
The Role of Information Technology in Supporting Accountant
Profession in the Era of Industrial Revolution 4.0
Titis Wahyuni
Vocational Education Program, University of Indonesia, Depok, Indonesia
Keywords: Industri 4.0, Information Technology, Digital Technology, Digital economy, Big Data, Cloud Computing.
Abstract: The purpose of this study is to identify the role of information technology in supporting accountant
profession in the era of Industry 4.0. The method used in this study is a descriptive analysis. The results of
this study indicate that information technology through the application of digital data technologies such as
the Internet of Things, AI, Cyber-Physical Systems in the industry helps accountants in carrying out their
work in the Industrial 4.0 era. The study provides an understanding, advice and recommendations to the
accountant profession about how information technology in Industry 4.0 works, helps the tasks undertaken
by accountants and directs the capabilities that accountants should have in facing the Industry 4.0 era. The
research enhances the prior works in the area of accountant’s tasks, not a job by discussing ways of how the
information technology could support tasks of accountant in the era of industry 4.0. Since the world is
moving towards the industry revolution 4.0 (IR 4.0), many technological infrastructures have been
developed. Hence, a new study discussing these new states of the art is needed, to ensure the competence of
accountant’s to-do their jobs. This study is essential to satisfy the new needs of the industry due to the
emerging IR 4.0. this study only discusses the role of information technology as a supporting tool for the
accountant. Our next research will further discuss the role of the accountant in industry 4.0.
1 INTRODUCTION
The presence of the fourth Industrial Revolution
(often referred to as Industry 4.0) is predicted to be
the most powerful driver of innovation over the next
few decades, which triggers the next wave of
innovation. Various applied technologies in Industry
4.0 emerged, including advanced robotics, artificial
intelligence, internet of things, virtual and
augmented reality, cyber-physical systems, additive
manufacturing, and distributed manufacturing. The
use of this technology is changing business
processes and business models that are applied in
various industries (Dorleta, Jaione, and Ignacio,
2017).
The main concepts of Industry 4.0 are
digitalisation, optimisation and personalisation of
production, automation and adaptation, human-
machine interaction, value-added services and
automatic data exchange and communication. The
full integration of information, communication
technology and automation technology in future
factories in Industry 4.0 is implemented to increase
productivity, efficiency and effectiveness of
operations in each value chain and production
process. The concept of Industry 4.0 is an industrial
process for adding value and knowledge
management (Ślusarczyk, 2018). (Weyer, Schmitt,
Ohmer and Gorecky, 2015). (Paprocki, 2016).
In the Industrial 4.0 era, the development of
digital technology increased and penetrated various
fields of industry. This development provides
opportunities as well as challenges in the economic,
social, technical, environmental, political, and
regulatory fields (Hecklau, Galeitzkea, Flachsa, and
Kohl, 2016). The world economy has changed
because of the significant development and
application of this technology. The integration of
information and communication technology in this
era creates opportunities for the growth of the digital
economy how economic values are created changes
fundamentally in the digital economy. In the digital
economy, economic and business activities are
carried out digitally through the internet and web-
based markets (Zimmermann,2019). (Berisha-
Shaqiri and Berisha-Namani, 2015).
The Indonesian Ministry of Research,
Technology and Higher Education states that the 4.0
590
Wahyuni, T.
The Role of Information Technology in Supporting Accountant Profession in the Era of Industrial Revolution 4.0.
DOI: 10.5220/0010706400002967
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference of Vocational Higher Education (ICVHE 2019) - Empowering Human Capital Towards Sustainable 4.0 Industry, pages 590-596
ISBN: 978-989-758-530-2; ISSN: 2184-9870
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

industrial revolution brought changes to the
adjustment of work done by humans, machines,
technology and processes in various fields of the
profession including accountants. Gerd Leonhard, a
futurist, stated that the threat of the digital era is that
the globalisation era will eliminate around 1 - 1.5
billion jobs during 2015-2025. This loss of work is
due to the replacement of work that was initially
done by humans with automatic machines. Therefore
the way of working and accounting practices must
be changed in order to improve service quality and
global expansion through online communication and
the use of cloud computing. Cloud computing and
big data for accounting data are needed in the era of
the digital economy. In the era of the digital
economy, the volume of information will continue to
grow and require cloud computing as its
infrastructure (Fariantoi, 2019).
The role of accountants in the era of the digital
economy will change. In the era of the digital
economy, the role of accountants has shifted from
recording transactions to financial analysis.
