
Antimicrobial Activities Assessment of Cinnamon Bark
(Cinnamomum burmannii Nees & T. Nees) Extract against Caries
Factors
Prasetyorini
1
, Dian Indah W.
2
, Yulianita
2
, Novi F. U.
2
and Neng Rani
2
1
Biology Study Program, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Science, Universitas Pakuan, Bogor, Indonesia
2
Pharmacy Study Program, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Science, Universitas Pakuan, Bogor, Indonesia
Keywords: Cinnamon Bark Extract; Streptococcus Mutan, Staphylococus Aureus; Candida Albicans.
Abstract: This research was conducted to test the antimicrobial activity of cinnamon bark (Cinnamomum burmani
Nees & T. Nees Blume) against Streptococcus mutans, Streptococcus aureus, and Candida albicans. The
gradual extraction method was employed using 3 types of solvents which were n-hexane, ethyl acetate, and
70% ethanol. The obtained extracts were dried from their solvents by vacuum-drying and weighed to obtain
the extraction yield. The dried extracts were each characterized to gain information about color, aroma, and
water content. Further characterization was conducted to qualitatively measure the phytochemical contents
such as alkaloids, flavonoids, tannins, and saponin, then followed by growth inhibition tests such as
minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and inhibition zone test. The result showed that the obtained
yields of n-hexane, ethyl acetate, and 70% ethanol were 3.75%, 3.70%, and 32.47%, respectively. All
extracts were brown-colored with a distinctive cinnamon aroma. The qualitative phytochemical
measurements were as follows: n-hexane extract showed the presence of tannins, ethyl acetate extract
showed the presence of flavonoids, while the 70% ethanol extract showed the presence of alkaloids,
flavonoids, tannins, and saponin. The MIC test result for n-hexane, ethyl acetate, and 70% ethanol extracts
were, in order, 12%, 12%, and 8% against Staphylococcus aureus, 2.5%, 2.5%, and 25% against
Streptococcus mutan, and 2.5%, 2.5%, and 25% against Candida albicans. The best inhibition zone test
results against Staphylococcus aureus were exhibited by n-hexane, ethyl acetate, and 70% ethanol extracts
in following concentrations: 50% (3.16 mm), 50% (5.90 mm), and 32% (6.83 mm), respectively. Against
Streptococcus mutan, the best n-hexane concentration was 2.5% (3.83 mm), while ethyl acetate and 70%
ethanol extract exhibited relatively the same results in all of their measured concentrations, which were 2.00
mm and 5.30 mm, respectively. Against Candida albicans, the best n-hexane extract concentration was 10%
(14.5 mm), and the best ethyl acetate concentration extract was 10% (7 mm). The 70% ethanol extract
exhibited relatively same results (1.5 mm) in all measured concentrations.
1 INTRODUCTION
Oral microorganisms that cause dental caries and
thrush are Streptococcus mutans, Candida albicans,
and Staphylococcus aureus (Brotosoetarno, 1997).
Dental caries can cause the quality of life disorders
including limited dental function, physical disability,
and psychological discomfort. One of the plants that
have the potential to improve the dental and oral
health is cinnamon bark. Cinnamon is a plant in
which bark and branches are contain alkaloids,
flavonoids, tannins and essential oils consisting of
camphor, safrol, eugenol, sinamaldehid,
cinamilacetate, terpenes, cineol, citral, citronellal,
polyphenols and benzaldehyde (Perry & Metzger,
1980).
According to Anandito et al. (2012) the main
components of cinnamon bark essential oils are
sinamaldehid (63.12%), p-Cineole (17.37%), benzyl
benzoate (11.65%), linalool (8.57%), α-Cubebene
(7.77%), and α-Terpineol (4.16%). According to
Bisset & Wichtl (2001), cinnamon bark essential oils
contain cinnamicaldehyde, whereas the leaves
contain more eugenol. According to Rismunandar &
Paimin (2001), in cinnamon bark, there are also
chemical components such as dammar, adhesive,
tannin, tanners, sugar, calcium oxalate, two types of
insecticide cinnzelanin and cinnzelanol, cumarin.
494
Prasetyorini, ., W., D., Yulianita, ., F. U., N. and Rani, N.
Antimicrobial Activities Assessment of Cinnamon Bark (Cinnamomum burmannii Nees T. Nees) Extract against Caries Factors.
DOI: 10.5220/0010205500002775
In Proceedings of the 1st International MIPAnet Conference on Science and Mathematics (IMC-SciMath 2019), pages 494-501
ISBN: 978-989-758-556-2
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Cinnamon bark has a sweet and slightly spicy,
fragrant and warm nature. Cinnamon contains
including essential oils of eugenol, safrole, tannins,
calcium oxalate, dammar and tanners.
Susanti et al. (2013) reported that cinnamon bark
essential oil is widely used as raw material for the
industry of making fragrance oil, cosmetics,
pharmaceuticals, and other industries. The cinnamon
essential oil can also be used as a mouthwash and
paste, refreshment, aroma soap, detergent, lotion,
perfume, and cream (Rismunandar & Paimin, 2001).
