
Analysis of the Effect of Grain Size on the Characteristics of Zeolite
as Adsorbents
Susilawati
1,2
, M. N. Nasrusddin
1
, Y. A. Sihombing
1,2
, Bonar Ferdiansyah
1
and Sri Ningsih Y. Pakpahan
1
1
Physics Department, Faculty of Mathematic and Natural Science, UniversitasSumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia
2
Pusat Unggulan Inovasi Green Chitosan dan Material Maju Universitas Sumatera Utara
Keywords: Pahae Natural Zeolite, Adsorbents, Grain Size.
Abstract: Zeolite is a material that has been widely used for various applications, and its availability in natureis also
abundant. Applications of zeolite materials are widely studied including adsorbents. The performance of
zeolites as adsorbents is influenced by the particle size. The purpose of this study was to determine the grain
size towards the zeolite characteristics as an adsorbent. Samples were taken from Pahae, North Tapanuli
Regency. Zeolites were sieved with 200 mesh, 325 mesh, and 400 mesh sizes. Then, the physical properties
of samples were characterized such as density, water adsorption, and Particle Size Analyzer (PSA) test. The
test results showed that the finer the grain size274.6 nm, the porosity81.90%, and water adsorption98.29%
increased. However, after the fineness of the grain reached 400 mesh, the porosity and water adsorption
values decreased.
1 INTRODUCTION
Zeolite is a hydrated porous alumina silicate crystal
mineral that has a three-dimensional skeletal
structure formed from tetrahedral [SiO4]4- and
[AlO4]5-. The two tetrahedral are connected by
oxygen atoms producing an open and hollow three-
dimensional structure in which metal atoms are
filled with usually alkali or alkaline earth metals and
freely moving water molecules (Breck, 1974;
Cheetham, 1992; Scott et al., 2003).
Zeolite is a material that has been widely
used in various applications and its availability in
nature is also abundant. Applicationsof zeolite
materials that are widely studied include adsorbents,
ion exchanger, and catalysts. Zeolite is most used as
an adsorbent because it has a three-dimensional
skeletal structure with a cavity in it and a large
surface area.
Wahono et al. (2014), made zeolite-based
adsorbents using natural zeolite in Gunungkidul with
a size of 100 mesh for bioethanol purification
(Wahono et al., 2014). Natural zeolites were
activated by Chemistry (HCl) and Physics
(Calcination 400°C) and compared with non-
activated natural zeolites and synthetic zeolites. The
results showed that natural zeolite activation had the
ability to purify bioethanol the same as synthetic
zeolite, but the results were lower. Mudjijono et al.
(2015), modified the natural zeolite of Gunungkidul
as a bioethanol dehydration agent with a size of 100
mesh. Modifications were conducted with variations,
namely non-activation, chemical activation,
chemical activationand calcination, chemical
activation zeolite and treatment with ammonium
nitrite, chemical activation and treatment with
ammonium nitrite and calcination. The results
showed that the best result of bioethanol dehydration
agent was zeolite with chemical activation
(Mudjijono et al., 2015). Nasution et al. (2015),
made zeolite-based water vapor filters by varying
the size of zeolites (60 mesh and 200 mesh) and the
types of zeolite (natural zeolites of Pahae and natural
zeolites of Cikalong). The results showed that the
natural zeolite filter of Pahae with a size of 200
mesh had optimum water vapor adsorption and was
suitable as an adsorbent (Nasution et al., 2015). In
this study, the size variations of zeolite were made
with 3 variations namely 200 mesh, 325 mesh, and
400 mesh, which aimed to determine the effect of
grain size variations on the characteristics of zeolites
as adsorbents.
308
Susilawati, ., Nasruddin, M., Sihombing, Y., Ferdiansyah, B. and Pakpahan, S.
Analysis of the Effect of Grain Size on the Characteristics of Zeolite as Adsorbents.
DOI: 10.5220/0010163300002775
In Proceedings of the 1st International MIPAnet Conference on Science and Mathematics (IMC-SciMath 2019), pages 308-313
ISBN: 978-989-758-556-2
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

2 RESEARCH AND METHODS
Zeolite samples were taken from Pahae Julu District,
North Tapanuli. Zeolite in the form of chunks was
crushed and sieved with a size of 200 mesh, 325
mesh, and 400 mesh. Characterization of zeolite
samples includes physical properties (porosity and
water adsorption) and grain size analysis using
Particle Size Analyzer (PSA).
2.1 Porosity
Porosity is defined as the ratio between the amount
of pore volume (volume of empty space) in solids
and the total volume of solids. The porosity was
calculated from the pore volume divided by the total
volume. The equation of porosity is:
%𝑝𝑜𝑟𝑜𝑠𝑖𝑡𝑦
100% (1)
When; m
b
= wet mass (Kg) and m
k
= dry mass (Kg).
