
Using Multimodal Information to Enhance Addressee Detection
in Multiparty Interaction
Usman Malik, Mukesh Barange, Julien Saunier and Alexandre Pauchet
Normandie University, INSA Rouen, LITIS – 76000 Rouen, France
Keywords:
Human-Computer Interaction, Intelligent Agents, Machine Learning.
Abstract:
Addressee detection is an important challenge to tackle in order to improve dialogical interactions between
humans and agents. This detection, essential for turn-taking models, is a hard task in multiparty conditions.
Rule based as well as statistical approaches have been explored. Statistical approaches, particularly deep
learning approaches, require a huge amount of data to train. However, smart feature selection can help improve
addressee detection on small datasets, particularly if multimodal information is available. In this article,
we propose a statistical approach based on smart feature selection that exploits contextual and multimodal
information for addressee detection. The results show that our model outperforms an existing baseline.
1 INTRODUCTION
Human-Agent Interaction has been a prominent re-
search topic for the past three decades. While ad-
dressee detection is straightforward in dyadic interac-
tionit becomes a challenge in multiparty interaction
as the speaker can address any of the other partic-
ipants, the whole group, or a sub-group. However,
detecting whom the speaker is speaking to is crucial
for seamless continuation of the dialogue. Usually,
speakers exploit multimodal information such as hand
gestures, speech utterances, focus of attention, ... in
order to express hints as to which participant is being
addressed. Contextual factors like previous speaker
and addressee, type of previous and current utterances
can also play a role in addressee identification.
In dyadic and multiparty interaction, each partic-
ipant produces Dialogue Acts (DAs), either verbally
or non-verbally. A DA is defined as the meaning of
an utterance at the level of illocutionary force (Searle,
1969). DAs are addressed to one or multiple con-
versation participants: the speaker itself, or to one
or more other participants. According to (Goffman,
1981), an utterance affects three types of recipient:
over-hearers, the ones whose dialogue states are not
changed and are not concerned by the interaction;
the participants whose dialogue states are affected by
the speaker utterances but are not addressed by the
speaker, and finally the direct addressees of the DA.
In this article, we focus only on the direct addressee(s)
of an utterance. A direct addressee is defined in (Goff-
man, 1981) as “those ratified participants oriented to
by the speaker in a manner to suggest that his words
are particularly for them, and that some answer is
therefore anticipated from them, more so than from
the other ratified participants”. Thus, in order for a
virtual agent to be able to decide who the next speaker
should be, detecting the agent(s) addressed in the cur-
rent utterance is of uttermost importance.
In the literature, both statistical and rule based ap-
proaches have been developed for direct addressee de-
tection. However, these works tend to be dependant
on specific tasks or settings and do not generalize to
other situations. Furthermore, to train deep learning
models, a large amount of data is required. To the best
of our knowledge, currently no such dataset contain-
ing a large number of instances for multiparty inter-
action with annotated multimodal information exists.
Section 2 presents related work on addressee de-
tection. Our theoretical model is proposed in section
3. Section 4 describes a statistical analysis on a mul-
timodal corpus. The proposed approach along with
experimental results are presented in section 5. Sec-
tion 6 concludes the article.
2 RELATED WORK
This section reviews rule based and statistical main
approaches for addressee detection and then identifies
the features that can be exploited.
Malik, U., Barange, M., Saunier, J. and Pauchet, A.
Using Multimodal Information to Enhance Addressee Detection in Multiparty Interaction.
DOI: 10.5220/0007574602670274
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2019), pages 267-274
ISBN: 978-989-758-350-6
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
267
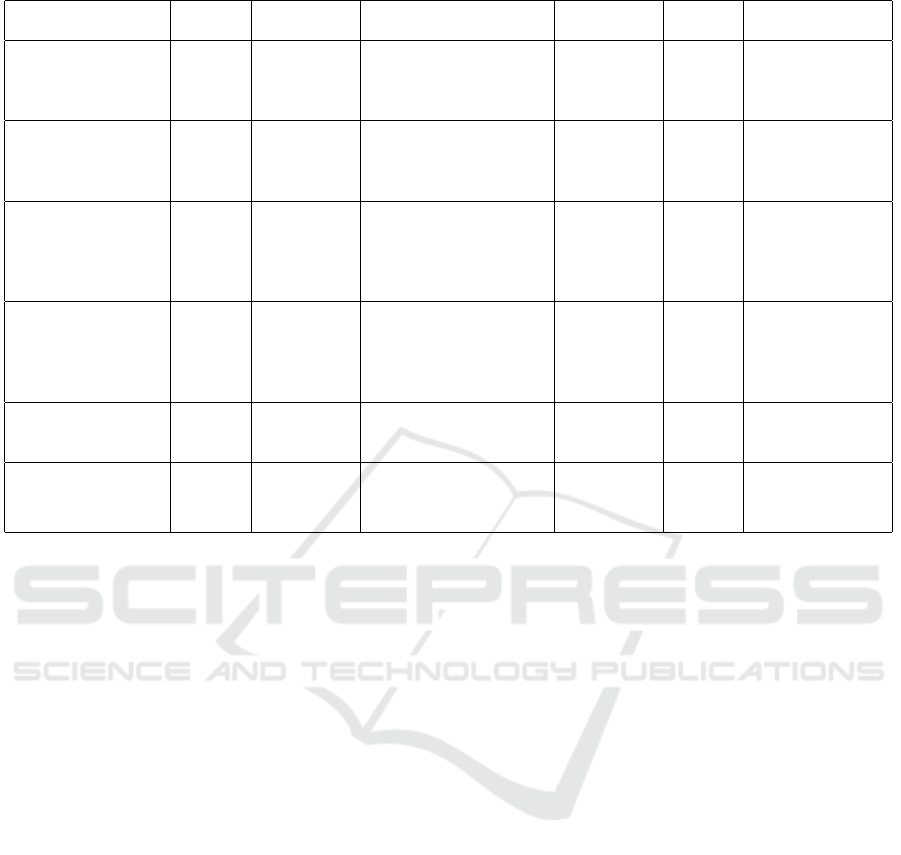
Table 1: Summary of existing works for addressee detection.
