
Two-dimensional Laser Scanner with Low Mechanical Cross
Coupling based on Piezoelectric Actuators
Chen Wei
1
, Luo Dong
2
, Liang Yuanbo
3
, Liu Peng
1
, Chen Liangpei
1
and Zhang Yizhou
1
1
Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 1068 Xueyuan Avenue, Shenzhen, China
2
Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
3
School of Microelectronics, Xidian University, Xi’an, China
Keywords: Laser Scanner, Piezoelectric Actuators, Mechanical Cross Coupling, Hysteresis Compensation.
Abstract: Traditional two-dimensional laser scanners usually employ two-degree-of-freedom flexible hinges.
However, these flexible hinges suffer from mechanical cross coupling between axes, which will reduce the
scanning accuracy and stability. To overcome the above disadvantages, a compact novel laser scanner based
on piezoelectric actuators is presented. The scanner uses only three one-dimensional flexible hinges to
achieve two-axis feature. The mechanical structure and principle are detailed. Then the capabilities of the
scanner are tested by a performance test system. The test results show that the scanner has a tilt angle of
43.19 mrad for X-axis with resonance frequency at 149.21 Hz and 2.41 mrad for Y-axis with resonance
frequency at 232.59 Hz. Its scanning nonlinearity is reduced from 3% to 0.5% for X-axis and from 6% to
1% after compensation. The test results and the actual scanning images prove the low mechanical cross
coupling.
1 INTRODUCTION
Due to high precision, fast response, large force
output and low power-consumption, amplified
piezoelectric actuators (APAs) are widely applied in
biological engineering, nanofabrication, and robotics
and so on (Bouchilloux et al., 2004, Domke et al.,
2011, Park et al., 2012, Yang et al., 2010).
Especially for laser scanners which can precisely
control the directions of laser beams, APAs are one
of the main driving methods (Sweeney et al., 2002).
In addition to APAs, flexible hinges are also the key
structure for laser scanner. They can withstands
stress and offers deformation when the scanner
works.
Generally, to achieve two-dimensional (2-D)
adjustments of laser beams, two-degree-of-freedom
(2-DoF) flexible hinges have to be used.
Unfortunately, almost all 2-DoF flexible hinges
suffer from mechanical cross coupling between axes.
In other words, motion of one axis can be affected
by the other one, which will significantly reduce the
accuracy and stability of laser scanner (Chen et al.,
2015b, Jing et al., 2015, Shao et al., 2018). Some
scanners employ two 1-D laser scanners to obtain
2-D features (Chen et al., 2015a). However, these
designs increase system complexity and volume.
There are two methods to deal with cross coupling
effect. One is to use decoupling control algorithm,
which is generally difficult to design and implement.
The other one is to reduce the mechanical coupling
ratio. Therefore, a novel structure with small or even
zero interference between axes is strongly demanded.
In this paper, a new two-dimensional laser
scanner based on three APAs is proposed. Through
special mechanical design, the scanner employs only
three 1-DoF flexible hinges to achieve two-
dimensional laser deflection, which can effectively
reduce the cross coupling. The structure and
principle of the scanner are detailed. To investigate
its performance, a test system is built up based on
position sensitive detector (PSD). The test results
show that the scanner has different resonant
frequency in the two axes. The scanning images also
prove the low mechanical cross coupling.
2 STRUCTURE AND PRINCIPLE
Flexible hinges are widely used in precision
positioning. Various geometries of flexible hinges
have been reported and studied (Wu et al., 2018).
Wei, C., Dong, L., Yuanbo, L., Peng, L., Liangpei, C. and Yizhou, Z.
Two-dimensional Laser Scanner with Low Mechanical Cross Coupling based on Piezoelectric Actuators.
