
A Secure Framework with Remote Configuration of Intellectual
Property
Nadir Khan
1
, Sven Nitzsche
1
and Jürgen Becker
2
1
FZI Research Center for Information Technology, Karlsruhe, Germany
2
Institute for Information Processing Technologies (ITIV) Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) Karlsruhe, Germany
Keywords: Field Programming Gate Array (FPGA), Intellectual Property (IP), Secure Embedded Systems, IP
Protection, Dynamic Partial Reconfiguration, Cryptography, Trusted Execution Environments (TEE).
Abstract: In this work, an intellectual property (IP) licensing framework is proposed that is secure against IP theft
(cloning and redistribution). This security is provided by utilizing built-in features of modern field
programmable gate arrays (FPGAs), e.g. secure boot, state-of-the-art cryptography and trusted execution
environments (TEE). The scheme is also the least restrictive in comparison to other publications in this area.
Using this scheme, multiple IP core vendors (CVs) can configure their IPs remotely by connecting directly
to an FPGA. Devices are booted securely using an authenticated and encrypted boot loader that initiates an
authenticated and encrypted hypervisor, which in turn provides a TEE by partitioning the system resources
into secure and non-secure sections. At this stage, a secure operating system (OS) is loaded that handles all
the security critical functions such as communication with CVs, storage and analysis of bitstreams,
enforcement of license constraints and configuration of IPs. Then, a second, non-secure OS is loaded, which
provides an isolated execution environment with unrestricted access to non-secure resources. Hence, they
are not limited to predefined APIs. Both OSes can interact via the hypervisor. The implementation of this
framework is a work-in-progress and results presented within this paper are subject to change.
1 INTRODUCTION
Production costs for integrated circuits (ICs) are the
key cost factor for low-volume applications.
Programmable devices like FPGAs can be a cost
effective alternative in such cases. With recent
advances in technology, these devices are offering
enough resources to accommodate even large
designs, making them suitable for a variety of
industrial applications.
FPGAs are programmed using a digital bitstream
that can be easily distributed independent of the
physical device, which makes FPGAs an ideal
platform for circuit trading. For example, system
developers (SD) can outsource the development of
parts of a circuit to or license them from third
parties, who might be more experienced in a specific
area. This kind of approach can reduce development
costs and give system developers an edge over their
competitor in performance but also in time-to-
market. Such licensable circuit designs are called
intellectual property (IP) and are sold by a core
vendor (CV). In general, they can be delivered in
different digital formats like register-transfer level
(RTL) code, netlist or bitstream. However, RTL and
netlist representations need to be integrated by
system developers during development and thus
must be in a readable format, offering no protection
against extraction of the original design. Bitstream,
on the other hand, are processed directly on an
FPGA, without direct access by SDs. Therefore,
they are comparatively more secure against reverse
engineering (RE), as they can be distributed in a
proprietary format that is only known to the FPGAs
themselves. Since this resilience against reverse
engineering is only based on obscurity through the
proprietary format, extraction of information is still
possible with enough effort. Furthermore, all of
these formats are vulnerable to overuse and
redistribution.
In response to these problems, modern FPGAs
offer several built-in security features, i.e. an
internal decryption engine and a secure hardware
key vault, so that bitstreams may be delivered in
encrypted form and only be configured on an FPGA
that stores the corresponding decryption key.
564
Khan, N., Nitzsche, S. and Becker, J.
A Secure Framework with Remote Configuration of Intellectual Property.
DOI: 10.5220/0007576305640571
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy (ICISSP 2019), pages 564-571
ISBN: 978-989-758-359-9
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
However, programming the key into a device also
causes several problems. If SDs perform this task,
they get access to any IP, exposing them to overuse
or redistribution. Similarly, if a specific CV
programs the key, it would mean that either only
their IPs could be used (as only, they know the key)
or that all involved CVs have to agree on one key,
which in turn creates more security problems, i.e. a
CV can access another CVs intellectual property.
Additionally, it would introduce the logistical
overhead of sending devices to the CV.
To cover these problems, this work provides a
detailed investigation of existing licensing and
remote configuration approaches. Their security and
feasibility issues are discussed and a method for a
secure licensing infrastructure with remote
configuration capability is derived.
1.1 IP Licensing
Typically, multiple entities are involved in the
secure delivery of intellectual property. Throughout
this paper, the following naming conventions are
used, which are common among related works in the
area of IP licensing and remote configuration:
FPGA Vendor (FV): Producers of FPGAs and
system-on-chip (SoC) devices. These products are
commercially available with necessary
documentation and development tools and can be
used as off-the-shelf products.
Trusted Third Party (TTP): This role can be
played by any entity, notably an FV or a Hardware
Manufacturer (HM). Its responsibilities include
preparing devices for a licensing scheme,
programming keys, adjusting security settings or
handling encryption of IPs.
