
LSTM Neural Networks for Transfer Learning in
Online Moderation of Abuse Context
Avi Bleiweiss
BShalem Research, Sunnyvale, U.S.A.
Keywords:
Offensive Comments, Transfer Learning, Recurrent Neural Networks, Long Short-term Memory.
Abstract:
Recently, the impact of offensive language and derogatory speech to online discourse, motivated social media
platforms to research effective moderation tools that safeguard internet access. However, automatically dis-
tilling and flagging inappropriate conversations for abuse remains a difficult and time consuming task. In this
work, we propose an LSTM based neural model that transfers learning from a platform domain with a rela-
tively large dataset to a domain much resource constraint, and improves the target performance of classifying
toxic comments. Our model is pretrained on personal attack comments retrieved from a subset of discussions
on Wikipedia, and tested to identify hate speech on annotated Twitter tweets. We achieved an F1 measure of
0.77, approaching performance of the in-domain model and outperforming out-domain baseline by about nine
percentage points, without counseling the provided labels.
1 INTRODUCTION
The wider dissemination of the network and social
media platforms have altered online discourse and al-
lowed disrespectful behavior to transpire in forums.
The public at large has since expressed increasing
concerns that the content, tone, and intent of on-
line interactions have undergone an evolution that be-
comes a liability. In a recently released large-scale
survey, conducted by the Pew Research Center (Pew,
2017) and covering more than 1,500 technologists and
academics, over 80% replied that they expect preva-
lence of online trolling to stay the course, while so-
cial platforms actively seeking best practices to bal-
ance security and privacy, freedom-of-speech, and
user protections (Poland, 2016).
Abusive language is a very broad category that
researchers struggle to define, and hence a reliable
quantitative detection of hateful speech at scale is still
an unresolved problem. Online conversations involve
a wide range of audience sizes, from a single partic-
ipant to an entire community, and the lack of a con-
sistent abuse signal to a classifier is a key implica-
tion for the difficulty of the detection task. In an in-
creasingly multicultural information society, ongoing
work to automate identification and moderation of un-
acceptable discourse, adapted natural language pro-
cessing (NLP) tools for building and annotating so-
cial media corpora. Diminishing the widespread pres-
ence of cyberbullying in online discussions turned to
a world global goal that had spurred work mostly ap-
plied to English context (Waseem and Hovy, 2016;
Wulczyn et al., 2017; Yenala et al., 2017) and seen
constantly expanding to other languages (Ross et al.,
2016; Prates De Pelle and Moreira, 2017; Pavlopou-
los et al., 2017; Fi
ˇ
ser et al., 2017).
Automated detection of abuse in online discourse
is a relatively new discipline in NLP research. The
work by Yin et al. (2009) is the earliest known to use
a machine learning approach to identify harassment
on the Web, by supplementing local TF-IDF (Baeza-
Yates and Ribeiro-Neto, 1999; Salton et al., 1975)
with sentiment and context features that are fed to a
support vector machine (SVM) classifier. More recent
work explored logistic regression (LR) and multi-
layer perceptrons (MLP) on either word or charac-
ter level n-grams (Wulczyn et al., 2017). Davidson et
al. (2017) showed that LR with L2 regularization per-
formed markedly better than other baselines, however
their model was biased toward classifying posts as
less hateful or offensive compared to human judges.
Proving compelling performance when applied to
a traditional NLP task as sentiment analysis (dos
Santos and Gatti, 2014; Huang et al., 2016; Qian
et al., 2017), deep learning models expressed in both
their recurrent and convolutional variants of neu-
ral networks (Elman, 1990) has recently become a
widespread foundation for sequential text classifica-
112
Bleiweiss, A.
LSTM Neural Networks for Transfer Learning in Online Moderation of Abuse Context.
DOI: 10.5220/0007358701120122
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2019), pages 112-122
ISBN: 978-989-758-350-6
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

tion (Kim, 2014; Lee and Dernoncourt, 2016; Yo-
gatama et al., 2017). Text sequences fed to the net-
work are often represented in a semantic vector space
with either character or word embeddings (Penning-
ton et al., 2014) that capture local context information
via global co-occurrence counts.
To detect toxicity in comments, Chu et al. (2017b)
explored separately long short-term memory (LSTM)
(Hochreiter and Schmidhuber, 1997) based recurrent
neural network (RNN) and convolutional neural net-
work (CNN) architectures. They observed that CNN
performed better and prove more computationally ef-
ficient when paired with character than with word em-
beddings. Yenala et al. (2017) propose an architecture
that synthesizes CNN and bidirectional LSTM to de-
tect inadequate queries in Web search. Their model
shown to significantly outperform pattern based and
laborious hand-coded features. More recently, a CNN
model fed by word vectors to classify hate-speech on
Twitter (Gamb
˜
ack and Sikdar, 2017), achieved an F1
score of 78.3% to improve performance over an LR
baseline. Rather than toxicity, identifying construc-
tiveness in news comments is studied in the work by
Kolhatkar and Taboada (2017) that uses an LSTM
based classifier with a highest test accuracy of 72.6%.
An impediment to algorithmic progress in detect-
ing hateful speech is the scarcity of large publicly
available datasets. Past work tends to use self curated
datasets that rely on either manual and costly human
annotations, or resort to searches of a limited set of
keywords (Sood et al., 2012; Kwok and Wang, 2013).
Saleem et al. (2017) found that widely used expletives
and slurs are not necessarily indicative of abuse, and
proposes self-identified hateful communities to label
training examples and improve scalability.
To the extent of our knowledge, the current open
datasets are limited to the Detecting Insults in So-
cial Commentary released by Impermium for a Kag-
gle competition (Impermium, 2013; Krishnamoorthy
et al., 2017), the Twitter Hate Speech annotations
(Waseem and Hovy, 2016), and the English corpora of
the Wikipedia Detox project (Wulczyn et al., 2017).
The Impermium dataset contains over 8K comments
annotated as either insulting or neutral, while the
Twitter set comprises over 16K tweets, each labeled
as one of racist, sexist, or neutral. Obtained from pro-
cessing a large dump of Wikipedia discussion pages,
the Wikipedia Detox annotations for personal attacks,
aggression, and toxicity, each of over 100K com-
ments, are by far the largest available and most well
curated to reliably label insult in comments. In our
work, we use both the Wikipedia and Twitter datasets.
