
Attack and Defence Modelling for Attacks via the Speech Interface
Mary K. Bispham, Ioannis Agrafiotis and Michael Goldsmith
Department of Computer Science, University of Oxford, U.K.
Keywords:
Cyber Security, Attack Modelling, Voice Control, Speech Interface, Human-computer Interaction.
Abstract:
This paper presents a high-level model of attacks via a speech interface, and of defences against such attacks.
Specifically, the paper provides a summary of different types of attacks, and of the defences available to counter
them, within the framework of the OODA loop model. The model facilitates an inclusive conceptualisation
of attacks via the speech interface, and serves as a basis for critical analysis of the currently available defence
measures.
1 INTRODUCTION
With the growing popularity of speech-based human-
computer interaction via voice-controlled digital as-
sistants such as Google Home and Amazon Alexa,
there is a need to consider the security of the
speech interface, and the new challenges this mode
of human-computer interaction may present for cy-
ber security research. The speech interface is inher-
ently difficult to secure, on account of the difficulty
of controlling access to a system by sound. Whereas
physical access to a system may be controlled by mea-
sures such as physical locks, and internet access can
be controlled by measures such as encryption, ac-
cess to a system by sound is more difficult to con-
trol. Furthermore, the speech recognition and natu-
ral language understanding technologies incorporated
in voice-controlled digital assistants are designed to
respond flexibly to speech input so as to ensure that
interaction with users is as natural as possible. This
design principle is at odds with the general cyber se-
curity principle of distrusting user input.
1
There has been a significant amount of prior work
demonstrating various types of attacks which may be
executed via a speech interface to gain control of a
victim‘s system. However, there have been few at-
tempts to conceptualise the security of the speech in-
terface in a comprehensive framework. The contri-
bution of this paper is to provide such a framework
1
See for example in ENISA Info notes published
1st June 2016, “The Dangers of Trusting User Input”,
https://www.enisa.europa.eu/publications/info-notes/the-
dangers-of-trusting-user-input [accessed 29th August
2018]
using the Observe-Orient-Decide-Act (OODA) loop
model. The remainder of this paper is organised as
follows. Section II provides background on voice-
controlled systems, on types of attacks via the speech
interface and different attack scenarios, as well as on
attack modelling techniques in cyber security. Section
III maps the various types of attacks via the speech
interface described in Section II to the OODA loop
model, and reviews the defence measures currently
available to counter such attacks, using the model as
a framework. Section IV concludes the paper and
makes some suggestions for future work.
2 BACKGROUND
Overview of Voice-Controlled Systems. Follow-
ing capture of the speech signal by a microphone,
the architecture of a voice-controlled system typically
consists of a speech recognition stage for translation
of acoustic features to a sequence of words, a nat-
ural language understanding component for extrac-
tion of user intent from the word sequence, a dia-
logue management component which determines the
action to be taken by the assistant based on the user
intent and contextual information, a response gener-
ation component which constructs a verbal or non-
verbal response (the non-verbal response being for
example a cyber-physical action such as turning on
a light), and, in the case of a verbal response, a
speech synthesis component which generates an au-
dio version of the response. This architecture is de-
tailed for example by Lison and Meena (Lison and
Meena, 2014). In the current generation of voice-
Bispham, M., Agrafiotis, I. and Goldsmith, M.
Attack and Defence Modelling for Attacks via the Speech Interface.
DOI: 10.5220/0007469705190527
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy (ICISSP 2019), pages 519-527
ISBN: 978-989-758-359-9
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
519

controlled systems, speech recognition and natural
language understanding are typically performed us-
ing some form of machine learning, whereas the di-
alogue management component maps input from the
natural language understanding component to output
to be generated by the response generation compo-
nent deterministically, based on hand-crafted rules
(McTear et al., 2016). Some research has been per-
formed on developing more complex dialogue man-
agement capabilities based on reinforcement learning
(Young et al., 2013), although these have not been im-
plemented in practice as yet.
Types of Attacks via the Speech Interface. Vari-
ous possibilities for attacks via the speech interface
have been identified. Bispham et al. (Bispham et al.,
2018b) have developed a taxonomy of potential at-
tacks via the speech interface which is organised ac-
cording to the nature of the attack in terms of hu-
man perception. The taxonomy divides such attacks
into two high-level categories; overt attacks, which
aim to take control of a target system using plain-
speech voice commands, and covert attacks, in which
malicious voice commands are concealed in a cover
medium so as to make them imperceptible to human
listeners.
