
Characterization of Physical Properties and Morphological
Ruberized Asphalt Paving Blocks based on Bituminous Coal and
Concentrated Natural Rubber Latex
Riri Indah Nitami Harahap
1
, Tamrin
2*
and Darwin Yunus Nasution
2
1
Postgraduate Chemistry Study Programme, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia
2
Department of Chemistry, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia
Keywords: Paving Block, Concentrated Natural Rubber Latex (CNRL), Bituminous Coal, Ruberized Asphalt,
Morphological.
Abstract: This research about the characterization physical properties and morphological ruberized asphalt paving block
using asphalt as a binder replacement and utilization of natural resources such as bituminous coal and natural
rubber latex concentrate (NRLC). This research aims to determine the optimum value of physical properties
and learn the effect of morphological control on the paving block that have been prepared. Morphological
control with varied the composition asphalt, bituminous coal, and natural rubber latex concentrate that mixed
using by an internal mixer with addition of aggregates and additive agents such as dicumyl peroxide as an
initiator and divinylbenzene as a crosslinker. After the mixing process, then the mixture on shaping/forming
process. The result of physical properties obtained optimum value at the variation of composition asphalt :
bituminous coal : natural rubber latex concentrate (70:25:5)(Paving Block E). The percentage of water
absorption is 0.85 % and compressive strenght is 154.23 Kgf (0.605 Mpa). At this optimum variation of
composition has been characterized the morphological using by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) which
is the result of surface morphology showed the mixture compactly and most effective homogenity of the
mixture.
1 INTRODUCTION
Infrastructure is a benchmark for developing a
country. Infrastructure development in developing
countries like Indonesia is urgently needed. One of
them is infrastructure in the field of road pavement.
The road pavement material used is paving block.
Interest in the use of paving blocks because it can
be applied to many areas such as parking lots,
residential streets, home yards, parks, industrial areas,
and other open spaces. Increased use of paving blocks
due to paving blocks including environmentally
friendly construction, good water absorption ability,
faster installation, lower cost, diverse shades and
colors so as to increase aesthetic value (Hastuty et al.,
2018). Based on ([Standar Nasional Indonesia] SNI-
03-0691-1996, n.d.), the constituent components of
paving blocks are made from a mixture of portland
cement or other adhesives with aggregates using or
without the addition of other materials which do not
reduce the quality of paving blocks.
Research on paving blocks has been carried out
by adding or replacing components in paving blocks.
The use of rice husk ash and lime as a partial
substitution of cement, addition of coconut shell, use
of spent catalyst waste. However, the physical
properties produced on the ability of water absorption
do not meet the water absorption standards on paving
blocks. The chemical composition of the constituent
of paving blocks also influences the characteristics of
paving blocks, such as physical, mechanical, and
morphological characteristics. One of the efforts
made to improve these characteristics is polymer
modification.
Asphalt can also be used as a substitute for
cement. Asphalt contains a long hydrocarbon chain,
where the longer the hydrocarbon chain content will
affect its polarity, so that the paving block produced
physical properties on good water absorption ability,
the use of cold mild catalyst waste results in better
water absorption. The characteristics of binder
substitutes such as asphalt can be modified with other
polymer materials. Asphalt modification can also be
30
Indah Nitami Harahap, R., Tamrin, . and Yunus Nasution, D.
Characterization of Physical Properties and Morphological Ruberized Asphalt Paving Blocks based on Bituminous Coal and Concentrated Natural Rubber Latex.
DOI: 10.5220/0010132700002775
In Proceedings of the 1st International MIPAnet Conference on Science and Mathematics (IMC-SciMath 2019), pages 30-36
ISBN: 978-989-758-556-2
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

done by using natural binders (natural binders) such
as pine resin (Yuniarti, 2015).