In the field of machine learning, transfer learn-
ing aims to reuse previously acquired knowledge be-
tween task domains (Pan and Yang, 2010; Ruder and
Plank, 2017; Joshi and Chowdhary, 2018). Often,
the primary motivation for transfer learning is to im-
prove performance of a task with limited training data
by leveraging pretrained features, or hyperparame-
ters, on a task with access to a large labeled resource.
Knowledge transfer has been successfully applied to
numerous domains in machine learning. Notably are
visual recognition models trained on the large-scale
ImageNet challenge (Russakovsky et al., 2015; Huh
et al., 2016) and proven to be effective feature ex-
tractors in a variety of tasks including semantic image
segmentation (Oquab et al., 2014), medical diagnos-
tics (Esteva et al., 2017), and image captioning (Don-
ahue et al., 2017). Shown to speed up training and
outperform in-domain model performance, transfer
learning benefited audio-related tasks such as speech
recognition (Kunze et al., 2017) and music classifica-
tion (Choi et al., 2017), and NLP specific tasks includ-
ing neural machine translation (NMT) (Zoph et al.,
2016), machine comprehension (Golub et al., 2017),
semantic parsing (Fan et al., 2017), cross-lingual POS
tagging (Kim et al., 2017), and text classification (Liu
et al., 2017). Similarly, in our work, we pretrained
a neural model on a large Wikipedia Detox dataset
and reused learned weights and biases to bootstrap an
abuse detection task on a small set of hateful speech
annotations extracted from Twitter.
Embedding
Forward
LSTM
Backward
LSTM
Concatenate
Softmax
Comments
Labels
Figure 1: BiLSTM neural model architecture: word se-
quences are each mapped by the embedding layer into a
series of dense vectors. Word embeddings are then fed into
both forward and backward LSTMs, with their outputs con-
catenated and passed through a softmax activation function
to produce probabilities for no-abuse and abuse labels.
The main contribution of this work is a novel
transfer-learning model that facilitates state-of-the-
art domain adaptation methods to benefit the perfor-
mance of low-resource abuse detection in comments.
Our study proposes to ameliorate the constraining
LSTM Neural Networks for Transfer Learning in Online Moderation of Abuse Context
113

Train
Out-Domain
Random
Weights
Train
In-Domain
Out-Trained
Weights
Test
In-Domain
Finetuned
Weights
F1 Score
(a) Low-Resource Domain Adaptation
Train
In-Domain
Random
Weights
Test
In-Domain
Out-In-Trained
Weights
F1 Score
Out-Domain
Sample
Train
In-Domain
Finetuned
Weights
(b) Low-Resource Domain Matching
Figure 2: Transfer learning scenarios including (a) AD model adaptation to a low-resource domain and (b) generalizing an
AD system to match a low to a high resource domain using oversampling.
scarcity of obtainable toxic-discourse corpora by mo-
tivating the creation of coarse-grained annotations,
along with only a few large datasets to learn from.
We show the effectiveness of our model by closely
matching in-domain baseline performance. The rest
of this paper is structured as follows. In Section 2, we
overview the architecture of our LSTM-based neural
model, and in Section 3, we proceed to highlight the
base and compound methods we explored for trans-
fer learning. Section 4 analyzes the semantical rela-
tion between the Wikipedia Detox and Twitter Hate
Speech datasets, and details our training procedures.
In Section 5, we present our evaluation methodology
and report extensive quantitative results over a range
of ablation studies. Summary and identified avenues
for prospective work are provided in Section 6.
2 MODEL ARCHITECTURE
In this section, we formalize the task of abuse detec-
tion (AD). Our AD model takes as input a tokenized
comment c = {c
1
, c
2
, . . . , c
n
}, where c
i
are text words,
and learns a function f (c) 7→ {no-abuse, abuse}.
Given a collection of l labeled comments {c}
l
i=1
from
a distinct domain s, such as Wikipedia or Twitter,
we can learn an AD model f
s
(c) to predict abuse in
that domain. Moreover, we can adapt an AD model
trained in one domain to classify abuse in another, and
avoid prohibitively expensive and time consuming hu-
man labeling of new data. In this paper, we propose
the task of knowledge transfer from an AD system
f
s
(c) that is trained in a source domain to detect abuse
over a target domain t with an unlabeled set {c}
k
i=1
of
k comments, where k l. We aim to improve rather
than adversely impact target performance, and avoid
negative transfer learning (Pan and Yang, 2010).
Our neural model (Figure 1) uses a bidirec-
tional long short-term memory network (BiLSTM)
(Hochreiter and Schmidhuber, 1997; Schuster and
Paliwal, 1997) fed with distributed word representa-
tion. First, we transform each comment word c
i
7→ c
x
i
into a continuous semantic vector-space through pre-
trained GloVe embeddings (Pennington et al., 2014).
We then parametrize the word distribution of an
input example c
x
= {c
x
1
, c
x
2
, . . . , c
x
n
} as an encoder-
decoder gated RNN (Cho et al., 2014; Chung et al.,
2014; Sutskever et al., 2014), and produce context-
dependent word representations h = {h
1
, h
2
, . . . , h
n
},
as h
i
consists of concatenations of
−→
h
i
and
←−
h
i
, the for-
ward and backward hidden states of the encoder, re-
spectively. The encoder output of the last time step,
h
n
, is further weighted to enter a softmax activation
function that renders the output probability distribu-
tion of comments, and produces no-abuse and abuse
classification labels for each.
3 TRANSFER LEARNING
Knowledge transfer in a neural model encourages the
sharing of statistical network regularities to help alle-
viate potential overfitting due to a large number of hy-
perparameters. In their recent work, Mou et al. (2016)
have made the observation that whether a neural net-
work is effectively transferable in NLP applications
depends largely on how semantically close the source
and target tasks are. We note that in our model, word
embeddings pretrained on large external corpora are
likely to be transferable even to semantically distant
tasks. Additionally, they assert that the output layer
of the underlying neural architecture is largely dataset
specific and thus not transferable. Motivated by their
results, this work explores two transfer learning sce-
narios, domain adaptation and domain matching, both
perceived from a low-resource target domain. We hy-
pothesize that these methods are plausible to achieve
performance comparable to in-domain baselines.
