
The Effect of Delignification Time on % Yield of Alpha-cellulose
from Bamboo Fiber (Bambuseae) Properties
Julika Sitinjak
1
, Halimatuddahliana Nasution
1*
and Maulida Lubis
1
1
Department of Chemical Engineering, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Padang Bulan, Medan, Indonesia
Keywords: Alpha-cellulose, Bamboo Fiber, Biocomposite, Biopolymer.
Abstract: Bamboo fiber (Bambuseae) has cellulose content that can be used as a filler in the composites. The
objective of this study is to obtain alpha cellulose from bamboo fiber, through the isolation process. This
study was carried out using the delignification method with NaOH solvent on temperature at 80
o
C and the
time variations of 30, 60, 90, 120, 180 minutes as the first stage of separation of alpha cellulose from other
compounds contained in bamboo fiber. The results showed that the optimum condition of delignification
time was 60 minutes with yield of 55.26%. The FTIR spectra was performed to confirm the formation of the
product (alpha cellulose) proved by spectrum indicating the presence of the cellulose compound
characterized by peak formation in 1641 cm
-1
absorption area by comparing the cluster on the reaction alpha
cellulose with the cluster on the bamboo fiber. XRD result showed that the crystalline portion of alpha
cellulose was higher than amorf portion of alpha cellulose itself with the total amount of crystallinity index
was 93.3%.
1 INTRODUCTION
Bamboo is a plant of tropical and subtropical
regions. Naturally, bamboo can growth in primer
forest and also in secunder forest (former farm and
grower). Bamboo is classified as a non-timber forest
product, which is known by the community as a
versatile plant. It is said like that because this plant
can be used for various purposes, one of the benefits
is as an alternative to wood. Bamboo is easily
obtained at a relatively cheap price and the
production age is relatively fast. Bamboo is included
in natural fibers where natural fibers that can be
directly obtained from nature. The amount of
cellulose in fiber varies according to the source and
it is usually related to materials such as water, wax,
pectin, protein, lignin and mineral substances.
As a source of fiber, bamboo has a cellulose
content of 60.8% and lignin 32.2% with mechanical
strength ranging from 140-800 MPa (Liu et al.,
2012). The high potential of bamboo causes bamboo
fibers can be processed and developed into products
with high economic value, one of them as a
reinforcement in the composite. One of the
cellulosic content is alpha-cellulose which has a high
glossy fiber tensile strength and settles on a
concentration of 17.5% NaOH solution.
Cellulosecan be differentiated based on the degree of
polymerization (DP) and solubility in the 17.5%
sodium hydroxide compound (Klemm et al., 1998).
Figure 1 and 2 show the cellulose and alpha-
cellulosestructures.
Figure 1: Cellulose Structure (Nuringtyas, 2010).
Figure 2: Alpha Cellulose Structure (Nuringtyas, 2010).
The previous research on the effect of
delignification time on % yield alpha cellulose
derived fromkepok banana peel showed the
optimum condition was at 2 hours with yields of
190
Sitinjak, J., Nasution, H. and Lubis, M.
The Effect of Delignification Time on % Yield of Alpha-cellulose from Bamboo Fiber (Bambuseae) Properties.
DOI: 10.5220/0010138500002775
In Proceedings of the 1st International MIPAnet Conference on Science and Mathematics (IMC-SciMath 2019), pages 190-195
ISBN: 978-989-758-556-2
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

23.72% (Yannasandy et al., 2017). Moreover, klutuk
banana stems (Musa Balbisiana Colla) showed the
best % yield of alpha cellulose was 28.77%
(Zulaekha et al., 2018)and the green coconut showed
(Cocos Nucifera L.) the best % yield of alpha
cellulose was 30.01% (Damanik et al., 2016).
The method that used to isolate alpha cellulose is
the method of deposition of alpha cellulose with
17.5% NaOH solution by heating it in a magnetic
stirred heater (Putri & Gea, 2018). In this study we
tried to examine the effect of cooking time on %
yield alpha cellulose from bamboo fiber.