Rubber plants have been supporting the
Indonesian economy, since a few decades ago, but the
performance of rubber is less than optimal. Indonesia
is one of the countries with the largest rubber
plantations in the world, but its productivity is still far
behind that of other natural rubber producing
countries. Natural rubber is an efficient polymer
added to asphalt. Asphalt modification has been done
by Kartika (2017) using fresh natural latex rubber.
Modification of asphalt has been carried out with
commercial liquid bitumen and (Kartika, 2017).
Bitumen can be classified into liquid bitumen and
solid bitumen. The source of solid bitumen is coal.
Coal is an option that needs to be developed as
much as possible, because coal is a natural resource
whose availability and distribution is very abundant
in Indonesia. One rank of coal is bitumen coal. The
rank of coal which is widely spread in Indonesia is
bitumen coal. Bitumen coal is an organic and
inorganic macromolecule. The chemical composition
of bitumen coal contains the main elements namely
C, H, O, N, S, P. Based on ([WCI] World Coal
Institute, 2005) data, coal quality depends on the
hydrocarbon group (Rajan et al., 2017). Bitumen has
been applied as adhesives, sealants, waterproof
agents, and binders on road pavement construction
materials (Zhu et al., 2014).
Modification of bitumen with other polymers is
the incorporation of polymers in bitumen by
mechanical mixing or chemical reaction. Fresh
natural latex with a combination of liquid bitumen
(Kartika, 2017) has an effect on increasing the
characteristics of asphalt. Fresh natural latex contains
60% water and 40% rubber (Suksup et al., 2017). The
water content also influences the characteristics of
paving blocks. To optimize the performance of
natural rubber can be done with concentration and
centrifugation to produce concentrated latex with
more rubber content that is 60% and reduce water
content to 40% (Suksup et al., 2017). In addition, the
performance of natural rubber can be improved by
chemical modification by grafting techniques using a
compatible agent such as a crosslinker such as divinyl
benzene (Ritonga et al., 2018). Thus, it can increase
the stability and density of asphalt mixes (NorFazira
et al., 2016).
In the mixture of asphalt with aggregate, bitumen,
concentrated latex will only occur physical bonds.
The use of dicumil peroxide (DCP) as an initiator and
divinyl benzene (DVB) as a crosslinker in the
mixture, the polymers used in asphalt, concentrated
latex or bitumen will be radical. This radicalism
encourages chemical bonds between concentrated
latex, asphalt, bitumen ie covalent bonds.
Based on the description, researcher interest in
research about the Characterization of Physical
Properties and Morphological Ruberized Asphalt
Paving Block Based on Bituminous Coal and
Concentrated Natural Rubber Latex (CNRL) with the
addition of dicumyl peroxide (DCP) initiators and
divinyl benzene crosslinker (DVB).
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Materials
Bituminous coal from PT. Amber and Coal Sumatra,
Asphalt from Iran Type Grade 60/70, Concentrated
latex from PT. Bridgestone Sumatera Rubber Estate,
Divinyl benzene (DVB) from Sigma-Aldrich,
Dikumil Peroxide (DCP) from Sigma-Aldrich,
Aggregate from Pebble Stone from CV. Setia Jaya,
Fine Sand Aggregate from CV. Setia Jaya
2.2 Preparation of Paving Blocks
5 ml of concentrated latex was put into a 50 ml glass
beaker and heated at 70 °C. Then put 70 ml of asphalt
into the beaker while heated. Then both of them were
mixed while being heated at 140 °C for 15 minutes,
then added 25 grams of solid bitumen while stirring.
The mixture was added 0.9 ml DVB and stirred for
10 minutes. 300 grams of sand and 50 grams of gravel
were added to the mixture while still stirring, then
added 0.9 grams of DCP while still stirring for 10
minutes under the same heating. The mixture is then
put into a cube mold. Then the molds are put into a
hydrolyc press which has been set at 140 °C for 30
minutes, then cooled to room temperature.
Table 1: Variation Asphalt, Bituminous Coal, and CNRL.
