
Morphological and Mechanical Properties of Old Newspaper Deinked
with Cellulase and Laccase Combination
Noni Oktari
1
, Saharman Gea
2*
, Andriayani
2
, Sri Rahayu
1
, Reka Mustika Sari
1
and Khatarina
Meldawati Pasaribu
1
1
Postgraduate Chemistry Study Programme, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Jl. Bioteknologi No. 1, Medan, Indonesia
2
Department of Chemistry, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Jl. Bioteknologi No. 1, Medan, Indonesia
Keywords: Cellulase, Deinking, Laccase, Old Newspaper.
Abstract: The utilization of enzyme in deinking process of recycle paper is still in development phase since it was
known that conventional deinking use large amount of chemicals such as sodium hydroxide, sodium
silicate, and hydrogen peroxide which are environmentally damaging. In the present study, cellulase
combined with laccase was used for deinking process of old newspaper pulp. The first step was repulping
the old newspaper, and then the pulp slurry at 10% consistensy was treated with cellulase and laccase with
different concentration from 0-2%. After washing process, the pulp was reforming in to the handsheet. The
tensile strength of the handsheet was tested and the morphological changes was analyzed using scanning
electron microscopy (SEM). The result showed that handsheet treated with 1% cellulase and 1% laccase had
the highest tensile strength (2.1 MPa) with 1493 MPa Young’s modulus. From the images of SEM, showed
that fiber surface pulp turned rough and microfibril also appeared on the fiber surface after enzymatic
treatment with cellulase and laccase, which indicated delignification process and facilitated the release of
ink particle entrapped.
1 INTRODUCTION
Paper is one of important materials which is
inseparable from human life and used for various
purposes in life. Based on survey conducted at 2014,
the global production of paper was 407 million
metric tons (Pandharipande & Ingle, 2018). The
demand of paper is continuously increase year by
year. This causes high demand of green plant as a
basic raw material for paper production. Recycling
of waste paper is an alternative process to preserve
the green plant. Old newspaper is one of waste paper
that has a potential amount especially in urban area
in Indonesia, because it was produced and consumed
every day (Saputra & Sagala, 2017).
Recycling of waste paper requires the removal of
ink from the paper by a process called deinking (A.
Singh et al., 2012). Deinking process involves ink
particle dislodgement from the fiber surface and the
separation of dispersed ink from fiber suspensions
(Muryeti et al., 2015). During chemical deinking or
also called conventional deinking, large quantities of
chemicals such as sodium hydroxide, sodium silicate
and hydrogen peroxide were used, which are not
environmentally friendly (Bajpai, 2014; K. C. Lee et
al., 2016; Liu et al., 2017). On the other hand,
enzyme mediated technologies are getting vast
popularity due to their potential to replace the use of
chemicals and also limit the wastage of water, save
energy and result helps to improve the product
quality (G. Singh & Arya, 2019).
Many researchers have reported the studies on
deinking process using various enzymes. As
compared to the conventional deinking, pulp treated
with enzymes reduce the load on waste water
treatment system due to reduced use of chemicals.
Enzymatic deinking has high efficiency and low
environmental impact. Moreover, enzymatically
deinked pulp also displays improved drainage, lower
residual ink, higher brighness and superior physical
properties (Saxena & Chauhan, 2016). Cellulase-free
xylanase preparation of Aspergillus niger DX-23
could cause efficient deinking of old newspaper pulp
and considerably reduce the use of chemicals (Desai
& Iyer, 2016). The use of cellulases and
hemicellulases mixtures has been described to be
able to deink high quality waste paper (C. K. Lee et
Oktari, N., Gea, S., Andriayani, ., Rahayu, S., Mustika Sari, R. and Meldawati Pasaribu, K.
Morphological and Mechanical Properties of Old Newspaper Deinked with Cellulase and Laccase Combination.
