
Regional Development Banking and Mobilization of Funds
Sapto Jumono
1
and Chajar Matari Fath Mala
1
,Slamet Seno Adji
1
, Leroy S. Uguy
1
1
Esa Unggul University, Economic Faculty and Business
Keywords: Loan to Deposits Ratio, Regional Economy, Market Structure, Panel Data, Regression Panel
Abstract: This study aims to find out the mobilization of funds by Indonesian RDB (Regional Development Bank)
and the factors influencing it. The interaction between external changes and the internal condition of the
bank may inhibit or even accelerate the fundsmobilization. The mobilization of funds is the main role of
banking as an intermediary institution between surplus units and deficit units. The data research is quarterly
data from 2010 to 2017. There are 26 RDBs as the sample. This research uses the regression data panel as
the research method. The result of this research explainsthat regional external economic variables such as
GDP, Exchange Rate and Inflation, market concentration, and banking characteristics affect
thefundsmobilizationof Indonesian RDBs. This means the pricing strategy must pay attention to external
and internal variables. In the future, Indonesian RDBs need to develop the products that are specific to
aintain and increase the mobilization of funds that have been achieved.
1 INTRODUCTION
The mobilization of funds in order to improve the
efficiency of intermediary performance is not an
easy matter. In reality, the central role of banking is
full of challenges and risks both from internal and
external sources. The mobilization of funds is
heavily influenced by factors such as trust,
expectation, security, timeliness, flexible service,
and prudent fund management. Also, fund
mobilization also poses risks such as liquidity risk,
interest rate risk, credit risk, and capital risk. These
risks are a consequence of the reaction of the
banking management behaviour in its reaction to
changes in external conditions as well as the internal
development of the bank itself.
The bank that has a high non-performing loan
will have an impact on the crisis (Abid et al., 2014),
it has potential to disrupt the financial system and
may result in the financial crisis (Mankiw, 2014).
Therefore, the risk mitigation is a priority for every
banker to maintain bank stability in order to make
banking to remain stable in the fierce competition
era especially in financial markets.
In a healthy economy, financial institutions
should be able tobeintermediary institutions that
efficiently mobilize funds from surplus units to
deficit units (Mishkin and Eakins, 2012). Therefore,
in the economic system, the primary role of banks
and financial institutions is to implement the task of
mobilizing public funds by operating their
intermediary functions to make efficient relations
between SU (supplement units) and DU (deficit
units). Banks as the largest element in the financial
system in mobilizing funds are given special
permission to raise public funds and redistribute in
the form of loans or credit to real business sectors.
Thus, the main task system of the financial or
banking sector is to play an agent role in order to
accelerate development and encourage economic
growth to improve economic welfare.
The role of banking in mobilizing public funds is
a not easy because of the dynamics of uncertain
economic conditions, rapid regulatory changes,
intense banking competition, and other
circumstances that force bankers to be very careful
about the collection and distribution of their funds.
A credit disbursement is not only oriented to profit
but should further think and lead to efforts to
improve the economic welfare.In accelerating the
fund mobilization, bankers are required to act
optimally. They should make the funds that can be
purchased at relatively low cost. This is a challenge
because there area tight regulation and competition
between banks. The development of deposits and
loan can represent the acceleration level of funds
mobilization. If the loan to deposit ratio (LDR)
increases, it means the speed of mobilization of
Jumono, S., Matari Fath Mala, C., Seno Adji, S. and S. Uguy, L.
Regional Development Banking and Mobilization of Funds.
DOI: 10.5220/0009949804790490
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Recent Innovations (ICRI 2018), pages 479-490
ISBN: 978-989-758-458-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
479

funds also increases. LDRreflects the ability of
banks to extend credit and collect public funds. The
higher LDR means the bank optimally do the
intermediation function. LDR reflects the bank's
ability to provide credits and raise public funds.
Table 1:Assets Market Share of Indonesian BankingDuring 2013-2017
Group 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 Average
State-owned Banks
35.50%
36.98%
37.72%
39.62%
40.43%
38.05%
Foreign Exchange
Banks
39.61%
39.18%
38.54%
39.71%
40.13%
39.43%
Non-Foreign
Exchange Banks
3.28%
3.33%
3.15%
1.09%
1.19%
2.41%
Regional
Development Banks
7.87%
7.85%
7.76%
7.87%
8.19%
7.91%
Joint Venture Banks 5.86% 4.96% 5.11% 4.74% 4.49% 5.03%
Foreign Banks 7.88% 7.70% 7.72% 6.96% 5.57% 7.17%
Total 100% 100% 100% 100% 100% 100%
Total (Million, IDR) 4.954.467 5.615.419 6.132.583 6.729.798 7.387.633
Assets Growth 11.77% 8.43% 8.87% 8.91%
Source: Indonesian Banking Statistic
According to Table 1, during 2013-2017, the assets
of Indonesian banking continued to increase with the
average growth of 9.5%. The proportion of majority
asset is controlled by state-owned banks (38.05%)
and foreign exchange banks (39.43%). Meanwhile,
regional development banks owned at 7.91%, non-
foreign exchange banks owned at 2.41%, foreign
banks owned at 7.17%, and joint-venture banks
owned at 5.03%. The data shows an imbalance in the
banking asset market. The structure of the banking
market is concentrated in state-owned banks and
foreign exchange banks meanwhile the other banks
are only market followers.
