
Pareto-based Soft Arc Consistency for Multi-objective Valued CSPs
Limeme Ben Ali
1
, Maher Helaoui
2
and Wady Naanaa
3
1
Faculty of Economics and Management of Sfax, University of Sfax, Tunisia
2
Higher Institute of Business Administration, University of Gafsa, Tunisia
3
National Engineering School of Tunis, University Tunis El Manar, Tunisia
Keywords:
Multi-objective Optimization, Multi-objective Valued Constraint Satisfaction Problems MO-VCSP, Soft
Local Arc Consistency, Lower Bound Set, Pareto Dominance.
Abstract:
A valued constraint satisfaction problem (VCSP) is a soft constraint framework that can formalize a wide
range of applications related to Combinatorial Optimization and Artificial Intelligence. Most researchers have
focused on the development of algorithms for solving mono-objective problems. However, many real-world
satisfaction/optimization problems involve multiple objectives that should be considered separately and sat-
isfied/optimized simultaneously. Solving a Multi-Objective Optimization Problem (MOP) consists of finding
the set of all non-dominated solutions, known as the Pareto Front. In this paper, we introduce multi-objective
valued constraint satisfaction problem (MO-VCSP), that is a VCSP involving multiple objectives, and we ex-
tend soft local arc consistency methods, which are widely used in solving Mono-Objective VCSP, in order to
deal with the multi-objective case. Also, we present multi-objective enforcing algorithms of such soft local
arc consistencies taking into account the Pareto principle. The new Pareto-based soft arc consistency (P-SAC)
algorithms compute a Lower Bound Set of the efficient frontier. As a consequence, P-SAC can be integrated
into a Multi-Objective Branch and Bound (MO-BnB) algorithm in order to ensure its pruning efficiency.
1 INTRODUCTION
Solving a Single-Objective Optimization Problem
amounts to determining the best solutions that satisfy
a set of constraints and optimize an objective function
defined by the user. The best solution, also known
as the optimal solution, is the solution with the high-
est assessment against the defined objective. Such
a problem can be formulated in terms of a Valued
Constraint Satisfaction Problem (VCSP). However,
when dealing with real-world problems such as Sup-
ply Chain Problem, Production Management Prob-
lems, Communication Problems, Time-cost trade-off
problem (Afruzi et al., 2013), Scheduling Problems
(Hazır et al., 2010) and many others, a single objec-
tive function may be insufficient. In fact, most of the
real-world applications require the integration of mul-
tiple simultaneous objective functions, often conflict-
ing. When considering multiple objectives functions,
the notion of optimal solution from single-objective
optimization does not apply anymore, and instead one
must rely on the notion of Pareto Dominance. A so-
lution s is better, in the Pareto sense, than another so-
lution s
0
if s is better than s
0
for at least one objective
and not worse for any of the remaining ones. If none
of the two solutions is better than the other, they rep-
resent two different trade-offs of the objectives func-
tion that, without knowledge of the decision maker’s
preferences, are considered to be equally valuable. A
very important task of interest in a multi-objective op-
timization problem (MOP) is to compute its efficient
frontier E (and, possibly, one or all efficient solutions
for each of its elements). In order to present a more
powerful modeling to these real problems, we propose
a generalization of VCSPs to Multi-Objective Valued
Constraint Satisfaction Problems (MOVCSPs).
The classical Constraint Satisfaction Problem
(CSP) model considers only the feasibility of sat-
isfying a collection of simultaneous requirements
(van Beek and Manchak, 1996; Jeavons and Cooper,
1995). Various extensions have been proposed to this
model, to allow it to deal with different kinds of op-
timization criteria, or preferences between different
feasible solutions. Two very general extended frame-
works that have been proposed are the semi-ring CSP
(Bistarelli et al., 1999) and the valued CSP (VCSP)
(Schiex et al., 1995). The semi-ring framework is
slightly more general, but the VCSP framework is
294
Ben Ali, L., Helaoui, M. and Naanaa, W.
Pareto-based Soft Arc Consistency for Multi-objective Valued CSPs.
DOI: 10.5220/0007401802940305
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2019), pages 294-305
ISBN: 978-989-758-350-6
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

simpler, and sufficiently powerful to describe many
important classes of problems (Cohen et al., 2008).
In this framework every constraint has an associated
cost function which assigns a cost to every tuple of
values for the variables in the scope of the constraint.
In the literature, many local consistency algorithms
have been proposed for soft CSPs. Soft Consistency
algorithms work by making explicit the inconsistency
level originally implicit in the problem. The general
idea is to safely move costs (i.e., without changing the
level of consistency of the solution) from high arity
constraint to smaller arity ones.
In this paper we address combinatorial problems
that can be expressed as MOVCSPs. We introduce
a generic formalization of multi-objective problems
in terms of Valued CSP framework. Several models
using the soft CSP framework have been presented in
the literature (Emma and Javier, 2006; Bistarelli et al.,
2008; Bistarelli et al., 2012; Wilson et al., 2015).
Our new MOVCSP model is important for two rea-
sons; first we pick up an understanding of the nature
of multi-objective optimization problems, and we ac-
cede to some theoretical results from the Valued CSP.
Given a MO-VCSP, we define the Lower Cost Vec-
tor (LCV) operator on cost. Furthermore, we present
its generalization to be applicable over sets of k-ary
cost functions. Also, we show how to use the LCV
value (i.e., the value returned by LCV) inside the soft
arc consistency techniques in order to deal with the
multi-objective case. Thereafter, we introduce new
definitions for the support notion based on LCV. As
consequence, the LCV value corresponds to the trans-
ferred cost vector in the new Pareto-based soft arc
consistency operations commonly known as Equiva-
lence Preserving Transformation (EPT).
The rest of the paper is organized as follows.
Section 2 summarizes the background notions about
valued constraint satisfaction problems and multi-
objective optimization. Section 3 shows how to ex-
tend the VCSP formalism to model multi-objective
optimization problems. Section 3 also, presents basic
operations over costs and their extension to costs sets.
In Section 4, we introduce soft local consistencies
based on the Pareto principle and the main differences
while considering multiple objective functions. Fur-
thermore in the same section, we describe the multi-
objective extension of Soft Arc Consistencies main-
taining algorithms (Maintain P-SAC). In Section 5,
we give a description of the extension of depth-first
branch-and-bound, to solve MOVCSP problems, that
maintain Pareto soft local consistencies during search.
Section 5 also presents the related work and a discus-
sion of potential extensions. At last, Section 6 wraps
up the paper, presenting our conclusions.
2 BACKGROUND
In this section, we point out the specific features of
the multi-objective problems and recall the main def-
initions of the VCSP framework.
2.1 Multi-objective Optimization
Multi-objective Optimization Problems deal with
multiple objectives, which should be simultaneously
optimized (Deb and Kalyanmoy, 2001; Le Thi et al.,
2008; Chiandussi et al., 2012).
Example 1. Π PROJECT MODELED AS A BI-
OBJECTIVES DISCRETE TIME COST TRADE-OFF
PROBLEM (VANHOUCKE AND DEBELS, 2007). Let
Π be a project defined as follows:
Π is a project comprised of 6 tasks: A, B, C, D,
E and F. The predecessors of each task are defined
in column 2 (Preds) of Table 1. The various options
of the executions times and the relative costs of each
tasks (option 1, option 2, option 3) are defined in
columns 3, 4 and 5.
Solving the problem is equivalent to finding one
option for each task such that:
1. The precedence constraints are satisfied.
2. Both global costs and global makespan are opti-
mized.
Table 1: Π project.