Reference Approach Dataset Salient Features Accuracy Accuracy
on AMI
Limitations
(Traum et al., 2004) Rule
Based
Mission
Rehearsal
Exercise
Current & previous utterance
current & previous speaker
65-100%
(Bbsed
on DA)
36%
Low accuracy
Not generic
(Akker and Traum, 2009)
Rule
Based
AMI
Gaze, current and
previous speaker,
current and previous utterance,
current and previous addressee
65% 65% Low accuracy
(Jovanovic, 2007)
Bayesian
Network
M4
Current utterance,
previous utterance,
speaker, topic of discussion,
gaze and several meta features
81% 62%
Fixed participant
positioning,
works only for
4 participants
hence Less generic
(Akker and Akker, 2009) Logistic
Model
Trees
AMI
Current utterance,
previous utterance,
speaker, topic of discussion,
gaze and several meta features
92% 92%
Fixed participant
positioning,
works only for
4 participants
hence not generic
(Baba et al., 2011) SVM
Custom Data
generated using
Wizard of OZ
head orientation,
acoustic features
and text as input features
80.28% NA
Binary
classification
Not generic
(Le et al., 2018) CNN,
LSTM
GazeFollow
dataset
Utterance and
gaze information
62% NA Addressee detection
from third party angle,
limited Accuracy
2.1 Addressee Detection Approaches
One of the earliest approach for addressee detection
in multiparty interaction was proposed by Traum et
al. (Traum et al., 2004). The proposed technique con-
tains a set of rules depending upon the current utter-
ance, the previous utterance, the current speaker and
the immediate previous speaker. Though the algo-
rithm reports F1 scores of 65% to 100% on different
dialogues in the Mission Rehearsal Exercise domain
(Traum et al., 2006), the algorithm does not general-
ize well to multimodality such as on the AMI cor-
pus (McCowan et al., 2005) with a reported accu-
racy of 36% (Akker and Traum, 2009). In this latter
work, the initial rule based approach is improved us-
ing gaze as additional information for predicting the
dialogue. They report an accuracy of 65% on the
AMI dataset. In addition to combining gaze and ut-
terance information, the authors have also tested gaze
as the only source of information for predicting the
addressee. The rule defines that, if during the utter-
ance the speaker looks more than 80% of the time at
an individual, then it is addressed to that particular
individual. Otherwise, the utterance is addressed to
the group. An accuracy of 57% is found with this ap-
proach on the AMI dataset.
Several statistical approaches have also been pro-
posed for addressee detection. Jovanovic et al. have
introduced a Bayesian network based approach for
addressee detection (Jovanovic, 2007) using utter-
ance, previous utterance, speaker, topic of discussion,
gaze and several meta features to train the Bayesian
network (Friedman et al., 1997) on the M4 multi-
modal, multiparty corpus (Jovanovic et al., 2006), and
reporting an accuracy of 81.05%. Akker and Traum
use the algorithm developed by (Jovanovic, 2007)
on the AMI corpus and report an accuracy of 62%
(Akker and Traum, 2009).
(Akker and Akker, 2009), in trying to answer the
question are you being addressed for the participants
of the AMI corpus, report a best case accuracy of 92%
using logistic model trees (Landwehr et al., 2005).
However, the output of this work is a special case of
binary classification. Moreover, it cannot be extended
to a different number of participants since classifica-
tion depends upon the position of the addressee and
not on the role or on the addressee name.
(Baba et al., 2011) propose a model that distin-
guishes whether an utterance is addressed to an agent
or a human, using human-human-agent triadic con-
versations collected through Wizard of OZ experi-
ments. They report an accuracy of 80.28 for the bi-
nary classification task using SVM with head orienta-
tion, acoustic features and text as input features.
Deep learning methods have also been proposed
for addressee detection by (Le et al., 2018), how-
ever they require very large datasets. They use CNN
(Krizhevsky et al., 2012) to identify the addressee
ICAART 2019 - 11th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
268

from visual scenes. The experiments are performed
on the GazeFollow dataset (Recasens et al., 2015).
For utterance understanding, RNN (LSTM (Hochre-
iter and Schmidhuber, 1997)) is used. An overall
recognition performance of 62.5% is reported. An-
other limitation of the model is that addressee detec-
tion is performed through third party angle.
2.2 Features for Addressee Detection
Existing works explore the best features for dialogue
management tasks such as addressee detection.
To this end, Galley et al. state that adjacency pairs
can be used as an indicator for the addressee (Galley
et al., 2004). An adjacency pair is a pair of utterances
where the second utterances (also known as b-pair) is
a response to the first utterance (known as a-pair).
DAs are also known to play a role in the identi-
fication of addressee. For instance, if a speaker asks
a yes-no question (a type of question that can have
only answer in the form of yes or no) and the ad-
dressee generates a positive response, the addressee
is most probably the previous speaker. The use of DA
in combination with other lexical cues are shown in
(Jovanovic and op den Akker, 2004).