2 METHODS
2.1 Materials
The chemicals that used in this study were aquadest,
HNO
3
, NaNO
2
, NaOH, Na
2
SO
3
, NaOCl, NaOH, and
H
2
O
2
which obtained as received. Bamboo fiber
obtained from residential housing in Deli Serdang,
North Sumatera.
2.2 Preparation of Fiber from Bamboo
Bamboo was cut into small pieces and washed with
water then curled under the sun for 2 hours. The
dried bamboo was mashed with a grinder to get 90
mesh. Fiber was carried out in three stages of the
chemical process, namely delignification,
alkalization, and bleaching to produce alpha
cellulose.
2.3 Isolation Alpha Cellulose
2.3.1 Delignification Process
Delignification processaims to remove lignin which
contained in the fiber.The bamboo fiber was
weighed 75g and then put into a beaker. It was
added 3.5% HNO
3
and 10 mg NaNO
2
and stirring for
120 minutes at90
o
C.
2.3.2 Alkaline Process
The alkalization process aims to remove impurities
which contained in the fiber. Alkalization process
consist of alkalization process I and II. Alkalization
process I added 2% NaOH and Na
2
SO
3
2% stirring
for 60 minutes with temperature 50
o
C. Alkalization
process II added 17.5% NaOH and stirring for30
minutes at 80
o
C.
2.3.3 Bleaching Process
The bleaching stage aims to remove the remaining
lignin from the alkali. Bleaching process consists of
bleaching process I and II. Bleaching process I used
1.75% of NaOCl with stirring process for20 minutes
at 60
o
C. The bleaching process II used 10% of H
2
O
2
with stirring process for60 minutes at 60
o
C.
2.4 Yield Calculation
The alpha cellulose results in the form of residual
residue on boiling flask are then dried by using an
oven at 80
o
C for 1 hour. Weighing the weight of the
fiber. Weighing the weight of the residue after
extraction. Yields Percentage is calculated using
equation (1).
𝑌𝑖𝑒𝑙𝑑
%
𝑥 100 % (1)
2.5 Lignin Content using Klason
Method
The delignification time was made by using 17.5%
of NaOH solution above the hot plate at 80
0
C with
variables of time are 30, 60, 90, 120, 180 minutes.
The delignification process by the klason method
aims to separate alpha cellulose from lignin.
Chemicals added during the delignification process
are expected to reduce % lignin.
Alpha cellulose was weighed 2g for samples (B)
were put 500 ml glass beaker for alpha cellulose and
then soaked in water that has been given ice for 20
minutes, then added 72% H
2
SO
4
as much as 40 ml
for alpha cellulose, stirred slowly while stirring for 2
hours then 400 ml of aquadest for alpha cellulose
into 2000 ml for alpha cellulose. 1540 ml of water
added for alpha cellulose. So the concentration of
sulfuric acid becomes 3%. Then the solution is
heated to boiling and left on a water bath for 4 hours
with low heat. Allow the sample to stand until the
lignin deposits settle completely. Then filtered with
filter paper in a beaker glass that has been known the
weight. The lignin wash deposits until acid free with
hot water (test with litmus). The filter paper are
dried in oven at 105
o
C for 3 hours, cooled in a
desiccator and weighed to a constant weight
(A).Calculation of lignin content can be calculated
with the equation below.
Calculation of Lignin Content:
𝑋
%
𝑥 100 % (2)
Information:
The Effect of Delignification Time on % Yield of Alpha-cellulose from Bamboo Fiber (Bambuseae) Properties
191
X = Value of lignin content,(%)
A = Weight of lignin precipitate, (g)
B = Weight of dry sample, (g).
2.6 Characterization of X-ray
Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
The determination of the crystallinity index of
cellulose material can be calculated through the
segal method, with the equation below.
Segal method:
𝐶𝑟𝑙
(3)
Information:
I
002
= The maximum intensity of the 002 diffraction
pattern which is a representation of the two
zones, namely the crystal zone and amorphous
zone.
I
AM
= The intensity of the diffraction in the same
unit which is a representation of the amorphous
zone.
