
Direct Shear Strength Improvement through Soil Stabilization using
Dry Dust Collector and Silica Sand from Industrial Waste
Anita Setyowati Srie Gunarti
1*
, Irwan Raharja
2
, Hermanto
3
1
Department of Civil Engineering, Universitas Islam 45, Jl. Cut Meutia No. 83, Bekasi, Indonesia
2
Departement of Computerized Accounting, AMIK Bina Sarana Informatika,
Jl. Banten No. 1, Karangpawitan, Karawang Barat, Indonesia
3
Departement of Geography Education, Universitas Islam 45, Jl. Cut Meutia No. 83, Bekasi, Indonesia
Keywords: Direct Shear, Soil Stabilization, waste, silica sand, dry dust collector
Abstract. Nowadays, Green technology call for research on the utilization of industrial waste to solve civil construction
problems, e.g. broken roads, foundation crack, etc. This study aims to analyze the characteristics of clay after
soil stabilization using Dry Dust Collector (DDC) and Silica Sand (SS) from industrial waste. Laboratory test
was employed for finding the parameters, i.e. water content, specific gravity, plasticity index, and mechanical
test (proctor compaction standard and direct shear strength). The result showed the best friction angle for mix
soil with SS and DDC with 5 percent of SS. Cohesion number increased for the mix soil which contained
only one type of waste. The shear strength increased 32.26 percent for the mix soil with 1.5 percent DDC and
5 percent SS. This study showed mechanical characteristic improvement of clay after DDC and SS addition.
1 INTRODUCTION
Industries often generate much waste when
producing any goods. Coloring and compounding
plastic resin industries in EJIP industrial park in
Cikarang, West Java, give three ton of dry dust
collector waste (DDC) every month. In the other
hand, mineralogy industries create 50 ton silica sand
waste (SS) every month. DDC and SS have chemical
characteristics which are useful for soil stabilization.
But there is a problem to implantation this method
related to high cost in collecting DDC and SS.
Therefore some innovations and infrastructure in
managing industrial waste are emerged. Factory
owners need a lot of collectors with very high cost.
Therefore, some researches on industrial waste
utilization are needed.
The novelty of this study is in stabilizing the
clay using DDC and SS which is useful to support
building constructions as well as roads. Two kinds of
stabilization, i.e. physical and chemical stabilizations,
were used for increasing the strength, decreasing the
swelling potential, and improving physical and
mechanical of clay. This study is useful in Indonesia
since industrial waste increase every year, and adhere
green technology by utilizing the waste for
infrastructure development.
Many studies have been conducted to utilize
industrial waste for additive in construction. Wardana
(2009) proposed soil stabilization through the use of
marble powder and other stabilizers. This research
shows that testing result showed decreasing of soil
swelling and rising the compression strength, but the
stabilizers use showed better in decreasing soil
swelling and the compression strength similar to lime
addition. This research also recommended the soil
depth and optimum composition of stabilizers. In
addition, it is recommended to test the performance
not only based on soil plasticity, but also the
allowance of soil swelling, so soil will have the ability
to support the foundation as well as the vehicles on
the road although in expansion. Paddle only affected
at the surface of the soil as well.
Aulia (2006) proposed to use the waste of
pulp and paper industry as clay stabilizer. The result
showed the clay from Grobogan regency with specific
gravity of 2.68 and solid paper-waste addition up to
15% showed the decreasing of liquid limit up to
58.40%, increasing of plasticity limit up to 44.74%,
decreasing of plasticity index by 13.66%, increasing
of shrinkage limit up to 17.16%, and decreasing of
clay fraction by 71.40%. Solid pulp and paper waste
addition up to 15% could change soil unified system
from class H to MH or OH which there is no class
change based on AASHTO. Cohesion value (c) for all
addition of solid pulp and paper waste up to 10% with
7 days aging are decreased, but the shear angles (ϕ)
are increased. For pulp and paper addition greater
than 10% and 7 days aging, the shear angle (ϕ) tends
to decreased again. Umam (2017) studied about sand
gradation and clay ratio influence on soil’s shear
2990
Setyowati Srie Gunarti, A., Raharja, I. and Hermanto, .