The indicator of funds mobilization which is
represented by LDR. Based on Table 2, the average
percentage of LDR is at 90%. This shows that
distributed funds are smaller than the collected funds.
Joint-venture banks and foreign banks show that
their LDRs exceeds 100%, this means the credit
given to the public exceeds the funds collected. This
is interesting to be investigated the factors that
influence it. Therefore, it can be detected for further
consideration of decision-making to manage an
efficient banking industry.
Although the asset of banking regional
development bank (RDB) only amounted to 7.91%
of the national banking assets, however, the
development of RDP assets is still very possible
regarding demographic factors. RDB is the host of
every province in Indonesia. Therefore the majority
ownership shares are owned by the local, provincial
government. RDB is more potential
mobilizingpublic funds, primarily to support the
financing of infrastructure development and SMEs.
Based on Table 3, the financial health indicator
of RDB group also shows that RDBs are in healthy
condition. The capital adequacy ratio (CAR) exceeds
the healthy criteria, which is more than 8%.
Meanwhile, return on assets (ROA) of RDBs are all
above 1.5%. Even though ROA is decreased,
whomever the number is still quite high. The cost
efficiency which is represented by the cost to
income ratio (CIR) shows that RDBs are efficient,
the percentage is under 79%.
There are some previous studies about the
mobilization of funds that have been researched.
Tomak (2013) discussed the determinants of
commercial credit loans of private banks and state
banks in Turkey. The result shows that the bank size,
total liabilities, non-performing loans, and inflation
have a significant effect on commercial credit
business. Meanwhile, GDP and interest rate have no
significant effect on credit business. Buchory (2014)
studied the implementation of the intermediation
role of RDB. The intermediation role is represented
by loan to deposit ratio (LDR). The result shows
CAR and ROA are significant to LDR.
ICRI 2018 - International Conference Recent Innovation
480
Table 2: Loan to Deposits Ratio of Indonesian Banking During 2013-2017
Group 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017
Commercial Banks 89.700% 89.420% 92.110% 90.700% 90.040%
State-owned Banks 86.700% 83.730% 88.580% 88.690% 88.670%
Foreign Exchange Banks 83.770% 85.660% 87.550% 84.830% 86.060%
Non-foreign Exchange
Banks 85.100% 87.810% 81.120% 88.370% 92.490%
Regional Development
Banks
92.340% 89.730% 92.190% 93.650% 87.620%
Joint Venture Banks 122.200% 123.610% 132.770% 129.010% 129.020%
Foreign Banks 130.050% 140.040% 131.490% 122.380% 122.330%
Source: Indonesian Banking Statistic
Table 3: Performance Indicator of Regional Development Banks During 2013-2017
Tahun
Performance Indicator
CAR ROA CIR NIM
2013
17.58% 3.18%
73.49%
7.04%
2014
17.79% 2.68% 78.08% 6.65%
2015
20.61% 2.40% 79.57% 6.66%
2016
21.69% 2.58% 78.08% 7.07%
2017
21.65% 2.40% 78.65% 6.42%
Source: Indonesian Banking Statistic
The general condition of banking, the factual
phenomenon of RDBs, and the gaps of findings from
previous relevant researchmotivate this study to find
out what factors influenced the development of fund
mobilization conducted by Indonesian RDBs.
Therefore, this study aims to determine the factors
that affect the LDR regarding external factors and
internal factors. The external factors are the regional
economic conditions, which are GDP-regional, CPI-
regional and Exchange Rate-regional, and the
structure of national banking market. Meanwhile,
the internal factors are NPL, OC/TA ratio, TE/TA
ratio, ROA, and NII/TA ratio.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Theoretically, the linkage of mobilization
of public funds with internal and external factors can
be seen if banking is seen as a system. The banking
system that is part of the financial system works in
the economic system in society. The Bank as the
largest element of the financial system seeks to
optimize its performance by following the dynamics
of changing basic economic conditions and market
structure (external factors), then the bank exploits
these changes by adjusting to its internal conditions
to achieve equilibrium.