Overt attacks are easily detectable by users if they
are consciously present with their device, therefore
the success of an overt attack relies on a user being
distracted or leaving their device unattended. An ex-
ample of an overt attack is the activation of a smart-
phone by a voice command which is delivered via a
malicious app whilst a user is away from their device
(Diao et al., 2014). Covert attacks are by definition
not detectable by users, and can therefore be executed
even if the user is present with their device. Exam-
ples of covert attacks include high-frequency attacks
which hide voice commands in sound which is in-
audible to humans (Zhang et al., 2017), attacks which
hide voice commands via an audio-mangling process
which makes them appear to humans as meaningless
noise (Carlini et al., 2016), and the targeted use of
nonsensical word sounds which trigger target com-
mands in a victim’s system (Bispham et al., 2018a),
despite these word sounds being perceived as mean-
ingless by human listeners. Covert attacks are divided
within the taxonomy into five sub-categories namely
silence, noise, music, nonsense and ‘missense’, the
hiding of malicious voice commands in speech which
appears to be unrelated to the attacker’s intent.
Overt attacks exploit the inherent vulnerability
of speech interfaces on account of the difficulty of
controlling access to such interfaces. Covert at-
tacks exploit unintended functionality in the han-
dling of speech input by a voice-controlled system
which allows it to accept input which is not a valid
voice command. The ‘silent’ attacks demonstrated
by Zhang et al. (Zhang et al., 2017) exploit non-
linearities in analog-to-digital conversion of speech
signals by a microphone, whereas the attacks demon-
strated by Carlini et al. (Carlini et al., 2016) and
the attacks demonstrated by Bispham et al. (Bispham
et al., 2018a) exploit vulnerabilities in speech recog-
nition. Attacks targeting natural language understand-
ing have not been demonstrated with respect to voice-
controlled systems as yet, although there has been
some related work on attacks on natural language
understanding in other areas, for example in work
on misleading question answering systems (Jia and
Liang, 2017). As regards the the dialogue manage-
ment and response generation components, as these
functionalities are fully dependent on input from the
preceding components in the current generation of
voice-controlled systems, there are no attacks target-
ing these functionalities at present.
Attack Scenarios. An attacker’s goal in executing
an attack via a speech interface will be to gain con-
trol of one of the three generic types of action which
can be performed via a voice-controlled digital assis-
tant or other speech-controlled system using a sound-
based attack. These three types of action are data ex-
traction, data input and execution of a cyber-physical
action. Specific attacks on each type of action which
might be possible based on the current capabilities
of voice-controlled digital assistants include, respec-
tively, prompting disclosure of personal information
such as calendar information (Diao et al., 2014), insti-
gating a reputational attack by posting to social media
in the victim’s name (Young et al., 2016), and caus-
ing psychological or physical harm to the victim by
controlling a device in their smart home environment
(Dhanjani, 2015).
Attacks via a speech interface require a channel
through which the sound-based attack is delivered,
and in the case of attacks involving theft of infor-
mation, successful execution also requires a channel
for data exfiltration. Sound-based attacks might be
delivered through various channels, including natu-
ral voice, radio or TV broadcasts or audio files which
users might be induced to open via a weblink or email
attachment (Dhanjani, 2015). Some researchers con-
sider the injection of voice commands via a malicious
smartphone app (Diao et al., 2014). A further pos-
sible attack delivery channel is via an intermediary
device under the attacker’s control. Some instances
of compromise of internet-connected speakers have
ICISSP 2019 - 5th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
520

been reported.
2
Speakers which have been compro-
mised in this way could be used as as an attack deliv-
ery channel for sound-based attacks on a target voice-
controlled digital assistant within the speakers’ vicin-
ity. Regarding data exfiltration channels, Diao et al.
(Diao et al., 2014) envisage for example that a system
could be prompted to call a phone number linking to
an audio recording device, which would then be used
to record personal information of the victim which the
system might be prompted to disclose by further voice
commands.
Attacks via the speech interface have the poten-
tial to expand in time by perpetuating over a num-
ber of dialogue turns, as well as in space by spread-
ing to other speech-controlled devices. Alepis and
Patskakis (Alepis and Patsakis, 2017) and Petracca et
al. (Petracca et al., 2015) both mention the possibil-
ity of attacks by voice ‘spreading’ from one device
to another by hijacking of a device’s speech synthesis
functionality. An example of an attack via the speech
interface spreading through both space and time was
seen in an instance in which a Google Home device
was prompted to provide data to its user in synthe-
sised speech which was perceived by a nearby Ama-
zon Echo device as a command. This prompted the
Echo to provide data which was in turn perceived by
the Google Home as a command, the consequence be-
ing to set in motion an ‘endless loop’ between the two
devices.
3
This instance represented an example of an
‘attack’ which spread both in space to another device
as well as in time over a potentially endless number
of dialogue turns. Whilst this particular instance rep-
resents merely a humorous anecdote, it is possible
that more malicious actions might be performed us-
ing similar mechanisms.
Attack Modelling Techniques. There are a number
of techniques for attack modelling in cyber security.
