
A Fuzzy Logic Controller for Demand Side Management in Smart
Grids
Sara Atef
and Amr B. Eltawil
Industrial Engineering and Systems Management, Egypt-Japan University of Science and Technology (E-JUST),
New Borg Elarab City, Alexandria 21934, Egypt
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence, Fuzzy-logic, HVAC, Demand Side Management, Residential Customer, Smart Grid,
IOT.
Abstract: Smart Grid Demand Side Management is the effective way for energy providers to encourage their customers
on reducing their consumption during peak loads through several Demand Response programs. In this paper,
An Artificial Intelligence approach based on a Fuzzy Logic control system is proposed for the home appliance
scheduling problem. This is typically used in Home Energy Management Systems for the control of Heating,
Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems (HVAC). The simulation results demonstrate the capability of the
proposed model to manage and control of HVAC systems in a smarter way than traditional techniques.
Furthermore, a reduction of 18.33% in total hourly energy consumption has been obtained after introducing
a new parameter among the fuzzy input variables.
1 INTRODUCTION
As a consequence of recent advancement in smart
grid communication and information systems,
demand-side management (DSM) has become an
efficient tool that can manage peak energy demand.
DSM aims to peak load demand reduction, energy
consumption optimization, reshaping the demand
load profile and improving the grid sustainability by
minimizing the total cost and carbon emission rates.
Dynamic DSM (DDSM) has been ignored for a long
time due to the inability of predicting users’
performance, poor computational techniques, and
complexity of consumption dynamics. Nowadays,
DDSM has attracted great attention as Demand
Response (DR) programs target the end-user
customers’ response by making changes to their
normal load profile which could lead to lower
electricity usage when it is required, hence improving
the system performance, reliability and sustainability.
There are three main categories of DSM
techniques, residential, commercial and industrial
energy management (Khan et al., 2016). One of the
major sectors in consuming energy is the residential
sector. It is also expected that the residential
electricity demand will keep increasing through the
upcoming decades(J. Conti, P. Holtberg, J. Beamon,
A. Schaal, 2010). In order to manage energy
consumption in the residential sector, Home Energy
Management Systems (HEMS) have been
implemented. HEMS can be classified under three
main categories: dynamic pricing schemes like Time
of Use (ToU), Real Time Pricing (RTP) and Critical
Peak Pricing (CPP), appliances scheduling and load
forecasting.
The heating, ventilation, and air conditioning
(HVAC) systems are considered an important target
for HEMS due to their huge share of the annual total
energy consumption in the world. In traditional
Building Automation Systems (BAS), users have the
capability to manage and control their load
consumption schedules manually through a single
application. Today, they do not need anymore to
physically interact with the system because of having
Internet Of Things (IoT) based operating systems.
According to (Emerson Climate Technologies, no
date), 33% of thermostats sold in 2014 were wifi-
enabled and this percentage will jump to 75% in
2019. IoT has several benefits for HVAC systems
such as: real-time monitoring, total controllability,
remote diagnostics, inherent connectivity, system
adaption, increased efficiency, continuous comfort
and predictive maintenance. Monitoring systems play
a vital role in smart grids as they help to keep the
system supervised and controlled all the time. Thus,
Atef, S. and Eltawil, A.
A Fuzzy Logic Controller for Demand Side Management in Smart Grids.
DOI: 10.5220/0007297202210228
In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems (ICORES 2019), pages 221-228
ISBN: 978-989-758-352-0
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
221

smart meters are commonly used for recording
customers’ energy consumption and send it as meter
readings to be transmitted as electronic signals to the
energy provider. Furthermore, using smart sensors,
actuators and controllers would help internet-based
systems to measure many parameters like
temperature, humidity, and air flow and predict other
external factors such as, weather forecast. Thus, IoT
is mainly considered in forming the connection with
objects and with each other. It is not only a connected
system, it is a more intelligent environment involved
in constant communication.