DOI: 10.5220/0007360301290133
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Photonics, Optics and Laser Technology (PHOTOPTICS 2019), pages 129-133
ISBN: 978-989-758-364-3
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
129
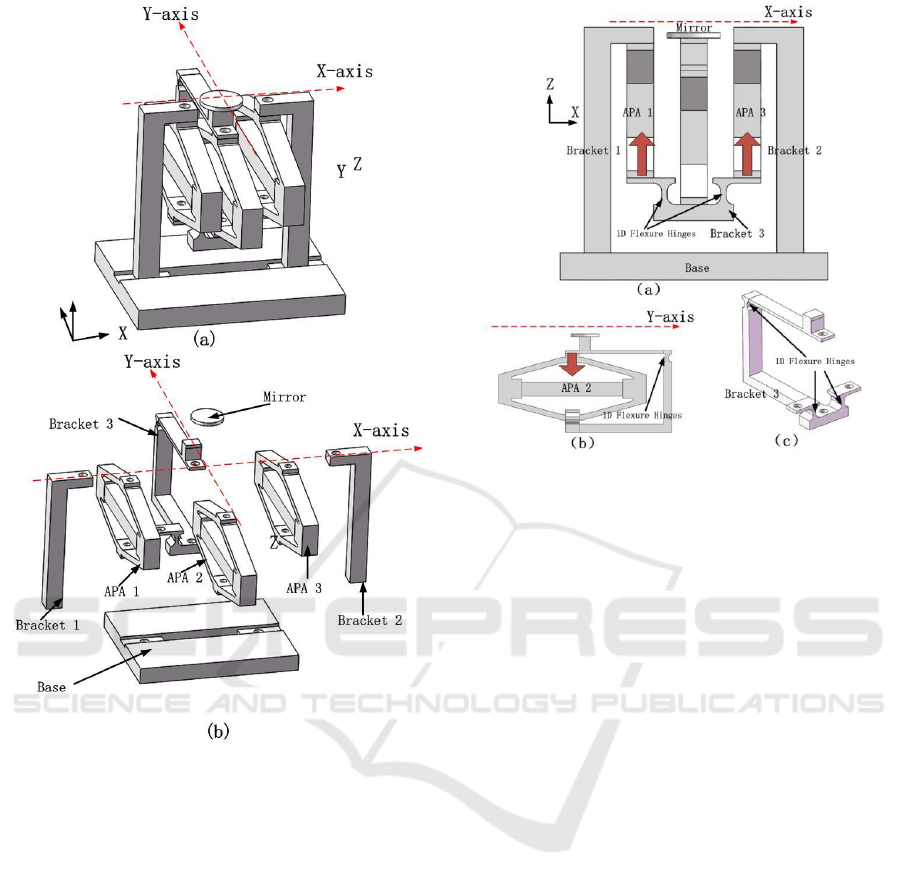
Figure 1: Structure of the scanner, (a) isometric view and
(b) exploded view.
However, mechanical cross coupling of multi-axis
flexible hinges is inevitable. Therefore, 2-D laser
scanner employs flexible hinges suffers from inter-
axis interference.
To overcome the above disadvantages, a novel
structure of laser scanner based on APAs is
introduced, as shown in Fig. 1. Figure 1(a) is the
isometric view of the scanner and Fig. 1(b) shows the
exploded view. The scanner consists of base, three
supports, three APAs and mirror.
Brackets 1 and 2 have same L-shaped features. Their
bottoms are fixed on the base. Two APAs
(P06.X100A, Harbin Core Tomorrow, China) are
fixed with the top edges of the two brackets, of
which their bottoms are connected to brackets 3.
Bracket 3 has a complex heterosexual structure, as
shown in Fig 2(c). APA 3 and mirror are fixed with
it.
Figure 2: Principle of the X-axis deflection (a) and Y-axis
deflection (b) and the structure of bracket 3 (c).
Figure 2 shows the working principle of the
proposed scanner. As shown in Fig 2(a), when
different voltages are applied to APAs 1 and 2, they
will have different displacement in the Z-direction.