2.2 Water Adsorption
Water adsorption in each sample can be done by
weighing the dry mass and wet mass of the sample.
Dry mass is the mass when the sample is dry, while
the wet mass is obtained after the sample has been
immersed for 24 hours at room temperature. The
equation of water adsorption is:
%𝑤𝑎𝑡𝑒𝑟 𝑎𝑑𝑠𝑜𝑟𝑝𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛
100% (2)
When m
b
= wet mass (Kg) and m
k
= dry mass (Kg).
Characterization of grain size analysis used the
Particle Size Analyzer (PSA). PSA measurement is
based on the principle of the dynamic light
scattering (DLC) method which is the best technique
for particle size measurement (Galuh & Rahmi,
2014; Prasmita, 2012). The method of particle
counting contained in the PSA tool consisted of
three methods, namely the pade-laplace method,
statistical method and cumulants method (Muchtar
et al., 2015).
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Porosity
Porosity of zeolite with size variations of 200 mesh,
325 mesh, and 400 mesh is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1 shows that zeolite size variations affect
the porosity value. The minimum porosity was
found at a size of 200 mesh with a porosity value of
49.58%, while the maximum porosity was found at
325 mesh with a porosity value of 81.90%. Zeolite is
a material mostly composed of oxygen, silica,
carbon, and aluminium, where oxygen is the largest
constituent element. Thus, zeolites have cavities or
pores that can adsorb water. In addition, the grain
size also affects the porosity value. The finer
thegrain size of a zeolite, the greater the porosity
value. However, in 400-mesh zeolite, the porosity
value decreased which means that the ability of
zeolite to be used as an adsorbent became lower.
According to SNI 13-7168-2006, the porosity value
will increase if the size of the zeolite becomes
smoother. However, if thegrain size is too, it will
result in a limited cavity structure so that porosity
becomes reduced (SNI 13-7168-2006, 2006).
Therefore, 325-mesh zeolite had a more optimum
porosity value than 400-meshzeolite.
3.2 Water Adsorption
The water adsorption of zeolite with size variations
of 200 mesh, 325 mesh, and 400 mesh is shown in
Figure 2.
Analysis of the Effect of Grain Size on the Characteristics of Zeolite as Adsorbents
309

Figure 1: The relationship between porosity and variations in the grain size of zeolite.