Core Vendor (CV): Producers of a specialized
licensable circuit.
System Developer (SD): System developers license
IPs from CVs and integrate them into their own
hardware design.
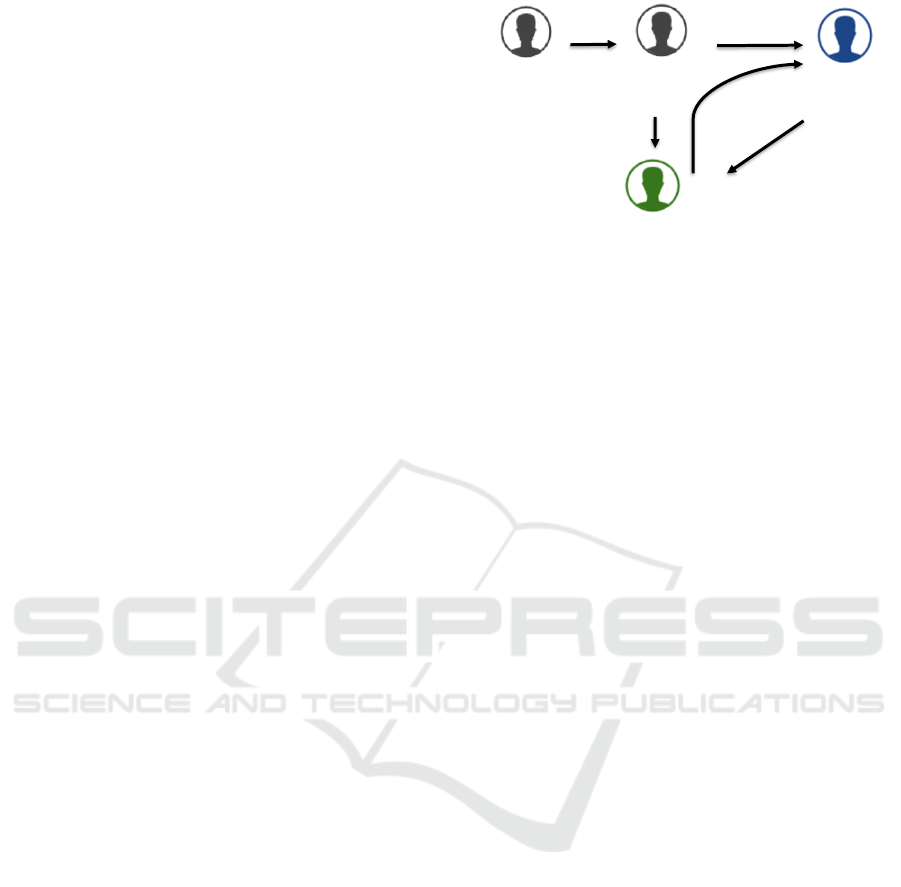
The relation between them is shown in Figure 1
along with the order of required tasks:
1. A TTP buys devices from an FV and prepares
them for IP licensing.
2. Necessary details (device type, location,
interfaces etc.) are shared with CVs so that they
can develop IPs accordingly.
3. Prepared FPGAs are delivered to SDs.
4. SDs acquire licenses from CVs for required IPs.
5. CVs provide SDs with the requested IPs via a
TTP that manages the security aspects of the
transaction.
Figure 1: Flow of a licensing scheme.
1.2 Remote Configuration
Remote configuration, in the context of IP licensing,
refers to the process of a CV remotely accessing the
device of an SD and configuring their IPs into it.
This direct access reduces the number of steps
required in the process of acquiring an IP and makes
the licensing scheme’s implementation easier. Since
IPs are configured on the device without further
processing, they must be in the bitstream format.
However, in the absence of appropriate security
features, overuse of the IP cannot be prohibited.
Therefore, a suitable licensing framework needs to
be present to provide CVs with measures against
threats like cloning, reverse engineering,
redistribution and tampering. Since both remote
configuration and IP licensing, are dependent on
each other, we will treat them holistically rather than
individually. Consequently, a secure IP licensing
methodology will be proposed and then a remote
configuration capability will be added on top of it.
2 RELATED WORK
2.1 IP Licensing
IP Licensing and remote configuration are both well-
researched areas. A commonly used approach by
researchers is the involvement of a trusted third
party (TTP). The primary reason for this
involvement is that it solves the conflict of pre-
programming a key into the non-volatile memory
(NVM) of a target device, as discussed before, with
the least impact on security.
The programmed key is then used by core
vendors to generate encrypted IPs, which are useable
only on the target device (Kean, 2002). However,
the drawback of this approach is that a high degree
of trust is put in the TTP as they have access to the
key and therefore all IPs.