Paving
block
Asphalt
(mL)
Bituminous
Coal
(gram)
CNRL
(mL)
A 70 5 25
B 70 10 20
C 70 15 15
D 70 20 10
E 70 25 5
F 80 0 20
G 80 20 0
Characterization of Physical Properties and Morphological Ruberized Asphalt Paving Blocks based on Bituminous Coal and Concentrated
Natural Rubber Latex
31

2.3 Characterization
2.3.1 Water Absorption Test
Water absorption test to find out the amount of water
absorption by polymer asphalt that has been made
refer to ASTM C C140 / C140M-15 by weighing and
recording it as a dry mass (Mk). Then soak the sample
in water for 24 hours then lift the sample and the
surface is dried with a tissue, then weigh the sample
weight after soaking and recorded as a saturated mass
(Mj) and calculate the value of water absorption test
using equation:
% 𝑊𝐴 =
𝑀𝑗 − 𝑀𝑘
𝑀𝑘
𝑥 100 %
2.3.2 Compressive Strength Test
Analysis of mechanical properties by compressive
strength test The tool used in the compressive test is
GOTECH AI - 7000M with a capacity of 2000 Kg.f
and refers to ASTM D-790 / C-293, with a sample
testing procedure in the form of a cube with a 5 cm
side in accordance with ASTM C-348-2002 by
placing a sample placed on a compressive testing
machine. Loading is given until the test object
collapses, ie when the maximum load is working. The
maximum load is recorded as P max. Then calculate
the compressive strength test value using equation
then the value of the compressive strength test of
polymer asphalt can be determined by using the
equation :
𝑃=
𝑀𝑎𝑥 𝐿𝑜𝑎𝑑
𝐴𝑜
2.3.3 Surface Morphology Analysis by using
SEM
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) is used to
analyze the surface of an object (solid) to find out
topographic, morphological, and composition
information of a sample. The instrument used was
SEM Hitachi TM-3000 with SEM specifications
including a resolution of 1-10 nm. SEM analysis was
conducted at the Integrated Research and Testing
Laboratory, Universitas Sumatera Utara.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
3.1 Results and Analysis of Water
Absorption Test
Water absorption analysis is carried out to determine
the capacity of paving block material produced in
absorbing water. This analysis refers to ASTM C140
/ C140M-15. The test is done by immersing all
samples in water for 24 hours. This test is carried out
on samples with different component variations to
find out the percentage content of the combination
components in an ideal mixture. The relationship
between the percentage of water absorption with
variations in asphalt components, solid bitumen, and
concentrated latex is presented following Table 2 and
Figure 1.
Table 2: Percentage water absorbtion paving block.
Pavin
g
Bloc
k
% WA
A1.56
B1.46
C1.27
D1.21
E0.85
F2.75
G2.30
In table 2 shows the minimum percentage of water
absorption value that is in samples with variations of
asphalt components: solid bitumen: concentrated
latex (70: 25: 5) which is 0.85%. It can also be seen
in the graph that with more levels of addition of solid
bitumen tends to reduce the value of water
absorption. This is because solid bitumens are
resistant to water (McNally, 2011). whereas in
samples without the addition of solid bitumen, a
higher water absorption value of 2.75% is produced.
This explains that the addition of solid bitumen to a
mixture of asphalt and concentrated latex can reduce
the percentage value of water absorption.
Inversely proportional to the increasing levels of
concentrated latex in a mixture of asphalt and solid
bitumen. Increased concentrated latex levels tend to
increase the ability of water absorption. In this
research, the percentage of absorption was 1.56% with
the addition of rubber at the most, 25%. The ability of
water absorption increases with increasing levels of
concentrated latex in the mixture (Kartika, 2017) so
that the water content of concentrated latex binds
water from the sample marinade. The minimum
percentage of water absorption in this study did not
differ significantly from the results reported by
IMC-SciMath 2019 - The International MIPAnet Conference on Science and Mathematics (IMC-SciMath)
32

Kartika (2017) using liquid bitumen, which is about
0.8%.