One of the more well-known modelling techniques
2
See Wired, 27th December 2017,”Hackers can rickroll
thousands of Sonos and Bose speakers over the internet”,
https://www.wired.com/story/hackers-can-rickroll-sonos-
bose-speakers-over-internet/ [accessed 29th August 2018]
and Trend Micro report 2017, ”The Sound of a Targeted
Attack”, https://documents.trendmicro.com/assets/pdf/The-
Sound-of-a-Targeted-Attack.pdf [accessed 29th August
2018]
3
See UPROXX, 12th January 2017 “You Can Make
Amazon Echo and Google Home Talk to Each Other
Forever”, http://uproxx.com/technology/amazon-echo-
google-home-infinity-loop/ [accessed 29th August
2018] and cnet.com 15th February 2018, “Make Siri,
Alexa and Google Assistant talk in an infinite loop” ,
https://www.cnet.com/how-to/make-siri-alexa-and-google-
assistant-talk-in-an-infinite-loop/ [accessed 29th August
2018]
Figure 1: The four stages of the OODA Loop.
for cyber security applications is the cyber kill-chain
(Al-Mohannadi et al., 2016) which is used to analyse
the different stages of malware attacks. Other estab-
lished attack modelling techniques in cyber security
include attack graphs (van Rensburg et al., 2016)) and
attack grammars (Patten et al., 2016). Another type of
attack model is the OODA loop. Originally developed
for the military context (Boyd, 1996), the OODA
loop has been applied in many different areas, includ-
ing cyber defence (Klein et al., 2011). The OODA
loop method represents the behaviour of agents in
adversarial interactions as each continuously cycling
through a four-stage loop in a shared environment, the
four stages of the loop being observation (Observe),
orientation (Orientation), decision (Decide) and ac-
tion (Act). The four stages of the loop as presented by
Klein (Klein et al., 2011) are shown in Figure 1. Rule
(Rule, 2013) explains that the Observe and Act stages
of the OODA loop are the points at which it makes
contact with the external world, whereas the Orient
and Decide stages are internal processes. Rule fur-
ther explains that an adversary’s aim as modelled by
the OODA loop is to interfere with decision-making
within their opponent’s loop by presenting them with
“ambiguous, deceptive or novel” situations, whilst at
the same time continuing to execute their own loop
independently.
3 ATTACK AND DEFENCE
MODELLING
For the purposes of this work, the attack modelling
technique considered to be the most suitable was the
OODA loop. The reason for this was that the OODA
model is capable of capturing the cyclical nature of
human-computer interactions by speech. Therefore
the OODA loop model is especially suitable for rep-
resenting the ways in which the processes of human-
computer interaction by speech may be hijacked by
adversarial actions. Specifically, the capture of the
speech signal by a microphone prior to speech and
language processing can be mapped to the Observe
stage of the OODA loop, the combined functional-
ity of the automatic speech recognition and natural
Attack and Defence Modelling for Attacks via the Speech Interface
521

language understanding components can be mapped
to the Orient stage, the dialogue management (DM)
component can be mapped to the Decide stage, and
the response generation and speech synthesis stages
can be mapped to the Act stage. Figure 2 shows
a mapping of non-malicious user-device interactions
via speech to the OODA loop model.
Figure 3 shows a mapping to the OODA loop
model of the different types of attacks via the speech
interface as categorised in the taxonomy presented by
Bispham et al. (Bispham et al., 2018b), in which an
attacker replaces a legitimate user in interactions with
the device. The position of each type of attack in
the loop model corresponds to the specific vulnera-
bility exploited by the attack, i.e. the point at which
the attacker gains control of the target device’s loop.
Plain-speech (overt) attacks and silent attacks are po-
sitioned at the Observe stage, as these types of attack
exploit inherent vulnerability of the speech interface
and unintended functionality in voice capture, respec-
tively. All other types of attack (noise, music, non-
sense and missense) are positioned at the Orient stage,
as these types of attack exploit unintended function-
ality in speech and language processing. The attack
model also shows an attack delivery channel for trans-
mission of malicious input by sound, and a data exfil-
tration channel which is used if the aim of the attack
is the extraction of data. The model further indicates
the potential expansion of an attack in time over sev-
eral dialogue turns, as well as the possible expansion
in space to a second target. The attacker may be any
agent which is capable of producing sound in an en-
vironment which it shares with a target. In the case
of attacks involving extraction of data, the agent will
also be capable of recording sound in the shared envi-
ronment.