DOI: 10.5220/0010152100002775
In Proceedings of the 1st International MIPAnet Conference on Science and Mathematics (IMC-SciMath 2019), pages 273-278
ISBN: 978-989-758-556-2
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
273

al., 2013). Treatment with laccase indicates several
characterictic and prominent changes including
degradation of the guaiacyl group and a high degree
of deformation of methyl group in lignin (Shankar et
al., 2018). Combining hemicellulase with laccase
mediator system on old newsprint deinking process
shows that surface coverage lignin of pulp is lower
than the control (Xu et al., 2011). Laccase is capable
to deink old newspaper where the mechanical pulp
contains a huge of lignin (Saxena & Chauhan,
2016). Waste paper pulp was deinked effectively
using laccase and xylanase without mediator
supplementation for laccase activity. It was the first
report on deinking of old newspaper pulp using a
bacterial laccase without the need of mediator,
resulting the process cost effective (Virk et al.,
2013).
This study was carried out to deink old
newspaper pulp using combination between
cellulase and laccase without any mediator.
Conventional deinking method was also done as the
comparison. The morphological and physical
properties of enzymatically and conventionally
deinked pulp were investigated.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Materials
Cellulase from Aspergillus sp. (Carezyme 1000 L)
with an activity of 1000 S-CEVU/g and laccase from
Aspergillus sp. (Novozym 51003) with an activity
1000 LAMU/g were purchased from Sigma Aldrich.
All the reagents used are analytical grade chemical.
The old newspaper used was collected from the
same publisher by a local supplier.
2.2 Methods
This study consists of 3 main stages, which are
repulping, deinking and reforming process.
2.2.1 Old Newspaper Pulp Preparation
The old newspapers were manually cut into length
size 2-3 cm
2
and then soaked overnight in distilled
water at room temperature. After that, the soaked
newspapers were washed and then disintegrated
using a mechanical stirrer until pulp slurry obtained.
The pulp slurry then squeezed to remove absorbed
water and after that oven dried at 50ºC. The dried
pulp was used for further experiments.
2.2.2 Chemical Deinking
The amount of 15 g dried old newspaper pulp was
soaked in 150 mL distilled water for 30 minutes to
obtain pulp with 10% (w/v) consistency. After that,
pulp was added with 2% NaOH, 2% Na
2
SiO
3
and
2% H
2
O
2
. The treatment was carried out at 70ºC for
2 h. The treated pulp was then washed with distilled
water until the pH to be neutral.
2.2.3 Enzymatic Deinking
The amount of 15 g dried old newspaper pulp was
soaked in 150 mL phosphate buffer (pH 7.5) for 30
minutes to obtain pulp with 10% (w/v) consistency.
Cellulase was added to the pulp and incubated at
40ºC for 30 minutes in inkubator shaker with 150
rpm. After 30 minutes reaction, laccase was added
and allowed to react for 30 minutes at 30ºC with 150
rpm in inkubator shaker. The enzymes were
inactivated by placing the pulp in a boiling water
bath for 15 minutes. The treated pulp was then
washed with distilled water until the pH to be
neutral. Cellulase and laccase enzymes used with 5
different variations of concentration (0%; 0.5%; 1%;
1.5% and 2% of dry weight old newspaper pulp).
2.2.4 Handsheet Formation
The treated pulp (chemically and enzimatically
treated) were suspended in distilled water in an
erlenmeyer flask, mixed and filtered using buchner
funnel under suction using whatman filter paper.
Pulp was recovered using 200 mesh wire and
pressed between two plates using napkin to remove
extra water and then oven dried at 50ºC.
2.2.5 Handsheet Characterization
The handsheets obtained were analyzed for
morphological properties using scanning electron
microscopy (SEM) (ZEISS) at an accelerating
voltage EHT of 20.00 kV, probe = 101 Pa and signal
A = SE1.
Mechanical properties was carried out using a
tensile test tool GOTECH AL-7000M under ambient
temperature and humidity (25ºC, 65 RH) with a
tensile speed 5 mm/min and 1 kN load.
IMC-SciMath 2019 - The International MIPAnet Conference on Science and Mathematics (IMC-SciMath)
274

3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
3.1 Scanning Electron Microscopy
Analysis
The analysis on newspaper pulp using SEM was
carried out to analyze the surface morphology of
untreated, enzimatically and chemically treated
newspaper pulp.
Surface morphology of handsheet on 500x
magnification can be seen in Figure 1, it shows that
the fiber surface was significantly changed after
enzymatic deinking process.
