
Efficient Keypoint Reduction for Document Image Matching
Thomas Konidaris
1
, Volker M
¨
argner
1,2
, Hussein Adnan Mohammed
1
and H. Siegfried Stiehl
1,3
1
Centre for the Study of Manuscript Cultures, Universit
¨
at Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany
2
Technische Universit
¨
at Braunschweig, Braunschweig, Germany
3
Department of Informatics, Universit
¨
at Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany
maergner@ifn.ing.tu-bs.de, stiehl@informatik.uni-hamburg.de
Keywords:
Document Analysis, Word Spotting, SIFT Features, Image Matching.
Abstract:
In this paper we propose a method for eliminating SIFT keypoints in document images. The proposed method
is applied as a first step towards word spotting. One key issue when using SIFT keypoints in document images
is that a large number of keypoints can be found in non-textual regions. It would be ideal if we could eliminate
as much as irrelevant keypoints as possible in order to speed-up processing. This is accomplished by altering
the original matching process of SIFT descriptors using an iterative process that enables the detection of
keypoints that belong to multiple correct instances throughout the document image, which is an issue that the
original SIFT algorithm cannot tackle in a satisfactory way. The proposed method manages a reduction over
99% of the extracted keypoints with satisfactory performance.
1 INTRODUCTION
Document image analysis has gained a lot of atten-
tion due to the increased need of exploitation of the
several manuscript collections found worldwide. Fur-
thermore, the technological advances in terms of im-
age acquisition and digitization have given access to
a vast amount of digital material. However, process-
ing this information manually requires a significant
amount of time as well as effort in order to complete
the underlying tasks. Furthermore, it is not uncom-
mon, due to this load, some of the tasks to be thought
of as non-realistic to be processed in a manual way
due to the time they require to complete. This re-
sulted to the development of computer vision methods
that can assist in a number of tasks and also, impor-
tantly, allow the batch processing of large amount of
information in much less time than the manual non-
computer based way. Tasks like, writer/scribe iden-
tification, manuscript indexing through word spotting
and layout analysis are among the tasks that can be
solved through the use of computer vision methods
and have become active research areas on the field of
computer vision and more specifically, on the area of
document image analysis.
As mentioned above, one of the tasks that needs to
be tackled is that of document indexing. Although,
in contemporary documents Optical Character Recog-
nition (OCR) methods have been dominant, this is
not the case when we refer to historical document
images. Various factors can severely affect the per-
formance of OCR systems rendering the whole pro-
cess as extremely challenging. Although there are at-
tempts to use OCR in historical documents(Jenckel
et al., 2016), there is still a lot of ground to cover until
we claim that we have approached the problem in a
satisfactory way. An alternative to OCR for historical
document indexing is word spotting. Word spotting
refers the the detection of the desired information di-
rectly on the document images without any OCR.
One of the most common ways to perform word spot-
ting is using feature-based methods where from the
query keywords and the target document images a,
usually large, number of features is extracted. Some
of these features belong to the information that we
desire to detect while the rest, which are the majority,
do not belong to the correct instances that we want
to spot. A very popular keypoint detection and de-
scriptor algorithm is Scale Invariant Feature Trans-
form (SIFT)(Lowe, 2004). Usually, the number of
SIFT keypoints that are extracted from document im-
ages is large and therefore, in this paper we present
a method for eliminating SIFT keypoints from doc-
ument images that do not belong to the areas that
we want to detect. The application of the proposed
method is presented as a first step of a word spotting
664
Konidaris, T., Märgner, V., Mohammed, H. and Stiehl, H.
Efficient Keypoint Reduction for Document Image Matching.
DOI: 10.5220/0007412006640670
In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods (ICPRAM 2019), pages 664-670
ISBN: 978-989-758-351-3
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

process.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows: In Sec-
tion 2 we present related work and in Section 3 we
give a detailed description of the proposed method.
In Section 4 experimental results are shown and in
Section 5 conclusions are drawn.
