
Zerosicks, Health and Safety Electrical Module in Vocational
Education Management
Ketut Ima Ismara, Reni Suratijo
Electrical Engineering Education Department, Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: Electrical health and safety, module, zerosicks, vocational education
Abstract: The research aims to: (1) develop training modules, (2) find out the feasibility level in terms of material aspect,
(3) find out the feasibility level in terms of media aspect, (4) find out the response of the users regarding the
developed electrical health and safety training modules based Zerosicks model. This research conduct with
R&D approach consists of 4-D stages: define, design, develop, and disseminate. The subjects of this study
were material experts, media experts and 35 students at Electrical Engineering Study Program, Yogyakarta
State University. Research findings According to material expert 1, modules feasibility got 70.7% and
categorized as "feasible" and categorized "highly feasible" for Material expert 2 with a percentage of 92.1%.
Material expert 3 got 78.6% categorized as "feasible". According to media expert 1 got 81.5%. Media expert
2, is 86.5%, and media expert 3 with 93.5%. The last, assessment of user responses which included material
and media aspects got 85.3% and 86.4% respectively, with both categorized "highly feasible". It's mean the
electrical health and safety module based on Zerosicks with the android operation is originality highly feasible
implemented in electrical vocational education management. The benefit of this module is using familiarity,
generating creativity, and understanding quickly. Unsafe behaviour evaluation can be limited to this research.
1 INTRODUCTION
Along with the increasingly modern technological
developments, electricity has an essential role in
everyday life and Industry. Electricity has become a
staple for some people as if it cannot live without
electricity. Electricity has driven many of the tools
that make life more comfortable. The increasing need
for electricity is a reason for the need for a proper and
safe electrical installation.
Electricity is vital in human life, but also a source
of danger that may threaten human safety and security
of the building and its contents. Various hazards
caused by electricity include electrical shock, thermal
effects, fires/ explosions and other electrical hazards.
Electricity as a hazard has the potential to cause work
accidents.
According to Buntarto (2015), occupational
accidents are unexpected events and unwanted
relating to employment, including disease because of
the employment relationship. The cause of the work
accident can be divided into groups: (1) Physical
factors, namely unsafe working environment
conditions, (2) Human factors, including (a) Lack of
knowledge and job skills, (b) bad attitude and work
behaviour.
According to Amier (1996), there are three
causes of work accidents: (1) unsafe act or unsafe act,
contributes 85% of the cause of the accident; (2)
unsafe condition, contributes 15% of the cause of the
accident. Nur Hidayat and Indah Wahyuni (2016)
argued that work accidents would result in losses. It
should, therefore, be prevented, where possible, to be
omitted or mitigated.
Based on data from BPJS employment
mentioned, there are 101.367 cases of work accidents
in 17.069 registered companies/ industries with the
victim died of 2.382 people until November 2016.
Meanwhile, the claims of the Ministry of Manpower
in throughout the year 2017, the number of accidents
that work recorded as many as 80.393 cases, down
about 20.975 cases from last year (Republika.co.id).
Although the number of work accidents in Indonesia
is still high. The high number of work accidents in
Indonesia shows the level of concern for health and
safety is still low.
The fact that humans play a crucial role in
accidents, vocational education management, and
training is one way to improve occupational health
578
Ismara, K. and Suratijo, R.
Zerosicks, Health and Safety Electrical Module in Vocational Education Management.
DOI: 10.5220/0010705300002967
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference of Vocational Higher Education (ICVHE 2019) - Empowering Human Capital Towards Sustainable 4.0 Industry, pages 578-584
ISBN: 978-989-758-530-2; ISSN: 2184-9870
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

and safety in Indonesia. According to Suma' mur
(1981), several ways can be used to improve
occupational health and safety: (1) legislation, (2)
supervision, (3) standardization, (4) research, (5)
statistics, (6) vocational education management and
training, (7) safety campaigns, (8) insurance.
According to Pellicer (2009), vocational
education management and training factors are an
essential issue for building occupational health and
safety. The initial effort of the improvement starts
from the teaching, explanation and socialization of
the issues discussed. When a person has mastered the
material, then attempts to improve attitudes can be
more easily done.
The observations made by researchers with
industries related to electrical safety found several
problems, namely: (1) No source is available about
the health and safety of systemically arranged
electrical systems such as pocketbooks, manual, etc.
