
Mobile Applications for Stroke: A Survey and a Speech Classification
Approach
Ariella Richardson
1
, Shani Ben Ari
1
, Maayan Sinai
1
, Aviya Atsmon
1
, Ehud S. Conley
1
,
Yohai Gat
1
and Gil Segev
2
1
Lev Academic Center, Jerusalem, Israel
2
BGSegev Ltd. (segevlabs.org), Jerusalem, Israel
Keywords:
Digital Health, m-Health, Mobile, Stroke, Speech, Cardiovascular, Machine Learning, Data Mining.
Abstract:
Strokes are a cause of serious long-term disability and create an immense burden on healthcare. Among the
sea of mobile applications for health, some target stroke patients, and most require active user cooperation.
Our proposed application, collects data, without user intervention. We apply data mining methods to create
personal feedback to the patient or doctor. We provide a survey of applications for mobile or wearables,
specifically for stroke. We also survey papers that apply data mining to stroke. In addition to the survey, we
present a feasibility study on using speech for classification of stroke patients. We created a new data set of
unstructured speech recordings, increasing applicability. We present experimental results on classification of
stroke patients. Our study provides promising insight to detecting stroke patients using a mobile application
without requiring active user participation.
1 INTRODUCTION
Strokes produce immense health and economic bur-
dens and are a leading cause of serious long-term dis-
ability. Projections show that by 2030, there will be a
20.5% increase in prevalence from 2012 (Centers for
Disease Control and Prevention, USA, , 2009; Writ-
ing et al., 2016). Between 2012 and 2030, total direct
medical stroke-related costs are projected to triple,
from $71.6 billion to $184.1 billion, with the majority
of cost increase arising from those 65 to 79 years of
age (Ovbiagele et al., 2013).
Health related applications for mobile phones and
smart-watches are capable of improving health mon-
itoring and detection for general health and specifi-
cally for stroke. The number of health related apps
available is astounding, approximating 40,000 apps in
2013 (Boulos et al., 2014) and 165,000 in 2015 (Terry,
2015). Applications that target stroke patients specif-
ically, and are aimed at managing risk factors (Seo
et al., 2015), rehabilitation (Zhang et al., 2015; Mi-
callef et al., 2016) and telemedicine (Nam et al., 2014;
Demaerschalk et al., 2012; Mitchell et al., 2011).
Other conditions are covered in several survey stud-
ies (Ozdalga et al., 2012; Boulos et al., 2014; Dobkin
and Dorsch, 2011; Patel et al., 2012; Pantelopoulos
and Bourbakis, 2010; King and Sarrafzadeh, 2017).
Everyday adoption of health apps is sometimes
compounded by factors such as confusion regarding
which app to use, slow adaptation of the traditional
healthcare community, the lack of integration with
electronic health records etc. (Crockett and Eliason,
2016; Terry, 2015). Despite these challenges, estab-
lishing patient self-monitoring with tools such as mo-
bile apps is important for improving patient health
(Dobkin and Dorsch, 2011; Writing et al., 2016). The
diversity of conditions that are covered ranges from
everyday diet apps (Recio-Rodriguez et al., 2016) to
critical oncology apps (de Bruin et al., 2015) and
touches on psychiatric symptoms (Place et al., 2017).
Among the surplus of medical apps, including
those that target stroke, many require the users to ac-
tively interact with the application in order to achieve
medical feedback, for example (Seo et al., 2015;
Zhang et al., 2015; Nam et al., 2014). In this study, we
demonstrate how an app will be able to provide mean-
ingful information, without requiring user actions for
data collection and input.
During regular phone usage, applications can col-
lect data that will be periodically analyzed and used
for monitoring patient health. Data can be collected
from a variety of sources, for example, sensors such
as the accelerometer or gyroscope, alongside key-
board usage. This data can be collected while the
Richardson, A., Ben Ari, S., Sinai, M., Atsmon, A., Conley, E., Gat, Y. and Segev, G.
Mobile Applications for Stroke: A Survey and a Speech Classification Approach.
DOI: 10.5220/0007586901590166
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health (ICT4AWE 2019), pages 159-166
ISBN: 978-989-758-368-1
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
159

device is used for regular unrelated tasks. This fact
enables us to collect data in a way that is transparent
to the user and does not impose on his daily phone us-
age. The application may run in the background and
then provide a service such as creating periodical re-
ports for self monitoring or for sharing with a health
provider. The data may also be used for applications
that detect and alert the user in case of an emergency
or deterioration (BGSEGEV, 2018).
We present a study that provides a proof of con-
cept for an application that performs stroke detec-
tion without the user having to actively provide input.
Our study, demonstrates stroke detection using data
mining performed on samples obtained with a smart-
phone/watch during regular use.
One of the main issues that affect stroke patients
is speech impairment. As speech impairments play
an important role in stroke detection and rehabili-
tation we decided to use data mining to determine
whether voice recordings can be classified as belong-
ing to stroke patients as opposed to healthy subjects.
We also study whether we can differentiate between
different types of speech impairments that may result
from having a stroke.