Accountants must be aware of the development of
emerging information technology and strive to
continue to improve capabilities in accordance with
the development of information technology and can
continue to survive in this digital economy era.
Accountants must be able to understand the support
of information technology in supporting their
profession in the digital age. This understanding will
direct accountants in learning the technology
needed.
Based on the aforementioned problems, the
researchers are interested in investigating the role of
information technology in supporting the accounting
profession in the industrial era 4.0. The discussion
about the role of information technology in
supporting the accounting profession in the
Industrial era 4.0 in this article formulates the
question: what is the influence of the industrial
revolution on the accounting profession? What is the
role of information technology in supporting the
accounting profession in the industrial era 4.0? What
skills should accountants learn about the support
provided by information technology in the industrial
era 4.0?
2 THEORETICAL REVIEW
2.1 Industrial Revolution 4.0
The Industrial Revolution 4.0 is a term that emerged
at the Hannover trade fair in Germany in 2011. This
term emerged as an initiative of the German
government to promote Germany as a global leader
in technological innovation. Subsequently, several
publications that defined Industry 4.0 emerged and
became popular. The concept of industry 4.0 in
several countries generally has the same goal, which
is to increase competitiveness in global markets due
to the development of digital technology in various
industrial fields Bartodziej, 2017).
The industrial revolution 4.0 was marked by the
emergence of five leading technologies to be
implemented as a new business model solution and
had a significant impact on the supply chain, namely
internet of things (IoT), artificial intelligence,
advanced robotics, enterprise wearables, and
additive manufacturing (Li, Hou, Yu, dan Yang,
2017).
2.2 Information Technology
Information technology is the hardware and software
needed to process data and other information.
Information technology includes all technologies
used to create, process, transmit, store, exchange and
use information in all forms. Accountants who have
different roles depending on the functions performed
must always be up to date with technological
changes and must comply with recognised
international standards (Zenuni, Begoli, and Ujkani,
2014).
2.3 Digital Economy
The term digital economy refers to various economic
activities that use digital information and knowledge
as the main factors of production. The internet,
cloud computing, big data, financial technology, and
other new digital technologies are used to collect,
store, analyse and share information digitally and to
change existing social interactions. Tapscott first
introduced the concept of the digital economy in
1998, which is a sociopolitical and economic system
that has the characteristics of an intellectual space,
including information, various information access
instruments, information capacity and information
processing. The components of the digital economy
that were identified for the first time were the ICT
industry, e-commerce activities, digital distribution
of goods and services.
2.4 Big Data
Gartner defines big data as data that has three
attributes, namely volume, variety, and velocity.
The Role of Information Technology in Supporting Accountant Profession in the Era of Industrial Revolution 4.0
591
Volume is related to the size by which data growth
reaches volumes of tens of terabytes to several
petabytes. Variety means the type or type of data,
which includes various types of data both data that
have been structured in a database or unorganised
data in a database such as text data on web pages,
voice data, video, click streams, log files, and
etcetera. Velocity is the speed at which data is
generated and how fast the data must be processed in
order to meet user requests.
2.5 Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing is a combination of the use of
computer technology and cloud-based Internet
Storage development. Cloud Storage is a metaphor
of the internet, as storage media are often depicted
on computer network diagrams. Cloud Computing
applies a computational method. Namely,
capabilities related to information technology are
presented as a service. Users can access cloud
computing via the internet without knowing what is
inside, expert with it, or have control over
technological infrastructure (Santiko, Irfan, Rosidi,
Wibawa, and Seta, 2017).
3 METHODOLOGY
The research design used in this study is a
descriptive analysis method. The descriptive
analysis describes the world or phenomenon.
Descriptive analysis is used to answer questions
about who, what, where, when and to what extent.
The purpose of descriptive analysis is to identify and
describe trends and variations in populations, make
new measurements of crucial phenomena, or
describe samples in studies aimed at identifying
causal effects. Descriptions play an essential role in
the scientific process in general and educational
research in particular.
Questionnaires are used to collect formal data
from accountants via Google form. Samples were
chosen based on purposive sampling with the criteria
graduated from Accounting major and works as
educator accountants, internal accountants, public
accountants, government accountants/auditors,
management accountants, business analysts,
entrepreneurs and corporate finance. Data collected
from the final survey was analysed.
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Result
Respondents are accountants who work as educator
accountants, internal accountants, public
accountants, government accountants/auditors,
management accountants, business analysts,
entrepreneurs and corporate finance. Questionnaires
were sent to more than 5 Whats Up Accountant
Groups. The number of accountants who became
respondents was as many as 286 people.