In the first transfer scenario, we investigate the
prospect of taking an existing AD model formerly
trained on large amount of data from one domain, and
finetune its network parameters on a small number
of examples in another domain (Figure 2a). The lat-
ter scenario merges the rich data from the source do-
main with the scarce data from the target domain and
concurrently trains samples in both domains (Figure
ICAART 2019 - 11th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
114
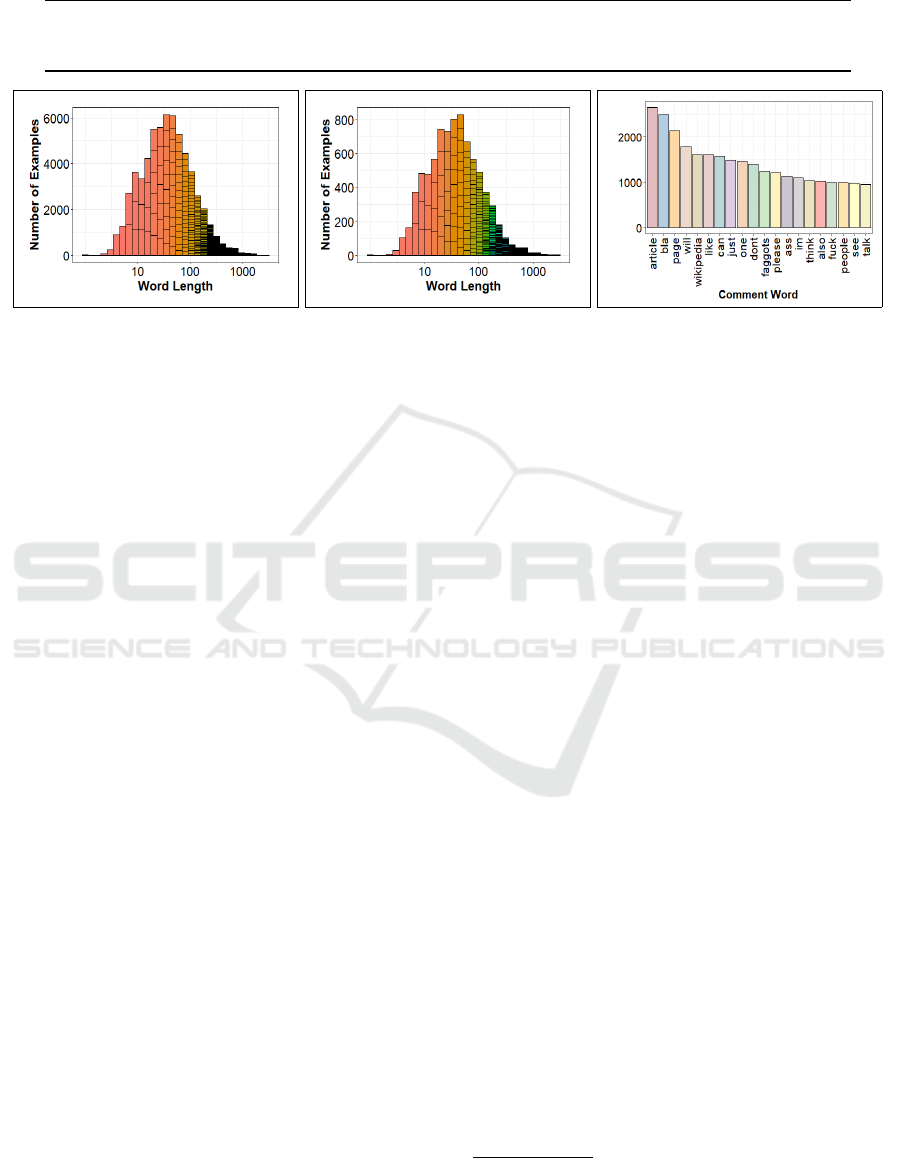
Table 1: Wikipedia Detox: comment distribution across train, development, and test sets.
No-attack Attack Total Min Length Max Length Mean Length
train 61,343 8,182 69,525 1 2,833 70.4
dev 20,429 2,731 23,160 1 2,376 69.7
test 20,501 2,677 23,178 1 2,500 71.5
(a) No-Attack Comments (b) Attack Comments (c) Vocabulary
Figure 3: Wikipedia Detox dataset: train set histograms of logarithmic-scaled word length across (a) no-attack annotated
comments and (b) comments labeled attack, and (c) vocabulary distribution of top-20 frequent tokens.
2b). To ensure a statistically balanced comment pres-
ence of the source and target domains, required for the
stochastic training process, we oversample the data of
the low-resource domain (Chu et al., 2017a).
The transfer learning methods we chose differ pri-
marily in the applied training protocol. In the domain
adaptation pipeline, training progresses in two stages.
Weights are randomly initialized first and trained next
on the out-domain using the large source dataset. We
then initialize the network with the weights learned
previously and trained on the out-domain to finetune
some of the weights using the sparse target dataset.
Our in-domain abuse dataset is already annotated and
hence we made the finetuning step an integral part of
our framework. Domain matching, on the other hand,
trains comment samples drawn from both the source
and target datasets simultaneously. In a one-time pre-
process, the low-resource in-domain is oversampled
to match the dimensionality of the resource rich out-
domain. We then alternate between the domains and
randomly select a data sample from either domain to
compute its gradient. The out-in trained weights we
generate in this process follow finetuning and are used
on the in-domain test set for abuse classification.
Combining domain adaptation and domain match-
ing is a reasonable knowledge transfer proposition we
further address in our evaluation analysis.
4 EXPERIMENTAL SETUP
In this section, we summarize the datasets we used in
our experiments and quantify their semantic relation-
ship. We review parameter settings for our model ar-
chitecture, and provide training details for the various
transfer learning methods we studied.
4.1 Wikipedia Detox
The Wikipedia Detox project
1
is part of Google’s Jig-
saw Conversation AI project
2
, and provides a high-
quality human-curated dataset of one million crowd-
sourced annotations for disciplines including personal
attacks, aggression, and toxicity. Annotated discourse
were obtained from 100K English Wikipedia talk-
pages with at least ten judgments per page (Wulczyn
et al., 2017). The data was sampled from a corpus
of 63 million comments processed from Wikipedia
online discussions related to user pages and articles
dated from 2001 to 2015. A classifier is then trained
on the human-labeled dataset and machine annotates
the entire corpus of comments. In our work, we chose
the human-curated Wikipedia personal-attack corpus
as the source for knowledge transfer that allows us to
reference out-domain model behavior in existed re-
search (Wulczyn et al., 2017; Chu et al., 2017b).
