
Participatory Training Model Development in Increasing of
Competence Cadre Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Sumatera Utara
Reni Asmara Ariga
1*
, Siti Zahara Nasution
1
, Cholina Trisa Siregar
1
, Muhammad Taufik
2
, Fajar
Amanah Ariga
1
and Sri Budi Astuti
1
1
Faculty of Nursing, Universitas Sumatera Utara. Medan, Indonesia
2
Chemistry Department, Faculty of Mathematic and Natural Science, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia
Keywords: Participatory Training Model, Competence Cadre, Pulmonary TB.
Abstract: The high rates of morbidity and mortality of pulmonary TB patients can be caused by the low competency
of health cadres. This competence is obtained through participatory training models. The aimed to
determine the effect of participatory training models on tuberculosis cadre competence. The research used a
pre-posttest without control group Quasi-experiment design. The sample consisted of 44 respondents. The
instrument was a questionnaire form with a validity value of 0.89 and a test of Cronbach-alpha reliability
0.86. The results showed that differences before and after the intervention participatory training model,
namely knowledge before and after intervention occurred 9% increase, attitudes before and after
intervention increased 34%, actions before and after intervention increased 24.2%. This training model is
expected to become a habit of cadres when mentoring in the community and integrated with empowerment
programs for patients such as HORAS (Health belief model, Observation, Relaxation, Action, Supporting).
1 INTRODUCTION
Pulmonary tuberculosis (pulmonary TB) is a chronic
disease that is a health problem in the world
including Indonesia (Ministry of Health Indonesian,
2017). WHO states that pulmonary TB is now a
global threat. An estimated 1.9 billion people or one-
third of the world's population are infected with this
disease. Every year there are about 9 million new
patients with pulmonary TB with a death of 3
million people. It is estimated that 95% of
pulmonary TB cases and 98% of deaths due to
pulmonary TB in the world occur in developing
countries. Likewise, the death of women due to
pulmonary TB is more than deaths due to pregnancy,
childbirth and postpartum. As many as 10.4 million
people are estimated to suffer from pulmonary TB in
2015 with a total of 5.9 million male patients (56%),
women as many as 3.5 million people (34%) and
children as many as one million people (10%).
Furthermore, the World Health Organization (WHO)
noted in 2015 that 60% of all cases were contributed
by six countries namely India followed by
Indonesia, China, Nigeria, Pakistan and South Africa
(Ministry of Health Indonesian, 2017).
In Indonesia, the coverage of tuberculosis cases
between men and women was 298,128 cases in
2016, while in North Sumatra province the coverage
of tuberculosis cases between men and women was
17,798 cases in 2016 which is the province with the
most number 5 coverage Indonesia (Ariga & Reni,
2017).
About 75% of pulmonary TB patients are the
most economically productive age group (15-50
years old). Meanwhile, it is estimated that an adult
pulmonary TB patient will lose an average of 3 to 4
months of work time. This situation resulted in a
loss of annual household income of around 20-30%.
If he/she dies from pulmonary tuberculosis, then
he/she will lose about 15 years of income. Besides
being economically detrimental, pulmonary
tuberculosis also has other socially stigmatizing
adverse effects and it is even excluded by the
community (Ariga & Reni, 2017).
Tuberculosis Eradication Program Data (P2
pulmonary TB) in Indonesia showed an increase in
cases from year to year. Prevention and prevention
efforts that have been attempted still have not
succeeded in solving the existing problems, namely
reducing morbidity and mortality. One of the
problems encountered was the difficulty of finding
Ariga, R., Nasution, S., Siregar, C., Taufik, M., Ariga, F. and Astuti, S.
Participatory Training Model Development in Increasing of Competence Cadre Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Sumatera Utara.
DOI: 10.5220/0010205100002775
In Proceedings of the 1st International MIPAnet Conference on Science and Mathematics (IMC-SciMath 2019), pages 469-474
ISBN: 978-989-758-556-2
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
469

smear (+) pulmonary TB patients, irregularity in
treatment and drop out of treatment. Cases of
untreated pulmonary TB will continue to be a source
of transmission3.
