
Environment Engine for Situated MAS
Halim Djerroud and Arab Ali Cherif
LIASD, Advanced Computing Laboratory of Saint-Denis (LIASD),
Paris 8 University, 2 Rue de la Libert
´
e, 93526 Saint-Denis, France
Keywords:
Situated Multi-agent, Multi-agent Environment, Modeling Environment, Framework.
Abstract:
In the multi-agent system research community, there is general consensus that the environment is important
for multi-agent systems (MAS). However, most researchers minimize the responsibilities of the environment
by reducing it to inter-agent communication, or neglecting to integrate it as a main element of their MAS
models, which can be sufficient depending on the focus and objectives of their work. As a consequence of
these decisions, the potential of MAS is not fully exploited. In some cases, the environment is a key element
that cannot be written off as inter-agent communication, as it currently is in classical MAS. In our opinion it is
important to focus the MAS around the environment. Reducing the environment to inter-agent communication
deprives multi-agent systems of great potential. Our point of view is that the environment is an active entity
with its own processes that can change its state, regardless of the activity of its embedded agents. We propose
including the environment as an entity with a set of laws. Laws can be considered rules that cannot be broken
by agents. However, some researchers have been interested in integrating the environment as first class and
have proposed some interesting models. Unfortunately, they are not sustained by practical applications. The
aim of this paper is to contribute in two ways: first, to propose an MAS model where an environmental engine
is integrated; the capabilities of this model are comparable to those of a physics engine. Second, we propose
an implementation of this model and some practical cases where it can bring concrete added value.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the multi-agent system research community, there
is general consensus that the environment is impor-
tant for multi-agent systems (MAS). Most multi-agent
frameworks used by the scientific community and in-
dustry, such as Mobile-C (Chen et al., 2006), JADE
(Bellifemine et al., 1999), JACK (Howden et al.,
2001), Restina (Sycara et al., 2003), Zeus (Nwana
et al., 1999) reduce the environment to a message
transport system or broker infrastructure. Some plat-
forms like MadKit (Gutknecht and Ferber, 2000) and
educational platforms such as NetLogo (Tisue and
Wilensky, 2004) include a system that allows the loca-
tion of agents in a 2D space, which can then be assim-
ilated into a minimalist environment. Even in other
important works such as FIPA specifications (Suguri,
1999), it is difficult to find functionality for the en-
vironment beyond message transport systems or bro-
kers. Some methodologies like Message (Bergenti
et al., 2006), Prometheus (Padgham and Winikoff,
2002) and Trops (Bresciani et al., 2004) offer the ba-
sic features of an environment, but it is not repre-
sented as a fundamental entity in multi-agent systems.
In the literature (Russell and Norvig, 2016; Ferber
and Weiss, 1999; Briot and Demazeau, 2001), envi-
ronments are discussed briefly.
In recent years, the scientific community has
talked more and more about integrating the environ-
ment as a main part of MAS. Among these works we
can mention SODA (Omicini, 2000), a methodology
in which the environment is taken into account and
that provides specific abstractions and procedures for
the design of agent infrastructures. In SODA, the en-
vironment is the space in which agents operate and
interact.
D.Weyns et al. have shown in (Weyns et al., 2004;
Weyns et al., 2015; Weyns and Michel, 2015) that
the environment is important for multi-agent systems,
and that environment must be considered a first-class
1
entity. To overcome the concept of the environment’s
absence in MAS, the scientific community launched
1
first-class: A module that is a first class data ob-
ject of the programming language, e.g. a record contain-
ing functions. In a functional language, it is standard to
have first class programs, so program building blocks can
have the same status. (Free on-line computing dictionary:
http://foldoc.org/first-class )
Djerroud, H. and Cherif, A.
Environment Engine for Situated MAS.
DOI: 10.5220/0007310501290137
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2019), pages 129-137
ISBN: 978-989-758-350-6
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
129

a series of E4MAS (Environments for Multi-agents
Systems) workshops in order to relaunch the debate
and find new ideas. The first series took place be-
tween 2004-2007
2
, and the second series ten years
later, from 2013-2014
3
.
In the literature, we find the concept of the sit-
uated agent. Agents live and act in the environment.
Situated agents choose their actions based on their po-
sition, the state of their perceived world, and their in-
ternal state. Unlike knowledge-based agents, situated
agents do not emphasize the internal modeling of the
environment. Instead, they use the environment as a
source of information. This type of MAS is supposed
to include the position of agents in the environment,
but Wooldridge and Jennings (Wooldridge and Jen-
nings, 1995) define an agent as: “...a computer sys-
tem that is situated in some environment, and that is
capable of autonomous action in this environment in
order to meet its design objectives”. In this definition,
”situated agent” refers to an agent in the environment,
however the concept of environment remains abstract.
The definition does not make explicit what it means
for an agent to be situated in an environment; noth-
ing in the definition explicitly refers to the fact that
the existence of an agent in an environment entails a
social component.
The word ”environment” can lead to confusion.