Tasks Preds option 1 option 2 option 3
A – (5,100) (3,250) (1,500)
B A (5,100) (4,300) (2,900)
C A (5,100) (3,350) (2,600)
D A (10,200) (8,500) (7,800)
E B,C (5,100) (3,300) (1,600)
F D,E (5,100) (4,580) (2,2500)
The project network G = (V,A) of the project Π is
depicted in Fig.1 where V = {A,B,C,D, E,F} is the
set of Tasks and A is the set of arcs representing the
precedence constraints. Each task can be executed in
three options (modes). Each node V
i
of G is labeled
by a set of pairs (time,cost) representing time, cost
values of each option of the task V
i
.
Optimizing simultaneously two functions can be
contradictory, since reducing the cost, φ
c
, often in-
creases the project execution period, φ
t
, and con-
versely.
The concept of looking for an optimal solution be-
comes more difficult to define. In this case, and in ac-
cordance with the Pareto optimal, the desired optimal
solution is no longer a single point, but a set of non-
dominated solutions. Otherwise, solving a problem
with several objective functions, commonly referred
Pareto-based Soft Arc Consistency for Multi-objective Valued CSPs
295
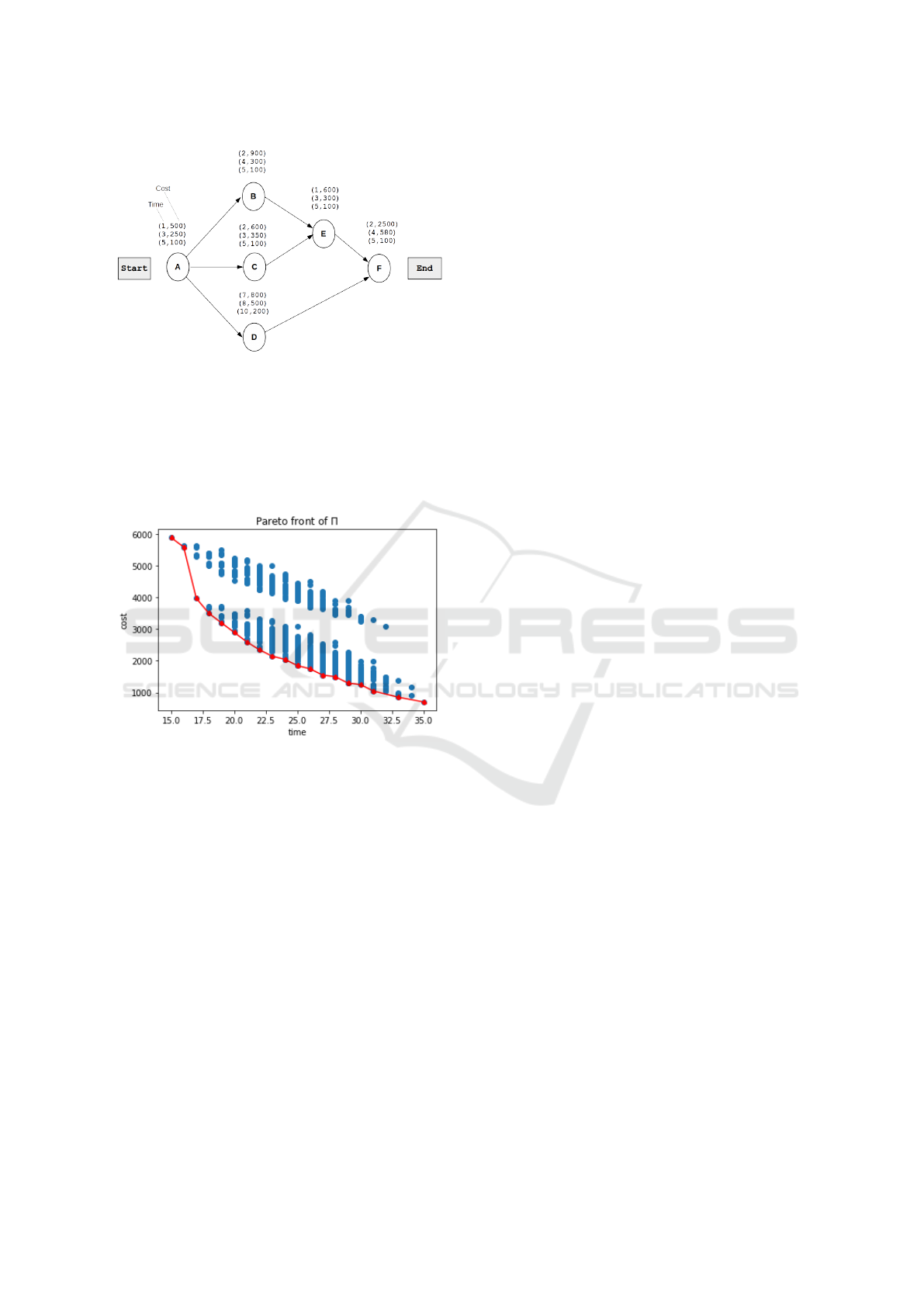
Figure 1: Project network of Π.
to a multi-objective problem, is to compute the best
set of trade-off solutions called the Pareto Front.
The Pareto front E
Π
of the Project Π is shown in
Fig.2. The set of non-dominated solutions after re-
moving redundant solutions is composed of 19 solu-
tions marked with red points in Fig.2.
Figure 2: The Pareto front of Π.
A multi-objective problem can be defined as a
problem where one seeks action that satisfies a con-
straint set and optimizes a set of objective functions.
A very important task of interest in a multi-objective
problem is to compute its efficient frontier E.
2.2 Valued Constraint Satisfaction
Problem and Soft Local Consistency
The Valued CSP (VCSP) framework is a generic op-
timization framework with a wide range of applica-
tions. Soft arc consistency operations transform a
VCSP into an equivalent problem by shifting weights
between cost functions. The principal aim is to pro-
duce a good lower bound on the cost of solutions, an
essential ingredient of a branch-and-bound search.
Valued Constraint Satisfaction Problem. The
Constraint Satisfaction Problem (CSP) consists of
finding an assignment to n finite-domain variables
such that a set of constraints are satisfied. Crisp con-
straints in the CSP are replaced by cost functions in
the Valued Constraint Satisfaction Problem (VCSP)
(Schiex et al., 1995). A cost function returns a val-
uation (a cost, a weight or penalty) for each combi-
nation of values for the variables in the scope of the
function. Crisp constraints can still be expressed by,
for example, assigning an infinite cost to inconsistent
tuples. In the most general definition of a VCSP, costs
lie in a valuation structure (a positive totally-ordered
monoid) (E,⊕, 4), where E is the set of valuations
which are totally ordered by 4 and combined using
the aggregation operator ⊕ (Schiex et al., 1995) and
> and ⊥ denotes maximum and minimum elements
of E given by 4. In this paper we only consider inte-
ger or rational costs.
A Valued Constraint Satisfaction Problem can be
seen as a set of valued constraints, which are simply
cost functions placed on particular variables. One can
propose this definition.
Definition 1 ((Schiex et al., 1995)). A Valued
Constraint Satisfaction Problem (VCSP) is a tuple
(X, D,C,S), where X is a set of n variables, each vari-
able x ∈ X has a domain of possible values D
x
∈ D,
C is a set of cost functions and S = (E,⊕,4) is a val-
uation structure. Each cost function hσ, φ
σ
i ∈ C is
defined over a tuple of variables σ ⊆ X (its scope) as
a function φ
σ
from the Cartesian product of the do-
mains Π
x∈σ
D
x
to E.
As we search for assignments with minimal val-
uation computed by combining violated constraints
by ⊕, one may see that the element > corresponds
to unacceptable violation and is used to express hard
constraints while ⊥ element corresponds to complete
satisfaction.
