
Solar Pumped Lasers for Free Space Laser Communication
Changming Zhao, Haiyang Zhang, Zhe Guan, Zitao Cai, Dongbing He and Yongheng Wang
Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, China
Keywords: Solar Pumped Lasers, Multi-Frequency, Free Space Laser Communication.
Abstract: Solar Pumped Lasers (SPL) is a kind of lasers that can transform solar light into laser directly, with the
advantages of least energy transform procedure, higher energy transform efficiency, higher reliability, and
longer lifetime, which is suitable for use in unattended space system, for solar light is the only form of energy
source in space. In order to exploring the possibility of using SPL for free space laser communication, multi-
frequency SPL is investigated and solar pumped laser amplification is initiated. The first demonstration of
SPL used in free space laser communication is also conducted in our group.
1 INTRODUCTION
Solar pumped laser (SPL) is a special kind of lasers,
that can transform broad-band, incoherent solar light
into narrow-band, coherent laser directly, with the
advantages of least energy transform procedure,
higher energy transform efficiency, higher reliability
and longer lifetime. It is suitable for application in
unattended space system, such as space laser
communication, space to earth wireless power
transmission and space laser propulsion(Mori et
al.,2006; Guan et al.,2017; Oliveira et al.2016; Yabe
et al., 2008).
SPL has a comparable long research history as
lasers itself. Shortly after lasers was invented in 1960,
solar light was considered as the pumping source of
solid state lasers, for all solid state lasers were light-
pumped and solar light is the mostly common light
source we encountered in daily life. SPL was first
demonstrated by Z. J. Kiss from RCA Laboratories in
1963(Kiss et al., 1963), a Dy
2+
: CaF
2
crystal was
cooled in liquid nitrogen and pumped by solar light.
Shortly thereafter, systems using solar light to pump
different kinds of laser mediums were considered.
Among various laser mediums (solid, liquid and
gaseous), solid state lasers appear to be most
competitive because of stable performance, lower
pumping threshold, and potential efficient of solar-to-
laser power conversion. The first Solar-pumped solid
laser was reported by Young from the American
Optical Company in 1966(Young, 1966), 1W of
continuous wave laser output was obtained at room
temperature via a Nd:YAG crystal. In 1988, Weksler
and Shwartz from Weizmann Institute of Science,
Israel, through a compound parabolic concentrator
(CPC) obtained 60 W CW output power of laser from
a Nd:YAG rod with a slope efficiency about
2%(Weksler and Shwartz, 1998) . In 2007, T. Yabe
from Tokyo Institute of Technology demonstrated an
18.7 W/m
2
laser output from a Cr
3+
, Nd
3+
co-doped
YAG ceramic with Fresnel lens as the primary solar
light concentrator, corresponding to a total slope
efficiency of 2.9%(Yabe et al., 2007). In 2011, Liang
from Universidade NOVA de Lisboa, Portugal, 19.3
W/m
2
laser collection efficiency was achieved from a
Φ425mm Nd:YAG rod, which is pumped by a 0.64
m
2
Fresnel lens(Liang and Almeida, 2011). T. Yabe’s
group reported a SPL with 120 watts CW output in
2012(Dinh et al., 2012). They used a 4 m
2
Fresnel lens
as first solar energy collector and a Φ6mm Nd:YAG
rod, the collection efficiency was 30W/m
2
. For
further thermal management, grooved Nd:YAG laser
rod was firstly used in SPL in 2014(Xu et al., 2014).
Zhao´s group from Beijing Institute of Technology
achieved 27 W laser power by utilizing a Φ695mm
Nd:YAG grooved rod pumped by a 1.03 m
2
Fresnel
lens, corresponding to a slope efficiency of 9.0%. The
grooved Nd:YAG rod offered better heat dissipation
and reduced the thermal lens effect, compared with
that of unpolished rod, leading to a superior efficiency
and beam quality. In 2017, D. Liang and J. Almeida
used the heliostat-parabolic mirror system to pump a
Nd:YAG rod and obtained a collection efficiency of
31.5 W/m
2
(Liang et al., 2017). The highest collection
efficiency of 32.1W/m
2
, for the time being, was
achieved by Beijing Institute of Technology, using a
268
Zhao, C., Zhang, H., Guan, Z., Cai, Z., He, D. and Wang, Y.
Solar Pumped Lasers for Free Space Laser Communication.
DOI: 10.5220/0007569702680275
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Photonics, Optics and Laser Technology (PHOTOPTICS 2019), pages 268-275
ISBN: 978-989-758-364-3
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

grooved and bonding Nd:YAG/YAG crystal rod and
a Fresnel lens as the primary concentrator(Guan and
Zhao, 2018).