To prevent any confusion about the use of the word
environment, for the rest of this article we consider
the environment to be the space in which the agents
evolve and not the software infrastructure on which
the agents are executed.
MAS are used in many fields. In the simulation of
complex systems, the aim is to reproduce an observed
natural system within a multi-agent system. The pro-
duced MAS can serve to understand the system and
predict its future state. In this paper the aim is to pro-
duce a model and implementation of MAS that allow
a robot to represent its environment in a multi-agent
system, in order to understand the evolution of its en-
vironment based on the robot’s own actions and then
adapt its behavior accordingly.
So, the robot must make an internal representa-
tion of its environment and the other agents evolving
within it as a multi-agent system. However, the en-
vironment in which the robot evolves is governed by
the laws of physics. In this case the environment is
considered an entity that acts upon the agents.
The challenge in this article is to propose a multi-
agent model that allows the representation of the envi-
2
E4MAS - Environments for Multiagent Systems: https:
//distrinet.cs.kuleuven.be/events/e4mas/
3
E4MAS - 10 years later: http://homepage.lnu.se/staff/
daweaa/events/E4MAS/2014.htm
ronment as a main entity, the implementation of envi-
ronmental laws, certainty that these laws are not trans-
gressed by agents, and finally the ability of the envi-
ronment to act upon agents.
As an alternative to using the multi-agent system,
the robot can use a physics engine to represent its
environment. This solution may seem efficient but
is difficult to implement; physics engines use New-
tonian laws to simulate the behavior of the environ-
ment, but to use these laws the robot must know the
exact characteristics of each element within the envi-
ronment, which makes the task complex or virtually
impossible. So, the use of MAS is a good compro-
mise.
The next section gives an overview of the princi-
pal studies and reflections on MAS environments by
different authors.
Afterwards, we highlight our disagreement with
these points of view and identify the weaknesses in
these concepts. Subsequently, in section 3 we propose
our definition of an MAS environment and propose a
model. In section 4 we present an implementation of
said model. We end by discussing the difficulties and
shortcomings of our approach before concluding.
2 REVIEW MULTI-AGENTS
ENVIRONMENT MODELS
In the study (Weyns et al., 2004; Weyns et al., 2015;
Weyns and Michel, 2015), several research tracks that
include some notion of the environment are shown. In
this section, our goal is to summarize the most impor-
tant among them.
In (Russell and Norvig, 2016), Russell and Norvig
propose a simple representation of the environment
and its interaction with agents. They argue that “An
agent is anything that can be viewed as perceiving its
environment through sensors and acting upon the en-
vironment through effectors”.
According to Russell and Norvig, the environ-
ment holds the following properties: 1) Accessible
or inaccessible: indicates whether agents can obtain
complete and accurate information about the environ-
ment’s state or not 2) Deterministic or nondetermin-
istic: indicates whether a change of state of the envi-
ronment is only determined by its current state and
the actions selected by the agents or not. 3) Static
or dynamic: indicates whether the environment may
change while an agent deliberates or not. 4) Discrete
or continuous: indicates if the number of percepts
and actions is limited or not. These properties of envi-
ronments have now been adopted by most researchers
in the multi-agent domain.
ICAART 2019 - 11th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
130

In (Ferber and Weiss, 1999) J.Ferber proposes an-
other view of an environment: 1) The environment is
discrete and composed of a set of cells. 2) Central-
ized or decentralized environment: the environment
can be centralized (the cells are grouped together in
a monolithic system) or decentralized (the cells are
linked together via a network). Agents evolve and
perceive their environment through these cells. How-
ever, a distributed environment cell differs in several
ways from a centralized environment. 3) Generalized
or specialized environment: a generalized model
of an environment is independent of the type of ac-
tions that can be performed by agents. A specialized
model of an environment is characterized by a well-
defined set of actions. 4) influences and reactions
to influences: influences come from agents and are
attempts to alter the course of events in the environ-
ment. The environment produces reactions which in
turn cause state changes by combining the influences
of all agents, given the local state of the environment
and the laws of the world.
In (Parunak, 1997) (Odell et al., 2003) Parunak,
Odell et al. define the environment as a space
which provides the conditions where agents exist.
Parunak, Odell and their colleagues make the dis-
tinction between physical and communication envi-
ronments. 1) The physical environment provides
the laws, rules, constraints, and policies that gov-
ern and support the physical existence of agents and
objects. 2) the communication environment pro-
vides processes that govern and support the exchange
of ideas, knowledge and information. Functions and
structures are commonly employed to exchange com-
munication, such as roles, groups and the interaction
protocols between roles and groups.
Specifically in (Parunak, 1997), an MAS is de-
fined as a three-tuple: a set of Agents, an Environ-
ment, and a Coupling between them, shown as fol-
lows:
MAS =< Agents, Environment,Coupling >
Agents = Agent
1
, ..., Agent
n
Agent
i
=< State
i
, Input
i
, Out put
i
, Process
i
>
Environment =< State
e
, Process
e
>
An agent is defined as set of states, inputs, outputs
and processes. A state is the set of attributes that de-
fine the agent, the differences in these attributes being
responsible for the variation between different types
of agents. Inputs and Outputs are subsets of State,
whose variables are coupled to the environment. In-
puts and Outputs can represent an agent’s sensors and
effectors; they relate the agent to its environment.