EPTs and Soft Arc Consistency. The soft local
consistency, we study below, has an important role
in the efficient resolution of VCSPs (Allouche et al.,
2016; Larrosa and Schiex, 2004; Bistarelli et al.,
2008). By definition, local consistency is a family
of increasingly harder properties about a Soft Con-
straint Satisfaction Problem. The control parameter is
the size of the sub-network (i.e., the number of vari-
able tuples) involved. The larger the tuples, the harder
the property is. The simplest form of local consis-
tency is node consistency, which only takes into ac-
count unary constraint. The next one is arc consis-
tency, which takes into account binary constraint. In
general, k-consistency takes into account constraints
with k variables in their scope (Cooper, 2005).
Various consistency notions have been proposed
for Valued CSP. Examples include NC
∗
(Larrosa and
ICAART 2019 - 11th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
296

Schiex, 2004), AC
∗
(Lee and Leung, 2012), FDAC
∗
(Larrosa and Schiex, 2004; Lee and Leung, 2012),
EDAC
∗
(de Givry et al., 2005), VAC (Cooper et al.,
2008) and OSAC (Cooper et al., 2010). Existential
Directional Arc Consistency EDAC* is the strongest
known polynomial-time achievable form of soft arc
consistency. Note, however, that EDAC* has only
been defined in the special case of binary (de Givry
et al., 2005) and ternary (Lee and Leung, 2012) VC-
SPs.
Enforcing such local consistencies requires apply-
ing equivalence preserving transformations (EPTs)
that shift costs between different scopes (Cooper and
Schiex, 2004). EPT is based on three cost trans-
fers operations which are also called SAC operations
(de Givry et al., 2005). Project operation which
projects costs from a cost function (on two or more
variables) to a unary cost function. Extend performs
the inverse operation, sending costs from a unary cost
function to a higher-order cost function. Finally, Pro-
jectUnary projects costs from a unary cost function to
the nullary cost function φ
∅
which is a lower bound
on the value of any solution.
Definition 2. For a VCSP (X,D,C,S), an equivalence
preserving transformation (EPT) on F ⊆ C is an op-
eration which transforms the sub-problem VCSP(F)
into an equivalent VCSP. When F contains, at
most, one non unary constraint, such an equivalence-
preserving transformation is called a Soft Arc Con-
sistency (SAC) operation.
For simplicity, we restrict ourselves to binary
VCSP. A binary VCSP is AC
∗
, DAC
∗
, FDAC
∗
, EAC
∗
,
EDAC
∗
if it is NC and respectively AC, DAC, FDAC,
EAC, EDAC (Larrosa, 2002).
Local consistency properties are used to transform
problems into equivalent simpler ones. From a prac-
tical point of view, the effect of applying local consis-
tencies at each node of the search tree of a branch and
bound algorithm is to prune values and to compute
good lower bounds.
3 MULTI-OBJECTIVE VALUED
CONSTRAINT SATISFACTION
PROBLEM
Compared to Integer Linear Programming (ILP)
(Le Thi et al., 2008; Teghem, 2009), the VCSP ap-
proach is an interesting alternative way to treat com-
plex (multi-objective) optimization problems. VC-
SPs are a pragmatic extension of the CSP dedicated
to optimization which authorizes an important effi-
ciency gains with regard to the usual approach in con-
straint programming. The latter approach consists
in encapsulating the objective function into a vari-
able. In this section, we formalize a Multi-Objective
Valued Constraint Satisfaction Problem (MO-VCSP).
Furthermore, we introduce operations over costs and
their extension to deal with MO-VCSP.
3.1 Model
In a Multi-Objectives Valued Constraint Satisfaction
Problem (MO-VCSP), as for a VCSP (Schiex et al.,
1995), for each objective j = 1,2,. .., k, we assume
that E
j
, the set of possible valuations for objective j,
is a totally ordered set with ⊥
j
as minimal element
and >
j
as maximal element. We also need a mono-
tone and binary operator ⊕
j
to aggregate valuations
for objective j. These components can be gathered
in k valuation structures each one can be specified as
follows:
Definition 3 (Valuation Structure). Each valuation
structure S
j
of a MO-VCSP is the triple (E
j
,⊕
j
,4
j
)
such as:
• E
j
is a set of valuations for objective function j;
• 4
j
is a total order on E
j
;
• ⊕
j
is commutative, associative and monotone.
Proposition 1. Let {S
j
= (E
j
,4
j
,⊕
j
,⊥
j
,>
j
)}
k
j=1
be a family of valuations structures. Then, the
structure S = (E, ⊕,4,⊥, >), where E = E
1
×
... × E
k
,⊕ =
⊕
1
,..., ⊕
k
,4=
4
1
,..., 4
k
,⊥ =
(⊥
1
,..., ⊥
k
) and > = (>
1
,..., >
k
), is a valuation
structure. The relation between valuations vectors
4 is based on Pareto dominance relation (Teghem,
2009). For distinction, S will be called a multi-
valuation structure.
Once the valuation structure S is specified, the
multi-objective valued constraint satisfaction problem
(MO-VCSP) can be defined as follows:
Definition 4 (MO-VCSP). A multi-objective valued
constraint satisfaction problem (MO-VCSP) is de-
fined by the tuple (X, D,C,S) such as:
• X is a finite set of variables;
• D is a finite set of domains, such that D
x
∈ D de-
notes the domain of x ∈ X.
• S =(E
1
×.. .×E
k
,(⊕
1
,..., ⊕
k
),(4
1
,..., 4
k
)) is a
multi-valuation structure.
• C is a set of multi-valued constraints. Each con-
straint is an ordered pair (σ,Φ
σ
) where σ ⊆ X
is the scope of the constraint and Φ
σ
is a func-
tion from Π
x∈σ
D
x
to Π
k
j=1
E
j
, such that Φ
σ
(t) =
(φ
1
σ
(t),...,φ
k
σ
(t)).
Pareto-based Soft Arc Consistency for Multi-objective Valued CSPs
297

For a variable x, we can only assign a value of
its domain. The valuation V of an assignment t to a
subset of variables V ⊆ X is obtained by
V (t) =
M
(σ,Φ)∈C,σ⊆V
Φ(t ↓ σ)
which can be written as
V (t) =
M
(σ,Φ)∈C,σ⊆V
φ
1
(t ↓ σ),. ..,
M
(σ,Φ)∈C,σ⊆V
φ
k
(t ↓ σ)
where φ
j
= Φ[ j] and t ↓ σ denotes the projection of
t on variables σ.
The arity of a multi-valued constraint is the size
of its scope. The arity of the problem is the maxi-
mum arity over all its constraints. In this work, we
are concerned with binary MO-VCSPs. These are
MO-VCSPs whose constraints are exclusively unary
or binary. Moreover, we suppose that all constraints
have distinct scopes. This allows us to identify every
constraint (σ, Φ) of C with its scope-indexed vector
Φ
σ
. We write Φ
x
as a shorthand for Φ
h
x
i
and Φ
xy
as a shorthand for Φ
h
x,y
i
. Without loss of generality,
we assume that C contains a unary multi-valued con-
straint Φ
x
for every variable x ∈ X as well as a zero-
arity multi-valued constraint Φ
∅
.
Finding an assignment that optimizes all objec-
tives simultaneously is not always possible. Indeed,
in general, such an ideal assignment does not exist or
cannot be reached, because of the trade-off between
the objectives. Thus, the (optimal) solution of MO-
VCSP can be characterized by using the concept of
Pareto Optimality.
Example 2. We return again to the DTCT project Π
presented in Example 1. This project Π can be mod-
eled as a bi-objectives VCSP P
1
defined as follows:
1. X
i
is a finite set of variables such that i = {Tasks};
2. D is a set of finite domains, where D
i
∈ D denotes
the set of options that can be taken by task i; we
therefore have D
i
= {v
1
,v
2
,v
3
}.