Family and community support have a major role
in improving medication adherence, with
supervision and encouragement of sufferers. The
role of the Drugs Supervisor (PMO) can come from
health workers, the community or the families of
patients. An important understanding of knowledge
about pulmonary TB for patients and families
through cadre empowerment4. The people who can
be involved in this activity are health cadre
(Kementerian Kesehatan RI Pusat Data dan
Informasi Kementerian Kesehatan RI, 2016).
Health cadres are people who are appointed by
the community who can help the community,
especially in health problems such as pulmonary
tuberculosis, health cadres should have the
competence so that in carrying out their duties in the
community, especially the prevention of pulmonary
TB6. This competency improvement can be done by
participatory model training. Where this training
provides the ability of knowledge, attitudes, and
skills to cadres in carrying out their roles in the
community, especially prevention and assistance in
the treatment of pulmonary TB.
2 METHOD
The Research on the development of a participatory
training model in improving cadre competency on
pulmonary TB in North Sumatra uses a quantitative
design with training methods consisting of three
stages: the first stage is the planning stage, which
includes identification of competencies, preparation
of objectives, establishment of training strategies,
preparation of training materials, apply the
andragogy principle and participatory techniques,
preparation of training planning. the second stage is
the implementation, which includes explaining the
concept and the third stage is the evaluation of
activities, namely the evaluation of the training
carried out.
The population and sample of this study were all
integrated service center cadres in Sari Rejo
Subdistrict, Medan Polonia Subdistrict who were
still active and willing to take part in this study as
many as 44 people. This research has been carried
out for 6 months starting from July to September
2016. The reason for the study was to choose Sari
Rejo Village, Medan Polonia Subdistrict as a place
of research because this location is a densely
populated area with pulmonary tuberculosis
residents, integrated service center and health
cadres. The community is active in community
activities and cooperates in the business of clean,
healthy living behavior and one of the fields of
nursing professional student practice in the USU
nursing faculty community. This research instrument
uses a demographic data questionnaire and
questionnaire to develop a participatory training
model in improving cadre competence about
pulmonary TB that has been tested for validity to
experts in the field of pulmonary TB obtained 0.89
The reliability test results obtained were 0.83.
Training is carried out 4 times a month for 3
consecutive months. The things that are done during
the training can be described as follows:
a. In July, training was conducted on the concept of
pulmonary tuberculosis, such as testing, causes,
signs and symptoms, prevention and mentoring
of pulmonary patients.
b. In the 2nd and 3rd month, all cadres simulate
prevention efforts carried out on TB patients,
namely preventing and mentoring pulmonary TB
patients, identifying the risk of pulmonary TB,
motivating the community to conduct treatment
programs
Implementation stage during the training process
1. First Stage
Explain the scope of the extension material that
is carried out. Describe the relevance and
benefits of the material to the cadre
2. Second stage
a. Outlines the material about the concept of
pulmonary TB
b. Do a simulation
3. Third Stage
Evaluate cadre competencies, including
cognitive, affective and psychomotor
Basic skills that cadres must possess
1. Questioning skills
a. Express questions in a short and clear
manner
b. Transfer of questions to all
participants
c. Give the time to pause thinking before
asking the answer to the cadre
2. Strengthening skills
a. Demonstrate verbal reinforcement like
the word: Right, good, right or very
good
IMC-SciMath 2019 - The International MIPAnet Conference on Science and Mathematics (IMC-SciMath)
470
b. Demonstrate non-verbal reinforcement
such as expression and body
movements
c. Strengthening: warmth and
enthusiasm, avoiding negative
responses
3. Explaining skills
a. Cadre explained using simple/general
sentences about pulmonary TB
b. Cadres provide examples in providing
counseling
c. Cadres use clear sentences
4. Skills for making variations
a. Cadres provide variations in tone of
voice during counseling
b. The cadre gave expressions and
gestures at the time of counseling
c. Cadres provide a point of contact
during counseling
5. The skill of opening and closing lessons
a. Cadres attract audience attention
b. Cadre raises motivation
c. The cadre evaluates the material
presented
3 DISCUSSION
Demographic data of respondents includes age,
gender, occupation, and education. The results of the
demographic data research obtained an early adult
age of 29 respondents (66%), all respondents were
female (100%), high school 30 respondents (%).
