
Study on Application of Floating Structure Technology in Indonesia
Christino Boyke
1,a
, Tri Achmadi, Hasan Iqbal Nur
1
Department of Marine Transportation Engineering, Institut Teknologi Sepuluh Nopember, Indonesia
Keywords: Application, Floating Structure, Technology.
Abstract: As the climate and global weather conditions change, the human environment also changes. Rising sea levels
and higher rainfall are driving people to find safer shelter. The increase in population causes the lack of
residential land that can be used as a residence. These problems also occur in Indonesia, the country with the
4th largest population globally and has waters covering 70% of the total area. One potential technology that
can be used to reduce the impact of the problems that have been conveyed is the use of floating structures.
With a large area of water and the number of residential lands is decreasing, this technology offers alternative
solutions to these problems. Floating structures are defined as structures that rely on water's buoyancy force
to support the structure's weight. Some floating technologies that can be utilized for development in Indonesia
include floating houses, floating breakwaters, floating bridges, floating docks, and other infrastructure
facilities. In this research, we will see the advisability of the floating structure technology application in
overcoming some of the problems that occur in Indonesia using comparative analysis. Several literature
reviews were carried out to study the various applications of floating structures in Indonesia. The study results
show that this technology is very likely to be applied and can solve several problems that occur in Indonesia.
1 INTRODUCTION
Infrastructure development in Indonesia continues to
grow to be able to encourage high economic growth.
The increasing level of international trade and the
needs of the maritime industry is promoting sea
reclamation. Without proper implementation and
planning, reclamation can have a negative impact.
Adverse impacts such as the destruction of animals'
living places and coastal plants can cause the balance
of nature to be disturbed. Besides, the seawater
hydrological system on the coast will change from its
natural state.
Maritime infrastructure development is mostly
done conventionally, using land as a foundation that
supports the structure's weight above it. In certain sea
areas, the seabed is very deep, so a deep foundation is
needed. In this condition, water buoyancy can be
utilized to support the weight of the existing structure.
Thus, infrastructure development in areas with deep
seabed can be more effective.
One potential technology that can be used to
reduce the impact of the problems that have been
conveyed is the use of floating structures. Floating
structures are defined as structures that rely on water's
buoyancy force to support the structure's weight.
Under broader conditions, structures that rest on the
soft seabed and use the buoyancy force to reduce the
reaction forces that occur can be categorized as
floating structures (Wang and Wang, 2015).
There have been many studies on the use of
floating structures in solving problems in the world.
Anderson (Anderson, 2014) examined amphibious
architecture, Drieman (Drieman, 2011) also
researched the use of A Floating Breakwater To
Protect a New Artificial Beach In Balchik, Bulgaria.
Research on the use of floating buildings has also
been carried out by Boyke (Boyke et al., 2019) with a
conceptual design of floating houses for disaster
response purposes.
With many uses of this floating technology, this
research seeks to identify what floating technologies
can be used to solve some of the problems that occur
in Indonesia. In this study, floating structures are all
structures that float on water with specific dimensions
that are static and have no movers. Therefore, boats
and ships are not included in the definition in this
study. This study's potential use of floating buildings
is a floating house, road, bridge, breakwaters, jetty,
and other possible functions.
10
Boyke, C., Achmadi, T. and Nur, H.
Study on Application of Floating Structure Technology in Indonesia.
DOI: 10.5220/0010854300003261
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Marine Technology (senta 2019) - Transforming Maritime Technology for Fair and Sustainable Development in the Era of Industrial
Revolution 4.0, pages 10-18
ISBN: 978-989-758-557-9; ISSN: 2795-4579
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

2 FLOATING STRUCTURE
In the development of floating technology, many
types of materials have been used for this structure.
In offshore buildings, steel structures have been
widely used as the primary material for aggressive
environments. For smaller-scale applications, such as
housing and marinas, concrete floating objects are
used more. The floating structure can be made from
several types of materials, including:
1. Caisson Concrete
2. Concrete tray
3. Steel structure
4. Concrete - EPS
From these various materials, diverse floating
technologies have been developed with several
functions: floating houses, floating bridges, floating
dock, and other public facilities.
2.1 Floating Structure Materials
2.1.1 Caisson Concrete
The term Caisson is French which means large box,
which refers to the Caisson form. The Caisson
structure has been widely used in Civil Engineering
works as pillars of bridges, docks, and tunnels. This
structure can float on water to be carried easily to the
installation location by the sea. After arriving at the
installation location, this structure will be submerged
to build a foundation. At present, the Caisson
concrete system is the most widely used structural
system as a base for floating buildings.