The technology maturity and efficiency of SPL
has arrived at a stage for application in a suitable
situation. And free space laser communication is
probably the best chance for SPL to be used, for solar
light is the only form of energy source in space.
1064nm wavelength laser has become one of a major
wavelength for laser communication. In 2007,
Germany launched TerraSA R-X satellite for
scientific and commercial purposes, where laser
communication terminal were used for inter-satellite
laser communication with a laser band of
1064nm(Liu, 2007.). Switzerland Contraves Space
Centre designed OPTEL high-performance laser
communication terminal series with 1064nm
wavelength, which use 808nm laser diode as the
pump source and Nd:YAG as the gain
medium(Baister et al.). Therefore we consider using
Nd:YAG crystal and its 1064nm wavelength as our
selection.
In order to increase the data rate of laser
communication system, multi-wavelength or multi-
frequency operation of the lasers is demanded,
completed by the technology of wavelength division
multiplexing(WDM). The possibility of multi-
wavelength and multi-frequency operation for solar
pumped both Nd:YAG lasers and amplifier are
investigated in the paper. One to three-frequency
operation of solar pumped Nd:YAG laser is realised
in experiment. A new bonding Nd:YAG slab
amplifier is designed and initial experiment is
performed. Based on the solar pumped Nd:YAG
lasers, the first solar pumped free space laser
communication system is demonstrated.
2 SOLAR PUMPED
MULTI-LONGITUDINAL
MODE LASERS
In free space laser communication systems, the total
data rate is equal to the data rate of one frequency
channel multiply the number of frequency channels.
Data rate is improved either by increase the date rate
of single frequency channel or by increase the number
of frequency channels. To increase the number of
frequency channel have two methods, the first one is
to oscillate simultaneously more wavelengths in a
certain laser medium, and the second one is to
oscillate simultaneously more longitudinal modes
within a single emitting wavelength, while keeping
the frequency separation suitable for frequency
discrimination.
For the mostly used laser medium Nd:YAG, there are
several emitting wavelengths around 1064nm, and
their emitting cross section are comparable with its
of 1064nm, means the possibility of lasing separately
under certain conditions, such as the wavelength of
1052nm, 1062nm, 1065nm, and 1074nm.
For a particular wavelength, such as 1064nm, its
linewidth of florescence (0.45nm) will allow multi-
longitudinal mode oscillating simultaneously, with
each longitudinal mode represents a frequency
channel. Indeed, Nd:YAG laser is usually oscillating
in multi-longitudinal mode without mode selecting
design. But, the multi-longitudinal mode output here
means to get the demanded number of longitudinal
mode output from a specially designed laser.
2.1 Design and Experimental Setup
Nd:YAG crystal is a four-level system, the most
important wavelength of 1064nm at room
temperature is generated by the two-level transition,
4
F
3/2
4
F
11/2
, and the average fluorescence linewidth
of the transition is 120GHz. The broadening of the
spectrum of solid laser gain medium is mainly due to
uniform widening caused by lattice thermal motion
and no-uniform widening caused by lattice defects.
Nd:YAG crystal is of good quality and isotropic, and
dominated by uniform widening in the whole
temperature range. The uniform broaden line has a
Lorentz line shape, the closer to the gain curve centre
frequency, the higher gain the longitudinal mode
obtained. According to the principle of resonator
longitudinal mode selection, the number of the lasing
longitudinal mode m is determined by the width of
gain curve 𝛥𝜈
𝐷
of the laser medium and the
longitudinal mode spacing 𝛥𝜈
𝑞
of the resonator,
written as:
𝑚 = (𝛥𝜈
𝐷
/𝛥𝜈
𝑞
) + 1
(1)
And
𝛥𝜈
𝑞
= 𝑐/2𝑛𝐿
(2)
Where c is the vacuum speed of light, n is the
refractive index of laser medium at certain
wavelength, and L is the geometry length of the
resonator. From equations (1) and (2), we can
calculate the resonator length for a given number of
m. In fact, for a small number of m, L is small too, and
Solar Pumped Lasers for Free Space Laser Communication
269
the laser rod is in fact a disk. For m=1,2,3, L will be
0.8mm, 1.1mm, and 2.4mm, respectively.