Based on this, variations with concentrated latex
levels will increase the mixing homogeneity to be less
effective. However, water absorption is increasing
without the addition of concentrated latex in the
material mixture which is 2.30%. This explains that
the added rubber content also affects the percentage
of water absorption.
The percentage of water absorption from paving
blocks produced meets the standards of SNI 03-0691-
1996. Based on this value, the resulting paving blocks
meet the quality requirements for all areas with a
maximum percent of each% WA, namely: 3% of the
road, 6% of the parking area, 8% of pedestrians, and
10% of parks and other uses.
3.2 Results and Analysis of
Compressive Strength Test
Compressive strength is the main mechanical
characteristic of road pavement material. This test
aims to determine the maximum compressive
strength characteristics that can be accepted by
paving block samples. This test refers to ASTM D790
/ C293. Compressive strength analysis has been
carried out on all samples using GOTECH AI-7000M
by giving a load of 20 KN or 2039.4 Kgf (1 KN = 101
Kgf). The results of the test are obtained in the form
of graphic output and max load data
Calculation of compressive strength value is
obtained from the price of P substituted into equation
3.2, so that the compressive strength value is obtained
in units of Kgf / mm2, then converted into units of
MPa (1 Kgf / mm2 = 9.81 MPa).
The variation of the ideal composition in the
paving block based on the compressive strength test
was obtained in the variation of the composition of
asphalt: solid bitumen: concentrated latex (70: 25: 5)
with a compressive strength value of 0.605 MPa. In
the mixture without the presence of solid bitumen, the
compressive strength value obtained is 0.085 MPa,
while without the addition of rubber the compressive
strength value of 0.103 MPa is obtained. Based on the
results of the data obtained, the addition of a
combination of concentrated latex and bitumen can
increase the strength of asphalt. Addition of polymer
materials around 2-6% is enough to improve the
quality of the asphalt mixture (Polacco & Berlincioni,
2005).
Figure 1: Percentage Value of Water Absorption for Asphalt, Bitumenous coal and Latex Variations.
The relationship between compressive strength
values and variations in the composition of asphalt
mixes: solid bitumen: concentrated latex is presented
in graphical form in the following Table 3 and Figure
2.
Based on the diagram in Figure 2. can be seen an
increase in compressive strength after the addition of
solid bitumen and concentrated latex. This shows that
in the asphalt mixing: solid bitumen: concentrated
latex (70: 25: 5), the dispersion of latex in the asphalt
and bitumen mixture is more homogeneous. The
more
addition of solid bitumen, which is as much as
Table 3: Compressive Strenght Value of Paving Block.
Paving Blocks
Compressive Strenght
(
MPa
)
A 0.180
B 0.222
C 0.299
D 0.452
E 0.605
F 0.085
G 0.103
Characterization of Physical Properties and Morphological Ruberized Asphalt Paving Blocks based on Bituminous Coal and Concentrated
Natural Rubber Latex
33

25%, shows an increase in compressive strength. This
works as a synergy with the addition of only 5% latex.
This is consistent with Azliandry (2011) reported,
where the highest mechanical properties were
obtained in asphalt mixtures with the addition of 5%
SIR 20 (95:5). This is because the dispersion of
rubber in asphalt is more homogeneous and the role
of rubber in the mixture slows the rate of permanent
deformation. DaSilva et al. (2015) also produced
paving blocks with cement binder and crumb rubber
obtained data on the addition of crumb rubber with
the least amount of content obtained the maximum
compressive strength in the resulting paving block. In
this variation crumb rubber is sufficient to be
distributed evenly throughout the matrix. Loading
strength is also distributed evenly, resulting in
increased compressive strength, but when there is no
addition of crumb rubber, the compressive strength
produced also tends to decrease. With increasing
levels of natural rubber in the mixture will reduce the
mechanical properties of the mixture. This is because
the elastomeric phase remains as dispersed particles,
also resulting in agglomeration and interaction of the
particles of rubber so that the stiffness in the mixture
will decrease (Ismail & Suryadiansyah, 2002).