Closed space that contains the air inside the
caisson is the cause of the large caisson buoyancy.
Caisson is made of hefty, reinforced concrete, so this
type of structure has an extensive draft and is suitable
for deep seabed areas.
Advantages:
has been widely used, so that a lot of
experience regarding the design and
implementation.
has excellent stability because of its weight.
has an internal space that can be utilized
relatively inexpensive compared to steel
has good durability, with low maintenance
costs.
Disadvantages:
has a small buoyancy
has a big draft
easy to sink if it leaks
2.1.2 Concrete Tray/Open Caisson
A concrete tray or open caisson is a type of caisson
that does not have a roof covering or is free. This type
has similarities with a boat. This type is widely used
for light construction such as houses.
2.1.3 Steel
The steel structure is a structural system that is widely
used in offshore buildings and ship buildings. Steel
structures can be made in various shapes. The box
pontoon is the most common type used for floating
installations. The steel structure has a thin wall
thickness, so it has a lighter weight and great
buoyancy. But with its lightweight, the steel structure
is more unstable than concrete. But this can be
overcome by using ballast water. The main
disadvantage of steel structures is susceptibility to
corrosion. Thus, routine maintenance is needed on
steel structures, so this type is rarely used for light
installations.
Advantages:
it has been widely used, so that a lot of
experience in designing and implementing it.
has an internal space that can be utilized
has a low draft
has a small weight
Disadvantages:
high maintenance costs
relatively more expensive when compared to
concrete
easy to sink if it leaks
can conduct heat and electricity.
2.1.4 Concrete - EPS
EPS (Expanded Poly Styrene) is a floating building
first introduced by International Marine Floatation
Systems Inc. (IMF) in 1980. This system consists of
a core EPS layer covered by a concrete layer as an
outer protector. EPS material has a specific gravity of
20 kg / m3, about 50 times lighter than water. With
an EPS system, a floating building's weight can be
much lighter compared to conventional Caisson
systems. This is because the plate's dimensions can be
thinner. After all, some EPS supports the inside.
Besides, the inner plate is no longer needed because
its function has been replaced with lightweight EPS.
With the use of EPS, floating objects can have smaller
drafts. Also, the risk of drowning due to leakage can
be reduced because the concrete's cavities are no
longer filled with air but instead contain EPS. The use
of EPS certainly adds to the cost, but this can be
Study on Application of Floating Structure Technology in Indonesia
11

compensated for by the reduced concrete volume and
weight.
Advantages:
EPS structure cannot sink
lightweight, large buoyancy
short draft
cheap maintenance
can be formed in various forms
Disadvantages:
Has no internal space that can be utilized
2.2 Application of Floating Technology
in the World
2.2.1 Floating Houses
The concept of floating housing is not a new thing or
new technology in human life. Floating housing has
become part of human history in the world. For
example, countries that know the floating settlement
culture are Cambodia, Vietnam, Indonesia, Thailand,
China, Peru, and Bolivia. This settlement is used as a
home for aquaculture and fisheries.
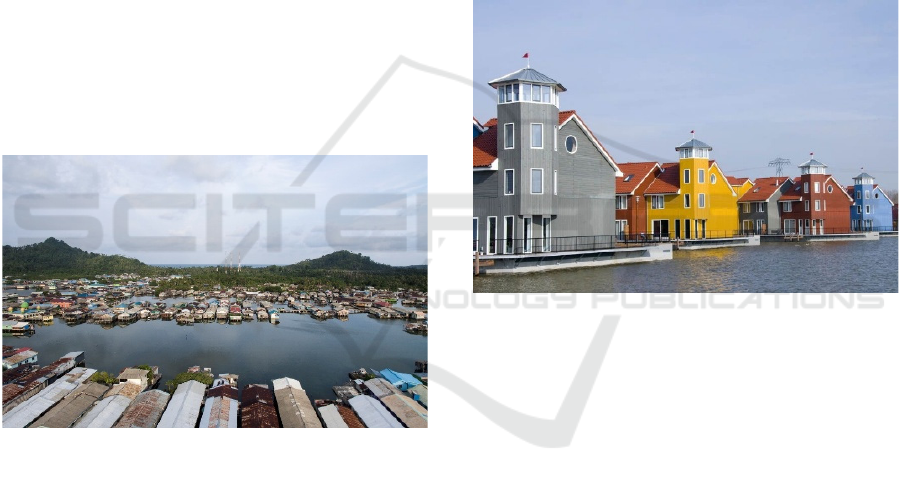
Figure 1: Floating city at Sedanau Island, Natuna (Masaul,
2013).