Direct Shear Strength Improvement through Soil Stabilization using Dry Dust Collector and Silica Sand from Industrial Waste.
DOI: 10.5220/0009947429902993
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Recent Innovations (ICRI 2018), pages 2990-2993
ISBN: 978-989-758-458-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
strength. This result concluded that clay addition to
the sand would increase internal shear angle of the
soil and decrease cohesion value. Cohesion value was
not influenced by granules size of sand but influenced
by small granules of sand. Stabilization method was
also developed through the use of waste from
PERTAMINA, i.e. spent catalyst RCC 15 (Gunarti,
2014), which showed the significant increase of
clay’s carrying capacity. These result that showing
carrying capacity improvement will be used as
preliminary data of this study. Another result was the
increase of constrained compressive strength (qu)
compared to the original soil from the stabilization of
soil using spent catalyst RCC 15 and lime because the
soil did chemical process that create the bond among
granules that change particles size into the sandy and
non-cohesive.
This paper proposed the soil stabilization
using dry dust collector (DCC) and silica sand (SS)
from industrial waste. This first time research also
utilized the industrial waste for improving capability
and strength for construction development that adhere
the green technology concept.
2
METHODS
2.1 Kind of Test and Location
The laboratory test for physical and mechanical
characteristic was done at Soil Mechanic laboratory
in Universitas Islam 45 Bekasi to find direct shear
strength, water content, specific gravity, and
plasticity index.
2.2 Materials
For laboratory tests, this study used some materials,
i.e. clay (disturbed and not disturbed clay in
Universitas Islam 45 Bekasi), Dry Dust Collector
(null and 1.5 percent composition compared to clay
dry weight), and silica sand (null, 2.5, and 5 percent
composition compared to clay dry weight). A direct
shear test tool was used with JIS standard (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Direct Shear Test
2.3 Methods
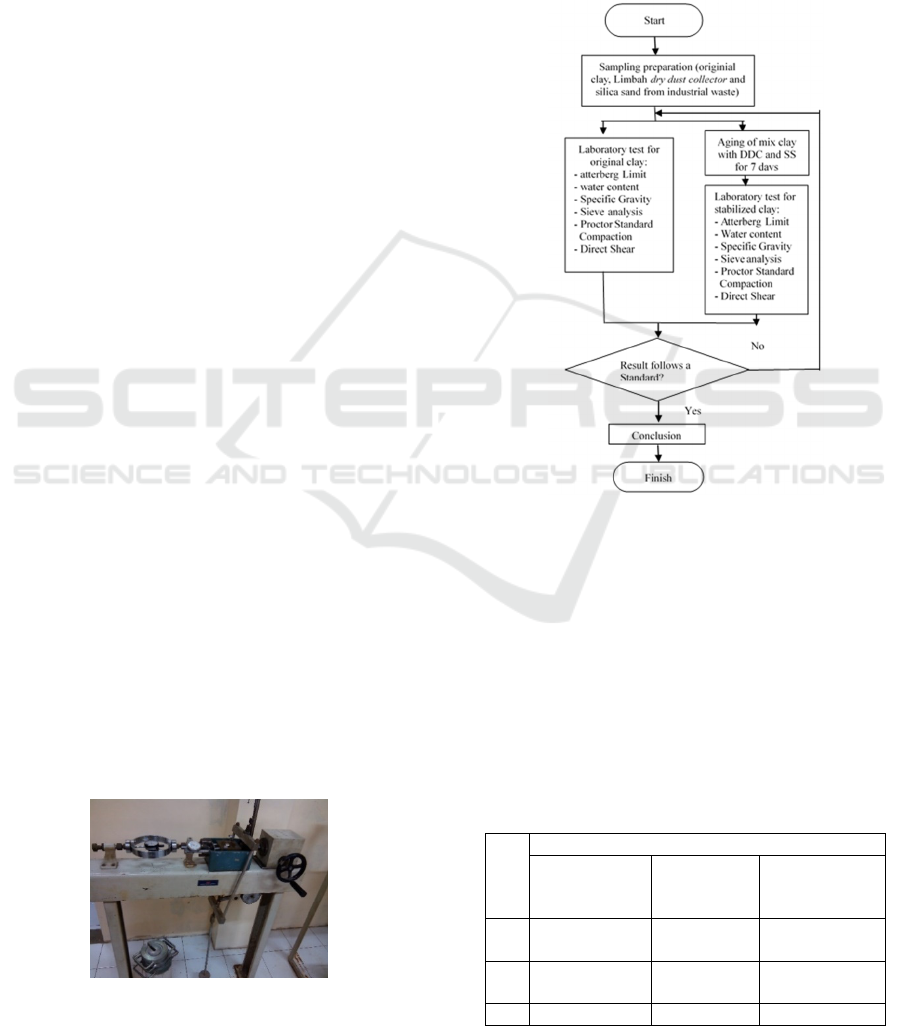
Figure 2 shows the research framework. Two separate
materials (original and stabilized through the use of
DDC and SS). Each material was tested to find:
atterberg limit, water content, specific gravity, sieve
analysis, Proctor standard compaction, and shear
strength. After testing and validation, the results were
concluded and discussed.
Figure 2: Research Framework
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Physical Characteristics of the
Original Clay