2 RELATED WORK
In this section we present the different works on
the field of word spotting and in particular Query-
by-Example(QBE) word spottting. The litera-
ture is divided into two main categories, namely,
segmentation-based and segmentation-free. The for-
mer employs the segmentation of the document im-
ages into lines (Kolcz et al., 2000)(Marcolino et al.,
2000)(Mondal et al., 2016), words(Rath and Man-
matha, 2003) or characters (Kim et al., 2005), while
the latter does not apply any kind of segmentation
on the document images (Leydier et al., 2009)(Rusi-
nol et al., 2011)(Konidaris et al., 2016)(Mhiri et al.,
2018). Deep learning is nowadays widely used and
word spotting has its share of attention. Various meth-
ods have been proposed that use CNNs and other
deep representations(Barakat et al., 2018)(Sudholt
and Fink, 2016)(Zhong et al., 2016)(Krishnan et al.,
2018).
The proposed method is a feature-based method for
word spotting and uses SIFT(Lowe, 2004) keypoints
and descriptors. There are various methods that are
also feature-based and try to tackle the task of word
spotting. In (Zagoris et al., 2017) word spotting is per-
formed using document oriented local features. HOG
features are used in the methods proposed in (Bolelli
et al., 2017)(Thontadari and Prabhakar, 2016). Bag-
of-visual-words (BoVW) for word spotting is em-
ployed in (Aldavert and Rusi
˜
nol, 2018)(Shekhar and
Jawahar, 2012)(Rothacker and Fink, 2015).
Here we will present the various works on word spot-
ting that use SIFT features. Concerning SIFT key-
point reduction, the work presented in (Fujiwara et al.,
2013) tries to tackle this specific task. However,
the authors try to reduce the number of keypoints
on an image assuming that if a number of keypoints
have close similarity with a keypoint on the same
image, than those are removed since they constitute
a repeated pattern. Concering document images, in
(Aldavert et al., 2015) word spotting in handwritten
documents is presented. The authors use SIFT fea-
tures with a Bag-of-Visual-Words (BoVW) represen-
tation. The method applies segmentation of the doc-
uments on word level. Another method that used
SIFT and BoVW is proposed in (Rusinol et al., 2011).
This work follows a segmentation-free approach al-
though they apply a grid-based segmentation of the
documents in order to extract the desired features.
Yalniz and Manmatha(Yalniz and Manmatha, 2012)
present a word spotting method based on SIFT de-
scriptors applied to FAST(Rosten and Drummond,
2006) keypoints. The extracted features are fur-
ther quantized using K-Means and the matching is
performed using the Longest Common Subsequence
(LCS) method. A Bag-of-Features (BoF) represen-
tation is presented in (Rothacker et al., 2013). The
method uses SIFT descriptors to feed an HMM in
order to apply word spotting in handwritten docu-
ment following a segmentation-free approach. Ghosh
and Valveny (Ghosh and Valveny, 2015) present a
segmentation-free word spotting method based on
word attributes. Query words are encoded using Fis-
cher Vector representation and are used together with
pyramidal histogram of characters labels (PHOC) to
learn SVM-based attribute models. For the matching
process a sliding window is applied. The word at-
tributes used as the representation involve the calcula-
tion of SIFT descriptors. Another approach that uses
PHOC, Fischer Vectors and densely extracted SIFT
descriptors is proposed in (Almaz
´
an et al., 2014). The
SIFT features are extracted by a variable size patch
and their dimension is reduced using PCA. In the
work of Sfikas et. al.(Sfikas et al., 2015) a Gaussian
mixture model (GMM) is trained using SIFT descrip-
tors. Fisher vectors are then calculated for each im-
age as a function of their SIFT description and the
gradients of the GMM with respect to its parameters.
This results to a fixed-length, highly discriminative
representation, that can be seen as an augmented bag
of visual words description that encodes higher order
statistics.
3 PROPOSED METHOD
In this paper we propose an alternative matching
scheme for matching SIFT descriptors as applied as
a first step towards word spotting. The task is to find
relevant keypoints on a target document image when
keypoints of a query keyword image are matched
against it. Ideally, the detected keypoints on the target
document image will be part of the correct instance of
the query keyword. The propose method aims to re-
duce the amount of keypoints detected in the images
but on the same time keeping the keypoints that are
most relevant to the keypoints of the query keyword
image. The method uses an iterative process to reduce
the keypoints following a different approach than the
one applied by the SIFT algorithm as proposed by
Efficient Keypoint Reduction for Document Image Matching
665

Lowe(Lowe, 2004). Instead of getting only a single
keypoint matched in the target image for every key-
point in the query keyword image as it occurs when
using the original SIFT, we try to get all the strong
keypoints in the target image for every keypoint in the
query keyword image using the same matching crite-
rion as proposed in the original SIFT algorithm.