Focus of attention is another important feature for
addressee detection. Vertegaal showed that 77% of
the time the person to whom the speaker is looking at
is the addressee of the utterance (Vertegaal, 1998).
2.3 Discussion
Table 1 summarizes some existing works on ad-
dressee detection in multiparty interaction, describing
approaches, datasets, features, model accuracy and
main limitations.
Although several researchers have tackled the
problem of addressee detection, most of them have
either solved binary classification problems e.g. if the
addressee is an agent or an individual (Baba et al.,
2011), or the approaches depend on the positioning
of the participants and is henceforth limited to a spe-
cific number of participants (Akker and Akker, 2009).
Deep learning models such as (Le et al., 2018) have
also been introduced but the results do not outper-
form rule-based approaches and require huge amount
of training data.
In this work, four hypotheses are considered:
firstly, the model should not be limited to any num-
ber of participants (h1); secondly, the tackled prob-
lem should remain addressee detection and not be re-
duced to a binary classification problem (h2); thirdly
the model should not depend upon the sitting posi-
tions of the participants (h3) and finally the model
should not require a huge dataset (h4). The rationale
behind the three first hypotheses is that the partici-
pants who are actually not being addressed should
also be aware of who is being addressed, indepen-
dently of how they are located in the room and how
many participants there are. The last hypothesis lim-
its the machine learning algorithms that can be used
but ensure a limited annotation effort.
Though several datasets have been used to learn
addressee detection model, the AMI dataset is the
most relevant for our own work because i) it is open
source and freely available, ii) it contains multimodal
data, iii) it contains annotated data by default and iv)
existing baselines are evaluated with it. To the best
of our knowledge, no other dataset combine all these
characteristics together.
Finally, only one work (Akker and Traum, 2009)
has used multimodal information in the AMI dataset
for multiclass classification of the addressee, yield-
ing an accuracy of 65%. We propose to consider this
work as baseline because hypotheses h1, h3 and h4
are respected.
3 THEORETICAL MODEL
The proposed approach intends to overcome the limi-
tations of the existing models by proposing a generic
model that solves multiclass classification problem
on small datasets. To fulfill these requirements, in
the proposed theoretical model the feature selection
is done so that i) the features are not dependent on
any particular dataset, ii) the features do not require
huge amount of data to yield good results.
Adjacency Pairs. Literature work has shown that
adjacency pairs is a marker for addressee detection
(Galley et al., 2004). Intuitively, a response in an ad-
jacency pair is addressed to the speaker of the first
utterance in the adjacency pair.
Dialogue Act. DAs play an important role in conver-
sational tasks such as addressee detection (Jovanovic
and op den Akker, 2004). If a DA is a question to an
individual, the response is normally addressed to the
speaker of the question.
Focus. Generally extracted from gaze information,
focus of attention is another feature used for ad-
dressee detection (Vertegaal, 1998; Akker and Traum,
2009; Le et al., 2018). The person in focus is fre-
quently the addressee of the utterance.
Previous and Current Speaker: Previous and cur-
rent speakers have also been used as features for
addressee detection (Traum et al., 2004; Jovanovic,
2007), although they, alone, may not provide infor-
mation (reported accuracy of only 36% on the AMI
Using Multimodal Information to Enhance Addressee Detection in Multiparty Interaction
269

dataset (Akker and Traum, 2009)).
Previous Addressee. Previous addressee is also an
important feature for addressee detection (Akker and
Traum, 2009).
You Usage. Research works show that utterances that
contain ‘you’ are usually addressed to an individual
user (Gupta et al., 2007).
Conjunction Usage. Since utterances can contain
multiple DAs and if addressees are annotated at DA
level, an intuition is that a new DA in an utterance
may start with a conjunction such as and, or, but, etc.,
with the addressee remaining the same.
Features that are too specific to a particular dataset
are not considered since the proposed model focuses
on generality. Unlike the chosen baseline model
(Akker and Traum, 2009), the usage of name and
role of the participants in the utterances have not
been taken into account for two reasons: i) different
datasets can have different participant names or roles
and ii) even if a user name is used in the utterance,
it does not always correspond to the addressee. For
instance, A tells B that C will perform X.
In the next section, a statistical analysis of these
features have been performed on the AMI corpus.
4 STATISTICAL ANALYSIS OF
THE PROPOSED FEATURES
This section describes the AMI corpus and statistical
evaluation of the proposed features on the dataset.
4.1 The AMI corpus
The AMI corpus (McCowan et al., 2005) is a multi-
modal interaction corpus consisting of 100 hours of
meeting recordings. The corpus includes two types
of meetings involving four participants: task oriented
sessions and open discussions. Task oriented meet-
ings come up with an innovative design of a remote
control while open discussion meetings have no re-
striction on the topic of discussion. The four partic-
ipants in the task oriented meetings are PM (Project
Manager), UI (User Interface Expert), ID (Industrial
Designer) and Marketing Executive (ME).
Several annotations are available for different sub-
sets of meetings including DA annotation, speaker
and listener information, focus of attention, adjacency
pairs, addressee information, hand gesture, etc. The
corpus contains over 117,000 utterances that have
been annotated with DAs, out of which 9,071 utter-
ances have been annotated with speaker focus and
8,874 utterances have been annotated with addressee
information. The number of utterances where the
three annotations - speaker focus, addressee, and DA-
are available is only 5,628. The utterances are cat-
egorized into 15 DAs. The utterances with back-
channels, stalls and fragments have not been assigned
any addressee, therefore technically only 12 cate-
gories remains for DAs.
