
Extraction and Analysis of Nicotine in the Urine of Active Smokers
after given by Vitamin C
Endang Susilawati
1
, Muhammad Taufik
2
, Afniwati
1
, Mariany Razali
3
, Desi Ardilla
4
, Rid Wanto
5
and Virda Lola Br Tarigan
5
1
Department of Nursing, Poltekkes Kemenkes, Medan, Indonesia
2
Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia
3
Department of Pharmacy, Universitas Tjut Nyak Dhien, Medan, Indonesia
4
Department of Agricultural Technology, Universitas Muhammadiyah Sumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia
5
Department of Pharmacy, Universitas Muslim Nusantara Al Washliyah, Medan, Indonesia
Keywords: Nicotine, Urine, Active Smoking, Extraction, UV-Vis spectrophotometry
Abstract: Nicotine is a class of addictive compounds that can cause dependence. Vitamin C contains antioxidants that
can ward off free radicals in the body. Nicotine extraction and analysis are a series of processes that are
indispensable in order to produce nicotine in optimal concentrations. This study aims to extract and analyze
nicotine in the urine of active smokers after giving vitamin C. The descriptive method was developed for the
extraction of nicotine in urine. Preliminary test using Cyanogen bromide showed the presence of nicotine in
the urine of smokers for 7 days. The same thing is evidenced by the thin layer chromatography data
resulting in an average Rf value of 0.6. The concentration of nicotine in urine decreased from the first day of
vitamin C administration to day 7. This indicates that there is an effect of vitamin C on the urine of active
smokers.
1 INTRODUCTION
Cigarettes are one of the most dangerous deadly
objects in the world (Rahmat Nur Hidayat, Adam M.
Ramadhan 2016). Consuming cigarettes
continuously can cause various health problems such
as cancer, respiratory problems, and heart problems.
Cigarettes are one of the biggest contributors to
death today. The death rate caused by smoking in
Indonesia has reached 57,000 people every year
(Sari, Zulaikhah, and PH 2019).
Cigarette consumption in Indonesia reaches 215
billion sticks per year. In Indonesia there are 60%
smokers, 59% of whom are men and 37% are
women. In Indonesia, tobacco plus cloves and other
ingredients are mixed to make kretek cigarettes. In
addition to kretek, tobacco can also be used as rolled
cigarettes, white cigarettes, cigars, pipe cigarettes,
and smokeless tobacco, cylinders of paper
measuring 70-120 mm in length and 10 mm in
diameter containing chopped tobacco leaves. The
basic ingredient of cigarettes is tobacco.
Tobacco contains a variety of chemicals that can
be addictive to a person, even if they don't want to
try again (Solarino et al. 2009).These health
problems are related to the content of free radicals in
cigarette smoke. in one suction, an estimated 1014
free radical molecules enter the body (Rahmat Nur
Hidayat, Adam M. Ramadhan 2016). Cigarette
smoke contains ± 4000 chemical compounds with 60
chemical compounds that have been identified as
cancer-causing and genotoxic. These chemical
compounds circulating in the testicular blood vessels
damage the spermatozoa with their cytotoxic effect.
These chemical compounds consist of nicotine, tar,
carbon monoxide, acetone, arsenic, ammonia,
hydrogen cyanide and so on (Clayton et al. 2013).
Vitamin C is one of the most widely taken
nutritional supplements (Pacier and Martirosyan
2015). Health professionals as well as a number of
health benefits for vitamin c such as boosting
immunity or preventing common diseases and
cancer (Lorensia et al. 2018). If free radicals are too
high, natural anti-oxidants alone are not enough to
ward off free radicals. Therefore, additional
antioxidants are needed to inhibit oxidation
Susilawati, E., Taufik, M., Afniwati, ., Razali, M., Ardilla, D., Wanto, R. and Tarigan, V.
Extraction and Analysis of Nicotine in the Urine of Active Smokers after given by Vitamin C.
DOI: 10.5220/0010614400002775
In Proceedings of the 1st International MIPAnet Conference on Science and Mathematics (IMC-SciMath 2019), pages 601-604
ISBN: 978-989-758-556-2
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
601

reactions, neutralize and scavenge free radicals.
Water-soluble vitamins that can function well as
antioxidants are commonly known as vitamin C or
ascorbic acid. This vitamin C plays an important role
in protecting cell damage caused by free radicals.
Because structural vitamin C is similar to glucose
and can replace glucose in various chemical
reactions (Pacier and Martirosyan 2015).