The interaction between the internal
banking condition and external factors can be both
directional and causality. According to the theory of
SCP (structure conduct performance) the
relationship between BC (Basic condition, S (market
structure), C (conduct) and P (performance) bank
direction.This means bank performance is a function
of external conditions and behaviour Structure affect
behaviour and behaviour also affects performance, it
makes the market inefficient, indicative of collusion,
while ESH theory actually states that the relationship
between S, C and P, is not the only direction but
causality: It can mean that in an efficient market it is
performance that becomes a function of behaviour
and market structure.The theory of financial
intermediation was first proposed by Schumpeter in
1939, stating that financial intermediation is based
on minimizing the cost of production of information
to solve incentive problems. The costs incurred by
the bank (intermediary) receive the delegation from
Regional Development Banking and Mobilization of Funds
481

the owner of the funds to monitor the funds lent to
the debtor. This has advantages regarding cost in
collecting information because this alternative is the
activity of each bank,so it is more profitable when
compared to the owner of the funds to monitor
directly. As an intermediary institution, the
intermediary function is measured by a comparison
between the number of third-party funds that can be
collected by the amount of credit or financing
disbursed or otherwise known as LDR (Ascarya and
Yumanita, 2010). To describe the relationship
between the performance of mobilization of public
funds by, here are the results of literary studies from
previous studies.
2.1 The Relationship between ROA
(Return on Asset) and LDR (Loan
to Deposit Ratio)
The bank that has a high operating profit will make
management increase the mobility of funds, which
means the bank will increase the credit obtained
from the fundscollectedfrom the public. Profitability
is represented by return on assets (ROA), which is a
profitability ratio that describes the company's
ability to generate profits from every asset used. A
high ROA indicates the banks have operating profit
more than assets
2.2 The Relationship between NPL and
LDR
The banks which have a low non-performing loan
(NPL) indicates they also have a low credit risk
decreases. This condition encourages banks to
increase the volume of loans obtained from public
funds. The high bad credit management will
decrease the bank liquidity. Non-performing loans
cause a loss of income opportunity from the credit;it
reduces profits and the ability of banks to provide
credit, particularlyto pay bank liabilities to
depositors. The high level of NPL will make the
bank more selective in distributing credits because
non-performing loans reduce the value of LDR
(Fitria and Sari, 2012).
2.3 The Relationship between OC/TA
with LDR
The ratio of OC/TA ratio describes the amount of
overhead cost compared to the total assets of the
bank. The concept of overhead cost still hasdifferent
between banking practitioners. Ideally, all costs
(excluding interest costs) which is incurred by the
bank in performing its activities are supposed to be
calculated as an overhead cost. Moreover, there is a
concept states that all costs of funds beyond the cost
used in collecting funds and the costs incurred in the
management of credit disbursement should be
calculated as an overhead cost. Therefore, earning
asset is assumed to bear the cost.If overhead cost
increases, this means all the banking activities
including fund mobilization activities will increase.
For example, technology will raise the overhead
cost,but the bank is expected to be more efficient.
2.4 The Relationship between TE/TA
and LDR
The high capital will make the bank's solvency
increases. This also will raise the banking trust and
encourage people to make a deposit. In the end, the
banking credit distribution will also be high. The
effect of CAR on LDR has also been reviewed
previously investigated by Nasiruddin (2005).
Nasiruddin (2005) found out that CAR has a positive
and significant effect on LDR.
2.5 The Relationship between NII / TA
and LDR
The high net interest income will make banking
management more enthusiastic to increase the
mobility of funds. The bank will encourage people
to save more so that the ability of banks to extend
credit also increase. The ratio of NII/TA is used to
measure the bank's management capability in
managing its earning assets to generate net interest
income. The volume of loans provided greatly
affects the bank's profit through interest income. If
interest income is high, the bank's profit isalso
predicted to increase so it can affect bank liquidity.
The amount of interest income depends on the
amount of credit volume provided. The results of
Rosadaria (2012) and Buchory (2014) found outthat
NIM has a positive and significant effect on bank
liquidity.
2.6 The Relationship between Market
Concentration and LDR
Market concentration can be interpreted as a
percentage of market share dominated by relatively
large companies to the total market share.
Accidental factors do not cause concentration but it
caused by the permanent forces that lie behind the
concentrations that usually do not change much over
time. Concentration also indicates the level of
ICRI 2018 - International Conference Recent Innovation
482

production of a market or industry that focuses only
on one or a few (2-10) largest companies.
Concentration is the number of market shares of
reputable companies or oligopolists, whereby
companies are aware of the interdependence of each
other.
If market conditions become more concentrated,
the market is increasingly monopolized, and the
competition is decreasing.Normally, the more
concentrated market share of the company's market
is narrowed so that the ability of banks in the
mobilization of public funds decreases. The ability
of mobilization of funds by the follower decreases,
this may not be true if the follower bank has certain
capabilities/advantages in expanding the market,
they penetrate the newmarket to increase the
mobility of public fund, the bank will increase
financial inclusion so that society save more and
bankability to distribute credit also increased.
2.7 The Relationship between
Exchange Rate and LDR
If the domestic currency exchange rate is
depreciated, then the value of bank asset in the form
of the domestic currency will decrease. This can
make interest rates rise and the acceleration of
mobilization of public funds to go down. The
opposite may happen if the interest rate set by the
bank already includes exchange rate risk, therefore if
the exchange rate of domestic currency depreciates
the bank does not need to raise the interest rate so
that the mobilization of public funds will increase.