Information can be seen in the table below (Table 1).
Table 1: Demographic characteristics.
Characteristic Frequency (f) Percent
(%)
Age
Early adult 29 66
Late adult 15 34
Genre
Male 0 0
Female 44 100
Education
Primary School 1 2,27
Secondary school 13 29,55
High School 30 68,18
Length of job experience
<5 Years (New) 14 32
>5 Years (Old) 30 68
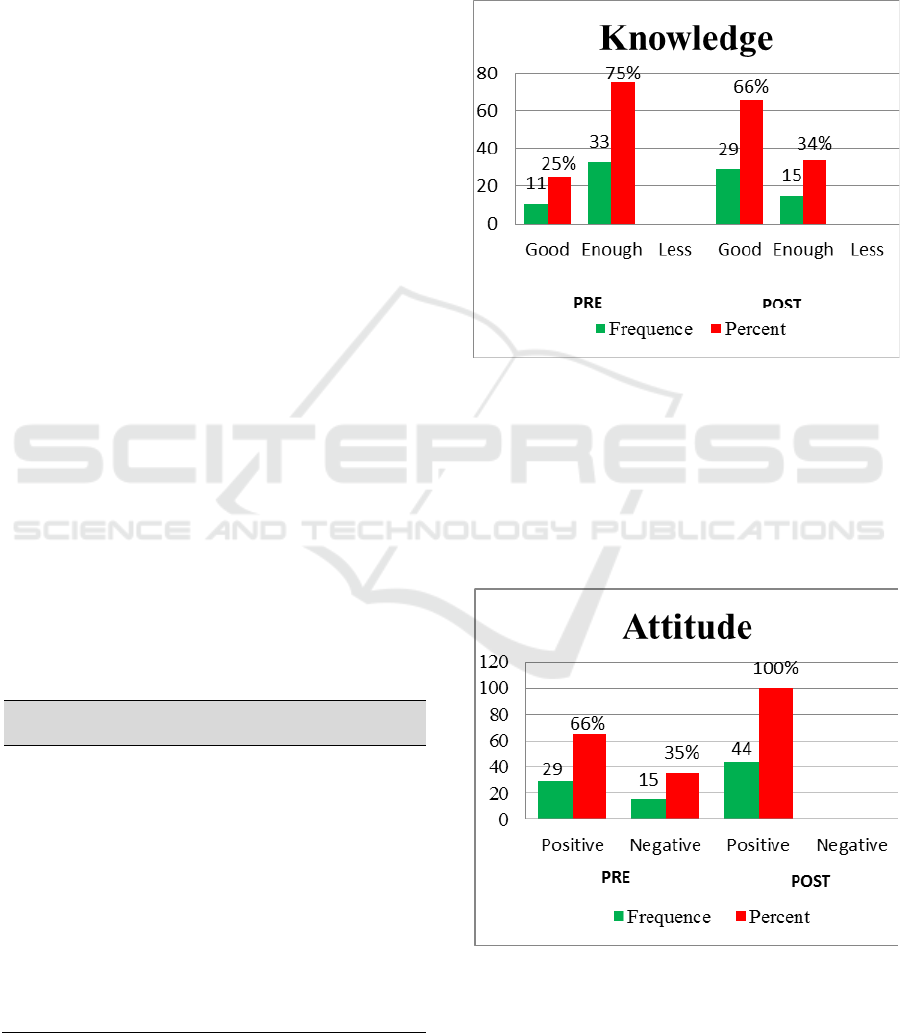
The results of research related to knowledge
were obtained before the participatory model was
conducted, the majority of patients' knowledge was
in the category of 75%. After a participatory model,
the majority of patients' knowledge was in the good
category of 66%. Information can be seen in the
graph below (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Patients Knowledge.
The respondents data includes age, gender,
occupation, and education. The results of the
demographic data research obtained an early adult
age of 29 respondents (66%), all respondents were
female (100%), high school 30 respondents (%).