In the original paper, every descriptor in the query im-
age is compared with all the descriptors in the target
image. If the ratio of the two closest descriptors for
every query descriptor is less than a certain threshold
t than the keypoint that correspond to the closest de-
scriptor is kept as a valid keypoint. The distance ratio
threshold is shown in Equation 1.
d
1
d
2
< t (1)
where d
1
and d
2
are the distances of the two clos-
est keypoint descriptors of the document image to
a query keyword keypoint descriptor and threshold
t = 0.8. The original paper claims that this matching
scheme with t = 0.8 eliminates 90% of the false key-
point matches while discarding 5% of the correct key-
point matches. Although this may be the case where
there is a single object located in the images, when
it comes to document images there is a very impor-
tant issue that needs to be taken under consideration.
In document images the desired information that we
need to detect may have multiple correct instances in
the same page. This is a very common scenario in
word spotting methods. Consider the following ex-
ample as illustrated in Figure 1. We want to detect the
keyword “Begriffe” on a document image. The case
follows a segmentation-free word spotting approach.
In this particular example, the query keyword image
is one of the instances found on the page. The origi-
nal SIFT matching algorithm manages to successfully
detect the word on the document image, since it is the
query keyword used for matching, but fails to do so
with the rest of the correct instances. The bounding
boxes on the image indicate the correct instances of
the query keyword as found in the ground truth.
In the proposed method, concerning historical docu-
ment images, we follow a different approach. The
idea lies on the fact that it is very common to have
multiple instances of the information we want to lo-
cate. For that reason we want to be able to use the
matching of the descriptors as proposed in the origi-
nal SIFT algorithm but also enable the process to find
all the relevant keypoints that belong to other correct
instances of the query keyword image. Based on that
thought, we introduce an iterative process that enables
us to succeed in the aforementioned task. For every
query keypoint we perform the original SIFT as de-
Figure 1: Matching the query keyword “Begriffe” with the
document image. The keyword is taken from the document
image. SIFT algorithm manages to detect only this word
omitting the other correct instances found in the document
image.
fined in Equation 1. If there are keypoints that meet
the threshold criterion, these are kept as valid for fur-
ther processing and the process is repeated. At the
next iteration, we use the same query keypoint but this
time, without taking into consideration the already
detected valid keypoints. This will enable the algo-
rithm to detect other strong keypoints for the same
query keypoint. The assumption is that there might
be other keypoints on the document image that sat-
isfy the threshold criterion for the same query key-
point that belong to other correct instances of the the
query keyword image. This iterative process over-
comes the limitation of the original SIFT algorithm
to detect multiple instances of the correct information
on a document image, especially when a document
image contains the query keyword image and other
correct instances as shown in Figure 2. Algorithm 1
shows the various steps of the proposed method.
ICPRAM 2019 - 8th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
666

(a) original SIFT (b) Proposed, t = 0.80 (c) Proposed, t = 0.85
(d) Proposed, t = 0.90 (e) Proposed, t = 0.95 (f) Proposed, t = 0.99
Figure 2: The proposed method as compared with the original matching of the SIFT algorithm. The query word is taken
directly from the illustrated page. (a) is the result of the original SIFT matching where the algorithm correctly spots the
query word image but fails to spot the additional correct instances. (b)-(e) the results of the proposed method with t =
{0.80, 0.85, 0.90, 0.95, 0.99} respectively. The green bounding boxes indicate correct instances of the word as found in the
ground truth. For clarity only a portion of the document image is shown.
Algorithm 1: Iterative SIFT Matching.