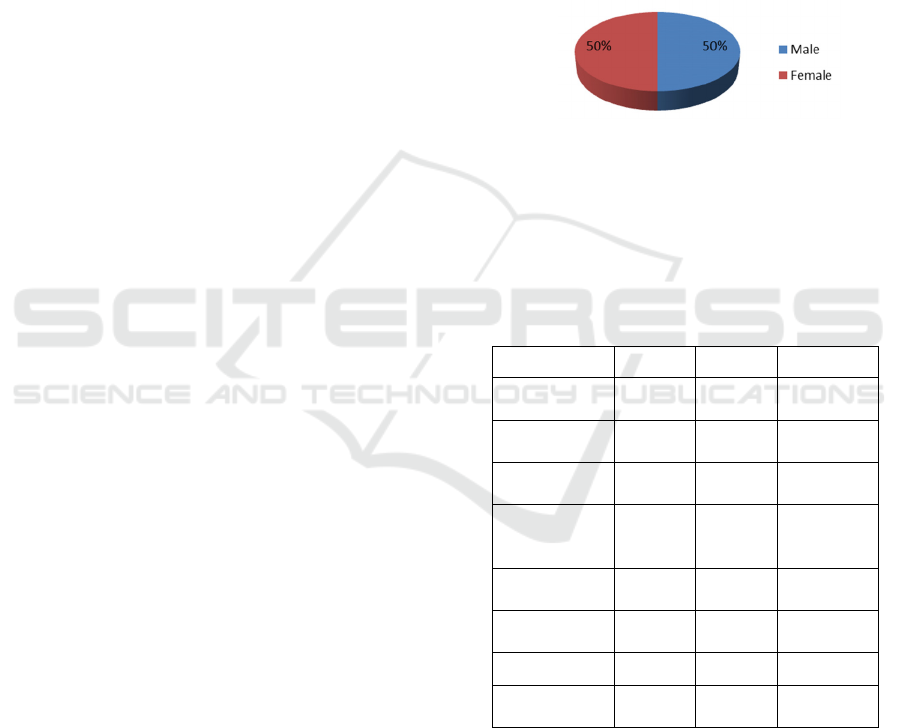
Figure 1: Sex of Respondents
Figure 2 shows that of 286 accountants invited to
participate, 78 submitted surveys for a response rate
of 27,
2
7%. Of the 78 respondents, 39 (50%)
reported their gender as female and 39 (50%) as
males.
Table 1: Gender and Type of Accountant.
Profesi % Total % Male % Female
Educator
Accountant
50% 35% 15%
Internal
Accountant
4% 3% 1%
Public
Accountant
10% 6% 4%
Government
Accountants /
Auditors
15% 14% 1%
Management
Accountant
0% 0% 0%
Business
Analyst
4% 3% 1%
Entreprneurs 4% 4% 0%
Corporate
Finance
13% 5% 8%
Table 1 shows that the majority of respondents
in this study were accountant educators consisting of
35% men and 15% women. The least respondents
were business analysts and internal accountants.
Each consists of only 7% of men and 0 women.
ICVHE 2019 - The International Conference of Vocational Higher Education (ICVHE) “Empowering Human Capital Towards Sustainable
4.0 Industry”
592
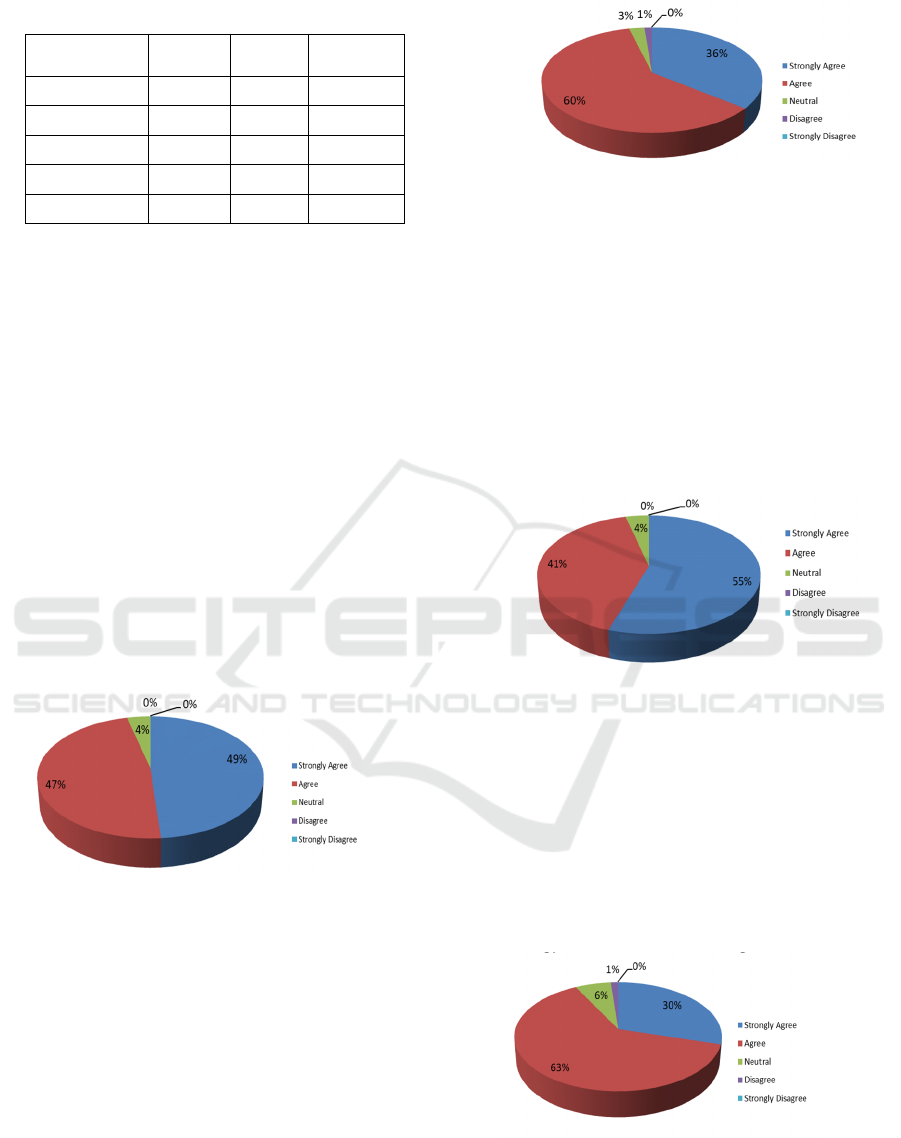
Table 2: Gender and Age of Respondent.
Age of
Responden
% Total % Male % Female
20 - 30 tahun 24% 9% 15%
31 - 40 tahun 26% 10% 15%
41 - 50 tahun 41% 24% 17%
51 - 60 tahun 9% 6% 3%
> 60 tahun 0% 0% 0%
Table 2 shows that most respondents in this
study were in the age 41-51 years old of 24% men
and 17% women. The fewest respondents were in
the age 51-60 years old. It consists of 6% of men
and 3% women.
4.1.1 The Effects of the Industrial
Revolution on Accountants
Based on the data obtained from the questionnaires,
the outline can be presented major findings obtained
are:
Approximately 47% and 49% of respondents
agreed and strongly agreed respectively due to the
emergence of the industrial revolution 4.0, the
workings and practices of accountants need to be