We randomly partitioned the English Wikipedia
dataset into train, development, and test splits using
a 3:1:1 ratio. The dataset consists of 115,863 com-
ments, 69,525 of which are used for training, 23,160
for development, and 23,178 for the test set (Table
1). Each comment was labeled by at least ten differ-
ent crowdsource annotators and categorized into one
of four different attack groups namely quoting, recip-
ient, third party, and other. A given comment might
be flagged by the same annotator for multiple attack
1
https://meta.wikimedia.org/wiki/Research:Detox
2
https://jigsaw.google.com/projects/#conversation-ai
LSTM Neural Networks for Transfer Learning in Online Moderation of Abuse Context
115
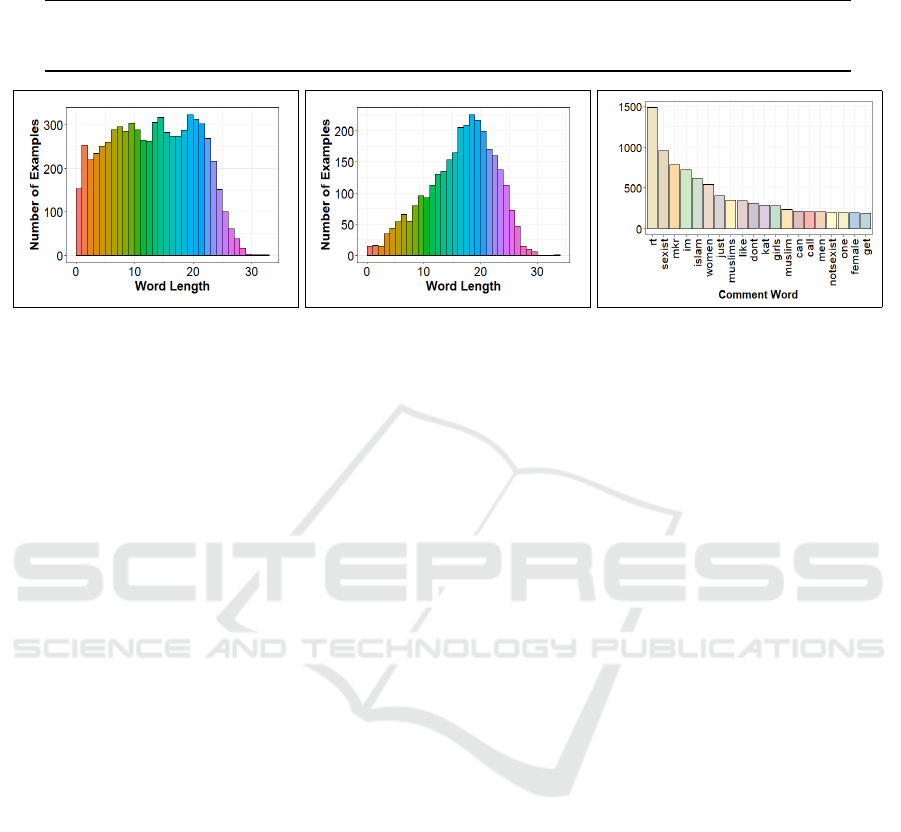
Table 2: Twitter Hate Speech: tweet distribution across train, development, and test sets.
No-Hateful Racism Sexism Total Min Length Max Length Mean Length
train 6,894 1,176 1,882 9,952 1 34 14.7
dev 2,309 394 630 3,333 1 30 14.6
test 2,287 390 624 3,301 1 31 14.8
(a) No-Hateful Tweets (b) Hateful Tweets (c) Vocabulary
Figure 4: Twitter Hate Speech dataset: train set histograms of word length across (a) no-hateful annotated tweets and (b)
hateful labeled tweets, and (c) vocabulary distribution of top-20 frequent tokens.
groups and is defined as a personal attack based on the
majority of attack ratings among the top-10 selected
judgments. On average, about 12 percentage points of
comments from each of the data splits were labeled
as attack (Table 1). In our work, we tag a comment
as either no-attack or attack and consider identifying
personal attacks in discourse as a two-class text clas-
sification task that we map onto a BiLSTM network.
The train set distribution of sequence lengths for
no-attack and attack labeled comments are shown on
a logarithmic scale in Figures 3a and 3b, respectively.
Histogram patterns are fairly resembling for both be-
nign and offensive type comments, with a comment
size that averages about 70 words and tops at 2,833
tokens (Table 1). This data is useful to understand our
model complexity for feeding sequential text into the
BiLSTM network. Figure 3c provides vocabulary dis-
tribution of twenty most frequently occurring terms in
the Wikipedia dataset, yet on their own, most are not
qualified to assess insult in comments.
4.2 Twitter Hate Speech
The Twitter Hate Speech dataset (Waseem and Hovy,
2016) was sampled from 136,052 tweets collected
from hundreds of users over a two-month period.
Bootstrapped from a small sample of frequently oc-
curring terms and slurs in hateful speech, the collec-
tion process used the public Twitter Search API to
construct the entire corpus, while filtering for non-
English tweets. The data was manually annotated for
hateful speech using a succinct decision list of easily
identified observations, and further reviewed objec-
tively to alleviate annotator bias. In total, the dataset
comprises 16,586 annotated tweets of which 1,960 are
labeled as racist content, 3,136 as sexist, and 11,490
are neutral. To evaluate our model, we randomly di-
vided each of the annotation classes into a 3-way data
split for the train, development, and test sets, as shown
in Table 2. We treat the problem of recognizing hate-
ful speech in social media tweets as a binary classi-
fication task, by concatenating the racist and sexist
short-text sequences into a single hateful speech cat-
egory. We note that about 30% of the dataset tweets
are tagged hateful.
The train set distribution of word lengths for both
no-hateful and hateful flagged tweets are shown in
Figures 4a and 4b, respectively. Despite the uniform
average tweet size of 15 words across all the data
splits, word lengths appear more evenly distributed
for tweets of no-hateful speech compared to the ones
tagged as hateful. The top-20 vocabulary terms occur-
ring most frequently in tweets (Figure 4c), evidently
require additional surrounding context to conclusively
identify hateful speech in tweets. In our experiments,
we used the Twitter dataset as the target for transfer
learning, since it is at a much smaller data scale when
contrasted with the Wikipedia domain.
4.3 Semantic Similarity
One of the prerequisites to a non-negative knowledge
transfer in NLP tasks is to ensure semantic relatedness
between the source and target domains (Mou et al.,
2016). In this section, we discuss our generalized
approach to quantitatively evaluate semantic close-
ness of a pair of textual datasets with arbitrary word
counts. To this extent, we leveraged our word embed-
ICAART 2019 - 11th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
116

Table 3: Training stage dispatch across the source and target BiLSTMs, as a function of the underlying domain operator.