1 Calculate descriptors for query and document
image
2 init valid pts
3 ∀ i ∈ query descr
4 while matched pts do
5 dist = kquery descr
i
, image descrk
2
6 sort(dist)
7 if
d
1
d
2
≤ t
8 idx = argmin(d
1
)
9 matched pts.append(image pts(idx))
10 remove image descr(idx)
11 else
12 matched pts = false
13 end
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
The experiments involve checking whether the re-
duction of the keypoints is efficient in the sense that
the remaining keypoints are located inside the ground
truth bounding boxes. For the purpose of the ex-
periments, the setup proposed in (Konidaris et al.,
2016) is used. There are 100 document images(von
Eckartshausen, 1778) and 100 keyword images. We
have used five different values for threshold t, 0.80,
0.85, 0.90, 0.95 and 0.99, respectively. The idea
behind the various threshold values is that if for a
query keypoint the two closest keypoints are valid,
this means that their threshold ratio will be high. Ac-
cording to our experiments this seems to hold. The
experiments concern the mean average recall (mAR),
the average number of remaining keypoints on the
document images and the ratio of the remaining key-
points found inside the ground truth bounding boxes
over the number of the remaining keypoints. The ex-
periments do not evaluate the proposed method as a
complete word spotting method. Rather, the idea is
to use the proposed method as a first step towards
word spotting where the keypoints that remain after
the elimination can be further processed yielding the
final results.
Efficient Keypoint Reduction for Document Image Matching
667
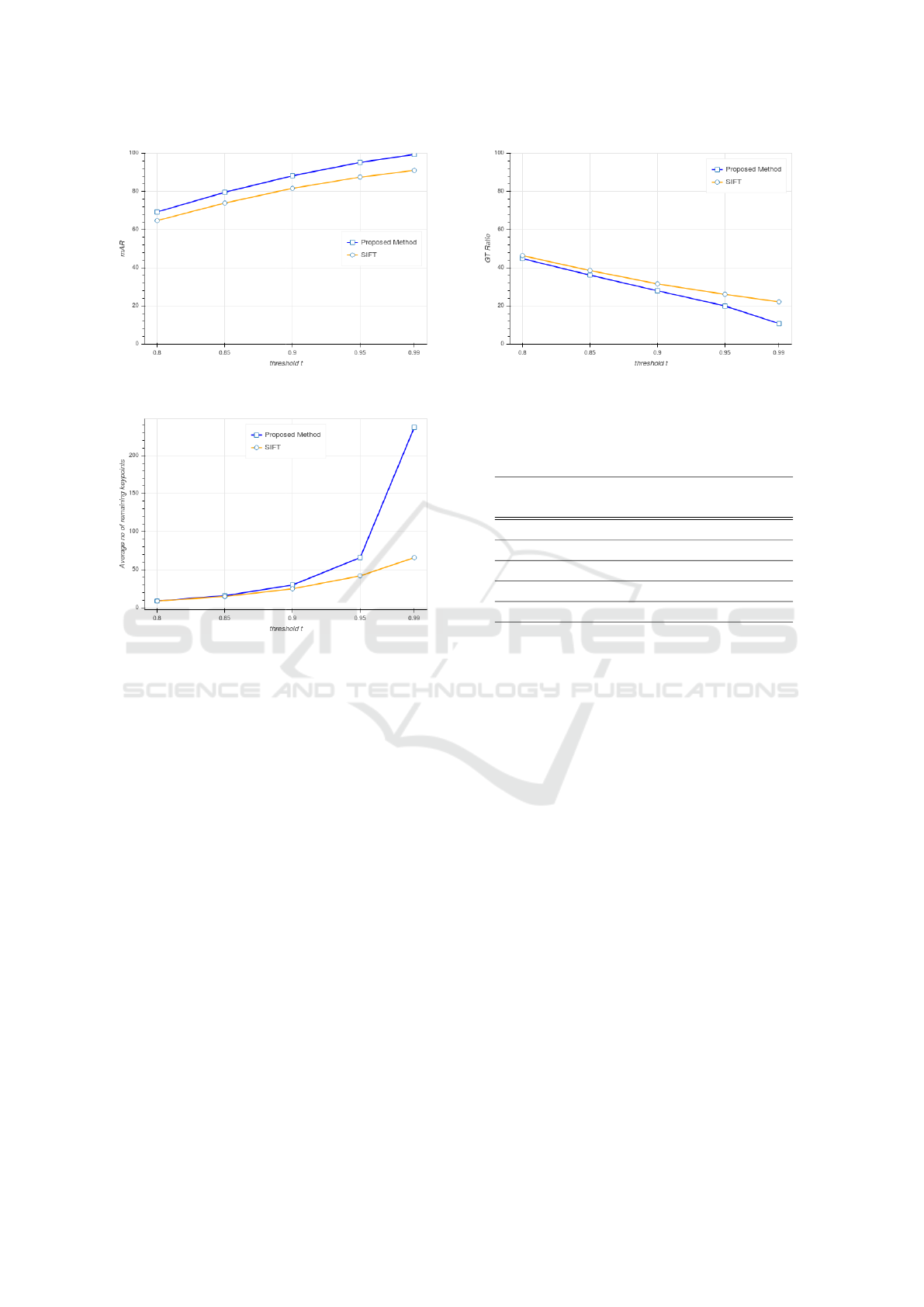
Figure 3: Mean average recall (mAR) for the different val-
ues of t for all query keywords.