changed to improve service quality and global
expansion through online communication and the
use of cloud computing (Figure 2).
Figure 2: Changes in Accountants’ Work Methods and
Practices
Figure 2 also shows that 4% of respondents were
neutral that the workings and practices of
accountants need to be changed to improve service
quality and global expansion through online
communication and the use of cloud computing.
Approximately 60% and 36% of respondents
agreed and strongly agreed respectively that in the
Industrial 4.0 era, information technology which was
defined as hardware and software now turned into
digital data technology (Figure 3).
Figure 3 Changes in information technology from
hardware and software to digital data technology.
Figure 3 also shows that 3% of respondents were
neutral with the statement that information
technology has changed from hardware and software
to digital data technology and the other 1% of
respondents disagree.
Approximately 41% and 55% of respondents
agreed and strongly agreed that in the Industrial 4.0
era, accountants should have the ability in terms of
data analysis, information technology development,
and leadership skills. (Figure 4).
Figure 4: Accountant’s ability in data analysis, data
analysis, IT development, and leadership skills.
Figure 4 also shows that 43% of respondents
were neutral that the accountants should have the
ability to data analysis, information technology
development, and leadership skills.
Approximately 63% and 30% of respondents
agreed and strongly agreed that the Industrial
Revolution 4.0 resulted in the full integration of
information, communication and automation
technology in future factories (Figure 5).
Figure 5: Industry 4.0 led to full integration of IT,
communication and automation in the future factory.
