
Online Risks Research in Teenagers: Survey on Teenagers as Social
Media Users in Medan
Hendra Harahap and Yovita Sabarina Sitepu
Department of Communication Science, Faculty of Social and Political Science, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan,
Indonesia
Keyword: Online Risks, Social media, Teenagers, Medan.
Abstract: This research aims to find the trend in teenagers while using social media to gratify their information seeking
and to knows how about their social media habits. This research specifically want to find the online risks that
encountered by them while looking for information through social media. It shows that teenagers’ use of
social media in Medan still in balance between educational needs, such as: doing assignments and looking for
information and entertainment needs (eg. Music, video clip and games). Online risks that experienced by them
such as receiving messages that make them scared, exposed by images of sexual videos or photos, seen
weebsite where people talk about or share their experiences of taking drugs. Meanwhile, contact risks that
have been experienced by the teenagers are from giving their private information to a person they have only
had contact with online, to being bullied by online.
1 INTRODUCTION
Internet has become an integral part of human life in
this digital era. People depends on internet for their
daily activities such as looking for information,
communicating with friends and family, looking for
online transportation, buying things that they need in
daily life, playing games, entertainment and online
bussiness.
The Indonesian Internet Service Providers
Association (APJI) releases that in 2017 the number
of Indonesian internet users has reach 143.3 million
people or 54.6% of Indonesian population. Based on
sex, 48.57% users are woman, and 51.43% are male.
About 16.68% of the internet total users are students,
age between 13-18 year old with an internet
penetration of 75.50% (APJII, 2016).
The growth of internet users is supported by the
availability internet connections in many countries
and so does in Indonesia. The quality of broadband
make people become easier to connect with internet
everytime and everywhere. Indonesia’s mobile
phone users have become bigger than its population.
Around 308.2 million people (34%) have been
connected with internet. The avarage time they are
connected with internet is about 2 hours 30 minutes.
Teenagers and pre-teenagers, age between 9-28-
year old, are named ‘digital generation’ (Livingstone,
2011); ‘generation next, generation z, net generation’
(Tapscot, 2009). Steiner-Adair & Barker (2013) give
name to this generation as ‘fast-forward children’,
‘the age of butt-dealing’, ‘the screen teens’ because
they are living surrounded by electronic things and
virtual world. Internet, games, social media, instant
messaging make them experience something that they
should not. Something that ‘too much, too soon, too
fast.’
Dotner (in Livingstone, 2011) gives name as
‘cultural pioneers’ to this generation because their
ability to make new media as a center of inovation,
interaction and integration. Inovation because they
able to combine many media, do some activities in the
same time, make unclear line between production and
meaning making, also know how to use every
possibilities through new media.
This generation has 8 norms, that are: (1) freedom,
because internet gives them a freedom to choose from
a lot of options; (2) customization, everything can be
adapted with needs and wants; (3) able to investigate
accurately; (4) integrity; (5) collaboration; (6)
entertainment, everything should make happy; (7)
fast; (8) innovation is a part of live (Tapscott, 2009).
Social media is very popular among teenagers.
But, their activities on internet can be devided into:
explorative, create something, learning, sharing,
making networks and even doing something nasty,
288
Harahap, H. and Sitepu, Y.
Online Risks Research in Teenagers: Survey on Teenagers as Social Media Users in Medan.
DOI: 10.5220/0010018302880293
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Social and Political Development (ICOSOP 3 2019) - Social Engineering Governance for the People, Technology and Infrastructure in
Revolution Industry 4.0, pages 288-293
ISBN: 978-989-758-472-5
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

mean or unkind to others (Livingstone, 2011).
Livingstone explains teenagers online activities, as
follow: doing homework (90%), information seeking
(94%), send/receive e-mail (72%), playing games
(70%), instant messaging (55%), visiting political
sites and social problems (55%, +12y.o),
downloading music (46%), looking for school
information/career (44%, +12y.o), quiz (44%), online
shopping (40%, +12y.o), reading news (26%, +12
y.o), looking for advice (25%, +12 y.o), visiting chat
room (21%), uploading photos/strories (17%),
intentionally visiting porn sites (10%).
The motives of internet using can be groupped
into four, that are: looking for information,
entertainment and excitement, communication and
transaction (buying or selling products).
Although teenagers use internet to do their school
tasks, internet activity on teenagers mostly for
fullfiling their excitement needs. They learn from
their friends how to make a social media account,
looking for information, playing online games and
visiting porn sites (Qomariyah, 2009).