Indonesia itself has several floating villages in
several provinces. The first floating village is in
Torosiaje Village, Popayato District, Gorontalo. Then
there is the Ayapo village located on Lake Sentani's
shores, Jayapura, and the Bajo Village in Sulawesi.
Besides, there are also villages on the Mahakam River
banks, Kalimantan, and the City on Sedanau Island,
Natuna. The towns are a form of local people's
wisdom in adapting to nature where they live.
The more modern floating house was first
introduced in the 80s. Then this concept is widely
applied in several countries, especially those with
large territorial waters. A company called
International Marine Flotation Systems Inc.
developed a floating house which later became a
trend in several countries in Europe. The house was
designed using concrete with EPS (Expanded Poly
Styrene) as the filling (System, 2013). This system
allows the concrete to have a lighter weight to be built
in shallow water areas. This development then
encouraged several companies to make similar
innovations. In the Netherlands, modern floating
homes have been developed as alternative housing for
residents (Figure 2). These floating houses have good
facilities and safety standards, so many people are
interested in using them.
Several other studies on floating houses were
carried out by Ambrica (Ambica, 2015), who
developed house designs in areas with high water
level fluctuations. Also, Muksin (Muchsin,
Fachruddin Purwono and Amiuza, 2011) researched
floating lodging for tourists in Indonesia.
Figure 2: Floating house at the Netherlands (System, 2013).
2.2.2 Floating Bridge
The floating bridge was first made from a series of
boats bound by a wooden frame and anchored to the
seabed. Floating bridges in the past were usually only
used temporarily because they could not last long and
were unable to support heavy loads. The first floating
bridge recorded in history was built by the Persian
King Xerses when he invaded Greece in 480 BC. This
bridge was built in the Strait of Dardenelles, Turkey,
to cross the war troops. This bridge consists of 300
boats tied and anchored at both ends with large
vessels.
Examples of floating bridges in the modern era are
the Bergsoysund Bridge with a span of 931 m and the
Nordhorland Bridge with 1614 m in Norway. The
largest steel frame floating bridge are located in
Japan, the Yumemai Bridge (Figure 3). This bridge
connects two reclamation islands, where underwater
tunnels and conventional bridges are not feasible.
There is also a floating concrete bridge in Dubai
senta 2019 - The International Conference on Marine Technology (SENTA)
12

which was built in 2007. This bridge connects Bur
Dubai and Deira.
Figure 3: Yumemai Bridge, Japan (Ltd, 2000).
2.2.3 Floating Piers
The floating pier was first used in World War II. At
that time, the construction and repair of conventional
ports became impractical because of the war.
Therefore, it needs a pier that can be dismantled and
moved quickly. Mulberry Harbour is an example of a
type of floating pier that Britain developed in World
War 2. This bridge consists of 3 parts, namely
Breakwater, pier head, and walkway.
A modern floating pier design was built in Alaska
and Japan. The first floating pier with a prestressed
system was constructed in Valdez, Alaska (Figure 4).
This pier opened in 1982 and serves container ships.
This pier has many advantages because of its minimal
maintenance and its ability to work in the deep sea
and follow the tides. In Japan, the floating dock is
located at Ujina Pier in Hiroshima, built-in 1993. This
pier functions as a ferry pier. Because the location has
a very high tidal difference of 4 m, a floating pier is
used to overcome this condition.
2.2.4 Floating Breakwater
Floating Breakwater is an innovation in coastal
engineering. This structure is made of a concrete box
with a hollow in the middle. (Biesheuvel, 2013) This
concrete box is anchored to the seabed to maintain
stability and effectiveness in breaking waves. This
Breakwater is made up of several segments which are
joined together and can be moved easily (Figure 5).
Figure 5: Ingemar Floating Breakwater (Engineering,
2000).