In a mixture, the attachment of a molecule to the
rubber chain cannot prevent the rate of fracture
quickly against the applied pressure. Conversely, the
lower level of rubber tends to increase its mechanical
properties, because if a smaller size and more uniform
dispersion in the dispersed phase will contribute to
improving the mechanical properties of the mixture
(Ismail & Suryadiansyah, 2002).
The results obtained in this study are greater when
compared to studies conducted (Kartika, 2017),
where the mixture of asphalt and fresh latex using
liquid bitumen without crosslinkers. In addition to the
higher rubber content factor in concentrated latex
when compared with fresh latex, the thing that
influences this is the presence of a crosslinker will
limit the flow and mobility of the mixture which
allows the particles to reach higher pressures, when
the same will also give mechanical strength to the
particles (Ismail & Suryadiansyah, 2002). So that the
use of solid bitumen with concentrated latex using
crosslinkers is more effective.
Based on the results of the compressive strength
values obtained in the material with the optimum
combination between asphalt, solid bitumen, and
concentrated latex, it shows that the compressive
strength of the resulting paving blocks has not been
effective with the standard compressive strength
values based on SNI 03-0691-1996. When viewed
from its polarity, the components used such as
bitumen have an excellent combination of
compositions that are both adhesives and water
resistant (McNally, 2011) and concentrated latex
which are nonpolar but still contain 40% water
(Suksup et al., 2017) which when mixed will produce
a mixture that is misible or can be mixed but the
compatibility is less effective so that it will affect the
mechanical properties obtained (Ismail &
Suryadiansyah, 2002).
Figure 2: Graph of Compressive Values with Variations in
Asphalt, Solid Bitumen and Concentrated Latex Mixture.
3.3 Results of Surface Morphology by
using SEM
In this study, an analysis using SEM was conducted
to determine the surface morphology of the resulting
paving block sample material. Objects that are
characterized are the results of asphalt mixing: solid
bitumen: concentrated latex with variations (70: 25:
5), (70: 5: 25), and control samples namely asphalt:
concentrated latex (80: 20) without the presence of
solid bitumen. SEM analysis is performed after
compressive strength testing. The results of the
characterization with SEM in the form of
micrographs. SEM analysis is carried out at
magnification 100 times which can be seen in the
figure 3.
The results of SEM micrographs show a
significant difference in surface morphology between
the mixture composition of the resulting paving block
material. Figure 3 a. is a control sample without the
addition of solid bitumen with a variation of asphalt:
concentrated latex (80: 20). In micrographs, it can be
seen that there are large piles which do not bind to
one another due to the lack of homogeneity from
mixing asphalt and concentrated latex. In all areas are
scattered small particles attached, which are small
particles which are aggregates of sand. This shows
that the sand aggregate is attached to asphalt and
concentrated latex.