2.7 Characterization of Fourier
Transform Infrared (FTIR)
Analysis
FTIR testing is carried out to determine the chemical
bonds of alpha cellulose fibers at chemical
treatment. The FTIR specification is Nicolet iS10
FT-IR Spectometer Instrument.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Effect of Delignification Time on
the % Yield of Alpha Cellulose
The analysis was used to know the % yield of alpha
cellulose obtained from bamboo fiber. The lignin
content in bamboo fiber is 24.88%. Table 1 shows
the effect of delignification time on the % yield of
alpha cellulose and remaining of % lignin.
Table 1: Effect of Delignification Time on The %Yield of
Alpha Cellulose and Remaining of %Lignin.
Delignification
time
% Yield of
Alpha Cellulose
% Lignin
30 49.56 1.65
60 55.26 1.62
90 50.54 1.58
120 48.41 1.55
180 46.17 1.45
From the table above, it can be seen that in
general there is an increase in the % yield of 30
minutes to 60 minutes, but there is a decrease for 90
minutes. The % yield value at 30 minutes is 49.56%,
increased to 55.26%, and decreased at 90 minutes to
50.54%. The increasing of the delignification time
will affect the delignification process. Where an
increase in delignification time will cause more
dissolved lignin and the impregnation process
between the solvent and alpha cellulose is more
perfect (Sjostrom, 1995).
However, at the time of delignification that is
long enough will trigger the degradation of alpha
cellulose compounds that cause a decrease in the
yield obtained (Daud et al., 2007). From the table
above, it can be seen that the longer the
delignification time, the lower of the lignin content.
This proves that the longer delignification time will
affect the level of lignin obtained (Jalaluddin &
Rizal, 2005).
The decreased percentage of lignin inside alpha
cellulose is affected by temperature. Lignin will
dissolve at high temperatures in the black leachate
because the hydroxyl phenolate lignin group is in an
ionized state to form its salt and. This treatment will
break lignin into smaller particles (Ariani &
Idiawati, 2011).
Lignin levels decrease with the addition of
NaOH. The addition of an alkaline base in the form
of NaOH will make it easier to break the bonds of
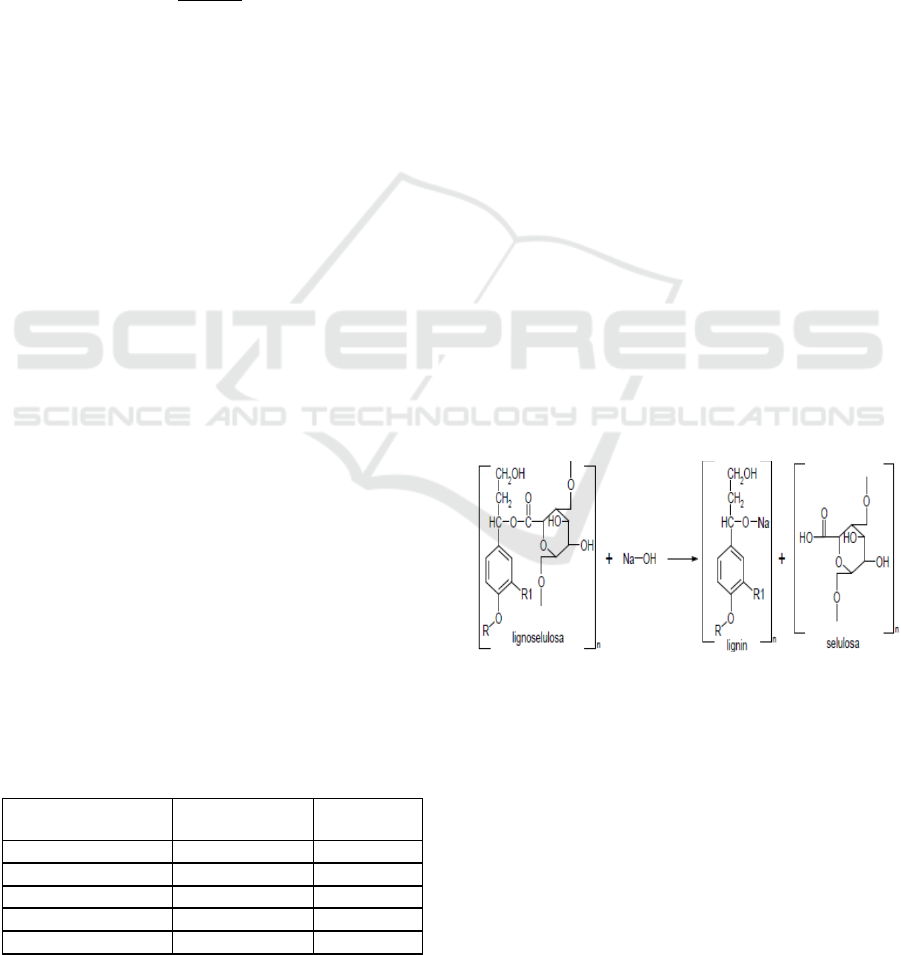
lignin compounds. Figure 3 show reaction of
lingocellulose bonds breaking using NaOH.
