
Growth Conditions for Alpha-amylase-producing Bacterium PLS 75
Strain Isolated from a High Temperature and Saline Area
Teuku M. Iqbalsyah, Jasmin P. Nabila
and Febriani
Biomolecules Application Research Group, Chemistry Department, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences,
Universitas Syiah Kuala, Banda Aceh, Indonesia
Keywords: Thermophilic, halophilic, α-amylase, 16S rRNA
Abstract: Extreme habitat has been explored to find microorganisms that are capable of producing industrial enzymes
with better activity and stability. Four thermo-halophilic bacteria strains isolated from undersea fumaroles
were screened for their ability to produce extracellular hydrolytic enzymes. The most potent α-amylase
producer was PLS 75 strain. The strain was Gram-negative with uniform basil-chained shaped. Homology
analysis of the 16S rRNA gene fragments shows that the strain was closely related to an uncultured
bacterium isolate, supporting the fact that the strain was difficult to culture. Fermentation study shows that
PLS 75 produced the highest biomass (5.48 mg/ml) and α-amylase activity (4.43 U/ml) when incubated at
60 °C, pH 7 for 31 h. The results provided information on PLS 75 culture conditions that may be used to
produce the enzyme for the study of its attributes and catalytic activity.
1 INTRODUCTION
Microbiological research has shifted more attention
to extremophilic microorganisms. Their ability to
grow well in extreme conditions makes them unique.
Not only as of the source of distinct metabolites, but
they also a subject of adaption mechanism studies
(Elleuche et al., 2015). Extremophiles are
microorganisms inhabiting and living in extreme
conditions, such as high temperature (thermophile
and hyperthermophiles), high acidity (acidophiles),
high alkalinity (alkaliphiles), high pressure
(piezophiles), high radiation (radiophiles) and high
metal content (metalophiles). Habitats of
extremophiles widely diverse, from natural to
artificial environments. The former includes
hydrothermal and geothermal area, acid soil, soda
lake, high salt lake, deep ocean, while the latter
includes nuclear reactor and toxic chemical waste
(Dalmaso et al., 2015).
Enzymes produced by extremophiles are in-
demand biocatalysts due to their high activity and
stability in the harsh industrial process conditions.
Most enzymes are hampered due to high
temperature, pH and salinity requirement in the
process. Therefore, extremozymes are preferable for
their resistance to high temperature and chemical
denaturation (Souza et al., 2012).
Among the enzymes, thermostable hydrolases
are the most used enzymes in industries requiring
elevated temperature (Elleuche et al., 2014; Dalmaso
et al., 2015). Hydrolytic enzymes (carbohydrase,
protease, lipase) are accounted for about 80% of the
total enzyme market in the US, with a sales value
approaching USD 3 billion in 2019 (Grand View
Research, 2019).
α-Amylase (1,4-D-Glucan glucanohydrolase, EC
3.2.1.1) is a carbohydrase enzyme that catalyses the
hydrolysis of α-1,4-glycosidic bonds in starch to
produce simpler sugar molecules, such as dextrin,
maltose, and glucose (Reddy et al., 2003). The
enzyme has been widely used in food, textiles,
paper, detergents, bioethanol production and
pharmaceuticals industries (Souza and Magalhaes,
2010). α-amylases in starch industries are required to
remain active at high temperature, particularly those
involved in gelatinisation (100-110 °C) and
liquefaction (80-90 °C).
Our group has previously isolated some
microbial strains from shallow sea fumaroles
(Iqbalsyah et al., 2018; Iqbalsyah et al., 2019a). The
area provides extreme environments of high
temperature and salinity, which is an ideal habitat
for the extremophiles to produce enzymes with
368
Iqbalsyah, T., Nabila, J. and Febriani, .
Growth Conditions for Alpha-amylase-producing Bacterium PLS 75 Strain Isolated from a High Temperature and Saline Area.