IMC-SciMath 2019 - The International MIPAnet Conference on Science and Mathematics (IMC-SciMath)
34
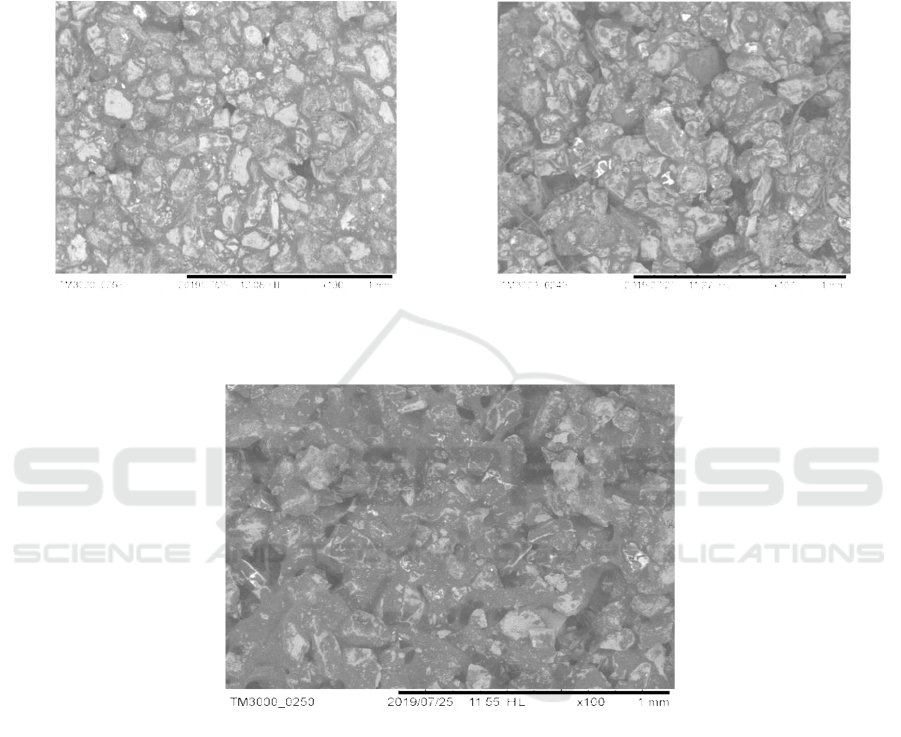
Figure 3 b. is a SEM micrograph of the sample
with the addition of solid bitumen with asphalt
variation: solid bitumen: concentrated latex (70: 5:
25). On the micrograph there is a very significant
difference with the micrograph in Figure 3 a, where
there are large piles that were previously not
homogeneous,
SEM micrograph in figure 4. is the result of a
sample with variations of asphalt: solid bitumen:
concentrated latex (70: 25: 5). Based on SEM
micrographs in this variation produce
(a)
(b)
Figure 3: Micrographs of SEM Analysis Results in Paving Blocks (a) Paving Block F (b) Paving Block A.
Figure 4: Micrographs of SEM Analysis Results in Paving Block E.
mixing with the most effective homogeneity between
one component with another component. Aggregates
which previously still look like in Figures 3 a and 3 b,
are no longer visible in Figure 4, where aggregates are
more bound to all components.
Surface structure density in asphalt variation:
solid bitumen: concentrated latex (70: 25: 5) is very
good compared to the structure density in Figures 3 a
and 3 b. The more even distribution of components in
micrographs indicates effective homogeneity
(Hardeli et al., 2018). This is due to the influence of
the addition of concentrated latex composition.
Addition of concentrated latex with less composition
results in a better surface structure compared to more
addition of concentrated latex composition, because
concentrated latex still contains water, so the
homogeneity of mixing concentrated latex with
bitumen and solid bitumen is less effective. Thus, the
dispersion of rubber in asphalt and with solid bitumen
is more homogeneous in this optimum variation,
binds to each other and plays a role in improving the
morphological properties of paving blocks with
asphalt as a binding.
Characterization of Physical Properties and Morphological Ruberized Asphalt Paving Blocks based on Bituminous Coal and Concentrated
Natural Rubber Latex
35

4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of the research and discussion, it
can be concluded that: Paving blocks based on
polymeric materials can be made by mixing asphalt
as a substitute for binder and solid bitumen and
concentrated latex as an adhesive (adhesive) with the
addition of dicumyl peroxide as an initiator and
divinyl benzene as a crosslinker using sand and gravel
aggregates. Utilization of asphalt, solid bitumen, and
concentrated latex can improve the physical and
mechanical properties of the resulting paving block
with an optimum ratio of asphalt: solid bitumen:
concentrated latex (70: 25: 5) (Paving Block E).
Physical properties of the water absorbing capacity is
0.85%. The mechanical properties of compressive
strength are 0.605 MPa. Morphological
characteristics by using SEM show differences in
surface structure by comparison of the composition of
each component used. At the optimum ratio, mixing
is produced with the homogeneity of the most
effective surface structures.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank to Mr. Prof. Dr.