(2) Awareness of the use of personal protective
equipment in work related to electrical installation is
also deficient. (3) No health and safety modules
available. Electrical installation is indispensable for
employees and for trainers as a practical learning
media to use. Therefore, researchers intend to
research the development of electrical safety module
based on Zerosicks model, which is expected to be a
part of the learning process in vocational education
management and training activities in Industry.
Electrical safety module can also be a source of non-
training learning for people who work as well as
people who will do safety work in the field of
electrical installations. Zerosicks model is an
approach to implement safety by hazard evaluation,
risks observation, solution, integration in
implementation, culture and climate conditioning,
knowledge education management, and
standardization procedure (Ismara and Prianto,
2016).
2 METHODOLOGY
This study uses research and development with a
model of development (4-D) developed by
S.Thiagarajan (1974). This study was conducted in
Electrical Engineering Study Program, Yogyakarta
State University from April to May 2018. The
subjects of this study were material experts, media
experts and 35 students at Electrical Engineering
Study Program, Yogyakarta State University.
2.1 Procedure
The electrical health and safety android modules
development procedure is done by referring to the 4-
D model and POAC as a vocational education
management approach in every step. The step consist
of define, design, develop and disseminate. Define,
this stage aims to define the requirements in the
development of work health and safety work android
modules on electrical installations. The define stage
consists of 5 steps, namely preliminary analysis,
analysis of training participants, task analysis,
concept analysis and objective learning analysis.
Design, this stage aims to start (draft 1) training
android modules and work health of the installation
to be developed. The design stage consists of 4 steps,
namely 1) preparation of criteria test, 2) media
selection, 3) election format, and 4) initial design. In
the initial design step (draft 1), the android module is
validated. Develop, this stage aims to produce
android modules that have been revised based on
input from experts. This stage includes two steps,
namely: expert validation and development trials.
Disseminate, this stage is the last in this study.
Modules that have been tested feasibility
disseminated on a broader scale. The purpose of this
stage is to disseminate or distribute products that have
been developed.
2.2 Data Collection Techniques
The data obtained in this study to assess the quality of
the resulting android module to be eligible to be used
as teaching materials. The data obtained in the form
of quantitative and qualitative. Data collection
techniques in this research using observation
techniques and questionnaires. Observations were
made to determine the availability of teaching
materials and the things needed in the developed
android modules. Questionnaires are used to
determine the feasibility of the android module as
teaching material and given to material experts,
media experts and users. The questionnaire that is
arranged using Likert with four scales. The
alternative answer used in the questionnaire.
2.3 Data Analysis Techniques
Data analysis techniques in this study using
descriptive statistics. According to Sugiyono (2015),
Descriptive statistics are statistics used to analyze
data by describing data that has been collected as is
without intending to make conclusions that apply to
the public or generalization. The determination of the
Zerosicks, Health and Safety Electrical Module in Vocational Education Management
579

feasibility category of this module fills the Likert
scale. Each answer from the respondent then
converted into a number form.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
The process of developing the training android
module consists of several stages that must be
implemented, namely, Define, Design, Development,
and Disseminate. The stages are as follows.
3.1 Define
This stage aims to define product needs to be
developed and identify the aspects underlying
product development that is the android module of
occupational health and safety (OHS) installation of
electricity.
3.1.1 Front-end Analysis
The results of the initial analysis in the form of
systematic reading sources such as pocketbooks,
manuals, android modules and so on the health and
safety of electrical installations, especially in the
utilization of electric power installation not yet
available. Training android module electrical
installation is necessary for trainees and instructors as
a practical learning media and relevant for use in the
implementation of training.
3.1.2 Learner Analysis
Users of this training android module are instructors
and participants of health and safety training of
electrical installations. User characteristics are
optimistic, visionary and excellent managerial skills.
The vocational education managemental background
of the user of the training android module is at least
diploma (3 years) graduates of electrical engineering.
3.1.3 Task Analysis
The competency of training participants is compiled
based on the practice of OHS electrical installation in
Industry and SKKNI of occupational health and
safety. Eight main tasks must be mastered by the
training participants. The main task is described in 8
learning activities.
3.1.4 Specifying Instructional Objective
Learning objectives is made as to the basis for the
preparation of training android modules. The
objective analysis that has been designed is then
integrated into the training android module to be
developed. The learning objective of the android
module development can be seen in Table 1.
Table 1: Learning objectives.
No Learnin
g
ob
j
ectives
1.
Training participants can understand the basic
concepts of occupational health and safety.
2.
Training participants can understand the potential
dan
g
er of electricit
y
utilization installation.
3.
