
Financial Feasibility Study of Home Care Business
Erwin Suhadi
1
, Lia Amalia
1
, Sudarwan
1
and Arief Kusuma Among Praja
1
1
F
aculty of Economics and Business, University of Esa Unggul, Jakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: Business Feasibility Study, Home Care, NPV, IRR, Pay Back Period.
Abstract: The main purpose of this business plan is to assess the feasibility of the health care business in the patient's
home. Developments in health services opened many opportunities to do business in the field of health
care,and one of them is Home Care services. There are many opportunities for Home Care business that
provide an opportunity for investors to develop this business. The opportunities that exist are many people
with degenerative diseases that need long-term care, the number of Home Care in Indonesia is still a little,
the existing Home Care is difficult to reach by consumers due to the lack of online services, and limitations
of health care providers to accommodate all patients who need Home Care services. The purpose of this
study is to know the feasibility of the establishment of a business plan of Home Care in Tangerang City.
This study uses quantitative and qualitative methods. For the quantitative method, we used 3 (three)
investment criteria, which are Net Present Value (NPV), Internal Rate of Return (IRR), Pay Back Period
(PBP), and qualitative methods, we used non-financial approach, which are the operational aspects,
marketing aspects, human resources aspects and business environtment aspects. Based on the analysis of
financial feasibility, NPV of this project is IDR16,350,215 IRR is 132%, and Payback Period is 1 year 3
months. Based on the analysis of quantitative and qualitative, it can be concluded that the establishment
plan of Home Care is feasible.
1 INTRODUCTION
Every company needs good planning, related to
the business strategy or financial strategy. Financial
planning is very important to do before starting the
business due to the preparation of financial planning
function to implement the steps to measure the
achievement of business strategy, as well as provide
an overview to investors regarding the feasibility of
the company's business. Through the information
presented in financial planning, investors can
identify business risks that may occur in the future
and could be useful for investment decision making.
Investors need to analyse the financial aspects in
order to know the projection of the company's
financial statements as a whole and the changes that
occur in the financial statements during a certain
period so that based on the analysis that has been
done, investors can find out whether the business is
feasible or not.
Financial planning is one of the important
elements of business planning in order to take
investment decision making based on analysis of
several aspects. This framework consists of 5 (five)
elements of financial planning which consist of
sales, expenses, investment, capital requirements,
and financing. These 5 (five) elements generate 3
(three) components which consist of the planning of
income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow
statement.
Financial planning is a systematic process and
uses quantitative forecasting of all cash inflows and
outflows that are in line with the company's
activities in order to find out the business
opportunities in the future. Financial planning from
this perspective is used as a mechanism to view and
handle uncertainty in business. The analysis of this
financial strategy consists of an income statement,
balance sheet, and cash flow statement. Financial
planning and budgeting is a series of processes by
the company in order to execute its operational
activities. The company needs operational funds to
perform its operational activities.
Financial planning for the establishment of a new
company will use the financial projections for the
next 5 (five) years. The preparation for the
establishment of the company will begin in 2017,
and the estimated operational activities will begin in
2728
Suhadi, E., Amalia, L., Sudarwan, . and Kusuma Among Praja, A.
Financial Feasibility Study of Home Care Business.
DOI: 10.5220/0009951627282733
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Recent Innovations (ICRI 2018), pages 2728-2733
ISBN: 978-989-758-458-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

early 2018. The company will begin selecting the
location of the business, renovation, purchase of
fixed assets and recruitment of human resources.
Purchases of medical support equipment will
commence in early 2018, in accordance with the
commencement of the company's operational
activities.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
A feasibility study is an evaluation and research
of a project designed to uncover the strengths and
weaknesses of the project and determine whether the
project is feasible or not. In other words, a feasibility
study is a preliminary study undertaken to assess
whether a planned project is likely to be practical
and successful to estimate its cost. We use a
feasibility study to make decisions about a project or
business ideas. By doing a feasibility study, people
will have strong recommendations if a business idea
is worthy of being achieved. We use 3 (three) tools
for financial feasibility analysis, which are Net
Present Value, Internal Rate of Return and Payback
Period.