2.8 The Relationship between Inflation
and LDR
If inflation occurs, the value of the bank's assets in
the form of the domestic currency will decrease.
Thiscould makebank interest rates rise,andthe
achievements of banks in the mobilization of public
funds are going down. The opposite may happen if
the interest rate set by the bank already includes the
risk of inflation, so if the inflation occurs then the
bank does not need to raise interest rates so that the
mobilization of public funds still running and still
rising.
The previous research on inflation has been
studiedby Hasanudin and Prihatiningsih (2010).
Theyused Rural Bank in Central Java as the sample;
the result shows inflation has a positive effect on
credit growth of Rural Bank.
2.9 The Relationship between GDP and
LDR
The relationship between GDP and LDR is by the
theory of money demand. If GDP rises, it means
income society rises, therefore demand for money
for transactions and keep watch also rises. On the
other hand, the ability of people to save also
increases. When the income of society is high, then
bank deposits will also increase which make the
increment of the ability of banks in distributing
credits.
3 RESEARCH METHOD
3.1 Data and Research Variables
This study is applied research because the purpose
of this study is to apply the previous research
method and then it will be developed theoretically.
This research is also explanatory research because
this study also aims to explain the causal
relationship between variables through hypothesis
testing.
The object of this research is the banking market
industry in Indonesia. While the subject of research
is RDBs (regional development bank). This research
observes the development of the regional economy,
market structure, banking characteristics, and the
research focus is banking liquidity. The data used
are secondary data from published financial
statements of the Bank Indonesia, World Bank, BPS,
and Indonesian Banking Statistics (SPI) in the period
of 2010-2017, quarterly data.
The population is all regional development banks
which operate in Indonesia from 2010 until 2017.
The sample is saturation sample which consists of
27 Indonesian regional development banks.
3.2 Model Specification
To create patterns of influence of regional economic
conditions, market structure and banking
characteristic on funds mobilization, the
econometric model as follows:
itititit
ititittit
eROAOCTATETANIITANPL
GDPRCPIRERRCRLDR
98765
43210
(1)
Symbol i indicates individual bank or individual
province while t is period ofthe quarter in a certain
year; LDR = loan to deposit ratio. The LDR is an
Regional Development Banking and Mobilization of Funds
483

indicator to measure the fund mobilization of banks.
A higher LDR implies a lower intermediation
banking; CR = Concentration ratio; ERR = regional
exchange rate; CPIR = regional consumer price
index; GDPR = regional gross domestic product;
NPL = non performing loan = credit risk; ROA =
return on total assets / banking profitability; TE / TA
= equity to assets Ratio; NII / TA = NII proportion
in total assets and OC / TA = proportion of overhead
of total assets
3.3 Research Variables
According to Table 4, the variables of internal
factors and external factorsrefer to previous theories
and research. The internal factors are banking
specific characteristics (Athanasoglou et al., 2008).
Banking specific characteristics are factors derived
from the internal condition of the bank, which can
be seen from the financial ratios in the balance sheet
and earnings report bank loss.
Table 4: Operational Definition Variables and Their Measurements
Variable Measurement/
Formula
Notation Impact
Dependent
Variable
Fund
Mobilization
Loan to
Deposit Ratio
(Loan/Deposit) X 100%
LDR
DETERMNAN(Independent Variable)
Internal
banking
Profitability, Assets
Capital, Cost & Revenue
Management
Return o
Assets
Non-
Performing
Loan
Net Interest
Income
Overheadcost
Ratio
Capital
(NOI/TA) X 100%
(NPL /
Total Loan ) X 100%
(NII/Total Assets) x
100%
(Overheadcost/Total
Assets) X 100%
(Equity/Total Assets)
x 100%
ROA
NPL
NIM
OC/TA
TE/TA
+
-
+
_
+
Banking Market
Structure
Market Share &
Competition
Market
Concentration
of Assets
Total market share assest
4 bank terbesar pada
pasar assets perbankan
(%)
CR4A
-
Macro
Economy
Exchange Rate
Inflation
Economy Activity
Exchange Rate-
regional
Inflation -
regional
GDP-regional
Rupiah/USD
(CPIt-CPIt-1)/CPIt-1
*100
GDR-riil (Constant
Price)
ER-r
Inf-r
GDP-r
-
-
+
ICRI 2018 - International Conference Recent Innovation
484
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
To make inferential analysis, firstly in this research
is done by making three models of panel data
regression,i.e OLS (Ordinary Least Square) model,
FE (Fixed Effect), and RE (Random Effect). After
that, selected the best among the three models by
using Chow test to choose between OLS model with
FE model; Hausman's test to choose between FE
model and RE model, and LM (Lagrange Multiplier)
to choose between OLS or RE models.