We study two types of speech impairments that
are caused by strokes: aphasia and dysarthria. Apha-
sia, is the loss or impairment of language (Berthier,
2005), whereas dysarthria is a speech neuro-motor
control problem (Sellars et al., 2005) (see Section 3.1
for more details). The data mining module that we
studied is proposed for use in an app for monitoring
stroke patients (patent request submitted (BGSEGEV,
2018)).
For classification of speech impairments we use
voice recordings. Voice recordings are of interest as
they are obviously available for collection on mobile
phones. By using voice data generated throughout
normal phone usage (i.e. during phone calls) we are
able to develop an app that can monitor stroke patients
without intervention in daily activity. For example an
application could periodically record the users voice
during phone calls. To the best of our knowledge there
is no such application for stroke.
Deciding on the source and type of data to ana-
lyze is complex. Many studies used controlled exper-
iments where patients are asked to repeat the same
passage or some predetermined sentences or words
(Frid et al., 2014; Sakar et al., 2013) or only use vow-
els (Hazan et al., 2012; Sakar et al., 2013). Our study
uses a different, more general approach. We studied
voice recordings without limiting the nature of the
recording. In our recordings there is a mix of free
speech and predefined speech tasks.
As part of this study, in order to study free speech,
for stroke detection we created a new data set. Our
data is obtained from a variety of online sources. The
criteria for video collection was that they are labeled
as belonging to stroke patients. We extracted the
voice signal from the videos we selected, and use it
to build our data set.
The data is recorded under a variety of conditions
and there is no known structure to what the subjects
say. Although this might sound like a strange strategy,
the motivation to using this type of data is that in a
real application subjects are expected to speak freely,
and classification should be possible without the bias
of a predefined set of words. Although our use of
free speech makes the classification problem harder, it
has the advantage of higher applicability to real world
data collected from a phone.
We performed classification of the speech data us-
ing several algorithms as detailed in Section 3.2. Our
successful comparative study provides promising in-
sight to detecting stroke patients from normal phone
usage. The results of this study demonstrate that we
can differentiate between stroke patients to healthy
subjects. The voice samples are of short recordings
enabling the detection of stroke in real-time. Further-
more, we successfully differentiate between the two
stroke conditions of aphasia and dysarthria. The abil-
ity to perform a finer classification could be useful in
monitoring stroke rehabilitation.
The contributions of this study are:
• We present a broad survey on stroke related apps
and on data mining for stroke.
• We build a data set of unrestricted speech of stroke
patients. This data set can be used in further stud-
ies, and also demonstrates the strengths of using
unstructured data.
• We compare several models for classification of
speech and show that we successfully classify
stroke patients vs. healthy subjects, along with
the ability to differentiate between different stroke
speech conditions.
The structure of the paper is as follows: We first
present a broad survey on mobile apps and data min-
ing for stroke. Next we present our study on classifi-
cation of stroke speech impairments. We describe the
data set we built alongside an experimental evaluation
of classification methods and a discussion of results.
Finally, we conclude our paper.
2 RELATED WORK SURVEY
This section presents a survey on applications and
data mining for stroke. We begin by discussing mo-
ICT4AWE 2019 - 5th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health
160

bile applications and other technologies and proceed
to cover studies on data mining for stroke.
2.1 Applications
We take look at applications targeting stroke patients
specifically. Mobile apps can be used for monitoring
and rehabilitation of patients after stroke. (Seo et al.,
2015) tested the feasibility of a mobile app for pa-
tients who had suffered a stroke. The app was aimed
at managing risk factors for stroke such as blood pres-
sure and diabetes management. The study was aimed
at testing adherence to app usage and concluded that
more work must be done in order to encourage adher-
ence. Another application, (Zhang et al., 2015), ac-
companies the patient by encouraging exercises, fol-
lowing up on taking pills, and logging mood reports.
(Micallef et al., 2016) introduced another exercise ori-
ented application for post stroke patients. This ap-
plication is aimed to help patients remember to exer-
cise more frequently. The application was evaluated
on a smartphone, tablet and smart-watch. The au-
thors found that stroke survivors seem to prefer smart-
phones compared to other mobile devices due to their
ease of use, usability, familiarity and being easier to
handle with one arm. An interesting study, (Beeson
et al., 2013) and views the cell phone as a device for
writing on, this case study demonstrates how writing
can be used as treatment for aphasia in a post stroke
patient.
Some of the apps are aimed at bridging the dis-
tance between the patients to medical assistance (Nam
et al., 2014; Demaerschalk et al., 2012; Mitchell et al.,
2011). (Nam et al., 2014) provide a stroke screen-
ing application. The application shows a set of car-
toons representing stroke symptoms. Potential pa-
tients can follow the cartoons and try to determine
whether they may be suffering from a stroke. Sugges-
tions of nearby hospitals providing appropriate treat-
ment are provided by the app. (Mitchell et al., 2011)
bridge the gap by providing a tele-radiology system
that enables a doctor to interpret a CT scan. This en-
ables diagnosis when the hospital does not have a ex-
pert on call. (Demaerschalk et al., 2012) introduce a
similar app that provides high-quality video telecon-
ferencing. Diagnosis is the aim of the app presented
in (Shin et al., 2012). Their app uses a smartphone
to perform the pronator drift test that is used to diag-
nose stroke. Mobile phones are tied on to the patients
wrists. The app uses the accelerometer in order to
measure changes in drift and test arm weakness.