It is expected that the increasing number of smart
HVAC systems will affect the pattern of the electrical
grid. Thus, various techniques have been proposed in
order to tackle related problems (Mirinejad et al.,
2008). In this paper, a DMS strategy is proposed for
managing the HVAC systems in smart grids. In the
proposed strategy, an appliance scheduling algorithm
based on a modified fuzzy logic control system, that
maintains the comfort level of end-use customers
saturated, is introduced considering a new input
parameter for the controller.
The rest of this paper is organized as follow.
Section 2 represents the literature review. In Section
3, the model description of house heating system is
presented. Section 4 introduces the proposed
algorithm. Section 5 discusses the simulation results.
Finally, conclusion and future work are explained.
2 REVIEW OF LITERATURE
Recent energy management systems aim to offer
efficient advantages for both the customers and the
utility. For the customer side, many studies based on
applying DR program have been proposed. DR
programs depend basically on motivating a customer
to reduce his consumption during peak periods. On
the other hand, it has to keep the level of customer
comfort satisfied. (Paterakis, Erdinç and Catalão,
2017) presented a survey of technologies, programs,
consumer response categories of DR and the
corresponding benefits and barriers from DR
programs application. Moreover, (Siano, 2014)
proposed a review on DR classification and
techniques regarding real case studies and research
projects.
Customer response for such DR programs may
differ according to customer profile. For residential
customers, it is more appropriate to apply Direct Load
Control (DLC) incentive-based and price-base DR
programs. Recently, in (Shakeri et al., 2018), an
adaptive HEMS control system was proposed to
manage and schedule the electric appliances in order
to reduce the electricity consumption and
corresponding cost. A TOU pricing model was
implemented that resulted in a cost reduction of 14%
with ensuring the user comfort. An intelligent
algorithm that could help users to Handle their
consumption rates was presented in (Fotouhi
Ghazvini et al., 2017). Both RTP and TOU DR
programs were investigated in addition to an
incentive-based program. The results showed that the
incentive-base DR program can perform better than
the RTP-based one under the pricing scheme of TOU
strategy. Furthermore, in (Wang et al., 2018), a multi-
agent system was established to investigate several
types of load demand in multi-agent household
considering the price-based DR scheme. They
concluded that shiftable loads outperform other loads
in DR potential and cost saving, while the sheddable
loads are better for energy saving. A structure of an
HEMS with reference to the management process of
thermostatically and non-thermostatically loads was
introduced in (Paterakis et al., 2015) under load
shaping and day-ahead pricing DR strategies.
Similarly, a classification of residential smart
appliances was proposed in (Qu et al., 2018).
Moreover, an optimal control algorithm was
submitted through day-ahead electricity prices and
real-time incentive measures.
An HVAC system is considered to have a great
attention of appliance scheduling systems due to their
widely spread over the world. (Sala-Cardoso et al.,
2018) introduced a data-driven based model for the
short-term load prediction of the HVAC systems in
smart homes. In (Adhikari, Pipattanasomporn and
Rahman, 2018), a hybrid algorithm based on both
greedy and binary search algorithms was proposed
to control and monitor HVACs. Their algorithm is
based on DLC DR scheme by using IoT-based
thermostats.
Fuzzy set theory was introduced by (Zadeh, 1965)
to tackle uncertainties and vague problems, also it has
been successfully applied to the field of control
engineering. In particular Fuzzy Logic (FL) is a
decision making-based tool which allows
intermediate values to be defined between
conventional evaluations like (True/False) and
(High/Low) (Caggiano, 2014). Thus, it can be
considered as an effective tool for appliance
scheduling problem. In (Soyguder and Alli, 2009), an
FL-based model was implemented for HVAC
systems to maximize the performance of the
controller in predicting the damper gap rate.
