
Increasing the Quantity of the Actuaries in Indonesia with
E-learning
Yulial Hikmah
Administration and Business Department, Vocational Education Program, Universitas Indonesia
Keywords: The Actuaries, E-learning, SWOT Analysis
Abstract: An actuary is an expert who can apply mathematical theory, probability and statistics, as well as economics
and finance to solve the actual problems in a business, especially those related to risk. The need for an actuary
profession in Indonesia is increasing along with the dynamics that occur both in economic, social and
regulatory aspects in Indonesia. However, the number of actuaries in Indonesia is still minimal. In Indonesia,
a person is said to be an actuary if he passed the exam of the Indonesian Actuary Association. The passing
rate of the exam is quite low. This profession is mostly only known by the people in the big cities. This study
aims to analyze the e-learning method as a way to increase the number of actuaries in Indonesia. This research
is a qualitative study. Data are collected by the electronic sources and interviews with the actuaries. The
analytical method used is the SWOT Analysis. This study finds that e-learning can increase the percentage of
passing Actuary Professional Exams. Thus, e-learning can increase the number of actuaries in the various
regions in Indonesia.
1 INTRODUCTION
Based on The Society of Actuaries of Indonesia
(PAI), the actuary is an expert who can apply
mathematical theory, probability and statistics,
economics and finance to solve actual problems in a
business, especially related to risk. Someone is said
to be an actuary if he follows a series of Actuarial
professional examinations held by The Society of
Actuaries of Indonesia (PAI). The Indonesian
government itself requires that every insurance
company has at least one actuary.
Moore, M.G. (1973).
This was confirmed by the Decree of the Ministry
of Finance of the Republic of Indonesia No. 426 /
KMK.06 / 2003 in article 3 paragraph 16 which states
that each life insurance company must have at least
one certified actuary. This is in line with the program
of Financial Services Authority (OJK) which targets
1000 actuaries in 2018. Based on Deputy Director of
Statistics and Information of IKNB, Arie Munandar,
The number of actuaries in Indonesia in 2018 was
571. This is still far from the OJK Program.
According to Rosenberg (2001) that e-learning refers
to the use of internet technology to deliver a series of
solutions that can increase knowledge and skills.
Therefore, actuarial science e-learning can be a
solution in fulfillment of the number of actuaries in
Indonesia because actuary candidates can study
independently wherever and whenever with modules,
questions and discussions offered by e-learning so e-
learning can increase the opportunity to pass the
exam.
Moore, M.G. & Thompson, M.M. (1990).
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 The Actuaries
Actuary is an expert who can apply the theory of
mathematics, Probabilita and statistics, as well as
economics and financial sciences to solve the actual
problems of a business especially related to risk.
(
Nielsen, et. Al 2007).
These business problems are linked to events that
occur in the future, the likelihood of such events
occur, when the event will occur and how much funds
need to be set aside to address the costs that arise if
the event The event. An actuary generally works in
the financial industry, such as life insurance
companies, general insurance companies, health
insurance companies, pension funds, actuarial
consultants and investments
Verduin, J.R. & Clark, T.A.
126
Hikmah, Y.
Increasing the Quantity of the Actuaries in Indonesia with E-learning.
DOI: 10.5220/0010048700002967
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference of Vocational Higher Education (ICVHE 2019) - Empowering Human Capital Towards Sustainable 4.0 Industry, pages 126-129
ISBN: 978-989-758-530-2; ISSN: 2184-9870
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

(1991). . Many also actuaries that have penetrated in
other areas related to risk management that require
strong analytical and logic skills.
The professional test of actuary consists of 11
(eleven) exam subjects as follows: Have taken and
passed the exam points for the level of actuarial Ajun
7 (seven) exam points and 1 (one) Professional
seminar, i.e. F-10: Investment and asset Management
, F-20: Actuarial Management , F-31: Actuarial
aspect in life insurance; Or, F-32: Actuarial aspect in
pension fund; Or , F-33: Actuarial aspect in general
insurance; Or F-34: Actuarial aspect in health
insurance.The professional test of Ajun Aktuaris
consists of 8 (eight) exam subjects as follows: A-10:
Financial Mathematics, A-20: Probabilita and
statistics , A-30: Economy , A-40: Accounting , A-
50: Statistical method , A-60: Actuarial Mathematics,
A-70: Modeling and risk theory , A-80:
Professionalism
2.2 SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis is a method used to analyze and
position environmental and environmental resources
within the region, in the form of strengths,
weaknesses, opportunities and threats.Strengths and
Weaknesses are internal (controlled) factors that
support and hamper organizations to achieve their
respective missions.
Garrison, D. R. 1993 , Porter, L.R.