Figure 4: Average number of remaining keypoints per page
for the different values of t.
The average number of keypoints per page in the doc-
ument images used for the experiments is 16154. Fig-
ure 3 shows the results concerning the mAR which
corresponds to the number of keypoints being found
in the ground truth bounding boxes. For this calcu-
lation a true positive requires at least one keypoint to
be found inside the ground truth. Furthermore, the
ground truth follows an extended format in the sense
that not only exact match words are included but also
words that include the query keyword in whole as
their part. This is primarily because the documents
have not undergone any segmentation and the cor-
rect instance of a word can be found anywhere on the
document images including when it is part of larger
words too.
It is clear that for the various values of threshold t,
the proposed method outperforms the original SIFT
matching process. This justifies the assumption that
a query keypoint may have other strong keypoint
matches on the document images that are detected us-
ing the iterative process proposed in this paper.
Figure 4 shows the mean average number of remain-
ing keypoints for all queries in the document images
for the different values of t. SIFT manages to have
Figure 5: The ratio of the remaining keypoints inside the
ground truth bounding boxes over the total number of re-
maining keypoints.
Table 1: Performance of the proposed method compared to
the original SIFT for the different values of the threshold t.
t mP
r
GTRatio mAR
(Prop./SIFT) (Prop./SIFT) (Prop./SIFT)
0.80 9 / 9 44.86% / 46.41% 69.26% / 64.77%
0.85 16 / 15 36.20% / 38.61% 79.58% / 73.93%
0.90 30 / 25 28.01% / 31.63% 88.24% / 81.63%
0.95 66 / 42 20.04% / 26.13% 95.20% / 87.54%
0.99 237 / 66 10.79% / 22.20% 99.45% / 94.01%
less remaining keypoints but this is reasonable since
it does not perform any kind of iterations, contrary to
the proposed method where for each query keypoint
a number of iterations is performed in order to detect
all the keypoints that satisfy the matching criterion.
Figure 5 illustrates the ratio of remaining keypoints
found in the ground truth bounding boxes to all the re-
maining keypoints. The matching scheme of the SIFT
algorithm seems to have a better ratio but this can be
justified by the less number of remaining keypoints
than the proposed method as shown in the previous di-
agram. As we have already mentioned, in the original
SIFT algorithm for every query keyword keypoint we
get only a single matching keypoint on the target doc-
ument image. Table 1 summarizes the experiments
performed between the matching scheme proposed in
this paper and the original matching scheme of the
original algorithm.
where, mP
r
is the mean average remaining points,
GT Ratio is the average ground truth to remaining
points ratio, and mAR is the mean average recall for
all the query keywords.
Through the above experiments we provided an in-
sight on how SIFT matching can be altered in order all
the relevant keypoints to be extracted for every query
keyword keypoint. The selection of the threshold lies
solely upon the needs of the underline task. Lower
ICPRAM 2019 - 8th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
668

values of t will result in faster processing but lower
accuracy, while larger values of t will yield better
results but more keypoints which some may not be-
long to areas of interest. The proposed method shows
better performance than the original SIFT matching
scheme.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we propose an alternative method for
matching SIFT keypoints using their descriptors. The
method manages to reduce the amount of keypoints
used for further processing on the document images.
The proposed method applies an iterative process that
manages to eliminate more than 99% of the keypoints
while, on the same time, the remaining keypoints are
located in the areas of interest. The method in this
paper is suggested as a first step for word spotting ap-
plications that follow a segmentation-free approach.