3.1.1 Undisturbed Clay’s Characteristics
Table 1 shows the five physical test results of undisturbed
clay.
Table 1: Physical test result of undisturbed clay
No Soil Description
Kind of Test
U
ndisturbed
S
oil depth
1
.00-1.50m
Undisturbed
Soil Depth
1.50-2.00m
1 Specific
Gravity
2.603 2.691
2 Water
Content
58.51 48.72
3 Liquid Limits 87.65% 74.80%
Direct Shear Strength Improvement through Soil Stabilization using Dry Dust Collector and Silica Sand from Industrial Waste
2991

4 Plasticity
Limits
31.02% 28.36%
5 Plasticity
Index
56.63 46.44
Plasticity index can be used as a base to
identify soil expansion. Fathani (1994) study, based
on Chen criteria gives an expansive criterion if PI
greater than 35%. If pass filter number 200 greater
than 95% and liquid limit > 60%, then the soil has a
very high expansive criterion. Table 1 shows
undisturbed soil has PI of 56.63% for 1.00 – 1.50
meters depth and 46.44% for 1.50 – 2.00 meters
depth. Percent of pass sieve fraction number 200 is
85.538% for 1.00 – 1.50 meters depth and 62.716%
for 1.50 – 2.00 meters depth. Liquid limits is 87.65%
for 1.00 – 1.50 meters depth and 74. 80% for 1.50 –
2.00 meters depth. The tests showed that soil has high
expansive criterion. Hardiyatmo (1994) said that soil
will degrade if having gradation coefficient (Cc) of 1
and 3, with uniformity coefficient (Cu) greater than
15. In this study, both Cc and Cu is null because none
of the samples has pass sieve below 10 percent.
Therefore, this kind of soil is categorized as bed in
degradation which is not pass for gradation and
uniformity coefficient. Based on unified criteria and
the liquid limits, it was found that the soil has liquid
limits of 87.65 for 1.00 – 1.50 meters depth and 74.
80% for 1.50 – 2.00 meters depth (greater that 50%).
Therefore, the soil is categorized as CH (organic clay
with high in plasticity).
3.1.2 Disturbed Clay’s and Stabilized Clay’s
Characteristics
Testing results for disturbed and stabilized clay are
shown in Table 2.
Table 2: Physical Test Result of Disturbed and Stabilized
Clay
Additive
Compositi
on
Code
Additive Kind of Test
DDC SS SG LL PL PI
% % % %
A
0 0 2.6232 58.10 31.54 26.55
B
1,5 0 2.5469 57.35 27.21 30.14
C
0 2,5 2.5767 55.50 27.62 27.87
D
0 5 2.6208 51.40 27.53 23.87
E
1.5 2.5 2.5642 52.75 27.60 25.15
F
1.5 5 2.5766 53.42 26.78 26.63
Table 2 shows the mix of DCC and SS decreased
Plasticity of 23.87 for original and disturbed soil from
26.55 (Code D). PI value for some composition code
were both decreased and increased because there is a
characteristic change of the granules as the result of
physical characteristic of granules change from clay
to sandy soil after chemical and aging of stabilized
clay.