Moreover, (Qela and Mouftah, 2014) proposed a
fuzzy system approach to reduce the peak loads using
ICORES 2019 - 8th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
222

the utility beak load data as the system inputs and the
DR power reductions as the system output with
different peak load scenarios and energy consumption
patterns. (Chekired et al., 2017) presented an FL-
based technique to control a grid-connected
photovoltaic home energy system by describing the
related demand as load priorities to meet customer’s
need and comfort. In (Keshtkar et al., 2015), an FL-
based approach was implemented to control the
initialized setpoints in HVAC systems by considering
the appropriate load reduction that can be performed
for energy saving and user comfort concerns. After
that, an extension study has been introduced in
(Keshtkar, Arzanpour and Keshtkar, 2016) to provide
an adaptive model by training the initialized setpoints
of thermostat over three different values of them.
Furthermore, (Javaid et al., 2017) investigated an
extended approach considering both hot and cold
regions through a world-wide adaptive thermostat
model. However, those studies consider the degree of
outside temperature or the relative humidity
separately which does not emulate the real conditions.
In this paper, a fuzzy controller for appliance
scheduling is proposed. An equivalent value for
outside temperature has been calculated with
consideration of the relative humidity which is used
to obtain the actual temperature that user feels over
the day.
3 THE HOUSE HEATING MODEL
Wireless sensor networks and smart thermostats
development offer many opportunities for HEMS in
smart grids. Wireless sensor networks are groups of
separately distributed sensors that are connected via
the internet, and typically used for depicting and
monitoring the environmental conditions, as well as
integrated data collection. On the other hand, smart
thermostats are fully-internet connected devices that
can be responsible for controlling the load of any
residential HVAC system.
A control system consists of a plant, controller,
and environment. For the house heating system these
components are a heater, smart thermostat, and room
respectively. It is a simplified model of a heat gain
and cool loss system that can observe the impact of
outdoor temperature variations on the indoor
temperature. Additionally, it is adaptive to add more
smart capabilities on the control system.
In a heating system, the thermal specification of
the house and the heater should be defined as well as
a thermostat for the heater management, also both the
indoor and outdoor environments must be
determined. Upon those settings, the smart thermostat
will switch the heater ON/OFF according to how
much the outdoor temperature differs from the room
temperature. When the heater is ON, the thermal
energy is gained to the room by convection of the
heated air. As a result of the process of conduction
that occurs through walls and windows, a thermal
energy loss is developed. The rate of temperature
change in the room (
) is calculated as:
dT
r
=
m
ha
.c
a
((M
ha
. c
a
. (T
h
−T
r
)) -(
(
T
r
−T
o
)
R
) ) (1)
Where m
ha
is a mass of air in the room or heater
, c
a
is the specific heat capacity, T
h
is the constant
air temperature from heater, T
r
is the air temperature
of room, M
ha
represents the constant rate of air mass
passing through the heater. The thermal resistance
is represented as (R) and T
o
is the outside
temperature.
4 THE PROPOSED FUZZY
LOGIC BASED CONTROLLER
The proposed FL control system is based on load
reduction that determines a reasonable reduction
value of the initialized set point in order to minimize
the energy consumption without causing
inconvenience for households. The controller consists
of fuzzy variables, membership functions and a set of
IF-THEN rules. Figure 1 shows the general
mechanism of the proposed control system. As it can
be observed, the fuzzification process is applied to
convert the real scalar values of the measured inputs
into fuzzy values using several types of fuzzifiers
called membership functions. After that, the
defuzzification process produces a crisp value of the
fuzzified load reduction (LR) output value using the
centre of gravity technique. By doing so, the new set
point and the corresponding energy consumption will
be calculated.
4.1 The Fuzzy Variables and Their
Related Membership Functions
The proper selection of fuzzy input variables results
in accurate output solutions. They should be selected
based on a precise description of the problem
conditions and the fuzzy inference system (FIS)
complexity.