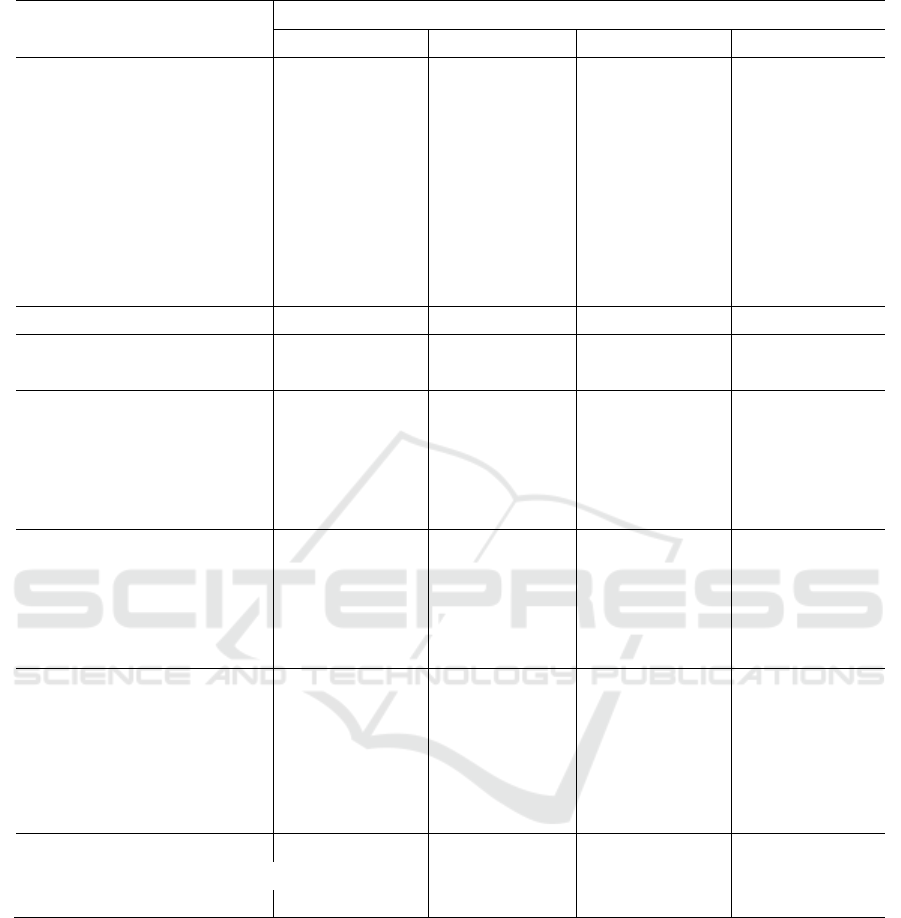
Table 5: The Factors Affecting Loan to Deposits Ratio in Regional Banking
Independent
Variables
Model
FE RE OLS GLS
NPL -1.2158385*** -1.2158385*** -1.2158385*** -1.2158385***
NII/TA 5.4877495*** 5.4877495*** 5.4877495*** 5.4877495***
OC/TA 0.60485704 0.60485704 0.60485704 0.60485704
ROA -3.5475949*** -3.5475949*** -3.5475949*** -3.5475949***
TE/TA 1.1549594*** 1.1549594*** 1.1549594*** 1.1549594***
CR4A 84.5836790** 84.5836790** 84.583679** 84.583679**
ER-R 0.00123691*** 0.00123691*** 0.0012369*** 0.0012369***
CPI-R 0.0402731300* 0.040273130* 0.040273130* 0.040273130*
GDP-R 1.501e-08** 1.501e-08** 1.501e-08** 1.501e-08**
_cons -20.656519 -20.656519 -20.656519 -20.656519
F( 9,791)/ Wald chi
2
(9) 50.380
449.08
41.650
379.57
Prob > F / Prob > chi
2
0.00000
0.00000
0.00000
0.0000
R-sq: within 0.3718 0.3711
between 0.0886 0.1384
overall 0.2845 0.3034
R-squared 0.3215
Adj R-squared 0.3138
Number of obs 801 801 801 801
Number of groups 26 26 26 26
Obs per group: min 30 30 30 30
avg 30.8 30.8 30.8 30.8
max 31 31 31 31
OLS/RE : chi
2
(1) 514.34
Prob > chi
2
0.0000
OLS/FE : F(25, 766) 10.830
Prob > F 0.00000
FE/RE : chi
2
(8) 14.920
Prob>chi
2
0.0606
Multicol test /Mean VIF 32.65
Autocorr test / F( 1,25) 18.513
Prob > F 0.0002
Source: Secondary Data, Processed
Regional Development Banking and Mobilization of Funds
485

Then, after chosen the best model is tested BLUE
(best linear unbiased estimation). If the escape is
interpreted the model, but if not pass will be made an
alternative model of GLS (Generalized Least
Square).
Chow test results show that prob-F = 0.0000 <0.05,
it means that the model selected is the FE model.