Figure 4 shows a mapping to the OODA loop
model of currently available defence measures. The
position of each defence measure in the loop corre-
sponds to the type of system vulnerability which the
defence measure aims to patch. Cyber security de-
fence measures are often categorised as either pre-
ventive or reactive (Loukas et al., 2013). Preventive
defence measures, such as authentication and access
control, prevent malicious payloads from being in-
putted to a system at all, whereas reactive defence
measures, such as anomaly-based or signature-based
defences, detect that a malicious payload has been in-
putted and trigger a response to counteract the attack
(Giraldo et al., 2017)). In terms of defence measures
for human-computer interaction by speech as repre-
sented by the OODA loop model, preventive defences
are defences which are applied prior to spoken lan-
guage processing by the target system, i.e. at the Ob-
serve stage of the loop, whereas reactive defences are
defences applied as part of spoken language process-
ing, i.e. at the Orient stage of the loop. The preventive
measures mapped to the Observe stage of the loop are
user presence, access control, audio-technical mea-
sures, and voice authentication. Reactive measures
mapped to the Orient stage are confidence thresh-
olds, input validation, signature-based defences, and
anomaly-based defences. As dialogue management
and response generation are fully controlled by input
from the preceding components in the current genera-
tion of voice-controlled systems, there is currently no
scope for additional defences at the Decide stage of
the loop.
User Presence. Overt attacks via the speech inter-
face using plain-speech voice commands are easily
detectable by users if they are consciously present
with their device. Whilst the ability to detect an overt
attack may not prevent such attacks from being suc-
cessful to some extent, as the attack may already be in
the process of being executing as the user detects it,
the immediate detection of an attack by a user clearly
limits the potential effects of the attack, in that the
attack is likely to be easily attributable, and the user
will be able to prevent any further propagation of the
attack. Therefore it is advisable for users to take pre-
ventative measures to ensure that overt attacks can-
not be executed on their device whilst they are not
present with it. Jackson and Orebaugh (Jackson and
Orebaugh, 2018) recommend some basic preventative
measures including unplugging a voice-controlled de-
vice when leaving the home and not placing a voice-
controlled device close to doors and windows to pre-
vent voice commands being inputted to the device
from outside a house. User prevention measures such
as these apply only to overt attacks and do not rep-
resent a defence against covert attacks which are im-
perceptible to humans and may therefore be executed
notwithstanding the conscious presence of the user.
Access Control. Some work has been done on the
potential for using formal access control methods to
secure interactions via a speech interface and other
types of cyber-physical interactions. Agadakos et al.
(Agadakos et al., 2017) use formal methods to de-
velop a scheme for identifying unintended interac-
tions which may be possible between devices in a
smart home environment over ‘hidden’ physical chan-
nels, including voice. Petracca et al. (Petracca et al.,
2015) propose a system of access controls to secure
audio channels to and from a smartphone. The paper
proposes an extension to the Android operation sys-
tem in smartphones, with the objective of enforcing
ICISSP 2019 - 5th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
522
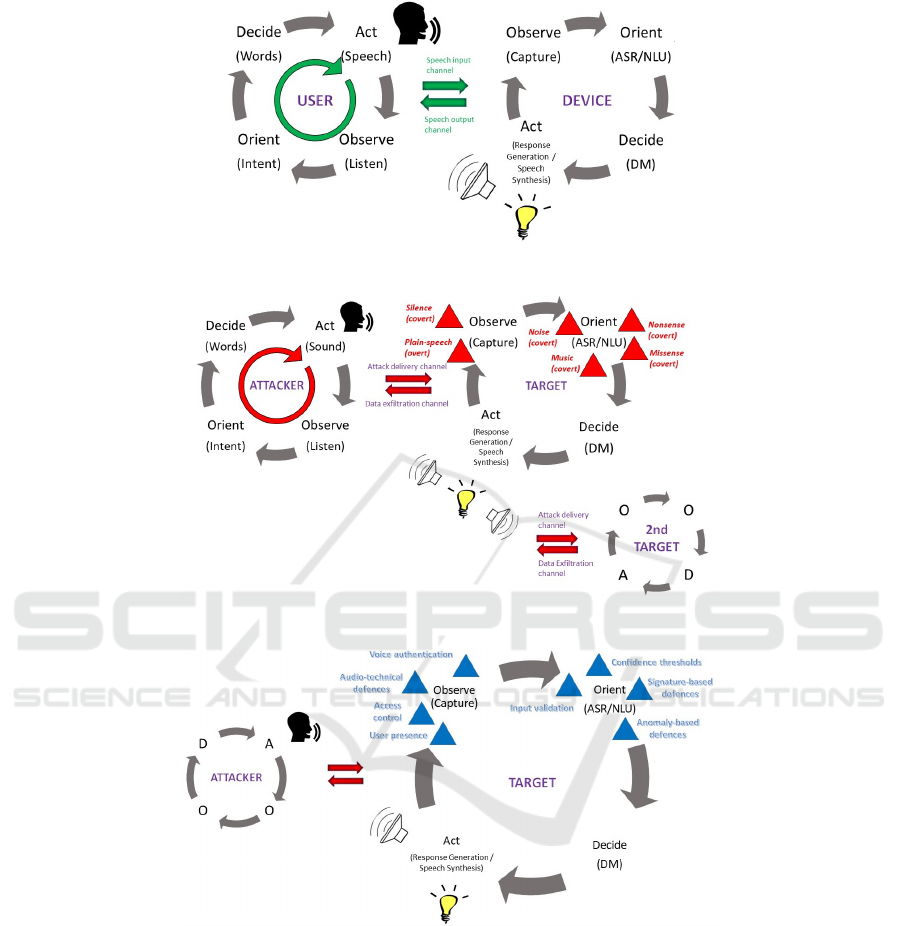
Figure 2: The OODA Loop in User-Device Interactions.
