
Resilience of Chronic Renal Failure Patients Undergoing
Hemodialysis in Medan, Indonesia
Cholina Trisa Siregar
1*
, Siti Zahara Nasution
1
, Reni Asmara Ariga
1
, M. Pahala Hanafi Harahap
2
and
Muhammad Taufik
3
1
Faculty of Nursing, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia
2
Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia
3
Faculty of Mathematic and Natural Science, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia
Keywords: Elderly, Hopes, Family Support, Awards, Emotional, Information, Instrumental.
Abstract: Chronic renal failure (CRF) is a failure of kidney function that progresses slowly and can’t recover so the
body is unable to maintain the metabolic, fluid and electrolyte balance in the body. Haemodialysis therapy is
used as one of the renal replacement therapy in CRF patients to prevent dangerous complications that can lead
to death. Patients suffering from chronic renal failure who underwent haemodialysis will face psychological,
financial, physical and social suffering. The patient will experience a meaningless state in which this situation
will lead the patient to the process of seeking meaning in suffering so that there is a need for resilience in the
face of his illness. This study aims to identify the resilience of patients with chronic renal failure who
underwent haemodialysis in Medan. Methods: the population in this study were patients with chronic renal
failure with a sample of 117 people using accidental sampling technique. Data were collected using
questionnaires and analysed by frequency distribution. The result showed that 84 of 117 responders were in
medium resilience (71.8%). Based on the results of the study can be concluded that patients who experience
chronic renal failure in Medan have
1 INTRODUCTION
A hemodialysis is a form of replacement therapy in
patients with kidney failure, both acute and chronic.
Patients suffering from renal failure are assisted with
the aid of a haemodialysis machine that takes over the
kidney function. Patients with renal failure who
undergo haemodialysis therapy, take 12-15 hours to
dialysa each week, or at least 3-4 hours per treatment.
This activity will take place continuously throughout
his/her life (Asiah, 2005).
Charuwanno suggests that the continued use of
haemodialysis therapy throughout his/her life can
lead to feelings of discomfort to the sufferer, increase
stress and affect the quality of life, including
psychological health. (Charuwanno, 2005) Increased
levels of stress experienced by hemodialysis patients
are caused by financial problems due to a decrease in
health conditions, difficulties in maintaining work,
sexual ability to disappear and impotence,
relationships with spouses and fear of death
(Asiah,
2005).
The results of Hanim's study showed that 18 of
the 27 patients undergoing haemodialysis therapy
were in the category of severe stress while 9 patients
were able to adapt to changes in Rantauprapat
hospital. (Hadiningsih, 2014) The condition depends
on how far the ability of the patient in adaptation to
changes that occur. This condition is known as
resilience (Hanim, 2013).
The resilience of patients undergoing
hospitalization is a matter that needs to be assessed to
achieve a rebalance due to the changes that happened.
Feelings of despair and helplessness are often faced
by patients because various treatments cannot help
him/her recover from chronic illness. The state of
severe stress can also arise due to the unpreparedness
of the body to accept the changes and demands of life.
(Hurlock, 2007) Research conducted by Iliescu and
Cotoi said that medical diagnosis and hospital
environment can also affect the patient's
psychological form of depression, anxiety, worry or a
combination of all if the individual is not able to do
resilience (Iliescu, 2013).
132
Trisa Siregar, C., Zahara Nasution, S., Asmara Ariga, R., Pahala Hanafi Harahap, M. and Taufik, M.
Resilience of Chronic Renal Failure Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis in Medan, Indonesia.
DOI: 10.5220/0010137500002775
In Proceedings of the 1st International MIPAnet Conference on Science and Mathematics (IMC-SciMath 2019), pages 132-137
ISBN: 978-989-758-556-2
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
Failure of the resilience process will cause severe
stress for a long time. The response of the body in
response to stress causes the body's energy to increase.
The energy released by the stressor will create a state
of tension that causes discomfort for the patient. The
discomfort that protracted will cause fatigue in the
human body that can lead to death
(Hanim, 2013).
2 METHODS
The research design used in this study is descriptive
that aims to obtain a picture of the resilience of
patients with chronic renal failure who underwent
haemodialysis in Medan. The sample in this research
were 117 people where the sampling technique used
by accidental sampling. This research was conducted
in the haemodialysis installation ward of Dr. Pringadi
Hospital and H. Adam Malik General Hospital in
Medan. The research instrument used was
demographic data and resilience scale consisting of
25 statements adapted from the Resilience Scale (RS)
owned by Wagnild and Young which then modified
by the researchers. Instrument validated by Dr.