FPGA Vendor
System
Developer
Trusted Third
Party
Core Vendor
1
2
3
4
5
A Secure Framework with Remote Configuration of Intellectual Property
565
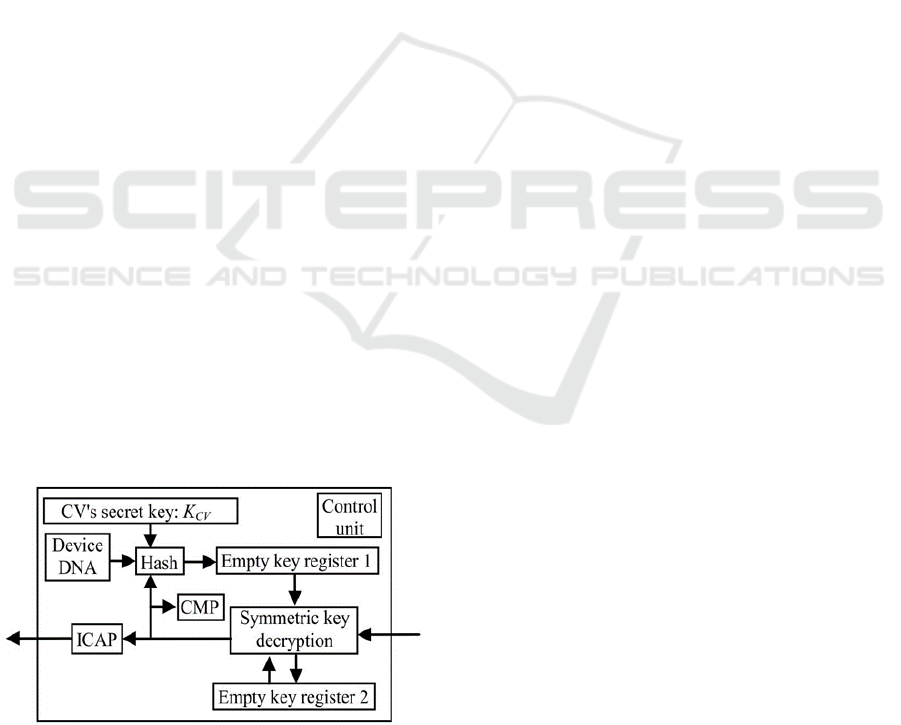
To avoid this, some researchers introduced an
additional security layer in the form of a Core
Installation Module (CIM) (Guneysu et al., 2007;
Maes et al., 2002; Zhang and Chang, 2014; Zhang
and Chang, 2015). These modules are developed by
CVs for the decryption of their IPs. They contain
another key, which is different from the pre-
programmed one and is only known to the CV. The
CIM bitstream itself is then delivered to TTPs that
encrypt it with the device root key and deliver it to
SDs. CIMs typically contain a custom decryption
logic. An example CIM is shown in Figure 2.
Such modules increase security because even if
the root key is leaked, adversaries have to reverse
engineer a CIM for the extraction of IP specific
keys, and only then single IPs can be decrypted. This
process has to be repeated for every IP, which makes
it an effort beyond financial gain in most cases.
Furthermore, cloning of CIMs can be avoided by
integrating device identifier checks into its logic.
Kumar et al. (K et al., 2017) proposed to avoid
the step of encrypting CIM (Maes et al., 2002).
Their scheme does not require any kind of third
party for programming internal keys or encrypting
CIMs, hence their scheme can work without the
involvement of a TTP. However, their work is based
on the assumption that a key cannot be extracted
from a plaintext bitstream and thereby completely
relies on obscurity introduced by the proprietary file
format.
More secure schemes with a reduced TTP
dependency are presented in (Guneysu et al., 2007)
and (Zhang and Chang, 2015), where Diffie-
Hellman Key Exchange (DHKE) algorithms
generate IP specific keys within the device itself
during runtime. This way all IP specific keys are
ephemeral, and thus TTPs and SDs cannot get access
to them by reverse engineering, unlike in previous
cases.
Figure 2: Core Installation Module using device identifier
(Zhang and Chang, 2014).
2.1.1 Readback
Despite of possible other limitations, all of
previously published schemes suffer from readback
attacks. SoC devices have a processing system (PS)
as a controlling entity that has full access to the
programming logic (PL). The PS can read any
previously configured data using the processor
configuration access port (PCAP) (Xilinx, 2017b),
and can extract secret information or even IP cores.