In addition to utterances, the focus of attention is
also preprocessed. During the course of a DA, the
focus of attention can be any individual (PM, ME, UI,
and ID), or any object such as laptop, table and slide-
screen. For the sake of simplicity, if the speaker looks
at more than one individual or thing during the course
of a DA, the focus of attention is labelled “Multiple”.
4.2 Analysis of the Selected Features
The AMI dataset is first exploited to test and select
the features of our theoretical model that either come
from existing research works, or are new features.
4.2.1 Adjacency Pair
To see if adjacency pairs actually play a role in ad-
dressee detection, the percentage of utterances where
the previous speaker is the current addressee is com-
puted. The result shows that of all the utterances
addressed to individual participants, only 32% ut-
terances has the current addressee as the previous
speaker, whereas 31% of the utterances are addressed
to the whole group. These results show that adjacency
pairs alone are not a good indicator of addressee.
4.2.2 Dialogue Act
Data analysis shows that if the current DA is elicit-
info and the focus of the speaker is participant X,
76.97% of the time X is the addressee. Another im-
portant observation is that if the previous DA is elicit-
info and the previous speaker is any participant X and
the previous addressee is participant Y, if the current
speaker is participant Y, then 93% of the time, cur-
rent addressee is participant X. The data analysis thus
shows that, at least some of the DAs are actually im-
portant indicators for addressee detection.
4.2.3 Focus of Attention
Existing works from literature show that focus is an
in important feature for addressee identification. This
claim has been evaluated on the AMI dataset as well.
Table 2 shows the percentage of addressee against
the focus of the speaker. The table depicts that when
the focus is on an individual during an utterance, the
individual is the addressee almost half of the times.
The values of 0.48, 0.52, 0.50 and 0.47 for ID, ME,
ICAART 2019 - 11th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
270
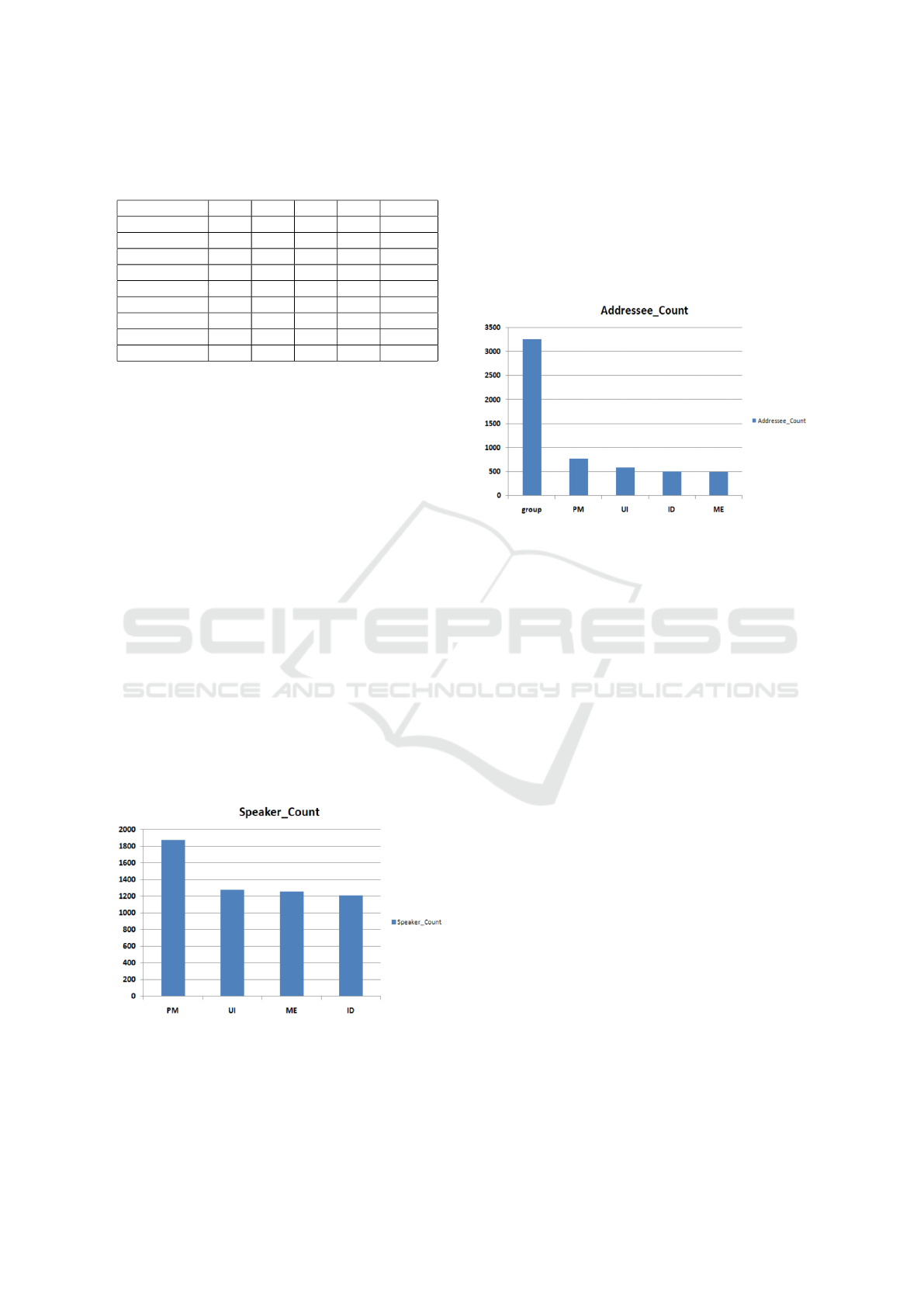
Table 2: Frequency of Focus vs Addressee (in percentage)
ID: Industrial Designer, ME: Marketing Executive, PM:
Project Manager, UI: User Interface Expert.