Hausman test shows prob-F value = 0.06> 0.05, it
means the model chosen is RE model. The LM test
shows the prob-F value = 0.0000 <0.05 which means
the model chosen is the RE model. Therefore, from
the model selection test it is evident that the suitable
or appropriate model is the RE model. The RE
model as the best model needs to be tested BLUE
via post-estimation test.
To find out whether the selected RE model meets
the BLUE criteria or not, a multicollinearity and
autocorrelation test is required. The multicollinearity
test results show a VIF (Variance Inflating Factor) of
32.65> 10; means there are indications of
multicollinearity. While the Autocorrelation test
shows prob-F = 0.0002 <0.05, there is an indication
of autocorrelation. So, RE does not meet the
qualification of BLUE test. Therefore, we need to
look for the alternative models. In this research, the
alternative chosen model is GLS (Generalized Least
Square).
Based on Table 5, the GLS model shows that the
mobilization of public funds by RDBs which is
represented by LDR is influenced by
macroeconomic factors, market structure, and
banking characteristics. This means the systemic
development of mobilization of public funds by
Indonesian RDBs is related to regional
macroeconomic conditions such as GDP-R, CPI-R
and ER-R; the structure of the national banking asset
market (CR4A) and the bank's internal conditions
such as NPL, NIM, ROA and TE/TA.
4.1 The Effect of NPL on LDR
The non-performing loan has a significant and
negative effect on LDR. This is a good condition
because a low NPL indicates smaller credit risk
which makes bank increase the allocation of credit.
This result is in accordance to research from Saryadi
(2013) which stated the higher NPL wouldresult in
the greater credit risk. Fitria dan Sari (2012)
statedthat a high NPL would make the bankmore
selective in distributing credit.
4.2 The Effect of NIM on LDR
The ratio of NII/TA variable has a significant
positive effect on LDR which means the greater net
interest margin will also make the greater LDR. This
indicates bank has managed to optimize the
difference between interest income and interest
expenses from total assets operated by the bank. The
optimal net interest margin drives to increase LDR.
The result isin accordance with the findings of
Rosadaria (2012) and Buchory (2014) which found
out that NIM had a significant positive effect on
bank liquidity.
4.3 The Effect of ROA on LDR
Return on assets has a significant negative effect on
LDR which means alow ROA will make a high
LDR. This does not mean if a low ROA will make
operating profit goes down. Mathematically, a lower
ROA occurs because the growth ofoperating profit is
smaller than the growth of asset. Asset growth
affects increasing market access which makes the
bank's ability to attract and distribute fund is getting
stronger. This study supports Myers's (1984) who
stated that a high level of profitability would make
firms use retained earnings as a source of funds
compared to outside sources of funds from debt (in
this case, third-party funds) and it results in a decline
of the intermediary function of banks especially in
lending.
4.4 The Effect of TETA on LDR
A high capital adequacy ratio can provide a large
space internally and externally for banks because the
adequacy of banks capital is a requirement of safety
regulations. The higher capital adequacy will
makean optimal an intermediary function of banks in
this case the credit distribution.
In this research, the ratio of TE/TA has a
significant and positive effect on LDR which means
the high capital will increase LDR. Increasing the
capital of banks to make the solvency of banks
increases, this berimpak on trust society sehinggan
ability of banks to collect public funds and
channelled back to the community in the form of
credit becomes increasingly rising.The study
supports the findings of Saryadi (2013) which states
that if CAR increases, it will increase LDR.
ICRI 2018 - International Conference Recent Innovation
486

4.5 The Effect of Concentration on
LDR
CRA4 variable is the level of assets market power of
the four largest banks. The result shows that
concentration has a significant and positive effect on
LDR which means that the direction of the national
banking assets market structure is in line with the
development of funds mobilization by RDBs. This is
reasonable because RDBs are one of the parts of the
national banking system. It only has a small market
share,so it becomes a market follower. Therefore,
funds mobilization of RDBs is affected by the
dynamics of the national banking market structure.
4.6 The Effect of Exchange Rate on
LDR
The trend of Rp/USD currency of regional-province
has a positive effect on LDR. Thismeansthe
dynamics of forex market provincehas a role in the
rise of the turmoil of the RDBs’ capability in
mobilizing funds. The more Rp/USD currency rises
nominally; it will help RDBs in mobilizing funds.
Banking management succeeded in utilizing the
depreciation of rupiah to keep increasing LDR. This
result supports the research from Mongid (2008)
which suggests thatthe exchange rate has a
significant positive effect on the provision of credit.
4.7 The Influence of Inflation on LDR
The regional inflation which represents the
development of provincial market output prices has
a significant and positive influence on LDR. This
means that price development in the regional
goods/services market plays a significant role in
RDBs’ capability in mobilizing funds. A high CPI
will support RDBs in mobilizing funds. This is
because banking management managed to anticipate
the impact of inflation in pricing strategy to keep
increasing LDR
4.8 Influence of GDP on LDR
The GDP-R variable or regional gross domestic
product development progress a significant and
positive influence on LDR. This means the regional
output market condition contributes to the rise of the
turmoil on the mobilization capability of RDBs’
funds. The greater the regional economic activity
means better people's income,so this encourages
people to be able to save, on the other hand, the
demand for public money also rises, especially the
demand for money for transactions. Therefore, the
access to BPD in collecting and channelling funds is
increasing.