Information can be seen in the table below (Figure
2).
Figure 2: Patients Attitude.
The results of the research related to attitudes
were obtained before the participatory model was
carried out, the majority of patients' attitudes were in
Participatory Training Model Development in Increasing of Competence Cadre Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Sumatera Utara
471
the positive category of 66%. After a participatory
model, the majority of patients' attitudes were in the
100% positive category. Information can be seen in
the graph below (Figure 3).
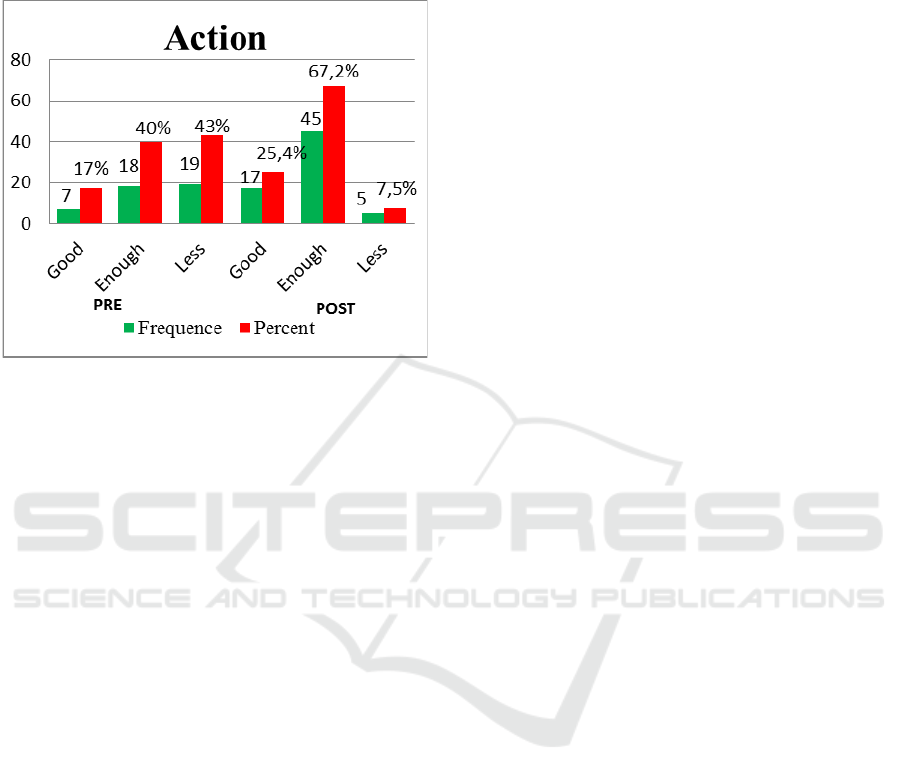
Figure 3: Patients Action.
The results of the study related to the action were
obtained before the participatory model was used,
the majority of the patients' actions were in the 43%
less category. After a participatory model, the
majority of patients' actions were in the good
category of 67.2% (Ministry of Health Indonesian,
2017).
The results of the study obtained the knowledge
of cadres before taking action in the category of
enough as much as 75%. This is because the cadres
have never received training, so the cadre has not
assumed that the discovery of pulmonary TB
suspects is their duty that must be carried out as well
as possible for increasing cases. Pulmonary TB in
the area. The focus of cadre activities so far is only
on the implementation of Posyandu and is related to
the health of infants and toddlers, so that the cadres
assume that the task of finding suspected pulmonary
TB is only side lined. This condition encourages
cadres to be less enthusiastic in finding information
about the mechanism of finding pulmonary TB
suspects.
The same thing was found by Chatarina in her
research on efforts to achieve positive BTA targets
on Suspek TB Pulmonary in South Middle East
District of NTT Province, which revealed that the
performance of cadres who were not equipped with
sufficient knowledge and only in a simple way to
refer suspects to subdistrict community health centre
is the target (Chatarina, 2007).