The definition of Net Present Value (NPV) by
Ross, Westerfield and Jordan (2008) is that an
investment is worth undertaking if it creates value
for the owner. Net Present Value is the difference
between an investment’s market value and its cost.
To determine the Net Present Value, we can simply
find the present value of after-tax cash flow of the
project. The net present value decision tool is a more
common and more effective process of evaluating a
project. Present value calculation essentially requires
calculating the difference between the project cost
(cash outflows) and cash flows generated by that
project (cash inflows).
The NPV tool is effective because it uses
discounted cash flow analysis, where future cash
flows are discounted at a discount rate to
compensate for the uncertainty of those future cash
flows. The term "present value" in NPV refers to the
fact that cash flows earned in the future are not
worth as much as cash flows today. Discounting
those future cash flows back to the present creates an
apple to apples comparison between the cash flows.
The difference provides the net present value. The
general rule of the NPV method is that independent
projects are accepted when NPV is positive and
rejected when NPV is negative. In the case of
mutually exclusive projects, we accept the project
with the highest NPV.
The definition of Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
by Lawrence L. Gitman (2009), is the discount rate
that equates the NPV of an investment opportunity
with $ 0 (because the present value of cash inflows
equals the initial investment). The IRR is closely
related to NPV. In this project, IRR of the project is
equal to a discounted rate which the net present
value (NPV) of the project is zero, which means that
the project revenue is equal to project costs. The
internal rate of return is commonly used to evaluate
the desirability of investments or projects. The
higher IRR of the project, the more desirable it is to
implement the project, and also the lower IRR of the
project, the less desirable it is to implement the
project. Based on the IRR rule, an investment is
acceptable if the IRR exceeds the required return.
The payback period (PBP) is the length of time
required to recover the cost of an investment. The
payback period of a given investment or project is an
important determinant to undertake the position or
project, as longer payback periods are typically not
desirable for investment positions. The shorter PBP
means, the more feasible investment, payback period
ignores the time value of money, unlike other
methods of capital budgeting, such as net present
value, internal rate of return or discounted cash flow.
Payback period is the most basic and straightforward
decision tool. With this method, we can determine
how long it will take to pay back the initial
investment to undergo a project. In order to calculate
this, we will take the total cost of the project and
divide it by how much cash inflow that we expect to
receive each year, this will give the total number of
years or the payback period.
Sensitivity analysis is a technique used to
determine how different values of an independent
variable impact a particular dependent variable
under a given set of assumptions. This technique is
used within specific boundaries that depend on one
or more input variables. Sensitivity analysis, also
referred to as what-if or simulation analysis is a way
to predict the outcome of a decision given a certain
range of variables. By creating a given set of
variables, the analyst can determine how changes in
one variable impact the outcome.
The sensitivity analysis is based on the variables
impacting valuation, which a financial model can
depict using some variables. The sensitivity analysis
isolates these variables and then records the range of
possible outcomes. A scenario analysis, on the other
hand, is based on a scenario. The analyst determines
a certain scenario such as a market crash or change
in industry regulation, then changes the variables
within the model to align with that scenario. The
Financial Feasibility Study of Home Care Business
2729

analyst has a comprehensive picture, by knowing the
full range of outcomes, given all extremes, and has
an understanding for what the outcomes would be
given a specific set of variables defined by real-life
scenarios.
3 METHODOLOGY
There are 5 (five) major steps in doing this
research, which are Problem Identification,
Literature study, Data Collection, Data Processing
and Analysing, and Conclusion and
Recommendation. These steps need to be taken in
order to complete the project. First, it needs to make
problem identification from the research so that it
will see the problem more clearly. This step is about
defining the problem and determining the research
objectives. The objective of this project is to
determine the feasibility of the project whether this
project is feasible or not, based on the NPV, IRR,
and PBP calculation.