Figure 3: The OODA Loop in Attacker-Target Interactions.
Figure 4: Defences against Attacks via the Speech Interface in the OODA Loop Model.
security policies for communications over three audio
channels, namely between the device’s speakers and
its microphone, between the device’s speakers and ex-
ternal parties, and between external parties and the
device’s microphone. The authors concede that their
access control system is based on the assumption of a
reliable means of authenticating the legitimate user of
a device, which may not be a valid assumption. Gong
and Poellabauer (Gong and Poellabauer, 2018) argue
that the ‘Audroid’ method developed by Petracca et al.
is not effective against adversarial learning attacks.
Audio-technical Defences. Some defence mea-
sures have been presented which are applied at the
voice capture stage of the handling of speech input by
a voice-controlled device, prior the speech recogni-
tion and natural language understanding stages, so as
to prevent ’silent’ attacks which exploit non-linearity
in microphone technology. As mentioned above,
such attacks mislead a voice-controlled digital assis-
tant or other voice-controlled device to execute com-
mands which are concealed in high-frequency sig-
nals which are outside the human audible range, an
example being the attack demonstrated by Zhang et
Attack and Defence Modelling for Attacks via the Speech Interface
523

al. (Zhang et al., 2017) mentioned above. Roy et
al. (Roy et al., 2018) present a defence against in-
audible attacks based on signal forensics which in-
volves software rather than hardware changes to mi-
crophone technology. The applicability of such de-
fence measures is limited to attacks which exploit vul-
nerabilities in the voice capture functionality of voice-
controlled digital assistants; such measures are not ef-
fective against attacks which exploit vulnerabilties in
the speech recognition or natural language processing
functionalities.
Voice Authentication. Biometric voice authentica-
tion, also known as speaker recognition, is perhaps
the most obvious defence measure which might be
implemented to prevent attacks on systems which are
accessible via a speech interface. Hasan (Hasan et al.,
2004) details how voice biometric authentication is
performed using a standard set of acoustic features. In
theory, voice biometrics represent a potential solution
to all types of attack via the speech interface by ensur-
ing that a speech-controlled device acts only on voice
commands from an authorised user. In practice, how-
ever, voice biometrics remain vulnerable to spoofing
attacks, as stated by Wu et al. (Wu et al., 2015). In
an overview of the state-of-the-art in speaker recogni-
tion, Hansen and Hasan state that unlike in the case of
other types of biometrics such as fingerprints, voice
is subject to a certain amount of variability within the
same individual as well between individuals, imply-
ing that some degree of potential for false positives
in voice biometric authentication may be inevitable
(Hansen and Hasan, 2015). The potential for false
positives is exploited by attackers in voice spoofing
attacks.
Confidence Thresholds. Voice-controlled systems
generally implement some form of confidence thresh-
old to prevent them from accepting input which can-
not be matched to one of their actions with sufficient
certainty (Khan and Sarikaya, 2016). Whilst confi-
dence thresholds are implemented as an error preven-
tion measure rather than as a defence measure, they
may have some defence functionality in preventing
covert attacks via the speech interface, by enabling
the system to reject malicious input which is not suf-
ficiently similar to the examples of legitimate input
which were used in training the system. However, a
confidence threshold is unlikely to be sufficient to pre-
vent all attacks. This was seen for example in the ex-
perimental work on nonsense attacks on Google As-
sistant described in Bispham et al. (Bispham et al.,
2018a).