Non-SoC FPGAs suffers from this attack too,
because a user logic can perform readback via the
internal configuration access port (ICAP) and
deliver the data to an external interface. Any control
logic around ICAP for protection against readback
can be overwritten using dynamic partial
reconfiguration (DPR) and after that, an attack can
be performed easily. Readback of an initially
encrypted IP is done in (Adetomi et al., 2017),
where it is relocated to another location after initial
configuration. (Maes et al., 2002) and (Zhang and
Chang, 2014) actually identified readback attacks as
a possible threat and concluded that this feature
should be disabled. However, it was not made clear
that readback can be disabled only for external
sources and hence internal logic or running software
could still perform such an attack.
2.2 Remote Configuration
Remote configuration of IPs relies on the
infrastructure of a secure licensing framework and is
performed by establishing a connection between
CVs and the target devices via a common network
such as the Internet. One of the first published
approaches in this field proposed delivering
bitstreams in an encrypted form over an unsecure
channel (Drimer and Kuhn, 2009). The key has to be
pre-programmed by the CV, which causes logistical
overhead. Besides, the scheme is also prone to
tampering because no bitstream authentication is
considered. Furthermore, all IPs are encrypted with
the same key, which leads to exposure of all
previously transmitted IPs in case of a successful
attack. Finally, this scheme again suffers from the
key pre-programming conflict described in section 1.
Works that are more recent use asymmetric
cryptography and per-session keys (Braeken et al.,
2011; Vliegen et al., 2015; Kashyap and Chaves,
2014). In these schemes, a new key is generated for
every session based on a DHKE algorithm. Once a
bitstream transfer is completed, they are either
configured on the device directly or encrypted using
a random key and then stored on the NVM (Kashyap
ICISSP 2019 - 5th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
566

and Chaves, 2014; Kashyap and Chaves, 2016). Even
though the latter approach has advantages like faster
reconfiguration time, it is prone to several key
extraction attacks because all keys are stored within
the programming logic itself. Except (Thanh et al.,
2012; Thanh et al., 2013), none of the proposed work
considers SoC-based FPGAs and therefore require the
implementation of all functions on the PL, which not
only introduces serious overhead but also makes them
prone to side-channel attacks (SCA) (Wollinger et al.,
2004). Available solutions, which make use of SoC
FPGAs to perform the key agreement tasks in
software (Thanh et al., 2012; Thanh et al., 2013), are
limited to using IPs from a single core vendor and do
not offer bitstream storage.
Based on the literature review, it is clear that
available remote configuration approaches do not
work within the context of IP licensing. In some
cases, access of SDs to their device is completely
blocked (Braeken et al., 2011) or SDs can only use
licensed IPs but no logic of their own on the PL
(Vliegen et al., 2013; Thanh et al., 2012; Thanh et
al., 2013). We conclude that remote configuration of
an IP is not possible in a secure and feasible way
with any of the exiting schemes, and a new solution
is required which provides the required
infrastructure.
3 SECURE REMOTE
CONFIGURATION SCHEME
We propose a new scheme, which aims to overcome
the described limitations such as readback and single
core vendor restrictions, based on remote
configuration for delivering IPs directly to target
devices. Before discussing the execution flow of the
scheme, basic functional blocks are explained in
section 3.1.
3.1 Basic Functionality and Security
3.1.1 Bitstream Format
IPs can be delivered in different formats as
explained in section 1. Among these formats, RTL
and netlist must be processed using vendor tools to
generate data that can be configured on the device.
Doing that on the fly, inside the device, would
require enormous effort and cause time overhead in
the magnitude of several hours. On the other hand,
bitstream format is ready-to-use blocks that can be
configured directly. Hence, we only consider IPs to
be delivered in bitstream form.
3.1.2 Layered Rights Management
In SoC devices, typically the CPU acts as system
master and has complete control over the system
including PL (Xilinx, 2017a; Xilinx, 2017b; Intel,
2018a). Therefore, both PS and PL need to operate in
a secure state at all time to guarantee licensing
integrity. This can be achieved by introducing layered
rights management, where users are categorized as
either privileged or non-privileged (Intel, 2016, p.
159).
Non-privileged users have restricted control over
certain system components while privileged users
have full access. In the FPGA market, ARM
microprocessors are the de-facto standard when it
comes to the CPU part in SoC devices. Through the
ARM TrustZone feature, they support layered rights
on hardware level, meaning that buses, memories and
peripherals can be divided into secure and non-secure
components. TrustZone is supported by most SoC-
based FPGAs (Intel, 2017b; Intel, 2018a; Gosain and
Palanichamy, 2014). As discussed earlier, the
configuration interfaces can be used for readback
attacks. TrustZone can be used to counter this attack
by restricting non-privileged users’ access to
interfaces. To achieve this, a hypervisor can be used
that hosts a secure and a non-secure operating system
(OS). Both, hypervisor and secure OS are running in
privileged mode and are not accessible from the
outside (i.e. by a user). Meanwhile, the non-secure OS
runs in a non-privileged mode with restricted
capabilities. It can access secure resources via secure
OS and non-secure resources directly. This trusted
execution environment protects security-critical
software, firmware and hardware components, while
not restricting SDs to a set of predefined APIs (Sabt
and Achemlal, 2015).