Focus ID ME PM UI Group
ID 0.48 0.04 0.02 0.02 0.42
ME 0.03 0.52 0.03 0.02 0.38
PM 0.01 0.02 0.50 0.03 0.44
UI 0.03 0.01 0.02 0.47 0.44
Multiple 0.05 0.05 0.07 0.07 0.74
no 0.10 0.08 0.15 0.08 0.57
Slide Screen 0.08 0.05 0.27 0.06 0.52
Table 0.07 0.12 0.14 0.10 0.55
Whiteboard 0.05 0.14 0.11 0.07 0.60
PM and UI substantiates this argument. Furthermore,
if the individual under focus is not the addressee, the
utterance is normally addressed to the whole group.
Only in rare cases does the speaker look at one indi-
vidual to then address another individual.
Similarly, if the speaker is looking at multiple
users, 74% of the time the utterance is addressed to
the whole group. If the Slide screen is the focus of the
speaker, he normally addresses the group as shown in
the table. The results show that the speaker focus is
actually crucial for addressee detection in this corpus.
4.2.4 Speaker Information
Figure 1 shows distribution of speaker role against ut-
terances. Since the corpus deals with task oriented
meetings, the utterances addressed to the PM are nat-
urally more numerous than those to the rest of the
participants since the PM is anchoring the interaction.
The result shows that the speaker actually play an im-
portant role. Also, current and previous speaker alone
may not play an important role in addressee detection,
but in combination with DA and previous addressee
they can be an important indicator.
Figure 1: Distribution of Speaker Role across utterances.
4.2.5 Addressee Information
Figure 2 shows frequency of addressees. More than
half of the utterances are addressed to the whole group
rather than individual participants. The addressee
count is higher for PM among individuals because the
PM has the highest frequency of speaking, and there
is thus a higher chance that people reply to her.
Figure 2: Distribution of Addressee Role across utterances.
4.2.6 You Usage
Statistical analysis reveals that of all the utterances
where the word “you” is used, the utterance is ad-
dressed to individuals and the focus of attention is
also an individual, only 42.44% of utterances are ad-
dressed to the focused individual. However this num-
ber increases to 78% when the group is addressed and
multiple objects are in focus. This indicates that the
you usage can be exploited to distinguish between in-
dividual and group addressees.
4.2.7 Conjunction
Statistical analysis on AMI dataset shows that when
the previous and current speaker of an utterance are
identical and the current utterance starts with a con-
junction, the current addressee is the previous ad-
dressee 90.73% of the time. Once again, conjunction
alone is not a good indicator, rather current and previ-
ous speaker information combined with conjunction
is crucial to addressee detection.
4.2.8 Summary
Statistical analysis of the features proposed in the the-
oretical model shows that apart from adjacency pairs,
the rest of the features should give information for au-
tomatic addressee detection. It is also worth mention-
ing that although individually some of the features
Using Multimodal Information to Enhance Addressee Detection in Multiparty Interaction
271
such as conjunction rule are not very useful, they be-
come good indicators when coupled with other fea-
tures such as previous and next speaker.
The next section details our approach regarding
the classification of the addressee along with the clas-
sifier information, evaluation results.
5 EXPERIMENTS AND RESULTS
The proposed approach revolves around a selection
of the most suitable features from literature review
and exploratory data analysis that can help develop
a flexible addressee detection model.Traditional ma-
chine learning algorithms are used to train the model
on the training set and consequently the performance
of the models is evaluated on the test set. Note that
deep learning models have not been considered due
to our hypothesis to use small datasets.
5.1 Feature Selection
The features used for training the models are selected
according to the literature review (section 2) and sta-
tistical analysis of features (section 4.2). They have
been divided into three categories: Contextual Fea-
tures, Focus of attention and Textual Features.
5.1.1 Contextual Features
Contextual features are not associated with any inter-
action modality. The selected contextual features are:
previous speaker, current speaker, previous DA, cur-
rent DA and previous addressee.
5.1.2 Focus of attention
During an utterance, a speaker can have one or mul-
tiple focuses of attention. Focus is simplified into in-
dividual or multiple categories. If during the whole
course of utterance, the speaker looks only at one sin-
gle participant or object, that participant/object is la-
belled as the focus of attention. On the other hand,
in case of multiple focus of attentions, the focus has
been labelled as ‘Multiple’.
