
Early Detection of Porn Addiction with ‘Piso Kertas’ Method for the
Elementary Student
Safitri M
1
, Yuli Asmi Rozali
1
, Aziz Luthfi
1
and Sulis Mariyanti
1
1
Fakulty of Psychology, Esa Unggul University, Jl. Arjuna Utara no.9 Kebon Jeruk, Jakarta Barat, Indonesia
Keywords: psychodrama, peer group discussion, pornography addiction, puberty preparation
Abstract: Puberty is a vulnerable period in child growth. Children are one of the targets of pornography producers, so
it is feared that as they enter puberty, they can have porn mentality, and become addicted to pornography.
Children who are addicted to pornography could have porn mentality. Therefore, it is necessary to make an
activity that aimed to find out the tendency of pornography addiction in Elementary School. The activities
method were quasi-experiment, with training called PISO KERTAS (Psychodrama and group discussion for
Puberty Readiness) for 51 Elementary School student, in West Jakarta. Modified addiction-measuring
instruments from Kimberley Young were used. The activities show that most of the elementary students have
seen pornography, mostly in internet cafes and their own homes, most have expressions of disgust but some
already find it normal or ordinary. A moderate level of addiction is most prevalent among the students, low
andhigh addicted level quite same. There is a relationship between the level of addiction and gender, where
more male students have a higher level of addiction, and more female students have a lower level of addiction.
1 INTRODUCTION
Technological development makes many changes.
Not only changing equipment from old-fashioned
equipment to sophisticated ones, but it also changes
values and morals. Many parents are not ready to face
the changes in life in this digital era. The changes can
be positive and negative. Children’s intelligence of
using cellular phones, computers and the internetare
not balanced with parents’ ability to explain the
negative effects thereof. For example, when a child
plays games, his/her parents sometimes don’t care
about the games he/she plays. Data from
TopTenReviews.com (2006) indicates that there are
totalling 4.2 million porn sites (2500/week) with 100
thousand child porn sites. Averagely, children know
porn internet when they attain the age of 11 years,
90% of the children of 8 - 16 years old ever access
porn materials (when doing homework). The names
of children’s idols/superheroesare used in thousands
of porn sites, 26 character names the children like are
among others naruto, pokemon, spiderman,
BartSimpson, etc). Even, Mark Castelmen in his book
entitled The Drug of the Millenium (2007) said that
children not yet reached puberty are the target of
pornography.
Mark Castlemen (2007) also reminds that the
effect of pornography addiction is the formation of
porn library in mind that can lead to brain damage
(free frontal cortex is not functioning well), frequent
masturbation, oral sex, and finally pornography
addict for life.
The results of the survey by Yayasan Kita and
Buah Hati in 2014 to the elementary students of
grades 4, 5, and 6 in Jabodetabek support the
abovementioned explanation. It is found that 92% of
the students have seen pornography, where 52% out
of which see pornography in their own homes, 27%
find it something ordinary and 2% feel stimulated
upon seeing pornography. The other results also
indicate that pornography media are movie
cinemas/DVDs by 20%, Video Clips by 17%, Sites
by 13%, Comics by 13%, Games by 13%, TV
Cinemas by 10%, Advertisements by 8%, Cellular
Phones by 4%, and Story Books by 3%.
According to Santrock (2007), puberty being a
“storm and stress” period can indeed lead to difficulty
and frustration in a child’s life due to the stresses from
school, family, and friends. Children who live in this
era find sex materials more frequently along with the
freedom of media and press. Many pornographic
contents in various media can be seen by children
unintentionally or intentionally due to inducements or
desires to try. Therefore, it is feared that teenagers
2788
M., S., Asmi Rozali, Y., Luthfi, A. and Mariyanti, S.
Early Detection of Porn Addiction with ‘Piso Kertas’ Method for the Elementary Student.
DOI: 10.5220/0009952727882793
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Recent Innovations (ICRI 2018), pages 2788-2793
ISBN: 978-989-758-458-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

will be addicted to pornography that can lead to porn
mentality and even brain damage to teenagers
(Castlemen, 2007).
Research by Afiyati Reno (2016), Informatics
Engineering Lecturer of UMB Jakarta, indicates that
65% of the grade 1 junior high school students have
seen porn videos, and grade 4 elementary students are
found to be addicted to pornography. Observation
results in several elementary schools in West Jakarta
indicate that some children are found unable to share
time to play games at the internet cafes and even talk
gross as adults.