This type of Breakwater is suitable for deepwater
areas because it is not limited to depth and can follow
tides. This structure is not large and massive, so the
manufacturing cost is relatively cheaper than other
types. There are also no environmental problems such
as erosion and sedimentation due to their floating
shape. The upper part of the floating Breakwater can
also be used for various facilities. Every breakwater
segment are connected using special connection that
allows all the units working together (Koekoek,
2013).
2.2.5 Floating Entertainment Facilities
As a supporting facility for residents, various
entertainment facilities are also needed. To overcome
the lack of land and provide a new experience,
floating entertainment facilities have been developed.
Examples are Jumbo Restaurant in Hong Kong and
floating restaurants in Yokohama, Japan. A seven-
story floating hotel has been built in Singapore to be
towed to Australia and established there. The largest
floating entertainment stage in the world is made at
Singapore Marina Bay (Figure 6). This floating
structure is designed as an entertainment stage. The
floating island on the Han River, Korea, is an artificial
floating island that is environmentally friendly.
Figure 4: Floating Container Pier Valdez (Engineering,
2000
)
.
Study on Application of Floating Structure Technology in Indonesia
13

Figure 6: Marina Bay Floating Stage (Wang and Wang,
2015).
2.2.6 Large Floating Storage Facilities
Various structures with storage functions have been
built using floating technology. An example is the
construction of oil storage facilities in Kamigoto and
Shirashima. This storage is intended as oil reserves
when an emergency occurs. Shirashima oil storage
consists of 8 floating steel structures measuring 397 x
82 x 25.4 m. One system can hold 7 million m3 of oil,
equivalent to Japanese oil consumption in 1 day.
Also, Japan has also made a floating solar power plant
in Kagoshima Prefecture. This structure is the largest
solar power plant in Japan.
3 STUDY OF APPLICATIONS IN
INDONESIA
In this section, a comparative analysis between
conventional technology and floating technology will
be performed to overcome some of the problems.
Floating technology that will be used includes
floating houses, a floating pier, and floating
breakwater.
3.1 The Problem of Abrasion on the
Nusa Dua Beach
Nusa Dua beach area with a beach length of ± 4 km
is located in Nusa Dua, Bali. At present, the condition
of the Nusa Dua beach is experiencing severe
abrasion. This can be seen from the reduction in trees
and the shrinking of beach sand eroded by abrasion.
The beach condition, which is eroded by abrasion,
damages Nusa Dua's image as an exclusive tourism
area with golf course facilities, four and 5-star hotels,
and other facilities with international standards.