Wiwik Sulistyaningsih with V = 0.97 and reliability
value of Cronbach alpha = 0.810 (Morton, 2012).
Data collection was done after getting permission
from the related institution, researcher look for
prospective respondent then explain to prospective
respondents assisted by family about purpose,
benefit, and how to fill questionnaires. After getting
informed consent, respondents are welcome to fill out
questionnaires or read by the researcher and gave the
opportunity to the respondent if there was anything to
ask. After all the data on the questionnaire had been
collected, it is analyzed through several stages,
starting from checking the completeness of the data
(editing), coding, ensuring clean data, and measuring
each respondent's answer by looking for percentage (
tabulating) which is then presented in the form of
frequency distribution tables.
3 RESULTS
The research design used in this study was descriptive
that aimed to obtain a picture of the resilience of
patients with chronic renal failure who underwent
hemodialysis in Medan. The sample in this research
was 117 people which the sampling technique by
using accidental sampling. This research was
conducted in the hemodialysis installation ward of
Dr. Pirngadi Hospital and H. Adam Malik General
Hospital in Medan. The research instrument used was
demographic data and resilience scale consisting of
25 statements adapted from the literature review.
Table 1. shows the majority of male respondents
as many as 64 people (54.7%), age range 41-60 years
as many as 66 people (56.4%), 53 senior high school
education (45.3%), 48 self-employed (41%), the
married status of 108 people (92.3%).
Table 1: Distribution of frequency based on the
characteristics of respondents in Dr. Pirngadi Hospital and
H. Adam Malik General Hospital in Medan (n = 117).
Characteristics of
Res
p
ondents
(f) (%)
Sex
Male 64 54,7
Female 53 45,3
A
g
e
20-40 years 31 26,5
41-60
y
ears 66 56,4
61-80 years 20 17,1
Education
Primary School 17 14,5
Secondar
y
School 21 17,9
High School 53 45,3
Bachelo
r
26 22,2
Occupation
Housewives 43 36,8
Student 3 2,6
Self-em
p
lo
y
e
d
48 41,0
Civil Servant 9 7,7
Retire
d
14 12,0
Marital Status
Sin
g
le 9 7,7
Marrie
d
108 92,3
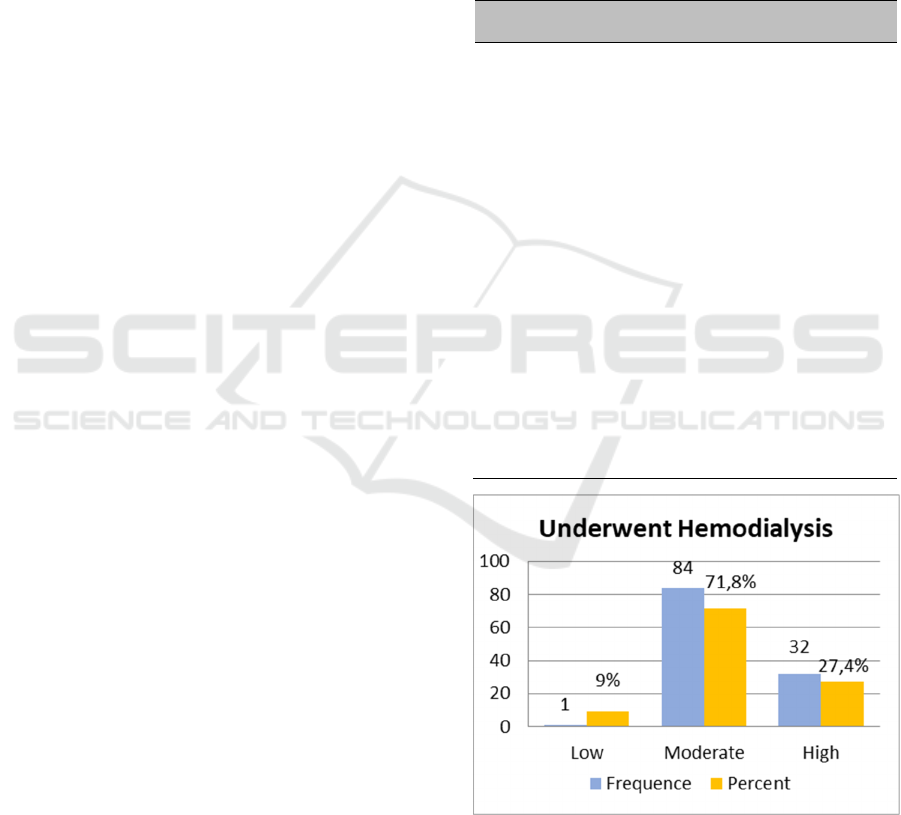
Figure 1: Resilience of respondents.
