
Improving Readability for Tweet Contextualization using Bipartite
Graphs
Amira Dhokar, Lobna Hlaoua and Lotfi Ben Romdhane
SDM Research Group, MARS Research Lab ISITCom, University of Sousse, Tunisia
Keywords:
Bipartite Graphs, Readability, Summarization, Tweet Contextualization.
Abstract:
Tweet contextualization (TC) is a new issue that aims to answer questions of the form What is this tweet about?
The idea of this task was imagined as an extension of a previous area called multi-document summarization
(MDS), which consists in generating a summary from many sources. In both TC and MDS, the summary
should ideally contain most relevant information of the topic that is being discussed in the source texts (for
MDS) and related to the query (for TC). Furthermore of being informative, a summary should be coherent,
i.e. well written to be readable and grammatically compact. Hence, coherence is an essential characteristic in
order to produce comprehensible texts. In this paper, we propose a new approach to improve readability and
coherence for tweet contextualization based on bipartite graphs. The main idea of our proposed method is to
reorder sentences in a given paragraph by combining most expressive words detection and HITS (Hyperlink-
Induced Topic Search) algorithm to make up a coherent context.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the diffusion of social networks such as Face-
book or YouTube, social media have become one of
the most popular Internet services in the world. Such
sites offer today’s youth a portal for entertainment and
communication and have grown exponentially in re-
cent years. Twitter stands actually as the most popu-
lar micro-blogging service (Duggan et al., 2015). It
allows its users to communicate with short messages
known as tweets, limited by a maximum number of
characters that does not exceed 280, often in real time
and from a mobile phone. But this type of messages
generates a large amounts of data and are sometimes
non understandable for a reader because of their lim-
ited size. Since they must be written respecting this
limitation, a particular vocabulary is used and provid-
ing additional informations seems to be necessary to
understand tweet’s context without time consuming.
In tweet contextualization, a context is a summary
related to the tweet and that does not exceed 500
words. This summary should be informative and co-
herent (readable). Given a tweet, and a set of relevant
documents, the task of producing an informative and
coherent summary of those documents in response to
this tweet has attracted a great deal of attention re-
cently. However, the problem of organizing informa-
tion for contextualization so that the generated sum-
mary is coherent has received relatively little atten-
tion.
In this paper, we propose an approach for tweet
contextualization based on semantic and coherence
between sentences: our objective is to select most rel-
evant and coherent information in relation with the
tweet, extract the most important ones to provide in-
formativeness excerpt and reorder phrases to guaran-
tee coherence and readability. In this respect, the fol-
lowing questions arise: how to select the most impor-
tant phrases coming from many documents and that
deal with topics expressed in the tweet? How to en-
hance the order of selected sentences to be able to ob-
tain a readable and coherent context?
This paper has been organized as follows. Sec-
tion 2 cites some related works. Section 3 presents
our motivation and the architecture of our model. Sec-
tion 4 discusses relevant sentences extraction from a
document. Section 5 develops the idea of sentence
aggregation based on cliques detection. Section 6 de-
tails the proposed approach for sentence reordering to
improve readability for a given context. Section 7 de-
scribes our experimental results. The conclusion and
future work are presented in Section 8.
60
Dhokar, A., Hlaoua, L. and Ben Romdhane, L.
Improving Readability for Tweet Contextualization using Bipartite Graphs.
DOI: 10.5220/0007313900600068
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2019), pages 60-68
ISBN: 978-989-758-350-6
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

2 RELATED WORK
In tweet contextualization, an excerpt provided from
many documents must be informative and readable.
Hence it should be grammatically correct. Coher-
ence is an essential characteristic in order to pro-
duce comprehensible texts. This aspect has received
relatively little attention in tweet contextualization.
Hence, the paper focused on document summariza-
tion to deal with this problem. In this context, several
approaches have been proposed. Barsilay and Lap-
ata (Barzilay and Elhadad, 2002) proposed to study
the proprieties of ordering information in the news
genre. They develop a method that combines con-
straints from chronological order of events and topi-
cal relatedness to improve order of sentences in multi-
document news summarization. In (Barzilay and Lee,
2004) another method is presented: it is an unsuper-
vised model that focus on text organization in a par-
ticular domain. An adaptation of algorithms for Hid-
den Markov Models is used to capture topic shift in a
text, where topics are represented by hidden states and
sentences are observations. In (Barzilay and Lapata,
2008) authors proposed a method based on entities to
assess and improve textual coherence. Their model
is inspired by Centering Theory (Grosz et al., 1995)
which supposes that adjacent sentences are coherent
if they share the same entities: authors created an en-
tity grid model to capture discourse transitions at the
sentence-to-sentence level. Following the same spirit,
Soricut and Marcu (Soricut and Marcu, 2006) and El-
sner et al.(Elsner et al., 2007) proposed a combination
between the entity-based and HMM-based models to
improve information ordering task. In 2011, Lin et al.