These are the mechanisms that implement the cou-
pling between the environment and the agents. The
process is an autonomously-executing mapping that
changes the agents states.
The environment is defined as an active entity. It
has its own Process that can change its State, inde-
pendent of the actions of its embedded agents. Inputs
and outputs of the embedded agents are coupled to el-
ements of the environment state, but the environment
does not distinguish which elements of state are cou-
pled in this fashion. That distinction depends on the
agents that exist at any moment, and the capabilities
of their sensors and effectors.
In (Rao et al., 1992) Rao et al. describe the char-
acteristics of a generic environment: 1) Agents can
evolve in many different ways in the environment;
2) the environment can be affected by several ac-
tions at the same time; 3) different goals may not
be achievable simultaneously; 4) the actions that best
meet the different objectives depend on the state of
the environment; 5) the environment can only be de-
tected locally; 6) the rate at which calculations and
actions can be performed is reasonably related to the
rate of change in the environment. Rao and his col-
leagues describe the typical characteristics of the out-
side world in which agent systems are deployed and
with which agent systems interact.
In (Demazeau, 2003) Demazeau considers the
four essential components of multi-agent systems to
be: 1) agents; 2) interactions (structuring elements of
internal interactions between entities), 3) organization
(structuring elements of entity sets within the MAS),
4) the environment defined as domain-dependent ele-
ments to structure external interactions between enti-
ties.
In (Ferber, 1997) J.Ferber pointed out that multi-
agent systems can be used for the resolution of two
major categories of problems: the simulation of com-
plex phenomena and distributed problem solving.
We believe that the models described above are too
generic to develop a model that can deal with these
two issues effectively, and we think that this is the
main reason that many researchers ignore integrating
the environment in their models; often, the environ-
ment is indispensable only in the simulation of com-
plex phenomena. For our part, we think that multi-
agent systems are an abstraction of the system we
want to simulate. So, it is important to take into ac-
count that the agents act on the environment and the
environment acts on the agents as well, which is also
the case in the previous models. However, our opin-
ions diverge in that (1) the effects of the environment
are not experienced in the same way by all agents
(2) the agents perceive the environment through sen-
sors, so have information that is likely to be skewed
(3) agents may not feel certain effects of the envi-
Environment Engine for Situated MAS
131

ronment on them and finally (4) the environment is
the physical medium of the agents, and is similar to a
physics engine in that it consists of a set of laws that
will determine its possible actions. We can say that
our approach consists of proposing an environment-
centered model for the representation of complex phe-
nomena, and to incorporate the ideas that we deem
relevant from the models described above.
3 DESCRIPTION OF THE
ENVIRONMENT MODEL
We can distinguish two main categories of MAS use:
the first being the study of complex phenomena, and
the second being distributed problem solving (Ferber,
1997). In the former, the environment plays an essen-
tial role. Studies of MAS focused on the environment
(Weyns et al., 2004; Weyns et al., 2015; Weyns and
Michel, 2015; Russell and Norvig, 2016; Ferber and
Weiss, 1999; Odell et al., 2003; Rao et al., 1992; De-
mazeau, 2003) show two types of difficulties: first,
the definition of the environment is too broad, and the
term environment has several interpretations, causing
a lot of confusion. Second, the functionalities associ-
ated with the environment are integrated in and pro-
cessed by the agents. From our point of view, the
environment must be a separate entity, and must in-
teract with and influence the behaviour of agents. In
the remainder of this section we describe our vision
for the environment and propose a new MAS model
along with how to implement it. The model proposed
below is strongly inspired by the MAS reviewed in
the previous section. We have chosen the points that
we think are important in each model.
We think that the environment must be an au-
tonomous and active entity and not integrated into
the agents as we have seen previously, for example
in messages or brokers. Basically, our approach is
to represent the environment as a fully-fledged entity,
as it is in (Parunak, 1997). First, we define the envi-
ronment as a space in which agents evolve. Second,
the environment is like a physics engine; it must in-
clude inviolable rules. Third, as is the case in classical
MAS, the agents act on the environment and change
its state. Finally, the environment can change the state
and attributes of agents in order to keep its rules invi-
olable; if an agent tries to transgress an environmental
rule, the environment changes the state of the agent in
order to maintain its integrity.
In order to think of the environment as a separate
entity, we must have a good idea of what the environ-
ment is. To this end, we will try to explain the com-
ponents and functions of an environment in parallel
with the real environment that we are representing.
Particularly in the simulation of complex phenomena,
we try to model the entities and the environment of
the system we want to simulate. If we take the exam-
ple of modelling a multi-agent system and a human
or robot agent that evolves in a natural environment,
the agent does not have a real view of its environ-
ment, but its knowledge of the environment is filtered
through and/or distorted by the sensors through which
it observes it. We can deduce that the environment is
much more complex than the belief of the agent. In
this article we propose a model in which users can
model MAS for complex environments such as nat-
ural ones, for example. Generally speaking, in com-
plex systems many things happen, the agents act on
the environment and the environment also acts on the
agents. However, the agents can only feel the effects
of the environment if they have sensors to feel these
effects, which is the major point that differentiates our
model from the other models discussed in the previ-
ous section.