Figure 1 shows that patients resilient is in
moderate resilience 84 of 117 respondents (71.8%),
32 respondents (27.4%) with high resilience, and 1
respondent (9%) with low resilience.
Resilience of Chronic Renal Failure Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis in Medan, Indonesia
133
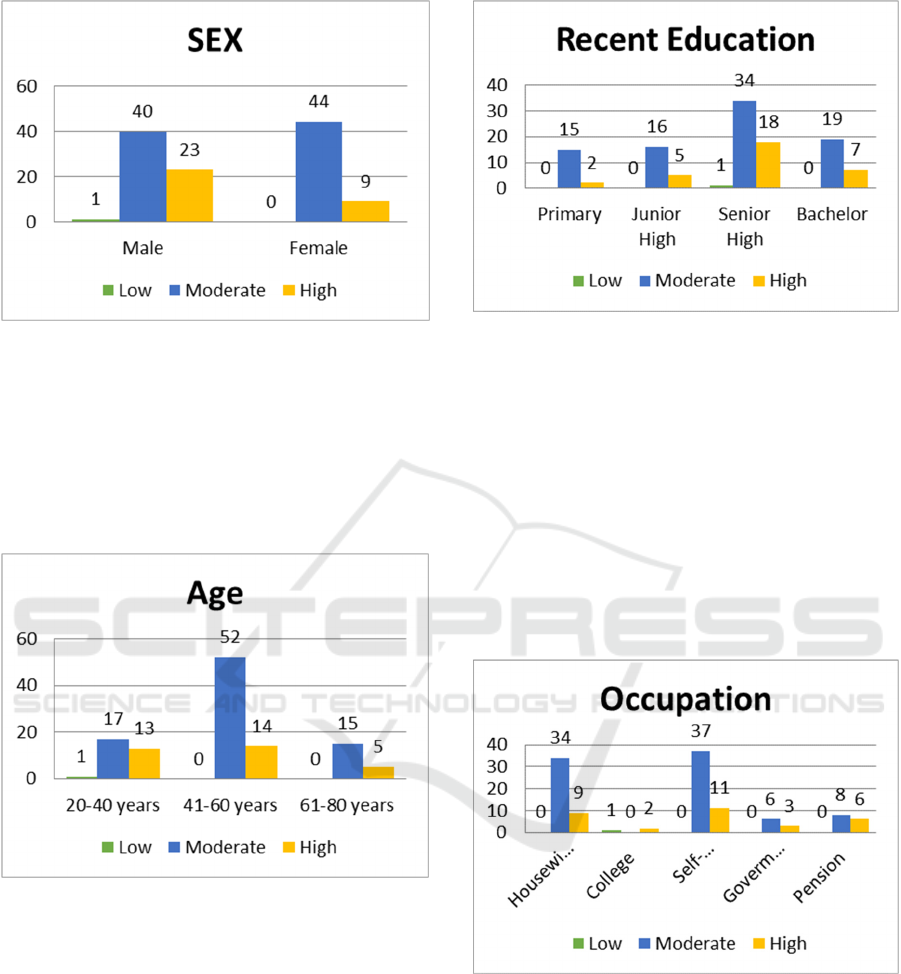
Figure 2: Sex of respondents.
Figure 2. shows that of 64 respondents of the male
sex, 1 respondent has low resilience, 40 respondents
have moderate resilience and 23 respondents have a
high resilience. Of the 53 respondents of the female
sex, there were no respondents had low resilience but
44 respondents had medium resilience and 9
respondents had a high resilience.
Figure 3: Sex of respondents.
Figure 3. showed that from 31 respondents aged
20-40 years there was 1 respondent with low
resilience, 17 respondents with medium resilience,
and 13 respondents with high resilience. A total of 66
respondents aged 41-60 had 14 respondents with
medium resilience, and 52 respondents with high
resilience. A total of 20 respondents aged 61-80 years
there were 15 respondents with medium resilience,
and 5 respondents with high resilience.