(Lin et al., 2011) proposed an approach of text order-
ing using discourse relation transitions. their method
is to transform the discourse relation into a discourse
role matrix that represents term occurrences with its
discourse roles in the text units (sentences). To dis-
tinguish coherence from incoherence, n-gram sub-
sequences of transitions per term in the discourse role
matrix are used. In (Guinaudeau and Strube, 2013),
authors modeled the text into a graph of sentences by
using a bipartite graph. They suppose that one set of
nodes represents entities and the other set represents
sentences of a document. Their work is based on the
fact of using a one mode projection on sentence nodes
(Newman, 2011), and then the average out degree of
sentence nodes is computed to determine how coher-
ent a document is. This method takes into account
the number of shared entities between sentences and
their grammatical functions. In (Parveen and Strube,
2015), authors proposed a graph-based method for
extractive single document summarization to improve
and evaluate local coherence for scientific articles.
They combine ILP (integer linear programming) and
a graph-based ranking algorithm to reorder and opti-
mize sentence ranking on the basis of importance. In
(Parveen et al., ), authors deal with single-document
summarization based on weighted graphical represen-
tation of the document where one set of nodes cor-
responds to topics. The Latent Dirichlet Allocation
(LDA) is used for topic modeling and to measure the
semantic relatedness between words and the topical
coherence of a given document. In (Li and Hovy,
2014), authors proposed an approach that learns a
syntactico-semantic representation for sentences au-
tomatically,using either recurrent or recursive neural
networks. The proposed architecture obviated the
need for feature engineering, and learns sentence rep-
resentations, which are to some extent able to cap-
ture the rules governing coherent sentence structure.
In (Ermakova, 2016) the author proposed three com-
pletely automatic approaches for sentence order as-
sessment where the similarity between adjacent sen-
tences is used as a measure of text coherence. Her
method is based on graph model, where the vertices
correspond to sentences and the edges represent the
similarity measure between them. She exploited the
similarities of terms, nouns and named entities. Re-
cently, authors in (Ermakova et al., 2017) presented
a self-sufficient metric for sentence ordering assess-
ment based on text topic-comment structure of a text
that requires only shallow parsing. they proposed a
metric that considers the pairwise term similarities of
the topics and the comments of the adjacent sentences
in a text since word repetition is one of the formal
signs of text coherence (Barzilay and Elhadad, 2002).
Methods using bipartite graph in document sum-
marization had encouraging results in ordering task.
Inspired by the above approaches, in this paper,
a method for improving readability for tweet con-
textualization combining cliques detection, bipartite
graphs and a ranking algorithm is proposed.
3 MOTIVATION AND
ARCHITECTURE OF THE
MODEL
In tweet contextualization, a context is a summary re-
lated to the tweet and that does not exceed 500 words.
Indeed, the main objective of a TC system is to en-
hance the readability of a given tweet (that acts as a
query), to identify a list of potential topic-related re-
sources (documents) that we attempt to summarize.
The process of tweet contextualization can be di-
Improving Readability for Tweet Contextualization using Bipartite Graphs
61

vided into three sub-tasks: tweet Analysis, passage
and/or XML elements retrieval and construction of
the answer (context). Respecting this process, the
proposed method for tweet contextualization is pre-
sented in Figure. 1. It involves the following three
steps: tweet analysis that aims to clean tweets and
eliminate unnecessary symbols such as #, @...and
URLs, passages/XML documents retrieval where
cleaned query is transmitted to the search engine
to determine the most relevant articles to the tweet
and tweet contextualization that aims to extract
then reorder most relevant sentences related to the
tweet. Top-ranked phrases are selected to form con-
text (within the limit of 500 word).
The main objective of this work is to guarantee in-
formativeness and coherence between different parts
of the context to be able to construct an appropri-
ate summary. In view of importance of both rele-
vance and coherence in a contextualization system,
we have considered that this work must combine these
two aspects to achieve good performances in infor-
mativeness and readability. Hence, it is interesting
to consider that a sentence included in the final con-
text should be relevant regarding the query, informa-
tive and coherent with other sentences. The proposed
method is divided into two main modules: the first
one aims to enhance the informativeness by select-
ing the most relevant sentences from many documents
considering some measures, and the second module
aims to improve the readability of the contextualiza-
tion system by reordering selected sentences to ensure
higher degree of coherence to the constructed context.
This approach will be detailed in next sections.
4 RELEVANT SENTENCE
EXTRACTION FROM A
DOCUMENT
The goal of this part of the proposed system is to
extract the most relevant phrases from the most
relevant documents. For that, this step into two
sub-tasks: document filtering regarding the tweet and
sentence scoring.