In early 2015, the Government through the
Ministry of Social Affairs has also stated that
Indonesia is in pornography alert. Real activities are
expected to protect children from pornography.
Therefore, early detection to children is required
whether or not they have been exposed to the effects
of pornography by the abovementioned media
through the right activities to the children before
puberty.
Based on the preceding, problems found by the
Elementary Students are:
a. Many students do not realize the effects of the
improper use of electronic devices particularly
those relating to the internet.
b. Many students do not know the effects of
pornography addiction.
c. The right approaches are required to find out how
far the elementary students are exposed to
pornography.
The main purposes of the activities to find out the
tendency of pornography addiction in Elementary
School, through active puberty preparation training,
namely psychodramas and group discussions with the
peers. From the questionnaires and peer group
discussions can expectedly illustrate the level of
pornography addiction in the elementary students for
early precaution.
2 METHOD
The activities method were quasi-experiment,
with training called PISO KERTAS (Psychodrama
and group discussion for Puberty Readiness ) for 51
Elementary School student, in West Jakarta.
Psychodrama is an acting technique in group
therapy, a rapport strategy to make the elementary
students more opened. Students are invited to get
acquainted, play, and play roles. After that, they are
asked to rest while filling questionnaires,
accompanied by the facilitators. The questionnaires
already filled will be a reference for the division of
the group. The group discussion led by 1 facilitator
and 1 observer (student from Esa Unggul University)
to assist in the recordingis held. Male and female
student are separated. The discussion talks about
Puberty Preparation.
Modified addiction-measuring instruments from
Kimberley Young were used. The inferential method
uses to see the effectiveness of the model by SPSS.
3 RESULT
3.1 Data on Respondent
Data on respondents by gender indicates that male
respondents are the most (27 students/52.9%) while
female respondents are 24 students (47.1%), totalling
51 students.
Data on the respondent by grade indicates that
grade 4 respondents are the most (25 students/49%),
followed by grades 5 and 6 respondents by 13
students respectively (25.5%).
Data on respondents by age indicates that 19
students of 9 years old are the most (37.3%), followed
by 18 students of 10 years old (35.3%), 10 students of
11 years old (19.6%), 3 students of 12 years old and
1 student of 13 years old (2.0%).
Table 1: The most favoured activities to fill students’
spare times
Favoured activities to
fill students’ spare times
Number %
Reading 18 35.3
Playing games 12 23.5
Watching television 8 15.7
sporting 6 11.7
surfing the internet 5 9.8
Chatting 1 2.0
Other 1 2.0
Total 51 100.0
The most favoured activities to fill students’ spare
times are reading by 18 students (35.3%), followed
by playing games by 12 students (23.5%), watching
television by 8 students (15.7%), sporting by 6
students, surfing the internet by 5 students (9.8%),
chatting by 1 student (2.0%), other activity by 1
student (2.0%).
Electronic items that are important to be owned
by students are mostly cellular phones by 30 students
(58.8%), laptop by 9 students (17.6%), Ipad by 6
students (11.8%), DVD Player by 3 students (5.9%),
Personal Computer by 2 students (3.9%), other by 1
student (2.0%), described in table 2.
Early Detection of Porn Addiction with ‘Piso Kertas’ Method for the Elementary Student
2789

Table 2: Electronic items that are important to be owned
by students
Electronic items
that are important
Number %
Hp
30 58,8
Lap top
9 17,6
I pad
6 11,8
DVD Player
3 7,8
PC
2 3,9
Other
1 2,1
Time(s) spent to surf the internet per day(table 3)
is mostly < 1 hour by 29 students (56.9%), 1-2 hours
by 14 students (27.5%), 3-4 hours by 4 students, 5-6
hours by 2 students, 7-8 hours by 1 student (2.0%), >
8 hours by 1 student (2.0%).
Time(s) spent to surf the internet per day (table 4)
is mostly < 1 hour by 29 students (56.9%), 1-2 hours
by 14 students (27.5%), 3-4 hours by 4 students, 5-6
hours by 2 students, 7-8 hours by 1 student (2.0%), >
8 hours by 1 student (2.0%).