The smooth fiber surface was observed on
untreated newspaper pulp (A). On contrary, fiber
surface on enzymatically treated pulp was turned to
be rough. As can be observed, more fibrillation was
appeared on fiber surface, which indicating
delignification process was occured (Xu et al.,
2011). This fiber surface change which facilitated
the release of high amount of lignin molecules and
the ink particles entrapped (Kumar et al., 2019).
Moreover, the change of the fiber surface had a
significant role increasing the strength of the
recycled pulp. Deinking process using cellulase
resulted two types of changes in pulp surface, it was
modification on internal structure and surface
roughening (Efrati et al., 2013). Laccase treatment
alone did not generated in rupturing of the fibers and
deform the structure of the cellulose fibers (Shankar
et al., 2018).
Fiber surface of chemically deinked pulp
(conventional deinking) can be seen in Figure 2, it
shows rupturing after the deinking process. The
rupturing increase with increasing the concentration
of the chemicals, which indicated that high
concentration on chemical deinking deforms the
structural integrity of the cellulose fibers (Shankar et
al., 2018). On the other hand, combine enzimatically
deiked pulp did not show any rupturing. It is clearly
observed that the detachment of the ink particles
from the surface of the fibers was more prominent in
case of pulp treated with cellulase and laccase
combination as compared to conventional deinking.
Figure 1: Scanning Electron Micrographs of A) Untreated newspaper pulp B) Laccase 2% C) Cellulase 0.5%; laccase 1.5%
D) Cellulase 1%; laccase 1% E) Cellulase 1.5%; laccase 0.5% and F) Cellulase 2%.
Morphological and Mechanical Properties of Old Newspaper Deinked with Cellulase and Laccase Combination
275
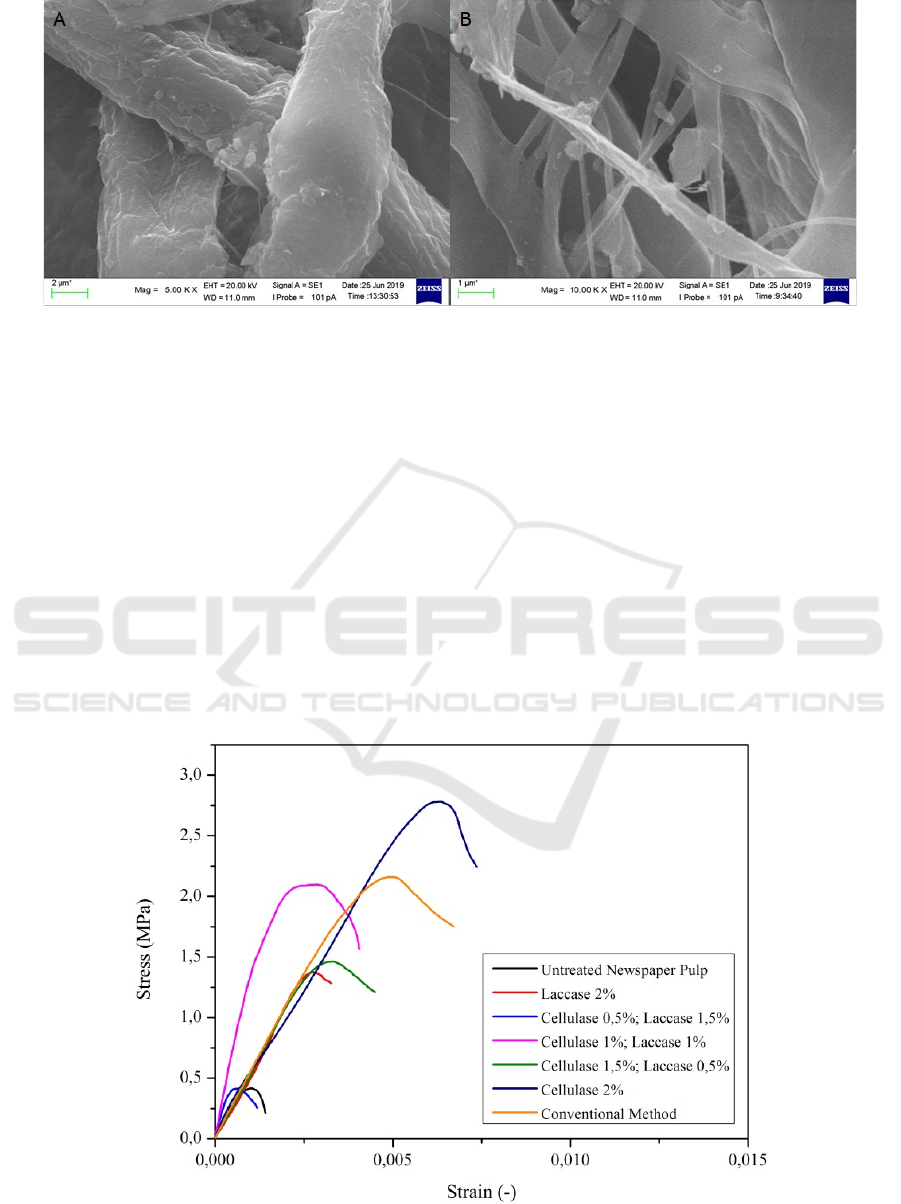
Figure 2: Scanning Electron Micrographs of A) Chemically deinked pulp and B) Combined cellulase and laccase deinked
pulp.