In document filtering regarding the tweet, our ob-
jective is to choose most informative sentences that
deal with topics expressed by the tweet. Hence
we opted for filtering the relevant document by
keeping only sentences that are correlated to the
query. This can be easily done by calculating the
cosine similarity between the tweet and the can-
didate sentences given by the following formula:
Similarity(Q, S) =
∑
n
i=1
Freq(q
i
, Q)
q
∑
n
i=1
(Freq(q
i
, Q))
2
×
∑
n
i=1
Freq(s
i
, S)
q
∑
n
i=1
(Freq(s
i
, S))
2
(1)
Where Q=q
1
,q
2
,...,q
i
is a query, S=s
1
,s
2
,...,s
i
is a
sentence, Freq(q
i
,Q) is the occurrence of the i-th to-
ken in a query and Freq(s
i
,S) is the occurrence of the
i-th token in a sentence. If the token is not presented
in the query or in the sentence, q
i
(resp.s
i
) is equal to
0 respectively.
In every filtered document, sentences do not have
the same importance in term of relevancy according
to the tweet. For that, we propose to make the dif-
ference between most relevant phrases and less ones
(Dhokar et al., 2017): for each candidate sentence, a
score is computed. This score takes into account the
relevance of the sentence compared to the title of the
document and the importance of the sentence in its
original document compared to other sentences in the
same article. Best scored sentences are selected and
the score of each phrase is given by:
Sp
i
= Similarity(T, S
i
) + Imp(S
i
) (2)
Where Sp
i
is the associated score of a sentence S
i
,
Similarity(T,S
i
) is the similarity estimated between
a sentence S
i
and the title of the document T and
Imp(S
i
) is the score that estimates the importance of a
sentence (S
i
) in a document. The similarity between
a sentence S
i
and the title of the document T is calcu-
lated using the following equation:
Similarity(T, S) =
∑
n
i=1
Freq(t
i
, T )
q
∑
n
i=1
(Freq(t
i
, T ))
2
×
∑
n
i=1
Freq(s
i
, S)
q
∑
n
i=1
(Freq(s
i
, S))
2
(3)
Where T=t
1
,t
2
,...,t
i
is the title of the corresponding
document, S=s
1
,s
2
,...,s
i
is a sentence, Freq(t
i
,T) is the
occurrence of the i-th token in a title and Freq(s
i
,S) is
the occurrence of the i-th token in a sentence. If the
token is not present in the title or in the sentence, q
i
(resp.s
i
) is equal to 0 respectively.
The importance of a sentence (S
i
) in a document is
calculated until divergence and given by (Brin and
Page, 2012):
Imp(S
i
) = (1 − d) + d
×
∑
S
j
∈Neighbors(S
i
)
Sim(S
i
, S
j
)
∑
S
k
∈Neighbors(S
i
)
Sim(S
k
, S
i
)
× Imp(S
i
) (4)
ICAART 2019 - 11th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
62
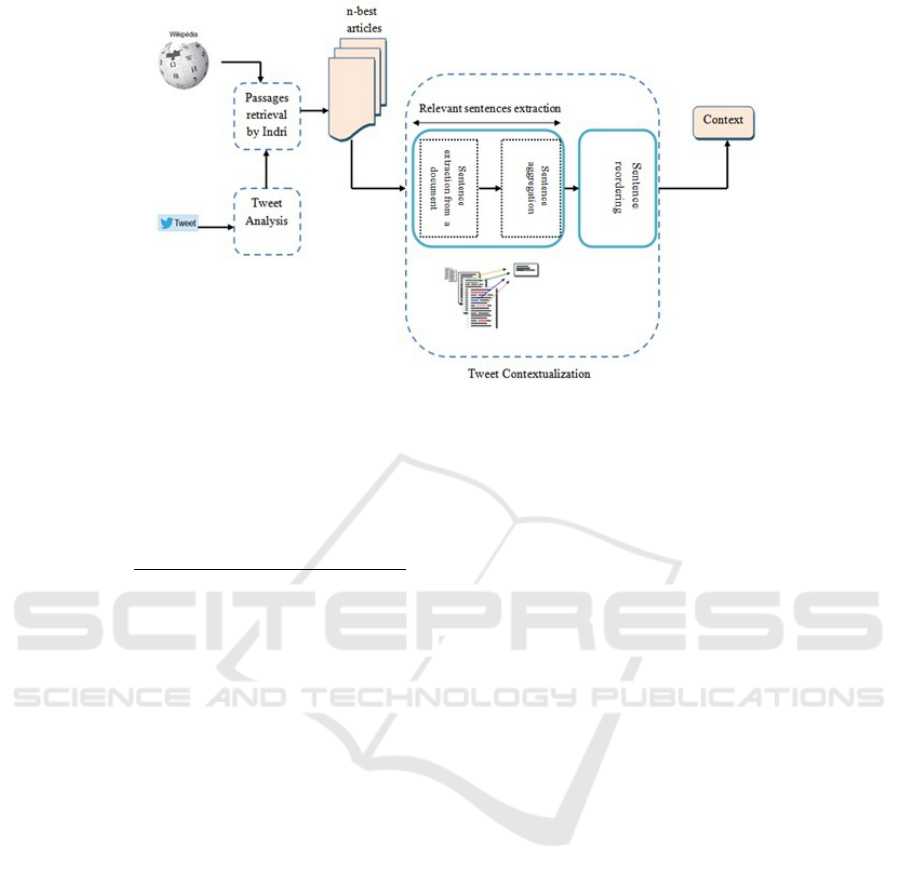
Figure 1: The proposed contextualization model.