Table 3: Time(s) spent to surf the internet per day
Time(s) spent to surf the
internet per day
Number %
< 1 hour 29
56,9
1 – 2 hour 14
27,5
3-4 hour 4
31,4
5-6 hour 2
7,8
7-8 hour 1
2,0
8 hour 1
2,0
Total 51
100.0
The parents’ reasons for giving electronic devices
( table 4 ) are mostly easy communication by 38
students (74.5%), following the trends and no reason
at all by 6 students respectively (11.8%), and for more
socialization (2.0%).
Table 4: The parents’ reasons for giving electronic devices
The parents’
reasons for giving
electronic devices
Number %
Communication 38 74.5
Following the trends 6 11.8
No reason at all 6 11.7
More socialization 1 2.0
Description of the students who have seen porn
images/scenes(Table 5) indicates that 47 students
(being the majority of students) have seen porn
images/scenes. The remaining 4 students (7.8%) have
never seen pornography.
Table 5: Description of the students who have seen porn
images/scenes
Have seen porn
images/scenes
Number %
Yes 47 92.2
No 4 7,8
Total 51 100.0
Reasons for Seeing Porn Images/Scenes ( table 6)
are mostly accidental by 46 students (90.2%), Just a
fad by 3 students (5.9%) and others by 2 students
(3.9%). Vide table 1 for the description of places
where students see pornography.
Table 6: Reasons for Seeing Porn Images/Scenes
Reasons for Seeing
Porn Images/Scenes
Number %
Accidental 46 74.5
Just a fad 3
5.9
Others 2 11.8
Total 51 100.0
The place to see pornography in the table 7 , we
find out that most of the students see porn
images/scenes at the internet cafes by 16 students
(31.4%), own house/friend’s house by 12 students
(23.5%), friend’s house by 8 students (15.7%), school
and from friends near home by 4 students respectively
(7/8%), others by 7 students (13.7%).
The students’ expressions after seeing
pornography ( table 8 ) are mostly disgusted by 38
students (74.5%), ordinary by 6 students (1.8%),
scared by 5 students (9.8%), they want to puke and
others by 1 student respectively (2.0%).
Table
7: Places To See Pornography
Places To See
Pornography
Number %
Own House/Relative’s
House
12 23.5
Friend’s House 8 15.7
Internet Café 16 31.4
School 4 7.8
Park Near Home 4 7.8
Others 7 13.7
Total 51 100.0
Table 8 : Students’ expressions after seeing pornography
Students’ expressions After
Seeing Pornography
Number %
Want to puke 1 2.0
Feel disgusted 38 74.5
Scared 5 9.8
Ordinary 6 11.8
ICRI 2018 - International Conference Recent Innovation
2790
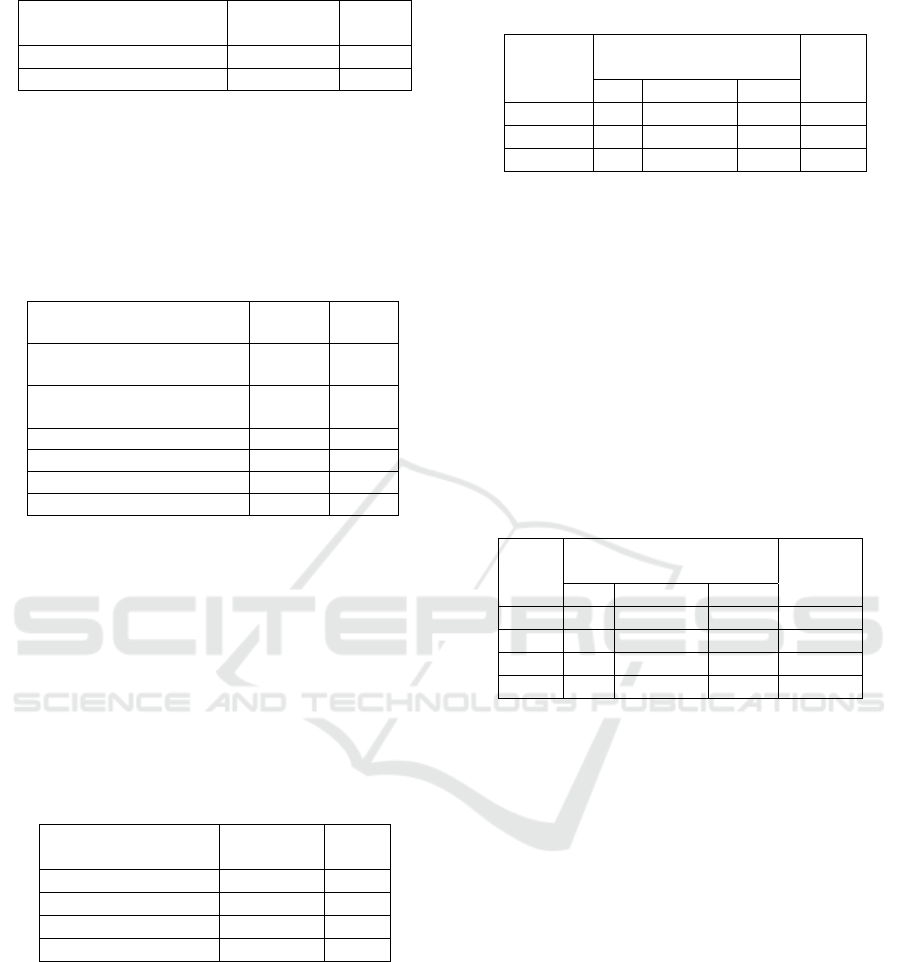
Students’ expressions After
Seeing Pornography
Number %
others 1 2.0
Total 51 100.0
The students’ expressions after seeing