3. S = (E
t
× E
c
,
h
⊕
t
,⊕
c
i
,
h
t
,
c
i
) is a multi-
valuation structure, where ⊕
t
and ⊕
c
is the sum
operator over time and cost values respectively.
4. C is a set of valued constraints. Each valued con-
straint C
i
is an ordered pair (σ,Φ
σ
) where σ ⊆ X
i
is the scope of C
i
and Φ
σ
(v) = (φ
t
(v),φ
c
(v)).
The predecessors of each task are defined in col-
umn 2 (Preds) of Table 2 which can be expressed by
crisp constraint C
p
taking bi-value (⊥
t
,⊥
c
) if prece-
dence is satisfied and (>
t
,>
c
) otherwise.
We get
P
1
= (X , D,S,C ∪C
p
)
Table 2: Bi-objectives VCSP P
1
= Π.
X
i
Preds Φ
i
(v
1
) Φ
i
(v
2
) Φ
i
(v
3
)
X
A
– (5,100) (3,250) (1,500)
X
B
X
A
(5,100) (4,300) (2,900)
X
C
X
A
(5,100) (3,350) (2,600)
X
D
X
A
(10,200) (8,500) (7,800)
X
E
X
B
,X
C
(5,100) (3,300) (1,600)
X
F
X
D
,X
E
(5,100) (4,580) (2,2500)
The Dominance relation among valuation vectors
is defined as follows:
Definition 5 (Dominance). Let V and V
0
be two k-
sized valuation vectors, and let V [ j] (V
0
[ j]) be the j
th
component of V (resp. V
0
). We say that V dominates
V
0
, denoted by V ≺
D
V
0
, iff (i) V [ j] 4
j
V
0
[ j] holds
true for all objective j ∈ 1..k. And (ii) there exist at
least one objective j ∈ 1..k such that V [ j] ≺
j
V
0
[ j].
A solution t is a complete assignment. It is said to
be efficient or Pareto optimal if it respects the defini-
tion 6 below.
Definition 6 (Pareto Optimal Solution). For a MO-
VCSP and a complete assignment t, we say t is a
Pareto optimal solution (resp. a non-dominated so-
lution) iff there does not exist another assignment t
0
,
such that V (t
0
) ≺
D
V (t).
Solving MO-VCSP is to find all Pareto Optimal
solutions representing the Pareto front corresponding
to the set off all non-dominated solutions called NDS.
Definition 7 (Pareto Front). For a MO-VCSP, a set
of cost vector obtained by Pareto optimal solution is
called Pareto Front. Solving a MO-VCSP is to find the
Pareto front.
3.2 Operations over Costs and their
Extensions
The following definitions require that assumed valu-
ation structures for the MO-VCSP are fair (Cooper
and Schiex, 2004). A valuation structure S
j
is fair if
for any valuation pair α, β ∈ E
j
, if α
j
β, there is a
maximum difference between β and α. The only max-
imum difference between β and α is noted by β
j
α.
Another requirement for the purpose of this paper, is
that the valuation structures must be a lattice which
mean that any pairs of valuation (costs) must have a
lower bound, denoted LC. In order to generalize, we
will stretch this notion of LC on costs sets.
In the multi-objective case, operations overs costs
will be extended to costs vectors. Let us consider
problems with k objectives. The only difference is
ICAART 2019 - 11th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
298

that cost are now k-vectors and cost functions are now
k-functions. > = (>
1
,..., >
k
) is a k-vector, where
each >
j
∈ E
j
is the maximum acceptable cost for the
objective j. ⊥ = (⊥
1
,..., ⊥
k
) is a k-vector, where
each ⊥
j
∈ E
j
is the lowest acceptable cost for the ob-
jective j.
A k-vector u = (u
1
,..., u
k
) is a vector of k-
components, where each u
j
∈ E
j
and u
j
4
j
>
j
. Let u
and v be two distinct k-vectors.
• The aggregation of two costs values for an objec-
tive j is defined as:
u
j
⊕
j
v
j
def
=
(
u
j
⊕
j
v
j
, if u
j
⊕
j
v
j
≺ >
j
.
>
j
, otherwise.
• The aggregation of two k-ary cost vectors is de-
fined as:
u⊕v
def
=
(
>, if ∃ j,u
j
⊕
j
v
j
= >
j
.
(u
1
⊕
1
v
1
,..., u
k
⊕
k
v
k
), otherwise.
• For two cost values u
j
,v
j
∈ E
j
, such that u
j
j
v
j
,
the subtraction of v
j
from u
j
for an objective j is
given by:
u
j
j
v
j
def
=
(
u
j
j
v
j
, if u
j
≺
j
>
j
.
>
j
, otherwise.
• The subtraction of a cost vector v from a cost vec-
tor u, such that, ∀ j ∈ {1, ...,k}, u
j
∈ u, and v
j
∈ v
we have u
j
j
v
j
is defined as:
uv
def
=
(
>, if ∃ j,u
j
j
v
j
= >
j
.
(u
1
1
v
1
,..., u
k
k
v
k
), otherwise.
Let V be a set of k-ary cost vectors. We define its
non-domination closure as
V
∗
= {u ∈ V | ∀v ∈ V, v ⊀
D
u}.
Let V
1
and V
2
be two sets closed under non-
domination. We say that V
1
dominate V
2
(noted
V
1
≺
D
V
2
) if ∀v ∈ V
2
,∃u ∈ V
1
s.t u ≺
D
v.
Theorem 1. Let S a multi-valuation structure. If each
S
j
is a fair valuation structure, then so is S.
The result above ensures that the equivalence pre-
serving transformation applied during soft arc consis-
tency operations for mono-objective VCSP can still
be applied for multi-objective VCSP.
Definition 8. Lower Cost (LC
j
) Let F
j
be a subset
of E
j
, an element c ∈ F
j
is minimal in F
j
iff: c
j
x,∀x ∈ F
j
. The set of all minimal elements of F
j
will
be denoted by LC
j
(F
j
).
The (LC) operator can be applied over cost vectors
as follows:
Definition 9. Lower Cost Vector (LCV) Let L =
{L
1
,..., L
m
} be a set of k-cost vectors, where L
i
=
(L
1
i
,..., L
k
i
). The Lower Cost Vector of L denoted by
LCV(L) is defined as follow:
LCV(L) =
LC
1
(L
1
1
,..., L
1
m
),...,LC
k
(L
k
1
,..., L
k
m
)
Similarly, we define the Upper Cost Vector (UCV)
of set of m k-cost vector U = {U
1
,...,U
m
} as be-
ing the k-vector UCV(U) corresponding to the upper
value, for each objective j ∈ 1..k, of the j
th
compo-
nents of U
1
,...,U
m
.
Note that, if k = 1, all previous definitions reduces
to the classical ones.
4 PARETO-BASED SOFT LOCAL
ARC CONSISTENCY (P-SAC)
The Pareto-based soft local arc consistency, presented
below, has an important role in the efficient resolu-
tion of MO-VCSPs. We propose to extend and adapt
soft arc consistency techniques for MO-VCSPs. P-
SAC, computing a lower bound set of the cost of the
Pareto optimal solutions set, avoids unnecessary ex-
plored branches and accelerates the convergence to
the Pareto front (see Definition 7).
4.1 Pareto-based Equivalence
Preserving Transformation (P-EPT)
Enforcing local arc consistencies requires applying
equivalence preserving transformations (EPTs) that
shift costs between different scopes. As for mono-
objective case, equivalence preserving transforma-
tion in the multi-objective case is based on three basic
operations (project, extend and project-unary). The
main difference is that the transferred data between
constraints is now a k-ary cost vector.