A Fuzzy Logic Controller for Demand Side Management in Smart Grids
223

Figure 1: The general mechanism of the Fuzzy Logic controller operation.
Based on this concept, the proposed approach
discusses two different scenarios. The first scenario
considers the outside temperature, while the second
one considers the humidity percentage, as the first
input. Both scenarios have the same remaining
parameters. Furthermore, the membership functions
for all fuzzy variables have been implemented by the
triangular geometric pattern.
4.1.1 Outside Temperature (Tout)
Continuous variation in weather conditions can
directly affect the energy consumption. Thus, the
outside temperature is an important input to reflect
the pattern of demand load profile. It can be measured
by a wireless temperature sensor. As presented in
Figure 2, it has four membership function: very cold,
cold, cool, and natural.
4.1.2 Equivalent Temperature (Teq)
Thermal comfort evaluation is affected by various
parameters, such as relative humidity. In particular, a
one hundred percent of relative humidity refers to that
the air is fully saturated with water vapor. So, in this
case, the human skin cannot lose its moisture. Thus,
the user can feel warmer in low temperature if the
humidity is high. For example, if the current Tout
equals 23° C and the relative humidity is equal to
100%, we would feel that the current Tout is 26.6° C.
on the other hand, it would be felt like 20.5° C in case
of 0% relative humidity is depicted. It is necessary to
have an input variable to describe the Teq which have
the same membership functions as Tout.
4.1.3 Electricity Price (EP)
The main reason that can force users to reduce their
consumption is a lower electricity bill. Thus, keeping
them aware of RTP values can significantly help to
manage demand load profile. The EP membership
functions are shown in Figure 3.
4.1.4 User Presence (UP)
The presence of an occupant can greatly help in
saving energy. If an occupant is absent, it is essential
to reduce the consumed load automatically. Smart
sensors are used to provide the fuzzy logic system
with occupancy information over the time. UP is
divided to two membership functions, Present (P) or
Absent (A) as introduced in Figure 4.
4.1.5 Initialized Setpoint (Tsp)
It is important to take the initialized setpoint (Tsp)
into account as one of the fuzzy input variables. It
assists to keep on the comfort level. For example, if
Tsp is already set to be low then the load reduction
must be low whenever the user is in the controlled
area. Figure 5 depicts the related membership
function of Tsp.
4.1.6 Load Reduction (LR)
The proposed fuzzy control system has one output
variable. The Mamdani-type of defuzzification is
proposed. Figure 6 presents the LR membership
functions.
ICORES 2019 - 8th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
224

Figure 2: Teq Membership Functions. Figure 3: EP Membership Functions.
Figure 4: UP Membership Functions. Figure 5: Tsp Membership Functions.
Figure 6: LR Membership Functions.
4.2 Fuzzy Rule Base
The process of creating a fuzzy IF-THEN rule is
logically based on the reduction degree of the Tsp.
For example, to decide LR value, each of Tout or HP,
EP, UP and Tsp should be measured. In this paper,
the proposed two scenarios have four inputs and one
output. Thus, there is a set of 81 IF-THEN rules in the
rule base. A summary of the proposed fuzzy inference
system 81 rules of the first scenario is presented in
Figure 7. For example, the first rule expresses that a
low load reduction is needed if the outside
temperature is very cold, the electricity price is low,
the user is present at home and the scheduled setpoint
is low.
Figure 7: A summary of 81 fuzzy IF-THEN rules.
5 SIMULATION RESULTS
This section contains the simulation analysis of the
results obtained from the proposed fuzzy logic control
system.
The proposed FL-based control system is
compared with the model in (Keshtkar et al., 2015)
with the new concept of combining both output
temperature and relative humidity through an
equivalent temperature. It can be declared that this
new concept would bring more logic to the model.