Figure 2: The relationship between water adsorption and variations in the grain size of zeolite.
Figure 2 shows that the size variations of zeolite
affect the water adsorption value. Based on the test
results, the minimum water adsorption was 59.50%
in 200-mesh size, while the maximum water
adsorption was 98.29% in 325-mesh size. The water
adsorption value was directly proportional to the
porosity value, where the greater the pore or cavity
of zeolite, the higher the value of water adsorption.
However, the 400-mesh zeolite had a smaller water
adsorption value compared to the 325-mesh zeolite
because the particle size is one of the factors that can
affect the capacity and rate of water adsorption of
zeolite to certain adsorbates. The particle size of
zeolite will affect the selectivity of zeolites to which
molecules will enter the zeolite cavity and which
will be rejected. The finer the particle size, the more
selective the adsorption process will be.
3.3 Particle Size Analyzer (PSA)
The PSA characterization to determine the grain size
of zeolites with 200 mesh, 325 mesh, and 400 mesh
size variations is shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3 is the PSA test results showing the
diameter of zeolite. The 200-mesh zeolite had an
average diameter of 569.9 nm, the 325-mesh zeolite
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
200 325 400
Porosity(%)
GrainSize(mesh)
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
200 325 400
WaterAdsorption(%)
GrainSize(mesh)
IMC-SciMath 2019 - The International MIPAnet Conference on Science and Mathematics (IMC-SciMath)
310
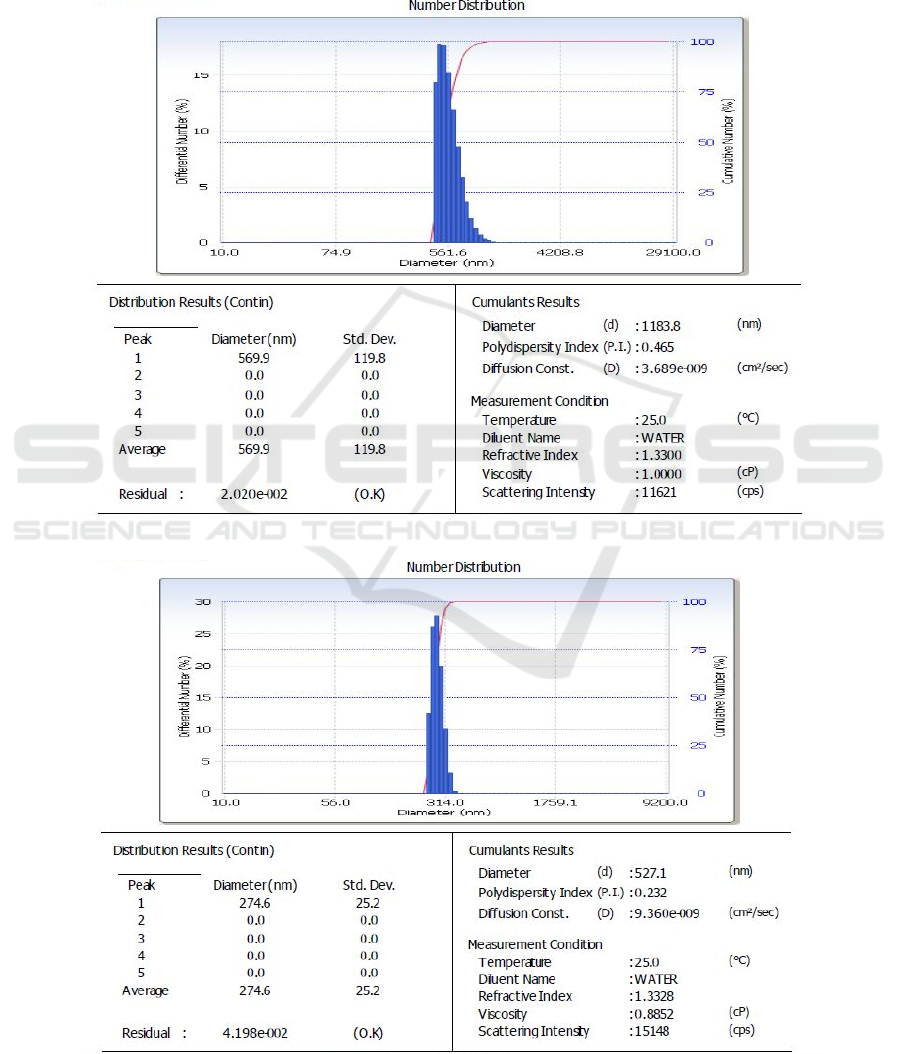
had an average diameter of 274.6 nm, and the 400-
mesh zeolite had an average diameter of 381.8 nm.
The relationship between diameter and variations in
the grain size of zeolite resulted from the PSA test
can be seen in Figure 4.
Figure 4 shows the finer the size of the zeolite,
the smaller the diameter of zeolite. However, the
400-mesh zeolite had a larger diameter than 325
mesh. The smaller the diameter of the zeolite, the
separation process using the nature of zeolite will be
more selective (Wulandari & Priyono, 2014). This is
in accordance with the optimum porosity and water
adsorption value in the 325-mesh zeolite.
a. 200 mesh.
b.325 mesh.
Analysis of the Effect of Grain Size on the Characteristics of Zeolite as Adsorbents
311
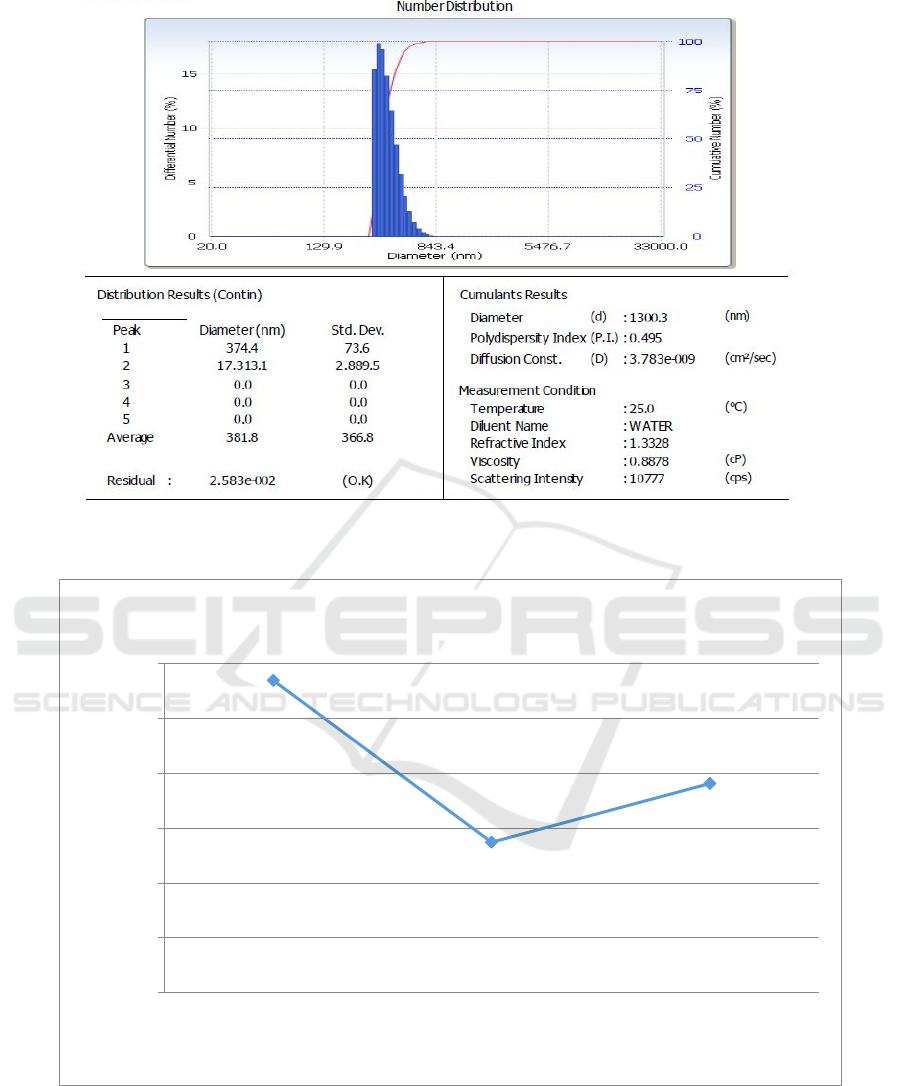
c.400 mesh.