Where d is a dumping factor (usually set to 0.85),
Neighbors S
i
is the set of sentences connected with
S
i
and Sim(S
i
,S
j
) is the similarity score between sen-
tences S
i
and S
j
and given by (Mihalcea, 2004):
Sim(S
i
, S
j
) =
∑
m∈S
i
,S
j
f req(m, S
i
) + f req(m, S
j
)
log|S
i
| + log|S
j
|
(5)
Where , freq(m,S
i
) is the occurrence of a word m in a
sentence S
i
, respectively S
j
and log |S
i
| is the length
of a sentence S
i
, respectively S
j
.
5 SENTENCE AGGREGATION
BASED ON CLIQUES
DETECTION (SACD)
As mentioned in the previous section, we work with n
top documents from the search phase. From each doc-
ument, best scored sentences are selected and aggre-
gated together. However, a good context should have
a good quality respecting two fundamental aspects of
a contextualization system: relevance and coherence.
We therefore propose to refine the choice of relevant
and coherent sentences to include in the context. In
this respect, it is proposed to model sentences in a
graph then use cliques detection to select most coher-
ent groups of phrases. Our hypothesis is that a set
of sentences belonging to the same clique can form a
coherent and semantically linked passages. Usually,
each node in a clique is, in some way, highly related
to every other node. This characteristic makes clique
identification a very important approach to uncover
meaningful groups of sentences from a graph. In this
work, we opted for finding maximal cliques of a graph
to identify coherent sentences in order to produce a
readable context (Dhokar et al., 2017).
5.1 Cliques Computation
In the literature, many pieces of work have been pro-
posed to model a set of sentences by a graph in order
to obtain links between phrases and passages (Salton
et al., 1997),(Yeh et al., 2008). In this work, we try to
adapt the same concept in order to model a group of
phrases (here aggregated sentences resulted from the
first step of the proposed system) as a graph, in order
to obtain a network of sentences that are related to
each others, resulting in a sentence similarity graph.
This graph is composed of nodes and edges linking
nodes and each node represents a sentence. A connec-
tion between two nodes exists if and only if they are
similar with respect to a similarity threshold α. The
degree of connection between two sentences S
i
and S
j
is measured by the formula used in equation 5. Our
approach to identify cliques is based on the notion of
a maximal clique. A maximal clique of a graph G is a
clique that cannot be extended by including one more
adjacent vertex (Regneri, 2007). Cliques are allowed
to overlap, which means that sentences can be mem-
bers of more than one clique. The purpose of this step
of this work is to detect all maximal cliques present
in the graph using Tomita algorithm (Tomita et al.,
2011).
5.2 Cliques Selection
In tweet contextualization, a context is a summary
related to the tweet, containing coherent and related
groups of sentences and that does not exceed 500
Improving Readability for Tweet Contextualization using Bipartite Graphs
63

words. Respecting this constraint, the aim of this
step is to propose a method for cliques selection to
determine cliques to be considered in the final con-
text. Hence the proposed method is depicted in fig-
ure 2. A set of cliques (resulted from the previous
Figure 2: Our proposed method for cliques selection.
step) is considered as an input of the algorithm. then,
the clique which has the highest size N is chosen to be
included in the final context. If the limited size of the
excerpt (500 words) is achieved, we consider only the
selected clique. If not (we didn’t achieve 500 words),
the clique which has the size N-1 is added. The oper-
ation of cliques selection is repeated until having 500
words in the final context. After merging all selected
cliques, redundant sentences are eliminated.
6 SENTENCE REORDERING
6.1 Motivation
This section highlights the proposed approach for sen-
tence reordering in order to generate a readable con-
text for a given tweet. According to the previous
step, the obtained context is composed of a set of
cliques. The proposed method is divided into two
steps: the first step aims to reorder sentences into
the same clique and the second step aims to reorder
cliques between them.
In this work, we focus on the first step and our goal
is to propose a method to reorder sentences into the
same clique. The intuition we have behind this idea is
that sentences belonging to the same clique are corre-
lated and treat the same themes. In this respect, their
reorganization remains indispensable in order to have
a coherent and grammatically compact passage (para-
graph). This section describes the adopted technique
to improve readability for tweet contextualization. In
this context, we model the text using a graphical rep-
resentation and then apply HITS algorithm to reorder
sentences belonging to the same clique. A graph can
easily capture the essence of the whole text without
leading to high computational complexity and a rank-
ing algorithm (here is HITS algorithm) takes into ac-
count global information to calculate the rank of a
corresponding node (sentence). These two character-
istics can help us to improve readability and coher-
ence to a given context. In this work we opted to
combine a bipartite graph and HITS algorithm. We
start by introducing the graphical representation of
a clique, followed by a description of the algorithm
used to quantify the importance of phrases in a clique
and reorder considered sentences.