It allows the reduction of the keypoints significantly,
which can lead to less document areas to be searched,
thus speeding up the entire process. The proposed
method as mentioned throughout this paper is not a
complete word spotting method. This is not the idea
behind it. Therefore, it could be possible to apply it
on other research areas where SIFT is used and there
is the need to discard non-relevant keypoints so as to
speed-up the entire process. The value of the thresh-
old t, can be chosen based on the needs of the un-
derlying task. The various values of t allows finding
keypoints with stronger relations between them, thus
leading to keypoints that belong to correct word in-
stances, as far as word spotting is concerned, or any
other type of information we need to locate on an im-
age.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been funded by the German Research
Foundation (DFG) within the scope of the Collabora-
tive Research Centre (SFB 950) at the Centre for the
Study of Manuscript Cultures (CSMC) at Hamburg
University.
REFERENCES
Aldavert, D. and Rusi
˜
nol, M. (2018). Synthetically gen-
erated semantic codebook for bag-of-visual-words
based word spotting. In 13th IAPR International
Workshop on Document Analysis Systems, DAS 2018,
Vienna, Austria, April 24-27, 2018, pages 223–228.
Aldavert, D., Rusi
˜
nol, M., Toledo, R., and Llad
´
os, J. (2015).
A study of bag-of-visual-words representations for
handwritten keyword spotting. IJDAR, 18(3):223–
234.
Almaz
´
an, J., Gordo, A., Forn
´
es, A., and Valveny, E. (2014).
Word spotting and recognition with embedded at-
tributes. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell.,
36(12):2552–2566.
Barakat, B. K., Alaasam, R., and El-Sana, J. (2018). Word
spotting using convolutional siamese network. In 13th
IAPR International Workshop on Document Analy-
sis Systems, DAS 2018, Vienna, Austria, April 24-27,
2018, pages 229–234.
Bolelli, F., Borghi, G., and Grana, C. (2017). Historical
handwritten text images word spotting through slid-
ing window HOG features. In Image Analysis and
Processing - ICIAP 2017 - 19th International Confer-
ence, Catania, Italy, September 11-15, 2017, Proceed-
ings, Part I, pages 729–738.
Fujiwara, Y., Okamoto, T., and Kondo, K. (2013). SIFT fea-
ture reduction based on feature similarity of repeated
patterns. In International Symposium on Intelligent
Signal Processing and Communication Systems, IS-
PACS 2013, Naha-shi, Japan, November 12-15, 2013,
pages 311–314.
Ghosh, S. K. and Valveny, E. (2015). A sliding win-
dow framework for word spotting based on word at-
tributes. In Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis
- 7th Iberian Conference, IbPRIA 2015, Santiago de
Compostela, Spain, June 17-19, 2015, Proceedings,
pages 652–661.
Jenckel, M., Bukhari, S. S., and Dengel, A. (2016). anyocr:
A sequence learning based OCR system for unlabeled
historical documents. In 23rd International Confer-
ence on Pattern Recognition, ICPR 2016, Canc
´
un,
Mexico, December 4-8, 2016, pages 4035–4040.
Kim, S., Park, S., Jeong, C., Kim, J., Park, H., and Lee,
G. (2005). Keyword spotting on korean document im-
ages by matching the keyword image. In Digital Li-
braries: Implementing Strategies and Sharing Experi-
ences, volume 3815, pages 158-166.
Kolcz, A., Alspector, J., Augusteijn, M., Carlson, R., and
Popescu, G. V. (2000). A line-oriented approach to
word spotting in handwritten documents. Journal of
Pattern Analysis and Applications, 3(2):153-168.
Konidaris, T., Kesidis, A. L., and Gatos, B. (2016). A
segmentation-free word spotting method for histori-
cal printed documents. Pattern Analysis and Applica-
tions, 19(4):963–976.
Krishnan, P., Dutta, K., and Jawahar, C. V. (2018).
Word spotting and recognition using deep embedding.
In 13th IAPR International Workshop on Document
Analysis Systems, DAS 2018, Vienna, Austria, April
24-27, 2018, pages 1–6.
Leydier, Y., Ouji, A., LeBourgeois, F., and Emptoz, H.
(2009). Towards an omnilingual word retrieval sys-
tem for ancient manuscripts. Pattern Recognition,
42(9):2089-2105.