Almost the same data are used in simulation to
demonstrate the proposed algorithm significance
A Fuzzy Logic Controller for Demand Side Management in Smart Grids
225

except for those that are missed or added. The
weather conditions such as outside temperature and
humidity percentage for the simulated day were
adopted from (Weather in Canada, 2014). Figure 8
shows the relative humidity over the simulated day.
Figure 8: Relative Humidity.
Moreover, Table 1 presents the initialized
Setpoints (Tsp) and User Presence periods over one
day. In addition, the TOU Electric Price (EP) is
illustrated in Table 2.
Table 1: User schedules for the simulated day.
Time of day Tsp UP
00:00–08:00 21 Present
08:00–12:00 18 Absent
12:00–17:00 19 Absent
17:00–20:00 22 Present
20:00–24:00 23 Present
Table 2: TOU prices for the simulated day.
Time of day EP
00:00–07:00 7.2
07:00–11:00 12.9
11:00–17:00 10.9
17:00–19:00 12.9
19:00–24:00 7.2
For model evaluation, four different scenarios are
introduced.
5.1 Scenario I
In the first scenario, Tsp is assumed to be fixed at
value of (21 °C) with no DR existence. In such a case,
the user is not allowed to control his setpoint or use a
smart thermostat. Figure 9 shows the difference
between Teq, fixed setpoint (Tsp_f), and room
temperature (Troom).
5.2 Scenario II
The second scenario discusses the situation in which
the DR is being applied through TOU pricing scheme
where Tsp is scheduled according to time of use
variations without any smart decisions taken. Figure
10 depicts the difference between Teq, Tsp, and
Troom.
5.3 Scenario III
In this scenario, the proposed FL-based algorithm is
simulated with selecting Tout as the first input. Figure
11 illustrates the difference between Tout, Tsp, and
resulted room temperature when the proposed FL
Control system is implemented (Troom_FL).
5.4 Scenario IV
Considering the Teq rather than Tout over a simulated
day can have another impact on load reduction. Thus,
this scenario includes the Teq as the first input of the
proposed FL-based model to figure out this reflection.
As shown in Figure 12, the Teq, Tsp, and room
temperature when scenario II is implemented using
Teq (Troom_FL) are plotted.
As it can be seen in scenario I and II, before
implementing FL, there are a response just to the
changes in predetermined setpoint patterns without
any intelligence decision. By contrast in scenario III
and IV, FL decision making tool results in a dynamic
response over the day which could save energy
consumptions more than the stable environment. On
the other hand, adding the relative humidity through
Teq in scenario IV increases the model reliability. For
illustration, a comparison between the hourly energy
consumption of the four discussed scenarios is given
in Figure 13. It can be observed that scenario IV
represents the best performance with a total hourly
energy consumption of 140.48 KWh. It is worth
mentioning that the result of the third scenario, which
is equal to 142.32 KWh, is not so far from the best
one. However, the main purpose is to clarify the
importance of considering Teq generally.
On the other hand, performing the proposed
model without including the FL concept results in the
largest total hourly energy consumption of 172.06
and 166.94 KWh in scenario I and II, respectively.
Moreover, scenario III and IV improve the system
performance with total reduction in energy
consumption of 17.26% and 18.33%, respectively.