A breakwater is planned to be built in this area to
reduce the wave pressure that causes abrasion.
Because the seabed in this area has been designated
as a coral reef reserve, the construction of
breakwaters must not damage the coral reefs. The
alternative comparisons used are floating breakwaters
and conventional breakwaters of mountain rocks or
tetrapods.
In conducting a comparative analysis, the first
step compares several criteria between alternatives 1
and 2, as listed in Table 1.
Table 1: Comparison between alternative breakwaters.
Evaluation Aspect Alt.1 Conventional Alt.2 Floating
Effectiveness of wave
attenuation
Able to reduce waves> 2m with attenuation up
to 100%
Able to reduce waves> 2m with attenuation of
50% - 80% de
p
endin
g
on desi
g
n re
q
uirements
Influence/impact on the
Marine Environment
It was causing environmental impacts because
dredging work is needed in coastal areas and
Breakwater's development that can damage
coral reefs
It does not cause environmental impacts
because there is no need for dredging work,
and the construction does not damage the
seabed corals
Construction
Permitting Process
Requires a special permitting process to carry
out dredging and construction that damages
coral reefs
Permitting is more comfortable because it
does not require dredging and does not
dama
g
e the coral reefs
The effective protected
water area
Smaller, because it cannot be installed in deep
waters
More extensive, because it can be installed in
dee
p
waters
Estimated Construction
Costs
Rp. 68.803.377,-/ m Rp.105.851.023, / m
Estimated completion
time
Eight months Ten months
Flexibility Massive and permanent construction (not
flexible to relocate
)
Flexible and can be moved if needed
Value-added Do not have the space that can provide added
value
It has a void space that can be used as a fuel
b
unker/water, restaurant, mini hotel
senta 2019 - The International Conference on Marine Technology (SENTA)
14
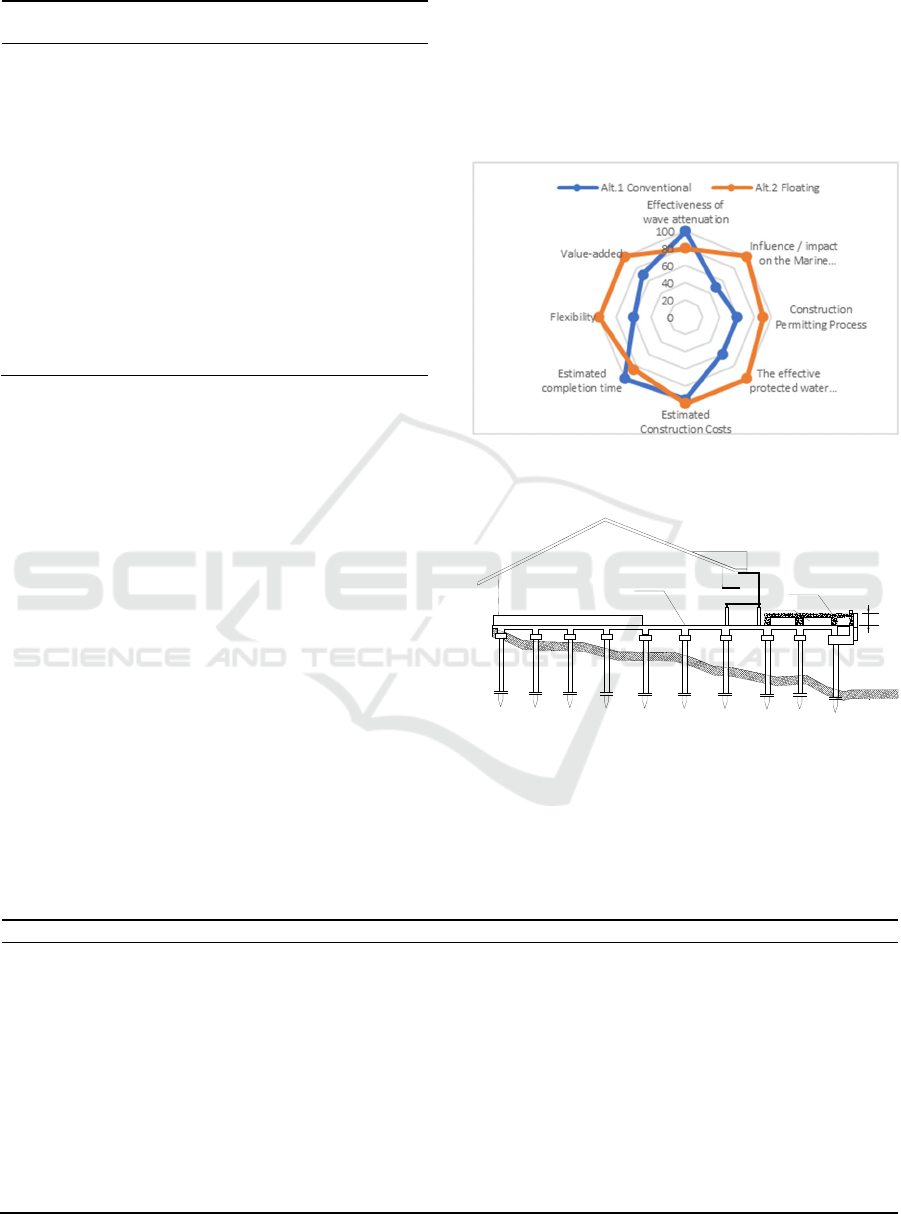
Table 2: Comparison value between alternative breakwaters.
Evaluation Aspect Alt.1
Conventional
Alt.2
Floatin
g
Effectiveness of wave
attenuation
100 80
Influence / impact on
the Marine
Environment
50 100
Construction
Permittin
g
Process
60 90
The effective protected
water area
60 100
Estimated Construction
Costs
95 100
Estimated completion
time
100 85
Flexibilit
y
60 100
Value-adde
d
70 100
TOTAL 595 755
From several comparisons in Table 1, an assessment
of each of the two alternative criteria can be made. The
evaluation is carried out on a scale of 0-100. The results
of the evaluation can be seen in Table 2.
From the results of the comparison in Table 2, it
was found that the greatest benefit obtained from
Alternative 2 (Floating) with a value of 755 is more
significant than Alternative 1 with 595. The results of
the comparison are illustrated in Figure 7.