6.2 Proposed Method for Sentences
Reordering
6.2.1 Graphical Representation of a Clique
Considering a graphical representation of a text is not
recent. It is adopted by various approaches (Mihal-
cea and Tarau, 2004; Radev et al., 2004). In 2014,
Parveen and Strube proposed to use a bipartite graph
representation of text based on the entity grid repre-
sentation proposed by Barzilay and Lapata (Barzilay
and Lapata, 2008). Employing this type of represen-
tation can help us to determinate the importance of
sentences and to detect correlations between phrases.
A bipartite graph is an unweighted graph G=(V
s
,V
e
,L),
containing two sets of nodes, where V
s
is the set of
sentences, V
e
is the set of most expressive words (
here we will consider two types of expressive words:
named entities and most frequent words) and L is the
set of edges. An edge exits between a sentence and
an expressive word only if the word is mentioned in
a sentence; and there are no edges between nodes of
the same set. Figures 3, 4 and 5 show an example of a
text, its associated entity grid and its bipartite graph.
ICAART 2019 - 11th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
64

Figure 3: An example of a text.
Figure 4: Entity grid of the model summary from Figure 3.
Figure 5: Bipartite graph derived from the entity grid from
Figure 4.
6.2.2 Using HITS Algorithm for Sentence
Reordering
The aim of this step is to reorder sentences in the same
clique to improve readability in the context. Hence,
coherence improvement is presented as a ranking
problem. Inspired by (Parveen et al., 2015), it is pro-
posed to use HITS algorithm to calculate the rank
of a sentence in a clique. This algorithm considers
two types of nodes: hub nodes and authority nodes.
Since our graph is a bipartite graph, we can consider
sentences as authority nodes and words as hub nodes
(Kleinberg, 1999), to reorder sentences in the associ-
ated bipartite graph. For every sentence in the graph,
the importance of the phrase should be calculated in
two steps:
1. Calculate the hub score of a node (word) using the
following formula:
HubScore = A.AuthorityScore (6)
Where A is an adjacency matrix which represents
the connection between nodes in a graph. Each
node’s hub score has to be updated and the asso-
ciated score is equal to the sum of authority scores
of each node that it points to.
2. Calculate the authority score of a node (sentence)
using the following formula:
AuthorityScore = A
T
.HubScore (7)
Hence the authority weight is high if it is pointed
at by a hub having high weights.
The rules given by equations 3 and 4 are applied
until convergence (values of authorities and hubs are
stable). Also, all nodes in the graph have to be initial-
ized. Initial rank of a sentence is given by the follow-
ing formula:
ItitialRank(S
i
) = 1 + similarity(S
i
, Tweet) (8)
Here similarity(S
i
, Tweet) is the cosine similarity be-
tween a sentence S
i
and a tweet. We consider that ini-
tial importance of a sentence S
i
is related to the tweet.
Initial rank of a word is given by:
InitialRank(w
i
) = 1 + t f (w
i
, C)
+ occurence(w
i
, tweet) (9)
Here t f (w
i
, C) is the term frequency of w
i
in a clique
C and occurence(w
i
, tweet) indicates the occurrence
of w
i
in a tweet. Hence if w
i
is not present in the
tweet then occurence(w
i
, tweet) = 0. If it is present
then occurence(w
i
, tweet) = 1. We consider that ini-
tial importance of a word depends on the clique and
the tweet.
7 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
This section highlights experimental results given by
the proposed contextualization system. Obtained re-
sults are compared with results provided by INEX
2014. Before reporting experimental results, it is es-
sential to indicate the Test Data and the evaluation cri-
teria that we will consider.
Improving Readability for Tweet Contextualization using Bipartite Graphs
65

7.1 Description of the Test Data
In this study, we use the collection of articles and
tweets made available by INEX . The corpus has been
rebuilt in 2013 from a dump of the English Wikipedia
from November 2012. All notes and bibliographic
references were removed to facilitate the extraction of
plain text answers. It is composed of 3 902 346 arti-
cles and 240 tweets selected from the CLEF RepLab
(Amig
´
o et al., 2013) 2013 to build the 2014 INEX
collection. 70 tweets were considered for evaluation.
7.2 Evaluation Measures
Contexts are evaluated according to readability and
informativeness (Bellot et al., 2013). Readability
aims at measuring how clear and easy it is to under-
stand the summary and is manually evaluated. How-
ever, informativeness aims at measuring how well the
summary explains the tweet or how well the summary
helps a user to understand the tweet content (Bellot
et al., 2013).