Aside from discussing mobile phone apps we
must also consider other related technologies for
stroke. We refer the interested reader to this survey:
(Nam et al., 2013). The survey covers existing tech-
nologies applied to stroke patients (some appear in
studies described above), these include:
• Remote diagnosis by doctors watching video and
audio recorded from stroke patients (Roine et al.,
2001; Demaerschalk et al., 2012).
• Teleradiology - doctors can view and interpret CT
scans from afar (Mitchell et al., 2011; Park and
Nam, 2009).
• Pre-hospital notification arrival, enabling the hos-
pital to prepare for the patient and be ready for
treatment on arrival. Or a mobile stroke unit con-
nected to hospital to administer treatment before
arrival (Gonzalez et al., 2011; Kim et al., 2009).
• Communication between stroke team members
within the healthcare facility (Nam et al., 2007).
• A decision support system for stroke classification
(Nam et al., 2012).
• Tele-rehabilitation for rehabilitation of stroke pa-
tients (Krpic et al., 2013).
These studies demonstrate various types of apps
that have been developed for stroke patients. They all
require patient input and active participation. This is
in contrast to our proposed approach where the mon-
itoring is performed without user intervention.
2.2 Data Mining
Data mining in healthcare is a topic of substantial in-
terest and has even been described as ”increasingly
popular, if not increasingly essential” (Koh et al.,
2011). However, despite the advances in healthcare,
data mining incorporation into everyday healthcare
practice is slow (Crockett and Eliason, 2016). Exam-
ples to domains within healthcare where Data min-
ing is used are Parkinson’s (Little et al., 2009; Tsanas
et al., 2010; Hazan et al., 2012; Sakar et al., 2013), oc-
cupational therapy (Richardson et al., 2008) and Med-
ical Imaging (Guo et al., 2016).
The previous section reviewed various applica-
tions for stroke. Many of these applications collect
and analyze data. This section will discuss various
studies that apply data mining methods to stroke data.
Some of the studies we cover acquired data using mo-
bile applications, some use data from other sources.
It is important to note, that the data mining studies we
found on stroke were very different to our study.
Brain CT scans are of major importance in stroke
detection, and as shown above, received attention
in mobile applications that enable viewing the scans
from afar (Mitchell et al., 2011; Demaerschalk et al.,
2012). Bently et al. (Bentley et al., 2014) take the
Mobile Applications for Stroke: A Survey and a Speech Classification Approach
161

next step and explore whether machine learning can
be applied to brain scans in order to automatically
detect thrombolysis. They use SVMs to differenti-
ate between patients who developed symptomatic in-
tracranial hemorrhage to those who did not. The im-
age voxels were used as feature vectors. Results us-
ing 10-Fold cross validation are reported reaching an
AUC of up to 0.744. This study provides a first step in
assisting doctors by automatic analysis of CT scans.
Khosla et al. (Khosla et al., 2010) use data from
the cardiovascular Health Study data set. Their study
pays special attention to the issue of missing values
in health records. They compare Cox regression to
SVM and Margin Based Sensor Regression (MCR)
for predicting stroke. 10-fold cross validation is used
on 5 random trials, average AUC is reported as high
as 0.774 for SVM, and 0.777 for MCR, while Cox
regression only reaches 0.747. A broad discussion of
variations on features selected and appropriate results
is described in the paper.
A slightly different type of study is presented by
(Mans et al., 2008). They use two sets of data be-
longing to stroke patients. The first refers to the clini-
cal course of stroke patients during hospital stay. The
second, refers to pre-hospital behavior. Both data sets
are used to perform Process Mining in order to con-
struct process models. Interesting results included de-
tecting differences treatment strategies between hos-
pitals, and causes of delay in arriving at hospital for
treatment - critical to stroke outcome.
3 STROKE SPEECH
CLASSIFICATION STUDY
In this section we present the study we performed on
classification of stroke speech samples. The study
shows how unstructured speech can be used for the
detection of stroke patients, and for the differentia-
tion between speech impairments that are common in
stroke. The results provide a step towards integrating
data mining into an application for stroke detection or
management in an unobtrusive manner. We describe
the data set that we built, the experimental setup used
and finally, results are presented and discussed.
3.1 Data Collection
In order to increase the generalization of our study,
we build a new data base. We use data found freely
on public sources. The variability in an uncontrolled
setting raises the applicability of our results. Our
data set was obtained from videos of stroke patients
with aphasia or dysarthria. Aphasia is the loss or im-
pairment of language caused by brain damage. It is
one of the most devastating cognitive impairments of
stroke (Berthier, 2005). Aphasia is present in 21 -
38% of acute stroke patients and is associated with
high morbidity, mortality and expenditure. Dysarthria
is a speech problem which can be caused by a num-
ber of brain disorders including conditions such as
stroke and head injury (Sellars et al., 2005). Typical
features of dysarthria include slurring of speech and
quiet voice volume. Psychological distress is often
experienced by people with dysarthria.