pornography (table 9) are mostly giving up and
refusing to see it anymore by 35 students (68.6%),
ordinary by 10 students (19.6%), curious and intend
to see it again by 3 students, glad to imagine by 1
student (2.0%), and others by 2 students (3.9%).
Table 9: The description of students’ expressions after
seeing pornography.
Students’ Expressions
After Seeing Pornography
Number %
Give up and refuse to see
them anymore
35 68.6
Curious and want to see
them anymore
3 5.9
Glad to imagine 1 20
Ordinary 10 19.6
Others 2 3.9
Total 51 100.0
3.2 Description of Level of
Pornography Addiction
Pornography addiction questionnaire scores indicate
that the minimum score is 9 and the maximum one is
29 while the average score is 17.02 with the standard
deviation by 4.62.
From the scores above, thenthe category of high
and low level of pornography addiction is made as in
table 10.
Table 10: Level of Pornography Addiction
Level of Pornography
Addiction
Number %
Low 14 27.5
Moderate 24 47.1
High 13 25.5
Total 51 100.0
The table 10 above indicates that level of
addiction of the majority of students is moderate by
24 students (47.1%), low by 14 students (27.5%) and
high by 13 students (25.5%).
The description of High and Low Level of
Addiction by Sex ( table 11) indicates that level of
addiction of female students tends to be low by 10
students (41.6%) and high by 7 students (29.16%)
while that of the majority of male students is
moderate (62.96%), high (22.22%) and low (14.8%).
Table 11 : Pornography Addiction By Gender
Gender
Level of
Pornography Addiction
Total
low moderate high
Female 10 7 7 24
Male 4 17 6 27
Total 14 24 13 51
The chi-square cross tab score level of
pornography by sex is 0.037 (<0.05). Therefore, there
is a relationship between the level of addiction and
gender.
The crosstab ofthe low and high level of addiction
with grade ( table 12) indicates that level of addiction
of the majority of grade 4 students is moderate while
that of the remaining students is high as much as low
by 6 students. Level of addiction of grade students 5
tends to be low (38.46%). Level of addiction of Grade
6 students tends to be moderate by 7 students (53.8%)
while that of the remaining students is high as much
as low by 3 students (23.07%).
Table 12: Level of Addiction by grades
Grade
Level of pornography
addiction
Total
low moderate high
4 6 13 6 25
5 5 4 4 13
6 3 7 3 13
Total 14 24 13 51
High and low chi-square cross tab score by grade
are 0.774 (>0.05). Therefore, there is no relationship
between the level of addiction and grades where the
students are.