The results of the study showed that the attitude
of cadres before the action was carried out in the
positive category was 66%. This is influenced by the
length of time of the cadre. The majority of cadres
have a working period of more than 5 years as much
as 68%. Long working periods make cadres have
sufficient experience in carrying out the
interventions. Individuals who have long work
problems can make individuals understand the
attitude to be taken6. Another opinion expressed by
Andira that the longer the working period of a cadre,
the more experience he has so that it can be used as
a basis for acting / making decisions. On the
contrary, novice cadres do not have much
experience and are foreign and hesitant. This
condition will hamper participation in an activity
(Mirowsky & Ross, 2017).
The results of the research showed that the
cadre's actions before being carried out in the less
category were 43%. This is influenced by the
majority of cadre knowledge is as much as 75%.
Individuals who have sufficient knowledge will tend
to be less focused on taking action6. Related parties
such as health centers have not involved cadres to do
prevention, find and assist pulmonary TB patients in
the cadre area. The cadre does not have much
knowledge about taking action directly into the
community to the importance of breaking the chain
of transmission of TB through a screening action
carried out as a cadre.
The results of the study obtained the knowledge
of cadres after the action in the good category as
much as 66%. Good knowledge in this study is
influenced by the frequency of training. The more
often training is carried out, it can increase cadre
knowledge and skills. Training is part of education
that involves the learning process to acquire and
improve skills outside the education system that
applies in a relatively short time with methods that
prioritize practice rather than theory. Training is
basically an effort to increase knowledge and skills
and the ability of individuals to be able to carry out a
task or work that is charged to him.
Another factor that influences good knowledge is
the length of service. The length of the work period
greatly affects the ability of participatory training,
where the longer the cadre profession goes the better
the performance. Andira suggested that work period
is one indicator of the tendency in jobs where the
longer a person works the higher the productivity
because the more experienced and skilled at
completing the task entrusted to him (Andira et al.,
2012).
The results of the study showed that the attitude
of cadres after doing the action in the positive
category was 100%. A positive attitude in this study
IMC-SciMath 2019 - The International MIPAnet Conference on Science and Mathematics (IMC-SciMath)
472

can be caused by factors of knowledge and
experience. Knowledge influences the attitude of
cadres, good cadre knowledge influences cadre
competence in conducting participatory training. As
revealed by Eka's research, cadre knowledge has an
effect on cadre skills on what material is to be
conveyed. Cadre knowledge influences positive
attitudes, then forms good behavior when cadres
conduct counselling9. The more positive the attitude
of cadres will be to improve the practice and
behavior of cadres in conducting counselling which
is their responsibility (Notoatmodjo, 2012).
In addition to the knowledge factors positive
attitude of cadres because all cadres have realized
that they have a function, motivate and strive so that
residents in the environment are healthy and
prevented from various diseases specifically
pulmonary diseases. This is supported by the
opinion of Djafar, the more positive the attitude of
cadres will be to improve the practice and behavior
of cadres in conducting counselling which is their
responsibility (Djafar, 2014).
The results of the study showed that the cadre's
actions after being carried out in the category of
enough as much as 67.2%. Efforts to control TB
disease as a whole are still not ideal, because there
are some inappropriate actions carried out by cadres
(Kritiawati & Diyan, 2014). In conducting referral
TB suspects, the actions of cadres are still wrong,
because in making referrals do not use forms. This is
probably due to the cadre's ignorance of how to fill
in TB patient forms and the possibility of TB
patients who have been found coming to the
subdistrict community health centre without being
accompanied by cadres. However, the cadre's
actions in finding and conducting counselling are
good enough, this is because the cadre's knowledge
of TB disease, especially in recognizing the
symptoms of TB patients is good enough. So that
TB cadres can recruit TB suspects and provide
counselling to the public about TB at the integrated
system service.
4 CONCLUSION
The development of participatory training is suitable
for cadres in order to reduce morbidity and mortality
of TB in the community with the implementation of
this training model can be received by cadres.
Development with participatory training approach is
an innovative training model and effective in
improving the competence of health workers about
TB so it is necessary to be applied in other health
fields. This training model is expected to become a
habit of cadres when mentoring in the community
and integrated with empowerment programs for
patients such as HORAS (Horas believed model,
Observation, Relaxation, Action, Supporting).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors gratefully acknowledge that the present
research is supported by Ministry of Research and
Technology and Higher Education Republic of
Indonesia.