The videos we collected include speech from both
stroke patients and healthy subjects. We extracted
the audio from the videos, as segments of unin-
terrupted speech. Each segment is labeled stroke-
aphasia, stroke-dysarthria or healthy. Although we
have labeling of the data from the notations provided
with the videos, the patients may suffer from different
intensities of the labeled condition. The advantage of
using the data from the same videos for healthy and
stroke subjects is that they all come from the same dis-
tribution of background noise and quality. We were
careful to note the patient ID for each audio sample,
this is important in the experimental setup. The exact
ages of our subjects is unknown, but the videos show
that they range from approximately 15 to 70. Our data
set consists of 16 stroke patients, of whom 8 are la-
beled with aphasia, and 8 are labeled with dysarthria
and 12 healthy subjects. 17 subjects are female and
11 male. For every patient there are many samples,
as we cut the videos into segments of uninterrupted
speech. In total there are There are 269 segments from
healthy subjects, 1902 segments for stroke subjects,
split as 987 aphasia and 915 dysarthria. The lengths
of audio vary from several seconds to several minutes.
Some of the samples were too small to generate fea-
tures from as they contained almost silent parts of the
speech. These samples were discarded.
3.2 Experimental Setup
We ran two sets of experiments, results are described
below in Section 3.3. The first experiment is aimed at
classifying stroke patients in the general population.
The data is split into two sets, and labeled stroke or
healthy. The second experiment uses data belonging
to stroke patients (no healthy samples) and is split into
two sets, labeled aphasia or dysarthria and differen-
tiates between the two speech impairments.
For all sets of experiments we used 4-fold cross
validation. Meaning, that we divided our data into 4
even sets, and ran 4 sets of tests. In each test we used
3 sets of the data for training and 1 set for testing. We
ICT4AWE 2019 - 5th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health
162

did this 4 times, each time leaving out a different set
for testing. The results presented are the average of 4
runs. Although it is usually standard practice to use
10 folds, we chose 4 as this provided a good split for
the numbers of subjects we had in the various classes.
It is very important to note that when we split the data
we were careful that all the data belonging to a single
subject was kept in the same group. For example if
the data from subject A is in the testing data, then all
the data from this subject is in the test, none of it in
the training data. This is a point often unnoticed when
using cross validation, experiments are often run with
random cross validation, thus contaminating the pro-
cess. The results must reflect our ability to diagnose a
new patient, meaning a patient that has not been sam-
pled, and is not used for the model creation. This is
an important restriction to adhere to.
Each audio segment is used for a single vector in
the data set. We use signal processing methods in
MATLAB as suggested in (Bunkheila, 2018). We ex-
tract standard audio features from the audio signal to
create the input vector for our classification algorithm.
Some of the features are: mean, median, standard de-
viation, skewness, kurtosis, Shannon’s entropy, spec-
tral entropy, dominant frequency (value, magnitude
and ratio), wavelet features and Mel-frequency cep-
stral coefficients.
We report on the the following algorithms: (im-
plemented in Mathworks Classification Learner App.)
Decision Trees (C4.5) (Quinlan, 1993), K- Nearest
Neighbor (KNN) (Altman, 1992), Logistic regres-
sion (Walker and Duncan, 1967), Support Vector Ma-
chines (SVM) (Platt, 1999) and AdaBoost (Freund
et al., 1999) with decision tree learners. Evalua-
tion is presented using several measures: Accuracy
is the first measure, it simply presents the percentage
of correctly classified samples, from both classes of
the data. Although this is an informative measure, it
does not always provide a complete evaluation of the
model. Precision and Recall provide the next layer of
evaluation. Precision defines the number of correctly
classified positive samples from among the samples
classified as being positive, In terms of our work, how
many samples of patients that are classified as having
stroke, actually had a stroke. Recall is the the number
of correctly classified positive samples from among
the samples labeled positive. In our case, from among
the samples belonging to patients that had a stroke
how many did we find. As there often exists a trade-
off between precision to Recall two other measures
are commonly used. The F1-measure (F1 Score) is
the weighted average of Precision and Recall. The last
measure we use is the Area under the curve (AUC)
that considers the trade-off between the Recall to the
False positive rate (the proportion of negative samples
(healthy) that are mistakenly considered as positive
(stroke)). Measures run between 0 to 1 (1 is better).
3.3 Experimental Results and
Discussion
The first set of experiments uses data from stroke pa-
tients and from healthy patients and builds a classifi-
cation model for detection of stroke patients. Results
are shown in Table 1. Each row describes a classi-
fication model, and results for the various measures
(described above) are displayed across columns.