The main Pareto-based EPT (P-EPT) is defined
below and described in Algorithm 1. This is an exten-
sion of the standard EPT version defined in (Cooper,
2005) for the multi-objective case.
Definition 10. Two MO-VCSP P = (X , D,C, S), P
0
=
(X
0
,D
0
,C
0
,S
0
) are equivalent if for all complete as-
signment t, we have: V
P
(t) = V
P
0
(t).
Definition 11. The sub-problem of a MO-VCSP
(X, D,C,S) induced by F ⊆ C is the MO-VCSP(F) =
(X
F
,D
F
,F,S ), where X
F
=
S
Φ
σ
∈F
σ and D
F
= {D
i
|
i ∈ X
F
}.
For a MO-VCSPs (X, D,C,S), a Pareto-based
equivalence preserving transformation (P-EPT) on
Pareto-based Soft Arc Consistency for Multi-objective Valued CSPs
299

F ⊆ C is an operation which transforms the multi-
objective sub-problem MO-VCSP(F) into an equiv-
alent MO-VCSP. When F contains at most one k-ary
cost functions Φ
σ
such that |σ| ≥ 2, such a P-EPT is
called a Pareto Soft Arc Consistency (P-SAC) opera-
tion.
The Pareto projection operation is defined as fol-
lows:
Definition 12. Let α be the Lower Cost Vector of u ∈
D
x
with respect to Φ
xy
.
α = LCV{Φ
xy
(u,v)}
v∈D
y
The Pareto Projection (P-Project) consists of adding
α to Φ
x
(u) as follows:
Φ
x
(u) ⊕ α, ∀u ∈ D
x
.
and subtracting α from Φ
xy
(u,v) as follows:
Φ
xy
(u,v) α, ∀v ∈ D
y
, ∀u ∈ D
x
.
the inverse operation is Pareto extend operation
defined as follows:
Definition 13. Let β be a cost k-vector such that β is
the Lower Cost Vector of u ∈ D
x
with respect to Φ
x
.
β = LCV{Φ
x
(u)}
u∈D
x
The Pareto Extension (P-Extend) consists of adding β
to Φ
xy
(u,v), as follows:
Φ
xy
(u,v) ⊕ β, ∀v ∈ D
y
.
and subtracting β from Φ
x
(u),
Φ
x
(u) β, ∀u ∈ D
x
.
Theorem 2. Given any fair binary MO-VCSP P =
(X, D,C,S), for any Φ
σ
∈ C,x ∈ σ and u ∈ D
x
, the
application of P-Project or P-Extend on P yields an
equivalent MO-VCSP.
Algorithm 1 gives three basic P-EPT which are
also P-SAC operations (Cooper and Schiex, 2004). P-
Project projects cost vectors from a set of cost func-
tions (on two or more variables) on a set of unary cost
functions. P-Extend performs the inverse operation,
sending cost vectors from a set of unary costs func-
tions to a set of higher arity cost functions. Each cost
vector contains k-ary cost function for each objective
j ∈ {1..k}. Finally P-ProjectUnary projects cost vec-
tors from a set of unary cost functions to the nullary
k-ary cost function Φ
∅
. Observe that Φ
∅
is a k lower
bound vector on the value of any solution. For each of
the P-SAC operations given in Algorithm 1, a precon-
dition is given which guarantees that cost values, for
each objective, remain non-negative after the Pareto-
EPT has been applied.
Algorithm 1: The basic equivalence-preserving transforma-
tions required to establish different forms of soft arc consis-
tency.
Precondition: (α ≺ LCV{Φ
xy
(u,v)}
v∈D
y
)
1: procedure P-PROJECT(x,u,y, α)
2: Φ
x
(u) ← Φ
x
(u) ⊕ α
3: for each v ∈ D
y
do
4: Φ
xy
(u,v) ← Φ
xy
(u,v) α
Precondition: (α ≺ LCV{Φ
x
(u)}
u∈D
x
)
5: procedure P-EXTEND(x,u, y,α)
6: for each v ∈ D
y
do
7: Φ
xy
(u,v) ← Φ
xy
(u,v) ⊕ α
8: Φ
x
(u) ← Φ
x
(u) α
Precondition: (α ≺ LCV{Φ
x
(u)}
u∈D
x
)
9: procedure P-PROJECTUNARY(x,α)
10: for each (u ∈ D
x
) do
11: Φ
x
(u) ← Φ
x
(u) α
12: Φ
∅
← Φ
∅
⊕ α
Example 3 (MO-VCSP). Consider the problem de-
picted in Figure 3(a). It has two variables x, y
with two values a,b in their domains. Unary multi-
objective costs are depicted within small circles. Bi-
nary multi-objective costs are represented by edges
connecting the corresponding values. The label of
each edges, which is a pair of integers, represents
the corresponding cost for each objective. If two val-
ues are not connected, the binary pair of cost between
them is (0, 0). In this problem, there are two Pareto
optimal solutions. The cost of solution 1 is the pair
(1,300) and it is attained by the assignment (a, a).
The cost of solution 2 is the pair (2, 200) and it is at-
tained by the assignment (a,b).
4.2 P-SAC Techniques
In this section we extend previously-defined notions
of soft arc consistency to deal with the multi-objective
case. To describe our P-SAC, we need to introduce
some new concepts related to the support notion. The
main idea in our extension is to take advantage of the
LCV operator in the definition of Pareto support.
Definition 14. (Maximal Subset) Let (hxi, Φ
x
) be a
unary multi-objective constraint and (hx,yi, Φ
xy
) a bi-
nary multi-objective constraint. We define a maximal
subset as follows:
• D
0
x
is a maximal subset of D
x
if D
0
x
⊆ D
x
and ∀c
0
∈
D
0
x
, ∃ j ∈ 1..k; φ
j
x
(c
0
) = ⊥
j
.
• D
0
y
is a simple maximal subset of D
y
, for a value
u ∈ D
x
, if D
0
y
⊆ D
y
and ∀ c
0
∈ D
0
y
, ∃ j ∈ 1..k;
ICAART 2019 - 11th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
300

Figure 3: Three equivalent MO-VCSP instances (> = (4, 400)).
φ
j
xy
(u,c
0
) = ⊥
j
.
• D
0
y
is a full maximal subset of D
y
, for a value
u ∈ D
x
, if D
0
y
⊆ D
y
and ∀ c
0
∈ D
0
y
, ∃ j ∈ 1..k;
φ
j
xy
(u,c
0
) ⊕ φ
j
y
(c
0
) = ⊥
j
.
Definition 15. Let (hxi,Φ
x
) be a unary multi-
objective constraint. A subset of values D
0
x
⊆ D
x
is
a Pareto Support for x if D
0
x
⊆ D
x
is maximal subset
of D
x
and LCV(D
0
x
) = LCV{Φ
x
(u)}
u∈D
0
x
= ⊥. Equiva-
lently,
P S(x)
def
=
(
a ∈ P S (x), if ∃ j, φ
j
x
(a) = ⊥
j
.
a /∈ P S (x), ∀ j, φ
j
x
(a) ⊥
j
.
We will denote the Pareto Support Set by P S .
The first level of Pareto local consistency is Pareto
node consistency. It is defined as follows:
Definition 16 (Pareto Soft Node Consistency). A
variable x is Pareto soft node consistent (P-NC
∗
) if
each value u ∈ D
x
satisfies Φ
∅
⊕ Φ
x
(u) ≺ > and
P S(x) 6= ∅. (i.e,. Φ
∅
⊕ LCV{Φ
x
(u)}
u∈D
x
= Φ
∅
). A
MO-VCSP is P-NC
∗
iff all variables are P-NC
∗
.