3.2 Pier Elevation Problems in Port of
Tanjung Emas Semarang
Semarang is one of the industrial cities in Indonesia,
which has a high level of sea traffic. Tanjung Emas
Harbor is the main gate of Semarang City from the
sea. This Port has a typical land that continues to
experience substantial settlement for each year. This
is a significant problem for the Port of Tanjung Emas
because the pier elevation decreases until it reaches
sea level. One solution to the Port's concern is to
elevate the pier elevation by adding a new structure
above the existing structure. As an alternative
solution to these problems, a floating pier can be
made in front of the existing pier. The floating pier
will always move to follow the water level and is not
affected by land subsidence.
Figure 7: Comparison value between alternative
breakwaters.
Figure 8: Alternative 1 (new construction above existing
pier).
In conducting a comparative analysis, the first
step compares several criteria between alternatives 1
1.30
Dermaga
Eksisting
Balok Memanjang
70 x130
Balok Melintang
70 x130
Table 3: Comparison between alternative pier.
Evaluation Aspect Alt.1 Conventional Alt.2 Floating
Effectiveness in
overcoming sea level rise
Ineffective, because it is static, it cannot keep
up with rising water levels.
Practical because the height of the
floating pier can always change
according to sea level.
Influence/impact on
Existing Pier
Significant impact, adding additional burden
to the existing pier. This can cause a decrease
in stren
g
th at the existin
g
Port in the lon
g
run.
No impact because it was built in front of
the existing pier, so it does not directly
b
urden the existin
g
p
ier structure.
The Pier area can be used 10x 100 m2 2 x 10x 100 m2
Estimated Construction
Costs
Rp. 50.000.000, - / m Rp. 150.000.000, -/ m
Estimated completion
time
Nine months 12 months
Flexibility Massive and permanent construction (not
flexible to relocate).
Flexible and can be moved if needed.
Study on Application of Floating Structure Technology in Indonesia
15

and 2, as listed in Table 3. And the second step is to
make a scoring of each of the two options. The
assessment is carried out on a scale of 0-100. The
evaluation result can be seen in Table 4.
Figure 9: Alternative 2 (new construction of floating
structure in front of the existing pier).
Table 4: Comparison value between alternative pier.
Evaluation Aspect Alt.1
Conventional
Alt.2
Floating
Effectiveness in
overcoming sea level
rise
60 100
Influence / impact on
Existin
g
Pie
r
70 100
The Pier area can be
use
d
100 100
Estimated construction
costs
100 30
Estimated completion
time
90 100
Flexibilit
y
60 100
TOTAL 480 530
From the scoring that has been done in Table 4, it
can be concluded that Alternative 1 (Conventional)
and Alternative 2 (Floating) can both be used at
Tanjung Emas Pier. From the assessment results, it
was found that the most significant benefit obtained
from Alternative 2 (Floating) with a value of 530 is
more significant than Alternative 1 with 480. The
results of the comparison are illustrated in Figure 10.
3.3 Temporary Shelters for Earthquake
Victim
When the earthquake strikes, thousands of residents
affected by the earthquake are forced to live in
refugee camps with emergency tents as temporary
shelters. Due to the immensity of the affected area
and the number of damaged roads, the aid that came
can be slow and insufficient. If this happens, refugees
are forced to live in makeshift tents that they made
themselves. Many of these tents are uncomfortable to
live in, causing refugees' physical and mental
conditions to decline. To help disaster victims with
such situations, there must be a temporary shelter that
is habitable, safe, comfortable, and delivery is not
affected by road damage. The floating house can be
used as an alternative solution. A floating home can
be placed on the coast, where most of the affected
victims live. Floating houses can be deployed by sea;
therefore, mobilization is not affected by road
damage. With this floating emergency house,
refugees are expected to live with better quality
housing.
Figure 11: Makeshift tents built by refugees.
Figure 12: Emergency floating house.
In conducting a comparative analysis, the first
step compares several criteria between alternatives 1
and 2, as listed in Table 5. And the second step is to
make a scoring of each of the two options. The
assessment is carried out on a scale of 0-100. The
results of the evaluation can be seen in Table 6.