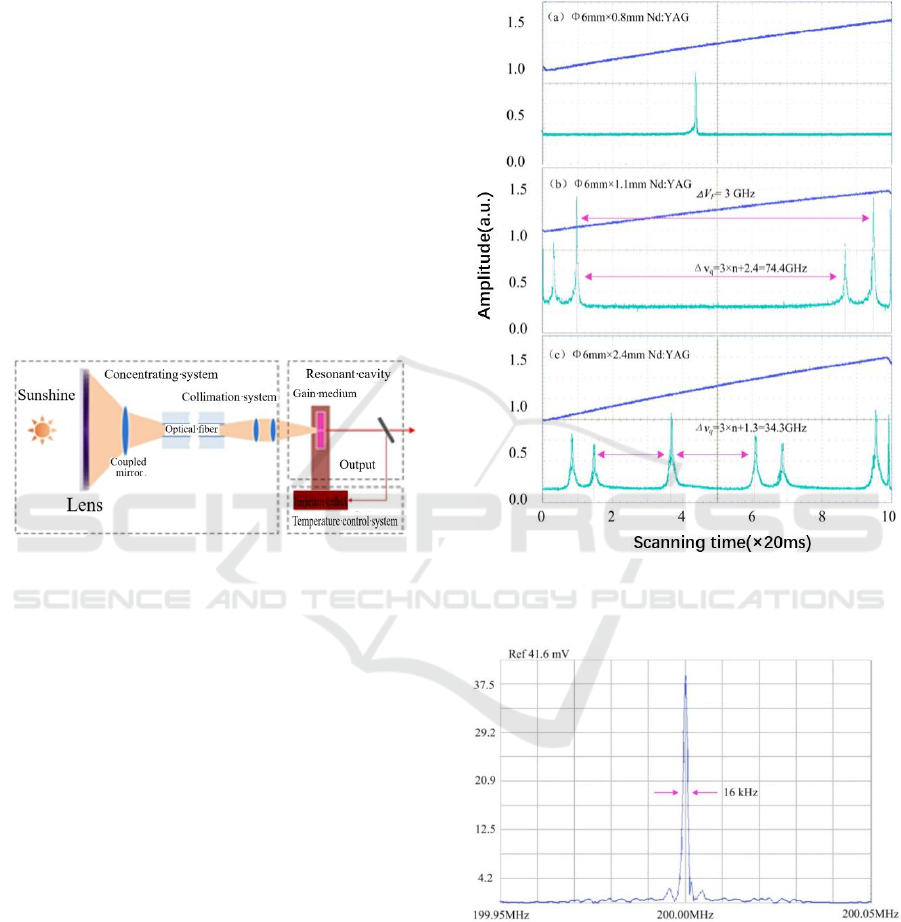
The experimental setup of multi-longitudinal
mode laser is shown in fig.1. It is composed of solar
light collecting system, the laser medium and the
temperature control system. The solar light collecting
system consists of focusing lens, coupling lenses, and
large aperture fibre. The solar light is focused and
coupled into the large aperture fibre firstly, and after
transmitted in the fibre, it is coupled into the laser
medium by the second coupling optics. The purpose
of using fibre as light transmitter is because of its
flexibility. The size of the laser medium is Ф6×0.8~
2.4mm, with its two surface form the resonator. One
surface is coated with AR coating @808nm and HR
coating @1064nm, as the pump light entrance,
another surface is coated with PR coating @1064nm,
as output coupler. The laser medium is temperature
controlled by a TEC cooler.
Figure 1: The experiment setup of solar-pumped multi-
frequency lasers.
2.2 Experimental Results
Before pumped by solar light, the multi-frequency
laser is firstly pumped by an 808nm LD indoors. The
output transverse mode is monitored by a laser beam
analyser, and the longitudinal mode is monitored by
a F-P spectrum analyser. From the measurement
result of the laser beam analyser, TEM
00
output from
the multi-frequency lasers is ensured.
The longitudinal mode of output laser for different
length of resonation is show in Fig.2, which
corresponding to one longitudinal mode, two
longitudinal modes and three longitudinal modes,
respectively.
For the single longitudinal mode output, the
linewidth is measured based on the fibre delayed
homodyne beat note method, and result is show as
Fig.3. From where, one can see, 16KHz of linewidth
is obtained. For the two longitudinal mode output,
the spacing of the longitudinal mode is 74.4GHz. For
the three longitudinal mode output, the spacing of the
longitudinal mode is 34.3GHz. In the experiments of
two frequencies and three frequencies, the measured
frequency spacing is a little bit smaller than
theoretical prediction raising from thermal expansion
of the laser medium.
Figure 2: The output longitudinal mode from LD pumped
different length of resonator lasers.
Figure 3: The linewidth of single frequency output based on
the measurement method of fibre delayed homodyne beat
note.
The output power of LD and thereafter the solid
state lasers is adjusted by tuning the pumping electric
current of LD. The output power of different
resonator length versus the pumping current is show
in Fig.4.