REFERENCES
Andira, R., Abdullah, A., & Sidik. (2012). Fakultas
Kesehatan Masyarakat. UNIVERSITAS
HASANUDDIN.
Ariga, & Reni, A. (2017). Parents’ behavior in giving drug
in children with tuberculosis in polyclinic children
RSUD. Dr. Pirngadi Medan. Asian Journal of
Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research, 11(13), 239.
Chatarina, U. (2007). Administrasi Kebijakan Kesehatan.
Universitas Hasanuddin.
Djafar, M. (2014). Jurnal Ilmiah WIDYA. PS GIZI
STIKES BINAWAN.
Kementerian Kesehatan RI Pusat Data dan Informasi
Kementerian Kesehatan RI. (2016). Temukan Obati
Sampai Sembuh.
http://www.depkes.go.id/download.php?file=downloa
d/pusdatin/infodatin/infodatin_tb.pdf
Kritiawati, Y. C., & Diyan, P. (2014). Publikasi Ilmiah.
Ministry of Health Indonesian. (2017). Data and
Information; Health Profile Of Indonesia 2016.
http://www.depkes.go.id/resources/download/pusdatin
/lain-lain/Data dan Informasi Kesehatan Profil
Kesehatan Indonesia 2016 - smaller size - web.pdf
Mirowsky, J., & Ross, C. (2017). Education, Social Status
and Health.
Notoatmodjo, S. (2012). Promosi Kesehatan dan Perilaku
Kesehatan. Rineka Cipta.
World Health Organization. (2015). Global Tuberculosis
Report WHO Library Cataloguing in Publication
Data.
Andira, RA., Abdullah AZ., Sidik., 2012. Fakultas
Kesehatan Masyarakat. UNIVERSITAS
HASANUDDIN.
Ariga, Reni A. Parents’ behavior in giving drug in
children with tuberculosis in polyclinic children
RSUD. Dr. Pirngadi Medan. Asian Journal of
Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research11(13):239
Chatarina UW.,. Jurnal Administrasi Kebijakan
Kesehatan. 2007. UNIVERSITAS HASANUDDIN
Djafar, M., 2014. Jurnal Ilmiah WIDYA. PS GIZI
STIKES BINAWAN.
Participatory Training Model Development in Increasing of Competence Cadre Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Sumatera Utara
473

Kementerian Kesehatan RI Pusat Data dan Informasi
Kementerian Kesehatan RI., 2016. Temukan Obati
Sampai Sembuh.
http://www.depkes.go.id/download.php?file=downloa
d/pusdatin/infodatin/infodatin_tb.pdf. [accesed 02
June 2018]
Kusuma, AR., 2015. Program Studi Kesehatan Masyarakat
Fakultas Ilmu Kesehatan. UNIVERSITAS
MUHAMMADIYAH SURAKARTA.
Ministry of Health Indonesian., 2017. Data and
Information; Health Profile Of Indonesia 2016.
http://www.depkes.go.id/resources/download/pusdatin
/lain-
lain/Data%20dan%20Informasi%20Kesehatan%20Pro
fil%20Kesehatan%20Indonesia%202016%20-
%20%20smaller%20size%20-%20web.pdf [accesed
02 June 2018]
Mirowsky J, Ross C.,. Education, Social Status and Health
(United State of America, Routledge). 2017
Notoatmodjo, S.,. Promosi Kesehatan dan Perilaku
Kesehatan. 2012. Rineka Cipta. Jakarta.
World Health Organization (WHO). Global Tuberculosis
Report 2015 WHO Library Cataloguing in Publication
Data. 2015.
YC., Kritiawati, Diyan P., 2014. Publikasi Ilmiah.
Program Studi Pendidikan Ners Fakultas
Keperawatan. UNIVERSITAS AIRLANGGA.
IMC-SciMath 2019 - The International MIPAnet Conference on Science and Mathematics (IMC-SciMath)
474