So, we begin by defining a Multi-Agent System
as a three-tuple: a set of Agents, an Environment, and
Interactions between them :
MAS =< Agents, Environment, Interactions >
Agents = Agent
1
, ..., Agent
n
3.1 Environment
We propose that the environment be split into two
parts, the first of which would be represented in a
monolithic process, while the second would be inte-
grated into the agents (distributed on all agents). 1)
The monolithic part of the environment represents the
physical and functional characteristics of the environ-
ment, such as: the size of the environment, the gravity,
etc., depending on the environment we want to rep-
resent. 2) Each agent in the system contains part of
the environment’s information, as shown in Figure 1.
Usually, this information concerns the agent itself; for
example: its position in the environment, its energy,
etc. It also includes all possible actions that can be
performed on the environment, such as move, leave a
trace, and so on.
The environment is governed by laws. The en-
vironment can be assimilated to a physics engine.
Agents evolve inside, and are consequently subject to
the laws of the environment. So we can consider that
the environment an entity that acts on the agents that
evolve within it. These agents can only actually feel
the effects of the environment only they are equipped
with sensors to perceive the impact of these laws. Of
course, the model considers that it is the responsibility
ICAART 2019 - 11th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
132
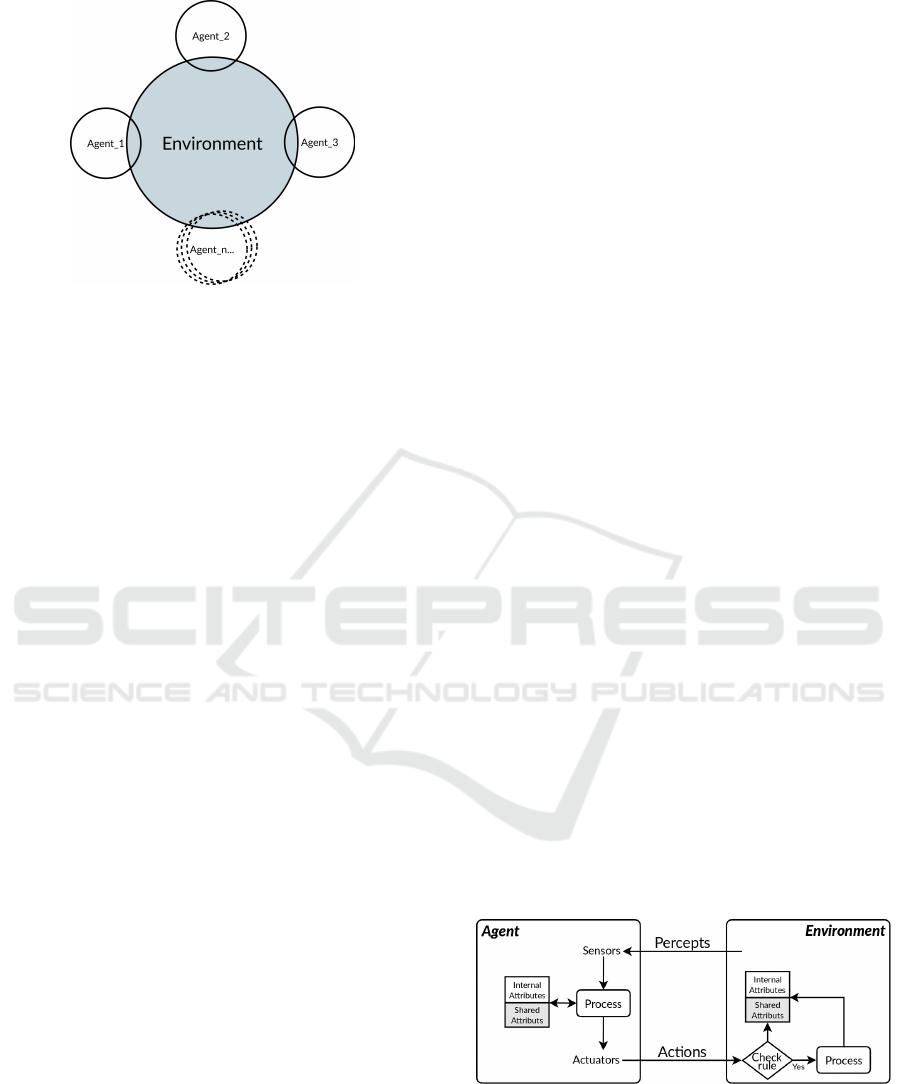
Figure 1: Agents and environment share attributes.
of the user (the MAS developer) to determine which
laws will be implemented by the environment, and it
is also up to the user to determine the attributes of
the agents and/or the environment that must change.