PHOTOPTICS 2019 - 7th International Conference on Photonics, Optics and Laser Technology
270
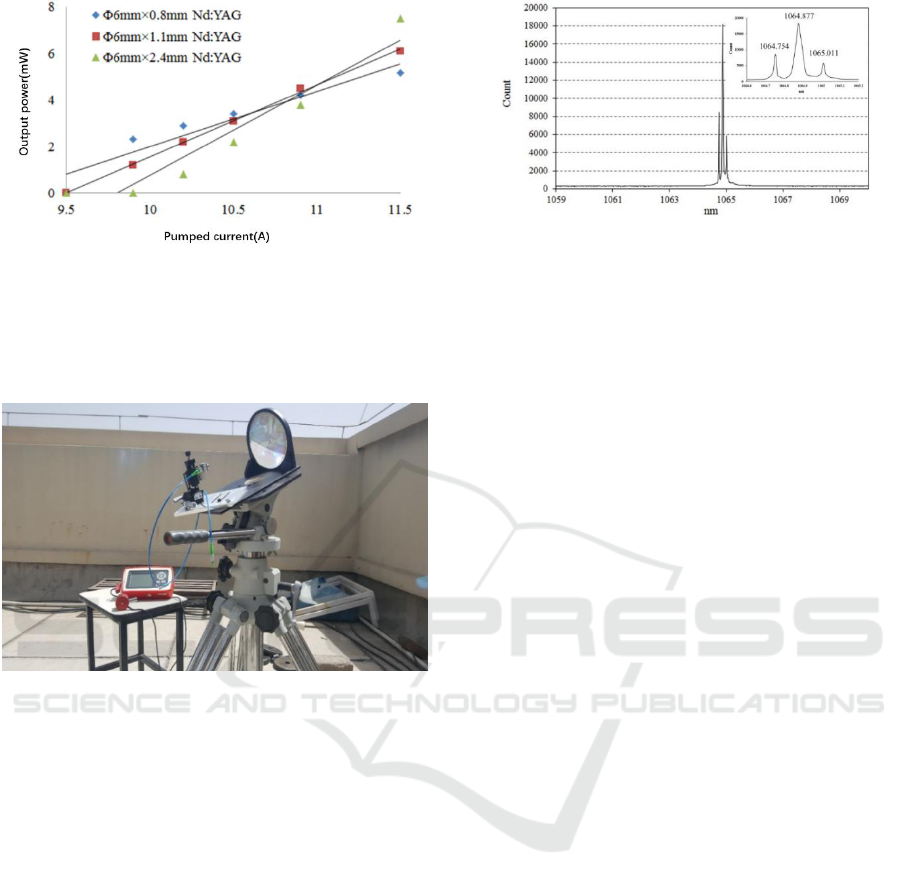
Figure 4: The output power of different resonator length
lasers versus pumping current.
After complication of indoors experiment, solar
pumped experiment outdoors is performed. The
picture of experimental facility is show in Fig. 5.
Figure 5: The picture of solar pumped multi-frequency
lasers experimental facility.
The experiment is performed in Beijing under
clear (with light cloud) weather, with measured solar
radiation density of 770W/m
2
. The output power of
different resonator length lasers versus pumping solar
power is show in Fig.6. Under the complexity outdoor
environment, SHR wavelength meter (SOLAR
LASER SYSTEM Co., ltd) is used to replace the F-P
interferometer as the frequency (wavelength)
measurement instrument, with the measurement
precision of 0.012nm around 1064nm. Fig.6 showed
the three wavelength output and the measured data for
each wavelength. The output wavelength is
1064.754nm, 1064.877nm and 1065.011nm,
respectively, corresponding to frequency of
281414.406GHz, 281449.906GHz and
281482.406GHz. Also, the measured frequency
(wavelength) spacing is a little bit different from
theoretical prediction, raising from thermal expansion
of the laser medium. The output power of each
frequency is different, with higher power in the
central frequency, for which obtaining higher gain
compared with the another two frequencies.
Figure 6: The three wavelength output and measured data
for each wavelength.
3 SOLAR PUMPED ND:YAG
SLAB AMPLIFIER
Another way to use the solar pumped lasers for free
space laser communication is to amplify
simultaneously multi-frequency seed lasers by the
same solar pumped amplifier. A new bonding slab
solar pumped amplifier is designed and initial
experiment is performed.
3.1 Design of the Bonded
YAG/Nd:YAG/YAG Slab
Amplifier
The rod and disk geometry is usually adopted in laser
amplifier. For the purpose of solar pump, the
matching between focused solar light spot and the
laser medium is a new problem. The primary focusing
optics used is a larger aperture Fresnel lens, with the
size of 1.40m1.05m and focus length of 1.20m. The
measured diameter of focusing spot is 11.2mm,
corresponding to the 9.2mrad divergence angel of
solar light. The effect area of the Fresnel lens,
eliminating shade area of support mechanic is
1.03m
2
.Based on above consideration, a new slab
crystal amplifier is designed, with the size of
18mm12mm5mm. The slab is bonded with
YAG/Nd:YAG/YAG to form the sandwich structure,
show in Fig.7.