5.1.3 Textual Features
‘You usage’ and ’conjunctions’, respectively, can be
helpful for addressee detection and hence have been
chosen for training the classifiers. The whole tex-
tual information is not selected as a feature because
full text can be too specific and thus would result in
an over-fitted model. For the same reason, features
where the name or role of the participant is directly
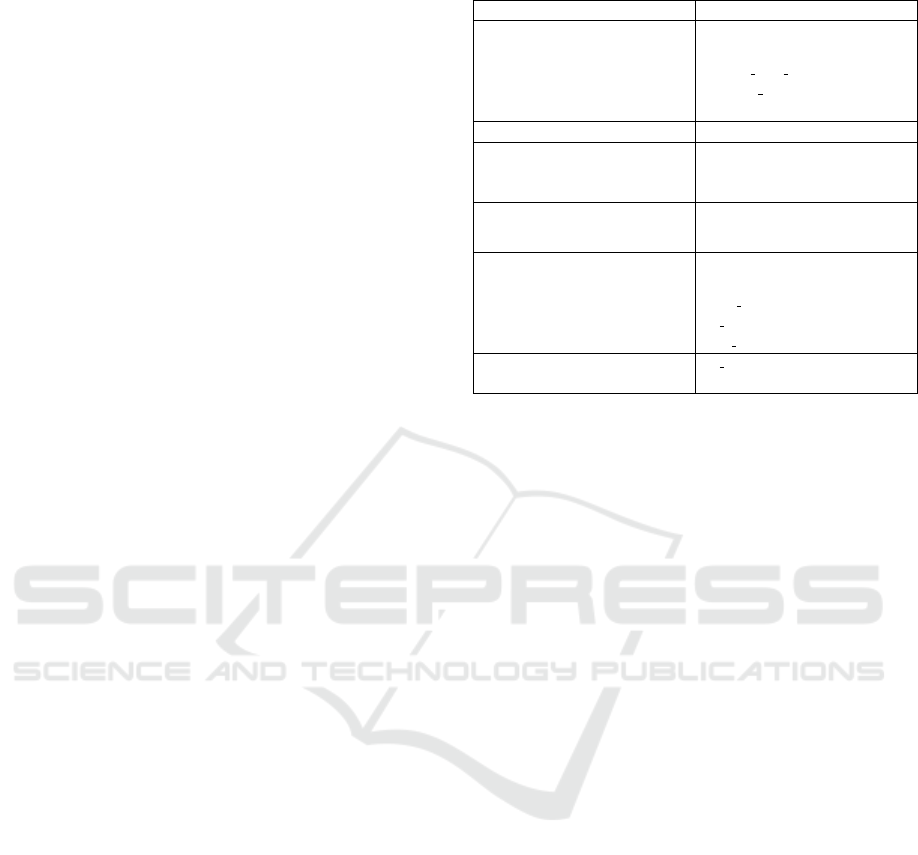
Table 3: Classifiers along with hyper parameter values.
Classifier Parameters
Multilayer Perceptron (Kruse et al.,
2013)
’activation’: ’tanh’,
’alpha’: 0.05,
’hidden layer sizes’: 100
’learning rate’: ’constant’,
’solver’: ’adam’
Naive Bayes (Rish et al., 2001) No hyper parameters
Support Vector Machine (SVM)
(Hearst et al., 1998)
’C’: 100,
’gamma’: 0.01,
’kernel’: ’rbf’
Logistic Regression (Hosmer Jr
et al., 2013)
’penalty’=’l2’,
’regularization’ = 100
Random Forest (Liaw et al., 2002)
’bootstrap’: True,
’criterion’: ’entropy’,
’max features’: ’auto’,
’n estimators’: 300
max iter=100
K Nearest Neighbours (KNN)
(Zhang and Zhou, 2005)
’n neighbors’: 12
being called are not considered. Such models tend to
not generalize well over different scenarios.
5.2 Experiments
The task is to predict the role of the addressee given
the proposed features. This is multi-class classifica-
tion problem where the output can be either Group,
PM, ID, UI or ME. To perform the experiments, a
conventional machine learning pipeline is followed.
During the preprossessing phase, the categorical
features are converted into one-hot vectors. 5-fold
cross-validation is performed in order to obtain the
final results. Six of the most commonly used ma-
chine learning classifiers are tested in order to evalu-
ate the performance of the model. Details of the clas-
sifiers along with some of the most important hyper-
parameters are presented in Table 3. The best pa-
rameters for each classifier are selected using grid
search algorithm (Smit and Eiben, 2009). For the
hyper-parameters that are not mentioned, default val-
ues are used as specified in Python’s Sklearn library
(Pedregosa et al., 2011).
In addition to performing cross validation, the per-
formance of the algorithm is evaluated on an unseen
test set in order to verify that the model is not over-
fitting and to produce an analysis of the classification
result for individual classes.
To evaluate the algorithms, accuracy and F1 mea-
sure are considered as performance metrics, since the
baseline results are reported in terms of accuracy and
F1. Nevertheless, the F1 measure should be favored
in the analysis of the results due to irregular class
distribution: the PM and group addressees are over-
represented in the dataset.
ICAART 2019 - 11th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
272
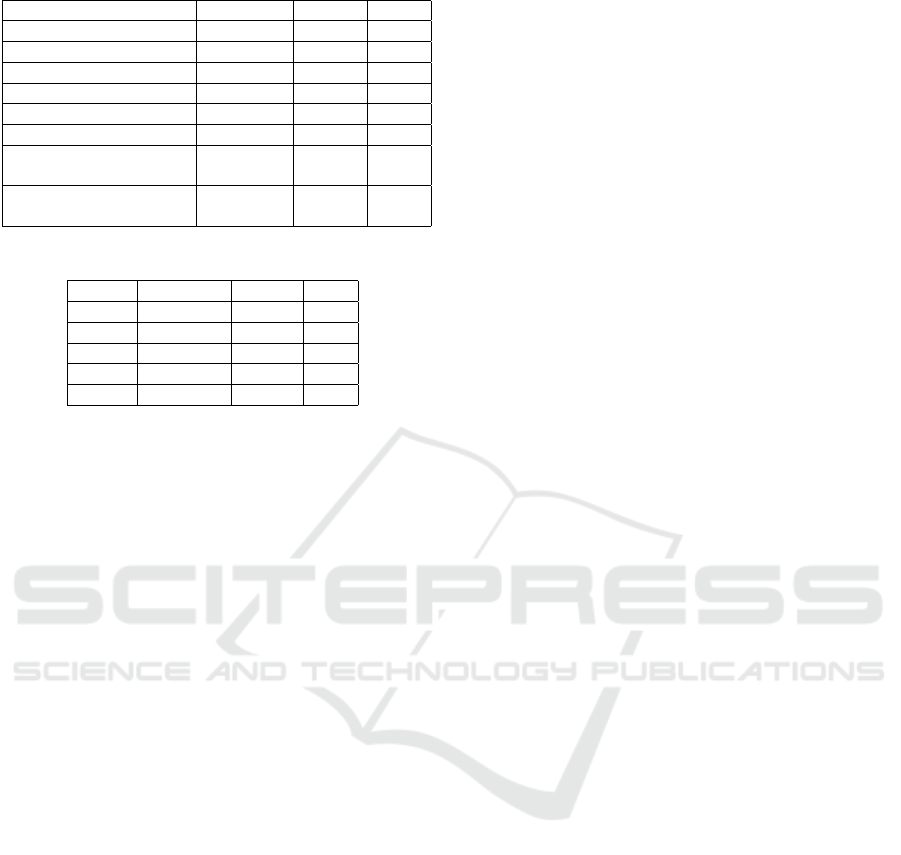
Table 4: Classification Results for Addressee Detection.