Literature reviews in this project are intended to
help the reader to get the information needed to
understand this project. It provides a literature study
to help the reader to get the information needed. The
literature reviews about this project are taken from
several sources and media, which are printed books,
brochures, an article from the internet, government
regulation, interview with people involved in the
health industry, interview with prospective clients,
and printed reports from related feasibility projects.
There are 2 (two) kinds of data which will be
used in this project, revenue calculation data and
cost calculation data. The data which is going to be
used for calculating the revenue is the data that we
have from the company projected sales for 5 (five)
years, and there are 3 (three) types of costs going to
be calculated in this project, investment cost, fixed
cost and variable cost. The data will be processed
and analyze by concluding the problem-solving
model based on the method of making a good
feasibility study; this model is a common type of
model of concluding feasibility study.
We take the calculation of the overall project’s
costs, revenues, NPV, IRR, and PBP to get the
conclusion of this research. The recommendation
will also be taken from the overall project’s costs,
revenues, NPV, IRR, and PBP. We need
recommendations to improve the quality of Home
Care Business.
4 ANALYST
4.1 Capital Requirements
In order to run this business, we need working
capital IDR 650,000,000. The working capital
consists of total initial investment and the required
cash reserves. Funding at the beginning of the
establishment of the company's operations comes
from investors. Investors as a provider of funding for
the establishment of the company are given the
option to include their capital with an investment
scheme scenario of having 60%, 70% and 80% of
the paid-up capital and enter into the corporate
modal structure.
Capital requirements, both capital investment
and working capital, can be searched from various
sources of existing funds, which are own capital or
loan capital. Own capital is the capital from the
business owner while the loan capital is capital from
outside the company. In practice, the financing of a
business can be obtained by a combination of its
capital and loan capital. The choice of whether using
their capital, loan capital or a combination of both
depends on the amount of capital required and the
policy of the business owner.
Own capital is the capital obtained from the
owners of the company by issuing shares. The
advantage of using own capital to finance a business
is the absence of interest charges, but will only pay
dividends. The dividend pay-out is made when the
company gains profit, and the amount of dividend
depends on profit. The disadvantages of using its
capital is the amount is very limited and relatively
difficult to obtain.
4.2 Financial Projection
To see the company's financial development and
analyze the feasibility of the business, then we make
a projection for the next 5 (five) years. The
projection of the financial statements consists of
three scenarios, which are Optimistic Scenario,
Normal Scenario, and Pessimistic Scenario, some
assumptions used in the projection of financial
statements. We prepare pre-operation activities since
August 2017 so that at the beginning of 2018, we
can conduct business operational process.
The growth rate of market share that is used in
Normal conditions is estimated at 5%. This is due to
the company's ability in the Normal scenario is in
constant demand growth to get the patient. In
optimistic condition, it is estimated that the growth
of market share owned by Home Care business is
ICRI 2018 - International Conference Recent Innovation
2730

8%. This is due to Home Care's ability in an
optimistic scenario that can gain a large market
share increase in a short time. In a pessimistic
condition, the growth of market share owned is 3%.
This is because there is still much demand for other
Home Care services as well as the emergence of
competitors in the same industry that will take the
Home Care market share.
4.2.1 Income Statement
In a normal scenario, we assume that the average
amount of income in one year is IDR7.447.635.000,
which consists of homestay and home visit services
IDR6.640,150,000 whereas from the estimates of
action services conducted in one year by doctors and
nurses is IDR355,685,000 and income from medical
equipment rental is IDR378.000.000. Cost of goods
sold is 77% of sales, and depreciation cost is
IDR67,392,250. The dividends as a form of profit
sharing to investors are distributed on a regular basis
every year amounting to 40% maximum. The
company will make the tax payments in accordance
with the provisions of corporate income tax.
4.3 Balance Sheet
In the projection of the balance sheet with
normal scenario in 2018, the total of current assets is
IDR683,774,734 which consist of cash and bank.
