-0.975034 + 0.152991i 0.986964
-0.975034 - 0.152991i 0.986964
-0.820279 - 0.542757i 0.983586
-0.820279 + 0.542757i 0.983586
-0.898787 + 0.379590i 0.975657
-0.898787 - 0.379590i 0.975657
-0.529881 + 0.807612i 0.965925
-0.529881 - 0.807612i 0.965925
0.207891 + 0.942804i 0.965452
0.207891 - 0.942804i 0.965452
0.458873 - 0.842485i 0.959346
0.458873 + 0.842485i 0.959346
-0.023307 - 0.957276i 0.957560
-0.023307 + 0.957276i 0.957560
-0.404443 - 0.858555i 0.949047
-0.404443 + 0.858555i 0.949047
0.919279 + 0.146570i 0.930890
0.919279 - 0.146570i 0.930890
0.640292 - 0.635954i 0.902448
0.640292 + 0.635954i 0.902448
0.748442 + 0.324116i 0.815608
0.748442 - 0.324116i 0.815608
-0.256055 - 0.713403i 0.757963
-0.256055 + 0.713403i 0.757963
0.422358 + 0.341532i 0.543167
0.422358 - 0.341532i 0.543167
-0.258676 0.258676
No root lies outs ide the unit circle.
VAR satisfies the stability condition.
Pairwise Granger Causality Tests
Date: 07/26/18 Time: 19:54
Sample: 2013M01 2017M12
Lags: 2
Null Hypothesis: Obs F-Statistic Prob.
IMP does not Granger Cause PDB 58 2.33515 0.1067
PDB does not Granger Cause IMP 1.34526 0.2692
EKS does not Granger Cause PDB 58 2.02093 0.1426
PDB does not Granger Cause EKS 1.36924 0.2631
EKS does not Granger Cause IMP 58 1.33607 0.2716
IMP does not Granger Cause EKS 0.16731 0.8464
The Role of International Trade to Economic Growth: The Case of Indonesia
2171

Import variables statistically insignificant affect
to the export (0.8464 > 0.05 this means that
hypothesis 0 is accepted, where there is no influence),
similarly, export also statistically insignificant affect
to the import (0.2716 > 0.05 this means that
hypothesis 0 is accepted, where there is no influence).
Therefore, we can conclude that there is no any
causality to both variables import and export.
4.4 Co-integration Test
Non-stationer data phenomenon at level can
produce the relationship of long-term balancing or
generally called as co-integration. Co-integration test
using Johansen co-integration test is aimed to identify
the co-integration relationship among variables. The
result of this test will determine the analysis method
that will be used whether VAR first difference or
VECM (Vector Error Correction Model)
Table 6: Johansen Co-integration Test
Table 6 identifies that trace statistic value and
eigenvalue maximum at r=0 are greater than critical
value at 5% significant level. This means that co-
integration test indicates that among the movement of
export, import, and GDP have the stability
relationship and the similarity of long-term
movement. In another word, every single short term
period, all variables tend to adjust to reach long-term
equilibrium.
4.5 VECM Estimation Model
VECM estimation result shows the short term and
long term relationship among variables (import,
export, and GDP). In this estimation, GDP is being
dependent variabels while independent variabels are
import and export. VECM estimation result used to
analyze short term and long term effect of
independent variable toward dependent variabels.
according to the table 7, it is clearly showed that there
is no significant effect export to GDP as well as
import to GDP in the short term.
Table 7: VECM Summary Result in Short Term
Variables Coefficient T-statistic
CointEq1
D(PDB(-1))
D(PDB(-2))
D(IMP(-1))
D(IMP(-2))
D(EKS (-1))
D(EKS (-2))
C
Meanwhile, table 8 provides longterm
information the influence of import and export toward
GDP. The result show that none of them has
significant influence in the long term.
Table 8: VECM Summary Result in Long Term
Variables Coefficient T-statistic
IMP (-1) -1.965642 -4.41480
EKS (-1) 2.767045 5.08545
4.6 Impulse Response Function
Impulse response function describes the evolution of
the variable of GDP along a specified time horizon
after a shock in a given moment.
0.00092
3
[ 2.72704]
-0.45721
8
[-3.21668]
-0.29329
1
[-2.01217]
0.00754
7
[ 0.77692]
0.00297
3
[ 0.32424]
-0.01244
6
[-1.11248]
0.00348
3
[ 0.31076]
0.01352
3
[ 7.01490]
Date: 07/26/18 Time: 19:58
Sample (adjusted): 2013M04 2017M12
Included observations: 57 after adjustments
Trend assumption: Linear deterministic trend
Series: PDB IMP EKS
Lags interval (in first differences): 1 to 2
Unrestricted Cointegration Rank Test (Trace)
Hypothesized Trace 0.05
No. of CE(s) Eigenvalue Statistic Critical Value Prob.**
None * 0.266968 31.63824 29.79707 0.0303
At most 1 0.214944 13.93595 15.49471 0.0847
At most 2 0.002487 0.141932 3.841466 0.7064
Trace test indicates 1 cointegrating eqn(s) at the 0.05 level
* denotes rejection of the hypothesis at the 0.05 level
**MacKinnon-Haug-Michelis (1999) p-values
-.002
.000
.002
.004
.006
5
10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 5
0
Response of PDB to EKS
ICRI 2018 - International Conference Recent Innovation
2172