3.2 Mechanical Properties Analysis
In this study, the mechanical properties of recycled
paper was analyzed. The specimen was cut into 80 x
25 mm
2
and then test with tensile test tensometer.
Stress (MPa) vs strain change curve can be seen in
Figure 3.
Tensile strength (MPa), elongation at break (%)
and Young’s modulus (MPa) of untreated and reated
newspaper pulp are shown in Table 1. As can be
seen, tensile strength increased significantly for
enzymatic treated pulp. Tensile strength for
untreated pulp was 0.42 MPa with Young’s modulus
714 MPa, whereas the highest tensile strength was
2.78 MPa with Young’s modulus 743 MPa which
obtained in 2% cellulase treated. Young’s modulus
is the ratio between stress and strain.
Pulp given an enzymatic treatment with 1%
cellulase and 1% laccase combination had the
highest Young’a modulus, it was 1493 MPa with 2.1
MPa tensile strength value. This indicated that there
was a synergestic deinking effect between cellulase
and laccase.
While compare with conventional deinking,
enzymatic deinking had a better tensile strength with
a significant difference. This results are in
accordance with the use of chemical that caused
damage during the deinking process which can also
observed from the morphology of pulp fibers.
Conventional
deinking method even decreases the
Figure 3: Stress-strain curve of untreated and treated handsheets of newspaper pulp.
IMC-SciMath 2019 - The International MIPAnet Conference on Science and Mathematics (IMC-SciMath)
276

Table 1: The Mechanical properties of untreated and treated newspaper pulp.
No Treatment
Tensile
Strength
(MPa)
Elongation at
Break (%)
Young’s
Modulus
(MPa)
1 Untreated News
p
a
p
er Pul
p
0.42 0.1 714
2 Laccase 2% 1.38 0.3 572
3 Cellulase 0.5%; Laccase 1.5% 0.41 0.07 1041
4 Cellulase 1%; Laccase 1% 2.1 0.3 1493
5 Cellulase 1.5%; Laccase 0.5% 1.46 0.3 523
6 Cellulase 2% 2.78 0.6 743
7 Conventional Metho
d
13 0.4 459
Young’s modulus compared to untreated newspaper
pulp. This study also in accordance with Shankar et
al. (2018) who reported the increasing of chemical
concentration caused substantial decrease in tensile
strength. The use of large concentration of chemical
may have reduced the tensile strength owing to high
degree of depolymerization of cellulose content of
the fibers (Shankar et al., 2018).
4 CONCLUSIONS
Cellulase combining with laccase effectively
deinked old newspaper pulps without mediator
supplementation for laccase activity. Morphological
properties of enzymatic treated pulp show that the
detachment of the ink particles from the surface of
the fibers is more prominent in case of pulp treated
with cellulase and laccase combination as compared
to conventional deinking. Tensile test observed pulp
treated with cellulase 1% and laccase 1% has the
highest mechanical properties with 1493 MPa
Young’s modulus and 2.1 MPa tensile strength.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Author would like to express a gratitude to the head
of Material and Polymer Reseach Unit Postgraduate
and Basic Science Laboratory Universitas Sumatera
Utara for the research facility provided.