Figure 3: PSA test results for zeolite in a size of(a) 200 mesh (b) 325 mesh, and (c) 400 mesh.
Figure 4: The relationship between diameter of zeolite and variations in the grain size.
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
200 325 400
AverageDiameter(nm)
GrainSize(mesh)
IMC-SciMath 2019 - The International MIPAnet Conference on Science and Mathematics (IMC-SciMath)
312

4 CONCLUSIONS
The study results prove that the grain influences the
characteristics of zeolite as an adsorbent. The 325-
mesh zeolite had optimum porosity and water
adsorption values compared to the 200-mesh zeolite
and 400-mesh zeolite. These results are consistent
with the Particle Size Analyzer (PSA) test results
which showed that the 325-mesh zeolite had the
smallest diameter compared tothe 200-mesh zeolite
and the 400-mesh zeolite.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors are very grateful to Universitas
Sumatera Utara for its funding throughout
TALENTA research program 2019 with given
contract numbers 4167/UN5.1.R/PPM/2019 on 01
April 2019.
REFERENCES
Breck, D. W. (1974). Zeolites Molecular Sieves: Structure,
Chemistry, and Use. John Wiley & Sons Inc.
Cheetham, A. K. (1992). Solid State Compound. Oxford
university press.
Galuh, S., & Rahmi, D. (2014). Pembuatan nanopartikel
dengan metoda high speed homogenization. Jurnal
Litbang Industri, 3(2), 67–131.
Muchtar, H., Anova, I. T., & Yeni, G. (2015). Pengaruh
Kecepatan Pengadukan dan Kehalusan Gambir Serta
Variasi Komposisi Terhadap Beberapa Sifat Fisika
dalam Pembuatan Tinta Cetak. Jurnal Litbang
Industri, 5(2), 131-139.
Mudjijono, H., Wahono, S. K., Maryana, R., & Pratiwi, D.
(2015). Modification of Gunungkidul Natural Zeolite
as Bioethanol Dehydrating Agents. Energy Procedia,
65, 116–120.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2015.01.042
Nasution, T. I., Zebua, F., Nainggolan, H., & Nainggolan,
I. (2015). Manufacture of Water Vapour Filter Based
on Natural Pahae Zeolite Used for Hydrogen Fueled
Motor Cycle. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 754–
755, 789–793.
https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.754-
755.789
Prasmita, K. (2012). Studi pendahuluan penentuan
distribusi ukuran nanopartikel logam Menggunakan
mikroelektroda. Universitas Indonesia.
Scott, E. K., Reuter, J. E., & Luo, L. (2003). BRIEF
COMMUNICATION Small GTPase Cdc42 Is
Required for Multiple Aspects of Dendritic
Morphogenesis. Journal of Neuroscience, 23(8),
3118–3123.
https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23
-08-03118.2003
SNI 13-7168-2006. (2006). Syarat mutu zeolit sebagai
bahan pembenah tanah pertanian. StandarNasional
Indonesia.
Wahono, S. K., Mudjijono, H., Kristiani, A., Tursiloadi,
S., & Abimanyu, H. (2014). Characterization and
Utilization of Gunungkidul Natural Zeolite for
Bioethanol Dehydration. Energy Procedia, 47, 263–
267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2014.01.223
Wulandari, R., & Priyono, C. (2014). Pengaruh Ukuran
Partikel Zeolit Terhadap PeningkatanKadar Bioetanol.
Indonsian Journal on Medical Science, 1(2).
Analysis of the Effect of Grain Size on the Characteristics of Zeolite as Adsorbents
313