Total of non-current assets consist of tangible and
intangible assets is IDR300,539,250, so the total
amount of assets is IDR984,313,984. The Company
does not have any accounts payable because the
daily operations of the company are engaged in
services, the use of operational funds is mostly used
to purchase medical supplies, that amount is
adjusted to consumer demand so it will not affect the
company's cash flow.
Loans from banks and third parties do not exist
because the company has just established, so it is
rather difficult to get a loan from a third party. Also,
the paid-up capital by investors is still positive and
sufficient to finance the company's operational
activities. The amount of paid-up capital is
IDR650,000,000 and retained earnings obtained
from the profit and loss scenario is IDR334,313,984,
so the total equity amounted to IDR984,313,984.
4.4 Equity Growth
We established this Business from independent
investment results, where the paid-up capital after
the planning of funding policy is IDR650,000,000,
and the paid-up capital result is from the investor as
a whole. The number of investors in terms of
depositing capital becomes the freedom of
shareholders to determine the portion of the joint
investment and becomes an option for business
planners due to the High Risk and High Return
factors for the investment results. We expect this
profit to provide positive value for investors in the
long term, and we also expect the value of the
company can provide good business continuity.
4.5 Cash Flow Statement
In this cash flow statement, we apply the cash
method in accordance with the application of
working capital. This is because we want to
anticipate the impact of cash flow turnover that is
not effective in its use. The cash flow statement
scenario is based on the assumptions of the values in
the projected income statement and balance sheet
year 2018 to 2022. The portion of the operating
activities, investment activities and financing
activities are described by their respective portions.
Based on the normal scenario calculation, the
company plans to provide cash flow from operating
activities IDR624,582,244, cash flow from
investment activity IDR278,026,500, and cash flow
from financing activities IDR222,875,990, so the
company will be able to generate positive net cash
flows IDR123,679,734 in the first year. The
differences in these scenarios lie in different
underlying assumption factors so that the elements
of the external factor are also accounted for cash
flow analysis of operating, investing and financing
activities.
5 CONCLUSION
5.1 Investment Feasibility Analysis
Analysis of feasibility is assessed using
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) with Net Present
Value (NPV) parameters. This model will show the