(1997). While Opportunities and Threats are external
(uncontrollable) factors that enable and sacrifice
employees from their mission. By identifying the
factors in these four areas, organizations can be
involved in decision-making, planning and strategy
development.
2.3 Importance Performance Analysis
The following Importance Performance Analysis
Matrix:
Figure 1. The Importance-Performance Analysis (IPA)
matrix (Hosseini & Bideh, 2013).
Based on the picture above are:
a. Quadrant 1 labeled attribute is very important
for customers, and the company provides a
high level of performance. Thus the attributes
in this quadrant are referred to as the main
strengths and opportunities to achieve or
sustain the competitive advantage of the firm.
b. Quadrant 2 labeled attributes are not important
to the customer, but the company provides a
high level. In this case, companies should look
for incoming resources for attributes in the
inner quadrant.
c. Quadrant 3 contains attributes with low
purpose and serves as a minor minor. So in this
quadrant there are not many priorities for
improvement.
d. Quadrant 4 attribute is very important for the
customer but the performance level is quite
low. These attributes are called major
weaknesses that require immediate attention to
improvement.
3 METHODOLOGY
3.1 Type of Research
This type of research is qualitative and descriptive
research. Descriptive method is the fact finding with
the right interpretation.
Taylor, J. C. 2000, Knowles,
M.S. (1975) .
Descriptive research studies the problems
of society, as well as procedures applicable in certain
communities and situations, including on
relationships, activities, attitudes, views, and ongoing
processes as well as the effects of a phenomenon
3.2 Operational Definition
The operational definitions of this research are:
1. Potential is internal condition owned by
company, that is excess or strength (strength)
owned by insurance company in Indonesia.
2. Constraints are internal conditions that exist
within the company, namely weaknesses that
can hamper insurance companies in Indonesia
in running insurance business.
3. Opportunities are the external conditions of the
company, namely the opportunities that
insurance companies can take in Indonesia to
assist in achieving business objectives.
4. Threat is the external condition of the company,
that is the existence of things from outside the
company that can hinder the insurance company
in Indonesia in running its business.
Increasing the Quantity of the Actuaries in Indonesia with E-learning
127
5. Strategy is the various forms of ways or policies
undertaken by the insurance company to
achieve business objectives by using existing
potential and minimize the constraints
.
3.3 Data Types and Data Sources
The types and sources of data used in this study are:
1. Primary Data. Primary data is data obtained
from first source either individual or group
become object in this research. Primary data
is obtained through direct interview with
several actuaries.
2. Secondary Data. This data is data that has
been available and obtained from various
literature and references such as journals,
articles, to internet sites. Secondary data was
obtained from literature studies, such as
journal articles, mass media, the official web
of institutions, etc. The data obtained
contains information relating to the issues
discussed in this study.
3.4 Data Collection Methods
Data collection methods used in this study are:
1. Interviews, data collection techniques
conducted by asking questions to
respondents or resource persons, namely
Actuaries in insurance companies.
Questions raised are related issues in
research, namely on the potential and
constraints in the development of insurance
in Indonesia.
2. Documentation, conducted by collecting
data on Insurance. The data collected is
insurance development data in some
developing countries. In addition, also
search, review and review information or
data sourced from books, journals and the
internet on insurance to find the rationale
and problem solving.
3.5 Technical Analysis
Data analysis technique used in this research is
qualitative descriptive analysis technique. Qualitative
descriptive technique is the processing of qualitative
data that has been obtained through a simple
representation of facts / characteristics. This study
used SWOT analysis.
Schank, R.C. (2002). Sharma, S.
(2002)
Based SWOT analysis is the systematic
identification of various factors to formulate a
strategy
(Silong, et al.,2001). The strategic decision-
making process is always related to development,
mission, goals, strategy and policy. Then from the
SWOT analysis results, can be seen how the potential
and constraints of Cyber insurance development in
Indonesia. These potentials include strengths and
opportunities, while constraints include weaknesses
and threats. Data analysis tools used are Internal
Factor Evaluation Matrix, External Factor Evaluation
Matrix, SWOT diagram, and SWOT Matrix.The form
should be completed and signed by one author on
behalf of all the other authors.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The company takes advantage of internal conditions
and external conditions in the development of the
company. A company cannot be separated from
understanding in the internal and external
environment of the company.