3.1.3 Mechanical Characteristics of
Disturbed and Stabilized Clay
Table 3 shows testing of direct shear results for
disturbed and stabilized clay.
Table 3: Direct Shear Test for Disturbed and Stabilized
Clay
Additive
Compositi
on Code
Additive Kind of Test
DD
C
S
S
Compaction Direct Shear
%
d
(t/m3)
Wopt
(%)
(
o
)
C
Kg/cm
2
A
0 0 1,380 30,50 18 0,0115
B
1,5 0 1,372 31,80 13 0,0415
C
0 2,
5
1,375 31,62 11 0,0440
D
0 5 1,384 31,00 21 0,0225
E
1,5 2,
5
1,364 30,75 19 0,0280
F
1,5 5 1,384 30,00 22 0,0255
Compaction value, d, for Code A is 1.380t/m
3
with
optimum water content (Wopt) of 30.50% for
disturbed clay. The highest d value is shown for code
D and F (1.384 t/m3 for 5% DDC and SS addition).
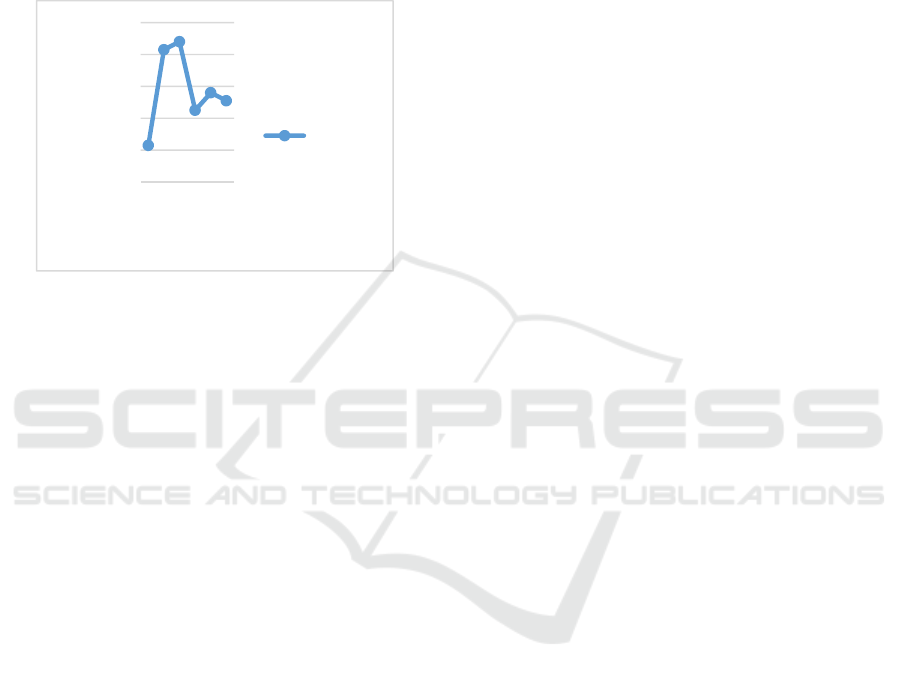
Figure 3: Friction Angle Chart
Figure 3 shows a fluctuation of friction angles. The
highest friction angle is code F (increased 22.22%
compared to original clay) with the composition of
DDC and SS are 1.5% and 5% respectively. SS
addition, physically, made clay more sandy, whereas
DDC addition made the clay more sticky. The
increase of friction angle for stabilized clay improve
the soil compactness because SS could change a
particle size, makes the soil more heterogeneous, and
the cavities are filled. Soil compactness of stabilized
0
5
10
15
20
25
ABCDEF
FrictionAngle
AdditiveCompositionCode
Friction
Angle
ICRI 2018 - International Conference Recent Innovation
2992
clay (code F) can be seen by comparing the d
max
value that is higher than the original clay.