Kadek (2011) mentioned the ethanol extract
compound of cinnamon bark has the antibacterial
power of Streptococcus mutans with a Minimum
Inhibition Concentration (MIC) of 5% and Inhibition
Zone of 5 mm. The content of cinnamon bark extract
compounds has the antifungal activity of Candida
albicans with a MIC of 1% and an inhibition zone of
25.5 mm. Nuryanti et al. (2015) stated that cinnamon
bark extract with n-hexane solvent had greater
inhibitory growth of Candida albicans when
compared to other solvents. Research by Puspita
(2014) stated that 96% ethanol extract of cinnamon
can reduce the growth of Staphylococcus aureus
bacteria with inhibitory zones of 20% (6.14 mm),
40% (13.01 mm), 80% (21, 04 mm), 100%
(23.61mm).
Cinnamon bark can be used as an antidiarrheal
drug, stomach cramps, and to reduce intestinal
secretions. Pharmacological effects of cinnamon are
carminative, diaphoretic, antirheumatic, stomachic
and analgesic pain relievers. Cinnamon bark can
also be used for medicinal ingredients; essential oils
can be used in the industry of perfume, cosmetics,
pharmaceutical, and food or beverage (Inna et al.,
2010; Shekar et al., 2012). Cinnamon bark is known
as one of the plants that have active compounds of
cinnamaldehyde and eugenol which has antibacterial
properties (Inna et al., 2010). In this research, the
extraction of active ingredients will use a multilevel
maceration method with three different solvents. The
first solvent is n-hexane, a type of nonpolar solvent
that can dissolve compounds that are nonpolar
(Maulida et al., 2010). The second solvent is ethyl
acetate, a semi-polar solvent that can dissolve semi-
polar compounds in the cell (Harborne, 1996). The
third solvent is ethanol, a polar solvent that can
dissolve polar compounds such as phenol groups
(Kusumaningtyas et al., 2008). The purpose of this
study was to obtain cinnamon bark extract with
different polarity solvents and test the extract as an
anti-bacterial and anti-fungal cause dental caries and
canker sores. Extract activity as antibacterial and
antifungal will be determined by measuring MIC and
inhibition zone on bacteria and fungus test.
2 METHODS
The study used a complete Randomized Design,
carried out in March to May 2019 in the Pharmacy
Laboratory, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural
Sciences at Pakuan University and in the
Microbiology Laboratory, Department of Biology,
Bogor Agricultural University. The tools utilized
include digital scales (LabPRO®, Kern®) grinders
(Zeppelin®), autoclaves (All American®), ovens
(Memmen®), test tubes (Pyrex®), test tube racks, 10
ml vials, dishes Petri (Pyrex, ose, beaker glass
(Pyrex), measuring glass (Pyrex), volume pipette
(Pyrex®), incubator (nuve®), stir bar, spirtus burner,
Laminar Air Flow (LAF), Vacuum Dry (Ogawa®) ,
furnace, Waterbath (Memment®), Hot plate stirrer
(Termo Scientific Cimarec®), magnetic bars and
other glassware. The ingredients utilized are 11000g
cinnamon bark, culture of Streptococcus mutans,
Staphylococcus aureus and Candida albicans, PDB
(Potato Dextrose Broth), BHI (Brain Heart Infusion),
70% Ethanol, N-hexane, Ethyl Acetate, Physiological
NaCl, Whatman paper disks, Clindamycin
antibiotics, Nystatin, 1% DMSO and other chemicals.
2.1 Extraction
Cinnamon bark used was obtained from the
Research Institute for Medicinal Herbs (Balitro) at
Jalan Tentara N0.3, Cimanggu, Central Bogor,
Ciwaringin, Bogor, West Java 16124 and has been
determined at the LIPI Bogoriense Hebarium Bogor.
Next, 1100g of cinnamon bark was made into
powder simplicia and measured the yield, moisture
content, and ash content. Water content is measured
by the gravimetric method and ash content is
measured by heating the powder simplicia in the
furnace at 6000C. 1000g extraction of cinnamon
barks powder using a multilevel maceration method
with three solvents, n-hexane, ethyl acetate, and 70%
ethanol. Initially, 500g of cinnamon powder was
macerated using 5 L n-hexane solvent for 3x24
hours, by putting 500g of cinnamon bark powder into
a brown bottle with capacity of 5 L, then adding 2.5
L of n-hexane, and shook. The solution allowed to
stand for 18 hours while occasionally shaken, then
the filtrate and residue are separated by filtering. In
the same way, the residue was re-macerated twice of
each using the remaining 1.5 L n-hexane.
Antimicrobial Activities Assessment of Cinnamon Bark (Cinnamomum burmannii Nees T. Nees) Extract against Caries Factors
495
The maceration filtrate was collected, poured for
± 24 hours, and the filtrate that had been poured was
then concentrated with vacuum dry until a dry
extract was obtained, then characterized for the
organoleptic character, water content and ash
content. Meanwhile, the residue is dried in an oven
at 50
0
C and then in the same way the residue is re-
macerated with different solvents of ethyl acetate
and 70% ethanol. Thus, three kinds of extracts will
be obtained, namely n-hexane extract, ethyl acetate
extract and 70% ethanol extract. The yield of the
extract obtained then calculated.