Lowe, D. G. (2004). Distinctive image features from scale-
invariant keypoints. International Journal of Com-
puter Vision, 60(2):91-110.
Efficient Keypoint Reduction for Document Image Matching
669

Marcolino, A., Ramos, V., Ramalho, M., and Pinto, J. C.
(2000). Line and word matching in old documents. In
Fifth IberoAmerican Symposium on Pattern Recogni-
tion (SIAPR), pages 123-135.
Mhiri, M., Abuelwafa, S., Desrosiers, C., and Cheriet, M.
(2018). Hierarchical representation learning using
spherical k-means for segmentation-free word spot-
ting. Pattern Recognition Letters, 101:52–59.
Mondal, T., Ragot, N., Ramel, J., and Pal, U. (2016).
Flexible sequence matching technique: An effective
learning-free approach for word spotting. Pattern
Recognition, 60:596–612.
Rath, T. M. and Manmatha, R. (2003). Features for word
spotting in historical manuscripts. In International
Conference of Document Analysis and Recognition,
pages 218-222.
Rosten, E. and Drummond, T. (2006). Machine learning for
high-speed corner detection. In European Conference
on Computer Vision, volume 1, pages 430-443.
Rothacker, L. and Fink, G. A. (2015). Segmentation-free
query-by-string word spotting with bag-of-features
hmms. In 13th International Conference on Docu-
ment Analysis and Recognition, ICDAR 2015, Nancy,
France, August 23-26, 2015, pages 661–665.
Rothacker, L., Rusi
˜
nol, M., and Fink, G. A. (2013). Bag-
of-features hmms for segmentation-free word spotting
in handwritten documents. In 2013 12th International
Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition,
Washington, DC, USA, August 25-28, 2013, pages
1305–1309.
Rusinol, M., Aldavert, D., Toledo, R., and Llad
´
os, J. (2011).
Browsing heterogeneous document collections by a
segmentation-free word spotting method. In 11th
International Conference on Document Analysis and
Recognition (ICDAR’11), pages 63-67, China.
Sfikas, G., Giotis, A. P., Louloudis, G., and Gatos, B.
(2015). Using attributes for word spotting and recog-
nition in polytonic greek documents. In 13th Interna-
tional Conference on Document Analysis and Recog-
nition, ICDAR 2015, Nancy, France, August 23-26,
2015, pages 686–690.
Shekhar, R. and Jawahar, C. V. (2012). Word image retrieval
using bag of visual words. In 10th IAPR Interna-
tional Workshop on Document Analysis Systems, DAS
2012, Gold Coast, Queenslands, Australia, March 27-
29, 2012, pages 297–301.
Sudholt, S. and Fink, G. A. (2016). Phocnet: A deep convo-
lutional neural network for word spotting in handwrit-
ten documents. In 15th International Conference on
Frontiers in Handwriting Recognition, ICFHR 2016,
Shenzhen, China, October 23-26, 2016, pages 277–
282.
Thontadari, C. and Prabhakar, C. J. (2016). Scale space co-
occurrence HOG features for word spotting in hand-
written document images. IJCVIP, 6(2):71–86.
von Eckartshausen, C. (1778). Aufschl
¨
usse zur Magie aus
gepr
¨
uften Erfahrungen
¨
uber verborgene philosophis-
che Wissenschaften und verdeckte Geheimnisse der
Natur. Bavarian State Library.
Yalniz, I. Z. and Manmatha, R. (2012). An efficient frame-
work for searching text in noisy document images.
In Proceedings of Document Analysis Systems (DAS),
pages 48-52.
Zagoris, K., Pratikakis, I., and Gatos, B. (2017). Unsu-
pervised word spotting in historical handwritten doc-
ument images using document-oriented local features.
IEEE Trans. Image Processing, 26(8):4032–4041.
Zhong, Z., Pan, W., Jin, L., Mouch
`
ere, H., and Viard-
Gaudin, C. (2016). Spottingnet: Learning the sim-
ilarity of word images with convolutional neural net-
work for word spotting in handwritten historical docu-
ments. In 15th International Conference on Frontiers
in Handwriting Recognition, ICFHR 2016, Shenzhen,
China, October 23-26, 2016, pages 295–300.
ICPRAM 2019 - 8th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods
670