net value of the investment to investors. Other
calculations are Internal Rate of Return (IRR),
Return on Investment (ROI) and discounted payback
period that will provide information to support the
feasibility analysis of this business. Details of
investment feasibility calculation can be seen in
table 8.1.
Financial Feasibility Study of Home Care Business
2731
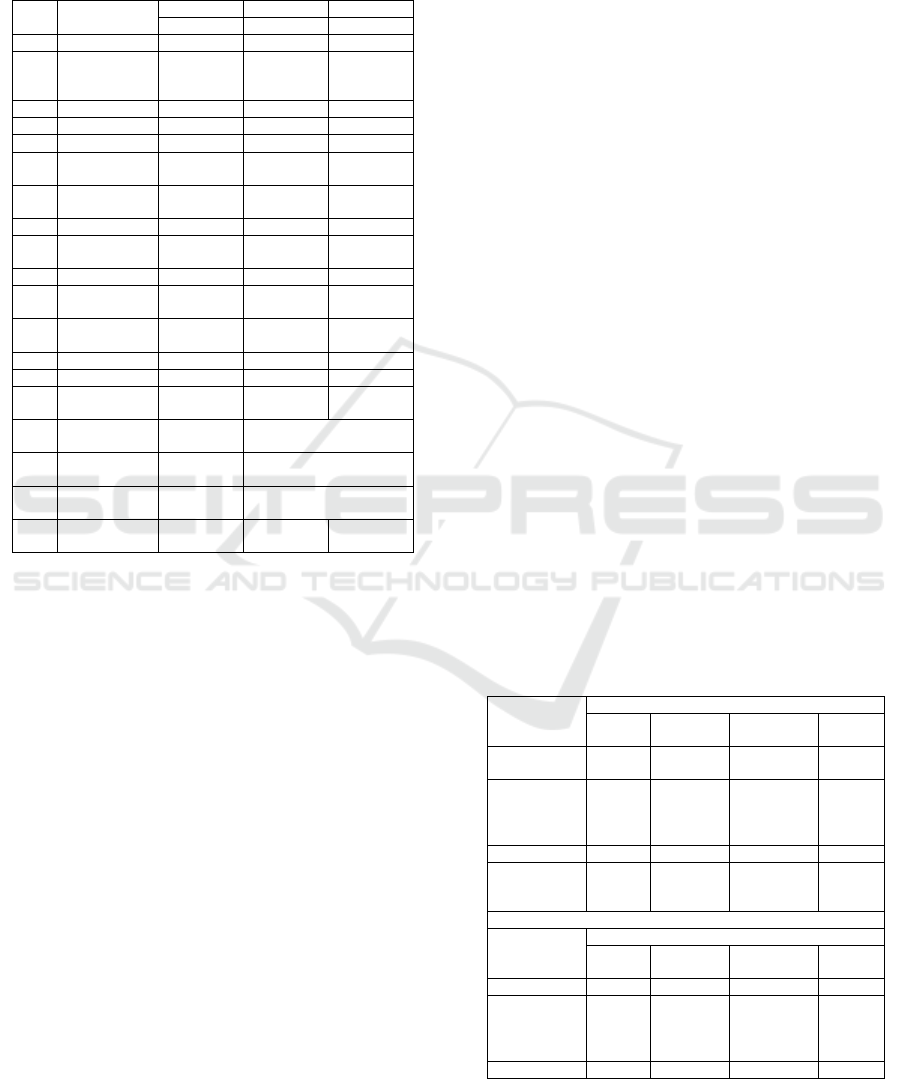
Table 8.1. Investment Feasibility Analysis
ODIS HOME CARE FINANCIAL HIGHLIGHT
2018
(in million IDR)
No.
DESCRIPTION
2018 2018 2018
Normal Optimist Pessimist
1. Revenue 7,448 10,685 4,424
2. Initial
Working
Capital Cost
650 650 650
3. EBIT 671 1,223 238
4. Gross Profit 1,724 2,399 1,106
5. Tax 114 237 30
6. Profit After
Tax
557 986 208
7. Net Profit
Margin
9% 11% 5%
8. Total Assests 984 1,242 796
9. Total
Liabilities
- - -
10. Equity 984 1,242 796
11. Return on
Equity
68% 99% 30%
12. Return on
Investment
134% 245% 48%
13. NPV 16 39 4
14. IRR 132% 185% 70%
15. Payback
Period
1 Year + 3
Months
10 Months 2 Year + 3
Months
16. Break Even
Price
295,763
17. Break Even
Unit
2,762
18. Break Even
Sales
1,756
19. WACC (Cost
of Capital)
20% 18% 22%
As explained in the Theoretical Foundations, the
Net Present Value, Internal Rate of Return and
Payback Period calculation will be the biggest aspect
which will conclude this project is feasible or not.
Based on the above calculation, it can be concluded
that the business of Home Care is feasible to be
realized. This can be seen from the positive balance
of NPV. The positive balance of NPV in business
indicates that the cash flow generates greater
revenue than the expenditures, the remaining profits
in the form of dividends will be distributed to
shareholders. NPV risk analysis can be analyzed
with WACC values of 20% in Normal scenario and
percentage of inflation growth. This business risk
can be categorized as high risk - high return.
In the Normal scenario, the rate of return is
indicated with IRR 132%, and Return on Investment
(ROI) is 134%. The IRR means that the business can
provide a rate of return and a profit greater than the
cost of capital. The duration of the Payback Period is
one year and three months for the Normal scenario
indicates the business of Home Care is a high risk -
high return.
In the calculation of Free Cash Flow for Equity
(FCFE) in the Normal scenario, the calculation of
NPV is at position IDR16 million, for the Optimistic
scenario is IDR39 million and IDR4 million for the
Pessimistic scenario. The projection in the free cash
flow has a very large proportion in the calculation of
business feasibility analysis. The result of the
company's growth rate assumption is equal to 30%,
20%, and 15% for Optimistic, Normal and
Pessimistic scenario (industrial growth and
inflation).