ICORES 2019 - 8th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
226
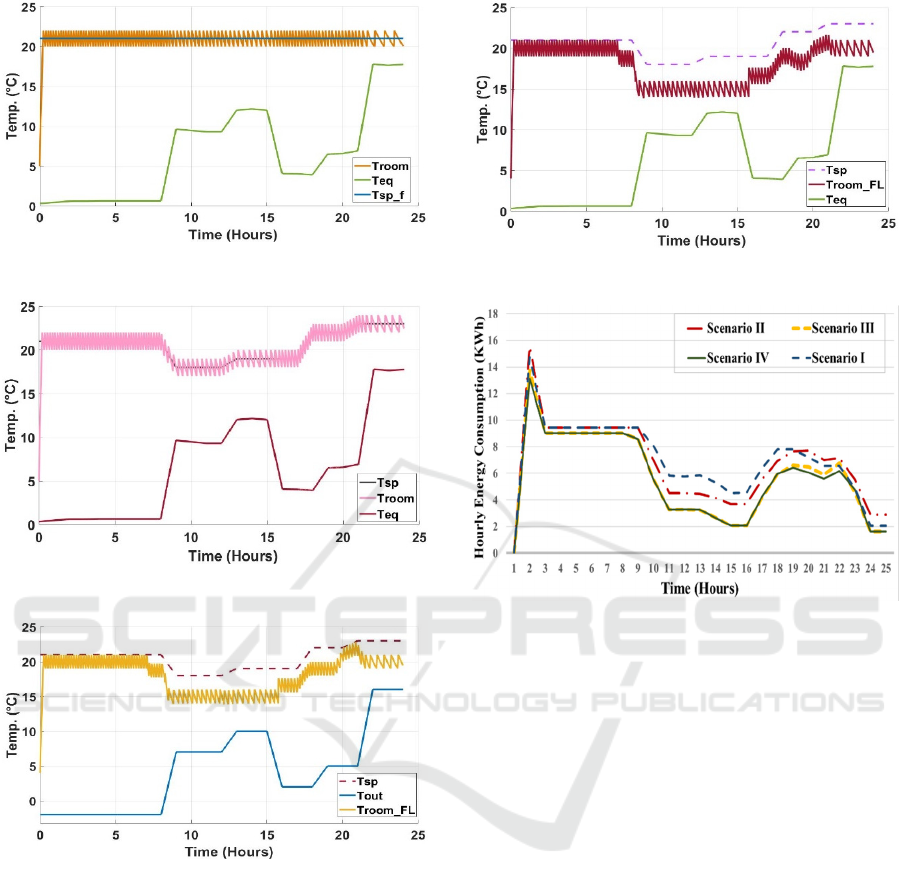
Figure 9: Scenario I result.
Figure 10: Scenario II result.
Figure 11: Scenario III result.
6 CONCLUSIONS
Providing the energy customer with real-time
information about his consumption pattern and the
current electric price would certainly encourage him
to manage his consumption more efficiently. In
addition, providing a smart thermostat that could be
able to make smarter decisions automatically would
absolutely increase the system sustainability. Fuzzy
logic control system can efficiently help in making
such smart decisions in reasonable time. From this
premise, this paper proposed a modified FL-based
control system which is implemented with intro
Figure 12: Scenario IV result.
Figure 13: Comparison of the four scenarios.
ducing a new input parameter of equivalent
temperature, to express both the outside temperature
and the relative humidity, instead of considering each
of them separately. The proposed model has been
compared with four different scenarios. The
simulation results illustrate the model efficiency with
a total improvement of 18.33% in the system
performance. Other parameters of the FIS may be
investigated in further researches to achieve higher
performance in HVAC systems.
REFERENCES
Adhikari, R., Pipattanasomporn, M. and Rahman, S. (2018)
‘An algorithm for optimal management of aggregated
HVAC power demand using smart thermostats’,
Applied Energy. Elsevier, 217(August 2017), pp. 166–
177. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.02.085.
Caggiano, A. (2014) ‘Fuzzy Logic’, CIRP Encyclopedia of
Production Engineering. Encyclopedia of Production
Engineering, pp. 562–568. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-
35950-7.
Chekired, F. et al. (2017) ‘Fuzzy logic energy management
for a photovoltaic solar home’, Energy Procedia.
Elsevier B.V., 134, pp. 723–730. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.
2017.09.566.
A Fuzzy Logic Controller for Demand Side Management in Smart Grids
227

Emerson Climate Technologies (no date). Available at:
https://climate.emerson.com/en-us.
Fotouhi Ghazvini, M. A. et al. (2017) ‘Demand response
implementation in smart households’, Energy and
Buildings. Elsevier B.V., 143, pp. 129–148. doi:
10.1016/j.enbuild.2017.03.020.