DOI: 10.5220/0010182900002775
In Proceedings of the 1st Inter national MIPAnet Conference on Science and Mathematics (IMC-SciMath 2019), pages 368-375
ISBN: 978-989-758-556-2
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

unique features. Therefore the objective of this study
was to screen the microbial strains, which were able
to produce hydrolytic enzymes, particularly α-
amylase. The potential strain was phenotypically and
genotypically identified. As it is essential to imitate
the conditions of the native sampling area for further
experiments in the laboratory, the optimum
fermentation time, temperature and pH for the
production of α-amylase by the strain was studied.
The results could be used to produce the enzyme for
the study of its attributes and catalytic activity.
2 MATERIALS AND METHOD
2.1 Microorganism
This study used four microbial strains, namely PLS
75, PLS 76, PLS 80 and PLS A, that were the stock
culture of the Biochemistry Laboratory, Faculty of
Mathematics and Natural Sciences Syiah Kuala
University. The strains were previously isolated
from the sea bead of fumaroles in Pria Laot and
initially cultivated from the sand sample on Thermus
medium.
2.2 Screening of Hydrolytic Enzymes
PLS 76, PLS 75, PLS 80 and PLS A was grown on
on separate agar plates to evaluate their ability to
produce protease, lipase, amylase and cellulase.
Media of ½ Thermus solid, containing 0.4%
peptone, 0.2% yeast extract, 1% NaCl, 0.25%
glucose, 3% bacto agar, was used. The medium was
added with 3% skim milk and 0.5% casein for
protease screening; 1% olive oil, 0.5% tween 80 and
200 µl of 0.001% of Rhodamine B for lipase
screening; 1% soluble starch for α-amylase
screening and 1% carboxymethylcellulose (CMC)
for cellulase screening. All media were incubated for
24 h at 70 °C.
Protease activity was indicated by a clear zone
around the colonies. Lipase activity was identified
by orange fluorescent around the colonies under UV
light. Strains with amylase activity showed by a
clear zone after staining with potassium iodium
iodate. Strains with cellulase activity were identified
by a clear zone formed after being washed by 1 M
sodium chloride.
2.3 Identification of Microorganism
The cells of the most potent strain in producing α-
amylase were centrifuged at 5000 ×g for 10 minutes.
The pellet was used for morphology identification
by Gram-staining and Scanning Electron
Microscope (SEM).
The strain genotype was analysed from the 16S
rRNA gene sequence. Genomic DNA was isolated
from the pellet by using a DNA isolation kit
(Genetika Science). It was then used as a template to
amplify the 16S rRNA gene fragments using a pair
of primers, i.e. Com 1F
5'-
CAGCAGCCGCGGTAATAC-3'
and Com-1R (5'-
CCGTCAATTCCTTTGAGTTT-3'
) (Schwieger
& Tebbe, 1998
). The amplification consisted of 30
cycles of denaturation at 95 °C for 5 minutes and
annealing at 55 °C for 1 minute, as well as an
extension at 72 °C for 2 minutes. The amplicons
were subjected to agarose electrophoresis. The 16S
rRNA gene was sequenced by direct sequencing
method and compared with GenBank entries by
BLAST search (www.ncbi.nml.nih.gov). Alignment
and phylogenetic analysis were done using ClustalW
and Mega 6 software (Tamura et al., 2013),
respectively.
2.4 Growth Curve Study
The most potent α-amylase-producing strain was
incubated in ½ T medium pH 7 (using 0.1M
phosphate buffer) enriched with 0.25% glucose and
1% soluble starch for 48 h at 70 °C and 150 rpm.
The media used in the experiments were diluted in
sterile seawater to maintain the native salt
conditions. The medium was inoculated with the
strain to a level of 1 x 10
6
cells/ml. The growth was
measured by cell dry weight.
The α-amylase activity was assayed by
measuring the amount of reducing sugar produced
from the starch hydrolysis by 3,5-dinitrosalicylic
acid (DNS) method (Miller, 1959), using a standard
curve of glucose (1–10 μg/mL) measured at 540 nm.