As shown in Table 1 the best results were obtained
using AdaBoost. These results show clearly that
stroke patients can be classified from voice record-
ings. A closer look at the results shows variations
in classification ability between models. For exam-
ple KNN (k=10) has a recall of 1 meaning all stroke
samples were discovered. However this comes at a
price, the precision in this case is only 0.88, mean-
ing that some healthy samples are mistakenly diag-
nosed as stroke. These differences are important
when transferring the academic study to technology,
as is done when using this technology in a proof-
of-concept (POC) (BGSEGEV, 2018). For each spe-
cific application it is important to decide whether one
prefers missing a few stroke samples over diagnosing
healthy samples as stroke, and selecting the appropri-
ate algorithm accordingly.
Our second experiment uses data only from stroke
but labels them as suffering from aphasia or dysarthria
(see Section 3.1 for an explanation) and builds a clas-
sification model for classification of these two impair-
ments. Results are shown in Table 2. Aphasia is la-
beled as positive, dysarthria as negative. Results show
the highest accuracy for the Decision Tree. The other
algorithms have lower accuracy rates. Taking a look
at the result table provides insight as to why. For most
algorithms presented the precision and the AUC are
high but the recall is low. The decision tree does not
suffer from this problem and as can be seen precision,
recall and AUC are all high. In this example the F1
measure is perhaps the best measure to use as it cap-
tures the trade-off between recall and precision and
clearly singles out the decision tree as building the
best model for this data.
What the results mean is that when the models
detect aphasia it is actually with a high probability
aphasia (tagged as positive). However, a large num-
ber of the aphasia samples are classified as dysarthria.
This may explained by the fact that the conditions of-
ten overlap, and some practitioners consider aphasia
more severe. The milder cases of aphasia may be sim-
Mobile Applications for Stroke: A Survey and a Speech Classification Approach
163
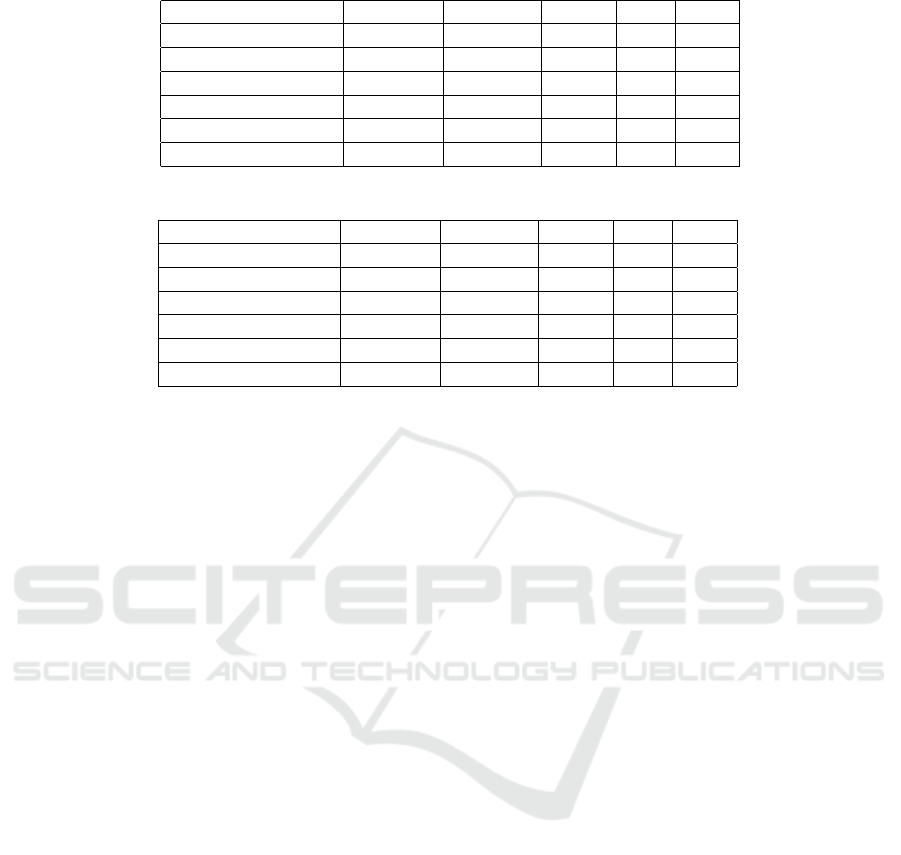
Table 1: Results of classification for stroke vs. healthy.
Accuracy Precision Recall F1 AUC
Decision Tree 0.87 0.88 0.98 0.93 0.77
KNN(k=1) 0.89 0.90 0.99 0.94 0.80
KNN(k=10) 0.88 0.88 1.00 0.94 0.88
Logistic Regression 0.87 0.89 0.97 0.93 0.82
SVM 0.89 0.90 0.99 0.94 0.90
AdaBoost (tree) 0.94 0.96 0.96 0.96 0.96
Table 2: Results of classification for aphasia vs. dysarthria.
Accuracy Precision Recall F1 AUC
Decision Tree 0.95 0.96 0.95 0.95 0.97
KNN(k=1) 0.86 0.93 0.78 0.84 0.97
KNN(k=10) 0.86 0.93 0.78 0.84 0.99
Logistic Regression 0.87 0.94 0.79 0.85 0.98
SVM 0.87 0.94 0.79 0.85 0.99
AdaBoost (tree) 0.88 0.96 0.80 0.85 0.92
ilar to dysarthria causing the model to confuse them.