Pareto soft node consistency can be established by
repeated calls to P-ProjectUnary until convergence.
Example 4. The variable x presented in the
Figure 4-a is not Pareto soft node consistent.
LCV{Φ
x
(a)}
a∈D
x
= (1, 2) 6= ⊥ = (0,0). After ap-
plying Pro jectUnary operation, variable x (see
Figure 4-b) become Pareto soft node consistent.
LCV{Φ
x
(a)}
a∈D
x
= (0, 0) = ⊥ and P S (x) = {u,v}.
Following (Cooper and Schiex, 2004), Pareto soft
arc consistency is based on the notion of Pareto Sim-
ple Support.
Definition 17. Let (hx, yi,Φ
xy
) a binary multi-
objective constraint. A subset of values D
0
y
⊆ D
y
is
a Pareto Simple Support for a value u ∈ D
x
, if D
0
y
is a simple maximal subset of D
y
and LCV(D
0
y
) =
Figure 4: Example of enforcing Pareto Soft NC* property
(⊥ = (0,0), > = (4,400)).
LCV{Φ
xy
(u,v)}
v∈D
0
y
= ⊥. We will denote the Pareto
Simple Support Set by P SS .
A Pareto soft arc consistent problem is defined as
follows:
Definition 18 (Pareto Soft Arc Consistency). A
variable x is Pareto soft arc consistent if for ev-
ery u ∈ D
x
has a non empty Pareto Simple Sup-
port set (P S S (x(u)) 6=
/
0), equivalently, Φ
x
(u) ⊕
LCV{Φ
xy
(u,v)}
v∈D
y
= Φ
x
(u).
A MO-VCSP is Pareto Soft arc-consistency (P-
AC
∗
) if all variables are Pareto soft node consistent
and Pareto soft arc-consistent.
Stronger Pareto local arc consistency levels rely
on the notion of Pareto Full Support.
Definition 19. Let (hx,yi,Φ
xy
) be a binary multi-
objective constraint. A set of values D
0
y
⊆ D
y
is a Pareto Full Support for a value u ∈ D
x
if
D
0
y
is full maximal subset of D
y
and LCV(D
0
y
) =
LCV{Φ
xy
(u,v)
L
Φ
y
(v)}
v∈D
0
y
= ⊥. We will denote the
Pareto Full Support set by P F S
Pareto Directional Arc Consistency consists in
combining the binary costs and unary cost in the cal-
culation of the minimum valuation to be projected.
Pareto-based Soft Arc Consistency for Multi-objective Valued CSPs
301

This consistency level requires a total order on the
variables.
Definition 20 (Pareto Directional Arc Consistency).
A variable x is Pareto directional arc consistent (P-
DAC*) if ∀u ∈ D
x
, ∀y, y > x, P F S (x(u)) 6=
/
0.
Equivalently,
Φ
x
(u) ⊕ LCV{Φ
xy
(u,v) ⊕ Φ
y
(b)}
v∈D
y
= Φ
x
(u)
A MO-VCSP is Pareto Soft directional arc-
consistency (P-DAC
∗
) if all variables are P-DAC
∗
and P-NC
∗
.
Inspired by the work of (de Givry et al., 2005), P-
FDAC
∗
is an improvement of P-AC
∗
and P-DAC
∗
.
Definition 21 (Pareto Full Directional Arc-consis-
tency). A MO-VCSP is Pareto FDAC (P-FDAC*)
with respect to an order < on the variables if it is
P-AC∗ and P-DAC∗ with respect to <.
Pareto full supports can be established in two di-
rections if this can produce an increase in the lower
bound set. This is a local natural consistency property,
called Pareto soft existential arc-consistency (P-EAC
∗
inspired by the work of (de Givry et al., 2005)). Pareto
Existential arc consistency (P-EAC) is independent of
a variable order. For each variable x in turn, P-EAC
shifts costs to Φ
x
if this can lead to an immediate in-
crease in Φ
∅
via P-ProjectUnary.
Definition 22 (Pareto Soft Existential Arc-consis-
tency). A variable x is Pareto soft existential arc-
consistent (P-EAC
∗
) if P S(x) 6= ∅, and ∀Φ
xy
∈
C, ∃a ∈ D
x
,P F S ((x,a)) 6= ∅.
A MO-VCSP is Pareto soft existential arc-
consistency (P-EAC
∗
) if all variables are Pareto
soft node consistent and Pareto soft existential arc-
consistent. A MO-VCSP is P-EDAC
∗
if it is P-FDAC
∗
and P-EAC
∗
.
4.3 Enforcing Pareto Soft Arc
Consistencies
Enforcement of such a Pareto local consistency prop-
erty previously defined requires applying P-EPT. Any
Multi-objective Valued CSP can be transformed into
an equivalent instance having the P-NC
∗
property by
projecting any unary multi-valued constraint towards
the zero-arity multi-objective constraint Φ
∅
and sub-
sequently pruning every unfeasible value.
Enforcing P-NC
∗
is described in Algorithm 2.
Procedure Enforce P-NC
∗
(see Algorithm 2) en-
force Pareto NC
∗
, where ProjectUnary() applies
EPTs that move unary costs towards Φ
∅
while keep-
ing the solution unchanged, and PruneVar() remove
unfeasible values.
Algorithm 2: Enforce P-NC*.
1: procedure ENFORCE P-NC
∗
(X )
2: for each x ∈ X do
3: Pro jectUnary(x)
4: for each x ∈ X do
5: PruneVar(x)
6: procedure PROJECTUNARY((x))
7: α ← LCV
u∈D
x
(Φ
x
(u))
8: for each u ∈ D
x
do
9: Φ
x
(u) ← Φ
x
(u) α
10: Φ
∅
← Φ
∅
⊕ α
11: procedure PRUNEVAR(x)
12: for each u ∈ D
x
, s.t.,Φ
x
(u) ⊕ Φ
∅
≺
D
{s ∈
NDS} do
13: D
x
← D
x
\ {u}
Theorem 3. Given a set of non-dominated solu-
tions NDS found during the exploration of the search
space: The value a ∈ D
x
deleted by the function
PRUNEVAR may only participate in solutions domi-
nated by some solutions in NDS.
Likely, P-AC
∗
can be enforced by projecting bi-
nary multi-valued constraints towards unary multi-
valued constraints and thereafter enforcing P-NC
∗
.
Since enforcing P-NC
∗
may prune some domain val-
ues, some variables may have become Pareto soft arc
inconsistent. Therefore, the entire process is repeated
until no changes are performed. Algorithm 3 allows
enforcing various levels of previously defined Pareto-
based soft local arc consistencies.
Property 1. The complexity of P-EDAC
∗
= |NDS| ∗
O(ed
2
max{nd,max{|E
j
|}
k
j=1
}), where n, e, k, E
j
and
d are the number of variables, the number of con-
straints, the number of objectives, the set of possible
valuations for the objective j and larger domain size
(de Givry et al., 2005).
Property 2. On a problem with a single objective
function (i.e., k=1), the enforcement algorithms of P-
AC*, P-DAC*, P-FDAC* and P-EAC*, are equiva-
lent to classical soft arc consistency algorithms AC*,
DAC*, FDAC* and EAC*.
5 DISCUSSION AND FUTURE
WORKS
Multi-Objective Branch-and-Bound (MO-BB) is a
general search scheme for multi-objective constraint
optimization problems. The search space is repre-
sented as a tree. The algorithm searches in a depth-
first manner the tree defined by the problem. Its out-
puts are the set of Non Dominated Solutions (NDS).