Input Validation. Aside from confidence thresh-
olds, another approach to error prevention for voice-
controlled systems has been to restrict in some way
the vocabulary which will be recognised by the sys-
tem as valid input. Controlled Natural Language
(CNL) has been used to prevent misunderstandings
between machines and humans as to the intended
meaning of natural language input. CNL is a gen-
eral term for various restricted versions of natural lan-
guage which have been constructed with a restricted
vocabulary and syntax in order to enable every sen-
tence in the language to be mapped unambiguously to
a computer-executable representation of its meaning
(Kuhn, 2014). Restricted language models like these
have been developed particularly for contexts where
avoiding misunderstandings is a critical concern, such
as human-robot interactions in military applications
(Ciesielski et al., 2017). Although primarily an er-
ror prevention rather than a security measure, CNL
enables natural language input to be validated in the
same way as other types of input to a system, as is
often done for security purposes in non-speech inter-
faces (Schneider et al., 2015). Kaljurand and Alum
¨
ae
(Kaljurand and Alum
¨
ae, 2012) discuss the use of CNL
in speech interfaces for smartphones. They point to
the additional challenges in using CNL in a speech-
based application as opposed to a text-based appli-
cation, noting the need to avoid homophones within
the CNL which can be distinguished in written but
not in spoken language. The approach proposed by
Kaljurand and Alum
¨
ae potentially addresses issues
of confusability between user utterances which are
within the intended scope of a speech-controlled sys-
tem. However, they may not be effective in preventing
confusion with out-of-vocabulary sounds which are
directed to the system by a malicious actor. Thus CNL
is unlikely to present a solution to preventing covert
attacks which target the speech recognition function-
ality of a voice-controlled interface. Enforcement of a
CNL in the design of a speech interface might also be
effective in preventing missense attacks which exploit
ambiguities in natural language input. However, such
an approach would clearly be contrary to the aim of
most providers of voice-controlled systems to enable
users to communicate with their devices in as flexible
and natural a way as possible (McShane et al., 2017).
Signature-based Defences. A potential defence
against some types of attacks via the speech interface
is detection of attacks based on detection of known
attack signatures using supervised machine learning.
Carlini et al. (Carlini et al., 2016), for example, pro-
pose a machine learning-based defence to their own
covert audio-mangling attack, in the form of a ma-
ICISSP 2019 - 5th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
524

chine learning classifier which distinguishes audio-
mangled sentences from genuine commands based on
acoustic features. They demonstrate that this classi-
fier is effective against the specific attacks presented
in their paper with 99.8 per cent detection rate of
attacks. However, the authors themselves note that
such defences do not represent a proof of security,
and are vulnerable to ‘arms race’ with attackers who
are likely simply to craft more sophisticated attacks to
evade such defences. Attackers have the upper hand
in such arms races with respect to machine learning
based systems, on account of the vast number of pos-
sible inputs to such systems, making it impossible for
defenders to prepare systems for all possible input in
training.
4
Anomaly-based Defences. One possibility for en-
abling voice-controlled systems to become resistant
to previously unseen attacks via the speech inter-
face could be defence measures based on some form
of anomaly detection. Anomaly detection-based de-
fences have been applied in other areas of cyber se-
curity, such as network defence (Rieck and Laskov,
2006), Bhuyan et al. (Bhuyan et al., 2014)). How-
ever, anomaly-based defence measures depend on re-
liable similarity and distance measures in terms of
which malicious input can be distinguished as anoma-
lous relative to legitimate input (Weller-Fahy et al.,
2015). In the context of attacks via the speech inter-
face, such quantifiably measurable indications of sus-
picious activity may be difficult to identify. Whilst a
number of both phonetic and semantic distance mea-
sures have been developed (Pucher et al., 2007)(Go-
maa and Fahmy, 2013), none of these are fully reli-
able in terms of their ability to separate sounds and
meanings which are perceived as different by human
listeners. Kong et al. (Kong et al., 2017) present the
results of an evaluative study which indicated signifi-
cant differences between error rates in human percep-
tion of speech sounds and their transcription by dif-
ferent types of automatic speech recognition in terms
of a phonetic distance measure. Budanitsky and Hirst
(Budanitsky and Hirst, 2001) compare different mea-
sures of semantic distance with implied human judge-
ments of word meaning via a task which involved
detection of synthetically generated malaproprisms,
finding that none of these measures were capable of
alignment with human understanding of word mean-
ing. Thus such distance and similarity measures do
4
See Cleverhans blog, 15th February 2017, “Is at-
tacking machine learning easier than defending it?”,
http://www.cleverhans.io/security/privacy/ml/2017/02/15/why-
attacking-machine-learning-is-easier-than-defending-
it.html [accessed 29th August 2018]
not provide a reliable basis for an anomaly detection-
based defence against attacks which seek to exploit
differences between human and machine perceptions
of speech, and may also prevent the system from ac-
cepting legitimate input.
4 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
This paper presents a comprehensive overview of the
security of the speech interface according to the the
OODA loop model, which has been used to model ad-
versarial interactions in many contexts. The cyclical
nature of the OODA loop model is especially well-
suited to representing dialogue interactions and the
ways in which these may be hijacked by malicious
actors. The OODA loop is used as a framework for
conceptualising attacks via the speech interface and
for analysing the defence measures currently avail-
able to counteract them. Our analysis concludes that
current defence measures are not adequate to prevent
all types of attacks via the speech interface. Future
work should consider the development of new types
of defence measures to ensure security of speech in-
terfaces. One possibility for future work might be
to attempt to incorporate defence measures in the di-
alogue management component of voice-controlled
systems, as represented by the Decide stage of the
OODA loop.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was funded by a doctoral training grant
from the UK Engineering and Physical Sciences Re-
search Council (EPSRC).