Many studies about intenet using in teenagers
show that internet is like a two-sided sword. At one
side is helpful for information source (Livingstone,
2009); useful in learning-teaching process (Bosch,
2009). But,the other side is a negative one such as
degradation of student achievement, have contact
with someone unknown, visiting porn sites, internet
addiction (Cho & Cheon, 2005; Leung & Lee, 2011),
and even a death (Livingstone, 2009).
All risks or the negative side as consequences of
the internet use and teenagers’ exploration on the
internet said by Livingstone (2011) as online risks.
Online risks are including: contact with pedophilia,
exposed by violence, sexual violence, rasism,
advertising, cyberbullying, being stalked, harrasment,
internet gambling, scam, hurting self like suicide,
bulimia, anorexia, and so on.
Online risks are differentiated into: (1) content
risks where children/teenagers are not allowed to get
messages that not appropriate with their age; (2)
contact risks where children in group or individual
participate in risk communication; (3) conduct risks
where children themselves make a risk content or
contact risks (Staksrud & Livingstone, 2009).
Uses and Gratifications theory is used in this
research to discover about online risks in Medan
teenagers moreover to know and explain how the
external and internal factors affect the online risks.
From many studies about internet use in teenagers,
actually there are not much researches which use the
uses and gratifications theory and media uses
approach. There are four (4) approaches about online
risks and internet function on children/teenagers
based on researches that done before. They are: 1)
internet in everyday-life; 2) media literacy; 3) media
uses; 4) media effects. Among those researches done
before, there is no research using the Uses and
Gratifications as an approach or framework.
McQuail (2010) said that media effects can be
intended or unintended, as expected or unexpected.
Kind of changes caused by media are: 1) intended
change, where media can make an intended change;
2) unintended change, where media can make an
unintended change; 3) minor change (form or
intensity), minimal change happens; 4) facilitate
change (intended or not), where media just as a
facilitator for the change happens as expected or not;
5) reinforce what exist (no change), where change
does not happen but just reinforcing existing beliefs;
6) prevent change, where media intend to prevent the
change through slowly delivering idological content
so can restrain the unintended change happen.
McQuail (2010) established the typology of
media effects based on process and link the intended
and unintended with short term and long term
effect.those typologies are: 1) planned
effect/intended- short term; 2) unplanned effect- short
term; 3) planned effect/intended- long term; 4)
unplanned effect/unintended-long term.
Typologies that relate with online risks are
unplanned/unintended- short term effect, and
planned/intended-short term. There are types of
effects in those typologies. They are: 1) individual
reaction, unpredictable and unplanned consequencies
as results of media exposure, such as imitation and
learn about agressive and deviant behavior including
suicide. McQuail (2010) states that this type of effect
is kinds of individual strong emotional respon, sexual
arrousal, anxiety and fear; 2) individual respon, a
process in which an individu is changing or refuse to
change as exposed by messages that are created to
affect someone’s cognitive, attitude and behavior.
Typology relates with online benefit is that media can
make a planned intended change and also unplanned
one.
Based on the discription how the online risks that
teenagers face while using the internet, this research
addresses questions, such as:
a. What are the Medan teenagers’ motives to access
information through social media?
b. How do the Medan teenagers’ habits while access
the information through social media?
c. What are content risks, contact risks, and conduct
risks that Medan teenagers meet while accessing
information through social media?
Online Risks Research in Teenagers: Survey on Teenagers as Social Media Users in Medan
289

2 METHOD
This research is using descriptive quantitative
approach. Survey is used to get a whole portrait of
online risks in teenagers. Descriptive study aims to
give a portrait and an explanation about social reality
and the link between variables which relates with that
reality.
Teenagers as social media users become the
subject of this research. There are some reasons why
the teenager is chosen. They are: 1) the intencity of
teenager being exposed by social media content is
big; 2) the probability of online risks that faced by the
teenager in Medan while using social media to fulfill
their needs of informations is also big. Total
population of teenager aged 15-19 year-old is
216.383 (BPS, Medan in Number 2018). Sampling
size is determined by Slovin’s with margin error
5.8%. It is found that 296 (≈ 300) as a sampling size.
In detail, this research is studying aspects, as
follows:
1. Formats and types of contents that are risky for
teenagers as online media users.
2. Socio-demographic characteristics are measured
in this research as part of teenagers socio-
environment aspects. Indicators of socio-
demographic are: level of education (SMP/SMA
and class), age, sex, level education of father,
level education of mother, utilities that available
in their house, and their pocket money per day.