Figure 2: Impulse Response Function of Variables
Second graph of graph 2 shows the response of
GDP if it is shocked by import variable. GDP will
response the shock positively (+) strat from the first
period and fluctutaitve to the period 12 and remain
stable positively after period 14. The third graph
shows the response of GDP after shocked by export.
GDP respons negatively (-) strat from the second
period and start increasing to the positive trend after
period 3 and remain stable positive in the 10th period.
4.7 Variance Decomposition
Variance decomposition uses to determined a number
of contribution independent variables effect toward
dependent variable. Graph 3 describes the fulcutaion
of GDP difference, in the first period, GDP is greatly
affected by GDP itself. Import remain in second
priority after GDP start from the first period to period
of 50. From this graph, we can conclude that import
made the highest contribution toward GDP
respectively. In contrast, export was the least
significant part of GDP.
Figure 3: Variance Decomposition of GDP
4 CONCLUSIONS
From the previous briefly discussion regarding to the
export and import contribution toward economic
growth with VAR method, the conclusions of this
study is described as follow:
1. According to the impulse response function
analysis of the GDP model, it shows that GDP
will response negatively in short term and
positively stable in the long term in period of 15
due to the shocked of export.
2. According to the impulse response function
analysis of the GDP model, it shows that GDP
will response positively in short term and
positively stable in the long term in period of 20
due to the shocked of import.
There are various areas that can be improved from
current study for stakeholders and also further future
studies, which could include:
1. Overall, the largest contribution of GDP is highly
dependent on the government policy. If the
changes of economic conditions is not
appropriate to the previous forecasting, therefore
the government policy also must be changed so
the relationship as appeared as well as the
existing theory.
2. In consonance with plethora theories that there are
some macro economic variables affected to the
economic growth. This study is specifically using
export and import variables to determine its effect
toward economic growth, both short term and
long term. The author suggest for further study to
insert more variables such as inflation, exchange
rate, etc as intended to previous empirical studies.
Another main variable from Islamic financial
-.002
.000
.002
.004
.006
5
10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 5
0
Response of PDB to PDB
-.002
.000
.002
.004
.006
5
10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 5
0
Response of PDB to IMP
Response to Cholesky One S.D. Innovations
0
20
40
60
80
100
5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50
PDB IMP EKS
Variance Decomposition of PDB
The Role of International Trade to Economic Growth: The Case of Indonesia
2173

variables may be inserted such as asset and
financing of Islamic bank.
3. For further research is suggested to separate
research period into two main periods, before
crisis and after crisis (pre crisis and post crisis).
It is expected to have a briefly described of real
economic condition and throw over of good or
bad economic condition..
REFERENCES
Adeleye, J.O., Adeteye, O.S., & Adewuyi, M.O. (2015).
Impact of International Trade on Economic Growth in
Nigeria (1988-2012). International Journal of Financial
Research Vol 6, No 3.
Akanni, O.P. (2007). Oil Wealth and Economic Growth in
Oil Exporting Countries.AERC Research Oaoer, 170.
Ascarya. (2009).The Determinant of Inflation Under Dual
Monetary System in Indonesia. Center of Education
and Central Banking Studies, Bank Indonesia.
Ascarya., Soekarno, M., & Arianti, D. (2008).Dampak
Suku Bunga Kebijakan Terhadap Suku Bunga
Perbankan Indonesia dan Perbandingannya Dengan
Negara Lain.Center of Education and Central Banking
Studies, Bank Indonesia.
Boediono. (1999). Teori Pertumbuhan Ekonomi.
Yogyakarta: BPFE.
Gujarati, D. (2003). Ekonometrik Dasar. Terjemahan Oleh
Sumarno Zain. Jakarta: Erlangga.
Hashim, K., & Masih, M. (2014). What Causes Economic
Growth in Malaysia: Exports or Imports?.Munich
Personal RePEc Archive Paper No. 62366.
Hye, Q.M.A. (2012). Exports, Imports and Economic
Growth in China: An ARDL Analysis. Journal of
Chinese Economics and Foreign Trade Studies, Vol. 5
No. 1, pp 42-55.
Jhingan, M.L. (2005). The Economics of Development and
Planning.Vrinda Publication.
Kravis, I.B., Heston, A., and Summers, R. (1982). World
Product and Income: International Comparisons of Real
Gross Product. London: the Johns Hopkins University
Press.
Mazumdar, J. (2002). Imported Machinery and Growth in
LDCs. Journal of Development Economics. 65. pp 209-
224.
Rivai.M. (2006). “Pengaruh Ekspor, Impor dan Investasi
terhadap Pertumbuhan Ekonomi di Kalimantan Timur”.
Program Magister Ilmu Ekonomi Fakultas Ekonomi,
Universitas Mulawarman Samarinda.
Roshan, S.A. (2007). Export Linkage to Economic Growth:
Evidence from Iran. International Journal of
Development, Vol. 6, No.1, pp 38-49.
Seyoum, B. (2009). Export-Import Theory, Practices, and
Procedures: Second Edition. London: The Haworth
Press.
Shahbaz, M. & Rahman, M.M. (2014).Export, Financial
Development and Economic Growth in
Pakistan.International Journal of Development, Vol.
13, No. 2, pp 156-170.
Tanjung, H. & Devi, A. (2013).Metode Penelitian Ekonomi
Islam. Jakarta: PT Gramata Publishing.
Velnampy, T., & Achchuthan, S. (2013). Export, Import
and Economic Growth: Evidence from Sri Lanka.
Journal of Economics and Sustainable Development,
Vol 4, No 9.
Vohra.(2001). Exports and Economic Growth in
Developing Countries.Evidence from Time Series and
Cross-Section Data.Journal of Economic Development
and Cultural Change, 36, pp 51-72.
Won, Y., Hsiao, F.S.S.T, and Yang, D.Y. (2008). FDI
Inflows, Exports, and Economic Growth in First and
Second Generation ANIEs: Panel Data Causality
Analyses. KIEP Working Paper 08-02.
ICRI 2018 - International Conference Recent Innovation
2174