2.2 Phytochemical Test of Extracts
The three types of extracts were carried out by
phytochemical screening for alkaloids, flavonoids,
saponins, tannins, and steroids/terpenoids. Alkaloids
test using Dragendrof reagents, Mayer test and
Bouchardat test (Ministry of Health of the Republic
of Indonesia, 1995). Flavanoid test using Mg powder
with a few drops of 5 M hydrochloric acid and Zn
powder with a few drops of 5M hydrochloric acid.
The tannin test uses 1% of gelatin in 10% NaCl and
with a solution of FeCl3. Tannin test carried out by
shaking for 10 minutes. Steroid and terpenoid tests
using chloroform of concentrated H2SO4 (Kumoro,
2015).
2.3 Media Making
Weighed 20g for each medium of GDP and BHI,
and 23g for NA media, then each of media was
dissolved in 1 L of water, then placed in an
Erlenmeyer and heated using a hot plate equipped
with a magnetic stirrer until boil and clear. Then the
media was covered with cotton and aluminum foil
(Hidayat & Sutarma, 1999), and sterilized in an
autoclave at 121
o
C with a pressure of 1 atm for 20
minutes (Waluyo, 2008). After the heat is reduced,
near the Bunsen burner was poured in a Petri dish
and test tube (tilted) @ 5 ml. After the media has
frozen, the sterilization test was done by putting it
into a 37
o
C incubator for 24 hours before the media
is used. Each batch of media that has been tested for
sterilization and quality then stored at 5
o
C-8
o
C
(Hidayat & Sutarma, 1999).
2.3.1 Preparation of Bacteria and Fungus
One ose pure Candida albicans culture was
inoculated on slanted solid PDB (Potato Dextrose
Broth) media, while the pure culture of
Streptococcus mutans in BHI (Brain Heart Infusion)
media and Staphylococcus aureus was inoculated in
slanted solid Nutrien Agar (NA) media. Then each
test tube is closed with a plug (Waluyo, 2008). All
the media then incubated at 37
0
C and 20-25
0
C for 24
hours. Bacteria and fungi that have been grown are
then stored in a refrigerator at 4
O
C as stock. The
colonies of bacteria and fungi that have grown on
each tilted media then made a suspension on a test
tube containing 0.9% NaCl (physiological Na) by
using ose, then homogenized. The turbidity of the
suspension is likened to the standard solvent of Mc
Farland 1 and then dilution is carried out up to 10
-6
.
2.3.2 Test of Minimum Inhibitory
Concentration (MIC)
The MIC test for the three types of extract produced
was carried out by the dilution method, the
concentration of the extract tested was presented in
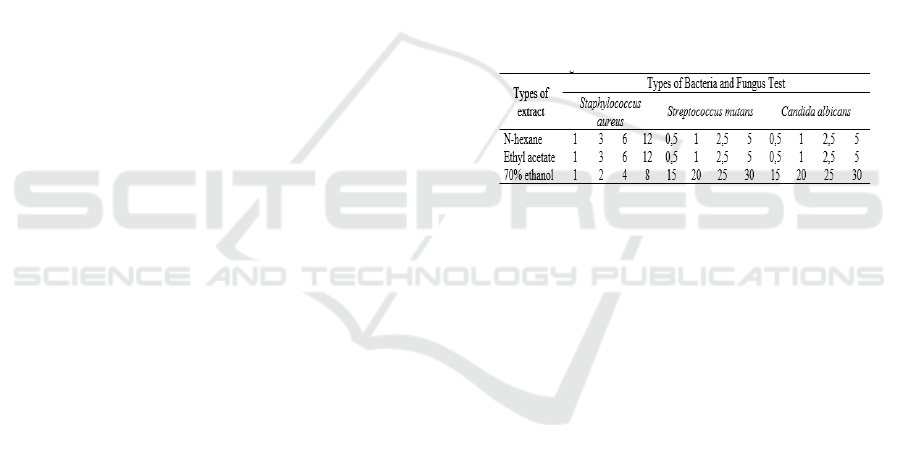
Table 1, and all treatments were duplicated.
Table 1: Extract concentration treatment (%) in testing the
minimum inhibitory concentrations of bacteria and fungi.
2.3.3 Test of Inhibition Zone
The inhibition zone test is carried out using the Paper
Disc Diffusion method. The active ingredient in the
form of an extract is placed in a 6 mm diameter disc
aseptically, then placed on a media that has been
inoculated with bacteria or fungi. The inhibition zone
is measured by measuring the clear zone that occurs
around the disc paper. This test is done in duplicate.
For the inhibition zone test, the concentrations tested
are based on the results of the MIC test. The positive
control for Staphylococcus aureus bacteria is 10 ppm
amoxicillin, mutant Streptococcus is 10 ppm
clindamycin, Candida albicans used Nystatin 100.000
IU/ml, and all negative controls are DMSO 1%. The
making of extract test solution is done by making 50%
concentrated parent dissolve of each dry extract. The
making of the test solution is carried out with a
dilution formula based on concentration. The making
of the paper disc was done by soaking the Whatman
filter paper with a 6 mm diameter in extracts according
to concentration for 30 minutes. Then dried in the
oven for 24 hours in a Petri dish container at 40-50
o
C
until dry and ready for use. The concentrations used in
the inhibition zones test are presented in Table 2 and
each with 3 replications.