3. The motives of social media use are determined
by: (1) expressing opinion and status gaining; (2)
social interaction; (3) information seeking; (4)
entertainment and pastime.
4. Media habits
5. Online risks: content risks, contact risks and
conduct risks.
2.1 Data Collection Techniques
1. Survey using questionnaire about online risks is
given to 300 teenagers in Medan.
2. Interview is conducted to teenagers who have
experience about online risks.
3. Focus group discussion with teenagers to know
deeper about their media habits and online risks
they have encountered.
2.2 Data Analysis
Data is analyzed using:
a) Descriptive statistic analysis to explore motives in
using social media, media habits, and online risks
that encountered by Medan teenagers.
b) Qualitative analysis to dig deeper about the
impacts of online risks in Medan teenagers.
3 RESULTS
The Table 1 shows that the use of social media in
Medan teenagers is still balance between the needs
for education- doing homework and information
seeking, and the needs for entertainment (music,
watching video clip and playing games). It is also
apropriate with the results of the research conducted
by Kementerian Komunikasi dan Informasi RI (The
Ministry of Communication and Information) and
UNICEF (2014) about “Children and Teenager
Behavior on Internet Use”. It says that 77.4% of
teenagers using internet to access social media
account, 64.5% relates with educational and doing
school tasks, 63.2% to play online game.
Table 1: Motives in using social media.
No Motives in using social media f %
1 Watching video clip 283 94.3
2 Music 296 98.7
3 Playing games 264 88
4 Doing homework 287 95.7
5 Sending messages to family/
friend
298 99.3
6 Social networking 282 94
7 Information seeking 298 99.3
8 Uploading photo 257 85.7
Smartphone, laptop and mobile phone are media
that commonly had by teenagers in Medan.
Smartphone using in Medan teenagers now has reach
91.3%. Survey conducted by APJII (2016) shows that
desktop computer/laptop ownership in Indonesia has
reach 25.75%. Smartphone ownership is 50.8% of
total population. Compared with the percentage of
medium ownership based on region, 35.5% urban
people have desktop computer and 70.98% have
smartphone/tablet.
Hendriyani et al., (2012) shows that sex and social
economic status affect the correlation between
children and media. Sex can predict what media are
available in a house or child’s room. Games stuffs are
more available in boy’s room and books are more
easy to find in girl’s room.
ICOSOP 3 2019 - International Conference on Social Political Development (ICOSOP) 3
290
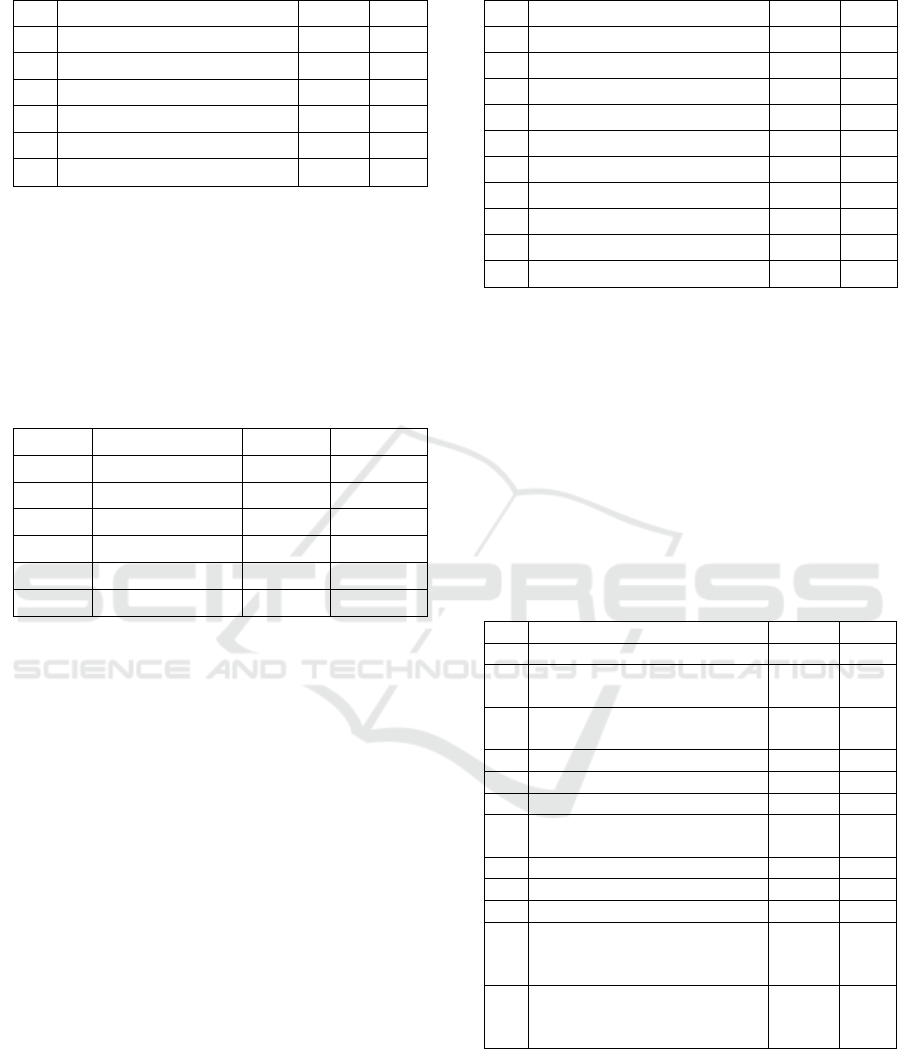
Table 2: Medium ownership.