Jembatan
Penghub ung
10
2,52,5
Dermaga
Eksisting
Struktur Apung
Beton Bertulang
t=0.5 m
Anchor Chain
Anchor Block
Figure 10: Comparison between alternative piers.
senta 2019 - The International Conference on Marine Technology (SENTA)
16
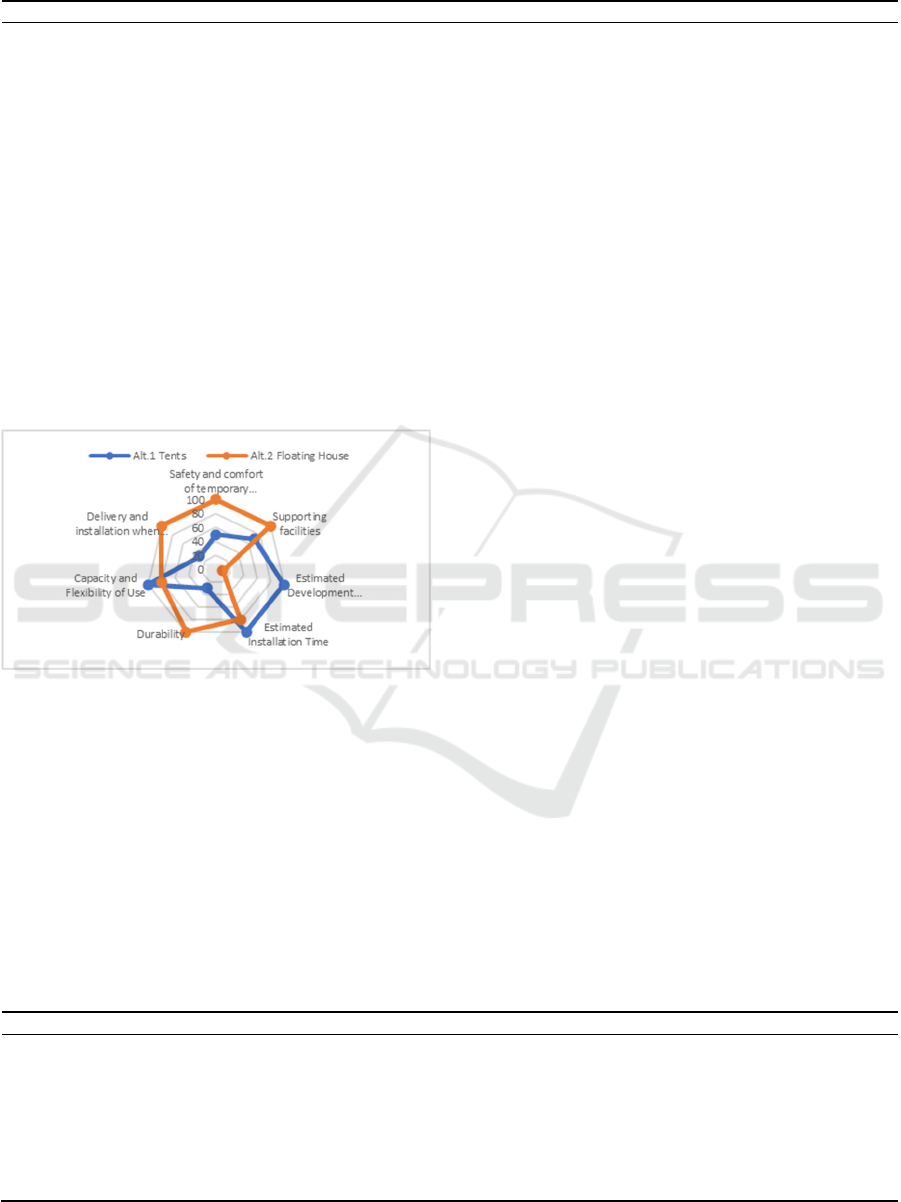
Table 5: Comparison between alternative temporary shelters.
Evaluation Aspect Alt.1 Tents Alt.2 Floating House
Safety and comfort of
temporary shelters
Unsafe and uncomfortable for refugees if
evacuated for an extended period.
Safer and more comfortable to live in the
long term because there are more
complete supporting facilities.
Supporting facilities Has limited supporting facilities. Have more complete supporting
facilities.
Estimated Development Cost
p
er unit
Rp.10.000.000, - per unit. Rp.100.000.000, - per unit.
Estimated Installation Time 1 hour. 8 hours.
Durability It has low durability, can be damaged at
one-time use onl
y
.
Very durable, can be used many times
durin
g
the buildin
g
p
eriod of 50
y
ears.
Capacity and Flexibility of Use It can accommodate many refugees and can
be demolished/disposed of when not in use.