IMC-SciMath 2019 - The International MIPAnet Conference on Science and Mathematics (IMC-SciMath)
496
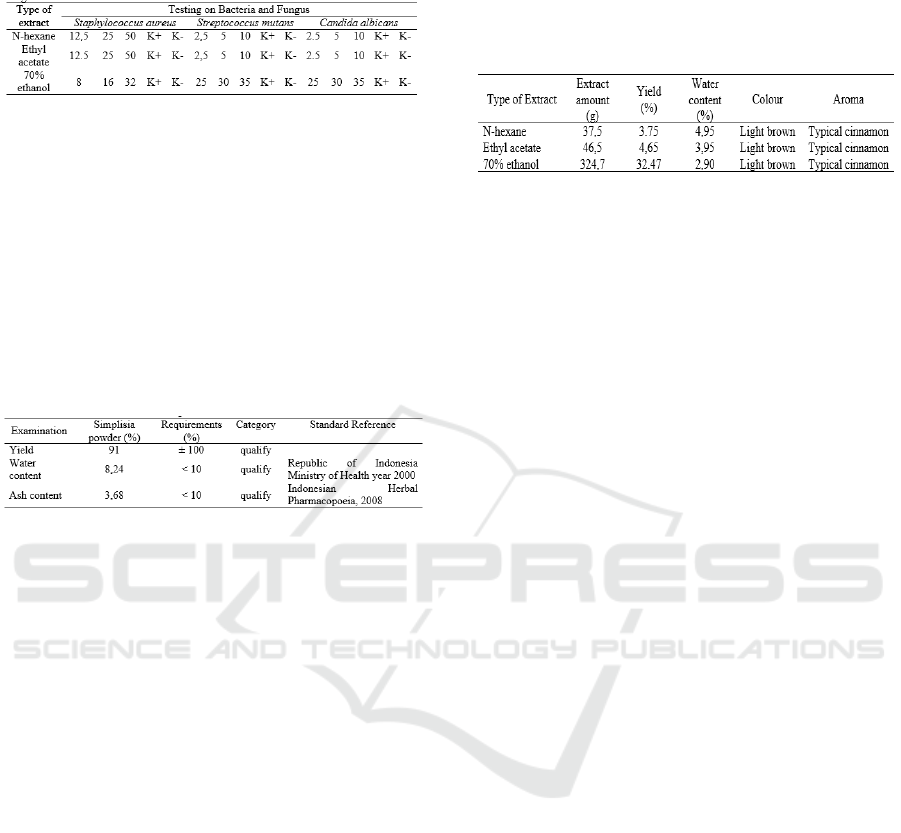
Table 2: Treatment of extract concentrations (%) tested on
the inhibition zone test of bacteria and fungus.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
From 1100g cinnamon bark produces 1000g of
simplicia cinnamon bark powder, brownish-colored
simplicia powder, a slightly spicy-sweet taste with a
characteristic aroma of cinnamon. The yield, water
content and ash content are all meet the applicable
requirements (Table 3).
Table 3: Characterization results of Simplisia Cinnamon
Bark Powder.
Water content is a quality indicator of the simplicia
powder that needs to be known because water is a
good medium for microbial growth so that it can
result in decreased quality of simplicia. Low water
content in simplicia can extend the shelf life of
simplicia powder. The ash content of the simplicia
powder of cinnamon bark obtained was 5.21%. The
qualified determination of ash content was less than
10.5% (Ministry of Health of the Republic of
Indonesia, 2008). The determination of ash content
aims to determine levels of inorganic substances and
minerals contained in simplicia originating from
plants or contaminants during the manufacturing
process of simplicia (Ministry of Health of the
Republic of Indonesia, 1995). Ash levels in
cinnamon bark powder simplicia still meet the
Indonesian Herbal Pharmacopeia of 2008, which is
3.68% (˂ 10%).
3.1 Extraction Results
Multilevel maceration was carried out with a
simplicia powder of 1000g, using three different
solvents namely n-hexane, ethyl acetate and ethanol
70%, each solvent used in a ratio of 1:10.
Maceration results obtained 3 filtrates with different
solvents, and then each filtrate was vacuum dried
until a dry extract of cinnamon bark was obtained.
The results of the characteristics of n-hexane extract,
Ethyl acetate extract, and 70% ethanol extract of
cinnamon bark can be seen in Table 4.
Table 4: Characterization extracts Results of Multilevel
Maceration Results of 1000g Simplisia Powder.
The water content obtained in the n-hexane
extract of cinnamon bark was 4.95%, ethyl
acetate extract was 3.95% and 70% ethanol
extract was 2.90%. The results of the water
content of cinnamon bark extract meet the
requirements of the dry extract water content of
<5%. Different types of solvents affect the amount
of extract produced. Ethanol (polar) extract has the
highest yield because ethanol has a polar group that
is stronger than non-polar groups; this can be seen
from the chemical structure of ethanol containing
hydroxyl (polar) groups and carbon (nonpolar)
groups.
Ethanol can extract phytochemical compounds in
higher amounts. The high yield in the ethanol
solvent shows that the solvent was able to extract
more bioactive components that have higher polarity
properties. This is probably because the cinnamon
bark component contains many polar compounds.