No Medium f %
1 Desktop computer/PC 78 26
2 Laptop 203 67.7
3 Mobile phone 144 48
4 Smartphone 274 91.3
5 E-book reader 53 17.7
6 Home games console 98 32.7
Table 3 shows that about 69.3% of teenagers aged
15-18 in Medan access or us internet more than 3
hours per day. The intencity of girl accessing the
internet more than 3 hours per day is higher than
boy’s (75.5%:63.1%). This finding is also parallel
with research conducted by APJII (2016) said that the
duration of internet use is about 73.5%
Table 3: Avarage time accessing internet per day.
No Average time f %
1 < 1 hour 22 6.7
2 1 hour 22 7.3
3 2 hours 50 16.7
4 3 hours 78 26
5 > 4 hours 130 43.3
Total 300 100
Youtube, Instagram, Whatsapp, Google+ and
Facebook are aplications that commonly used by
teenagers in Medan. Spesifically, there are 73.7%
teenagers who access Facebook, Instagram 72.3%,
Youtube 72.1%, Google+ 73.5% and Whatsapp 71%.
Moreover, it is found that 76.7% teenagers in Medan
access Facebook more than 3 hours per day.
Most of Indonesian smartphone users use their
smartphone to access social media. This condition
makes Indonesia as the fourth of the biggest country
with 130 millions Facebook users, and 70% of those
Facebook users are teenagers. There are 46% of
Indonesia internet users, aged 15-24, who access
Youtube. Moreover, 75% teenagers of Facebook
users and 22% of Youtube users access those social
media through their smartphone (Global Web Index,
2015).
Table 4: The uses of social media.
No Social media f %
1 Facebook 182 60.7
2 Instagram 278 92.7
3 Youtube 278 93
4 Facebook messanger 125 41.7
5 Whatsapp 265 88.3
6 Twitter 98 32.7
7 Google+ 185 61.7
8 Tumblr 65 21.7
9 Snapchat 111 37
10 Pinerest 102 34
There are 4 main activities that commonly used by
teenagers in Medan while using social media. They
are: 1) added people who they only had contact with
online into their contact list; 2) change or edit a photo;
3) make a video; 4) join an online discussion.
There is a difference between boys and girls
particularly about adding a person they only had
contact with online innto their contact lists. Girls
(80.7%) tend easier than boys (71.8%) when added a
person they only had concact with online into their
contact list.
Table 5: Activities on social media.
No Activities f %
1 Sign petition 19 6.4
2 Share news via Facebook or
Twitter
34 11.4
3 Give comments on Online
news
35 11.7
4 Join online discussions 74 24.8
5 Write a blog 22 7.3
6 Make their own music 36 12
7 Make an animation, moving
picture or image
40 13.3
8 Make a video 85 28.3
9 Change or edit a photo 165 55
10 Make a drawing or picture 68 22.7
11 Added people who only had
contact with online into
contact list
229 76.4
12 Sent a photo/video of self to a
person who only have had
contact with online
57 29
Table 6 shows that there are 56.3% of teenagers
who have been received messages that make them
scared. Additionally, those kind of messages
frequently received by teenagers (16%).