J. Conti, P. Holtberg, J. Beamon, A. Schaal, G. S. (2010)
Annual energy outlookwith projections to 2035, report
of U.S. Energy Information Administration(EIA).
Available at: http://www.eia.doe.gov.
Javaid, S. et al. (2017) ‘Controlling energy consumption
with the world-wide adaptive thermostat using fuzzy
inference system in smart grid’, pp. 66–71.
Keshtkar, A. et al. (2015) ‘Smart residential load reduction
via fuzzy logic, wireless sensors, and smart grid
incentives’, Energy and Buildings. Elsevier B.V., 104,
pp. 165–180. doi: 10.1016/j.enbuild.2015.06.068.
Keshtkar, A., Arzanpour, S. and Keshtkar, F. (2016)
‘Adaptive residential demand-side management using
rule-based techniques in smart grid environments’,
Energy and Buildings. Elsevier B.V., 133, pp. 281–294.
doi: 10.1016/j.enbuild.2016.09.070.
Khan, A. R. et al. (2016) ‘Load forecasting, dynamic
pricing and DSM in smart grid: A review’, Renewable
and Sustainable Energy Reviews. Elsevier, 54, pp.
1311–1322. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2015.10.117.
Mirinejad, H. et al. (2008) ‘Control Techniques in heating,
ventilating and air conditioning systems’, Journal of
Computer Science, 4(9), pp. 777–783. doi:
10.3844/jcssp.2008.777.783.
Paterakis, N. G. et al. (2015) ‘Optimal household
appliances scheduling under day-ahead pricing and
load-shaping demand response strategies’, IEEE
Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 11(6), pp.
1509–1519. doi: 10.1109/TII.2015.2438534.
Paterakis, N. G., Erdinç, O. and Catalão, J. P. S. (2017) ‘An
overview of Demand Response: Key-elements and
international experience’, Renewable and Sustainable
Energy Reviews. Elsevier, 69(July 2016), pp. 871–891.
doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2016.11.167.
Qela, B. and Mouftah, H. T. (2014) ‘Peak Load Curtailment
in a Smart Grid Via Fuzzy System Approach’, 5(2), pp.
761–768.
Qu, X. et al. (2018) ‘Optimal Control of Intelligent
Electricity Consumption for Residential Customers
Considering Demand Response’, Energy Procedia.
Elsevier B.V., 145, pp. 510–515. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.
2018.04.074.
Sala-Cardoso, E. et al. (2018) ‘Activity-aware HVAC
power demand forecasting’, Energy and Buildings.
Elsevier B.V., 170, pp. 15–24. doi: 10.1016/j.en
build.2018.03.087.
Shakeri, M. et al. (2018) ‘Implementation of a novel home
energy management system (HEMS) architecture with
solar photovoltaic system as supplementary source’,
Renewable Energy. Elsevier Ltd, 125, pp. 108–120.
doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2018.01.114.
Siano, P. (2014) ‘Demand response and smart grids - A
survey’, Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews.
Elsevier, 30, pp. 461–478. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2013.
10.022.
Soyguder, S. and Alli, H. (2009) ‘An expert system for the
humidity and temperature control in HVAC systems
using ANFIS and optimization with Fuzzy Modeling
Approach’, 41, pp. 814–822. doi: 10.1016/j.enbuild.
2009.03.003.
Wang, Y. et al. (2018) ‘Management of household
electricity consumption under price-based demand
response scheme’, Journal of Cleaner Production.
Elsevier B.V. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.09.019.
Weather in Canada (2014). Available at: https://www.time
anddate.com/weather/canada (Accessed: 17 September
2018).
Zadeh, L. A. (1965) ‘Fuzzy Sets’, Information and control,
8, pp. 338–353.
ICORES 2019 - 8th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
228