BiLSTM
Domain Operator
Adaptation Matching Adaptation-Matching Matching-Adaptation
Source
Wikipedia Wikipedia+Twitter Wikipedia Wikipedia+Twitter
Wikipedia+Twitter Wikipedia
Target Twitter Twitter Twitter Twitter
dings representation and flattened both the source and
target datasets to a linear set of word vectors we de-
note a
(s)
= {c
x
}
l
i=1
and a
(t)
= {c
x
}
k
i=1
, respectively.
We explored a concept that allows us to compute sim-
ilarity more flexibly than with just a dot product, by
expanding on the Chebychev distance between a pair
of matrices with non-conformant dimensionality, de-
fined by the formula
d(s, t) =
1
a
(s)
∑
j
max
i
sim(a
(s)
j
, a
(t)
i
)
,
where |a
(s)
| is the dataset cardinality that amounts to
the total number of distributed word vectors for repre-
senting the dataset, and |a
(s)
| 6= |a
(t)
|. Whereas sim()
is a similarity function that operates on two word vec-
tors and takes either a Euclidean or an angle form.
We chose cosine similarity (Baeza-Yates and Ribeiro-
Neto, 1999) that performs an inner product on a pair
of normalized vectors u and v,
u·v
T
kuk
2
kvk
2
, and returns a
scalar value as a measure of proximity.
After flattening each of the Wikipedia and Twit-
ter abuse datasets to a continuous set of word em-
beddings, we computed an inter-domain semantic dis-
tance of about 0.83. This appears a reasonably high
similarity score in a [0, 1] range, despite the striking
context difference between the abuse disciplines we
used, namely personal attacks and harassment.
4.4 Training
In our experiments, we used distinct source and target
BiLSTM networks that cooperate in conducting pro-
gressive training in either one, two, or three stages.
Based on the knowledge transfer mode, we train the
source BiLSTM model on either the Wikipedia train
dataset or concurrently on the Wikipedia and Twit-
ter train sets, with tweets of the latter oversampled
to match the dimensionality of the Wikipedia dataset.
The target BiLSTM is subsequently initialized with
network weights learned on the source BiLSTM, and
optionally follows finetuning of a subset of network
settings on the Twitter train set. In practice, our im-
plementation invokes a sequence of training stages
over the source and target BiLSTMs that is prescribed
by the various domain operators for transfer learning,
and are illustrated in Table 3.
As a one-time preprocess, all comments from both
the Wikipedia and Twitter datasets were tokenized
and lowercased using R (R Core Team, 2013). Word
embeddings were initialized with 200-dimensional
GloVe vectors (Pennington et al., 2014) pretrained on
large 6B token corpora including English Wikipedia
dumps and GigaWord newswire text
3
. As the largest
300-sized vectors resulted in a diminishing perfor-
mance return. Uniformly, all embeddings of unknown
tokens are set to zero, and the combined source and
target domains use a vocabulary size of 54,949 words.
We used BiLSTMs with 200 memory cells in the
hidden layer for the source domain, and 100 mem-
ory cells for the low-resource target domain that is
less memory intensive. We have trained both the AD
source and target models with the Adam stochastic
gradient optimizer (Kingma and Ba, 2014) using its
provided default settings with a mini-batch size of
128 examples. In a batch, sequences of embeddings
are expected of the same length, and are hence either
clipped or padded to the mean and maximal length
of Wikipedia comments (Table 1) and Twitter tweets
(Table 2), respectively. Hyperparameters in the form
of weight matrices and bias vectors were bootstrapped
using Xavier initialization (Glorot and Bengio, 2010)
and are further tuned in the validation phase. In total,
our model has over two million parameters of which
161,202 are trainable.
To avoid overfitting, we regularized our networks
by applying dropout (Srivastava et al., 2014) with a
rate of 0.2 probability for randomly switching off con-
nections between the input and hidden layers during
training. Additionally, our model supports early ter-
mination of training by observing, after each epoch,
the rate-of-change of both the loss and the quality of
abuse detection on the participating development sets
of either the source, target, or both domains, as out-
lined in the currently executed train stage (Table 3).
Dropout and early stop of training were sufficient to
reduce overfitting in our model, with a difference be-
tween training and development F1 scores of less than
five percentage points before convergence.
As part of the analysis we conducted, we mon-
itored after each epoch both the cross-entropy error
and performance as the stochastic training and vali-
3
https://nlp.stanford.edu/projects/glove/
LSTM Neural Networks for Transfer Learning in Online Moderation of Abuse Context
117

0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Epoch
Loss
training
validation
(a) No Transfer Learning
0.2
0.4
0.6
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Epoch
Loss
training
validation
(b) Domain Adaptation
0.2
0.4
0.6
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Epoch
Loss
training
validation
(c) Domain Matching
Figure 5: Contrasting training with validation loss behavior for transfer learning: showing loss as a function of epoch pro-
gression for (a) no knowledge transfer, (b) domain adaptation, and (c) domain matching scenarios.
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Epoch
F1
training
validation
(a) No Transfer Learning
0.80
0.85
0.90
0.95
1.00
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Epoch
F1
training
validation
(b) Domain Adaptation
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Epoch
F1
training
validation
(c) Domain Matching
Figure 6: Contrasting training with validation performance for transfer learning: showing F1 score as a function of epoch
progression for (a) no knowledge transfer, (b) domain adaptation, and (c) domain matching scenarios.
dation processes progress iteratively. We show train-
ing and validation plots of our model loss and perfor-
mance for the first ten epochs in Figure 5 and Figure 6,
respectively. As corresponding split sets of the Twit-
ter target, Wikipedia source, and combined source
and oversampled target are used for (a) no knowl-
edge transfer, (b) domain adaptation, and (c) domain
matching scenarios, respectively. Apart from domain
adaptation mode that shows almost identical training
and validation performance for the first seven epochs,
our performance plots mostly depict a desired behav-
ior with validation scores slightly lower than the train-
ing scores. These results strongly support the network
regularization steps we incorporated to alleviate po-
tential data overfitting to the various training sets.
We chose to report F1 score for our metrics,
consistent with the published non-transferable target
baseline (Waseem and Hovy, 2016).
5 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
We analyzed our model performance for each of the
basic transfer-learning schemes we laid out, namely
domain adaptation and domain matching, and in ad-
dition we evaluated the performance impact of fus-
ing the pair of basic methods in a two-stage training
sequence. The fusion of the principal domain oper-
ators is inherently directional and thus has adapta-
tion either precede or trail domain matching in the
training cascade. Table 3 illustrates the order of train
events that occur in fusing adaptation and matching.