The yield of ethyl acetate solvent is smaller than the
ethanol solvent but larger than the n-hexane solvent;
it is suspected that there is a methoxy group
contained in the chemical structure of ethyl acetate.
The presence of the methoxy group in the hydrogen
bond sample formed in the ethyl acetate solvent is
weaker than the hydrogen bond formed in the
ethanol solvent; so that it can affect the yield of less
solvent of the ethyl acetate.
3.2 Phytochemical Screening
This test was conducted to determine the class of
compounds contained in extracts of n-hexane, ethyl
acetate and ethanol of cinnamon bark after
extraction. Tests carried out are alkaloid, flavonoid,
tannin, and saponin. Phytochemical test results of n-
hexane extract, ethyl acetate and ethanol of
cinnamon bark can be seen in Table 5.
Antimicrobial Activities Assessment of Cinnamon Bark (Cinnamomum burmannii Nees T. Nees) Extract against Caries Factors
497
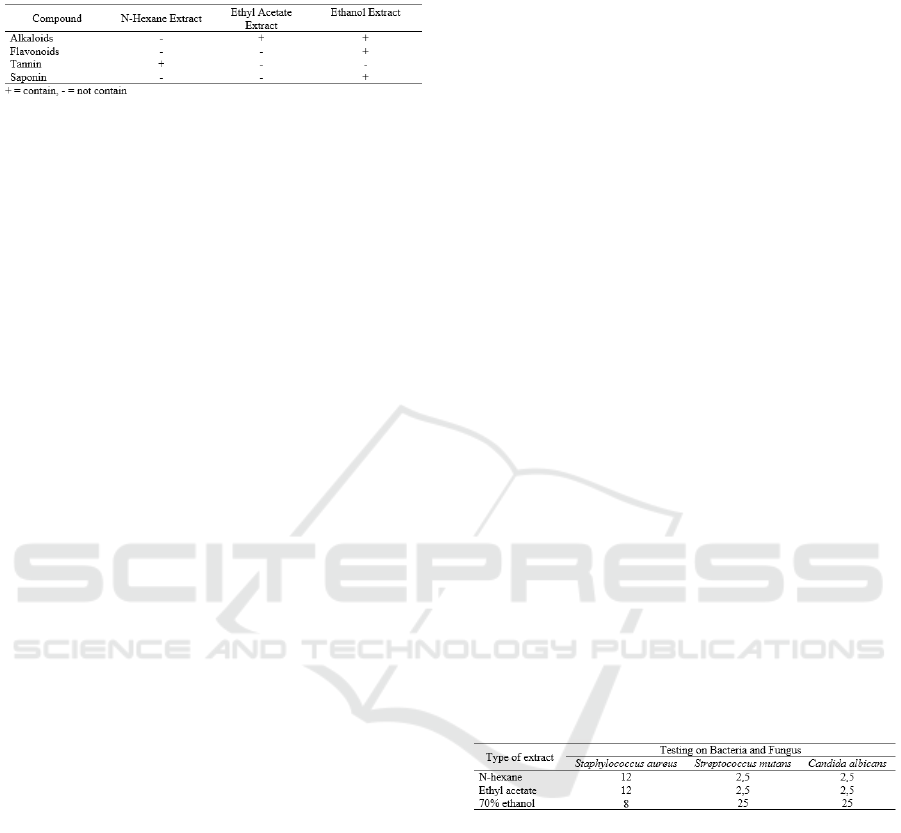
Table 5: Results of Qualitative Phytochemical Tests of
Extracts.
Phytochemical test results indicate the presence
of tannin compounds in n-hexane extract. The
tannins contained in the n-hexane solvent are
hydrolyzed tannins because it has a polyester
structure that is easily hydrolyzed by acids or
enzymes, and as a result of its hydrolysis is a
polyphenic acid and simple sugar (Maldonado,
1994). Hydrolyzed tannins are present in non-food
ingredients (Makkar et al., 1993). The positive ethyl
acetate extract contains alkaloids because alkaloids
can dissolve in semi-polar solvents. Alkaloids in
plants are generally in the form of salts so that only
soluble in inorganic solvents (chloroform, ethyl
acetate, acetone, benzene, alcohol, ethanol, and
methanol). In the 70% ethanol extract contains
alkaloid, flavonoid and saponin compounds because
the 70% ethanol is polar in nature so that it can
attract polar compounds. From these results, it can
be seen that there are other compounds that have
efficacy as antimicrobials other than essential oils
revealed by the research of Kadek (2011).
Alkaloids are the largest group of secondary
metabolites and are mostly sourced in plants
(Ningrum et al., 2016). Alkaloid compounds which
have basic groups containing nitrogen will react with
amino acid compounds that make up bacterial cell
walls and bacterial DNA. This reaction results in
changes in the structure and composition of amino
acids. So it will cause changes in genetic balance in
the DNA chain that will be damaged and encourage
bacterial cell lysis that will cause death in bacterial
cells. Flavonoids are polar compounds that are
usually spread in plants and belong to the phenol
group. Flavonoids are polar so it is easier to penetrate
the peptidoglycan layer which is also polar in gram-
positive bacteria than in the nonpolar lipid layer
(Dewi, 2010). The mechanism of action of
flavonoids as antimicrobials is by binding to
extracellular proteins and dissolved proteins so that
they lose their normal function, deactivate enzymes,
and damage cell walls and bacterial cell membranes.