Robinson, B. (2001). on
the results of interviews conducted with several
actuaries and leaders of the company to review the
importance of the actuarial function of insurance
companies along with the study of literature,
identifying authors included in internal factors and
external factors. The following table identifies the
results of internal factors and external factors:
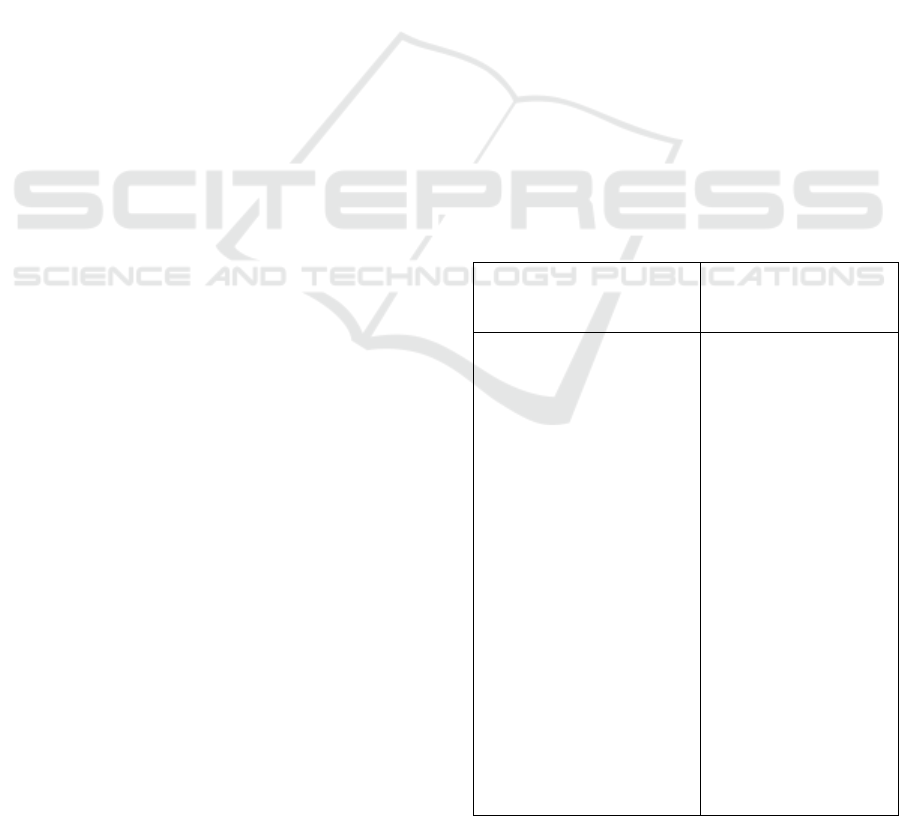
Table 1.
Internal
Environmental Analysis
External
Environmental
Analysis
1. E-learning Media: Web-
based and Android / iOS
2. The cost of
implementing E-learning
was still expensive
3. Promotion of E-learning:
socialization to
universities or
companies / electronic
media
4. E-learning Facilities:
Online modules,
questions and
discussion, exam
simulation
5. Competent human
resources needs:
6. Adequate human
resources involved:
Teachers
(competencies), IT
supports,
Administrators, etc.
7. Market Segments;
Students Backgrounds
(educations and regions)
1. Technological
Development: Students in
various regions (the
Internet has been reached
everywhere), but the
disruptions of internet
connection can inhibit the
learning process
2. Government Policy:
The obligation of insurance
companies and financial
sector to have at least one
actuary
3. Competition: Appear
the similar learning
methods
4. Students' interest was
high because a high of
actuaries’ salary
ICVHE 2019 - The International Conference of Vocational Higher Education (ICVHE) “Empowering Human Capital Towards Sustainable
4.0 Industry”
128
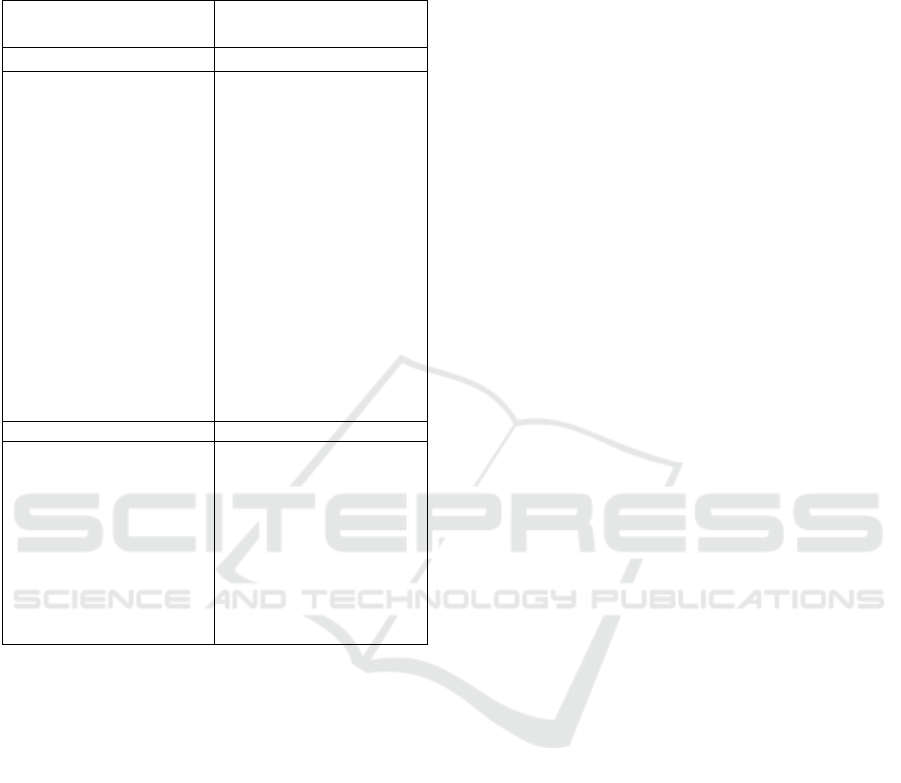
From external and internal factors above, then
obtained the SWOT matrix analysis as follows:
Table 2.