Nicotine extraction from smoker's urine can be
done in several ways, namely extraction, maceration,
reflux, and distillation. Extraction by means of
maceration gives an advantage, so that it is not
damaged and so that more tends to be obtained.
Extraction by maceration was identified by
sonication and electrosynthesis methods (Taufik et
al. 2017). Fidrianny (2004) has carried out the
preparation and analysis of nicotine contained in
smoker's urine where chloroform is used as a solvent
in sample preparation The electrolysis coupling
maceration method is the best extraction method
compared to the results of the maceration method
(Muhammad Taufik, Rid Wanto, Athaillah, Anny
Sartika Daulay, Lilis Karlina Siahaan, Desi Ardilla,
Mariany Razali 2017). However, this study has a
weakness where the solvent used has not been
optimized. In this work, the use of UV spectroscopy
was also developed at a wavelength of 260 nm.
However, this study is a basic study in order to
search for nicotine in the urine of smokers simply in
the laboratory.
2 MATERIALS AND METHOD
2.1 Sample Collection
The sample was collected purposively, namely based
on the criteria determined by the researcher. The
sample obtained was the urine of volunteers who
consumed cigarettes that had been given vitamin C
and not given vitamin C. The samples were taken
within 24 hours after the volunteers consumed
cigarettes. The urine sample used was from Garu II
Medan Amplas. The dose of with Vitamin C = 50
mg x 2. Samples were taken until day 7.
2.2 Administration of Vitamin C
Filling in the questionnaire sheet including name,
age. Followed by giving vitamin C 50 mg / tab x 2
for 2 times a day morning and evening to volunteers
for 7 days.
2.3 Preparation and Extraction
Each 25 ml active smoker's urine sample was added
with 25 ml of chloroform inserted into a separating
funnel. The lower layer was put into a 50 ml beaker
glass and followed by maceration of the
electrosynthetic coupling for 15 minutes. The result
of maceration is evaporated until the solvent
evaporates. The nicotine evaporated was diluted at
pH 9 then continued with qualitative and
quantitative analysis.
2.4 Preliminary Test using Cyanogen
Bromide
The extracted sample was dripped with Cyanogen
bromide reagent until a yellow color was obtained
which indicated positive nicotine, observed the
yellow color that occurred and compared it with the
standard differentiated into + (slightly), ++
(moderate), +++ (abundant).
2.5 TLC Analysis
Thin layer chromatography (TLC) analysis was
performed using the mobile phase of Methanol:
Chloroform (50:50). The stain appearance solution
used was dragendorff reagent. Physically, the stain
analysis uses UV light.
2.6 UV Analysis
The results of the smoker's urine sample which was
macerated with electrosynthetic coupling were
analyzed quantitatively using MDA 50 UV-Vis
spectrophotometry. This instrument was switched on
for 10-15 minutes and used a wavelength of 200-800
nm. The cuvette used was a glass cuvette with a
thickness of 10 mm, a square shape. In this work, the
blank used is methanol.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1
Preparation and Extraction
The sample was taken from 5 respondents who were
active smokers. The preparation has a very
important role in determining the success of the
extraction and analysis process. The extraction
process uses chloroform as a solvent. This sample
extraction aims to separate nicotine from the urine of
active smokers. The electro synthetic method was
IMC-SciMath 2019 - The International MIPAnet Conference on Science and Mathematics (IMC-SciMath)
602
developed to shorten the extraction time. This
technique is a way to synthesize which is based on
electrochemical techniques. In this study, the electro
synthetic coupling maceration was developed for 15
minutes with a voltage of 20 V.
3.2
Preliminary
Test using Cyanogen
Bromide
Preliminary test results using Cyanogen bromide can
be seen in Table 1 in the following:
Table 1: Preliminary test results
Sample Da
y
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
A ++ ++ ++ + + + +
B + ++ ++ ++ + + +
C ++ ++ ++ + + + +
D ++ ++ ++ + + + +
E ++ ++ + + + + +
Table 1 showed that the urine of active smokers
in the analysis showed positive results for nicotine
compounds. This is indicated by the appearance of
orange deposits. In this study, the greatest nicotine
was obtained on the third day then decreased until
the 7th day.