In a similar fashion, the PL can be divided into
secure and non-secure sections, as depicted in Figure
3. The secure section should include a controlling
interface that restricts ICAP usage to authorized
commands only. Unauthorized commands, such as
modification and/or readback of secure sections
and/or IPs, are blocked by this circuit.
Figure 3: PL showing secure/non-secure locations.
IP
System
ICAP
Controller
ICAP
IP
IP
Non-secure
Secure
A Secure Framework with Remote Configuration of Intellectual Property
567

3.1.3 Bitstream Analysis
Applications running on the non-secure OS must
have the capability to perform configuration of IPs
and custom logic using software, so SDs can
configure their own design. Therefore, an API with
this capability will be provided to non-privileged
users. However, for security against unauthorized
configuration and readback, bitstream analysis is
required. It can be achieved by analysing the
bitstream’s frame addresses (FAs) which represent
the target locations in the PL. The FAs are compared
against a table stored in the secure OS that defines
secure, non-secure, custom logic or IP locations.
3.1.4 Secure Boot
After shipment, devices are in possession of SDs and
fully under their control. However, a malicious SD
would benefit greatly from breaking device security,
as this would allow them to clone IPs at will instead
of paying licensing fees. Consequently, SDs must be
treated as potential attackers and critical components
must be secured against attacks based on physical
access. For this purpose, the "secure boot" feature is
used, which is typically supported by modern
FPGAs (Intel, 2018c; Sanders, 2015). Secure boot
means that the complete boot chain, from loading
the FSBL to loading the secure OS, is encrypted and
authenticated using asymmetric cryptography. The
corresponding key and authentication certificate is
pre-programmed in the device before distribution. At
start-up, the device only decrypts an authenticated
boot loader with the previously programmed key,
which in turn contains the key for the next boot
stage, e.g. the hypervisor, and so on. With setting up
devices to perform secure boots only (Xilinx, 2017a,
p. 288; Intel 2017a, p. 35), it can be guaranteed that
no unauthorized software runs on the device outside
the control of the hypervisor.
3.1.5 Enabling Remote Configuration
Remote configuration is the establishment of a
network connection between a CV and a device,
which is used to configure the bitstream directly on
this device. The network connection must be secure,
so that threats like man-in-the-middle attacks can be
avoided. For this purpose, a protocol like Transport
Layer Security (TLS) including key exchange and
authentication can be used. Additionally, the
bitstream itself can be encrypted, too, but then the
required key needs to either be agreed upon or sent
via a secure channel, which would create more
problems. We are focusing on the delivery of
unencrypted bitstreams using a secure channel.
Since bitstream sizes are in the range of several
megabytes for modern devices, they cannot be
stored in on-chip memory, which typically has a
capacity of a few hundred kilobytes. Storing them
off-chip on the other hand makes them vulnerable to
bus probing and cold boot attacks. As described in
section 3.1.2, the ARM TrustZone feature can be
used to counter this type of attack. In the secure OS,
a software module needs to be implemented which
encrypts the bitstream with a random key on the fly.
This key can either be stored in another secure
software module (Software key-vault), a hardware
secure key storage component or the secure section
of the PL. Before encrypting the IPs for storage, they
are checked for unauthorized commands through
bitstream analysis, as explained in section 3.1.3.
Finally, IPs can be configured using PCAP. The
entire flow is shown in Figure 4.
3.1.6 Target Hardware
The proposed scheme can be implemented on most
available devices as long as they support dynamic
partial reconfiguration (DPR), an internal decryption
engine and a secure key vault. This includes most
devices from Xilinx and Intel and therefore a major
share of the SRAM-based FPGA market. Optimally,
a processing system is present on the device that
handles remote communication, bitstream
configuration and layered rights management. Such
SoC-FPGAs can be found on many modern devices
from low-cost to absolute high-end. Nevertheless,
this solution also works with non SoC-based FPGAs
by configuring a PS soft core on the PL as it has
been done in related publications (Vliegen et al.,
2015). However, there will be significant resource
overhead.
3.2 Execution Flow and
Implementation
The proposed scheme is implemented on a Xilinx
Zynq UltraScale+ (EK-U1-ZCU102-G), which is a
SoC-type device supporting all required features.