Online Risks Research in Teenagers: Survey on Teenagers as Social Media Users in Medan
291
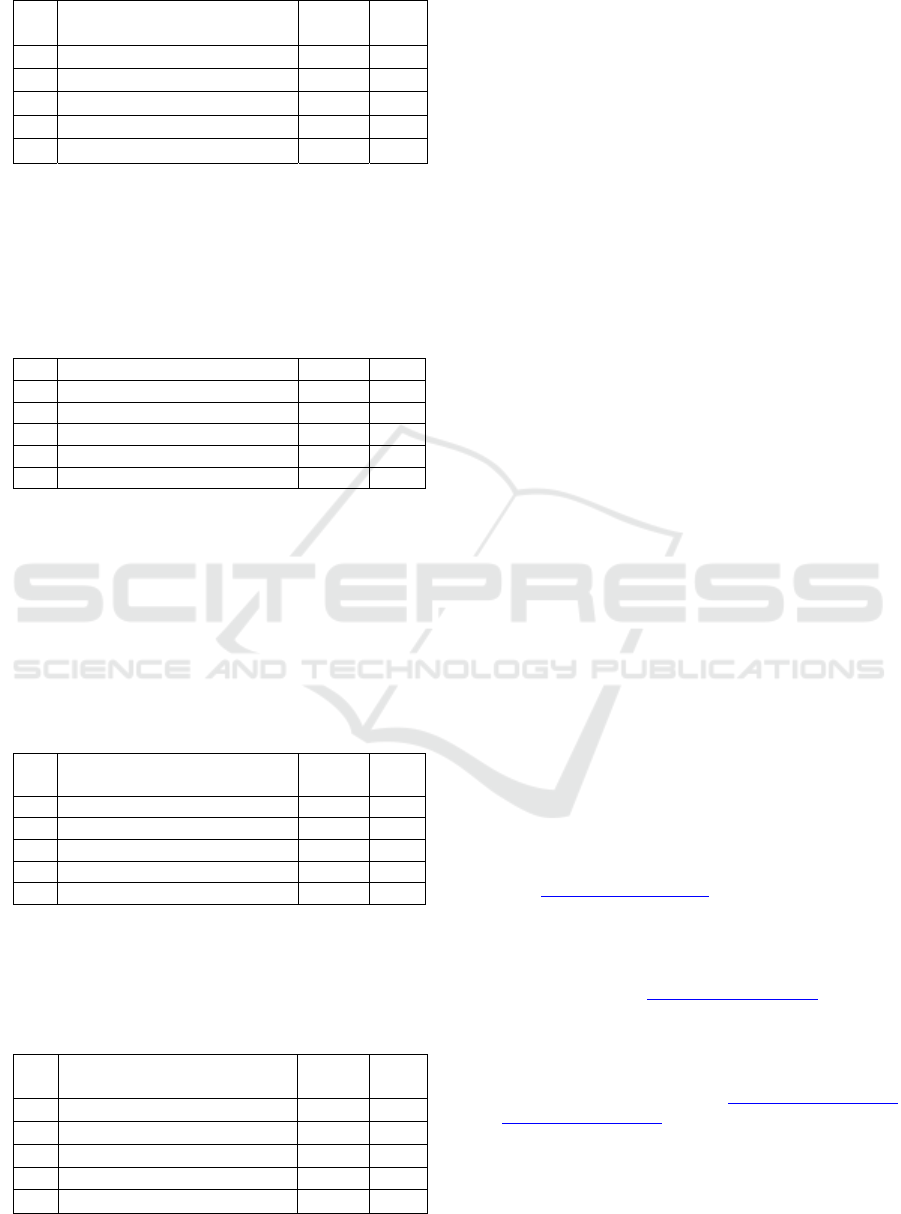
Table 6: Receive something that makes them scared.
No Receive something that makes
them scary
f %
1 Always 11 3.7
2 Often 37 12.3
3 Seldom 121 40.3
4 Never 131 43.7
Total 300 100
Table 7 shows that there are 46.3% of teenagers
who frequently receive sexual messages. Those
messages consist of audio (phone call), video (video
call), image (GIF, picture) and text (sms, whatsapp)
that contain sexual things.
Table 7: Receive sexual messages.
No Receive sexual messages f %
1 Always 5 1.7
2 Often 21 7
3 Seldom 112 37.6
4 Never 160 53.7
Total 298 100
There are 64% of teenagers in Medan who have
been exposed by hateful speech with frequency
around 27.6%. Lately, website with hateful content is
very popular as topic of discussion. Goverment
representated by Ministry of Communication and
Information with stakeholders are always planning
programs which can minimize the impact of
hatespeech.
Table 8: Seen websites with hateful content.