Training participants can understand the accidents
caused b
y
electric
p
ower installation.
4.
Training participants can understand risk
management.
5.
Training participants can understand hazard
control.
6.
Training participants can understand hazard
communication.
7.
Training participants can understand the OHS
requirements of Electricity Utilization
Installation.
8.
Training participants can understand First Aid in
Accidents.
3.2 Design
The training android modules developed in this
research is the work health and safety module of
electrical installation. The design stage is done to
compile the framework of training module contents
that will be developed. The framework has been
prepared to facilitate the development of the contents
of the training android module. There are four steps
in the stage, namely:
3.2.1 Criteria Testing
The preparation of the criteria test is used to develop
the achievement criteria that the training participants
must achieve after attending the training activities.
3.2.2 Media Selection
Media in the development of this training android
module is the print media in the form of training
android modules and worksheets, also can operate by
android. Consideration of selected print media and
operate by android because that is flexible and cost of
procurement is relatively cheaper when compared
with another type of media. The form of training
android modules and worksheets can motivate the
training participants to record the instructor's
explanation so that the training participants more
easily understand the contents of the material. The
other advantages are more easily understanding, more
ICVHE 2019 - The International Conference of Vocational Higher Education (ICVHE) “Empowering Human Capital Towards Sustainable
4.0 Industry”
580

familiarity using, and more creativity generating, in
term electrical safety matter.
3.2.3 Format Selection
Format selection refers to the literature review
include:
Consistency of each sheet format in the training
android module to facilitate page search, the
spacing between lines, shape and font size.
The column format is adjusted to the paper size
(A4), and the iconic symbol is easy to
understand.
The content of the material is designed
coherently and systematically based on zerosicks
model.
The mindmap/ material coverage chart is inside
the android module.
The cover of the training android module is made
with a combination of white, green, blue, grey
and yellow as well as a selection of matching
sizes and fonts.
Design the header look, and footer made
attractive with a blend of colours that match the
cover of the training android module.
The typeface used by Verdana with size ten is
arranged proportionally between the title, subtitle
and content of the training android module.
The space between lines used is 1.5 for ease of
readability or readability.
We are using proportional spaces.
3.2.4 Draft
Preparation of training android modules by using the
program Microsoft Word 2013 and Corel X7 through
3 stages of writing.
Cover. The front cover of the training module for the
instructor presents the title of the training module, the
name of the compiler, the name of the supervisor and
the illustration drawing by the contents of the training
module and given the health and safety logo and
Yogyakarta State University logo on the lower right
side. The back cover of the module for the instructor
was given the writing of the Electrical Engineering
Vocational education management of the Yogyakarta
State University 2018 and the writing of the content
of the module. The front cover of the module training
workbook presents the title of the training module, the
author's name, the name of the supervising lecturer
and given the health and safety logo and Yogyakarta
State University logo on the lower right side. The
front cover is also equipped with a column for the
name of the training participants and training
participants.
Table of Contents. The table of contents displayed
in the training android module contains the page title,
introduction, table of contents, table list, list of
images, coverage map, introduction, learning,
evaluation, cover, glossary and bibliography.
Map/ Chart of Material Coverage. The mindmap/
chart of material coverage displays the chapter and
subsections of the training android module.
Learning. Subtitle cover design contains learning
number, subtitle name, safety logo and occupational
health.
3.3 Develop
The development stage is generated by module
product that has been validated by material experts
and media experts. The development stage includes
expert validation stages and development trials.
Expert validation results are then used to revise the
module to get a decent category.
3.3.1 Expert Appraisal
Instrument Validation. Questionnaires to be used in
this study were tested for validity. Instrument
validation in this research is conducted by expert
judgment consisting of three expert lecturers from
Electrical Engineering Vocational education
management Study Program of Yogyakarta State
University. The instrument validation results by the
three experts stated that the questionnaire used in this
development research was feasible to be used with
improvement. Expert suggestion and comments are
then used as the researcher to improve the
questionnaire before being used to measure the
feasibility of the training android module.
Instrument Reliability. Reliability questionnaire
testing used SPSS software. The questionnaire
obtained user reliability value of 0.889. Thus
reliability in the user questionnaire gets the category
"Highly Reliable".
Material Expert Validation. The material
assessment consists of 5 aspects, namely: Self
Instruction, Self-Contained, Stand Alone, Adaptive,
and User Friendly. The results of the expert material
assessment on each aspect can be seen in Table 2.