3.3 TLC
Analysis
The results of TLC analysis is presented in Table 2
as follows:
Table 2: Sample Rf value
Sample Day Stain
distance
Rf
A
I 6.5 0.92
II 6.6 0.94
III 6.6 0.94
IV 6.5 0.92
V 6.6 0.94
VI 6.6 0.94
VII 6.6 0.94
VIII 6.6 0.94
B
I 6.4 0.91
II 6.3 0.90
III 6.2 0.88
IV 6.0 0.85
V 5.9 0.84
VI 6.0 0.94
VII 6.0 0.94
C
I 6.6 0.94
II 6.6 0.94
III 6.6 0.94
IV 6.6 0.94
V 6.6 0.94
VI 6.6 0.94
VII 6.6 0.94
VIII 6.1 0.87
D
I 6.1 0.87
II 6.2 0.88
III 6.6 0.94
IV 6.6 0.94
V 6.6 0.94
VI 6.6 0.94
VII 6.6 0.94
VIII 6.6 0.94
E
I 6.6 0.94
II 6.6 0.94
III 6.6 0.94
IV 6.7 0.95
V 6.5 0.92
VI 6.5 0.92
VII 6.6 0.94
VIII 6.6 0.94
N
icotine
standar
d
6.6 0.94
Table 2 shows that the Rf values of samples A,
B, C, D, and E from Day 1 to 7 are almost the same
as for standard nicotine (Rf = 6.6).
3.4
Quantitative
Analysis using UV
UV-Vis spectrophotometry was developed to
generate quantitative data. Initially, the standard
solution was made from nicotine standard solutions
with concentrations of 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, and 2.5
ppm. The blank used is methanol. To determine the
nicotine concentration, first the maximum
wavelength must be determined at 260 nm.
Determination of wavelength used a concentration
of 2 ppm. The results of the analysis of nicotine
concentration for the 5 samples used can be seen in
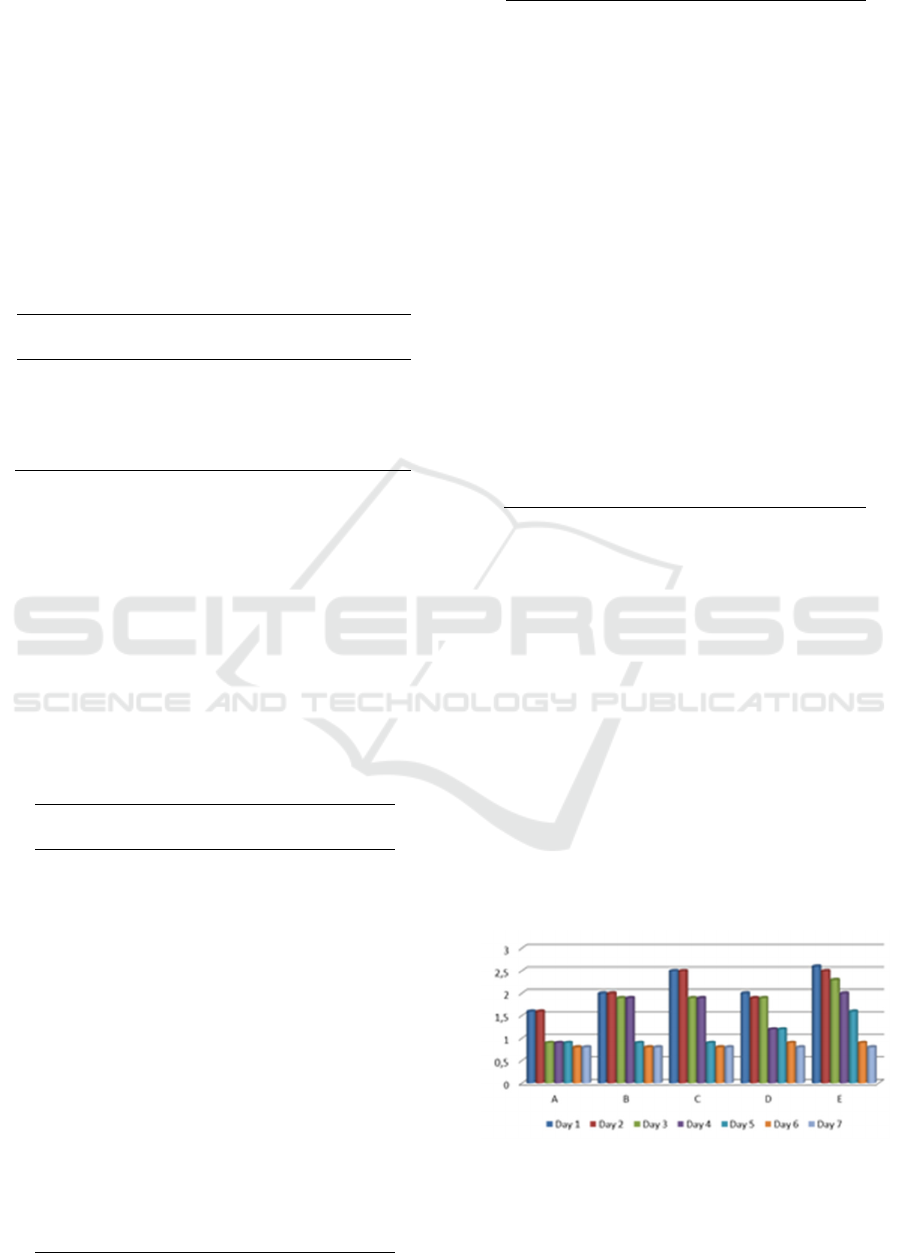
Figure 1.