Classifier Accuracy St Dev F1
Multilayer Perceptron 73.26 % 0.02 0.722
Naive Bayes 68.25 % 0.01 0.63
Logistic Regression 73.44% 0.02 0.727
SVM 72.52 % 0.02 0.720
Random Forest 69.94 % 0.019 0.68
K Nearest Neighbours 68.19 % 0.006 0.68
Corpus Baseline (Al-
ways Group)
54 % NA NA
Baseline (Akker and
Traum, 2009)
65% NA 0.55
Table 5: Results for single test set using logistic regression.
Class Precision Recall F1
ID 0.68 0.67 0.67
ME 0.67 0.59 0.63
PM 0.71 0.57 0.63
UI 0.69 0.47 0.56
Group 0.76 0.86 0.80
5.3 Results
The results for 5-fold cross-validation are reported in
table 4. The table contains the accuracy, standard de-
viation and F1 measure of the 6 classifiers used for
the addressee prediction. The results show that Lo-
gistic Regression, with l2 loss function and regular-
ization value of 100, yields an accuracy of 73.44 that
outperforms the baseline algorithm in terms of both
accuracy and F1 measure. Multi-layer perceptron and
SVM are only slightly below.
The detailed classification report for logistic re-
gression for the unseen test set has been reported in
table 5. The results show that an F1 value of 80 is
achieved for the group. For individual participants the
F1 values vary between 0.56 for UI and 67 for ID. The
reason for the variation between the F1 values for in-
dividual participants is yet to be studied.
5.4 Discussion
The results show that our best model yields an ac-
curacy of 73.44% which is greater than the base-
line accuracy of 65% reported by (Akker and Traum,
2009) for the classification of all the participants. Our
model also outperforms the baseline model with al-
most all algorithms, which indicates the relevancy of
the selected features. Furthermore, unlike (Akker and
Akker, 2009), our proposed model is not dependent of
the location of the participants in the meeting. In ad-
dition, the F1 score also shows that our model is better
at classifying the dataset with irregular class distribu-
tion. For instance, in the case of baseline model the
F1 score of 75% was achieved for the class ‘Group’,
however our model achieves an F1 score of 80% for
the ‘Group’. Similarly, for the baseline model, the av-
erage F1 score for the individual addressees is 0.36,
while in our model the average F1 score for the indi-
vidual addressee is 0.62.
The results from the best performing algorithm
(logistic regression) are interpreted with the help of
logistic regression coefficients (Peng et al., 2002).
Mean value of -0.003 is obtained for the coefficients
of all the features in the data set. The results show that
the features previous speaker, previous addressee,
current speaker and current focus have coefficient
values greater than the mean coefficient values and
hence can be regarded as the top contributors to the
performance of the algorithm.
Experiments performed with only these four fea-
tures resulted in an accuracy of 70.57% with an F1
value of 0.70 which verifies the key role of these fea-
tures in the classification of the addressee. It is impor-
tant to mention that the importance of the remaining
four features (previous and current DA, conjunction
and you usage) cannot be ignored since they actually
contribute to a 3% improvement. However from the
results, it is safe to assume information about con-
textual features i.e. previous and current speaker, the
previous addressee, and focus features like the focus
of the current speaker play a major role on addressee
detection compared to textual features such as con-
junctions and you usage.
6 CONCLUSION
Addressee detection in multiparty interaction is a cru-
cial tasks. To this end, the previous rule based ap-
proach yields an accuracy of 65% for all different
participants. Works from (Akker and Akker, 2009)
achieved an accuracy of 92% but their model solves
binary classification problem of “are you being ad-
dressed or not”. Furthermore, their model depends
upon the location of the meeting participants and can
only work for a fixed number of participants (four
and only four). In this article, a generic addressee
detection model has been proposed that solves mul-
ticlass class problem of addressee detection (hypoth-
esis h2) and does not depend upon the number (h1)
and location of the participants (h3) in the multiparty
interaction. Finally, the results show that our model
works well on small dataset (h4), and outperforms the
baseline model (Akker and Traum, 2009) with an im-
provement of 8% in accuracy.
Though the approach is promising, certain limita-
tions remain. The approach was only tested on a sin-
gle dataset and even though the features are generic,
Using Multimodal Information to Enhance Addressee Detection in Multiparty Interaction
273

how well the model generalizes on other datasets is
yet to be studied. Another limitation is the small size
of the dataset, which is a major difficulty in the use of
more advanced deep learning techniques. Thus, the
next step would be to perform an experiment to col-
lect a larger dataset.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by the DAISI project, co-
funded by the European Union with the European
Regional Development Fund (ERDF), by the French
Agence Nationale de la Recherche and by the Re-
gional Council of Normandie.