One enzyme unit (U) is defined as the amount of
enzyme required to produce 1 μmol of reducing
glucose per minute under the assay conditions. All
measurements were done in triplicates.
2.5 Effect of Temperature, pH and Salt
on Biomass and α-amylase
Production
The optimum temperature for growth and α-amylase
production was determined by inoculating the strain
in ½ T medium in 0.1 M buffer phosphate pH 7,
enriched with 0.25% glucose and 1% soluble starch.
The incubation was conducted at 60, 65 and 70 °C
and 150 rpm until optimum incubation time.
Growth Conditions for Alpha-amylase-producing Bacterium PLS 75 Strain Isolated from a High Temperature and Saline Area
369
The optimum pH for α-amylase production was
determined by varying the pH of the media. The pH
was adjusted using 0.1M sodium acetate (pH 5),
0.1M dipotassium hydrogen phosphate (pH 7) and
0.1M glycine-NaOH (pH 9.0). The culture was
incubated at optimum incubation time and
temperature.
The effect of salt addition on α-amylase
production was determined by adjusting the ½ T
media to contain 1%, 2%, 3%, 4% sodium chloride.
The media was already dissolved in seawater, so the
final salt concentrations of the media were higher.
The culture was incubated at the optimum
incubation time, temperature and pH.
All experiments of temperature, pH and salt
variation were done in triplicates. Cell dry weight
and α-amylase activity were determined as described
in Section 2.4.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Enzyme Assay
All strains produced α-amylase, with PLS 75
showed the most profound activity. Only PLS A was
able to produce protease. PLS 80 was the only strain
that showed a lipase activity. Meanwhile, PLS 75
exhibited better cellulase activity than PLS 80
(Table 1). PLS 75 was therefore selected for further
α-amylase production experiment.
Table 1: Screening results of the isolated strains for
hydrolytic enzymes activity.
Strain
Enzyme
Amylase Protease Lipase Cellulase
PLS A + ++ - -
PLS 75 +++ - - ++
PLS 76 + - - -
PLS 80 ++ - + +
3.2 Identification of PLS 75
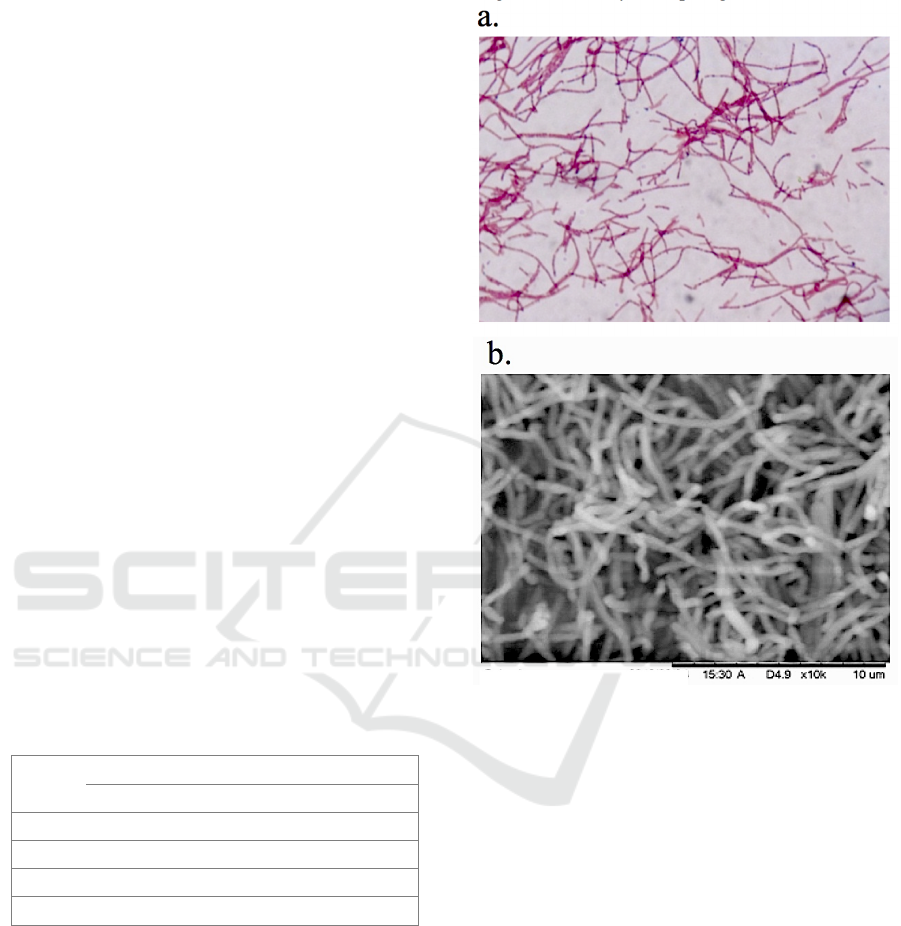
Gram-staining result shows that PLS 75 was a
Gram-negative bacterium. The SEM image supports
the information that PLS has a uniform long rod-
chained shaped, with roughly 5-10 mm in length
(Figure 1).
The size of PLS 75 strain chromosomal DNA
was well over 10 kbp. The primers used in the