In adaptation-matching mode, we first train our model
on the source Wikipedia dataset, and then resume
training on both the Wikipedia and Twitter domains.
As the matching-adaptation process, swaps the former
train stages. In total, we explored four domain opera-
tors for experimenting with transfer learning, and for
each we optionally invoked a final step of finetuning
a subset of network parameters before evaluating the
low-resource domain on the target test set.
In our work, we used Keras (Chollet et al., 2015),
a high-level deep learning interface that runs on top of
the TensorFlow
4
software library for executing high-
performance numerical computation on a variety of
platforms. Keras attractive quality of saving and load-
ing the entire history of a pretrained neural-network
4
https://www.tensorflow.org/
ICAART 2019 - 11th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
118

Table 4: In-domain baseline performance: F1 scores for
a logistic regression classifier with word and character n-
gram representations (Waseem and Hovy, 2016), and for our
BiLSTM model without transfer learning.
Model Baseline F1
Feature Based
word n-gram features 0.65
character n-gram features 0.74
BiLSTM no transfer learning 0.79
model, played a pivotal role in our paradigm that dis-
patches multi-stage training, as illustrated in Table 3.
Moreover, training can be set to resume at a user spec-
ified epoch and thus aid in boosting performance. In
Keras early stopping, we set the threshold to quantify
validation loss improvement or not to zero, and the
patience parameter to two epochs with no observed
improvement, after which training will be terminated.
We first provide in-domain baseline performance
over the Twitter target dataset. In Table 4, we contrast
a logistic regression classifier that uses both word and
character n-gram representations (Waseem and Hovy,
2016) to our BiLSTM network stripped of knowledge
transfer capacity. Our word embedding based neural-
model achieved 0.79 F1 score and outperforms the
manual feature-based system with F1 of 0.65 and 0.74
for word and character n-grams, respectively.
Next, we report our AD model performance of
out-domain transfer learning for the basic and fused
domain operators. In Table 5, we show both our raw
and finetuned F1 scores, for each scenario. Our top-
most scoring operator is domain matching with a raw
F1 score of 0.77, only slightly under our in-domain
baseline with an F1 rate of 0.79 (Table 4), and out-
performing out-domain baseline performance of the
LSTM model used in Chu et al. (2017b), by about
nine percentage points. On the other hand, basic do-
main adaptation scores the lowest with a raw F1 score
of 0.68. Evidenced by the scores of individual seg-
ments, the linking of basic domain operators appears
to have little impact on our model performance, with
observed F1 scores of 0.75 and 0.69 for adaptation-
matching and matching-adaptation, respectively. We
note that the non-leading domain operator of a fused
pair, matching in adaptation-matching and adaptation
in matching-adaptation, dominates the outcome rate
of the model, and hence the obtained F1 scores are
comparable to the respective basic operators. The op-
tional training step of finetuning a subset of target net-
work parameters has a larger performance impact on
domain adaptation, yet it affects the matching oper-
ator end-result only mildly, as shown in Table 5. In
all, finetuned F1 scores across domain operators are
almost on par.
Conceptually, in transfer learning from a large-
resource domain to a small domain data, we per-
Table 5: Wikipedia to Twitter transfer learning perfor-
mance: F1 scores for our basic and fused domain operators
configured with and without finetuning.
Domain Operator Raw F1 Finetuned F1
adaptation 0.68 0.76
matching 0.77 0.77
adaptation-matching 0.75 0.73
matching-adaptation 0.69 0.75
ceive training as a stochastic process applied to pairs
of samples chosen alternately from the source and
the target domains, with the latter conditioned by a
given probability p. Hence in domain adaptation form
we let p = 0 and all samples are drawn from the
source domain. Whereas p = 1 for domain matching
that uses balanced source and target data through in-
domain oversampling, by generating an l-sized vector
of random permutation of replicating indices ∈ (1, k).
Moreover, this warrants that all examples of both the
source and target datasets are sampled. However, us-
ing fractional probabilities p ∈ (0, 1) to compute the
example gradient may not uphold robust sampling
(Mou et al., 2016). Barring the finetuning step, we
expected adaptation to perform lower due to absolute
out-domain learning compared to the matching sce-
nario that evens the distribution of in and out domain
data. Thus our corresponding F1 scores of 0.68 and
0.77, appear entirely explicable.
Although the fused and basic domain operators
performed practically identical, compound transfer
learning incurs an appreciable runtime cost of train-
ing that is often overlooked. Since training time com-
plexity is about linear with the number of examples
in the dataset, by letting domain adaptation train in a
normalized unit time, domain matching would hence
train twice as slow, and each of the fused operators
would triple the basic training time.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we have explored transfer learning from
a large corpus to a low-resource domain for the task
of abuse detection in online discourse. We conducted
our experiments under the interesting adaptation and
matching scenarios over source and target datasets
from orthogonal domains. We showed that the match-
ing domain operator is most effective and performs
just slightly lower than the in-domain baseline, as
our neural network model is pretrained on the large
source dataset mixed with an oversampled small tar-
get data. Fusing adaptation and matching methods,
revealed however inconsequential performance gains
over independent domain operators.
Despite the practical importance for the public at-
LSTM Neural Networks for Transfer Learning in Online Moderation of Abuse Context
119

large to benefit from curbing abusive language on-
line, high cost linguistic annotation and resource cre-
ation are unlikely to be undertaken in the near future.
Our contribution is intended to ameliorate the scarcity
of large datasets that presently hinders advancement
toward the ultimate automation of early intervention
and moderation of offensive posts. To the extent of
our knowledge, this paper is first to introduce trans-
fer learning for the task of insult detection in com-
ments. Our work motivates the curating of a multi-
tude of low-resource abuse corpora that is substan-
tially less time consuming, in conjunction with only a
few, more elaborate large datasets.
A direct progression of our work is expanding our
AD model to use an ensemble of low-resource tar-
get datasets for each abuse discipline, and improve
robustness of knowledge transfer. This will also facil-
itate discipline centered multi-class classification to-
wards a more fine-grained abuse moderation. Extend-
ing our model input representation to character em-
beddings and better address unedited and slang-filled
toxic comments is one plausible approach to boost our
classification performance. To mitigate the high spar-
sity of abuse data in foreign languages, we plan to
incorporate an NMT model that translates in-domain
data to English first. Efficient integration of the at-
tention based sequence-to-sequence network, used for
language translation, and our transfer learning model
provides streamlined abuse detection in multi-lingual
knowledge-transfer setting.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for
their insightful suggestions and feedback.