Then the bracket 3 will tilt with APA 3 and
mirror in the X-axis. If a voltage is applied to APA 3,
it will have a –z direction displacement and the
mirror will tilt in the Y-axis (Fig. 2(b)). If applying
three different voltages to the APAs, the mirror will
tilt in X-axis and Y- axis simultaneously. Note that
there are only three 1-d flexible hinges on the
bracket 3 and they are working in different
directions. These hinges have no mechanical cross
coupling, as same as the scanner.
After design, the scanner has been manufactured and
assembled.
3 PERFORMCE TEST
3.1 Performance Test System Design
To study the performance of the scanner, a test
system was built up, as shown in Fig. 3. It consists
of a He-Ne laser, a PSD (DRX-2DPSD-0A01-X,
Daruixin, China), a drive circuit and power supply, a
data acquisition card(USB 6361, National
Instrument (NI), USA), and a software system (in
PC).The software system was designed based on
NI’s LABVIEW software. Different control signals
were generated by the software, output by the data
PHOTOPTICS 2019 - 7th International Conference on Photonics, Optics and Laser Technology
130

Figure 3: Performance test sytem.
acquisition card and amplified by the drive circuit.
The circuit can provide maximum voltage of
150volts and power of 30 watts, which enough drive
the scanner to work. Then, the PSD can real-time
detect and output the position information of laser
spot reflected by the scanner, which is collected by
the same data acquisition card. At last, the software
can figure out the performance of scanner, such as
deflection angle, open-loop frequency response,
hysteresis effects and nonlinearity.
3.2 Performance Test
Voltages from 0 volt to 150 volts are applied to the
scanner and the relationship between the deflection
angle and drive voltage is shown in Fig. 4. The
maximum angle of the scanner is 43.19 mrad for X-
axis and 2.41 mrad for Y-axis. It is clear that the
Figure 4: Relationship between the deflection angle and
drive voltage.
scanning angles of both axes are linear to the drive
voltages. The great difference in angles of different
axes may be attributed to the different mechanical
structures. The tilt mechanism of Y-axis needs to be
optimized and improved.
Figure 5: Frequency response of the scanner.
Figure 6: Scanning waveforms of the scanner with a drive
voltage of a 5-Hz triangle wave for X-axis (a) and Y-axis
(b).
Sine waveforms of different frequencies are used
to the scanner to study the dynamic response of the
scanner, as shown in Fig. 5. The first resonant
frequency of X-axis is 149.21 Hz and 232.59 Hz for
Y-axis.
Triangle waves of different frequencies are
applied to the scanner to study its relative
performance, as shown in Fig. 6. It can be found that
the rising line and falling line of the waveform
deviate from standard triangle waveform, which is
caused by the hysteresis effect of the PZT stack in
the APA. The amplitude of the drive triangular
Two-dimensional Laser Scanner with Low Mechanical Cross Coupling based on Piezoelectric Actuators
131

Figure 7: Scanning hysteresis loops of the scanner before
and after compensation and the comparison of
nonlinearities for X-axis and Y-axis.
waveform for Y-axis is much bigger than X-axis.
Hence, the distortion in Fig. 6(b) is larger than Fig. 6
(a).
The hysteresis effect of the piezoelectric ceramic
is originated from its inherent characteristics. In our
previous work, a hysteresis compensation algorithm
is introduced to restrain the hysteresis and proves its
Effectiveness (Sweeney et al., R. 2002). Therefore,
the algorithm is also applied to the scanner in this
paper. As shown in Fig. 7, the nonlinearity
produced by the hysteresis effect is reduced from
3% to 0.5% for X-axis and from 6% to 1%.
Some scanning images (Fig. 8) show single-axis
scans and a 2D scan. The single-axis scans are very
straight thus demonstrating the high linearity and
low inter-axis interference of the scanner. The 2D
image, produced with the x-axis driven by a 30-Hz
sine waveform and the y-axis was driven by a 20-Hz
cosine wave, shows a Lissajous-Figure.