amplification of the 16S rRNA gene fragments
(Com 1F and Com 2R) were able to produce gene
fragments of nearly 500 bp (Figure 2).
Figure 1: a. Gram Staining result; b. SEM image of PLS
75 with 10000× magnifications.
The phylogenetic tree was constructed from
some homologous genes in the GenBank (Figure 3).
PLS 75 has the closest homology with Uncultured
bacterium clone YE-DC-B41 with sequence
similarity of 98%. Until the intact 16s rRNA gene
(1500 bp) is amplified and sequenced, the PLS 75
species is still indefinable.
Growing PLS 75 was indeed difficult. The ½
Thermus (½ T) medium needed enrichment with a
small amount of glucose to promote biomass
production. Thermus medium is designed for culture
Thermus genera. The use of ½ T medium in this
study was to isolate more robust microorganisms
that can survive in minimum nutrition supply. The
use of enriched media (for example LB or NB) was
avoided, as they would host common
microorganisms.
IMC-SciMath 2019 - The International MIPAnet Conference on Science and Mathematics (IMC-SciMath)
370

Figure 2: a. Electrophoresis results of chromosomal DNA
of PLS 75; b. Electrophoresis results of 16S rRNA gene
fragments of PLS 75. M = DNA ladder, C = Chromosomal
DNA, S = 16S rDNA fragments.
3.3 Growth Curve of PLS 75
The growth curve study was conducted to determine
the optimum fermentation time for PLS 75 to
produce α-amylase. Fermentation was done at 70 °C
on ½ T medium containing starch. The starch
induced the production of the enzyme. Excreted α-
amylase then catalysed the starch digestion. The
products were further used for biomass and product
formation.
Figure 4 shows that the lag phase occurred up to
8 h, indicated by the relatively stagnant amount of
biomass. PLS 75 was in the exponential phase
between 8 to 30 h, marked by an increase in the
biomass. The highest amount of biomass produced
at 30 h (3.66 mg/ml). PLS 75 then entered the
stationary phase up to 42 h. The death phase
occurred afterwards.
Similar to biomass, the highest α-amylase
activity was also detected at the end of the
exponential phase (30 h). The activity then dropped
significantly. α-amylase production did not follow
the trend of biomass. There were fluctuations before
24 h of fermentation. Nevertheless, the enzyme was
still produced to utilise the starch in the medium.
The enzyme production declined when the biomass
decreased, implying the nutrition already exhausted.