These experiments demonstrate that data collected
from an unrestricted environment, where speech is
not limited to the use of vowels, or predefined pas-
sages can be used for the classification of stroke or
even specific speech impairments. This step is one
step needed towards providing a mobile application
for the detection or monitoring of stroke in an unob-
trusive manner. During usual phone use, given ad-
vance permission by the user, any speech collected on
the phone such as phone calls can be used for detec-
tion of stroke. This could for example be very useful
for high risk patients, and automatically emergency
contacts if deterioration in speech is detected. Aside
from the emergency usage a mobile application could
be used to monitor progression during rehabilitation.
These results motivate future expansion of the data set
to other impairments, other diseases etc.
4 CONCLUSION
We presented a study on the use of mobile applica-
tions for stroke. We performed a broad survey on
studies related to the use of mobile applications for
stroke. We also surveyed work on the use of data min-
ing for stroke.
Aside from the survey study, we present an exper-
imental study on the use of speech samples for the
classification of stroke. This study provides a step
towards building a mobile application for stroke de-
tection and monitoring such as those developed by
(BGSEGEV, 2018). Our study provides a proof of
concept for an app that uses non intrusive data collec-
tion for medical detection (in this case stroke). As part
of the experimental study we built a database of voice
samples. The data base is special as it uses free speech
collected in unrestricted environments and provides a
good source for studying real data.
Our experiments were run in two settings. One
used to classify stroke patients from a group of
healthy subjects. And the other to differentiate be-
tween two types of stroke speech impairments aphasia
and dysarthria. Both experiments show high success
rates and indicate that using free speech samples in
unrestricted environments for detection is feasible.
Future work will look at expanding the data base
and enriching it with other types of speech impair-
ments, and forwarding the classification study on the
new data. We will also study other types of sensor
data such as typing and walking. As we expand our
work we will also look at other cardiovascular dis-
eases such as Peripheral vascular diseases.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
First and foremost we thank BGSegev Ltd.
(SegevLabs.org) for leading the technological
aspects of this study. Thanks to Shani Hilkiya,
Odaya Krombein, Sara Tayer, Chen Danino, Yehudit
Matzliach and Ruchama Amsalem, students from the
Lev Academic Center, for their assistance. We also
thank Gabriele Bunkheila, Ronen Cohen and Roy
Fahn from Systematics MathWorks for their support
and guidance in adapting tools for this study Website:
http://www.sunrise-setting.co.uk
ICT4AWE 2019 - 5th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health
164

REFERENCES
Altman, N. S. (1992). An introduction to kernel and nearest-
neighbor nonparametric regression. The American
Statistician, 46(3):175–185.
Beeson, P. M., Higginson, K., and Rising, K. (2013).
Writing treatment for aphasia: A texting approach.
Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research,
56(3):945–955.
Bentley, P., Ganesalingam, J., Jones, A. L. C., Mahady, K.,
Epton, S., Rinne, P., Sharma, P., Halse, O., Mehta, A.,
and Rueckert, D. (2014). Prediction of stroke throm-
bolysis outcome using ct brain machine learning. Neu-
roImage: Clinical, 4:635–640.
Berthier, M. L. (2005). Poststroke aphasia. Drugs & aging,
22(2):163–182.
BGSEGEV (2018). BGSegev STROKETOR - stroke detec-
tor. https://stroketor.segevlabs.org/.
Boulos, M. N. K., Brewer, A. C., Karimkhani, C., Buller,
D. B., and Dellavalle, R. P. (2014). Mobile medical
and health apps: state of the art, concerns, regula-
tory control and certification. Online journal of public
health informatics, 5(3):229.
Bunkheila, G. (retrieved Jan 2018). Signal processing
and machine learning techniques for sensor data an-
alytics. https://www.mathworks.com/videos/signal-
processing-and-machine-learning-techniques-for-
sensor-data-analytics-107549.html.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, USA, (2009).
Prevalence and most common causes of disability
among adults–united states, 2005. MMWR: Morbidity
and Mortality weekly report, 58(16):421–426.
Crockett, D. and Eliason, B. (2016). What is data mining in
healthcare. Insights: Health Catalyst.
de Bruin, J. S., Schuh, C., Seeling, W., Luger, E., Gall, M.,
H
¨
utterer, E., Kornek, G., Ludvik, B., Hoppichler, F.,
and Schindler, K. (2015). Assessing the feasibility
of a mobile health-supported clinical decision support
system for nutritional triage in oncology outpatients
using arden syntax. Artificial intelligence in medicine.
Demaerschalk, B. M., Vegunta, S., Vargas, B. B., Wu, Q.,
Channer, D. D., and Hentz, J. G. (2012). Reliability
of real-time video smartphone for assessing national
institutes of health stroke scale scores in acute stroke
patients. Stroke, 43(12):3271–3277.