7.2.1 Informativeness
This criteria calculates the dissimilarity between a ref-
erence text and the proposed summary (Bellot et al.,
2013), (SanJuan et al., 2012). It is a measure that
varies between 0 and 1, and the lower this dissimilar-
ity, the more the proposed summary is similar to the
reference text. It is given by:
Dis(T, S) =
∑
t∈T
(P − 1)
×
1 −
min(log(P), log(Q))
max(log(P), log(Q))
Where: P =
f
T
(t)
f
T
+ 1 and Q =
f
S
(t)
f
S
+ 1
T, is a set of query terms present in a reference sum-
mary and for each t ∈ T , f
T
(t), the frequency of a
term t in a reference summary, S, a set of query terms
present in a submitted summary and for each t ∈ S
and f
S
(t), the frequency of term t in a submitted sum-
mary. T may takes three forms: unigrams made of
single lemmas, bigrams made of pairs of consecutive
lemmas (in the same sentence) and bigrams with 2-
gaps also made of pairs of consecutive lemmas but
allowing the insertion between them of a maximum
of two lemmas.
7.2.2 Readability
In this evaluation the assessor indicates where he
misses the point of the answers because of highly in-
coherent grammatical structures, unsolved anaphora,
or redundant passages. Each summary consists in a
set of passages and for each passage, assessors had to
tick four kinds of check boxes. The guideline was the
following(Bellot et al., 2013): syntax (S) box is ticked
if the passage contains a syntactic problem (bad seg-
mentation for example), anaphora (A) box is ticked
if the passage contains an unsolved anaphora, redun-
dancy (R) box is ticked if the passage contains a re-
dundant information, and trash (T) box is ticked if the
passage does not make any sense in its context.
To evaluate summary’s readability, three metrics
are used based on relevancy or relaxed metric where
a passage is considered as valid if the T box has not
been ticked, syntax metric where a passage is consid-
ered as valid if the T or S boxes have not been ticked
and structure or strict metric where a passage is con-
sidered as valid if no box has been ticked.
7.3 Results and Disscussion
This section highlights experimental results of the
proposed method. Hence we can evaluate our system
according to informativeness and readability.
7.3.1 Informativeness Evaluation
To evaluate informativeness for tweet contextualiza-
tion, we conducted a simulation, namely run-1, in
which we evaluate our system considering the pro-
posed method of cliques selection proposed in sec-
tion 5.2. We have compared our runs with the follow-
ing different runs submitted by INEX 2014 partici-
pants: in Best-run, participants (Zingla et al., 2014)
used mining association rules between terms and in
REG-run, participants (Torres-Moreno, 2014) used
an automatic greedy summarizer named REG (RE-
sumeur Glouton) which uses graph methods to spot
the most important sentences in the document. The
proposed method has ameliorate our informativeness
results. We can note that our proposed approach
gives encouraging informativeness results compared
to other systems proposed at INEX 2014 (see table
1).
Table 1: Table of informativeness results.
Run Unigram Bigram Bigrams with 2-gaps
Best-run 0.7632 0.8689 0.8702
run-1 0.8180 0.9072 0.9102
REG run 0.8731 0.9832 0.9841
7.3.2 Readability Evaluation
As mentioned in the previous section, readability is
manually evaluated. Hence, contexts readability were
provided by 77 assessors. To evaluate readability for
ICAART 2019 - 11th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
66
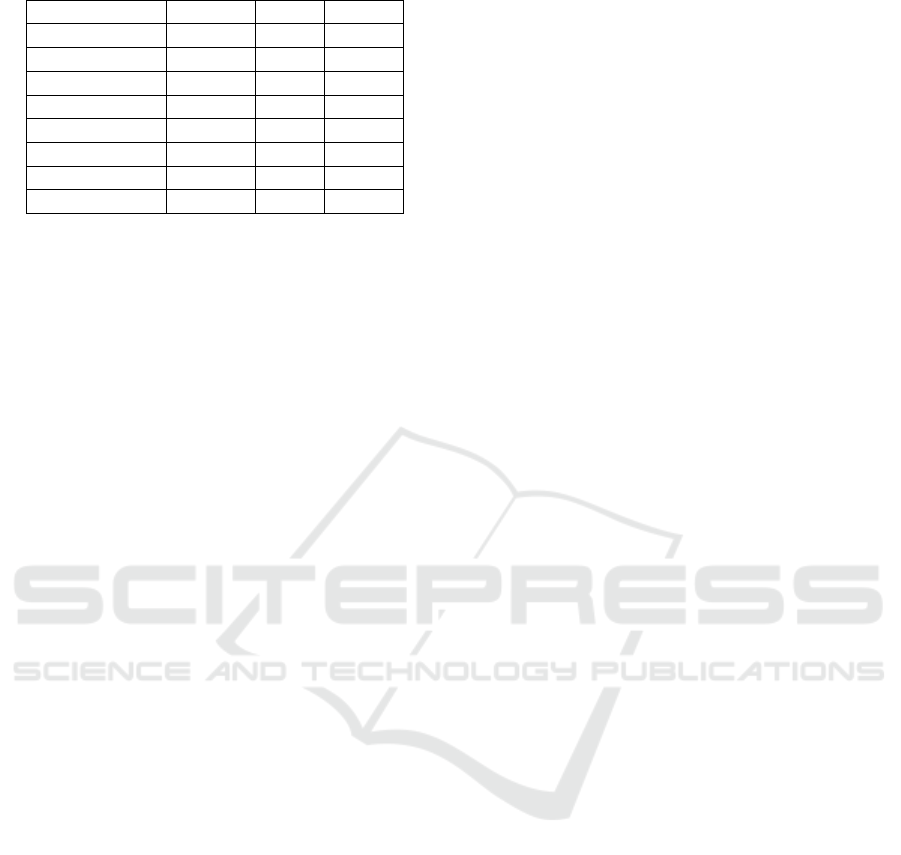
Table 2: Table of readability results.