The behaviour of microorganisms during
metabolites production depends on the strain, the
availability of the nutrients and the growth
conditions. Generally, α-amylase is optimally
produced at stationary phase (Malhotra et al., 2000;
Liu et al., 2008; Annamalai et al., 2011). However,
some are produced optimally in the exponential
phase (Moshfegh et al., 2013; Berekaa et al., 2007).
It has been suggested that the addition of glucose as
the carbon source in the media may lead to
catabolite repression that suppresses α-amylase
production (Berekaa et al., 2007). The same
suppression might also occur in this study, as a small
amount of glucose was added to the fermentation
medium.
Figure 3: Phylogenetic relationship of the 16S rRNA gene (480 bp) from PLS 75 with 17 most related gene sequence. The
phylogenetic tree was constructed using the neighbour-joining method of the Mega 6 software with 1000 bootstrap
replicates.
Growth Conditions for Alpha-amylase-producing Bacterium PLS 75 Strain Isolated from a High Temperature and Saline Area
371

Figure 4: Growth curve of PLS 75 in ½ T medium
enriched with 0.25% glucose. The incubation was
conducted at temperature 70 °C, pH 7 and 150 rpm. The
data was an average of triplicates ± SD.
3.4 Effect of Incubation Temperature
on Biomass and α-amylase
Production
The effect of temperature on biomass and α-amylase
production was studied at 60 °C, 65 °C, and 70 °C in
a narrow time window (27 – 32 h). Figure 5a shows
that the biomass, measured as cells dry weight, was
best produced at 60 °C. The highest biomass
concentration (5.5 mg/ml) was observed at 60 °C
and 28 h. The biomass at 70 °C was roughly half of
that at 60 °C. Optimum α-amylase activities of all
temperature were observed at a slightly delayed
time. The highest activity (4.43 U/ml) was achieved
at 60 °C and 31 h. The optimum time was also
applicable to all other temperature (Figure 5b).
The number of cells and enzyme activity is
generally interrelated. On the one hand, the increase
in cells mass will produce more enzymes. On the
other hand, biomass formation is catalysed by
enzymes. Enzyme production increases with
increasing temperature until a certain level. A
temperature above the optimum causes a decrease in
enzyme activity. It gives adverse impacts on
metabolic activity, which reduce growth and product
formation (Sundarram and Murthy, 2014). High
temperature affects enzyme activity in two ways, i.e.
changing the reaction rate constant and causing
thermal denaturation of the enzyme (Demirkan et al.,
2017). However, cells formation and α-amylase
production are controlled by different regulatory
mechanisms (Baysal et al., 2003).
Figure 5: Effect of fermentation temperature on; a.
Biomass production; b. α-amylase activity. The incubation
was conducted at pH 7 and 150 rpm. The data was an
average of triplicates ± SD.
The results are in agreement with several studies
employing thermophilic bacteria. Devi et al. (2010)
reported that the optimum incubation temperature
for two of Bacillus spp. strains to acquire high α-
amylase activity was in the range 60-80 °C. The
enzyme is already produced in the exponential phase
and reaches a maximum at the stationary phase.
Meanwhile, a thermo-halophilic Bacillus sp.
NRC22017 produces optimum α-amylase at 45 °C.
A 10 °C increase in the temperature reduces the
enzyme activity by two-third (Elmansy et al., 2018).
3.5 Effect of pH of Medium on Biomass
and α-amylase Production
The effect of pH on biomass and α-amylase
production was studied at pH 5, 7 and 9. The
biomass at pH 5 and 7 was about twice as much as
that at pH 9 (Figure 6a). The highest biomass (3.57
mg/ml) was observed at pH 7 and 30 h. The highest
α-amylase activity (4.4 U/ml) was also produced at
pH 7 and 31 h. The enzyme activity at acidic and
alkaline pH was low (Figure 6b).