Accommodate fewer refugees. After not
being used, it must be brought back to the
p
lace of origin to be stored.
Delivery and installation when
land infrastructure is damage
d
Difficult to do because construction and
delivery are mostly done on land.
Can be sent by sea and installed at
sea/beach.
Figure 13: Comparison Between Alternative Temporary
Shelters.
From the assessment conducted in Table 5, it can
be concluded that Type 1 (Conventional Emergency
Tents) and Type 2 (Floating Houses) can both be used
as temporary shelters after an earthquake. From the
evaluation of several criteria in Table 6, it was found
that the most significant benefit was obtained from
Type 2 with a value of 570, more significant than
Type 1 with 480. The results of the comparison are
illustrated in Figure 13.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Some problems in Indonesia require alternative
solutions in the form of the application of floating
technology. Issues that occur include sea-level rise,
land subsidence, increased urbanization to cities, and
a large seabed depth. Applications of floating
technology that can be implemented in Indonesia
include floating breakwaters, floating docks, floating
bridges, floating houses, and other infrastructure that
may be needed. Examples of applying floating
technologies suitable for Indonesia's application are
Floating Breakwater, with a sample of Bali's Nusa
Dua beach; Floating Pier, for example, Pier at
Tanjung Emas Semarang and Floating Houses, with
examples of post-earthquake emergency shelters.
More detailed research is needed to apply the
conceptual design that has been made to be applicable
following existing field conditions in Indonesia.
Table 6: Comparison value between alternative temporary shelters.
Evaluation As
p
ect Alt.1 Tents Alt.2 Floatin
g
House
Safety and comfort of temporary shelters 50 100
Su
pp
ortin
g
facilities 70 100
Estimated Development Cost per unit 100 10
Estimated Installation Time 100 80
Durabilit
y
30 100
Ca
p
acit
y
and Flexibilit
y
of Use 100 80
Delivery and installation when land infrastructure is damage
d
30 100
TOTAL 480 570
Study on Application of Floating Structure Technology in Indonesia
17

REFERENCES
Hydrophilic Floating House for Fluctuating Water Level.
Indian J. Sci. Technol. 8, 1–5.
https://doi.org/10.17485/ijst/2015/v8i32/84304
Anderson, C.H., 2014. Amphibious Architecture Living
with a Rising Bay. Faculty of California Polytechnic
State University, San Louis.
Biesheuvel, C.., 2013. Effectiveness of Floating
Breakwaters Wave Attenuating Floating Structures.
Faculty of Civil Engineering, Technical University of
Delft.
Boyke, C., Achmadi, T., Iqbal, H., 2019. The Conceptual
Design of Floating House for Post-Earthquake
Temporary Shelters in Difficult Land Access Areas in
Indonesia. Int. J. Civ. Eng. Technol. 10, 198-213.
Drieman, R., 2011. Feasibility Study on the use of A
Floating Breakwater To Protect a New Artificial Beach
In Balchik, Bulgaria. Faculty of Civil Engineering,
Technical University of Delft.
Engineering, I.M., 2000. Floating breakwaters [WWW
Document]. URL http://www.ingemar.it/en/products-
services/product/Floating-breakwaters-9
Koekoek, M., 2013. Connecting Modular Floating
Structures A General Survey and Structural Design of a
Modular Pavilion. Faculty of Civil Engineering,
Technical University of Delft.
Ltd, K.D.C., 2000. Movable Floating Bridge (MFB)
[WWW Document]. URL
http://157.205.186.22/en/project/project01_002.html
Masaul, A., 2013. Sungguhan Ada, Ini Kota Terapung di
Indonesia [WWW Document]. Detik.com. URL
https://travel.detik.com/domestic-destination/d-
3809150/sungguhan-ada-ini-kota-terapung-di-
indonesia
Muchsin , Fachruddin Purwono, E.H., Amiuza, C.B., 2011.
Penginapan Terapung Waduk Batujai Sebagai Fasilitas
Penunjang Kegiatan Wisata di Pulau Lombok. Jurusan
Arsitektur Fakultas Teknik Universitas Brawijaya.
System, I.M.F.I., 2013. Technology [WWW Document].
URL
https://www.floatingstructures.com/product/floating-
homes/
Wang, C.., Wang, B.., 2015. Large Floating Structures
Technological Advances. Springler, Singapore.
senta 2019 - The International Conference on Marine Technology (SENTA)
18