Figure 1: The results of the analysis of nicotine levels
Figure 1 showed data from five urine samples of
active smokers that had been extracted using
Extraction and Analysis of Nicotine in the Urine of Active Smokers after given by Vitamin C
603

chloroform. The nicotine concentration table in the
sample can be seen in Table 3.
Table 3: Nicotine concentration
Figure 1 and Table 3 shows the nicotine
concentration generated from the five analyzed
samples. The concentration of urine generated from
day 1 to day seven is reduced. This shows that
Vitamin C given to active smokers has an effect on
urine levels.
4 CONCLUSION
The extraction of nicotine in the urine of active
smokers can be developed using electro synthetic
coupling maceration. The extraction results were
analyzed using a preliminary test and thin layer
chromatography indicated the presence of nicotine
in the smoker's urine. The urine concentration
decreased until the 7th day after administration of
Vitamin C by testing using UV spectroscopy at a
wavelength of 260 nm.
REFERENCES
Clayton, P.M., Carl A.V., Bui T.A.M, Alex F.D., nd Kevin
M. 2013. Spectroscopic Studies on Nicotine and
Nornicotine in the UV Region † Spectroscopic Studies
on Nicotine and Nornicotine in the UV Region, no.
May. https://doi.org/10.1002/chir.22141.
Fidrianny, I. 2004. Analisis Nikotin Dalam Beberapa
Organ Mencit Jantan Yang Telah Menghirup Asap
Rokok Analysis of Nicotine in Various Organs of
Male Mice after Inhalation of Cigarette
Smoke.Majalah Farmasi Indonesia 15 (4): 207–10.
Lorensia, A., Virlando R.S. 2018. Asupan Vitamin C Dan
E Dengan SQ-FFQ Terhadap Fungsi Paru Perokok
Dan Asupan Vitamin C Dan E Dengan SQ-FFQ
Terhadap Fungsi Paru Perokok Dan Non-Perokok
Departemen Ilmu Kesehatan Masyarakat , Fakultas
Kedokteran , Universitas Surabaya. Jurnal MKMI 14
(June): 101–7.
https://doi.org/10.30597/mkmi.v14i2.3998.
Muhammad, T., Wanto R., Daulay A.S., Siahaan L.K.,
Ardilla D., Razali M., Sinaga M.H. 2017. Analisis
Nikotin dalam daun Tembakau Deli (Nicotiana
Tabacum L). Jurnal Stikna 01 (02).
Pacier, C., Martirosyan D.M. 2015. Vitamin C : Optimal
Dosages , Supplementation and Use in Disease
Prevention. Functional Foods in Health and Disease 5
(3): 89–107.
Rahmat, M .Adam, Ramadhan, Rusli R. 2016. Analisis
Kadar nikotin dalam Rokok Herbal Indonesia. In
Prosiding Seminar Nasional Kefarmasian Ke-3, 1:20–
21.
Sari, R.K., Zulaikhah S.T., Livana PH. 2019. Perbedaan
Pengetahuan Perokok Aktif Dan Perokok Pasif
Tentang Bahaya Rokok. Jurnal Ilmiah STIKES Kendal
9 (April): 85–94.
https://doi.org/10.32583/pskm.9.2.2019.85-94.
Solarino, B., Rosenbaum F., Rießelmann B, Claas T
Buschmann, Tsokos M. 2009. Death Due to Ingestion
of Nicotine-Containing Solution : Case Report and
Review of the Literature. Forensic Science
International 195 (November): 18–22.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2009.11.003.
Taufik, M., Wanto R.,, Cibro S.R.,, Ardilla D., Razali M,
Tarigan D.M. 2017. Studi Pendahuluan Maserasi
Coupling Elektosintesis Dalam Mengekstraksi Nikotin
Yang Terkandung Dalam Puntung Rokok. In
Prosiding Seminar Nasional Kimia Unmul, 182–90.
IMC-SciMath 2019 - The International MIPAnet Conference on Science and Mathematics (IMC-SciMath)
604