The Role of Information Technology in Supporting Accountant Profession in the Era of Industrial Revolution 4.0
593

Figure 5 also shows that 6% of respondents were
neutral and 1% disagreed that Industry 4.0 is causing
full integration of information, communication and
automation technology in future factories.
Approximately 51% and 44% of respondents
agreed and strongly agreed that as technology
became more sophisticated and present in all aspects
of the business, the role of accountants shifted
towards a more strategic and analytical role (Figure
6).
Figure 6: The role of accountants shifted towards a more
strategic and analytical role
Figure 6 also shows that 4% and 1% of
respondents were neutral and disagreed that the role
of accountants shifted towards a more strategic and
analytical role, and the other 2% of respondents
disagree.
Approximately 46% and 53% of respondents
agreed and strongly agreed that accountants must
have the expertise needed in the industrial era 4.0
such as the use of AI-based and Big Data
technology, the ability to analyse data,
understanding of customer needs, the ability to use
data forms, interpret data to produce information
which is more meaningful for decision making
(Figure 7).
Figure 7: Accountants must have the expertise needed in
the industrial era 4.0
Figure 7 also shows that 1% of respondents
disagree that accountants must have the expertise
needed in the industrial era 4.0.
4.1.2 the Role of Information Technology in
Accounting Profession in the
Industrial Age 4.0
Approximately 36% and 59% of respondents agreed
and strongly agreed that the Industrial Revolution
4.0 was the convergence of information technology
into the industrial world. Through the Internet of
Things (IoT) and Big Data, technology can be used
to collect and process data used by accountants in
their function as financial information provider
experts (Figure 8).
Figure 8: Industrial Revolution 4.0 was the convergence of
IT into the industrial world
Figure 8 also shows that 5% of respondents were
neutral that the Industrial Revolution 4.0 was the
convergence of information technology into the
industrial world.
Approximately 46% and 30% of respondents
agreed and strongly agreed that the use of Robotics
and data analytics (big data) takes over the necessary
work done by accountants (records transactions,
processes transactions, sorts transactions). This use
increases the efficiency and effectiveness of work
(Figure 9).
Figure 9: the use of Robotics and data analytics (big data)
increase the efficiency and effectiveness of work
Figure 9 also shows that 15% and 9% of
respondents were neutral and disagreed that the use
of Robotics and data analytics (big data) increase the
efficiency and effectiveness of works while 10% of
respondents disagree.
Approximately 55% and 26% of respondents
agreed and strongly agreed that technology in
Industry 4.0 allows accountants to obtain data that
ICVHE 2019 - The International Conference of Vocational Higher Education (ICVHE) “Empowering Human Capital Towards Sustainable
4.0 Industry”
594

previously could not be obtained in real-time,
through embedded sensors (Figure 10).
Figure 10: Technology in Industry 4.0
Figure 10 also shows that 17% and 2% of
respondents were neutral and disagreed that the use
of Robotics and data analytics (big data) increase the
efficiency and effectiveness of work while 3% of
respondents disagree.
Approximately 56% and 35% of respondents
agreed and strongly agreed that Technology in
Industry 4.0 improves data quality, namely through
better timeliness and accuracy and greater detail to
improve efficiency, the certainty of data and other
decision-making goals (Figure 11).
Figure 11: Technology in Industry 4.0 improves data
quality
Figure 11 also shows that 9% of respondents
were neutral that the use of Robotics and data
analytics (big data) increase the efficiency and
effectiveness of work.
11. Approximately 60% and 26% of
respondents agreed and strongly agreed that the use
of information technology (IT) in the audit is getting
wider, namely with general audit software that is
increasingly being used by public accounting firms
to increase productivity in carrying out audit work
(Figure 12).
Figure 12: The use of IT in the audit
Figure 12 also shows that 11% and 3% of
respondents were neutral and disagreed that the use
of information technology (IT) in the audit is getting
wider.
12. Approximately 64% and 27% of
respondents agreed and strongly agreed that non-
financial data that can be used to assist specific
decisions and provide the big data analytics could
provide new sources of assessment and hard
evidence needed by management accountants in
carrying out their work (Figure 13)
Figure 13: Non-financial data that can be used to assist
specific decisions and provide big data analytics
Figure 13 also shows that 6% of respondents
were neutral that non-financial data that can be used
to assist specific decisions and provide big data
analytics, while 3% of respondents disagreed.