The upper layer is YAG crystal, with thickness of
1mm, the middle layer is Nd:YAG crystal, with
thickness of 3mm, and the bottom layer is YAG
crystal, with thickness of 1mm. The entrance and exit
windows for seed laser are coated with AR
coatings@1064nm ( T99.8% ) . The seed laser
travels in zigzag rout inside the gain medium. The
front (except the part of seed laser entrance and exit)
and rear surface of the crystal are coated with HR
Solar Pumped Lasers for Free Space Laser Communication
271
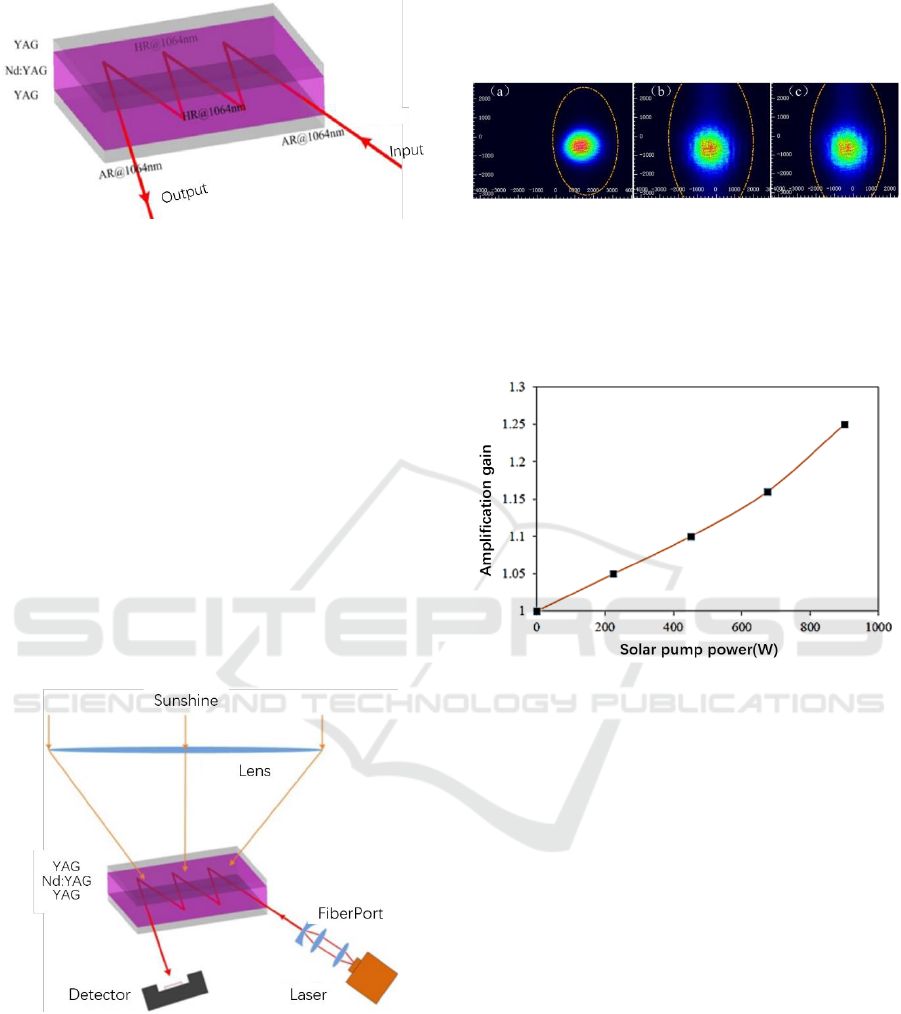
Figure 7: Bonded YAG/Nd:YAG/YAG crystal structure
and its coatings at each surfaces.
coating@1064nm. The upper surface of the crystal is
coated with AR coating@300-900nm (T95%), for
solar light to irradiate. The bottom surface of the
crystal is coated with HR coating@300-900nm
(T95%), for remaining solar light re-absorption. The
bonding crystal is favourable for protecting the
coatings under high temperature and increase the
utilization of pump solar light.
3.2 Initial Experimental Result of the
Solar Pumped Laser Amplifier
The experimental setup of the solar pumped laser
amplifier is show in Fig.8, which is composed of
Fresnel lens, seed laser, bonded slab laser crystal, and
temperature control system.
Figure 8: The experimental setup of the solar pumped laser
amplifier.
A 1064nm single mode seed fibre laser is firstly
aligned through a fibre port and then enter into the
laser crystal with a certain angle. After four times of
reflection inside the crystal, the amplified laser
emitted through the exit.
The beam profile of the seed laser, of the laser
after four times of reflection inside the crystal, and of
the laser after amplification are show in Fig.9(a), (b),
and (c), respectively, showing the beam quality
remain the same after amplification.