Figure 4: Education of respondents
Figure 4. shows that 17 respondents with primary
school education had 15 respondents who had
moderate resilience and 2 respondents had a high
resilience. A total of 21 respondents with secondary
school education had 16 respondents with medium
resilience and 5 respondents have a high resilience.
At the high school education there was 1 respondent
have low resilience, 34 respondents with medium
resilience and 18 respondents had a high resilience.
Bachelor education as many as 26 respondents there
were 19 respondents had moderate resilient and 7
respondents had a high resilience.
Figure 5: Occupation of respondents.
Figure 5 showed that of 43 housewives’
respondents, 34 respondents with moderate resilience
and 9 respondents with high resilience. A total of 3
respondents a college where 1 have low resilience and
2 respondents with high resilience. In the self-
employed work of 48 respondents, there were 37
respondents with a moderate resilience and 11
respondents with high resilience. A total of 9
respondents work as government employees there
were 6 respondents with medium resilience and 3
IMC-SciMath 2019 - The International MIPAnet Conference on Science and Mathematics (IMC-SciMath)
134
respondents with high resilience, while 14
respondents who had been pension there were 8
respondents with moderate resilience and 6
respondents with high resilience.
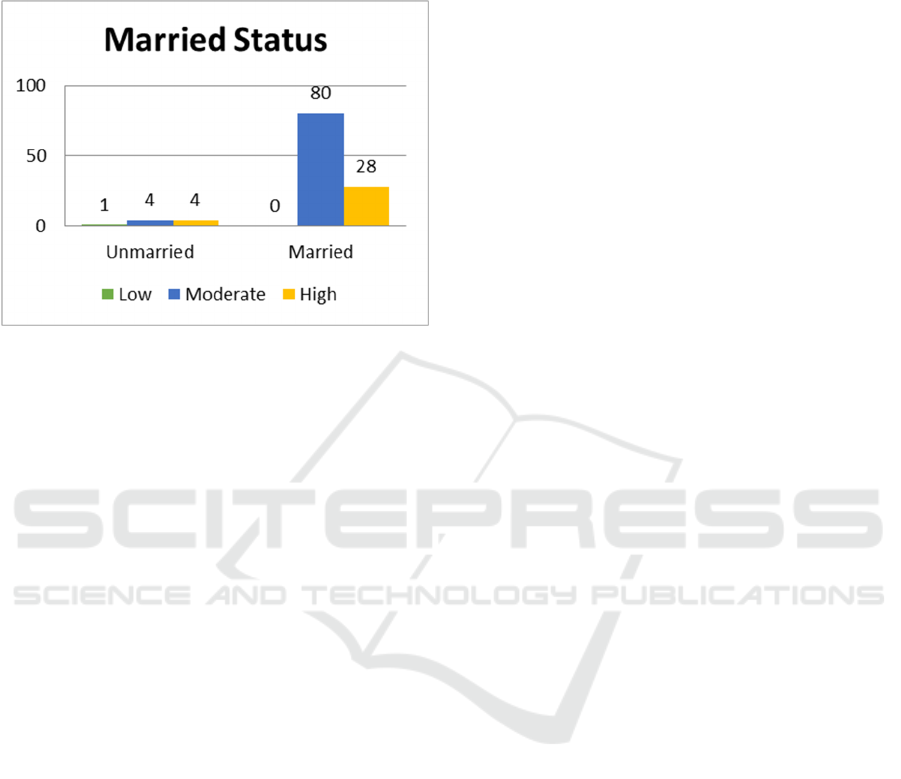
Figure 6: Married status of respondents.
Figure 6 Show that from 9 respondents with
unmarried status there are 1 respondent had low
resilience, 4 respondents with medium resilience and
4 respondents with high resilience. A total of 108
respondents with married status there were 80
respondents with medium resilience and 28
respondents with high resilience.
4 DISCUSSION
The results of this study showed that the resilience
among 84 of 117 respondents of chronic renal failure
who underwent haemodialysis in the city of Medan is
in moderate resilience category with a percentage of
71.8%. Nisa argues that individual in the moderate
resilience category shows that individuals have been
able to adapt and survive in the face of illness but they
have ups and downs and tend to be unstable in attitude
(Mailani, 2015).