Some flavonoids are bactericidal, bacteriostatic,
fungicidal, and deactivate the lipophilic virus.
Saponin is a secondary metabolite compound that
functions as an antiseptic so that it has the ability as
an antibacterial. The presence of these antibacterial
substances will inhibit the formation or transport of
components to the cell wall which results in the
weak structure of the cell wall accompanied by loss
of cell walls and release of cell contents which will
ultimately kill or inhibit the growth of the bacterial
cell. In addition, saponin compounds cause a
decrease in cell surface tension and cause cells to
become lysis.
3.3 Test Results of MIC
Test results on Streptococcus mutans and Candida
albicans showed that n-hexane and ethyl acetate
extracts had the same MIC at 2.5% concentration,
and at 70% ethanol extract had 25% higher marked
by the absence of a growing bacterial colony. In
Staphylococcus aureus, on the contrary, n-hexane
extract and ethyl acetate have the same MIC
(12%), but the concentration is higher than ethanol
extract, 8% ethanol extract in Staphylococcus
aureus has shown no bacterial colonies. The results
of the MIC test for 70% ethanol on Staphylococcus
aureus get lower concentrations compared to n-
hexane and ethyl acetate because the ethanol
extract contains alkaloids, flavonoids, and tannins.
Whereas in ethyl acetate and n-hexane the
concentration used is higher because in ethyl
acetate only contains flavonoid compounds and in
n-hexane only contains tannin compounds. The
MIC values for each microorganism are presented
in Table 6.
Table 6: Test Results of MIC Extract (%) on
Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus mutans, and
Candida albicans.
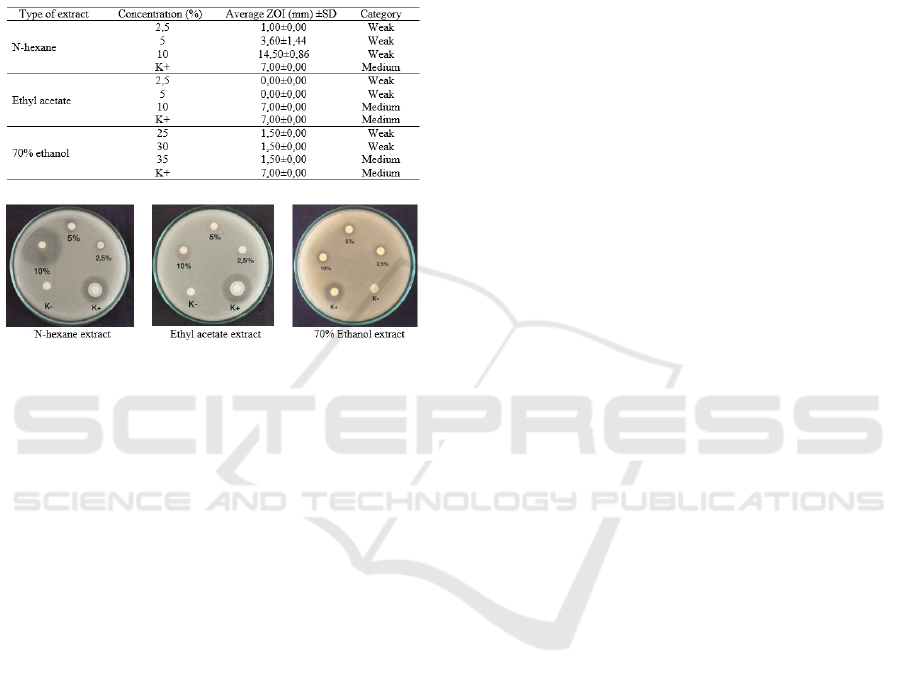
3.4 Test Results of Inhibiton Zone
Antimicrobial testing was carried out to see the
concentration of each extract that had the greatest
antimicrobial activity. This test is carried out using
the Paper Disc Diffusion method. This method is
used because it is more sensitive to new
antimicrobial compounds whose activity is
unknown. The inhibition of growth in the method is
shown by the wide clear area (inhibition zone) that
forms around the paper disk (Brander et al., 1999).
(Davis & Stout, 2009) divides the strength of
antibacterial power into four categories, namely
inhibition weak (<5mm), moderate (5-10mm),
strong (10-20mm), and very strong (> 20mm).
IMC-SciMath 2019 - The International MIPAnet Conference on Science and Mathematics (IMC-SciMath)
498

3.5 Staphylococcus aureus
Inhibition zone test results of ethanol extract, ethyl
acetate and n-hexane extract in Staphylococcus
aureus bacteria can be seen in Table 7.
Table 7: Average Test Results of Inhibition Zone (mm)
Extracts on Staphylococcus aureus Bacterial Growth.
Figure 1: Inhibition Zone Test Results of Cinnamon bark
extract against bacteria Staphylococcus aureus.