REFERENCES
Bajpai, P. (2014). Deinking with Enzymes. Recycling and
Deinking of Recovered Paper, 2006, 139–153.
https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-416998-2.00008-8
Desai, D. I., & Iyer, B. D. (2016). Biodeinking of old
newspaper pulp using a cellulase-free xylanase
preparation of Aspergillus niger DX-23. Biocatalysis
and Agricultural Biotechnology, 5, 78–85.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2015.11.001
Efrati, Z., Talaeipour, M., Khakifirouz, A., & Bazyar, B.
(2013). Impact of cellulose enzyme treatment on
strength, morphology and crystallinity of deinked
pulp. Cellulose Chemicstry and Technology, 47(7–8),
547–551.
Kumar, N. V., Rani, M. E., Centre, R., Nadu, T., & Nadu,
T. (2019). Microbial enzymes in paper and pulp
industries for bioleaching application. Research
Trends of Microbiology.
Lee, C. K., Ibrahim, D., & Che Omar, I. (2013).
Enzymatic deinking of various types of waste paper:
Efficiency and characteristics. Process Biochemistry,
48(2), 299–305.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2012.12.015
Lee, K. C., Tong, W. Y., Ibrahim, D., Arai, T., Murata, Y.,
Mori, Y., & Kosugi, A. (2016). Evaluation of
Enzymatic Deinking of Non-impact Ink Laser-Printed
Paper Using Crude Enzyme from Penicillium rolfsii
c3-2(1) IBRL. Applied Biochemistry and
Biotechnology, 181(1), 451–463.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-016-2223-4
Liu, M., Yang, S., Long, L., Wu, S., & Ding, S. (2017).
The enzymatic deinking of waste papers by engineered
bifunctional chimeric neutral Lipase - Endoglucanase.
BioResources, 12(3), 6812–6831.
https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.12.3.6812-6831
Muryeti, Mulyani, E. B., & Sinurat, E. (2015). Adsorption
of Carbon Black Using Chitosan in the Deinking
Process. Procedia Chemistry, 17, 106–110.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proche.2015.12.117
Pandharipande, S., & Ingle, A. P. (2018). Novel Use of
Wheat Grass Extract in Enzymatic Deinking of Printed
Paper. 3549–3558.
https://doi.org/10.15680/IJIRSET.2018.0704048
Saputra, A. A., & Sagala, R. (2017). Limbah Koran
Sebagai Bahan Campuran. 16(1), 77–84.
Saxena, A., & Chauhan, P. S. (2016). Critical Reviews in
Biotechnology Role of various enzymes for deinking
paper : a review. 8551(July).
https://doi.org/10.1080/07388551.2016.1207594
Shankar, S., Shikha, Bhan, C., Chandra, R., & Tyagi, S.
(2018). Laccase based de-inking of mixed office waste
and evaluation of its impact on physico-optical
properties of recycled fiber. Environmental
Morphological and Mechanical Properties of Old Newspaper Deinked with Cellulase and Laccase Combination
277

Sustainability, 1(3), 233–244.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s42398-018-0021-3
Singh, A., Dutt, R., Kaur, A., & Mahajan, R. (2012). An
ecofriendly cost effective enzymatic methodology for
deinking of school waste paper. Bioresource
Technology, 120, 322–327.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.06.050
Singh, G., & Arya, S. K. (2019). Utility of laccase in pulp
and paper industry: A progressive step towards the
green technology. International Journal of Biological
Macromolecules, 134, 1070–1084.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.05.168
Virk, A. P., Puri, M., Gupta, V., Capalash, N., & Sharma,
P. (2013). Combined Enzymatic and Physical
Deinking Methodology for Efficient Eco-Friendly
Recycling of Old Newsprint. PLoS ONE, 8(8).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0072346
Xu, Q. H., Wang, Y. P., Qin, M. H., Fu, Y. J., Li, Z. Q.,
Zhang, F. S., & Li, J. H. (2011). Fiber surface
characterization of old newsprint pulp deinked by
combining hemicellulase with laccase-mediator
system. Bioresource Technology, 102(11), 6536–6540.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.03.051
IMC-SciMath 2019 - The International MIPAnet Conference on Science and Mathematics (IMC-SciMath)
278