Figure 9: Comparison of the beam profile of the seed
laser(a), of the laser after four times of reflection inside the
crystal(b), and of the laser after amplification(c).
The gain of solar pumped laser amplifier versus
pumping solar power is show in Fig.10. The max gain
is 1.25, much lower the theoretical simulation.
Figure 10: The gain of solar pumped laser amplifier versus
pumping solar power.
4 DEMONSTRACTION OF FREE
SPACE LASER
COMMUNICATION USING
SOLAR PUMPED LASER
A free space laser communication system with a solar
pumped laser as the signal transmitter was
demonstrated. A 0.6m × 0.6 m Fresnel lens was used
as the primary concentrator to collect the solar light.
6.8 W continuous wave laser power was obtained
from a 4 mm diameter grooved Nd:YAG rod. The
output intensity was modulated with a video signal
via a LiNbO
3
Mach–Zehnder optoelectronic
modulator. The video signal with a resolution of
19201080/frame and the frame rate of 25 Hz was
transmitted over five-meter free space in real time
with high fidelity. The transmission rate was 125
Mbps and bit error rate was lower than 10
−6
.
PHOTOPTICS 2019 - 7th International Conference on Photonics, Optics and Laser Technology
272
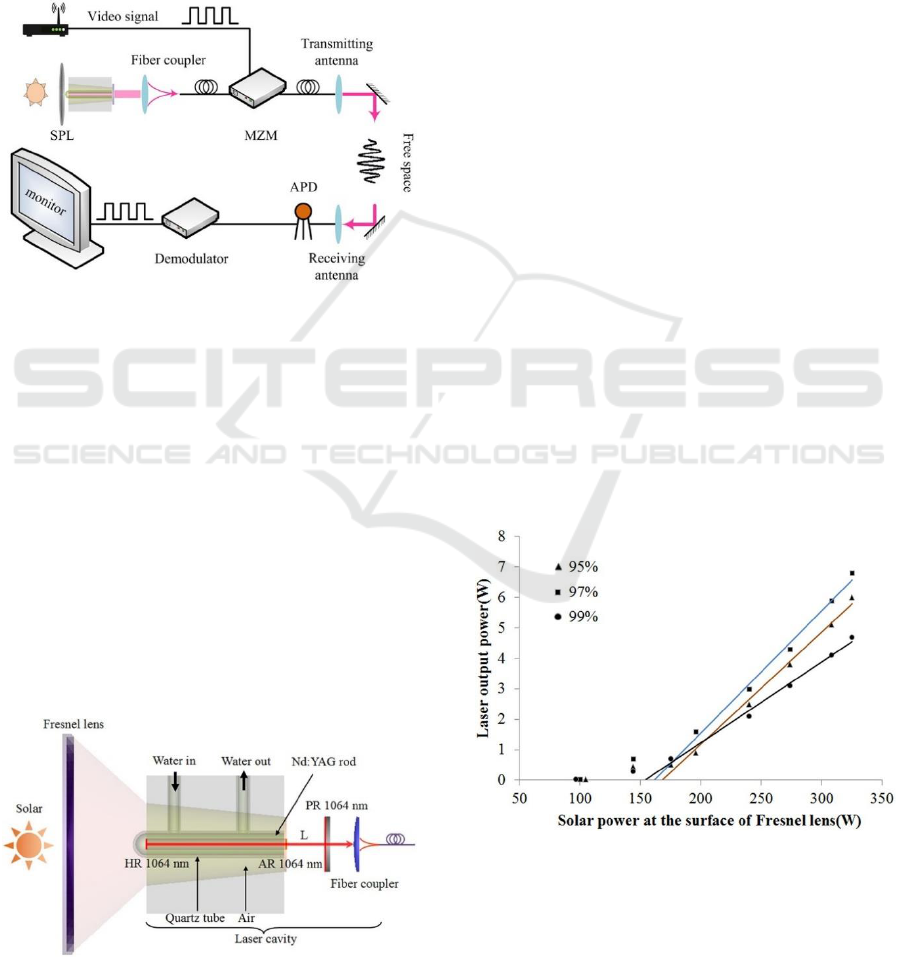
4.1 Experimental Setup of the Free
Space Laser Communication
System
The free space laser(FSL) communication system
was composed of a SPL with fibre coupler, a Mach–
Zehnder modulator (MZM), a set of optical
transmitting/receiving antennas, an avalanche photo
diode (APD), a demodulator and a monitor, as shown
in figure 11.
Figure 11: Scheme of the free-space laser communication
system. SPL, solar-pumped laser; MZM, Mach–Zehnder
modulator; APD, avalanche photo diode.