Zerosicks, Health and Safety Electrical Module in Vocational Education Management
581
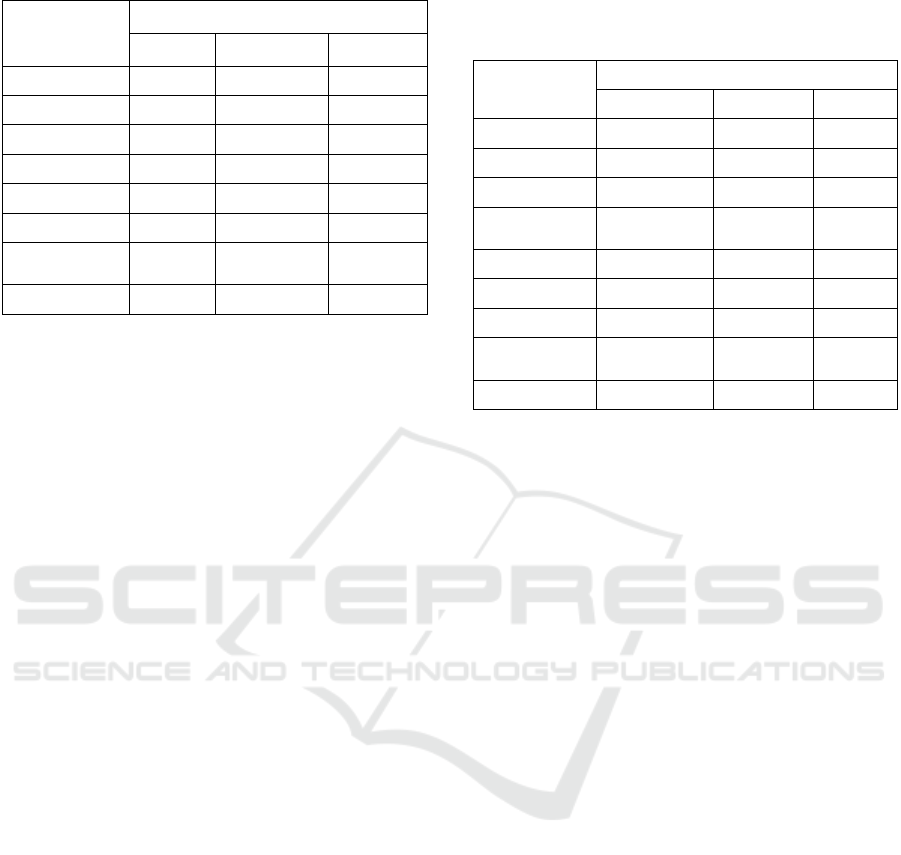
Table 2: Material Expert Validation.
Aspects
Material Experts
1 2 3
Self Instruction 54 66 59
Self Contained 17 23 18
Stand Alone 6 11 9
Adaptive 7 10 10
User Friendly 15 19 14
Total 99 129 110
Category Feasible
Highly
feasible
Highly
feasible
Percentage 70.7 92.1 78.6
According to material experts, android module
feasibility categorized feasible. Modules deserve to
be a medium of learning in training activities because
it contains relevant learning objectives with
competency standards, clearly presented and module
materials by learning objectives—packaging specific
materials, easy to understand and to guide active users
to self-learning. Materials are supported by examples
and illustrations that are relevant, clear and easy to
understand and the mindmap, and images presented
clarify real understanding. The availability of
evaluation encourages a user's material
understanding, guiding independent and critical user
learning. The language used by the android module is
clear, easy to understand and by the correct
Indonesian rules. Summaries are available in each
chapter that makes it easy for users to understand the
material and can strengthen user memories. The
android modules developed have self-contained
characters because the training modules have been
compiled based on competence on the syllabus, the
contents of the module by the competence of the
syllabus and all the competencies in the syllabus
contained in the material. The theory, symbols and
images presented are correct and appropriate to the
material. Android modules can be studied without the
help of other modules and media, structured
according to technological developments and can
serve as relevant references. Android modules display
clear instructions, easy to understand, general, easy to
understand terms used. The glossary is still
incomplete because of many unfamiliar foreign
terms.
Media Expert Validation. Media assessment
consists of 6 aspects, namely: format, organization,
attraction, shape and size of letters, space (space), and
consistency. Once the android module is finished
validated by the media expert, then calculated the
average number of module evaluations. The results of
media expert's assessment on each aspect can be seen
in Table 3.
Table 3: Media Expert Validation.