The results showed ethanol extract was an
extract with inhibition zone results that were
stronger than ethyl acetate extracts and ethyl acetate
showed inhibition zone results that were stronger
than n-hexane. Among the three solvents, extract
with 70% ethanol solvent produced an average
inhibition zone that was closer to positive control at
32% extract concentration. From the observations, it
can be seen that the antibacterial activity of n-
hexane extract produces a weak inhibitory power at
the three concentrations used against Staphylococcus
aureus. These results indicate that n-hexane extract
has less antibacterial activity compared to ethyl
acetate and 70% ethanol solvent. In observing the
antibacterial activity of ethyl acetate extract at a
concentration of 50%, it produces an inhibition zone
with a moderate category of 5.9 mm, but when
compared with 70% ethanol extract with a
concentration of 32% it produces an inhibition zone
of 6.83%. These results showed that extracts with
70% ethanol solvent had better antibacterial activity
on Staphylococcus aureus than ethyl acetate or n-
hexane solvents. According to other research
conducted shows that the difference in the level of
the polarity of the solvent affects the antibacterial
properties. The research of S. muticum extract on S.
aureus has the highest antibacterial properties in
extracts using 96% ethanol solvent followed by ethyl
acetate and n-hexane solvents according to the
decrease in polarity. The higher the level of polarity,
the better the antibacterial activity (Hidayah, 2016).
3.6 Staphylococcus mutans
The inhibition zone test results on Streptococcus
mutans can be seen in Table 8 and in Candida
albicans fungus can be seen in Table 9.
Table 8: Test Results of Inhibition Zone (mm) Cinnamon
Bark Extract against Streptococcus mutans Bacteria.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Figure 2: Inhibition Zone Test Results on Streptococcus
mutans bacteria.
The statistical analysis results of the inhibition
zone test on Streptococcus mutans showed that n-
hexane and ethyl acetate extracts for all
concentrations tested did not have a significant
effect. For the n-hexane and ethyl acetate extracts,
all the concentrations had inhibitory power with
weak categories (˂5mm). While the ethanol extract
of all concentrations has inhibition in the medium
category (5-10mm). This might be caused by the
compounds contained in ethanol extracts including
alkaloids, flavonoids, and saponins.
3.7 Candida albicans
The results of the inhibition zone test on Candida
albicans showed that n-hexane extract at a
concentration of 2.5% and 5% had inhibition zone of
the weak category (<5 mm), and the concentration of
10% is very strong that is 14.50mm (10-20mm). The
ethyl acetate extract with a 10% concentration has
inhibition zone with a medium category of 7 mm (5-
10 mm) equal to the positive control. The inhibition
Antimicrobial Activities Assessment of Cinnamon Bark (Cinnamomum burmannii Nees T. Nees) Extract against Caries Factors
499
zone test on ethanol extract of all concentrations
tested has a weak inhibition power of 1.5 mm. The
results of inhibition Test of cinnamon bark extract
against the fungus Candida albicans are presented in
Table 9.
Table 9: Test Results of Inhibition Zone (mm) on
Cinnamon Bark Extract against Candida albicans.
Figure 3: Inhibition Zone Test Results in Candida
albicans.
Statistical test results showed that there were no
significant differences in extract concentration on
the inhibition zone. Quantitatively showed that
inhibition zone extract of n-hexane 10% against the
fungus Candida albicans was greater than the
positive control, which is 14.5mm (2 times of the
positive control). This might be due to the tannin
content in n-hexane extract. Tannin is a complex
organic compound that acts as an antimicrobial. The
presence of tannin as an antibacterial will disrupt the
synthesis of peptidoglycan so that the formation of
cell walls becomes less perfect. Circumstances that
caused the bacterial cells to become lysis were due
to osmotic and physical pressure so that bacterial
cells became dead. In addition tannin compounds
work by binding to protein walls so that the
formation of bacterial cell walls is inhibited (Fahria
& Muktiana, 2007).
4 CONCLUSION
From this study can be concluded:
1. Different solvents produce different
antimicrobial effects. The effectiveness of
cinnamon bark extract against the antibacterial
Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus mutans
respectively are ethanol extract, ethyl acetate
extract, and n-hexane extract.
2. The effectiveness of cinnamon bark extract
against fungus Candida albicans respectively is
n-hexane extract, ethyl acetate extract, and
ethanol extract.
3. The 10% concentration of n-hexane ethanol
extract of cinnamon bark has strong
antimicrobial power against Candida albicans
with an inhibition zone of 14.50 mm over the
positive control.
REFERENCES
Anandito, B. K., Lia, U. K., & Fuki, T. . (2012). Pengaruh
Ukuran Bahan dan Metode Destilasi (Destilasi Air
Dan Destilasi Uap-Air) Terhadap Kualitas Minyak
Atsiri Kulit Kayu Manis (Cinnamomum burmani).
Journal of Teknosains Pangan, 1(1).
Bisset, N. G., & Wichtl, M. (2001). Herbal Drugs and
Phytopharmaceuticals (2nd ed.). Medpharm Scientific
Publishers.
Brander, G. ., Pough, D. M., Bywater, R. ., & Jenkins, W.
L. (1999). Veterinary Applied Pharmacology and
Therapeutic (5th ed.). Brailler Tindal.