Dobkin, B. H. and Dorsch, A. (2011). The promise of
mhealth: daily activity monitoring and outcome as-
sessments by wearable sensors. Neurorehabilitation
and neural repair, 25(9):788–798.
Freund, Y., Schapire, R., and Abe, N. (1999). A short in-
troduction to boosting. Journal-Japanese Society For
Artificial Intelligence, 14(771-780):1612.
Frid, A., Safra, E. J., Hazan, H., Lokey, L. L., Hilu, D.,
Manevitz, L., Ramig, L. O., and Sapir, S. (2014).
Computational diagnosis of parkinson’s disease di-
rectly from natural speech using machine learning
techniques. In Software Science, Technology and En-
gineering (SWSTE), 2014 IEEE International Confer-
ence on, pages 50–53. IEEE.
Gonzalez, M. A., Hanna, N., Rodrigo, M. E., Satler, L. F.,
and Waksman, R. (2011). Reliability of prehospital
real-time cellular video phone in assessing the simpli-
fied national institutes of health stroke scale in patients
with acute stroke. Stroke, 42(6):1522–1527.
Guo, X., Yu, Q., Li, R., Alm, C. O., Calvelli, C., Shi, P., and
Haake, A. (2016). Intelligent medical image grouping
through interactive learning. International Journal of
Data Science and Analytics, 2(3-4):95–105.
Hazan, H., Hilu, D., Manevitz, L., Ramig, L. O., and Sapir,
S. (2012). Early diagnosis of parkinson’s disease via
machine learning on speech data. In Electrical &
Electronics Engineers in Israel (IEEEI), 2012 IEEE
27th Convention of, pages 1–4. IEEE.
Khosla, A., Cao, Y., Lin, C. C.-Y., Chiu, H.-K., Hu, J.,
and Lee, H. (2010). An integrated machine learn-
ing approach to stroke prediction. In Proceedings of
the 16th ACM SIGKDD international conference on
Knowledge discovery and data mining, pages 183–
192. ACM.
Kim, D.-K., Yoo, S. K., Park, I.-C., Choa, M., Bae,
K. Y., Kim, Y.-D., and Heo, J.-H. (2009). A mobile
telemedicine system for remote consultation in cases
of acute stroke. Journal of telemedicine and telecare,
15(2):102–107.
King, C. E. and Sarrafzadeh, M. (2017). A survey of
smartwatches in remote health monitoring. Journal
of Healthcare Informatics Research, pages 1–24.
Koh, H. C., Tan, G., et al. (2011). Data mining applica-
tions in healthcare. Journal of healthcare information
management, 19(2):65.
Krpic, A., Savanovic, A., and Cikajlo, I. (2013). Telere-
habilitation: remote multimedia-supported assistance
and mobile monitoring of balance training outcomes
can facilitate the clinical staff’s effort. International
Journal of Rehabilitation Research, 36(2):162–171.
Little, M. A., McSharry, P. E., Hunter, E. J., Spielman, J.,
Ramig, L. O., et al. (2009). Suitability of dysphonia
measurements for telemonitoring of parkinson’s dis-
ease. IEEE transactions on biomedical engineering,
56(4):1015–1022.
Mans, R., Schonenberg, H., Leonardi, G., Panzarasa, S.,
Cavallini, A., Quaglini, S., and van der AALST, W.
(2008). Process mining techniques: an application to
stroke care. Studies in health technology and infor-
matics, 136:573.
Micallef, N., Baillie, L., and Uzor, S. (2016). Time to ex-
ercise!: an aide-memoire stroke app for post-stroke
arm rehabilitation. In Proceedings of the 18th Inter-
national Conference on Human-Computer Interaction
with Mobile Devices and Services, pages 112–123.
ACM.
Mitchell, J. R., Sharma, P., Modi, J., Simpson, M., Thomas,
M., Hill, M. D., and Goyal, M. (2011). A smartphone
client-server teleradiology system for primary diagno-
sis of acute stroke. Journal of medical Internet re-
search, 13(2).
Nam, H., Cha, M.-J., Kim, Y., Kim, E., Park, E., Lee,
H., Nam, C., and Heo, J. (2012). Use of a hand-
held, computerized device as a decision support tool
Mobile Applications for Stroke: A Survey and a Speech Classification Approach
165

for stroke classification. European journal of neurol-
ogy, 19(3):426–430.
Nam, H. S., Han, S. W., Ahn, S. H., Lee, J. Y., Choi, H.-Y.,
Park, I. C., and Heo, J. H. (2007). Improved time in-
tervals by implementation of computerized physician
order entry-based stroke team approach. Cerebrovas-
cular Diseases, 23(4):289–293.
Nam, H. S., Heo, J., Kim, J., Kim, Y. D., Song, T. J., Park,
E., and Heo, J. H. (2014). Development of smartphone
application that aids stroke screening and identifying
nearby acute stroke care hospitals. Yonsei medical
journal, 55(1):25–29.
Nam, H. S., Park, E., and Heo, J. H. (2013). Facilitating
stroke management using modern information tech-
nology. Journal of stroke, 15(3):135.