Figure 8: Scanning images of the scanner.
4 CONCLUSIONS
A compact new 2-D laser scanner based on
piezoelectric actuators is designed, prototyped, and
experimentally tested. The scanner proposed a novel
mechanical structure to reduce the mechanical cross
coupling ratio. Different from traditional 2-D laser
scanner, it uses only 1-D flexible hinges to achieve
2-D deflection. A performance test system was built
up to test the capabilities of the prototype scanner. In
addition, a hysteresis compensation algorithm is
applied to the scanner to improve the scanning
linearity. From the test results, the scanner has a tilt
angle of 43.19 mrad for X-axis with resonance
frequency at 149.21 Hz and 2.41 mrad for Y-axis
with resonance frequency at 232.59 Hz. Its scanning
nonlinearity is reduced from 3% to 0.5% for X-axis
and from 6% to 1%. Some actual scanning images
are presented as well.
Some improvement of the scanner, such as structural
optimization for the Y-axis and closed-loop control
technology is undertaking to achieve larger scanning
angle and higher accuracy.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by National Natural
Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61605234)
and Shenzhen Science and Technology
Development Foundation (Grant No.
JCYJ20160531174039457).
REFERENCES
Bouchilloux, P., Claeyssen, F. & Le Letty, R. 2004.
Amplified piezoelectric actuators: From aerospace to
underwater applications. In: ANDERSON, E. H. (ed.)
Smart Structures and Materials 2004: Industrial and
PHOTOPTICS 2019 - 7th International Conference on Photonics, Optics and Laser Technology
132

Commercial Applications of Smart Structures
Technologies.
Chen, W., Chen, S. & Luo, D. 2015a. Design and
experimental investigations of a two-dimensional laser
scanner based on piezoelectric actuators. Optical
Engineering, 54.
Chen, W., Chen, S., Luo, D. & Jiao, G. 2015b. A compact
two-dimensional laser scanner based on piezoelectric
actuators. Review of Scientific Instruments, 86.
Domke, J. F., Rhee, C. H., Liu, Z., Wang, T. D. &
Oldham, K. R. 2011. Amplifying transmission and
compact suspension for a low-profile, large-
displacement piezoelectric actuator. Journal of
Micromechanics and Microengineering, 21.
Jing, Z., Xu, M. & Feng, B. 2015. Modeling and
optimization of a novel two-axis mirror-scanning
mechanism driven by piezoelectric actuators. Smart
Materials and Structures, 24.
Park, J.-H., Lee, H.-S., Lee, J.-H., Yun, S.-N., Ham, Y.-B.
& Yun, D.-W. 2012. Design of a Piezoelectric-Driven
Tilt Mirror for a Fast Laser Scanner. Japanese Journal
of Applied Physics, 51.
Shao, S., Tian, Z., Song, S. & Xu, M. 2018. Two-degrees-
of-freedom piezo-driven fast steering mirror with
cross-axis decoupling capability. Review of Scientific
Instruments, 89.
Sweeney, M., Rynkowski, G., Ketabchi, M. & Crowley,
R. 2002. Design considerations for fast steering
mirrors (FSMs). In: Sagan, S. F., MarshalL, G. F. &
Beiser, L. (eds.) Optical Scanning 2002.
Wu, J., Zhang, Y., Lu, Y., Wen, Z., Bin, D. & Tan, J.
2018. Modeling and design of a two-axis elliptical
notch flexure hinge. Review of Scientific Instruments,
89.
Yang, W., Lee, S.-Y. & You, B.-J. 2010. A piezoelectric
actuator with a motion-decoupling amplifier for
optical disk drives. Smart Materials & Structures, 19.
Two-dimensional Laser Scanner with Low Mechanical Cross Coupling based on Piezoelectric Actuators
133