Aspects
Media Experts
1 2 3
Format 23 20 22
Organization 40 42 43
Attractiveness 33 33 37
Letters and
Sizes
22 21 28
Empty Space 18 22 23
Consistensy 27 35 34
Total 163 173 187
Category
Highly
feasible
Highly
feasible
Highly
feasible
Percentage 81.5 86.5 93.5
According to media experts, android modules
feasibility categorized highly feasible. Android
modules deserve to be a medium of learning in
training activities because of the format of the
proportional column, the paper size is right, and the
paper format by the typing layout. The use of the icon
is appropriate, i.e. italics to emphasize the different
term, bold to emphasize the importance and the use
of correct punctuation. The scope of the android
module is easy to find the user and by the description
of the contents of the module material. The material
is arranged systematically in mindmap form, the
order correctly and efficiently understood in steps of
zerosicks model. The table presented as needed; the
presentation of the picture does not disturb the
writing. The selection of attractive cover colours with
matching colour combinations, the shape and size of
the proportional letter and the corresponding cover
illustration images. The use of bold, italics, underline
is appropriate. Packaging evaluation is attractive,
clear and appropriate to the material. Android module
does not use too many fonts, type and font size easy
to read. The shape and size of the letters in the title,
subheadings and contents of the chapter are
proportional. Space (blank space) cover, proportional
chapter, proportional edge, the spacing between lines,
between paragraphs and proportional chapters. The
use of letter variation is not excessive. The size of
lines between lines, between paragraphs, between
sub-chapters, is consistent. Typing layouts between
sub-chapters, paragraphs and page numbering are
consistent. There are some images in the android
module that are less clear, and the evaluation
presented is less varied.
ICVHE 2019 - The International Conference of Vocational Higher Education (ICVHE) “Empowering Human Capital Towards Sustainable
4.0 Industry”
582

User Trial. Modules that have been validated and
declared eligible by material experts and media
experts then conducted trials to the user to get
responses and feedback on the feasibility of
developed modules. User questionnaire consists of 2
aspects, namely: media and materials. The feasibility
level of the module is seen from the score obtained
through a questionnaire of 35 point statements using
a Likert scale model with intervals of 1 to 4. The
results of user ratings on each aspect can be seen in
Table 4.
Table 4: User Results.
No. Aspects Average Pe
r
centage Category
1. Media 65.7 86.4 % Highly feasible
2. Material 54.6 85.3 % Highly feasible
Total 102.2 85.9% Highly feasible
Assessment of user responses which included
material and media aspects got 85.3% and 86.4%
respectively, with both categorized "highly feasible".
Android module is very suitable to be used as learning
media in vocational education management activity.
The android module presented contains materials
relevant to technological developments. The
language used is clear and easy to understand. The
selection of colours and drawings on the cover is
exciting and by the electrical safety installation. The
font type and size are appropriate. The combination
of colours used accordingly. The tables and pictures
presented do not interfere with the writing.
3.4 Disseminate
The disseminate stage is the stage of the use of
training android modules developed on a broader
scale. The deployment stage is carried out after the
training modules developed through various tests
include testing by material experts, media experts and
user judgments, and improvements made based on
assessment results. The dissemination stage is
limited, by disseminating the final product in the form
of OHS training android module to the user that is the
Industry that holds the activity of vocational
education management and training.
3.5 Module Advantages
The advantages of this Android module are:
containing learning objectives relevant to
competency standards, clearly presented, easy to
understand and to guide active users to learn
independently. The material is supported by examples
and illustrations that are relevant, clear and easy to
understand and mind map; the images presented
clarify the understanding of the material. A summary
is available in each chapter that makes it easy for
users to understand the material and can strengthen
the user's memory. Android modules can be studied
without the help of modules and other media and are
arranged based on technological developments and
can function as relevant references. The format and
systematics of android modules are made
proportionally, and the material is arranged
systematically
Compared to research by Rikanita (2017) on the
development of a website-based school information
system at Makassar State Vocational School
containing only school profile data, as well as the
development of management information systems
Susanto, et al., (2015) contains management
educators and education staff. This android module
includes material about health and safety in SMK.
Another study by Milka (2014) on the use of
management information systems in vocational high
schools using SMS Gateway media, Website schools
and e-learning, while in this research development
using android module media so that it is more
practical and systematic.