Ovbiagele, B., Goldstein, L. B., Higashida, R. T., Howard,
V. J., Johnston, S. C., Khavjou, O. A., Lackland, D. T.,
Lichtman, J. H., Mohl, S., Sacco, R. L., et al. (2013).
Forecasting the future of stroke in the united states.
Stroke, 44(8):2361–2375.
Ozdalga, E., Ozdalga, A., and Ahuja, N. (2012). The smart-
phone in medicine: a review of current and potential
use among physicians and students. Journal of medi-
cal Internet research, 14(5).
Pantelopoulos, A. and Bourbakis, N. G. (2010). A survey on
wearable sensor-based systems for health monitoring
and prognosis. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man,
and Cybernetics, Part C (Applications and Reviews),
40(1):1–12.
Park, E. and Nam, H. S. (2009). A service-oriented medical
framework for fast and adaptive information delivery
in mobile environment. IEEE transactions on infor-
mation technology in biomedicine, 13(6):1049–1056.
Patel, S., Park, H., Bonato, P., Chan, L., and Rodgers, M.
(2012). A review of wearable sensors and systems
with application in rehabilitation. Journal of neuro-
engineering and rehabilitation, 9(1):21.
Place, S., Blanch-Hartigan, D., Rubin, C., Gorrostieta, C.,
Mead, C., Kane, J., Marx, B. P., Feast, J., Deckers-
bach, T., et al. (2017). Behavioral indicators on a
mobile sensing platform predict clinically validated
psychiatric symptoms of mood and anxiety disorders.
Journal of medical Internet research, 19(3).
Platt, J. (1999). Using sparseness and analytic QP to speed
training of support vector machines. In Advances in
Neural Information Processing Systems, pages 557–
563.
Quinlan, J. R. (1993). C4.5: Programs for Machine Learn-
ing. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc., San Fran-
cisco, CA, USA.
Recio-Rodriguez, J. I., Agudo-Conde, C., Martin-
Cantera, C., Gonz
´
alez-Viejo, M. N., Fernandez-
Alonso, M. D. C., Arietaleanizbeaskoa, M. S.,
Schmolling-Guinovart, Y., Maderuelo-Fernandez, J.-
A., Rodriguez-Sanchez, E., Gomez-Marcos, M. A.,
et al. (2016). Short-term effectiveness of a mobile
phone app for increasing physical activity and adher-
ence to the mediterranean diet in primary care: A ran-
domized controlled trial (evident ii study). Journal of
medical Internet research, 18(12).
Richardson, A., Kraus, S., Weiss, P. L., and Rosenblum,
S. (2008). COACH - cumulative online algorithm for
classification of handwriting deficiencies. In IAAI’08
Proceedings of the 20th national conference on In-
novative applications of artificial intelligence, pages
1725–1730.
Roine, R., Ohinmaa, A., and Hailey, D. (2001). Assess-
ing telemedicine: a systematic review of the literature.
Canadian Medical Association Journal, 165(6):765–
771.
Sakar, B. E., Isenkul, M. E., Sakar, C. O., Sertbas, A., Gur-
gen, F., Delil, S., Apaydin, H., and Kursun, O. (2013).
Collection and analysis of a parkinson speech dataset
with multiple types of sound recordings. IEEE Jour-
nal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 17(4):828–
834.
Sellars, C., Hughes, T., and Langhorne, P. (2005). Speech
and language therapy for dysarthria due to non-
progressive brain damage. Cochrane Database Syst
Rev, 3.
Seo, W.-K., Kang, J., Jeon, M., Lee, K., Lee, S., Kim, J. H.,
Oh, K., and Koh, S.-B. (2015). Feasibility of using
a mobile application for the monitoring and manage-
ment of stroke-associated risk factors. Journal of Clin-
ical Neurology, 11(2):142–148.
Shin, S., Park, E., Lee, D. H., Lee, K.-J., Heo, J. H., and
Nam, H. S. (2012). An objective pronator drift test
application (ipronator) using handheld device. PLoS
One, 7(7):e41544.
Terry, K. (2015). Number of health apps soars but use does
not always follow. Medscape Medical News.
Tsanas, A., Little, M. A., McSharry, P. E., and Ramig, L. O.
(2010). Accurate telemonitoring of parkinson’s dis-
ease progression by noninvasive speech tests. IEEE
transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 57(4):884–
893.
Walker, S. H. and Duncan, D. B. (1967). Estimation of the
probability of an event as a function of several inde-
pendent variables. Biometrika, 54(1-2):167–179.
Writing, G. M., Mozaffarian, D., Benjamin, E., Go, A., Ar-
nett, D., Blaha, M., Cushman, M., Das, S., de Fer-
ranti, S., Despr
´
es, J., et al. (2016). Heart disease and
stroke statistics-2016 update: A report from the amer-
ican heart association. Circulation, 133(4):e38.
Zhang, M. W., Yeo, L. L., and Ho, R. C. (2015). Harness-
ing smartphone technologies for stroke care, rehabili-
tation and beyond. BMJ innovations, 1(4):145–150.
ICT4AWE 2019 - 5th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Ageing Well and e-Health
166