5.2 Sensitivity Analysis
For the sensitivity analysis, there will be some
assumptions to analyze, which are price, sales level,
inflation, change of industry regulations. The price
and sales level are internal factors which are an
important part of the cash inflow on the company
that has a revenue stream only from the home care
service. Meanwhile, the inflation, change of industry
regulations s are external factors which occurred on
the cash outflow, so we cannot control that factor,
this a fluctuation factor that can be changed at any
time due to a new government policy
Sensitivity analysis is a variation in scenario
analysis to know the risk type of forecasting whether
tested properly. We use sensitivity analysis by
selecting a key variable that affects the Net Present
Value of the data previously. We use the assumption
of a decline in sales caused by external factors.
Details of sensitivity analysis can be seen in table
8.2.
Table 8.2. Sensitivity Analysis
Description
Total Sales Per Year Period
Unit Normal Optimist Pessim
ist
Number of
Sales Target
Amount 2,415 3,863 1,449
NPV
IDR
(in
million
)
16 39 4
IRR
% 132 60 70
PBP
Year 1 Year +
3 Months
10 Months 2 Year
+ 3
Months
Description
Sales Per Service
Unit Normal Optimist Pessim
ist
Sales Down
30% 1,691 2,704 1,014
NPV
IDR
(in
million
)
29 60 19
IRR
% 45,4 138 43
ICRI 2018 - International Conference Recent Innovation
2732

In the calculation of this sensitivity analysis, we
use the assumption of 30% reduction in sales from
the previous sales scenario, which are from normal,
optimistic and pessimistic. Sales down 30% for
pessimistic scenarios will have an impact on firm
value. However, pessimistic sales targets is a
scenario when economic conditions are not good,and
we cannot achieve sales targets. In normal and
optimistic scenario still shows a positive signal and
stable economic conditions. Thus, the value of the
company can still be maintained if the scenario is
optimistic and normal in real conditions.
5.3 Feasibility Study Result
From the analysis, it concludes that the Business
Project of Home Care is FEASIBLE and can be
implemented.
REFERENCES
Brigham, Eugene F, Houston, Joel F. (2011). Principles of
Managerial Finance. Edisi 11. Jakarta: Salemba
Empat.
Cooper, Donald R, & Schindler, Pamela S. (2014).
Business Research Methods. 12
th
Edition. International
Edition. McGraw-Hill Education.
David, Fred. R. (2009). Strategic Management
Manajemen Strategi Konsep. (Dono Sunardi,
Penerjemah). Buku 1. Edisi 12. Jakarta: Salemba
Empat.
Diehl, Barbara & Dr Maria Nikolou. (11 November 2013).
From Business Models to Business Plans. Said
Business School. University of Oxford.
Gitman, L. G. (2009). Principles of Managerial Finance.
Boston: Pearson Education.
Investopedia (2017) Capital Budgeting, [online] Available
at http://www.investopedia.com/university/capital-
budgeting/decision-tools.asp.
Jiambalvo, J. (2010). Managerial Accounting. New Jersey:
Wiley.
Kotler, Philip, & Keller, Kevin Lane. (2008). Manajemen
Pemasaran. Edisi 13. Jilid 1. Jakarta: Penerbit
Erlangga.
Ross, Westerfield and Jordan. (2008). Corporate Finance
Fundamentals. New York: McGraw Hill.
Saltelli, A. (2008) Global Sensitivity Analysis. The Primer,
New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons.
Seitz, N. & Ellison, M. (2003). Capital Budgeting and
Long-Term Financial Decision. Ohio: South-Western.
Sullivan, W. G., Wicks, E. M. & Koelling, C. P. (2009).
Engineering Economy. New Jersey: Pearson
Education.
Wheelen, Thomas L, and Hunger, J. David. (2011).
Strategic Management and Business Policy Toward
Global Sustainability. 13
th
Edition. Prentice Hall.
Financial Feasibility Study of Home Care Business
2733