5 CONCLUSIONS
5.1 Finding
The fundsmobilization of RDBs in all provinces in
Indonesia is influenced by the external factor of
internal banking. The external factors consist of
regional GDP, regional exchange rate, regional
inflation and national banking concentration. They
have the significant and positive effect of the loan to
deposit ratio. Meanwhile, the internal banking
factors that have a significant positive effect are
NIM (net interest margin) and TE / TA (equity/asset
ratio). The variable which has a negative significant
effect is non-performing loan and return on assets.
This indicates that bank operations in Indonesian
RDBs are systematically working to optimize the
rotation of funds, the fundsmobilization is affected
by changes in regional economic conditions and the
structure of the national banking market. Therefore,
the RDBs need to mitigate the risk. Moreover, the
utilization and anticipation of the opportunities and
threats sourced from these external factors need to
be oriented in long-term perspective without neglect
on short-term interests especially in managing the
health aspects of profitability, capital, interest rate
spread, earning assets and cost-revenue
management.
5.2 Implications
The implementation of intermediation role of RDBs
by increasing the effectiveness of funds mobilization
can be enhanced to prioritize management pricing.
Net interest income can be increased by increasing
the volume of third-party fund and loan by making
loan growth bigger than third party fund growth. It
also can be increased by arising financial inclusive
to penetrate and explore new potential market,but it
still should consider the prudential aspect of
reducing risk.
The effectiveness of fund mobilization can also
be done by developing specific banking products.
Therefore the customers will be still loyal. The
product development is not only focused on credit
and deposit market, but it is also important to
develop fee-basedincome-based products. This is
important because the future of the market will be
more competitive so that the NIM must be thinning.
Regional Development Banking and Mobilization of Funds
487

The development of fee-based income products is an
alternative to maintain the stability of bank revenue.
It is important to prioritize and upgrade EWS
(early warning system) to anticipate changes in
regional macroeconomic conditions and market
structure changes, as these external variables are
significant to the accelerated mobilization of funds.
These external factor changes need to be included in
every decision making especially in the pricing
strategy which greatly affects the rapid mobilization
of public funds by banks.
REFERENCES
Abid, L., Ouertani, M. N., and Zouari-Ghorbel, S. (2014).
Macroeconomic and bank-specific determinants of
household's non-performing loans in Tunisia: A
dynamic panel data. Procedia Economics and Finance,
13: 58-68.
Ascarya, A., & Yumanita, D. (2010). Determinants of
bank’s net interest margin in Indonesia. In
International Conference on Eurasian Economies.
Athanasoglou, P. P., Brissimis, S. N., and Delis, M. D.
(2008). Bank-specific, industry-specific and
macroeconomic determinants of bank profitability.
Journal of international financial Markets, Institutions
and Money, 18(2): 121-136.
Buchory, H. A. (2014). Analysis of the effect capital,
credit risk and profitability in the implementation of
banking intermediation function: study on regional
development bank all over Indonesia in 2012. In
Proceeding Kuala Lumpur International Business,
Economics and Law Conference, 4: 311-327.
Fitria, N., and Sari, R. L. (2012). Analisis Kebijakan
Pemberian Kredit Dan Pengaruh Non Performing
Loan Terhadap Loan to Deposit Ratio Pada PT. Bank
Rakyat Indonesia (Persero), Tbk Cabang Rantau, Aceh
Tamiang.(Periode 2007-2011). Jurnal Ekonomi dan
Keuangan, 1(1).
Hasanudin, M., and Prihatiningsih. (2010). Analisis
Pengaruh Dana Pihak Ketiga, Tingkat Suku Bunga
Kredit, Non Performance Loan (NPL) dan Tingkat
Inflasi Terhadap Penyaluran Kredit Bank Perkreditan
Rakyat (BPR) di Jawa Tengah. Jurnal Teknis, 5(1).
Mankiw, N. G. (2014). Principles of Macroeconomics.
Seventh Edition. Stamford: Cengage Learning.
Mishkin, F. S, and Eakins, S. (2012). Financial Market
and Institutions Seventh Edition. United State of
America: Prentice Hall.
Mongid, A. (2008). The Impact of Monetary Policy on
Bank Credit during Economic Crisis: Indonesia's
Experience. Jurnal Keuangan dan Perbankan, 12(1):
100-110.
Myers, S. C. (1984). The capital structure puzzle. Journal
of Finance, 39 (3): 575-592.
Nasiruddin, N. (2005). Faktor-Faktor Yang
Mempengaruhi Loan to Deposit Ratio (LDR) Di BPR
Wilayah Kerja Kantor Bank Indonesia Semarang.