The environment and the agents are two distinct en-
tities: 1) The agents consist of a set of attributes and
knowledge of their possible actions on the environ-
ment; these agents can consult their attributes and can
perform actions on the environment. 2) The envi-
ronment has laws; it has the responsibility to enforce
them, and checks compliance with these laws at reg-
ular time intervals, otherwise automatically changing
the attributes of agents in order to respect those laws.
So, we can define the environment as a three-
tuple, States, Agents and Process:
Environment =< States, Rules, Process >
States =< SharedAttributes, InternalAttributes >
States. Is a set of attributes that completely define
the environment. The values of the attributes repre-
sent the state of the the environment at a given the
time. The attributes of the environment represent its
characteristics, such as the size of the environment,
positions of agents evolving in it and so on. We dis-
tinguish two types of attributes: Shared Attributes and
Internal Attributes. The first kind of attribute is shared
with agents. The second is not shared with the agents,
typically being the inner properties of the environ-
ment itself.
Rules. The environment’s laws are rules that it must
uphold. For example, two agents must not be in the
same place at once, and the rules are written as fol-
lows:
rule =< expression ? action1 : action2 >
A rule is represented as an expression. It corre-
sponds to the law that the environment must check,
the two actions corresponding respectively to the ac-
tions that must be performed according to whether the
rule is respected or not. In the previous example (the
rule that prohibits two agents from being in the same
place at once), this can represented as follows: if an
agent tries to move to a place already occupied by
another agent, then prevent the movement; if not do
nothing.
The environment is represented as a monolithic
process with a set of attributes, and carries out checks
from time to time in order to respect its laws. Agents
using the environment must first register with the en-
vironment. Whenever the agents modify their at-
tributes, they must inform the environment via a mes-
sage. For example, an agent that moves must there-
fore modify one or more of its attributes, and at this
point the agent informs the environment.
The environment also has the ability to change the
attributes of the agents. For example, if the shifting
is not possible because of a rule that is not respected,
then it informs the agent and returns the values of the
attributes to their old values.
Process. An environment has its own process that
can change its state, independently of the actions of
the embedded agents. The primary purpose of Pro-
cess is to implement dynamism in the environment
e.g. processes that check rules and execute actions,
the behavior of objects in the environment, etc.
3.2 Agent
Each agent is a tuple of State and Process:
Agents = Agent
1
, ..., Agent
n
Agent
i
=< States, process >
States =< SharedAttributes, InternalAttributes >
Figure 2: This image illustrates the relationship between
an agent and its environment. Agent and environment have
shared attributes, and each of them has its own attributes
that define it. The environment is also composed of laws.
Agents act on the environment through actions, and the en-
vironment can directly change agent attributes if the laws
are transgressed.
Environment Engine for Situated MAS
133

States. Agent attributes are a set of values that de-
fine the agent. The structure and variability of these
values are not constrained by this definition, and dif-
ferences in these features are responsible for much of
the variation among different kinds of agents.
Agents are defined with two types of attributes:
”Shared Attributes” and ”Internal Attributes”. Shared
Attributes are the part of the environment concerning
the agent e.g. position of agent in the environment.
Internal Attributes define the internal state of the en-
vironment e.g. the log of its movements, its goal, in-
ternal time etc.
Process. Processes are standalone mappings that
change the state of the agent. The agent can perform
these processes without being called by an external
entity. In terms of calculation, an agent has its own
virtual processor.
3.3 Agents and Environment
Interactions
We propose that the multi-agent system be composed
of agents and the environment; when both agents and
environment are time-based, the state values can vary
continuously. The change in a variable resulting from
such a flow may be infinitesimal, depending on the
Process in the receiving entity and the other energy
flows in the system.
To summarize our approach, we can define an Envi-
ronmental engine-centered situated MAS as follows:
• The agent has filtered (partial) and sometimes dis-
torted knowledge of its environment
4
.
• The environment is governed by laws, and these
laws may be known or unknown by the agents.
• The environment acts on the agents.
• Agents act on the environment with actions.
• Agents observe the environment through at-
tributes that can be influenced by the environment.
4
In our opinion, this definition is not always true for sim-
ple and non-complex environments, and for this reason we
have emphasized that our approach is suitable for complex
environments. In the contributions of Russell and Norvig
(Russell and Norvig, 2016), he speaks of a fully observable
and partially observable environment. We can take the two
examples quoted in (Russell and Norvig, 2016): 1) the au-
tomatic taxi which is confronted by a complex environment
and thus partially observable and 2) chess player that has a
complete view of their observable environment.
4 IMPLEMENTATION
In recent decades, many multi-agent architectures, de-
signs and models have emerged. This proliferation is
a sign of great interest for multi-agent systems. How-
ever, in many cases, the proposals are conceptual and
not supported by implementations to validate them.
This lack of implementation is due to the difficulty of
producing multi-agent systems due to the complexity
of the underlying concepts (coordination, interaction,
organization, etc). This complexity makes the major-
ity of existing systems difficult to use, and virtually
impossible to use by non-specialists of multi-agent
systems.