The scheme execution on this device begins with
booting it into a secure state. First, the Power
Management Unit (PMU) boots, powers all required
components and performs an integrity check on the
subsequent Configuration Security Unit (CSU)
firmware. Afterwards, control is passed to the CSU,
which sets security levels authenticates and decrypts
a First Stage Boot Loader (FSBL). It then hands
over control to the PS while it continues to run in the
ICISSP 2019 - 5th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
568

background where it provides cryptographic
accelerators, key management and PCAP access. The
PS then executes the decrypted FSBL, which
initializes necessary components like buses and
organizes security states of system resources based on
ARM TrustZone. Finally, it authenticates and
decrypts the next boot stage, which could either be a
hypervisor or another boot loader stage. In favour of
maintainability and portability, we chose the latter
approach and load a Second Stage Boot Loader
(SSBL), which is then used to initialize the
hypervisor, while the FSBL only focuses on system
security initialization. Xen is used as hypervisor,
which is open source and available free of charge
(xenproject.org, 2018). It builds on top of TrustZone
and supports devices from both Xilinx and Intel. It
acts as a control and communication monitor for a
secure and a non-secure OS (User OS). Any OS can
be chosen for either category, however, for the given
implementation we chose "FreeRTOS" as secure OS
since it is lightweight, supports the necessary
communication features and devices from both Xilinx
and Intel (freertos.com, 2018). In addition, Xilinx'
Petalinux is used to create a non-secure user OS. It
comes with many drivers, has official tool support
and therefore allows a fast and reliable scheme
evaluation.
At this stage, the processing system is fully booted
and the PL can be configured. To expand the secure
state to the programmable logic, an initial (full)
bitstream is loaded that includes secure logic, i.e. for
ICAP control, and interconnects for SD and CV
designs. Once the initial bitstream is configured,
additional logic can be loaded. When initiating the
configuration of an SD’s custom design using the
corresponding APIs, its bitstream is first passed to the
Bitstream Analysis module, which ensures it does
not contain any unauthorized commands, e.g. writes
to a secure section. Finally, the bitstream is
configured to a corresponding slot by the
Configuration Manager module.
For requesting and configuring an IP from a CV,
a similar API is defined in the secure OS. The full
flow is shown in Figure 4. First, to download an IP, a
secure remote communication channel to the CV's
server is established using the Remote Access
module. This request is only granted if a valid
license was bought for the respective device. Device
identification in this case is done by using the unique
96-bit serial number that is available on the Xilinx
Zynq UltraScale+. Once an IP is downloaded, it
passes the same process of bitstream analysis and
configuration as for a custom design. Configuration
times in both cases will be significantly shorter than
for the initial bitstream.
4 SECURITY ANALYSIS
Security of the proposed work is provided by a trust
chain based on pre-programmed keys and
certificates in the device. A TTP performs this pre-
programming; hence, our scheme also relies on a
TTP. Since FPGA vendors produce the devices, it
would be straightforward for them to take the role of
the TTP and program keys before distributing the
devices. In addition, they would also be responsible
for publishing the matching software, i.e. boot
loader, hypervisor and secure OS. Since trust is
already placed by using their devices, no further
trust dependencies would be introduced.
Figure 4 Remote Configuration Scheme flow.
Request
IP
Send request
& device ID
Verify license
for device
Return IP
& license
IP
System
IP
IP
IP
CPU
FPGA
Core Vendor
Server
IP
IP
Bitsream
Analysis
Remote
Access
APP
API
Monitor
Configuration
Manager
Secure OS
User OS
A Secure Framework with Remote Configuration of Intellectual Property
569

All cryptographic primitives used in the scheme,
i.e. AES and RSA, are considered computationally
secure. Furthermore, these algorithms are
recommended for long-term security by
government-funded organizations (German Federal
Office for Information Security, 2018; US National
Institute of Standards and Technology, 2001).
Nevertheless, some successful side channel attacks
like differential power analysis have been conducted
on older devices before, e.g. Xilinx’ Virtex-II/4/5
series (Moradi et al., 2011a; Moradi et al., 2011b)
and on PS (Ramsay, 2017). However, even if an
attack were successful in extracting the AES device
key, it would not be sufficient to boot a tampered
OS, as any boot software also needs to be
authenticated, and the required private certificate
never leaves the TTP. Thus, it cannot be extracted
from the device. One possible attack vector would
be to decrypt the boot loader using the retrieved
AES key, then extract the key for decrypting the
hypervisor from the plaintext boot loader, again use
this to decrypt the hypervisor and finally extract the
key for the secure OS. Once the secure OS is
available in plaintext, the private certificate for
establishing a secure communication channel with
CVs can be extracted from it and used to spoof the
device during communication. Several approaches to
prevent this attack scenario are currently analysed
and will be implemented in the future, for instance a
run-time calculated identifier could be sent along
with the certificate. This identifier could be a hash of
specific sections of the secure on-chip memory.