Brotosoetarno, S. (1997). Peran Serta Mikroorganisme
Dalam Proses Terjadinya Karies Gigi. Journal of
Dentistry Universitas Indonesia, 7.
Davis, & Stout. (2009). Disc Plate Method of
Microbiological Antibiotic Essay. Journal of
Microbiology, 22(4).
Dewi, F. K. (2010). Aktivitas Antibakteri Ekstrak Etanol
Buah Mengkudu (MorindaCitrifolia, Linnaeus)
Terhadap Bakteri Pembusuk Daging Segar. Sebelas
Maret University.
Fahria, & Muktiana, S. (2007). Ekstraksi Zat Aktif
Antimikroba danTanamanYodhium (Jatrophamultifida
L.) sebagai Bahan Baku Alternatif Antibiotik Alami.
Harborne, J. . (1996). Metode Fitokima Penuntun Cara
Modern Menganalisis Tumbuhan (K. Padmawinata
(ed.); II). Institut Teknologi Bandung.
Hidayah, N. (2016). Uji Efektivitas Ekstrak Sargassum
muticum Sebagai Alternatif Obat Bisul Akibat
Aktivitas Staphylococus aureus. Journal of Creativity
Students.
Hidayat, Y., & Sutarma. (1999). Teknik Pembuatan Kultur
Media Bakteri. Veterinary Research Institute.
Inna, M., Atmania, N., & Primasari, S. (2010). Potential
Use of Cinnamomum burmanii Essential Oil-based
Chewing Gum as Oral Antibiofilm Agent. Journal of
Dentistry Indonesia, 17(3), 81–82.
Kadek, R. . (2011). Daya Antibakteri Minyak Atsiri Kulit
Batang Kayu Manis (Cinnamomum burmannii BI.)
Terhadap Streptococcus mutans Penyebab Karies
Gigi. Sanata Dharma University.
Kumoro, A. C. (2015). Teknologi ekstraksi senyawa
bahan aktif dari tanaman obat. Plantaxia.
IMC-SciMath 2019 - The International MIPAnet Conference on Science and Mathematics (IMC-SciMath)
500

Kusumaningtyas, E., Widiati, R. R., & Gholib, D. (2008).
Uji Daya Hambat Ekstrak dan Krim Ekstrak Daun
Sirih (Piper betle) terhadap Candida albicans dan
Trichophytonmentagrophytes. Manuscript of Animal
Husbandry and Veterinary Technology, 805–812.
Makkar, H. P. S., Blummel, M., Borowy, N. K., & Becker,
K. (1993). Gravimetric determination of tannins and
their correlations with chemical and protein
precipitation methods. Journal of Science Food
Agriculture.
Maldonado, R. A. P. (1994). The Chemical Nature and
Biological Activity of Tannins in Forages Legumes
Fed to Sheep and Goat. University of Queensland
Australia.
Maulida, Dewi, Zulkarnaen, & Naufal. (2010). Ekstraksi
antioksidan (likopen) dari buah tomat dengan
menggunakan solven campuran, n – heksana, aseton,
danetanol. Diponegoro University.
Ministry of Health of the Republic of Indonesia. (1995).
Indonesian Pharmacopoeia fourth edition.
Ministry of Health of the Republic of Indonesia. (2008).
Indonesian Herbal Pharmacopoe.
Ningrum, R., Purwanti, E., & Sukarsono. (2016). Alkaloid
compound identification of
Rhodomyrtustomentosastem as biology instructional
material for senior high school X grade. Jurnal
Pendidikan Biologi Indonesia, 2(3), 231–236.
Nuryanti, S., Jura, R. M., & Nursucianti. (2015). Uji
Aktivitas Anti Jamur Ekstrak Kayu Manis
(Cinnamomum burmanii Blume) Terhadap Jamur
Candida albicans. Jurnal Pendidikan Kimia.
Universitas Tadulako.
Perry, L. ., & Metzger, J. (1980). Medicinal Plants of East
and Southeast Asia Attributed Properties and Uses.
The MIT Press.
Puspita, A. (2014). Pengaruh Konsentrasi Ekstrak Kayu
Manis Dalam Menurunkan Pertumbuhan Streptococus
mutans secara invitro. University of Muhammadiyah
Surakarta.
Rismunandar, & Paimin, F. B. (2001). Kayu Manis
Budidaya dan Pengolahan. Penebar Swadaya.
Shekar, M., Shetty, S., Lekha, G., & Mohan, K. (2012).
Evaluation of In Vitro Antioxidant Property and Radio
Protective Effect of The Constituent Medicinal Plants
of a Herbal Sunscreen Formulations. International
Journal of Pharmaceutical Frontier Research
(IJPFR), 2(2), 5.
Susanti, N., Gandidi, M., Indra, Dyan, M., & Susila.
(2013). Potensi Produksi Minyak Atsiri dari Limbah
Kulit Kayu Manis Pasca Panen. Journal of FEMA,
1(2), 45.
Waluyo, L. (2008). Teknik dan Metode Dasar dalam
Mikrobiologi. University of Muhammadiyah Malang
Press.
Antimicrobial Activities Assessment of Cinnamon Bark (Cinnamomum burmannii Nees T. Nees) Extract against Caries Factors
501