IMC-SciMath 2019 - The International MIPAnet Conference on Science and Mathematics (IMC-SciMath)
372
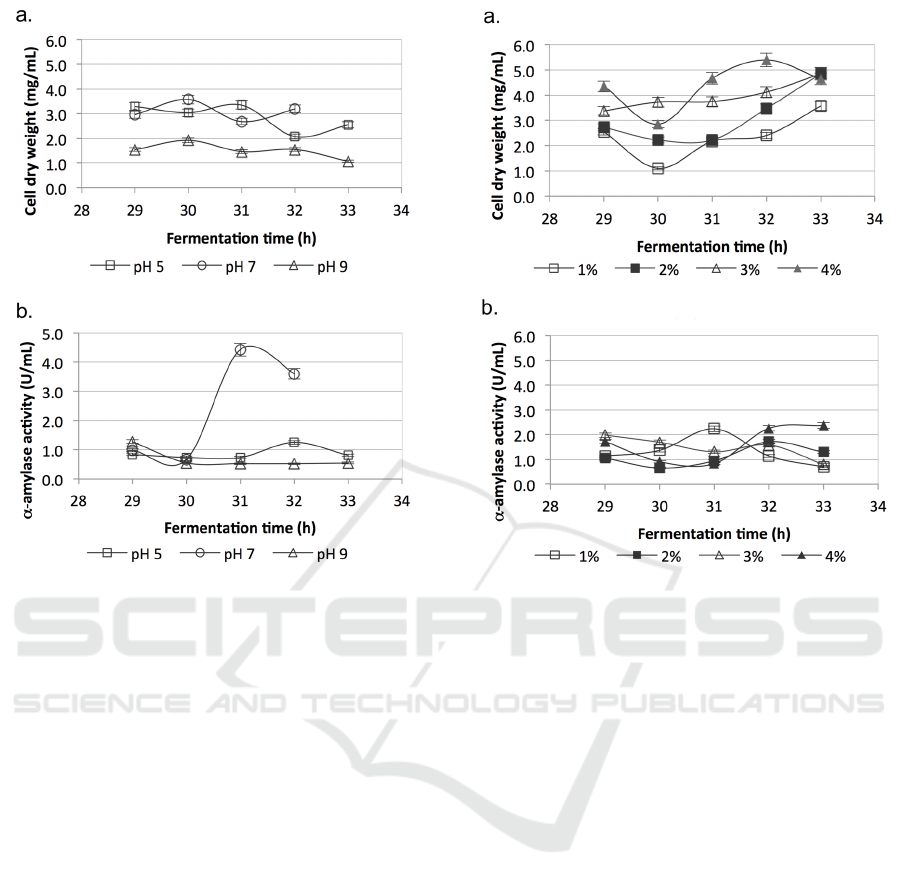
Figure 6: Effect of pH of the medium on; a. Biomass
production; b. α-amylase activity. The incubation was
conducted at temperature 60 °C and 150 rpm. The data
was an average of triplicates ± SD.
We have previously reported that the highest
activity of the purified amylase from PLS 75 strain
was at pH 5 (Iqbalsyah et al., 2018). Other
molecules might have affected the activity as the
enzyme was still in the crude form. Most microbial
α-amylases perform the best catalytic activity at low
pH (Zhang et al., 2017). However, some may work
across a wide range of pH (Ghorbel et al., 2009).
3.6 Effect of Salt Addition on Biomass
and α-amylase Production
On the top of the available salts in the medium, as it
was dissolved in seawater, various concentrations of
sodium chloride were added to the media to contain
an additional 1%, 2%, 3% and 4% to study the
halophilic character of PLS 75 strain. The highest
biomass concentration (5.40 mg/mL) was observed
with the addition of 4% salt (Figure 7a). The highest
α-amylase activity (2.38 U/mL) was also observed at
the same salt concentration, although the difference
was inconsequential (Figure 7b).
Figure 7: Effect of NaCl addition on; a. Biomass
production; b. α-amylase activity. The salt addition was
made to a final concentration of the media. The incubation
was conducted at temperature 60 °C, pH 7 and 150 rpm.