There are two problems (as shown in our brief
analysis) to overcome: 1) to present a practical re-
alization to validate our multi-agent model and 2) to
present an easy implementation of use. In order to
propose a framework compliant with the standard and
easy to use for the MAS community, we have chosen
to implement the FIPA standard where possible. Cur-
rently, FIPA is limited in its capacity to describing the
architecture of the system as a whole, the structure
agents and communication between agents, etc. As
we have already mentioned earlier in this article, un-
fortunately it is difficult to find the concept of the en-
vironment in FIPA. As a result, regarding the imple-
mentation of the environment, we have not respected
any standard. Currently, the JADE multi-agent plat-
form is widely used by the scientific community, and
we have tried to take as much inspiration from it as
possible, always with the aim of proposing an easy-
to-use framework, and not making the task difficult
for users with this new tool.
The FIPA standard proposes a reference model for
multi-agent platforms. It proposes a general archi-
tecture (see image 3) for which it requires the exis-
tence of a certain number of specialized agents: 1)
Agent Management System (AMS): the agent that ex-
ercises supervisory control over the access and use of
the platform; they are responsible for resident agent
authentication and record control. Agent 2) Com-
munication Channel (ACC): the agent that provides
the route for basic interactions between agents in and
out of the platform; it is the implicit communication
method that offers reliable and accurate service for
message routing. 3) Directory Facilitator (DF): the
agent that provides a yellow page service to the multi-
agent platform.
The standard also specifies the Agent Communi-
cation Language (FIPA-ACL). Agent communication
is based on sending messages. It should be noted
that there is no restriction on the technology used for
the implementation of the platform; for example, for
ICAART 2019 - 11th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
134

Figure 3: FIPA compliant platform to which we added the
environment module; the communication with the environ-
ment module and the platform is carried out by message
exchange.
communication the system can use email, CORBA,
etc. For our framework we used the CORBA com-
ponent for platform-to-queue exchange offered by the
OS for internal platform communication.
In order to integrate our contribution (environ-
ment) into a FIPA architecture, we have chosen to use
the same messaging system to ensure the exchange of
data between the environment and the agents, the im-
age 3 shows how the environment integrates into the
FIPA multi-agent architecture.
From the beginning, we have wanted to provide
an easy-to-use architecture in the form of a frame-
work, and so we have provided a set of classes as a
dynamic C++ library (see image 4; classes in gray are
the classes that make up the framework). Users must
use this library to create agents and the environment
(see image 4, classes in white that the user must over-
load). The framework also offers a graphical interface
that allows the user to choose the attributes to display
in order to enable them to have a graphical tool that is
sometimes useful, particularly in the simulation and
analysis of complex phenomena. We have also inte-
grated some features that go beyond the scope of this
article. They consist of a mechanism that allows a
snapshot to be made and the ability to return to this
snapshot state if you need to change the simulation
parameters and compare the results.
Figure 4: This image illustrates the general class diagram
of the MAS platform; in gray are the set of classes that con-
stitutes the framework, while white classes are classes that
the user must add.
We are providing a new FIPA-compliant multi-
agent framework, written to simplify situated MAS
implementation. Our framework is written in C++
and is available under the GPL license, for which the
source code and documentation can be downloaded
here
5
.
5 USE CASE
This section presents a practical case that is difficult to
solve using conventional MAS that does not take the
environment and its laws into account. Subsequently,
we will propose an approach to solve this problem
with the architecture proposed in this article.
As an example we will be able to look at the prob-
lem of navigation among movable obstacles, as de-
scribed in (Wu et al., ; Stilman and Kuffner, 2007).
The robot evolves in a congested environment with
different obstacles. The obstacles are more or less
movable or immovable according to their sizes, their
weights and their shapes. The robot aims to reach a
certain position. So, the robot must find a path among
the obstacles and push the obstacles that hinder its
passage in order to pass. The solutions proposed in
(Levihn et al., 2013; Van Den Berg et al., 2009; Stil-
man and Kuffner, 2005) are essentially based on de-
liberative and non-reactive approaches, which is to
say by determining the complete path of the robot be-
tween an initial and final position using the robot’s
vision. In the presented article, the emphasis is on
how to move the objects and not on finding the opti-
mal path of least resistance. We propose that the robot
make an internal representation of its environment,
and then perform simulations before acting. Indeed,
drawing its path in the same way but simulating ac-
tions before taking them in the physical environment
will give the robot the advantage of predicting the be-
havior of the other agents and said environment. We
want to propose a solution that uses the multi-agent
system proposed in this article to perform the simula-
tion and the choice of the action.
The robot wants to make an internal representa-
tion of its environment in the form of an MAS in order
to perform simulations before acting. The simulation
will allow it to anticipate the behavior of other agents
in the environment, and will also allow it to simulate
an action before choosing to apply it in the real en-
vironment. In this way, the robot in the environment
already has an idea of the results of an action before
even applying it. This will enable it to verify whether
the action applied to the environment produces the
5
Last version available: http://djerroud.halim.info/
index.php/recherche/mas/gagent/
Environment Engine for Situated MAS
135

desired results in the long-term, thus reinforcing its
knowledge of the different environmental agents and
the laws that govern the environment.