The crosstab of the high and low level of
addiction by places to see pornography. (table 13)
Indicates that level of addiction of the students seeing
pornography at own home is high and low by
respectively 5 students (41.66%). Level of addiction
of the students seeing pornography at their friends’
houses is moderate, but the low level of addiction is
more than the high one. Level of addiction of the
students seeing pornography at the internet café is
moderate, but the high level of addiction is more than
the low one. Level of addiction of the majority of
students at school is moderate, but the low level of
addiction is more than the high one. Level of
addiction of the students seeing pornography at the
park near home is more than the moderate one,and the
high level of addiction is more than the low one.
Early Detection of Porn Addiction with ‘Piso Kertas’ Method for the Elementary Student
2791

Table 13: Level of pornography addiction by
places to see pornography
Places to See
Pornography
low moderate high
Own
House/Relative’s
House
5 2 5
Friend’s House 2 5 1
Internet Café 3 9 4
School 1 3 0
Park Near Home 0 3 1
Others 3 2 2
Total 14 24 13
High and low chi-square cross tab score by places
to see pornography are 0.378 (> 0.05). Therefore,
there is no relationship between the level of addiction
and places here students see pornography.
4 DISCUSSION
Student activity data indicates that the majority of
students are playing games and reading outside
school hours. The favoured places are school and
home. Electronic device that is important to be owned
is cellular phone on the grounds of communication
and more games to play for < 1 hour at the most by
29 students (56.9%), 7-8 hours by 1 student (2.00%),
> 8 hours by 1 student (2.0%), already categorized as
internet addiction. The results of the research by Siti
Nurina Hakim (2017) show that internet addiction has
more negative effects than positive impacts. It is
feared that many students have already been addicted
to the internet, seeing pornographic content on the
internet.
Most student respondents (92,2%) have seen
pornography contents. It complies with Yayasan Kita
and Buah Hati (Risman, 2017) data that 98% of the
elementary students of grades 4, 5 and 6 have seen
pornography contents. With the majority of students
already seeing pornography and already being
addicted to the internet, the likelihood of students
seeing pornography on the internet will have more
and more mental porn
Reasons for seeing pornography contents are
mostly incidental, but some are curious, follow
friends or afraid of being considered out-dated by
friends. While, places to see pornography contents are
mostly at homes (own home, relatives and friends’
homes) because many homes provide internet facility
and subscribed television.
Student’s expression after pornography contents
are mostly refusing to see them anymore, but some
feel ordinary and are even addicted. It complies with
the statement of Mark Castlemen (2007) that more
children will have porn library to affect the mind in
case of failure to pay attention to the same. While,
media where students see pornography contents are
mostly cellular phone, comics, and games already
being a part of their life. These results are in line with
the research of Rahmatia (2017) that 73% of students
(55 children) have seen pornographic content by
accident via YouTube and Instagram 21% of students
(16 children) have seen pornographic content
intentionally via YouTube and Instagram
Based on the preceding, we find out that many
elementary students have seen pornography contents
because many parents fail to know that electronic
devices they give to their children, considered as the
main needs for easy communication, seem to be
vulnerable to seeing pornography contents.
Moreover, porn industries incessantly put
pornography contents in social media in demand by
the elementary students preceded with inadvertency
due to schoolwork, television shows and movies,
tourism spots, and the favoured games whose
contents are full of porn scenes.
Ideally, the elementary students spend most of the
time to interact with other people directly
(microsystem). Electronic devices are media to
interact with other people directly (macrosystem) and
also get information from other people indirectly.
Giving electronic devices without any obvious
explanation and direction from parents will endanger
the users. Data indicates that cellular phones are the
basic needs of children. Even though most of the
children use cellular phones for communication, but
they could incidentally see much info about
pornography.
Elementary children are still at the phase of
concrete thought by cognitive development.
Therefore, direct interaction with other people is still
much better and required for self-development.
Working parents and mother’s educational level
make direct interaction with parents diminish. While
children get much information onthe internet.
Elementary children approaching puberty will
change sexual organs that urge them to know what
happens to them about their sexual development.
Facilities they receive facilitate them to get any
information from friends or the internet. Moreover,
awareness and times to surf the internet are getting
higher.
Their curiosity of information on sexual
development is not directly received from close adults
ICRI 2018 - International Conference Recent Innovation
2792

in their microenvironment. Therefore they find out
the information on their own or together with the
peers who are also curious. Information received by
the internet can cause children to behave badly, while
parents as directors fail to realize the effects thereof
fully.