Suggestions
The advantages of this Android module are:
containing learning objectives relevant to
competency standards, clearly presented, easy to
understand and to guide active users to learn
independently. The material is supported by examples
and illustrations that are relevant, clear and easy to
understand and mind map; the images presented
clarify the understanding of the material. A summary
is available in each chapter that makes it easy for
users to understand the material and can strengthen
the user's memory. Android modules can be studied
without the help of modules and other media and are
arranged based on technological developments and
can function as relevant references. The format of
android modules are made proportionally, and the
material is arranged systematically.
4 CONCLUSION
Based on the results of research and discussion of
"Electrical Safety Training Modules" can be
concluded as follows: (1) development of training
modules of Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) of
electrical installation using 4D method produces the
product in the form of training android module and
worksheet of training android module. This module
Zerosicks, Health and Safety Electrical Module in Vocational Education Management
583

discusses the Zerosicks of health and safety concepts
in electrical installations. Include potential electrical
installation hazards, risk analysis, accidents due to
electric power installation, risk management, solution
of hazard control, unsafe behaviour, hazard
communication, OHS electrical power installation
and first aid requirements, and personal protective
equipment. The material in the module refers to
competence (SKKNI) Employment of Occupational
Health and Safety Sector and Permenaker No. 12
Tahun 2015. (2) According to material expert 1,
modules feasibility got 70.7% and categorized
"feasible". According to material expert 2, modules
feasibility got 92.1% and categorized "highly
feasible". According to material expert 3, modules
got 78.6% and categorized "highly feasible". (3)
According to media expert 1, modules feasibility got
81.5% and categorized "highly feasible". According
to media expert 2, modules feasibility got 86.5% and
categorized "highly feasible". According to media
expert 3, modules feasibility got 93.5% and
categorized "highly feasible". (4) Assessment of user
responses which included material and media aspects
got 85.3% and 86.4% respectively, with both
categorized "highly feasible". Overall the electrical
health and safety module based on Zerosicks with the
android operation is originality highly feasible
implemented in the electrical vocational education
management process. The android module is using
more familiarity, can generating creativity, and
understanding quickly. The other side, unsafe
behaviour evaluation, and learning media integration
can be limited to this research.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Our thanks go to Anton S. Wahjosoedibjo (President
Director of PT Pranata Energi Nusantara), Hery
Sarjono Wibowo (director of PT SMART ENERGI
SEMESTA), and Joko Riyanto (maintenance division
of CV. Karya Hidup Sentosa/ Traktor Quick) who has
reviewed electrical books safety as a result of
research.
REFERENCES
Amier, R. S. Safety, Health and Work Environment:
Persatuan Insinyur Indonesia. 1996.
Buntarto. A Practical Guide to Occupational Health and
safety for Industry. Yogyakarta: Pustaka Baru Press.
2015.
Hidayat, N & Wahyuni, I. Study of Occupational Health
and Safety Workshop in the Department of Civil
Engineering Vocational education management and
Planning Faculty of Engineering UNY. Jurnal
Pendidikan Teknologi dan Kejuruan, 2016: 23,52.
Mardapi, D. Technique of Preparation of Test and Non Test
Instruments. Yogyakarta: Mitra Cendikia. 2008.
Ismara, K.I,. & Prianto, E. Electrical Safety. Adimeka, CV.
Adicandra Media Grafika. Solo Indonesia. 2016.
Milka. Pemanfaatan Sistem Informasi Manajemen Di
Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan. Jurnal Keguruan dan
Ilmu Pendidikan, Vol III No. 1. 2014.
Pellicer, E & Molenaar, K.R. Discussion of "Developing a
Model of Construction Safety Culture" Journal of
Management in Engineering. 2009.
Rikanita. Pengembangan Sistem Informasi Sekolah
Berbasis Website di SMK Negeri Makassar. Tesis.
Program Pascasarjana, Universitas Negeri Makassar.
2017.
Sugiyono. Vocational education managemental Research
Methods. Bandung: Alfabeta. 2015.
Suma' mur. Safety And Accident Prevention. Jakarta:
Gunung Agung. 1981.
Susanto, H.M., Mantja, W., Bafadal, I., & Sonhadji, A.
Pengembangan Sistem Informasi Manajemen Pendidik
dan Tenaga Kependidikan. Jurnal Pendidikan
Humaniora, Vol. 3 No. 2. 2015.
S.Thiagarajan, Semmel, D. S., & Semmel, M.I.
Instructional Development for Training Teacher of
Exceptional Children: A Sourcebook. Bloomington:
University of Indian. 1974.
ICVHE 2019 - The International Conference of Vocational Higher Education (ICVHE) “Empowering Human Capital Towards Sustainable
4.0 Industry”
584