The data was an average of triplicates ± SD.
The results suggest that the α-amylase from PLS
75 strain was an extreme halophilic enzyme as it was
still active in the presence of 2.5–5.2M NaCl. This
result is in agreement with our previous report of
PLS A strain isolated from the same area in
producing protease (Iqbalsyah et al., 2019a). This
result suggests that the enzyme may be able to
escape denaturation in high salt concentrations. It
can thus be useful to catalyse reactions in non-
aqueous solution (Moreno et al., 2013).
The fumaroles from which the PLS 75 strain was
isolated had an onset temperature around 80-100 °C,
a neutral pH and a salt concentration of around 3.5
M. Magnesium, chloride, iron, lead and copper ions
are much higher than those in typical seawater
(Iqbalsyah et al., 2019b). The different chemical
composition than the typical seawater implies
unique physiology of PLS 75 strain.
Growth Conditions for Alpha-amylase-producing Bacterium PLS 75 Strain Isolated from a High Temperature and Saline Area
373

4 CONCLUSION
Four poly-extremophilic strains isolated from
undersea fumaroles in Pria Laot Sabang were able to
secrete extracellular hydrolytic enzymes. PLS 75
was the most potent strain to produce thermostable
α-amylase and cellulase. The strain had a close
relationship with uncultured microorganism after
16s rRNA gene sequence analysis. The results of
growth condition experiments show that PLS 75
optimally produced thermostable α-amylase at 60°C
and pH 5 for 30 h incubation. It resisted high salt
concentration. This study provided preliminary
information on PLS 75 cultivation conditions. may
The results may be used for scaling-up of the
enzyme production for various uses.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This work was financed by the Fundamental
Research Grant Number 383/UN11/A.01/
APBNP2T/13 from Universitas Syiah Kuala.
REFERENCES
Annamalai, N., Thavasi, R. and Vijayalakshmi, S. and
Balasubramanian, T. 2011, 'Extraction, purification
and characterisation of thermostable, alkaline tolerant
α-amylase from Bacillus cereus', Indian Journal of
Microbiology 51 (4), 424–429.
Baysal, Z., Uyar, F. and Aytekin, C. 2003, 'Production of
α-amylase by thermotolerant Bacillus subtilis in the
presence of some carbon, nitrogen-containing
compounds and surfactants', Annals of Microbiology
53 (3), 323–328.
Berekaa, M. M., Soliman, N. A. and Abdel-Fattah, Y. R.
2007, 'Partial characterisation and cloning of
thermostable α-amylase of a thermophile Geobacillus
thermoleovorans YN', Biotechnology 6, 175–183.
Dalmaso, G. Z. L., Ferreira, D. and Vermelho, A. B. 2015,
'Marine extremophiles a source of hydrolases for
biotechnological applications', Marine Drugs 13 (4),
1925–1965.
Demirkan, E., Sevgi, T. and Başkurt, M. 2017,
'Optimisation of physical factors affecting the
production of the α-amylase from a newly isolated
Bacillus sp. M10 strain’, Karaelmas Fen ve
Mühendislik Dergisi 7 (1), 23–30.
Devi, L. S., Khaund, P. and Joshi, S. R. 2010,
Thermostable α -amylase from natural variants of
Bacillus sp. prevalent in Eastern Himalayan range.
African Journal of Microbiology Research 4 (23),
2534-2542.
Elleuche, S., Schafers, C., Blank, S., Schroder, C. and
Antranikian, G. 2015, 'Exploration of extremophiles
for high-temperature biotechnological processes',
Current Opinion in Microbiology 25, 113–119.
Elmansy, E. A., Asker, M. S., El-Kady, E. M., Hassanein,
S. M and El-Beih F. M. 2018, 'Production and
optimisation of α-amylase from thermo-halophilic
bacteria isolated from different local marine
environments', Bulletin of the National Research
Center 42: 31.