(Doctoral dissertation, Program Pascasarjana
UNIVERSITAS DIPONEGORO).
Rosadaria, G. (2012). Analisis Faktor-Faktor Yang
Mempengaruhi Loan to Deposit Ratio Sebagai
Likuiditas Perbankan. Thesis. Economics Faculty.
University of Indonesia.
Saryadi, S. (2013). Faktor-faktor Yang Berpengaruh
Terhadap Penyaluran Kredit Perbankan (Studi Pada
Bank Umum Swasta Nasional Devisa). Jurnal
Administrasi Bisnis, 2(1).
Tomak, S. (2013). Determinants of commercial banks’
lending behavior: Evidence from Turkey. Asian
Journal of Empirical Research, 3(8): 933-943.
ICRI 2018 - International Conference Recent Innovation
488
Tabel 3: The Factors Influence Loan to Deposits Ratio in Indonesian RDBs
Independent
Variable
Model
FE RE OLS GLS
NPL (Non performing loan) -1.2158385*** -1.2158385*** -1.2158385*** -1.2158385***
SPREAD (Spread rate) 5.4877495*** 5.4877495*** 5.4877495*** 5.4877495***
OC/TA (overhead cost) 0.60485704 0.60485704 0.60485704 0.60485704
BEP (Basic Earning Power) -3.5475949*** -3.5475949*** -3.5475949*** -3.5475949***
TE/TA (total equity/total asset) 1.1549594*** 1.1549594*** 1.1549594*** 1.1549594***
CRA4 (concentration of assets) 84.5836790** 84.5836790** 84.583679** 84.583679**
ER-R (Exchange rate-Region) 0.00123691*** 0.00123691*** 0.0012369*** 0.0012369***
CPI-R (Inflation-Regional) 0.0402731300* 0.040273130* 0.040273130* 0.040273130*
GDP-R (GDP-Regional) 1.501e-08** 1.501e-08** 1.501e-08** 1.501e-08**
_cons -20.656519 -20.656519 -20.656519 -20.656519
F( 9,791) / Wald chi
2
(9) 50.380
449.08
41.650
379.57
Prob > F / Prob > chi
2
0.00000
0.00000
0.00000
0.0000
R-sq: within 0.3718 0.3711
between 0.0886 0.1384
overall 0.2845 0.3034
R-squared 0.3215
Adj R-squared 0.3138
Number of obs 801 801 801 801
Number of groups 26 26 26 26
Obs per group: min 30 30 30 30
Avg 30.8 30.8 30.8 30.8
Max 31 31 31 31
OLS/RE : chi
2
(1) 514.34
Prob > chi
2
0.0000
OLS/FE : F(25, 766) 10.830
Prob > F 0.00000
FE/RE : chi
2
(8) 14.920
Prob>chi
2
0.0606
Multicol test / Mean VIF 32.65
Autocorr test / F( 1,25) 18.513
Prob > F 0.0002
Regional Development Banking and Mobilization of Funds
489

Table 4: The Factors Which Influence Loan to Deposits Ratio in Indonesian RDBs
Independent
Variable
model
fe re ols gls
Nplgipt -1.2158385*** -1.2158385*** -1.2158385*** -1.2158385***
Spreadsipt 5.4877495*** 5.4877495*** 5.4877495*** 5.4877495***
Octaipt 0.60485704 0.60485704 0.60485704 0.60485704
Bepipt -3.5475949*** -3.5475949*** -3.5475949*** -3.5475949***
Tetaipt 1.1549594*** 1.1549594*** 1.1549594*** 1.1549594***
cra4t 84.5836790** 84.5836790** 84.583679** 84.583679**
kurspt 0.00123691*** 0.00123691*** 0.0012369*** 0.0012369***
ihkpt 0.0402731300* 0.040273130* 0.040273130* 0.040273130*
pdrbcppt 1.501e-08** 1.501e-08** 1.501e-08** 1.501e-08**
_cons -20.656519 -20.656519 -20.656519 -20.656519
F( 9, 791) 50.380 41.650
Prob > F 0.00000 0.00000
Wald chi
2
(9) 449.08 379.57
Prob > chi
2
0.00000 0.0000
R-sq: within 0.3718 0.3711
between 0.0886 0.1384
overall 0.2845 0.3034
R-squared 0.3215
Adj R-squared 0.3138
Number of obs 801 801 801 801
Number of groups 26 26 26 26
Obs per group: min 30 30 30 30
avg 30.8 30.8 30.8 30.8
max 31 31 31 31
OLS/RE : chi2(1) 514.34
Prob > chi
2
0.0000
OLS/FE : F(25, 766) 10.830
Prob > F 0.00000
FE/RE : chi2(8) 14.920
Prob>chi
2
0.0606
Multicol test /Mean VIF 32.65
Autocorr test / F( 1,25) 18.513
Prob > F 0.0002
ICRI 2018 - International Conference Recent Innovation
490