The robot uses its various sensors to observe its
environment. For each object detected in the environ-
ment, the robot represents it as an agent in the MAS.
So, each agent represented in the MAS corresponds to
an object in the environment. Moreover, the robot en-
riches this agent with attributes and possible actions
to perform on this agent. For example, the robot ob-
serves its environment in which an obstacle hinders
its passage, the robot makes a representation in the
form of an MAS of its environment, it represents the
obstacle as being an agent which is at a distance (x,y)
with respect to it, and the agent is enriched with at-
tributes (shape of the object, size, weight). Of course,
if the robot does not know the exact characteristics, it
will make an estimate and check its database to see if
it is already familiar with said object. The robot also
enriches the environment by describing how this en-
vironment reacts through laws. In this article we limit
ourselves to describing the advantages of using the
ADM presented previously, and we do not describe
the methods used for obstacle detection and estima-
tion.
For the robot to apply the proposed solution, it
needs an MAS with an environment and agents.
6 DISCUSSION
In this section, we seek to compare our model of
the environment in relation to Ferber’s (Ferber et al.,
2004) well-known approach, namely AGRE (Agent-
Group-Role and Environment).
In their AGRE (Agent-Group-Role and Environ-
ment) architecture, Ferber and his colleague offer an
architecture centered around organization, in which
agents are organized into groups according to their
skills and the environment is a space that may be
physical (i.e. geometrical) or social. Physical
spaces (called areas) and social spaces represent AGR
groups. But, the environment plays the role of a phys-
ical medium to locate agents. Agents can do actions
in the environment through primitives.
We believe that this approach only allows the
modelling of phenomena for which the organization
is already known, or those which are already known
to be naturally organized. In our approach, however,
we model only the characteristics (attributes) and the
constraints (laws) of the system to bring out the orga-
nization. Moreover, for perspective on our work, we
want to put this model into practice in that the agents
must discover the environment as well as the laws that
govern it only through experimentation. We will give
a practical case for our model. The idea is to entrust
the task of modelling a multi-agent system to a ma-
chine that observes a real environment. The objec-
tive is for the machine to observe its environment and
build its own model, modifying the parameters until it
(and you) have obtained observations that you under-
stand to be the laws that govern the real environment.
So, the difficulty of our approach lies in the fact
that there is no generic way to represent the environ-
ment; we must first define the components of the en-
vironment and the laws that govern it, and finally the
way in which it interacts with the agents that evolve
in it.
It is important to emphasize that we are forced
to propose a new implementation of a multi-agent
platform that integrates the two new elements of our
model: 1) the environment and its characteristics and
2) the attributes of the agents. We have experimented
with integrating these two elements into an existing
platform before; as JADE is a platform that is widely
used by the MAS community and is under an open
source license, which made it easy for us to add mod-
ifications. In our previous proposal (Djerroud and
Cherif, 2018), we chose to propose an extension for
JADE without modification of the existing code. Un-
fortunately, we were not able to integrate all the ele-
ments while respecting this latter constraint, and for
this reason we are proposing a new platform.
7 CONCLUSIONS AND
PERSPECTIVES
A study on the role of environment in MAS has taught
us that the environment is an implicit part of MAS; it
is often represented as integrated into agent commu-
nication or brokers. This leads to poor engineering
practices and prevents MAS users from harnessing the
full potential of the environment in MAS.
In this article, we present the environment as be-
ing an explicit part of MAS. In addition, we define the
environment as a first-order abstraction in MAS that
has multiple roles: First, the environment is the part
of the world with which agents interact, and in which
agents’ effects will be observed and evaluated. Sec-
ond, the environment describes the world in which the
agents evolve through laws and attributes, and it has
the ability to act on the agents and modify their states
in order to respect the rules of the represented world.
Finally, we propose an implementation that inte-
grates an environment in order to provide a design
space that can be exploited by the designer and help
ICAART 2019 - 11th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
136

manage the enormous engineering challenges of com-
plex MAS applications.
REFERENCES
Bellifemine, F., Poggi, A., and Rimassa, G. (1999). JADEA
FIPA-compliant agent framework. In Proceedings of
PAAM, volume 99, page 33. London.
Bergenti, F., Gleizes, M.-P., and Zambonelli, F. (2006).
Methodologies and software engineering for agent
systems: the agent-oriented software engineering
handbook, volume 11. Springer Science & Business
Media.
Bresciani, P., Perini, A., Giorgini, P., Giunchiglia, F., and
Mylopoulos, J. (2004). Tropos: An agent-oriented
software development methodology. Autonomous
Agents and Multi-Agent Systems, 8(3):203–236.
Briot, J.-P. and Demazeau, Y. (2001). Principes et architec-
ture des systmes multi-agents. Herms-Lavoisier.
Chen, B., Cheng, H. H., and Palen, J. (2006). Mobile-C: a
mobile agent platform for mobile C/C++ agents. Soft-
ware: Practice and Experience, 36(15):1711–1733.