Ghorbel, R. E. Maktouf, S., Massoud, E. B., Bejar, S., and
Chaabouni, S. E. 2009, 'Thermostable amylase from
Bacillus cohnii US147 with broad pH applicability',
Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology 157, 50–60.
Grand View Research 2019, Enzymes market size, share
and trends analysis report by product (carboydrases,
proteases, lipases), by application (industrial,
specialty), by end use, by region, and segment
forecasts, 2019 - 2025. [online] Available at:
https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-
analysis/enzymes-industry [Accessed 26 August
2019].
Iqbalsyah, T. M., Fajarna, F. and Febriani 2018,
'Purification and partial characterisation of α-amylase
produced by a thermo-halophilic bacterium isolate
PLS 75', Biosaintifika 10 (3), 574–580.
Iqbalsyah, T. M., Malahayati, M. Atikah, A. and Febriani,
F. 2019a, 'Cultivation conditions for protease
production by a thermo-halostable bacterial isolate
PLS A', Jurnal Natural 19 (1), 18–23.
Iqbalsyah, T. M., Malahayati, Atikah and Febriani 2019b,
'Purification and partial characterisation of a thermo-
halostable protease produced by Geobacillus sp. strain
PLS A isolated from undersea fumaroles', Journal of
Taibah University for Science 13 (1), 850–857.
Liu, X.D. and Xu, Y. 2008, 'A novel raw starch digesting
α-amylase from a newly isolated Bacillus sp. YX-1:
Purification and Characterisation', Bioresources
Technology 99, 4315–4320.
Malhotra, R., Noorwez, S. and Satyanarayana, T. 2000,
'Production and partial characterisation of
thermostable and calcium‐independent α‐amylase of
an extreme thermophile Bacillus thermooleovorans
NP54', Letters in Applied Microbiology 31, 378–384.
Miller, G. L. 1959, 'Use of Dinitrosalicylic Acid reagent
for determination of reducing sugar', Analytical
Chemistry 31 (3), 426–428.
Moreno, M. de L., Perez, D. and Garcia, M. T. Mellado, E.
2013, 'Halophilic bacteria as a source of novel
hydrolytic enzymes', Life 3, 38–51.
Moshfegh, M., Shahverdi, A. R., Zarrinni, G. and
Faramarzi, M. A. 2013, 'Biochemical characterisation
of an extracellular polyextremophilic α-amylase from
the halophilic archaeon Halorubrum xingjiangense’,
Extremophiles 17, 677–687.
Reddy, N. S., Nimmagadda, A. and Rao, K.R.S.S. 2003,
'An overview of the microbial α-amylase family',
African Journal of Biotechnology 2 (12), 645–648.
Schwieger, F. and Tebbe, C.C. 1998, 'A New Approach to
Utilise PCR-Single Stranded Conformation
IMC-SciMath 2019 - The International MIPAnet Conference on Science and Mathematics (IMC-SciMath)
374

Polymorphism for 16S rRNA Gene-Based Microbial
Community Analysis, Applied Environmental
Microbiology 64, 4870-4876.
Souza, P. M. de and Magalhaes, P. de O. 2010,
Application of microbial α-amylase in industry - A
review’, Brazilian Journal of Microbiology 41, 850–
861.
Sundarram, A. and Murthy, T. P. K. 2014, 'α-Amylase
production and application: A review', Journal of
Applied and Environmental Microbiology 2 (4), 166–
175.
Tamura, K., Stecher, G., Peterson, D., Filipski, A. and
Kumar S. 2013, 'MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary
genetics analysis version 6.0', Molecular Biology and
Evolution 30, 2725–2729.
Zhang, Q., Han, Y. and Xiao, H. 2017, 'Microbial α-
amylase: A biomolecular overview', Process
Biochemistry 53, 88–101.
Growth Conditions for Alpha-amylase-producing Bacterium PLS 75 Strain Isolated from a High Temperature and Saline Area
375