Run Relaxed Strict Syntax
Best-Read-run 94.82 72.16 72.27
run-1 88.47 50.65 67.20
run-2 91.17 60.79 75.86
run-3 90.77 55.93 74.91
run-4 84.67 54.17 70.18
run-5 82.16 52.66 71.23
run-6 92.33 62.65 77.53
Last-Read-run 90.10 24.68 53.83
the proposed system, we considered the following
simulations: run-2 where we consider contexts with
sentence reordering in cliques using named entities,
run-3 where we consider contexts with sentence re-
ordering in cliques using most frequent words (MFW)
and the number of considered MFW is weighted ac-
cording to sentences, run-4 where we consider con-
texts with sentence reordering in cliques using most
frequent words (Here we consider that the number of
considered MFW is equal to 10), run-5 in which we
consider contexts with sentence reordering in cliques
using most frequent words and the considered num-
ber of MFW is higher then 10, and run-6 in which we
consider overlapping words between named entities
and most frequent words. We have compared our runs
with the following different runs submitted by INEX
2014 participants: Best-Read-run which is the best
readability run and Last-Read-run which is the last
readability run. Simulation results are summarized in
table 2.
By observing the results given in table 2, we can
note that there is an interesting improvement for the
readability results considering the used three metrics:
comparing run-1 (without sentence reordering) and
run-2 (with sentence reordering) we can confirm that
sentence reordering based on combining HITS algo-
rithm and named entities is efficient to ameliorate the
readability of our system. We can also see that us-
ing most frequent words in sentence reordering im-
proves readability results, in particular in run-3 com-
pared with run-4 and run-5, what confirms the inter-
est of sentence reordering using bipartite graphs. An
other important observation is that the provided re-
sults from run-2 and run-3 are very close. this can
be explained by the fact that the set of most fre-
quent words and the set of named entities are over-
lapping.i.e, many words are in common between the
two sets. For that we proposed an other run namely
run-6 where we consider overlapping words. Accord-
ing to the Table 2, we can see that using overlap-
ping words between named entities and most frequent
words in sentence reordering improves readability re-
sults. Comparing our results with official results given
by INEX 2014, we can see that our proposition gives
encouraging results that are in line with the values ob-
tained at INEX 2014.
8 CONCLUSION
In this paper we focus on the problem of readability of
tweet contextualization. Our main contribution is the
proposition of a method based on the use of bipartite
graphs to reorder sentences in cliques and to improve
readability for Tweet Contextualization. We opted to
combine HITS algorithm and two types of words in
the graph: most frequent words and named entities to
make up coherent contexts. These proposals and their
formal studies are complemented by an experimen-
tal study to compare them with results from INEX.
We found that our model obtains encouraging results
since that our returns are in line with the results of
the INEX 2014 and it is essential to point out that our
system proposed a compromise between informative-
ness and readability. We propose in our future work
to make an order for cliques (paragraphs) in the con-
text to improve the quality of the context with respect
to informativeness and readability.
REFERENCES
Amig
´
o, E., De Albornoz, J. C., Chugur, I., Corujo, A., Gon-
zalo, J., Mart
´
ın, T., Meij, E., De Rijke, M., and Spina,
D. (2013). Overview of replab 2013: Evaluating on-
line reputation monitoring systems. In International
Conference of the Cross-Language Evaluation Forum
for European Languages, pages 333–352. Springer.
Barzilay, R. and Elhadad, N. (2002). Inferring strategies
for sentence ordering in multidocument news summa-
rization. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research,
17:35–55.
Barzilay, R. and Lapata, M. (2008). Modeling local co-
herence: An entity-based approach. Computational
Linguistics, 34(1):1–34.
Barzilay, R. and Lee, L. (2004). Catching the drift: Prob-
abilistic content models, with applications to genera-
tion and summarization. arXiv preprint cs/0405039.
Bellot, P.and Moriceau, V., Mothe, J., Sanjuan, E., and Tan-
nier, X. (2013). Overview of inex tweet contextualiza-
tion 2013 track. CLEF.