Demazeau, Y. (2003). Multi-Agent Systems Methodol-
ogy, In Second Franco-Mexican School on Cooper-
ative and Distributed Systems (LAFMI 2003).
Djerroud, H. and Cherif, A. A. (2018). Visualization tool
for jade platform (jex). In Proceedings of the Future
Technologies Conference, pages 481–489. Springer.
Ferber, J. (1997). Les systmes multi-agents: un aperu gnral.
Techniques et sciences informatiques, 16(8).
Ferber, J., Michel, F., and Bez, J. (2004). AGRE: Integrat-
ing environments with organizations. In International
Workshop on Environments for Multi-Agent Systems,
pages 48–56. Springer.
Ferber, J. and Weiss, G. (1999). Multi-agent systems: an
introduction to distributed artificial intelligence, vol-
ume 1. Addison-Wesley Reading.
Gutknecht, O. and Ferber, J. (2000). Madkit: a generic
multi-agent platform. In Proceedings of the fourth in-
ternational conference on Autonomous agents, pages
78–79. ACM.
Howden, N., Rnnquist, R., Hodgson, A., and Lucas, A.
(2001). JACK intelligent agents-summary of an agent
infrastructure. In 5th International conference on au-
tonomous agents.
Levihn, M., Scholz, J., and Stilman, M. (2013). Hierarchi-
cal decision theoretic planning for navigation among
movable obstacles. In Algorithmic Foundations of
Robotics X, pages 19–35. Springer.
Nwana, H. S., Ndumu, D. T., Lee, L. C., and Collis, J. C.
(1999). ZEUS: a toolkit for building distributed mul-
tiagent systems. Applied Artificial Intelligence, 13(1-
2):129–185.
Odell, J., Parunak, H. V. D., and Fleischer, M. (2003). Mod-
eling agents and their environment: The communi-
cation environment. Journal of Object Technology,
2(3):39–52.
Omicini, A. (2000). SODA: Societies and infrastructures
in the analysis and design of agent-based systems. In
International Workshop on Agent-Oriented Software
Engineering, pages 185–193. Springer.
Padgham, L. and Winikoff, M. (2002). Prometheus: A
methodology for developing intelligent agents. In
International Workshop on Agent-Oriented Software
Engineering, pages 174–185. Springer.
Parunak, H. V. D. (1997). ” Go to the ant”: Engineering
principles from natural multi-agent systems. Annals
of Operations Research, 75:69–101.
Rao, A. S., Georgeff, M. P., and Sonenberg, E. A. (1992).
Social plans: A preliminary report. Decentralized AI,
3:57–76.
Russell, S. J. and Norvig, P. (2016). Artificial intelligence: a
modern approach. Malaysia; Pearson Education Lim-
ited,.
Stilman, M. and Kuffner, J. J. (2005). Navigation among
movable obstacles: Real-time reasoning in complex
environments. International Journal of Humanoid
Robotics, 2(04):479–503.
Stilman, M. and Kuffner, J. J. (2007). Navigation among
movable obstacles. PhD thesis, Citeseer.
Suguri, H. (1999). A standardization effort for agent
technologies: The foundation for intelligent physical
agents and its activities. In hicss, page 8061. IEEE.
Sycara, K., Paolucci, M., Van Velsen, M., and Giampapa, J.
(2003). The retsina mas infrastructure. Autonomous
agents and multi-agent systems, 7(1-2):29–48.
Tisue, S. and Wilensky, U. (2004). Netlogo: A simple en-
vironment for modeling complexity. In International
conference on complex systems, volume 21, pages 16–
21. Boston, MA.
Van Den Berg, J., Stilman, M., Kuffner, J., Lin, M., and
Manocha, D. (2009). Path planning among movable
obstacles: a probabilistically complete approach. In
Algorithmic Foundation of Robotics VIII, pages 599–
614. Springer.
Weyns, D. and Michel, F. (2015). Agent environments for
multi-agent systemsa research roadmap. In Agent En-
vironments for Multi-Agent Systems IV, pages 3–21.
Springer.
Weyns, D., Parunak, H. V. D., Michel, F., Holvoet, T., and
Ferber, J. (2004). Environments for multiagent sys-
tems state-of-the-art and research challenges. In Inter-
national Workshop on Environments for Multi-Agent
Systems, pages 1–47. Springer.
Weyns, D., Parunak, V. D., Boissier, O., Michel, F., Schu-
macher, M., and Ricci, A. (2015). Agent environments
for multi-agent systems. In Agent Environments for
Multi-Agent Systems IV: proceedings of the 4th Inter-
national Workshop Environments for MAS (E4MAS)
2014. 6 mai 2014.
Wooldridge, M. and Jennings, N. R. (1995). Intelligent
agents: Theory and practice. The knowledge engineer-
ing review, 10(2):115–152.
Wu, H.-n., Levihn, M., and Stilman, M. Navigation among
movable obstacles in unknown environments. In In-
telligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2010 IEEE/RSJ
International Conference. IEEE.
Environment Engine for Situated MAS
137