A more compact SPL was designed to meet the
requirements for FSL communication. A 0.6m×0.6 m
Fresnel lens which supplied by Shandong Yuying
Optical Instrument Co., LTD was used as the primary
concentrator. The Fresnel lens was made of
Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) material. The
focal length of the Fresnel lens was 0.89 m. A conical
cavity was used to further concentrate the solar light
into the laser rod, a quartz tube filled with cooling
water confines the solar light in the crystal. The
conical cavity also was cooled by cooling water. The
fibre coupling system with a single lens and a
multimode fibre was designed. Schematic of the SPL
is shown in figure 12.
Figure 12: Schematic of the solar pumped laser with Fresnel
lens and conical cavity.
The solar light was converged by a Fresnel lens and
was focused into the laser head. The input window of
the conical cavity was 30mm in diameter and 50mm
in length. The inner wall of the cavity was gold plated.
The outer diameter of quartz tube was 9mm. These
parameters were numerically optimized by
TracePro@ software. The grooved rod was cooled by
deionized water at 4.5lmin
−1
flow rate. The focal
length of the coupling lens was 100 mm and the
diameter of the fibre was 62.5 µm. We use a grooved
laser rod for a better heat dissipation effect. The
1.0at% grooved Nd:YAG rod with 4mm diameter,
70mm length, 0.6mm grooved pitch and 0.1mm
grooved depth was used.
4.2 Experimental Result of the Free
Space Laser Communication
System
The solar irradiance in Beijing during the experiment
was 930 W/m
2
. The Fresnel lens had an effective solar
energy collection area of 0.35 m
2
. For 326W solar
power at the surface of Fresnel lens, output couplers
of different reflectivity with same radius of curvature
(RoC) of 900 mm were tested individually to
maximize the output laser power. Figure 13 shows the
results of laser output with respect to various input
solar power levels. The maximum output power was
6.8 W corresponding to a slope efficiency of 3.9%
when R=97% output coupler was used. The optical-
optical efficiency was 2.1%. The maximum output
power from the R= 99%, R=95%, and R=97% output
coupler were 5.2W, 6.0W, and 6.8W, respectively.
Figure 13: Laser output power versus solar power at the
surface of Fresnel lens for three output couplers with
different reflectivity.
The video signal from a media player with the
resolution of 19201080/frame and the frame rate of
25 Hz is transmitted. A LiNbO
3
MZM modulates
Solar Pumped Lasers for Free Space Laser Communication
273
laser intensity with the encoded video signal. The
bandwidth of the MZM is 10GHz, and the frequency
limit of the video signal carrier is 4 GHz in the
experiments. Optical transmitting antenna collimates
the output light from the fibre and sends into free
space within 40 µrad angle of divergence.
Meanwhile, the optical receiving antenna focuses the
laser signal onto a high speed APD gain controller,
then a data decision circuit, successively. The decoder
restores the digital video signal and transmits to a
monitor.
During the testing of the free space laser
communication system with a distance of 5 meters, a
Lecory Labmaster 10-36Zi oscilloscope was used for
monitoring the communication system. The bit error
rate (BER) was measured lower than 10
−6
. The video
transmission rate was measured higher than 125
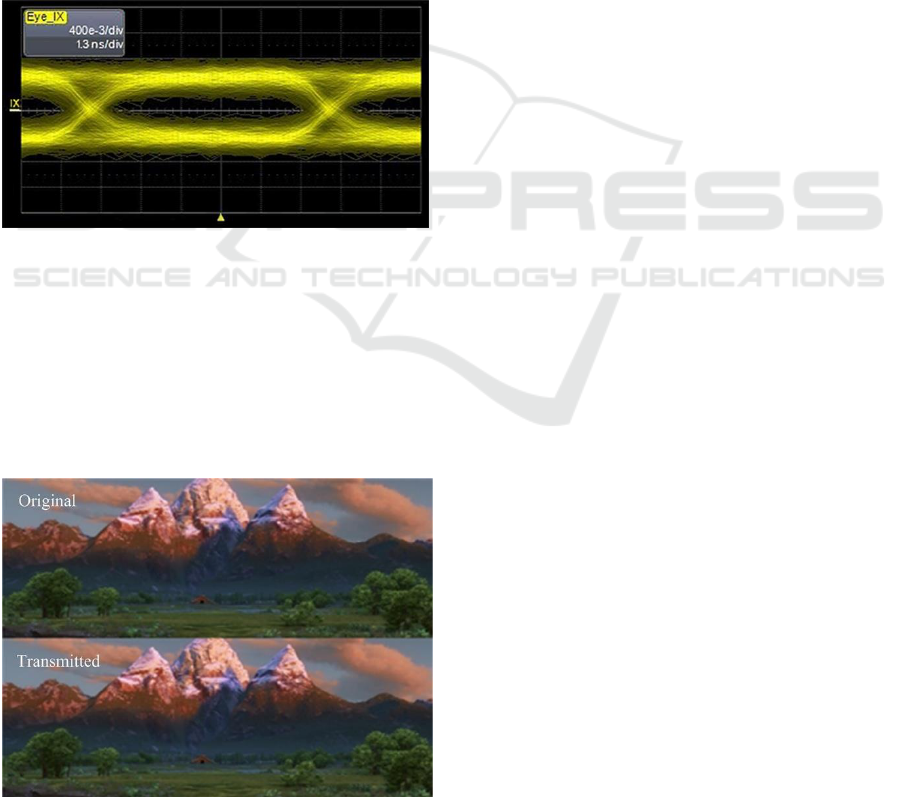
Mbps from an eye diagram shown in figure 14.