However, attacking the secure boot chain is highly
complicated and further requires extracting the AES
root key from a device’s hardware key vault in the
first place, which is highly unlikely on modern
devices. Furthermore, if successful, this attack
would only affect a single device and the effort for
applying it to other devices stays constant.
Therefore, we consider it a minor threat only. When
such a security breach is identified, CVs can add the
device ID and certificate to a black list, which means
all future requests for these devices will be declined.
Since this scheme relies on a trusted execution
environment, we also consider the security of the
implementation at hand, i.e. ARM TrustZone. So
far, very few successful attacks have been published.
One of them is the Rowhammer attack, where secure
areas of DDR memory are accessed by a non-secure
system master (Carru, 2017). In this attack,
neighbouring rows of memory cells are rapidly
accessed, which causes bit flips in the secure
memory cells. However, not only is the complexity
of this attack very high, as it requires inside
knowledge of the secure memory mapping, but it
can also be countered by simply keeping secure
memory rows consecutive or by using the on-chip
memory for secret data instead of DDR.
Another attack monitors cache access behaviour
to extract secrets of an application (Zhang et al.,
2016). It is executed by filling the cache with data of
a non-secure application and then triggering a secure
application. Thus, the secure application's data will
be cached during its execution, which will replace
previously cached data. After this, the non-secure
application data is read again. By measuring
memory access times, an attacker can get
information on data access patterns of the secure
application. If the attacker furthermore has detailed
knowledge of the secure application, he can predict
certain secrets like keys from this information.
Again, this kind of attack requires detailed system
knowledge and is hence highly unlikely. A possible
countermeasure would be to restrict cache to secure
OS only, though this would significantly slow down
the non-secure OS. Consequently, this measure
should only be applied for very high security
systems, which perform sensitive cryptographic
tasks like AES encryption and where the used
algorithm is publicly available. For common use-
cases, this attack scenario can be ignored.
Overall, we believe that the security of the
presented scheme is sufficient with minimal attack
surface exposed and any known attack will only
work in a specialised environment such as a
laboratory.
5 CONCLUSION
In this paper, we proposed an IP licensing
framework with the capability of remotely
configuring devices. An intellectual property design,
in a proprietary obfuscated format, is delivered from
CVs to the device directly using a secure channel,
while the device itself runs in a secure execution
environment. In addition, an extensive security
analysis of previous as well as the proposed scheme
is presented, and it is shown that this scheme is
secure, least restrictive for SDs in term of device
resource usage and has no resource overhead. This is
a work-in-progress, and feasibility and security will
be further improved, as described throughout the
paper.
A flow based on this scheme will provide extra
guarantees against IP theft; this could get more CVs
invested, which we believe can increase growth in
the IP licensing market.
ICISSP 2019 - 5th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
570

REFERENCES
Kean, T. (2002). Cryptographic rights management of
FPGA intellectual property cores. FPGA '02, ACM,
Monterey, CA, USA, pp. 113–118
Guneysu, T., Moller, B., Paar, C. (2007). Dynamic
Intellectual Property Protection for Reconfigurable
Devices. FPT, IEEE, Piscataway, NJ, pp. 169-176.
Maes, R., Schellekens, D., Verbauwhede, I. (2002). A
Pay-per-Use Licensing Scheme for Hardware IP Cores
in Recent SRAM-Based FPGAs. IEEE
Trans.Inform.Forensic Secur. 7, pp. 98–108.
Zhang, L., Chang, C.-H. (2014). A Pragmatic Per-Device
Licensing Scheme for Hardware IP Cores on SRAM-
Based FPGAs. IEEE TIFS. 9, pp. 1893–1905.
Zhang, L., Chang, C.-H. (2015). Public Key Protocol for
Usage-based Licensing of FPGA IP Cores, 2015 IEEE
ISCAS, Lisbon, pp. 25-28.
K., S. K., Sahoo, S., et al. (2017). A Flexible Pay-per-
Device Licensing Scheme for FPGA IP Cores. 2017
ISVLSI, Bochum, pp. 677–682.
Xilinx, (2017b). Zynq-7000 All Programmable SoC.
Technical Reference Manual.
Adetomi, A., Enemali, G., Arslan, T. (2017). Towards an
Efficient IP Protection in Dynamically Reconfigurable
FPGAs. EST, IEEE, pp. 150-156.
Drimer, S., Kuhn, M. G. (2009). A Protocol for Secure
Remote Updates of FPGA Configurations. ARC 2009,
Springer, Berlin, pp 50-6.
Braeken, A., Genoe, J., et al. (2011). Secure remote
reconfiguration of an FPGA-based embedded system.
ReCoSoc 2011, IEEE, Montpellier, pp. 1-6.
Vliegen, J., Mentens, N., Verbauwhede, I. (2015). Secure,
Remote, Dynamic Reconfiguration of FPGAs. ACM
Trans. Reconfigurable Technol. Syst. 7, pp. 1–19.