Mailani adds that chronic disease patients always
try to use strategies to deal with the disease. They tend
to get closer to God, get attention from family and
spouse, have great hopes for recovery, and accept
sincerely illness as part of God's trial. This can
provide reinforcement and motivation for patients to
stay their life as it once was (Nisa, 2016).
The results of this study obtained data that male
respondents as much as 64 people (54.7%) more
resilient than women as many as 53 people (45.2%).
Purnomo argues that men tend to use problem-
focused coping because men usually use ratio or
logic, otherwise men are sometimes less emotional so
they prefer to directly solve the problems and directly
face the source of stress (Reivich & Shatte, 2002).
Women are more likely to use emotion-focused
coping because they are more emotionally or
emotionally used, so they rarely use logic or ratios
that make women more likely to regulate emotions in
coping with sources of stress or religious settlement
where women feel closer to God than men. Rinaldi
argues that men often use a problem-solving approach
and have an optimistic attitude than women, while
women use patterns of helplessness than men. Men
have confidence in solving problems and believe in
their ability (competence) to master difficult tasks or
situations, more positive than women (Rinaldi, 2010).
High resilient individuals (males) are able to adapt
to a variety of conditions to change circumstances and
are flexible in solving problems, whereas low
resilient individuals (women) have little adaptive
flexibility, are unable to react to changing
circumstances, tend to be stubborn or chaotic when
faced with change or pressure, as well as having
difficulty adjusting after experiencing traumatic
experiences (Rinaldi, 2010).
In this study, the most resilient group was in the
41-60 years age range of 66 people (56.4%). Hurlock
argues that individuals between a 41-60 years age
range are referred to as middle adulthood where at
this time there will be a decline in physical and
psychological ability, but individuals in this period
have been able to determine their problems
adequately both so stable enough and mature
emotionally in the face of life problems, especially
the diseases he suffered. Individuals who have
reached emotional maturity will be able to control
their emotions, can think well by looking at the
problem objectively and able to take attitude and
decision
(Septiyan, 2013). According to Hurlock this
period is a period of financial and social success
including power and prestige. This is also a happy
time for some couples, although at this time the
children do not live with parents anymore, but
actually feel happier because they feel free to reach a
career and spend more free time with a partner than
young adult so that tend to respond to an illness with
an open attitude towards their partner (Septiyan,
2013).
The results of this study obtained data that the
respondent’s education at high school level has more
resilient as many as 53 people (45.2%). According to
Entjang (1985 in Asiah, 2005) argues that the level of
education influences the individual mindset where
high levels of education will broaden his way of
thinking. (Setiasih, 2012) The higher the level of
education the tolerance and control of the stressor will
Resilience of Chronic Renal Failure Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis in Medan, Indonesia
135

be better, other than that individuals who have a
higher education will be better cognitive development
than a lower education so that will have a more
realistic assessment and make the disease is
something that must be faced (Sarafino, 2006).
Widakdo and Besral argue that higher-educated
patients have better skills and knowledge that tend to
be able to overcome life problems, whereas low
education will have low knowledge and ability so that
it has limited in coping pattern to the problems
experienced (Siburian & Wahyuni, 2012).
Reivich & Shatte also add that individuals who
have a broad mindset will have good cognitive
flexibility so that individuals with good cognitive
flexibility will have good resilience as well (Smeltzer
& Bare, 2002).
Work is also very influential on mental health.
The results of this study obtained data that the
majority of respondents who work as self-employed
more resilient as many as 48 people (41%). Setiasih
argues that work is one of the most important aspects
of life for the individual. Work also serves as a source
of identity, a source of autonomy, giving
opportunities to develop skills and creativity, a source
of purpose in life, a source of income and a sense of
security, and the source of other activities, such as
recreation. Individuals who have jobs have a positive
effect on mental health, where the subjective well
being of individuals who have a job is better than
subjective wellbeing individuals who do not have a
job. Individuals who do not have a job indicate that
there is no experience to gain employment benefits
that make individual subjective wellbeing low. If they
do not have a job, they have no income and no access
to psychological experience, whereas by having a job
the individual will have a good psychological
experience
(Tama, 2009).
Judging from the marital status of respondents, as
many as 108 people (92.3%) married status are more
resilient than unmarried. Taylor and Francis argue
that the support of spouse and family is very
influential on the mental health of family members.