Hakam et al (2010) said that in direct shear strength
test, the more compact the clay, the higher its friction
angle (), and vice versa. In addition, the higher the
clay added, the higher cohesive (c) value but the
smaller of its friction angle.
Figure 4: Cohesive Value Chart
Figure 4 shows the change of cohesive value. The
highest cohesive value is code C (0% DDC and
2.5%SS) which increased 282.62% from its original
value. Large number SS addition (code D and F with
5% addition) affect sandy characteristic of the clay.
Therefore, decreasing the cohesive force between
particles. The increase of cohesive, significantly
showed at clay with only one additive as shown in
table 3 (code B and C). However, the addition of DDC
and SS still increase the cohesive value and stabilized
the original clay.
Maximum shear strength value was found at
composition of 1.5% DDC and 5% SS (code F) which
improve 32.36% compared to the original clay. It
implies that the stabilization through addition of DDC
and SS improve the mechanical characteristics
.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Clay in Universitas Islam 45 Bekasi has high
expansion and bed degradation which does not follow
the gradation and uniformity coefficient. This soil is
categorized as CH (un-organic clay with high
plasticity). Friction angle is increased for clay with
5% silica sand (with or without DDC). But, cohesion
value increased for only one additional stabilizer
(silica sand or dry dust collector). Best shear strength
found at composition of 1.5% DDC and 5% SS (code
F). This composition increase the shear strength of
32.26% compared to the original clay. This study
concludes that a mix clay with additional DDC and
SS has better mechanical characteristics.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was supported by ministry of research,
technology, and higher education of Indonesia
(RISTEK-DIKTI). We thank our colleagues from
Universitas Gadjah Mada who provided insight and
expertise that greatly assisted the research.
REFERENCES
Aulia,K., 2006. Stabilisasi Tanah Lempung menggunakan
Limbah Padat Pabrik Kertas Terhadap Kuat Geser
Tanah, Jurnal Universitas Negeri Semarang, Semarang.
Fathani, T.F., dan Adi, D.A.1994. Perbaikan Sifat Lempung
Expansif dengan Penambahan Kapur, Prosiding
Seminar Nasional Geoteknik, Jurusan Teknik Sipil
UGM, Yogyakarta.
Gunarti, A.S.S, 2014. Daya Dukung Tanah Lempung yang
Distabilisasi dengan Spent Catalyst dan Kapur,
BENTANG Jurnal Teoritis dan Terapan Bidang
Rekayasa Sipil,Vol 2 No 1 Januari 2014, Program Studi
Teknik Sipil Universitas Islam 45, Bekasi.
Hakam, A., Yuliet, R., Donal, R. 2010. Pengaruh
Penambahan Tanah Lempung pada Tanah Pasir Pantai
Terhadap Kekuatan Geser Tanah, Jurnal Rekayasa Sipil
Vol 6 No 1 Februari 2010, Universitas Andalas,
Padang.
Hardiyatmo, H.C, 1994. Mekanika Tanah 1, Gadjah Mada
University Press, Yogyakarta, 1994.
Umam, K., Nugroho, S.A., Wibisono, G., 2017. Pengaruh
Gradasi Pasir dan Kadar Lempung terhadao Kuat Geser
Tanah, Jom FTEKNIK Vol 4 No 1 Februari 2017,
Universitas Riau, Riau.
Wardana, IGN, 2009. Kelakuan Tanah dengan Sifat
Kembang Susut yang Tinggi Pada Stabilisasi Tanah
Dengan Bahan Serbuk Marmer dan Bahan Stabilia,
Jurnal Teknik Sipil Universitas Udayana, Denpasar
0
0.01
0.02
0.03
0.04
0.05
ABCDEF
Cohesion
AdditiveCompositionCode
Cohesion
Direct Shear Strength Improvement through Soil Stabilization using Dry Dust Collector and Silica Sand from Industrial Waste
2993