Figure 14: The 125 Mbps eye diagram of the demodulated
signals in 1.3 ns/div was measured by oscilloscope.
A real-time, high-fidelity transmission of video
signals had been realized in this system. The video
signal was divided into two paths: one was
transmitted by the free space laser communication
system, and the other one directly connected to the
display as a comparison. Figure15 shows a snapshot
of the video signal before and after the transmission.
Figure 15: The original and transmitted video snapshot.
5 CONCLUSION
A research works on the free space laser
communication system using solar pumped Nd:YAG
laser and related research is explored. Based on the
advantages of solar pumped laser, a simple, high
efficiency, and long lifetime free space laser
communication system is feasible in the near future.
Multi-frequency output solar pumped laser is
realised. The initial progress in the amplification of
1064nm seed laser by solar pump is achieved. A free
space laser communication system based on a SPL is
built. A high resolution video signal was transmitted
by the laser beam in a 5 meters free-space. 125 Mbps
bit rate was demonstrated, BER was measured lower
than 10
−6
. The feasibility of using SPL for high rate
communication application in free space was
demonstrated for the first time.
We hope our research can promote the
development of SPLs as well as their applications.
Future efforts will be made to increase the number of
channel for communication, and increase the data
transmission rate.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work is supported by the National Natural
Science Foundation of China (61775018).
REFERENCES
Mori et al., 2006. Summary of studies on space solar power
systems of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency
(JAXA). Acta Astronaut. 59 (2006) 132– 138.
Guan et al., 2017. Demonstration of a freespace optical
communication system using a solar-pumped laser as
signal transmitter. Laser Phys. Lett. 14 (2017) 055804.
Oliveira et al., 2016. A path to renewable Mg reduction
from MgO by a continuous-wave Cr, Nd:YAG ceramic
solar laser. Sol, Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 155 (2016)
430–435.
Yabe et al., 2008. 100 Wclass solar pumped laser for
sustainable magnesium-hydrogen energy cycle. Appl.
Phys. 104 (2008) 1–8.
Kiss et al., 1963. Sun pumped continuous optical maser.
Appl. Phys. Lett. 2 (1963) 93–94.
Young, 1966. A sun-pumped CW one-watt laser. Appl. Opt.
5 (1966) 993–998.
Weksler and Shwartz, 1998. Solar-pumped solid-state
lasers. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 24 (1998) 1222–
1228.
Yabe et al., 2007. High-efficiency and economical solar-
energy-pumped laser with Fresnel lens and chromium
PHOTOPTICS 2019 - 7th International Conference on Photonics, Optics and Laser Technology
274

codoped laser medium. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90 (2007)
261120.
Liang and Almeida, 2011. Highly efficient solar-pumped
Nd:YAG laser. Opt. Express. 19 (2011) 26399–26405.
Dinh et al., 2012. 120 watt continuous wave solar pumped
laser with a liquid light-guide lens and an Nd:YAG
rod.Opt. Lett. 37 (2012) 2670–2672.
Xu et al., 2014. High efficiency solar-pumped laser with a
grooved Nd:YAG rod. Appl.Opt. 53 (2014) 3941–3944.
Liang et al., 2017. Solar-pumped Nd:YAG laser with 31.5
W/m
2
multimode and 7.9 W/m
2
TEM00-mode
collection efficiencies. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells
159 (2017) 435–439.
Guan and Zhao, 2018. 32.1 W/m
2
continuous wave solar-
pumped laser with a bonding Nd:YAG/YAG rod and a
Fresnel lens. Optics and Laser Technology, 2018,
107:158-161.
Liu, 2007. Satellite laser communication I link and terminal
technology. Chin J Las34(1),3–10(2007).
Baister et al., 2003. The OPTEL Terminal Development
Programme-Enabling Technologies for Future Optical
Crosslink Applications. AIAA, space (2003).
Solar Pumped Lasers for Free Space Laser Communication
275