It complies with Hurlock’s theory (2007) that
each age has certain stages of development. One of
the aspects is socio-emotional and social
development affected by successive waves from
family, friends, and teachers. The small world of
children widens because they grow bigger and
develop their relationships with many new people that
will influence their socio-emotional development.
According to the ecological theory of Bronfenbrenner
(in Hurlock 2007), five environments are ranging
from interpersonal interaction to extensive culture-
based effects. The five systems are microsystem,
mesosystem, exosystem, macrosystem, and
chronosystem. Therefore, children ideally need step-
by-step guidance by completing well the tasks of their
development in the microsystem to enter the
microsystem. However, parents generally fail to
realize that giving electronic devices able to access
the internet can force children toenter the macro
system without any preparation of what to face.
Many children think that electronic devices are
concrete goods in their territory as they interact with
their friends (as if playmates). They get information
from electronic media and think that it is concrete and
can be imitated without realizing that they are in the
macro system where the information is connected in
such a way and controlled by those who have interests
that they cannot understand because their phases of
thought are still concrete.
Times spent to surf the internet indicate that
children tend to access pornography, intentionally or
unintentionally. When their thinking ability is still
dominated by cerebellum than their pre-frontal
cortex, then the information can easily be absorbed
without any filter. Therefore, it is nothing impossible
if children will directly practice things related to
pornography in the real world. Even though, the
tendency of pornography addiction is mostly still a
moderate and low level of pornography addiction is
more than the high one but we should alert those with
the high level. Otherwise, it is feared that their
addictive pornography behaviour will increase.
Likewise, those with moderate level should be
maintained.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the activities, we can conclude that the
majority of students (92.2%) have seen pornography,
mostly at the internet cafes (31.4%) and their own
homes (23.5%); most have expressions of disgust
(74.5%),but some already find it normal or ordinary
(11.8%). A moderate level of addiction is most
prevalent among the students, but 25.5% were found
to be strongly addicted. There is a relationship
between the level of addiction and sex, where more
male students have a higher level of addiction, and
more female students have a lower level of addiction
.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The research was supported by Faculty of
Psychology, Esa Unggul University.
REFERENCES
Elly Risman, :https://jatim.antaranews.com/berita/190965/
elly-risman-98-persen-anak-pernah-lihat-konten-
pornografi, 4December 2017
Hurlock, Elizabeth, Psikologi Perkembangan : Suatu
Pendekatan Sepanjang Rentang Kehidupan, Erlangga
Jakarta, 2007
Kastlemen, Mark ;The Drug of The New Millenium; Power
Think Publishing, United States of America, 2007.
Kimberly Young, Tes kecanduan internet: http://
www.globaladdiction.org/dldocs/GLOBALADDICTI
ON-Scales-InternetAddictionTest.pdf,, June 15, 2016
Moreno, Jacob L,
http://www.escuelasistemica.com.ar/wp-
content/uploads/2013/01/13-PSICODRAMA-
MORENO.pdf
Rahmawati Diah V dkk; Hubungan antara kecenderungan
perilaku mengakses situs porno dan religiusitas pada
Remaja; Jurnal Psikologi, Universitas Gajah Mada,
2002
Safitri, M., Respati, W. S., & Luthfi, A. (2015). Model
Konseling Melalui Psikodrama dan Hipnoterapi untuk
Meningkatkan Potensi Mahasiswa.
Siti Nurina Hakim, Alifffatullah Alyu Raj, ( 2017) Dampak
Kecanduan internet pada remaja, Prosiding Temu
Ilmiah Ikatan Psikologi Perkembangan Indonesia,
Agustus ,
Tia Rahmatia, 2017, Pesepsi Pornografi Pada Aak ( Studi
Pendahuluan Pada Anak Studi Siswa Kelas 5 Sekolah
Dasar Islam “X”, Jurnal Ilmiah Psikologi Paramadina,
Vol 8 No 1, Juli 2017
http://www.academia.edu/26630865/Industri Pornografi
Kontemporer dan Pergeseran relasi Kuasa Gender
dalam teori World-System, June 6, 2016
UU Pornografi RI No 44 tahun 2008
Early Detection of Porn Addiction with ‘Piso Kertas’ Method for the Elementary Student
2793