REFERENCES
Baeza-Yates, R. and Ribeiro-Neto, B., editors (1999). Mod-
ern Information Retrieval. ACM Press Series/Addison
Wesley, Essex, UK.
Cho, K., van Merrienboer, B., Bahdanau, D., and Ben-
gio, Y. (2014). On the properties of neural machine
translation: Encoder-decoder approaches. CoRR,
abs/1409.1259. http://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1259.
Choi, K., Fazekas, G., Sandler, M. B., and Cho, K. (2017).
Transfer learning for music classification and regres-
sion tasks. CoRR, abs/1703.09179. http://arxiv.org/
abs/1703.09179.
Chollet, F. et al. (2015). Keras. https://keras.io.
Chu, C., Dabre, R., and Kurohashi, S. (2017a). An em-
pirical comparison of domain adaptation methods for
neural machine translation. In Proceedings of the
55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computa-
tional Linguistics (ACL), pages 385–391, Vancouver,
Canada. Association for Computational Linguistics.
Chu, T., Jue, K., and Wang, M. (2017b). Comment abuse
classification with deep learning. Technical report,
Stanford University. http://web.stanford.edu/class/
cs224n/reports/2762092.pdf.
Chung, J., G
¨
ulc¸ehre, C¸ ., Cho, K., and Bengio, Y. (2014).
Empirical evaluation of gated recurrent neural net-
works on sequence modeling. CoRR, abs/1412.3555.
http://arxiv.org/abs/1412.3555.
Davidson, T., Warmsley, D., Macy, M. W., and We-
ber, I. (2017). Automated hate speech detection
and the problem of offensive language. CoRR,
abs/1703.04009. http://arxiv.org/abs/1703.04009.
Donahue, J., Hendricks, L. A., Rohrbach, M., Venugopalan,
S., Guadarrama, S., Saenko, K., and Darrell, T.
(2017). Long-term recurrent convolutional networks
for visual recognition and description. IEEE Trans-
actions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,
39(4):677–691.
dos Santos, C. and Gatti, M. (2014). Deep convolu-
tional neural networks for sentiment analysis of short
texts. In Proceedings of COLING 2014, the 25th
International Conference on Computational Linguis-
tics: Technical Papers, pages 69–78, Dublin, Ireland.
Dublin City University and Association for Computa-
tional Linguistics.
Elman, J. L. (1990). Finding structure in time. Cognitive
Science, 14(2):179–211.
Esteva, A., Kuprel, B., Novoa, R. A., Ko, J., Swetter, S. M.,
Blau, H. M., and Thrun, S. (2017). Dermatologist-
level classification of skin cancer with deep neural net-
works. Nature, 542(7639):115–118.
Fan, X., Monti, E., Mathias, L., and Dreyer, M. (2017).
Transfer learning for neural semantic parsing. In
Proceedings of the 2nd Workshop on Representation
Learning for NLP, pages 48–56, Vancouver, Canada.
Association for Computational Linguistics.
Fi
ˇ
ser, D., Ljube
ˇ
si
´
c, N., and Erjavec, T. (2017). Legal frame-
work, dataset and annotation schema for socially un-
acceptable online discourse practices in slovene. In
Proceedings of the First Workshop on Abusive Lan-
guage Online, pages 46–51, Vancouver, Canada.
Gamb
˜
ack, B. and Sikdar, U. K. (2017). Using convolutional
neural networks to classify hate-speech. In Proceed-
ings of the First Workshop on Abusive Language On-
line, pages 85–90, Vancouver, Canada.
Glorot, X. and Bengio, Y. (2010). Understanding the diffi-
culty of training deep feedforward neural networks. In
Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, pages 249–256,
Sardinia, Italy.
Golub, D., Huang, P.-S., He, X., and Deng, L. (2017).
Two-stage synthesis networks for transfer learning in
machine comprehension. In Empirical Methods in
Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), pages 835–
844, Copenhagen, Denmark. Association for Compu-
tational Linguistics.
Hochreiter, S. and Schmidhuber, J. (1997). Long short-term
memory. Neural Computation, 9(8):1735–1780.
ICAART 2019 - 11th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
120

Huang, M., Cao, Y., and Dong, C. (2016). Model-
ing rich contexts for sentiment classification with
LSTM. CoRR, abs/1605.01478. http://arxiv.org/abs/
1605.01478.
Huh, M., Agrawal, P., and Efros, A. A. (2016). What
makes ImageNet good for transfer learning? CoRR,
abs/1608.08614. http://arxiv.org/abs/1608.08614.
Impermium (2013). Dataset for detecting insults in social
commentary. https://www.kaggle.com/c/detecting-
insults-in-social-commentary/data.
Joshi, G. and Chowdhary, G. (2018). Cross-domain trans-
fer in reinforcement learning using target appren-
tice. CoRR, abs/1801.06920. http://arxiv.org/abs/
1801.06920.
Kim, J.-K., Kim, Y.-B., Sarikaya, R., and Fosler-Lussier,
E. (2017). Cross-lingual transfer learning for POS
tagging without cross-lingual resources. In Empirical
Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP),
pages 2832–2838, Copenhagen, Denmark. Associa-
tion for Computational Linguistics.
Kim, Y. (2014). Convolutional neural networks for sentence
classification. In Proceedings of the 2014 Conference
on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Process-
ing (EMNLP), pages 1746–1751, Doha, Qatar. Asso-
ciation for Computational Linguistics.
Kingma, D. P. and Ba, J. (2014). Adam: A method for
stochastic optimization. CoRR, abs/1412.6980. http:
//arxiv.org/abs/1412.6980.
Kolhatkar, V. and Taboada, M. (2017). Constructive lan-
guage in news comments. In Proceedings of the First
Workshop on Abusive Language Online, pages 11–17,
Vancouver, BC, Canada.
Krishnamoorthy, P., MacQueen, R., and Schsuter,
S. (2017). Detecting insults in online com-
ments. Technical report, Stanford University.
http://www.rorymacqueen.org/wp-content/uploads/
2017/07/cs224u report4.pdf.
Kunze, J., Kirsch, L., Kurenkov, I., Krug, A., Johannsmeier,
J., and Stober, S. (2017). Transfer learning for speech
recognition on a budget. In Proceedings of the 2nd
Workshop on Representation Learning for NLP, pages
168–177, Vancouver, Canada. Association for Com-
putational Linguistics.