REFERENCES
Agadakos, I., Chen, C.-Y., Campanelli, M., Anantharaman,
P., Hasan, M., Copos, B., Lepoint, T., Locasto, M.,
Ciocarlie, G. F., and Lindqvist, U. (2017). Jumping
the air gap: Modeling cyber-physical attack paths in
the internet-of-things.
Al-Mohannadi, H., Mirza, Q., Namanya, A., Awan, I.,
Cullen, A., and Disso, J. (2016). Cyber-attack mod-
eling analysis techniques: An overview. In Fu-
ture Internet of Things and Cloud Workshops (Fi-
CloudW), IEEE International Conference on, pages
69–76. IEEE.
Alepis, E. and Patsakis, C. (2017). Monkey says, monkey
does: Security and privacy on voice assistants. IEEE
Access.
Attack and Defence Modelling for Attacks via the Speech Interface
525

Bhuyan, M. H., Bhattacharyya, D. K., and Kalita, J. K.
(2014). Network anomaly detection: methods, sys-
tems and tools. Ieee communications surveys & tuto-
rials, 16(1):303–336.
Bispham, M. K., Agrafiotis, I., and Goldsmith, M. (2018a).
Nonsense attacks on google assistant. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1808.01947.
Bispham, M. K., Agrafiotis, I., and Goldsmith, M. (2018b).
A taxonomy of attacks via the speech interface. pend-
ing publication in The Third International Conference
on Cyber-Technologies and Cyber-Systems (CYBER
2018).
Boyd, J. R. (1996). The essence of winning and losing.
Unpublished lecture notes, 12(23):123–125.
Brehmer, B. (2005). The dynamic ooda loop: Amalgamat-
ing boyd’s ooda loop and the dynamic decision loop.
Budanitsky, A. and Hirst, G. (2001). Semantic distance in
wordnet: An experimental, application-oriented eval-
uation of five measures. In Workshop on WordNet and
other lexical resources, volume 2, pages 2–2.
Carlini, N., Mishra, P., Vaidya, T., Zhang, Y., Sherr, M.,
Shields, C., Wagner, D., and Zhou, W. (2016). Hid-
den voice commands. In 25th USENIX Security Sym-
posium (USENIX Security 16), Austin, TX.
Ciesielski, A., Yeh, B., Gordge, K., Basescu, M., and Tun-
stel, E. (2017). Vocal human-robot interaction in-
spired by battle management language. In Systems,
Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), 2017 IEEE Interna-
tional Conference on, pages 3379–3384. IEEE.
Dhanjani, N. (2015). Abusing the Internet of Things: Black-
outs, Freakouts, and Stakeouts. O’Reilly Media, Inc.
Diao, W., Liu, X., Zhou, Z., and Zhang, K. (2014). Your
voice assistant is mine: How to abuse speakers to steal
information and control your phone. In Proceedings
of the 4th ACM Workshop on Security and Privacy in
Smartphones & Mobile Devices, pages 63–74. ACM.
Giraldo, J., Sarkar, E., Cardenas, A. A., Maniatakos, M.,
and Kantarcioglu, M. (2017). Security and privacy in
cyber-physical systems: A survey of surveys. IEEE
Design & Test, 34(4):7–17.
Gomaa, W. H. and Fahmy, A. A. (2013). A survey of text
similarity approaches. International Journal of Com-
puter Applications, 68(13):13–18.
Gong, Y. and Poellabauer, C. (2018). An overview of
vulnerabilities of voice controlled systems. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1803.09156.
Hansen, J. H. and Hasan, T. (2015). Speaker recognition by
machines and humans: A tutorial review. IEEE Signal
processing magazine, 32(6):74–99.
Hasan, M. R., Jamil, M., Rahman, M., et al. (2004).
Speaker identification using mel frequency cepstral
coefficients. variations, 1(4).
Jackson, C. and Orebaugh, A. (2018). A study of security
and privacy issues associated with the amazon echo.
International Journal of Internet of Things and Cyber-
Assurance, 1(1):91–100.
Jia, R. and Liang, P. (2017). Adversarial examples for eval-
uating reading comprehension systems. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1707.07328.
Kaljurand, K. and Alum
¨
ae, T. (2012). Controlled natural
language in speech recognition based user interfaces.
In International Workshop on Controlled Natural Lan-
guage, pages 79–94. Springer.