Family social support can provide positive results on
health and wellbeing in patients with chronic diseases
(Wagnild & Young, 1993).
Couples 'and families' social support have a
positive or significant influence with high resilience.
Social support is one factor that can make a person
survive in any situation or in psychology is
categorized as a manifestation of resilience. The
higher the social support of spouses and families to
sick family members, the higher the resilience
(Widakdo & Besral, 2013).
5 CONCLUSION
The resilience of chronic renal failure patients
undergoing hemodialysis in Medan City is in
moderate resilience category, meaning that
individuals have been able to adapt and survive in the
face of illness but they have ups and downs and tend
to be unstable in their attitude. The mental health of
the patient facing his illness is also influenced by
several factors which will affect the ability of the
individual to adapt and face the psychosocial effects
he/she experienced, including the factors of gender,
age, education, occupation, and status.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The author would like to thank the Ministry of
Research and Technology Higher Education of the
Republic of Indonesia. This research is financed by
TALENTA Year 2017.
REFERENCES
Asiah, M. D. (2005). Hubungan tingkat pendidikan dengan
pengetahuan kesehatan reproduksi ibu rumah tangga
di desa rukoh di kec. FKIP Unsyiah.
Charuwanno, R. (2005). Meaning of quality of life among
that ESRD patient onmaintenance hemodialysis. The
Catholic University of Amerika.
Hadiningsih. (2014). Hubungan antara dukungan sosial
dengan resiliensi pada remaja di panti asuhan keluarga
yatim muhammadiah surakarta. Muhammadiah
Surakarta.
Hanim, H. (2013). Gambaran tingkat pengetahuan, sikap
dan stres pasien rawat jalan hemodialisa di rumah
sakit umum daerah rantau prapat kabupaten labuhan
batu tahun 2013.
Hurlock. (2007). Hubungan antara tingkat pendidikan
dengan kematangan emosi pada wanita dewasa madya.
Iliescu, A. C. (2013). Patient’s Adaptation Difficulties to
the Hospital Environment; Nurse’s Part in That
Transition. Craiova: General Nursing. Illness
Experince, 14(2), 187–201.
Mailani. (2015). Pengalaman spiritualitas Pada Pasien
Penyakit Ginjal Kronis yang menjalani Hemodialisa.
USU.
Morton, P. G. (2012). Keperawatan Kritis Pendekatan
Asuhan Holistik. EGC.
Nisa, M. K. (2016). Studi tentang daya tangguh (resiliensi)
anak di panti asuhan sidoarjo a study of children
resilience in sidoarjo. Universitas Negeri Surabaya.
Reivich, K., & Shatte, A. (2002). The Resilience Factor: 7
Essential Skill For Overcoming Life’s Inevitable
Obstacle. Broadway Books.
IMC-SciMath 2019 - The International MIPAnet Conference on Science and Mathematics (IMC-SciMath)
136

Rinaldi. (2010). Resiliensi Pada Masyarakat Kota Padang
Ditinjau dari Jenis Kelamin. Universitas Sebelas
Maret.
Sarafino, E. P. (2006). Health psychology: Biopsychosocial
interactions. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 5th ed.
Septiyan, A. (2013). Hubungan Mekanisme Koping dengan
Kinerja Perawat Pelaksana di Ruang Rawat Inap.
Universitas Riau.
Setiasih. (2012). Hubungan Antara Manfaat Kerja dan
Kepuasan Kerja. University of Surabaya.
Siburian, C., & Wahyuni, S. (2012). Dukungan Keluarga
dan Harga Diri Pasien Kanker Payudara Di RSUP H.
Adam Malik Medan.
Smeltzer, S. ., & Bare, B. . (2002). BukuAjar Keperawatan
Medikal Bedah Brunner & Suddarth. EGC.
Tama, D. K. (2009). Tingkat Depresi Pada Pasien Kanker
Serviks di RSUP H. AdamMalik. USU.
Wagnild, G., & Young, H. M. (1993). Development and
Psychometric Evaluation of Resilience Scale. Journal
of Nursing Measurment, 1(2).
Widakdo, & Besral. (2013). Efek Penyakit Kronis Terhadap
Gangguan Mental Emosional. Jurnal Kesehatan
Masyarakat Nasional, 7(7).
Resilience of Chronic Renal Failure Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis in Medan, Indonesia
137