4.2 Discussion
Based on data obtained from the result section
shows that industrial revolution 4.0 is the
convergence of information technology to the
industrial world. The industrial 4.0 era produced
developments in digital technology such as the
Internet of Things, Cyber-Physical Systems,
Artificial Intelligence, Cloud Computing, and Big
Data. Industry 4.0 produces full integration of
information and communication technology,
resulting in automation technology in future
factories. Smart robots and Artificial Intelligence
will largely replace personal work. All business
transactions will be carried out automatically and
produce a substantial volume of transaction data that
grows at high speed (big data). Big data requires
The Role of Information Technology in Supporting Accountant Profession in the Era of Industrial Revolution 4.0
595

cloud computing as an infrastructure to support it.
The role of accountants will shift from a bookkeeper
to an expert provider of financial data or as a data
analyst. Accountants must be able to analyse
customer needs, financial data, and interpret data to
be more meaningful for decision making.
Accountants must be able to understand technology
in order to carry out future tasks.
The result section also shows some capabilities
that accountants should have in this industrial era
include data science, data analysis,
coding/programming, real-time accounting, and
understanding the Artificial Intelligence model in
order to adapt with technology applied in the digital
era. In addition, accountants must also have the right
attitude and mentality and be critical of
technological developments. Accountants should try
to learn new technology, attend training to obtain the
required competencies and certifications to be able
to survive in this industrial era.
5 CONCLUSIONS
All business transactions will be carried out
automatically and produce a substantial volume of
transaction data that grows at high speed (big data)
and requires cloud computing as infrastructure to
support it.
The role of accountants will shift from a
bookkeeper to an expert provider of financial data or
as a data analyst. Accountants must be able to
analyse customer needs, financial data, and interpret
data to be more meaningful for decision making.
Accountants must be able to understand technology
in order to carry out future tasks.
Some capabilities that accountants should have
in this industrial era include data science, data
analysis, coding/programming, real-time accounting,
and understanding the Artificial Intelligence model.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank the Vocational
Education Program University of Indonesia, Depok,
Indonesia, for supporting the study.
REFERENCES
Ibarra, D., Ganzarain, J., & Igartua, J. I. (2018). Business
model innovation through Industry 4.0: A
review. Procedia Manufacturing, 22, 4-10.
Ślusarczyk, B. (2018). Industry 4.0: Are we ready?. Polish
Journal of Management Studies, 17.
Weyer, S., Schmitt, M., Ohmer, M., & Gorecky, D.
(2015). Towards industry 4.0-standardization as the
crucial challenge for highly modular, multi-vendor
production systems. IFAC-PapersOnLine 48 (3): 579–
584.
Paprocki, W. (2016). Industry 4.0 Concept and Its
Application in the Conditions of the Digital Economy.
In Digitization of the Economy and Society.
Opportunities and Challenges for Infrastructure
Sectors. Gdansk: European Financial Congress (pp.
39-57).
Hecklau, F., Galeitzke, M., Flachs, S., & Kohl, H. (2016).
Holistic approach for human resource management in
Industry 4.0. Procedia Cirp, 54, 1-6.
Zimmerman, H. D. (2000). Understanding the digital
economy: Challengers for new business
models. AMCIS 2000 Proceedings, 402.
Berisha-Shaqiri, A., & Berisha-Namani, M. (2015).
Information technology and the digital
economy. Mediterranean Journal of Social
Sciences, 6(6), 78.
Farianto, D. (2015). Fenomena Big Data dan Komputasi
Awan (Cloud Computing). PUSINFOLAHTA TNI.
https://pusinfolahtatni.mil.id/wp-
content/uploads/2015/07/Artikel-I-FENOMENA-BIG-
DATA-dan-KOMPUTASI-AWAN.pdf [Accessed 4
August 2019].
Jan, B. C. (2016). The Concept Industry 4.0: An Empirical
Analysis of Technologies and Applications in
Production Logistics.
Li, B. H., Hou, B. C., Yu, W. T., Lu, X. B., & Yang, C.
W. (2017). Applications of artificial intelligence in
intelligent manufacturing: a review. Frontiers of
Information Technology & Electronic
Engineering, 18(1), 86-96.
Zenuni, M. B., Begolli, M. T., & Ujkani, M. (2014).
Impact of information technology in the accounting
profession. In Conference Paper, ResearchGate.
Computing. Jurnal Teknik Informatika, 10(2), 137–146.
ICVHE 2019 - The International Conference of Vocational Higher Education (ICVHE) “Empowering Human Capital Towards Sustainable
4.0 Industry”
596