ICAART 2019 - 11th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
302

Algorithm 3: Enforcement algorithms of P-AC*, P-DAC*,
P-FDAC*, P-EAC*.
1: procedure ENFORCE P-AC
∗
(x,y)
2: for each u ∈ D
x
do
3: α ← LCV{Φ
xy
(u,v)}
v∈D
y
4: if Φ
x
(u) ⊕ α 6= Φ
x
(u) then
5: Pro ject(x,u,y,α)
6: Pro jectUnary(x)
7: PruneVar(x)
8: procedure ENFORCE P-DAC
∗
(x,y)
9: for each u ∈ D
x
do
10: P[u] ← LCV{Φ
xy
(u,v) ⊕ Φ
y
(v)}
v∈D
y
11: for each v ∈ D
y
do
12: Extend(y,u,x, P[u]
~
Φ
xy
(u,v))
13: Pro ject(x,u,y,P[u])
14: Pro jectUnary(x)
15: PruneVar(x)
16: procedure ENFORCE P-FDAC
∗
(x,y)
17: if x < y then
18: Enforce P-DAC(x,y)
19: Enforce P-AC(y,x)
20: procedure ENFORCE P-EAC
∗
(x)
21:
α ← LCV{Φ
x
(u)
M
Φ
xy
∈C s.t. y<x
LCV{Φ
xy
(u,v) ⊕ Φ
y
(v)}
v∈D
y
}
u∈D
x
22: if Φ
∅
⊕ α 6= Φ
∅
then
23: Enforce P-FDAC(x,y)
24: procedure ENFORCE P-EDAC
∗
(x,y)
25: if x < y then
26: Enforce P-EAC(x,y)
27: Enforce P-FDAC(x,y)
The efficiency of the algorithm greatly depends on its
pruning ability which, in turns, depends on the com-
putation of a good lower bound set at each visited
node.
Algorithms that compute lower bound such as
mini-bucket elimination MBE (Emma and Javier,
2006; Larrosa and Schiex, 2004) or Existential Direc-
tional Arc consistency EDAC* (de Givry et al., 2005)
are a fundamental component of mono-objective
Branch and Bound because they can be executed at
every search node in order to detect infeasible nodes
(Larrosa and Schiex, 2003; de Givry et al., 2005).
The elementary operations made during applying P-
SAC on MO-VCSPs are deleting values, the projec-
tion and extension of costs vector. All these opera-
tions cannot add to the problem of binary constraints
on which the filtering technique P-SAC
∗
is applied.
So the problem remains binary. In addition, generally
the filtering algorithms are incremental. This means,
if a consistency is established in the search tree node
then determining the local consistency in a son node
can be done by considering only the changes between
it and the parent node. This property is very useful
since the filtering is performed at each node of the
search tree. Another key property is that the filtering
technique P-SAC
∗
computes a lower bound set for
the cost of the optimal solution. For the resolution of
MO-VCSP, Pareto SAC
∗
can be used to obtain good
quality lower bounds set (LB) or it can be integrated
into multi-objective branch and bound in order to in-
crease its pruning efficiency to generate the set of all
non-dominated solutions.
In practice, this set of solutions can be important
(risk of memory explosion) and it is going to slow
down Pareto-NC
∗
. In order to reduce this set we can
calculate a lower bound and/or an upper bound for
every objective on the set of non-dominated solutions
then, we compare to an under/over-approximation of
several solutions at once.
Alternatively, we can proceed for a decomposi-
tion scheme of an initial problem in order to solve
small instances of MO-VCSP. As a first step, we want
to identify some new tractable classes of MO-VCSP.
Where, we can solve instances of MO-VCSP in poly-
nomial time with MO-BnB+P-SAC by restrictions of
objectives functions to be in a specific class C (such
as; modular objective functions (Helaoui and Naanaa,
2013), sub-modular objective functions (Helaoui and
Naanaa, 2012) or even Directional Substitutable Val-
uation Functions (Naanaa, 2008)). As a natural exten-
sion of this work, we will propose a problem decom-
position scheme for MO-VCSPs that takes advantage
of restricted objective Functions even when the stud-
ied problem is not limited to these Functions. This
decomposition scheme can work within a backtrack-
based search and consists in decomposing the orig-
inal problem into a set of
S
|NDS|
i=1
P
i
∈ C , and then
tractable sub-problems. This decomposition scheme
can be distinguished by the possibility of instantiat-
ing variables by assigning to them subsets of values
instead of single values for the
S
|NDS|
i=1
P
i
, where each
one is in C . On a more practical side, we plan to im-
plement our algorithms and to integrate them into an
existing VCSP solver.
6 CONCLUSION
The Valued Constraint Satisfaction Problem (VCSP)
is a generic optimization problem consisting in a net-
work of local cost functions defined over discrete
variables. It has applications in Artificial Intelli-
Pareto-based Soft Arc Consistency for Multi-objective Valued CSPs
303

gence, Operations Research, Bio-informatics and has
been used to tackle optimization problems in other
graphical models (including discrete Markov Random
Fields and Bayesian Networks).
In this paper, we introduce a Multi-Objective
VCSP (MO-VCSP), that is a VCSP involving mul-
tiple objectives. We propose a new extension of lo-
cal arc consistency to the MO-VCSP. The incremental
lower bounds set produced by Pareto-based soft local
arc consistency can be used for pruning inside Branch
and Bound search. The latter algorithm enables the
calculation of the set of all Pareto Optimal (PO) so-
lutions, an algorithm that enforces a Pareto soft local
arc consistency property takes into account the Pareto
principle by updating the set of Non-Dominated So-
lutions during a Branch and Bound search.
REFERENCES
Afruzi, E. N., Roghanian, E., Najafi, A., and Mazinani, M.
(2013). A multi-mode resource-constrained discrete
time–cost tradeoff problem solving using an adjusted
fuzzy dominance genetic algorithm. Scientia Iranica,
20(3):931 – 944.
Allouche, D., Bessiere, C., Boizumault, P., de Givry, S.,
Gutierrez, P., Lee, J. H., Leung, K. L., Loudni,
S., M
´
etivier, J.-P., Schiex, T., and Wu, Y. (2016).
Tractability-preserving transformations of global cost
functions. Artif. Intell., 238(C):166–189.
Bistarelli, S., Gadducci, F., Larrosa, J., and Rollon, E.
(2008). A soft approach to multi-objective optimiza-
tion. In Proceedings of the 24th International Confer-
ence on Logic Programming, ICLP ’08, pages 764–
768, Berlin, Heidelberg. Springer-Verlag.
Bistarelli, S., Gadducci, F., Larrosa, J., Rollon, E.,
and Santini, F. (2012). Local arc consistency
for non-invertible semirings, with an application to
multi-objective optimization. Expert Syst. Appl.,
39(2):1708–1717.
Bistarelli, S., Montanari, U., Rossi, F., Schiex, T., Verfail-
lie, G., and Fargier, H. (1999). Semiring-based csps
and valued csps: Frameworks, properties, and com-
parison. Constraints, 4(3):199–240.
Chiandussi, G., Codegone, M., Ferrero, S., and Varesio, F.
(2012). Comparison of multi-objective optimization
methodologies for engineering applications. Comput-
ers and Mathematics with Applications, 63(5):912 –
942.
Cohen, D., Jeavons, P., and Zivny, S. (2008). The expres-
sive power of valued constraints: Hierarchies and col-
lapses. Theoretical Computer Science TCS, 409:137–
153.
Cooper, M., De Givry, S., Sanchez, M., Schiex, T., and Zyt-
nicki, M. (2008). Virtual arc consistency for weighted
csp. In Proceedings of the 23rd National Conference
on Artificial Intelligence - Volume 1, AAAI’08, pages
253–258. AAAI Press.