Kwok, I. and Wang, Y. (2013). Locate the hate: Detecting
tweets against blacks. In Conference on Artificial In-
telligence (AAAI), pages 1621–1622, Bellevue, Wash-
ington. AAAI Press, Palo Alto, California.
Lee, J. Y. and Dernoncourt, F. (2016). Sequential short-
text classification with recurrent and convolutional
neural networks. In Human Language Technologies:
North American Chapter of the Association for Com-
putational Linguistics (NAACL), pages 515–520, San
Diego, California.
Liu, P., Qiu, X., and Huang, X. (2017). Adversarial multi-
task learning for text classification. In Proceedings of
the 55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Com-
putational Linguistics (ACL), pages 1–10, Vancouver,
Canada. Association for Computational Linguistics.
Mou, L., Meng, Z., Yan, R., Li, G., Xu, Y., Zhang, L., and
Jin, Z. (2016). How transferable are neural networks
in nlp applications? In Proceedings of the Conference
on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Process-
ing (EMNLP), pages 479–489, Austin, Texas. Associ-
ation for Computational Linguistics.
Oquab, M., Bottou, L., Laptev, I., and Sivic, J. (2014).
Learning and transferring mid-level image represen-
tations using convolutional neural networks. In Pro-
ceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision
and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pages 1717–1724,
Washington, DC, USA. IEEE Computer Society.
Pan, S. J. and Yang, Q. (2010). A survey on transfer learn-
ing. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data En-
gineering, 22(10):1345–1359.
Pavlopoulos, J., Malakasiotis, P., and Androutsopoulos, I.
(2017). Deep learning for user comment moderation.
In Proceedings of the First Workshop on Abusive Lan-
guage Online, pages 25–35, Vancouver, Canada.
Pennington, J., Socher, R., and Manning, C. D. (2014).
GloVe: Global vectors for word representation. In
Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing
(EMNLP), pages 1532–1543, Doha, Qatar.
Pew (2017). The future of free speech, trolls, anonymity
and fake news online. Technical report, Pew Research
Center. www.pewinternet.org/2017/03/29/the-future-
of-free-speech-trolls-anonymity-and-fake-news-
online/.
Poland, B. (2016). Haters: Harassment, Abuse, and Vio-
lence Online. Potomac Books, Lincoln, Nebraska.
Prates De Pelle, R. and Moreira, V. P. (2017). Offensive
comments in the brazilian web: a dataset and base-
line results. In Brazilian Workshop on Social Net-
work Analysis and Mining (BRASNAM), pages 510–
519, S
˜
au Paulo, Brazil.
Qian, Q., Huang, M., Lei, J., and Zhu, X. (2017). Lin-
guistically regularized lstm for sentiment classifica-
tion. In Proceedings of the 55th Annual Meeting of
the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL),
pages 1679–1689, Vancouver, Canada. Association
for Computational Linguistics.
R Core Team (2013). R: A Language and Environment
for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Sta-
tistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. http://www.R-
project.org/.
Ross, B., Rist, M., Carbonell, G., Cabrera, B., Kurowsky,
N., and Wojatzki, M. (2016). Measuring the reliability
of hate speech annotations: The case of the european
refugee crisis. In 3rd Workshop on Natural Language
Processing for Computer-Mediated Communication,
pages 6–10, Bochum, Germany.
Ruder, S. and Plank, B. (2017). Learning to select data
for transfer learning with bayesian optimization. In
Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing
(EMNLP), pages 372–382, Copenhagen, Denmark.
Association for Computational Linguistics.
Russakovsky, O., Deng, J., Su, H., Krause, J., Satheesh,
S., Ma, S., Huang, Z., Karpathy, A., Khosla, A.,
Bernstein, M., Berg, A. C., and Fei-Fei, L. (2015).
ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge.
International Journal of Computer Vision (IJCV),
115(3):211–252.
LSTM Neural Networks for Transfer Learning in Online Moderation of Abuse Context
121

Saleem, H. M., Dillon, K. P., Benesch, S., and Ruths, D.
(2017). A web of hate: Tackling hateful speech in
online social spaces. CoRR, abs/1709.10159. http:
//arxiv.org/abs/1709.10159.
Salton, G. M., Wong, A., and Yang, C. S. (1975). A vector
space model for automatic indexing. Communications
of the ACM, 18(11):613–620.
Schuster, M. and Paliwal, K. K. (1997). Bidirec-
tional recurrent neural networks. Signal Processing,
45(11):2673–2681.
Sood, S. O., Churchill, E. F., and Antin, J. (2012). Auto-
matic identification of personal insults on social news
sites. American Society for Information Science and
Technology,, 63(2):270–285.
Srivastava, N., Hinton, G., Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I.,
and Salakhutdinov, R. (2014). Dropout: A simple way
to prevent neural networks from overfitting. Machine
Learning Research, 15(1):1929–1958.
Sutskever, I., Vinyals, O., and Le, Q. V. (2014). Se-
quence to sequence learning with neural networks. In
Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems
(NIPS), pages 3104–3112. Curran Associates, Inc.,
Red Hook, NY.
Waseem, Z. and Hovy, D. (2016). Hateful symbols or
hateful people? predictive features for hate speech
detection on twitter. In Human Language Technolo-
gies: North American Chapter of the Association
for Computational Linguistics (NAACL), Student Re-
search Workshop, pages 88–93, San Diego, Califor-
nia.
Wulczyn, E., Thain, N., and Dixon, L. (2017). Ex Machina:
Personal attacks seen at scale. CoRR, abs/1610.08914.
http://arxiv.org/abs/1610.08914.
Yenala, H., Chinnakotla, M. K., and Goyal, J. (2017). Con-
volutional bi-directional LSTM for detecting inappro-
priate query suggestions in web search. In Advances
in Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pages 3–
16, Jeju, South Korea.
Yin, D., Xue, Z., Hong, L., Davison, B. D., Kontostathis,
A., and and, L. E. (2009). Detection of harassment
on Web 2.0. In Workshop on Content Analysis in Web
2.0, pages 1–7, Madrid, Spain.
Yogatama, D., Dyer, C., Ling, W., and Blunsom, P. (2017).
Generative and discriminative text classification with
recurrent neural networks. CoRR, abs/1703.01898.
https://arxiv.org/abs/1703.01898v2.
Zoph, B., Yuret, D., May, J., and Knight, K. (2016). Trans-
fer learning for low-resource neural machine transla-
tion. In Empirical Methods in Natural Language Pro-
cessing, (EMNLP), pages 1568–1575, Austin, Texas.
Association for Computational Linguistics.
ICAART 2019 - 11th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
122