Khan, O. Z. and Sarikaya, R. (2016). Making personal dig-
ital assistants aware of what they do not know. In IN-
TERSPEECH, pages 1161–1165.
Klein, G., Tolle, J., and Martini, P. (2011). From detec-
tion to reaction-a holistic approach to cyber defense.
In Defense Science Research Conference and Expo
(DSR), 2011, pages 1–4. IEEE.
Kong, X., Choi, J.-Y., and Shattuck-Hufnagel, S. (2017).
Evaluating automatic speech recognition systems in
comparison with human perception results using dis-
tinctive feature measures. In Acoustics, Speech and
Signal Processing (ICASSP), 2017 IEEE International
Conference on, pages 5810–5814. IEEE.
Kuhn, T. (2014). A survey and classification of con-
trolled natural languages. Computational Linguistics,
40(1):121–170.
Lison, P. and Meena, R. (2014). Spoken dialogue sys-
tems: the new frontier in human-computer interaction.
XRDS: Crossroads, The ACM Magazine for Students,
21(1):46–51.
Loukas, G., Gan, D., and Vuong, T. (2013). A taxonomy of
cyber attack and defence mechanisms for emergency
management networks. In Pervasive Computing and
Communications Workshops (PERCOM Workshops),
2013 IEEE International Conference on, pages 534–
539. IEEE.
McShane, M., Blissett, K., and Nirenburg, I. (2017). Treat-
ing unexpected input in incremental semantic analy-
sis. In Proceedings of The Fifth Annual Conference on
Advances in Cognitive Systems. Palo Alto, CA: Cog-
nitive Systems Foundation.
McTear, M., Callejas, Z., and Griol, D. (2016). The conver-
sational interface. Springer.
Patten, T., Call, C., Mitchell, D., Taylor, J., and Lasser, S.
(2016). Defining the malice space with natural lan-
guage processing techniques. In Cybersecurity Sym-
posium (CYBERSEC), 2016, pages 44–50. IEEE.
Petracca, G., Sun, Y., Jaeger, T., and Atamli, A. (2015).
Audroid: Preventing attacks on audio channels in mo-
bile devices. In Proceedings of the 31st Annual Com-
puter Security Applications Conference, pages 181–
190. ACM.
Pucher, M., T
¨
urk, A., Ajmera, J., and Fecher, N. (2007).
Phonetic distance measures for speech recognition vo-
cabulary and grammar optimization. In 3rd congress
of the Alps Adria Acoustics Association, pages 2–5.
Rieck, K. and Laskov, P. (2006). Detecting unknown net-
work attacks using language models. In International
Conference on Detection of Intrusions and Malware,
and Vulnerability Assessment, pages 74–90. Springer.
Roy, N., Shen, S., Hassanieh, H., and Choudhury, R. R.
(2018). Inaudible voice commands: The long-range
attack and defense. In 15th USENIX Symposium on
Networked Systems Design and Implementation NSDI
18), pages 547–560. USENIX Association.
ICISSP 2019 - 5th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
526

Rule, J. N. (2013). A Symbiotic Relationship: The OODA
Loop, Intuition, and Strategic Thought. US Army War
College.
Schneider, M. A., Wendland, M.-F., and Hoffmann, A.
(2015). A negative input space complexity metric as
selection criterion for fuzz testing. In IFIP Interna-
tional Conference on Testing Software and Systems,
pages 257–262. Springer.
van Rensburg, A. J., Nurse, J. R., and Goldsmith, M. (2016).
Attacker-parametrised attack graphs. 10th Interna-
tional Conference on Emerging Security Information,
Systems and Technologies.
Weller-Fahy, D. J., Borghetti, B. J., and Sodemann, A. A.
(2015). A survey of distance and similarity mea-
sures used within network intrusion anomaly detec-
tion. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials,
17(1):70–91.
Wu, Z., Evans, N., Kinnunen, T., Yamagishi, J., Alegre, F.,
and Li, H. (2015). Spoofing and countermeasures for
speaker verification: a survey. Speech Communica-
tion, 66:130–153.
Young, P. J., Jin, J. H., Woo, S., and Lee, D. H. (2016). Bad-
voice: Soundless voice-control replay attack on mod-
ern smartphones. In Ubiquitous and Future Networks
(ICUFN), 2016 Eighth International Conference on,
pages 882–887. IEEE.
Young, S., Ga
ˇ
si
´
c, M., Thomson, B., and Williams,
J. D. (2013). Pomdp-based statistical spoken dia-
log systems: A review. Proceedings of the IEEE,
101(5):1160–1179.
Zhang, G., Yan, C., Ji, X., Zhang, T., Zhang, T., and Xu, W.
(2017). Dolphinattack: Inaudible voice commands.
arXiv preprint arXiv:1708.09537.
Attack and Defence Modelling for Attacks via the Speech Interface
527