Figure 3: Reaction of Lignocellulose Bonds Breaking
Using NaOH (Fengel & Wegener, 1989).
NaOH molecules will enter the lignocelluloses
and break down the structure of lignin (Elwin et al.,
2013). So that lignin is more soluble which results in
decreased levels of lignin.
3.2 Results and Discussion of X-ray
Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
The more orderly arrangement of atoms in a material
is directly proportional to the higher level of
IMC-SciMath 2019 - The International MIPAnet Conference on Science and Mathematics (IMC-SciMath)
192
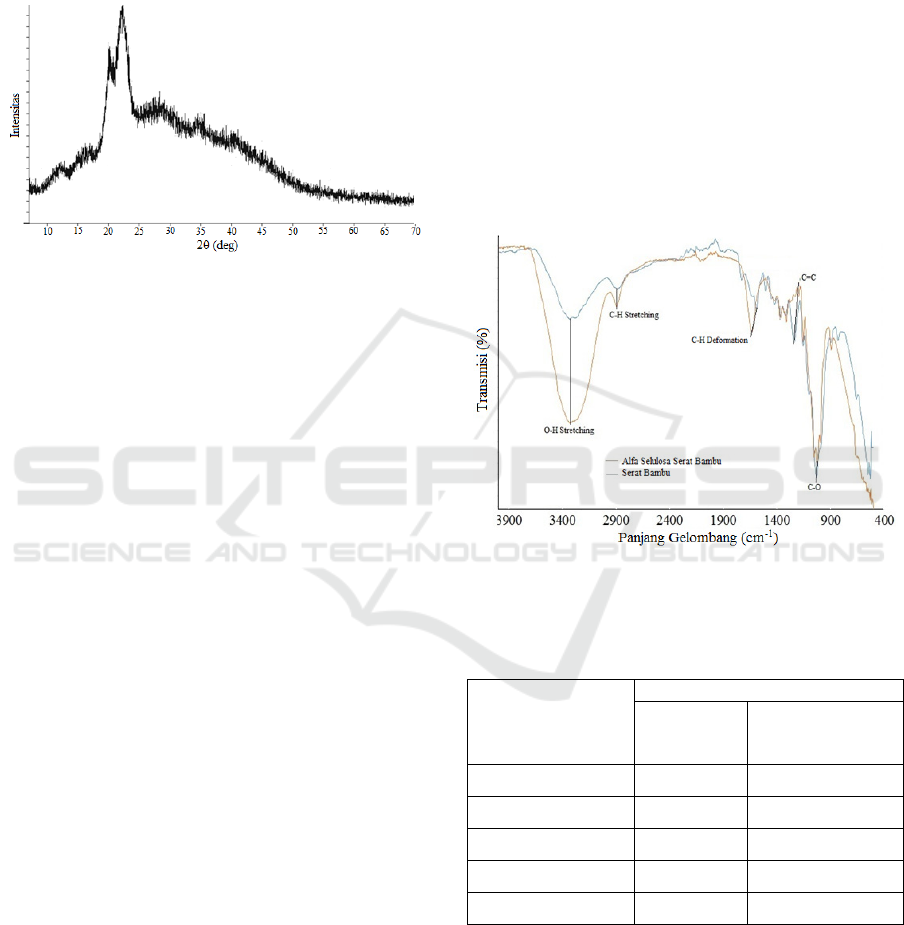
crystallinity. The determination of crystallinity of
alpha cellulose was carried out by the X-ray
Diffraction (XRD) method based on the amorphous
crystal diffraction spectrum pattern. The results of
the crystallinity test using XRD can be seen in
Figure 4 below.