Internal
Factors
External
Factors
Strength Opportunity
1. The media used were
almost owned by
everyone (easily
accessible and not a
luxury thing)
2. The cost of e-learning was
affordable by students
3. Students Background
from various fields of
competence
4. Students became
independent, active, and
have initiative individuals
5. Students can learn
anywhere and anytime
6. Teachers and students can
use modules that were
structured and scheduled
1. The needs of actuary
numbers was increasing
2. There was a program of
1000 actuaries by
Financial Services
Authority (OJK)
3. There was no Actuarial
science E-learning in
Indonesia
4. Students’ interest to be an
actuary was increasing
because it’s salary
5. Students can come from
various regions
6. Students spend the low
costs to be an actuary
Weakness Threat
1. Requires a high cost for
organizers to make the
good facilities.
2. Lack of human resources
who have the internet
skills
3. The learning and teaching
process more inclined to
training than education
1. Internet connection that
has a problem can hamper
the learning process
5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of SWOT analysis conducted, it
can be obtained that: Based on the government policy
that existence a program of 1000 actuaries and
increasing of students interest to be an actuary, e-
learning can be a good method to increase the
numbers of actuary in Indonesia.; E-learning method
can make the students study independently wherever
and whenever. Students also can do exam simulation
in order to increase competencies opportunity of
passing the exam.; Actuary candidates (students)
come from various region because the accessibility pf
internet, various competencies backgrounds because
e learning don’t require the linearity of competency
(actuarial science, statistics, and mathematics), and
the backgrounds of economics capability because the
cost of e-learning is achieved by students.;Required
the competent and technology adaptability human
resource in order to the e-learning process can works.
REFERENCES
Moore, M.G. (1973). Toward a theory of independent
learning and teaching. Journal of Higher Education, 44,
66-79.
Moore, M.G. & Thompson, M.M. (1990). The effects of
distance learning: A summary of the literature.
Research Monograph Number 2. University Park, PA: The
Pennsylvania State University, American Center for the
Study of Distance Education. (ED 330 321).
Nielsen, H.D., Tatto, T., Djalil, A., & Kularatne, N. (2007).
The cost-effectiveness of teacher training.
Verduin, J.R. & Clark, T.A. (1991). Distance education:
The foundations of effective practice. San Francisco:
Jossey-Bass Publishers.
Garrison, D. R. 1993. Quality and access in distance
education:Theoretical considerations. Dalam D.
Keegan (Ed.),Theoretical principles of distance
education, pp. 9-21. NewYork: Routledge
Taylor, J. C. 2000. New millennium distance education.
Knowles, M.S. (1975). Self directed learning, a guide for
leaners and teachers. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Hall
Regents..
Porter, L.R. (1997). Creating the virtual classroom:
distance learning with the internet. New York:John
Wiley & Sons .
Robinson, B. (2001). Innovation in open and distance
learning: some lessons from experience and research. In
Lockwood, F., & Gooley, A (eds). Innovation in open
& distance learning: Successful development of online
and web-based learning. London: Kogan Page Limited.
Schank, R.C. (2002). Designing world-class e-Learning.
New York: McGraw-Hill.
Sharma, S. (2002). Modern methods of life-long learning
and distance education. New Delhi: Sarup and Sons.
Silong, A. D., Ibrahim, D. Z., & Saham, B. A. (2001).
Perception of working adults toward online learning in
a virtual university. Makalah disajikan pada the
International 7th Symposium on Open and Distance
Learning, 12-14 Nopember 2001, Yogyakarta,
Indonesia.
Increasing the Quantity of the Actuaries in Indonesia with E-learning
129