Brin, S. and Page, L. (2012). Reprint of: The anatomy of a
large-scale hypertextual web search engine. Computer
networks, 56(18):3825–3833.
Dhokar, A., Hlaoua, L., and Romdhane, L. B. (2017).
Cliques detection vs maximum spanning tree for tweet
contextualization. IADIS International Journal on
Computer Science & Information Systems, 12(2).
Duggan, M., Ellison, N. B., Lampe, C., Lenhart, A., and
Madden, M. (2015). Social media update 2014. Pew
Research Center, 19.
Improving Readability for Tweet Contextualization using Bipartite Graphs
67

Elsner, M., Austerweil, J. L., and Charniak, E. (2007). A
unified local and global model for discourse coher-
ence. In HLT-NAACL, pages 436–443.
Ermakova, L. (2016). Automatic sentence ordering assess-
ment based on similarity. In EVIA@ NTCIR.
Ermakova, L., Mothe, J., and Firsov, A. (2017). A met-
ric for sentence ordering assessment based on topic-
comment structure. In Proceedings of the 40th In-
ternational ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and
Development in Information Retrieval, pages 1061–
1064. ACM.
Grosz, B. J., Weinstein, S., and Joshi, A. K. (1995). Center-
ing: A framework for modeling the local coherence of
discourse. Computational linguistics, 21(2):203–225.
Guinaudeau, C. and Strube, M. (2013). Graph-based local
coherence modeling. In ACL (1), pages 93–103.
Kleinberg, J. M. (1999). Authoritative sources in a hy-
perlinked environment. Journal of the ACM (JACM),
46(5):604–632.
Li, J. and Hovy, E. (2014). A model of coherence based on
distributed sentence representation. In Proceedings of
the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural
Language Processing (EMNLP), pages 2039–2048.
Lin, Z., Ng, H. T., and Kan, M.-Y. (2011). Automatically
evaluating text coherence using discourse relations. In
Proceedings of the 49th Annual Meeting of the Asso-
ciation for Computational Linguistics: Human Lan-
guage Technologies-Volume 1, pages 997–1006. As-
sociation for Computational Linguistics.
Mihalcea, R. (2004). Graph-based ranking algorithms for
sentence extraction, applied to text summarization. In
Proceedings of the ACL 2004 on Interactive poster
and demonstration sessions, page 20. Association for
Computational Linguistics.
Mihalcea, R. and Tarau, P. (2004). Textrank: Bringing order
into texts. Association for Computational Linguistics.
Newman, M. E. (2011). Complex systems: A survey. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1112.1440.
Parveen, D., Mesgar, M., and Strube, M. Generating coher-
ent summaries of scientific articles using coherence
patterns. In Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on
Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing,
pages 772–783.
Parveen, D., Ramsl, H.-M., and Strube, M. (2015). Topical
coherence for graph-based extractive summarization.
Parveen, D. and Strube, M. (2015). Integrating importance,
non-redundancy and coherence in graph-based extrac-
tive summarization. In IJCAI, pages 1298–1304.
Radev, D. R., Allison, T., Blair-Goldensohn, S., Blitzer, J.,
Celebi, A., Dimitrov, S., Drabek, E., Hakim, A., Lam,
W., Liu, D., et al. (2004). Mead-a platform for multi-
document multilingual text summarization. In LREC.
Regneri, M. (2007). Finding all cliques of an undirected
graph. In SeminarCurrent Trends in IE WS Jun.
Salton, G., Singhal, A., Mitra, M., and Buckley, C. (1997).
Automatic text structuring and summarization. Infor-
mation Processing & Management, 33(2):193–207.
SanJuan, E., Moriceau, V., Tannier, X., Bellot, P., and
Mothe, J. (2012). Overview of the inex 2012 tweet
contextualization track. Initiative for XML Retrieval
INEX, page 148.
Soricut, R. and Marcu, D. (2006). Discourse generation us-
ing utility-trained coherence models. In Proceedings
of the COLING/ACL on Main conference poster ses-
sions, pages 803–810. Association for Computational
Linguistics.
Tomita, E., Akutsu, T., and Matsunaga, T. (2011). Efficient
algorithms for finding maximum and maximal cliques:
Effective tools for bioinformatics. INTECH Open Ac-
cess Publisher.
Torres-Moreno, J.-M. (2014). Three statistical summariz-
ers at clef-inex 2013 tweet contextualization track. In
CLEF (Working Notes), pages 565–573.
Yeh, J. Y., Ke, H. R., and Yang, W. (2008). ispreadrank:
Ranking sentences for extraction-based summariza-
tion using feature weight propagation in the sentence
similarity network. Expert Systems with Applications,
35(3):1451–1462.
Zingla, M., Ettaleb, M., Latiri, C. C., and Slimani, Y.
(2014). Inex2014: Tweet contextualization using as-
sociation rules between terms. In CLEF (Working
Notes), pages 574–584.
ICAART 2019 - 11th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
68