Tamrin, M.Sc as advisor I and Mr. Dr. Darwin Yunus
Nasution, MS as advisor II in this research.
REFERENCES
[Standar Nasional Indonesia] SNI-03-0691-1996. (n.d.).
Persyaratan Mutu Bata Beton (Paving Block). Badan
Standarisasi Nasional.
[WCI] World Coal Institute. (2005). Sumber Daya Batu
Bara Tinjauan Lengkap Mengenai Batu Bara. World
Coal Institute.
Azliandry, H. (2011). Pemanfaatan Karet SIR-20 Sebagai
Bahan Aditif Dalam Pembuatan Aspal Polimer Dengan
Adanya Dikumil Peroksida Dan Divenil Benzena
Menggunakan Proses Ekstruksi. Universitas Sumatera
Utara.
DaSilva, F. M., Barbosa, L. A., Lintz, R. C., & Jacintho, A.
(2015). Investigation on the Properties of Concrete
Tactile Paving Blocks Made with Recycled Tire
Rubber. Construction and Building Materials, 91, 71–
79.
Hardeli, H., Sanjaya, H., Resikarnila, R., & Nitami, R.
(2018). Solar Cell Polymer Based Active Ingredients
PPV and PCBM. IOP Conference Series: Materials
Science and Engineering, 335, 1–8.
Hastuty, I. P., Sembiring, I. S., & Nursyamsi. (2018).
Comparison of Compressive Strength of Paving Block
with a Mixture of Sinabung Ash and Paving Block with
a Mixture of Lime. IOP Conf. Series: Materials Science
and Engineering, 309.
Ismail, H., & Suryadiansyah. (2002). Thermoplastic
elastomers based on polypropylene/natural rubber and
polypropylene/recycle rubber blends. Polymer Testing,
21(4), 389–395.
https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/S0142-
9418(01)00101-5
Kartika, Y. (2017). Modifikasi Resipren dan Bitumen dalam
Peningkatan Kekuatan Aspal. Universitas Sumatera
Utara.
McNally, T. (2011). Polymer Modified Bitumen. Properties
and Characterisation. Woodhead Publishing.
NorFazira, NorHidayah, Jaya, R. P., Aida, M., Zurairahetty,
N., & Mahmud, M. Z. H. (2016). An Overview On
Natural Rubber Application For Asphalt Modification.
International Journal of Agriculture, Forestry and
Plantation, 2, 212–218.
Polacco, G., & Berlincioni, S. (2005). Asphalt Modification
with Different PolyethyleneBased Polymer. European
Polymer Journal, 41, 2831.
Rajan, S., Sutton, M. A., Oseli, A., Emri, I., & Matta, F.
(2017). Linear Viscoelastic Creep Compliance and
Retardation Spectra Of Bitumen Impregnated
Fiberglass Mat And Polymer Modified Bitumen.
Construction and Building Materials, 155, 664–679.
https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2
017.08.030
Ritonga, A. H., Aritonang, B., & Zai, L. I. (2018).
Modifikasi Kopolimer Karet Alam Siklis Grafting
Asam Oleat Menggunakan Inisiator Benzoil Peroksida
dan Bahan Pengisi Bentonit-Cetil Trimetil Amonium
Bromida. Jurnal Kimia Mulawarman, 16(1), 42–48.
Suksup, R., Imkaew, C., & Smitthipong, W. (2017). Cream
concentrated latex for foam rubber products. IOP
Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering
,
272.
Yuniarti, R. (2015). Modifikasi Aspal dengan Getah Pinus
dan Fly Ash untuk Menghasilkan Bio-Aspal. Jurnal
Sains Teknologi Dan Lingkungan, 1(2).
Zhu, J., Birgisson, B., & Kringos, N. (2014). Polymer
Modification of Bitumen: Advances and Challenges.
European Polymer Journal, 54(1), 18–38.
IMC-SciMath 2019 - The International MIPAnet Conference on Science and Mathematics (IMC-SciMath)
36