Cooper, M., de Givry, S., Sanchez, M., Schiex, T., Zytnicki,
M., and Werner, T. (2010). Soft arc consistency revis-
ited. Artificial Intelligence, 174(7):449 – 478.
Cooper, M. and Schiex, T. (2004). Arc consistency for soft
constraints. Artif. Intell., 154(1-2):199–227.
Cooper, M. C. (2005). High-order consistency in valued
constraint satisfaction. Constraints, 10(3):283–305.
de Givry, S., Zytnicki, M., Heras, F., and Larrosa, J. (2005).
Existential arc consistency: Getting closer to full arc
consistency in weighted csps. In Proceedings of the
19th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intel-
ligence, IJCAI’05, pages 84–89, San Francisco, CA,
USA. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc.
Deb, K. and Kalyanmoy, D. (2001). Multi-Objective Opti-
mization Using Evolutionary Algorithms. John Wiley
& Sons, Inc., New York, NY, USA.
Emma, R. and Javier, L. (2006). Bucket elimination for
multiobjective optimization problems. J. Heuristics.
Hazır, O., Haouari, M., and Erel, E. (2010). Robust schedul-
ing and robustness measures for the discrete time/cost
trade-off problem. European Journal of Operational
Research, 207(2):633 – 643.
Helaoui, M. and Naanaa, W. (2012). A submodular-
based decomposition strategy for valued csps. The
Sixth ”Starting Artificial Intelligence Research” Sym-
posium. Montpellier, France.
Helaoui, M. and Naanaa, W. (2013). Modularity-based de-
compositions for valued csp. Annals of Mathematics
and Artificial Intelligence.
Jeavons, P. G. and Cooper, M. C. (1995). Tractable con-
straints on ordered domains. Artificial Intelligence,
79(2):327 – 339.
Larrosa, J. (2002). Node and arc consistency in weighted
csp. In Eighteenth National Conference on Artifi-
cial Intelligence, pages 48–53, Menlo Park, CA, USA.
American Association for Artificial Intelligence.
Larrosa, J. and Schiex, T. (2003). In the quest of the best
form of local consistency for weighted CSP. In IJCAI-
03, Proceedings of the Eighteenth International Joint
Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Acapulco, Mex-
ico, August 9-15, 2003, pages 239–244.
Larrosa, J. and Schiex, T. (2004). Solving weighted CSP by
maintaining arc consistency. Artif. Intell., 159(1-2):1–
26.
Le Thi, H. A., Bouvry, P., and Pham Dinh, T., editors
(2008). Solving the Multiple Objective Integer Linear
Programming Problem, Berlin, Heidelberg. Springer
Berlin Heidelberg.
Lee, J. and Leung, K. (2012). Consistency techniques
for flow-based projection-safe global cost functions in
weighted constraint satisfaction. J. Artif. Intell. Res.
(JAIR), 43:257–292.
Naanaa, W. (2008). Substitutability based domain decom-
position for constraint satisfaction. CP.
Schiex, T., Fargier, H., and Verfaillie, G. (1995). Valued
constraint satisfaction problems: Hard and easy prob-
lems. In Proceedings of the 14th International Joint
Conference on Artificial Intelligence - Volume 1, IJ-
CAI’95, pages 631–637, San Francisco, CA, USA.
Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc.
ICAART 2019 - 11th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
304

Teghem, J. (2009). Multi-objective integer linear program-
ming. Springer US, Boston, MA.
van Beek, P. and Manchak, D. W. (1996). The design and
experimental analysis of algorithms for temporal rea-
soning. J. Artif. Intell. Res., 4:1–18.
Vanhoucke, M. and Debels, D. (2007). The discrete
time/cost trade-off problem: extensions and heuristic
procedures. Journal of Scheduling, 10(4):311–326.
Wilson, N., Razak, A., and Marinescu, R. (2015). Com-
puting possibly optimal solutions for multi-objective
constraint optimisation with tradeoffs. In Proceedings
of the 24th International Conference on Artificial In-
telligence, IJCAI’15, pages 815–821. AAAI Press.
APPENDIX
Proof of Theorem 1
Proof. We have for all j ∈ 1..k, S
j
is fair then for any
valuation pair α,β ∈ E
j
, if α
j
β, there is a max-
imum difference between β and α, denoted β
j
α.
For each pair of multi-valuation u, v ∈ Π
k
j=1
E
j
, if
∀ j, u
j
j
v
j
which implies by definition that u ≺
D
v
(u dominates v), there is a maximum difference be-
tween v and u which is equal to (u
1
1
v
1
,..., u
k
k
v
k
). Where k denotes the number of objectives.
Proof of Theorem 2
Proof. Following (Cooper and Schiex, 2004), and un-
der assumption that every valuation structure S
j
is
fair, to demonstrate equivalence, it is sufficient to
prove that the cost vector Φ
xy
(u,v) ⊕ Φ
x
(u) is an in-
variant of P-Project(x,u,y,α) and P-Extend(y,u, x,α).
For any v ∈ D
y
, let γ be the initial k-cost value of
Φ
xy
(u,v) and δ the initial k-cost value of Φ
x
(u). Af-
ter the execution of P-Project , we have Φ
xy
(a,b) ⊕
Φ
x
(a) = (γ α) ⊕ (δ ⊕ α) = γ ⊕ δ. After the ex-
ecution of P-Extend, we have Φ
xy
(a,b) ⊕ Φ
x
(a) =
(γ ⊕ α) ⊕ (δ α) = γ ⊕ δ. This proves the invari-
ance.
Proof of Theorem 3
Proof. Given a set of non-dominated solutions NDS
found during the exploration of the search space:
Denote by SP
u∈D
x
the set of solutions of a MO-
VCSP to which a value u ∈ D
x
may participate.
The function PRUNEVAR
∗
deletes a value u ∈ D
x
if and only if for each objective i it ∃ a non dominated
solution s ∈ NDS such that Φ
x
(u) ⊕ Φ
∅
= >
s
Since s ∈ NDS then >
s
is an element of the solu-
tion s ∈ NDS, so if Φ
x
(u) ⊕ Φ
∅
= >
s
(element of the
solution s ∈ NDS) then unary cost of the value u ∈ D
x
denoted by Φ
x
(u) combined with the total of the min-
imum unary costs of other variables denoted by Φ
∅
is dominated by at least one solution s ∈ NDS:
for each objective j ∃ s ∈ NDS such that
M
v∈(y∈s)
φ
j
y
(v) φ
j
x
(u) ⊕
i
φ
j
∅
⇒ ∃ s ∈ NDS ≺
D
Φ
x
(u) ⊕ Φ
∅
Secondly, any solution where u ∈ D
x
denoted by s
u
∈
SP
u∈D
x
is dominated by unary cost of value u ∈ D
x
:
Φ
x
(u) combined with the total of the minimum unary
costs of other variables denoted by Φ
∅
.
Φ
x
(u) ⊕ Φ
∅
≺
D
∀ s
u
∈ SP
u∈D
x
And since the unary cost combined with the unary
total minimum cost of the other variables is domi-
nated by a solution s ∈ NDS we have:
∃ s ∈ NDS ≺
D
Φ
x
(u) ⊕ Φ
∅
∧
Φ
x
(u) ⊕ Φ
∅
≺
D
∀ s
u
∈ SP
u∈D
x
We can therefore conclude, as there is a partial or-
der between dominated solution.
∃ s ∈ NDS ≺
D
∀ s
u
∈ SP
u∈D
x
And thereafter the value u ∈ D
x
may only partici-
pate in solutions dominated by at least one of the so-
lutions s ∈ NDS.
Pareto-based Soft Arc Consistency for Multi-objective Valued CSPs
305