Figure 4: Alpha Cellulose XRD Spectrum Results from
Alpha Cellulose.
The crystallinity index of alpha cellulose for
bamboo fiber was calculated using the Segal
method. The peak absorption of the spectra
produced by alpha cellulose samples from bamboo
fibers is at 2θ = 22° and I
AM
at 2θ = 16° indicating
the crystalline portion of cellulose. From the peak of
the absorption can be determined the crystallinity
index of alpha cellulose.
From the Segal method, the crystallinity index of
alpha cellulose for bamboo fiber is equal to 93.3%, it
indicated by the sharp peak absorption (sharp peak)
of the spectrum produced in the alpha cellulose for
bamboo fiber samples. High crystallinity shows that
the arrangement of the polymer chains in the
material is arranged regularly or the crystalline
portion is more perfect (Lu & Hsieh, 2010). This
increase in crystallinity is caused by a decrease in
the amorphous fiber composition due to chemical
treatment. Chemical treatment is directed at
removing hemicellulose, lignin, pectin, which are
fiber components that contribute to the amorphous
part of the fiber (Susheel et al., 2009).
The amorphous part is more easily hydrolyzed
compared to the crystalline part, so the hydrolysis
treatment causes the fibers to become more
crystalline (Elanthikkal et al., 2010). Alpha cellulose
for bamboo fibers obtained has a high crystallinity
index where the crystallinity index of alpha cellulose
is usually in the range of 55-80% (Zeinali et al.,
2014).
3.3 Results and Discussion of Fourier
Transform Infrared (FTIR)
Analysis
Bamboo fiber has components, namely lignin,
hemicellulose and cellulose. The three components
are composed of alkanes, esters, aromatics and
alcohol (Gian et al., 2017). The characterization of
Fourier Transform Infra Red (FTIR) is to identify
the functional groups that exist in the alpha cellulose
and compared with bamboo fiber as raw material for
alpha cellulose. The characterization of FTIR and
functional group absorbance regions of alpha
cellulose and bamboo fiber fillers can be seen in
Figure 5 and Table 2 below:
Figure 5: FTIR Spectrums of (a) Bamboo Fiber(b) Alpha
Cellulose Bamboo Fiber.
Table 2: TheAbsorption peak of Bamboo and Alpha
Cellulose Bamboo Fiber.
Bond Type
Wave Number (cm
-1
)
Bamboo
Fiber(cm
-1
)
Alpha Cellulose
Bamboo
Fiber(cm
-1
)
O-H Stretching 3331 3334
C-H Stretching 2891 2905
C-HDeformation 1602 1641
C=C 1241 1225
C-O 1031 1024
The figure above shows the absorption peak of
bamboo and alpha cellulose bamboo fibers. In the
process of alkalization reduced the hydrogen bonds
due to the removal of hydroxyl groups by reacting
with sodium hydroxide. The results of the
alkalization process showed the concentration of the
-OH stretching group. The wave frequency of 3350-
The Effect of Delignification Time on % Yield of Alpha-cellulose from Bamboo Fiber (Bambuseae) Properties
193

3175 cm
-1
indicates the presence of OH bonds
(Zhbankov, 1966).
As seen in bamboo fibers with an absorption
peak of 3346 cm
-1
whereas in alpha cellulose
bamboo fibers showed an area of absorption that
was sharper at 3341 cm
-1
. It indicates that the O-H
bond was stretching due to the influence of
alkalization. Alkalization reduces hydrogen bonds
because the hydroxyl group reacts with sodium
hydroxide which causes an increase in the
concentration of -OH when compared to bamboo
fibers (Łojewska et al., 2005).