Kashyap, H., Chaves, R. (2014). Secure partial dynamic
reconfiguration with unsecured external memory. 24th
FPL, IEEE. pp. 1-7.
Kashyap, H., Chaves, R. (2016). Compact and On-the-Fly
Secure Dynamic Reconfiguration for Volatile FPGAs.
ACM Trans. Reconfigurable Tech. Syst. 9, pp. 1–22.
Thanh, T., Nam, P. N., Vu, T. H., van Cuong, N. (2012).
A framework for secure remote updating of bitstream
on runtime reconfigurable embedded platforms. ICCE,
IEEE, Hue, Vietnam, pp. 471-476.
Thanh, T., Vu, T. H., van Cuong, N., Nam, P. N. (2013).
A protocol for secure remote update of run-time
partially reconfigurable systems based on FPGA.
ICCAIS 2013, IEEE, Nha Trang, 2013, pp. 295-299.
Wollinger, T., Guajardo, J., Paar, C. (2004). Security on
FPGAs. ACM Trans. on Embedded Computing Sys
(TECS), vol 3, pp. 534–574.
Vliegen, J., Mentcns, N., Verbauwhede, I. (2013). A
single-chip solution for the secure remote
configuration of FPGAs using bitstream compression.
ReConFig, IEEE, Cancun, Mexico, pp. 1-6.
Xilinx, (2017a). Zynq UltraScale+ Device Technical
Reference Manual.
Intel, (2018a). Intel Stratix 10 Hard Processor System
Technical Reference Manual.
Intel, (2016). Intel 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software
Developer’s Manual.
Intel, (2017b). Intel Arria 10 - Hard Processor System -
Technical Reference Manual.
Gosain, Y., Palanichamy, P. (2014). TrustZone
Technology Support in Zynq-7000 All Programmable
SoCs. WP429, Xilinx.
Intel, (2018c). Using the Design Security Features in Intel
FPGAs.
Sanders, L. (2015). Secure Boot of Zynq-7000 All
Programmable SoC. XAPP1175, Xilinx.
Intel, (2017a). Intel Arria-10 SoC-Secure Boot User
Guide.
toppers.com, (2018). TOPPERS's official website. [online]
Available at: http://www.toppers.jp/en/safeg.html
[Accessed 27 Oct. 2018].
xenproject.org (2018). Linux Foundation
COLLABORATIVE PROJECTS website. [online]
Available at: http://www-
archive.xenproject.org/products/xenhyp.html
[Accessed 15 Nov. 2018].
freertos.com, (2018). FreeRTOS's website. [online]
Available at: https://www.freertos.org/ [Accessed 27
Oct. 2018].
Xilinx, (2018b). Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC Data Sheet:
DC and AC Switching Characteristics.
Xilinx, (2018c). UltraScale Architecture Configuration:
User Guide.
Federal Office for Information Security (2018).
Cryptographic Mechanisms: Recommendations and
Key Lengths BSI TR-02102-1, Bonn.
National Institute of Standards and Technology (2001).
Federal Information Processing Standards Publication
197 FIPS 197, Gaithersburg, USA.
Moradi, A., Barenghi, A., Kasper, T., Paar, C. (2011). On
the Vulnerability of FPGA Bitstream Encryption
Against Power Analysis Attacks. CCS '11, ACM, New
York, NY, pp 111-124.
Moradi, A., Kasper, M., Paar, C. (2011). On the
Portability of Side-Channel Attacks - An Analysis of
the Xilinx Virtex 4 and Virtex 5 Bitstream Encryption
Mechanism. IACR Cryptology ePrint Archive, pp. 391.
Ramsay, C., Lohuis, J. (2017). TEMPEST attacks against
AES. Fox-IT.
Carru, P. (2017). Attack TrustZone with Rowhammer
eshard.
Zhang, N., Sun, K., et al. (2016). TruSpy: Cache Side-
Channel Information Leakage from the Secure World
on ARM Devices. IACR Cryptology ePrint Archive,
pp. 980.
Gotzfried, J., Müller, T. (2013). ARMORED: CPU-Bound
Encryption for Android-Driven ARM Devices. ARES,
IEEE, Regensburg, Germany, pp. 161-168.
Müller, T., Freiling, F., Dewald, A. (2011). TRESOR
Runs Encryption Securely Outside RAM. 20
th
USENIX, Francisco, California, pp 17.
Sabt, M., Achemlal, M., Bouabdallah, A. (2015). Trusted
Execution Environment: What It is, and What It is
Not, IEEE Trustcom/BigDataSE/ISPA, Helsinki, pp.
57-64.
A Secure Framework with Remote Configuration of Intellectual Property
571