No Seen websites with hateful
content
f %
1 Always 10 3.3
2 Often 73 24.3
3 Seldom 115 38.3
4 Never 102 34
Total 300 100
Table 9 indicates that 51.3% of teenagers in
Medan have seen websites contain a person
experience about using drugs.
Table 9: Seen websites contain how to use drugs.
No Seen websites contain how to
use drugs
f %
1 Always 5 1.7
2 Often 7 2.3
3 Seldom 76 25.3
4 Never 212 70.7
Total 300 100
4 CONCLUSION
Teenagers in Medan, aged 15-18, access the internet
more than 3 hours per day (69.3%). The intencity of
internet use in girls is higher than boys. There are
several social media sites that frequently visited by
them: Youtube, Instagram, Whatsapp, Google+ and
Facebook.
Those teenagers that also as students use internet
for their educational needs and entertainment. This
result is along with research conducted by The
Ministry of Communication and Information
(Kominfo RI) and UNICEF (2014) about “Children
and Teenagers Behavior on Internet Use” and said
that teenagers access social media for educational,
doing homework and playing online games.
Forms of online risks that experienced by the
teenagers in Medan are: 1) receive messages that
make them scared; 2) see and receive sexual
messages (text and video); 3) see websites with
hateful content (hatespeech); 4) see website that
potrays people with eating disorders; 5) see website
that contain people share their experience in using
drugs; 6) see website that contain how to do suicide;
7) too many adverts on internet.
Forms of contact risks that experienced by the
teenagers in Medan are: 1) give their personal data to
a person that they had contact with online; 2) being
asked to add a person that they do not know into their
friend list; 3) some of their personal data was stolen;
4) feeling under pressure to give personal data to
someone; 5) cyberbullied; 6) met online contact
offline.
REFERENCES
APJII, 2016. Infografis Penetrasi dan perilaku pengguna
internet indonesia. Survey 2016. Jakarta. Retrieved
from https://www.apjii.or.id/
Bosch, T.E., 2009. Using online social networking for
teaching and learning: Facebook use at the University
of Cape Town. South African Journal for
Communication Theory and Research, 35(2), 185-200.
Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1080/025001609
03250648
Cho, C.H., & Cheon, H.J., 2005. Children‟s exposure to
negative internet content: effects of family context,
Journal of Broadcasting & Electronic Media, 49(4),
488–509. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1207/
s15506878jobem4904
Global Web Index, 2015. Social Media Engagement
Report-Summary.
Hendriyani, Hollander, E.H., d’Haenens, L., Beentjes,
J.W.J., 2012. Children's media use in Indonesia. Asian
ICOSOP 3 2019 - International Conference on Social Political Development (ICOSOP) 3
292

Journal of Communication, 22(3):1-16 Retrieved from
doi:10.1080/01292986.2012.662514
Kementrian Komunikasi dan Informasi RI, 2014. Siaran
pers hasil riset kominfo dan unicef mengenai perilaku
anak dan remaja dalam menggunakan internet. Jakarta.
Leung, L., Lee, P.S.N., 2011. The influences of information
literacy, internet addiction and parenting styles on
internet risks, New Media & Society, 14(1), 117–136
https://doi.org/10.1177/1461444811410406
Livingstone, S., 2011. Internet, Children, and Youth. In M.
Consalvo & C. Ess (Eds.), The Handbook of Internet
Studies (pp. 348–368), Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Sussex, UK.
Mcquail's, D., 2010. Mcquail's Mass Communication
Theory, Sage Publications Ltd.
Staksrud, E., Livingstone, S., 2009. Children and online
risk: powerless victims or resourceful participants?
Information, Communication & Society, 12(3), 364–
387. https://doi.org/10.1080/13691180802635455
Steiner-Adair, c., Barker, T.H., 2013. The big disconnect:
protecting childhood and family relationships in the
digital age, Harper Business. New York.
Tapscott, D., 2009. Grown up digital: How the net
generation is changing the world, McGraw Hill. New
York.
Qomariyah, A.N., 2009. Perilaku penggunaan internet pada
kalangan remaja di perkotaan (Studi deskriptif tentang
perilaku penggunaan internet siswa-siswi SMP Negeri
37 Surabaya, SMP IMKA/YMCA-1 Surabaya SMA
Negeri 5 Surabaya, SMA Trisila Surabaya. Thesis.
Universitas Airlangga: Surabaya.
Online Risks Research in Teenagers: Survey on Teenagers as Social Media Users in Medan
293