Furthermore, wave frequencies from 3000-
2850cm
-1
indicates the presence of CH stretching
groups (Zhbankov, 1966). Bamboo fibers are shown
in the absorption area of 2891cm
-1
and in alpha
cellulose bamboo fibers appear sharper absorption
area at 2905 cm
-1
. The absorption peak shows the
stretching of the C-H aliphatic group where the
residual hemicellulose from the delignification
process and the structural changes of the C-H bond
cause the peak to shift toward the maximum
(Zhbankov, 1966).
Concentration of -CH
2
deformation bonds was
shown in bamboo fibers with an absorption area of
1602cm
-1
. Whereas the alpha cellulose bamboo fiber
looks sharper with the absorption area of 1641 cm
-1
.
It shows the crystalline area, where the absorption
area will increase along with the purification process
(Alves et al., 2014)
The double bond C=C of aromatic compounds is
shown to have a peak at susceptible 1200-1300 cm
-1
.
The uptake of the 1241cm
-1
area in the bamboo fiber
looks sharper compared to the alpha cellulose
bamboo fiber in the absorption area of 1225cm
-1
. In
the aromatic group C=C, it can be seen that lignin is
still present, which means that the alkaline treatment
has not completely eliminated lignin but only
reduced the level of lignin (Han, 2015).
In the picture above it can also be seen that there
are concentrations of C-O groups in the absorption
area between 1000-1200cm
-1
. In bamboo fiber, it can
be seen that the absorption peaks appear sharper at
1031cm
-1
, whereas in alpha cellulose bamboo fibers
have absorption peaks at 1024cm
-1
. Both samples are
thought to originate from the vibration of the
pyronose ring group on the cellulose unit (1035–
1170cm
-1
referring to the pyronose ring) where the
absorption peak indicates enrichment of cellulose
fibers and it can be proven that the sharp peak
absorption of the C-O group contained in the alpha
cellulose of bamboo fiber further indicate the
presence of a pyronese ring which is a typical group
that only belongs to the cellulose unit and is not
owned by the lignin and hemicellulose components
(Peng et al., 2011).
4 CONCLUSION
Alpha cellulose had been obtained succesfully from
bamboo fibers by using sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
solvent. It was revealed that the longer the
delignification time, the higher of the yield of alpha
cellulose up to 60 minutes. However, the longer
delignification time up to 180 minutes, the lower of
the yield of alpha cellulose. It was caused by the
degradation of alpha cellulose to glucose molecules.
FTIR showed that alpha cellulose from bamboo
fibers have the similar structure with cellulose
structure. XRD result showed that the crystalline
portion of alpha cellulose was higher than amorf
portion of alpha cellulose itself with the total amount
of crystallinity index was 93.3%.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors gratefully acknowledge that the research
was supported by Department of Chemical
Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Universitas
Sumatera Utara in facilitating this research.
REFERENCES
Alves, L., Medronho, B., Antunes, F. E., Fernández-
García, M. P., Ventura, J., Araujo, J. P., Romano, A.,
& Lindman, B. (2014). Unusual Extraction and
Characterization of Nanocrystalline Cellulose from
Cellulose Derivatives. Journal of Molecular Liquids,
210, 106–112.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2014.12.010
Ariani, & Idiawati. (2011). Determination of Lignin and
Glucose Levels in Organosolv Hydrolysis and Acid
Hydrolysis. Journal of Science and Applied
Chemistry, 5(2), 140–150.
Damanik, T. A., Indah, M., Yulianti, M., & Wibowo, N. J.
(2016). The Ability of Alpha Cellulose from Green
Coconut Fibre (Cocosnucifera L.) as Bioadsorbent of
Heavy Metal Cadmium (Cd). In Journal of
Technology. Atma Jaya University.
Daud, W. R. W., Zainuddin, Z., Law, K. N., & Asro, R.
(2007). Pulp from oil palm fronds by chemical
processes. Industrial Crops and Products - IND
CROPS PRODUCTS, 25, 89–94.