REFERENCES
Akker, H. and Akker, R. (2009). Are you being addressed?-
real-time addressee detection to support remote par-
ticipants in hybrid meetings. In Proceedings of the
SIGDIAL 2009 Conference, pages 21–28.
Akker, R. o. d. and Traum, D. (2009). A comparison of
addressee detection methods for multiparty conversa-
tions. In Workshop on the Semantics and Pragmatics
of Dialogue, pages 99–106.
Baba, N., Huang, H.-H., and Nakano, Y. I. (2011). Iden-
tifying utterances addressed to an agent in multiparty
human–agent conversations. In International Work-
shop on Intelligent Virtual Agents, pages 255–261.
Friedman, N., Geiger, D., and Goldszmidt, M. (1997).
Bayesian network classifiers. Machine learning, 29(2-
3):131–163.
Galley, M., McKeown, K., Hirschberg, J., and Shriberg,
E. (2004). Identifying agreement and disagreement
in conversational speech: Use of bayesian networks
to model pragmatic dependencies. In Proceedings of
ACL’04, page 669.
Goffman, E. (1981). Forms of talk. university of pennsyl-
vania publications in conduct and communication.
Gupta, S., Niekrasz, J., Purver, M., and Jurafsky, D. (2007).
Resolving you in multiparty dialog. In In Proc. SIG-
dial, pages 227–230.
Hearst, M. A., Dumais, S. T., Osuna, E., Platt, J., and
Scholkopf, B. (1998). Support vector machines. In-
telligent Systems and their applications, 13(4):18–28.
Hochreiter, S. and Schmidhuber, J. (1997). Long short-term
memory. Neural computation, 9(8):1735–1780.
Hosmer Jr, D. W., Lemeshow, S., and Sturdivant, R. X.
(2013). Applied logistic regression, volume 398.
Jovanovic, N. (2007). To whom it may concern-addressee
identification in face-to-face meetings.
Jovanovic, N., Akker, R. o. d., and Nijholt, A. (2006). A
corpus for studying addressing behaviour in multi-
party dialogues. LREC’06, 40(1):5–23.
Jovanovic, N. and op den Akker, R. (2004). Towards
automatic addressee identification in multi-party dia-
logues. In Proc. of SIGdial@HLT-NAACL’04.
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., and Hinton, G. E. (2012). Im-
agenet classification with deep convolutional neural
networks. In Advances in neural information process-
ing systems, pages 1097–1105.
Kruse, R., Borgelt, C., Klawonn, F., Moewes, C., Stein-
brecher, M., and Held, P. (2013). Multi-layer percep-
trons. In Computational Intelligence, pages 47–81.
Landwehr, N., Hall, M., and Frank, E. (2005). Logistic
model trees. Machine learning, 59(1-2):161–205.
Le, T. M., Shimizu, N., Miyazaki, T., and Shinoda, K.
(2018). Deep learning based multi-modal addressee
recognition in visual scenes with utterances. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1809.04288.
Liaw, A., Wiener, M., et al. (2002). Classification and re-
gression by randomforest. R news, 2(3):18–22.
McCowan, I., Carletta, J., Kraaij, W., Ashby, S., Bourban,
S., Flynn, M., Guillemot, M., Hain, T., Kadlec, J.,
Karaiskos, V., et al. (2005). The ami meeting cor-
pus. In Proc. of the 5th International Conference on
Methods and Techniques in Behavioral Research, vol-
ume 88, page 100.
Pedregosa, F., Varoquaux, G., Gramfort, A., Michel, V.,
Thirion, B., Grisel, O., Blondel, M., Prettenhofer,
P., Weiss, R., Dubourg, V., et al. (2011). Scikit-
learn: Machine learning in python. Journal of ma-
chine learning research, 12(Oct):2825–2830.
Peng, C.-Y. J., Lee, K. L., and Ingersoll, G. M. (2002). An
introduction to logistic regression analysis and report-
ing. The journal of educational research, 96(1):3–14.
Recasens, A., Khosla, A., Vondrick, C., and Torralba, A.
(2015). Where are they looking? In Adv. in Neural
Information Processing Systems, pages 199–207.
Rish, I. et al. (2001). An empirical study of the naive bayes
classifier. In IJCAI 2001 workshop on empirical meth-
ods in artificial intelligence, volume 3, pages 41–46.
IBM New York.
Searle, J. (1969). Speech Acts: An Essay in the Philosophy
of Language.
Smit, S. K. and Eiben, A. E. (2009). Comparing parameter
tuning methods for evolutionary algorithms. In Proc
of CEC’09, pages 399–406.
Traum, D. R., Robinson, S., and Stephan, J. (2004). Evalua-
tion of multi-party virtual reality dialogue interaction.
In In Proc. LREC’04, pages 1699–1702.
Traum, D. R., Robinson, S., and Stephan, J. (2006). Evalu-
ation of multi-party reality dialogue interaction. Tech-
nical report, University of Southern California Marina
Del Rey CA Inst For Creative Technologies.
Vertegaal, R. (1998). Look who’s talking to whom. Medi-
ating Joint Attention in multiparty.
Zhang, M.-L. and Zhou, Z.-H. (2005). A k-nearest neigh-
bor based algorithm for multi-label classification. In
Granular Computing, 2005 IEEE International Con-
ference on, volume 2, pages 718–721. IEEE.
ICAART 2019 - 11th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
274