Elanthikkal, S., Gopalakrishnapanicker, U., Varghese, S.,
& Guthrie, J. T. (2010). Cellulose microfibres
produced from banana plant wastes: Isolation and
IMC-SciMath 2019 - The International MIPAnet Conference on Science and Mathematics (IMC-SciMath)
194

characterization. Carbohydrate Polymers, 80, 852–
859. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2009.12.043
Elwin, Lutfi, & Hendrawan. (2013). Analysis of the Effect
of Pretreatmet Time and NaOH Concentration on
Cellulose, Lignin, and Water Hyacinth Hemicellulose
Content in the Pretreatment Process of Making
Bioethanol. The Engineering of Tropical Agriculture
and Biosystems, 2(2), 104–110.
Fengel, D., & Wegener, G. (1989). Wood-chemistry,
ultrastructure, reactions. Walter de Gruyter.
Gian, A., Farid, M., & Ardhyananta, H. (2017). Cellulose
Isolation from Oil Palm Empty Fruit Bunches for
Nanofiller Sound Absorption Composites: FTIR
Analysis. ITS Technical Journal, 6(2).
Han, H. (2015). Study of Agro-composite
Hemp/Polypropylene: Treatment of Fibers,
Morphological and Mechanical Characterization.
Universite de Technologie Troyes.
Jalaluddin, & Rizal, S. (2005). Making Pulp From Rice
Straw Using Sodium Hydroxide. Journal of Industrial
Engineering Systems, 6(5).
Klemm, D., Philipp, B., Heinze, T., & Heinze, U. (1998).
Comprehensive Cellulose Chemistry: Fundamentals
and Analytical Methods.
Liu, D., Song, J., Anderson, D. P., Chang, P. R., & Hua,
Y. (2012). Bamboo fiber and its reinforced
composites: structure and properties. Cellulose, 19,
1449–1480.
Łojewska, J., Miskowiec, P., Łojewski, O., & Proniewicz,
L. M. (2005). Cellulose oxidative and hydrolytic
degradation: In situ FTIR approach. Polymer
Degradation and Stability - POLYM DEGRAD
STABIL, 88, 512–520.
Lu, P., & Hsieh, Y.-L. (2010). Preparation and properties
of cellulose nanocrystals: Rods, spheres, and network.
Carbohydrate Polymers, 82, 329–336.
Nuringtyas, T. R. (2010). Carbohydrates. ugm press.
Peng, B. L., Dhar, N., Liu, H. L., & Tam, K. C. (2011).
Chemistry and applications of nanocrystalline
cellulose and its derivatives: A nanotechnology
perspective. The Canadian Journal of Chemical
Engineering, 1–16.
Putri, E., & Gea, S. (2018). Isolation and Characterization
of Cellulose Nanocystral from Palm Oil Bunches (Jack
Elaeisguineensis). Journal of Islamic Science and
Technology, 4(1).
Sjostrom, E. (1995). Chemistry of Wood. Using and
Method. (2nd ed.).
Susheel, K., Kaith, B. S., & Inderjeet, K. (2009).
Pretreatments of Natural Fibers and Their Application
as Reinforcing Material in Polymer Composites.
A
Review. P. Engg. Sci., 49, 1253–1272.
Yannasandy, D., Habibah, U. H., & Fitriyano, G. (2017).
Effect of Delignification Time on The Formation Of
Alfa Cellulosa And Identification of Acetic Cellulose
From Acetication Results From Banana Skin Waste.
Journal of Chemical Engineering.
Zeinali, E., Haddadi-Asl, V., & Roghani-Mamaqan, H.
(2014). Nanocrystalline cellulose grafted random
copolymers of N-isopropylacrylamide and acrylic acid
synthesized by RAFT polymerization: effect of
different acrylic acid contents on LCST behavior. RSC
Advances, 4, 31428–31442.
Zhbankov, R. G. (1966). Infrared spectra of cellulose and
its derivatives. Consultants Bureau.
Zulaekha, R., Nawafil, S. A., Harianti, S. F.,
Mujiburohman, M., & Hidayati, N. (2018). Isolation
of Alfa Cellulosa Banana Plant Klutuk (Musa
BalbisianaColla) Using Magnetic Stirring With
Ultrasonic. Journal of Natural Materials Technology,
2(2).
The Effect of Delignification Time on % Yield of Alpha-cellulose from Bamboo Fiber (Bambuseae) Properties
195
