
Usability Evaluation of an Educational Robot for STEM Areas
Rolando Barradas
1,2 a
, José Alberto Lencastre
3b
, Salviano Soares
1,4 c
and António Valente
1,2 d
1
School of Sciences and Technology, University of Trás-os-Montes and Alto Douro, Quinta de Prados, Vila Real, Portugal
2
INESC TEC, Porto, Portugal
3
CIEd - Research Centre on Education, Institute of Education, University of Minho, Campus de Gualtar, Braga, Portugal
4
IEETA, UA Campus, Aveiro, Portugal
Keywords: Robotics, Usability, STEM, Technology-enhanced_learning, Scratch, mBlock.
Abstract: This article describes the development cycle of an educational robot designed to act as an interdisciplinary
teaching tool integrated into the curriculum of STEM areas (Science, Technology, Engineering and
Mathematics). We focused on the creation of the alpha version of the prototype and its heuristic evaluation
by three experts, with the objective of appraising both usability and potential design problems. After all the
issues and suggestions from the experts have been resolved and implemented, a beta version was developed
and evaluated in its usability by five representatives of end-users with different age ranges and robotics
knowledge. The System Usability Scale score of 92.5 points - Best Imaginable - show a very stable and
satisfactory robot, with almost no usability problems detected.
1 INTRODUCTION
STEM areas (Science, Technology, Engineering and
Math) are continuously growing, but the number of
technical workers do not accompany that growth. As
the 21st century brings new challenges, students
should be prepared for increasingly complex life and
work environments that will privilege proficiency in
Learning and Innovation Skills that include Creativity
and Innovation, Critical Thinking and Problem
Solving, Communication and Collaboration
(Partnership, 2016). This article describes the
usability tests of an educational robot developed for
kids and teens (8 to 18 years old).
This robot is meant to work as an interdisciplinary
teaching tool to be applied in the curriculum,
promoting students’ technical competences and
allowing them to develop skills such as
Computational Thinking and Problem Solving.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9399-9981
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7884-5957
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5862-5706
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5798-1298
2 BACKGROUND
2.1 Computational Thinking and
Problem-Solving Skills
Computational thinking is a mental activity carried
when formulating a problem to admit a computational
solution that can be carried out by a human or a
machine (Wing, 2017) and involves solving problems
and designing systems using concepts fundamental to
computer science (Wing, 2006). Problem-Solving
skills is the most relevant learning activity students
can engage in because the knowledge constructed is
better comprehended and retained (Jonassen, 2011).
2.2 Micromouse Portuguese Contest
This contest is an international competition held in
Portugal since 2011. The main challenge is to have a
full autonomous micro-controlled robot vehicle,
explore an unknown maze and find out the optimum
route for the shortest travel time from start to end
(Silva et al., 2015).
218
Barradas, R., Lencastre, J., Soares, S. and Valente, A.
Usability Evaluation of an Educational Robot for STEM Areas.
DOI: 10.5220/0007675102180225
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2019), pages 218-225
ISBN: 978-989-758-367-4
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Competition is one of the key factors for
motivation and getting physical results contributes to
the formation of student’s independence, developing
their leadership skills and promoting a positive
educational process (Bazylev et al., 2014). As robot
competitions encourage students to apply their
knowledge to real-world problems and motivates
them to learn new concepts for themselves (Pack et
al., 2004), participating in a contest like this may aid
the development of Computational Thinking and
Problem Solving capabilities.
2.3 Visual Programming Languages
As the robot is aimed mostly to small children, its
complexity needs to be somehow reduced; thus, the
use of visual programming languages (VPL). VPL
helps children start programming by reducing the
level of abstraction using graphical program elements
rather than text.
2.3.1 Scratch
Scratch is a VPL created by the Lifelong
Kindergarten group at the MIT Media Lab. Originally
thought as an approach to programming, designed to
be easy for all ages, backgrounds and interests, to
program interactive stories, games, animations, and
share their creations (Resnick et al., 2009).
Scratch was made with a simple grammar, based
on graphical programming and blocks that are put
together to create programs. To make it even easier,
the blocks have connectors that suggest how they can
connect, allowing only the creation of code that
makes sense (Resnick, 2012).
2.3.2 mBlock
Also marking its presence in the VPL world, mBlock
appeared as a graphical programming environment
based on Scratch 2.0 Open Source Code, thus
maintaining all its features, and adding some others
that make it possible to program Arduino projects
within the same interface (Mblock.cc, 2017). This
fact and the feature that allows programmers to create
custom software extensions adapted to specific
hardware, turn it into a perfect tool to work with the
product we are developing.
3 METHOD
To develop the prototype we decided to follow an
Instructional System Design model (Clark, 2000),
which we will refer to as ADDIE, the acronym of its
five phases: Analysis, Design, Development,
Implementation and Evaluation (Figure 1). In this
article, we will only describe the Analysis, Design
and Evaluation phases.
The Evaluation phase is fundamental and should
be a part of the process from the beginning because it
supplies information that feeds all the cyclic process
of design and development and is very useful when as
a part of the spiral of analysis, design, evaluation, etc.,
by contributing to the continuous improvement of the
prototype (Lencastre, 2012).
Figure 1: The ADDIE Model.
3.1 Analysis
The analysis phase is the foundation of a learning or
training process (Clark, 2000), and allowed us to
study the target audience of our educational product.
By knowing their previous experience, education
level, age, computer experience, among others, it is
possible to anticipate learning difficulties and create
boundaries to the complexity of the product (Nielsen,
1993).
Through documentary analysis and classroom
observations, we tried to create a profile for the target
audience of our product.
As we are targeting both Primary and Secondary
school students, the first thing we have to consider is
the age difference between the younger and the older
students. In our analysis, the average age is 11.3 years
old. In addition, the concepts and academic level
differences are an important fact to consider. A
relevant information is the fact that some of the
students in our study already have some basic
knowledge of robotics and programming in Scratch
(Resnick et al., 2009), because Introductory
Programming classes are a part of their curriculum. In
addition, we also need to consider the latest
government recommendations stating that every
children from Primary to Upper Secondary education
should have Programming and Robotics classes.
Usability Evaluation of an Educational Robot for STEM Areas
219
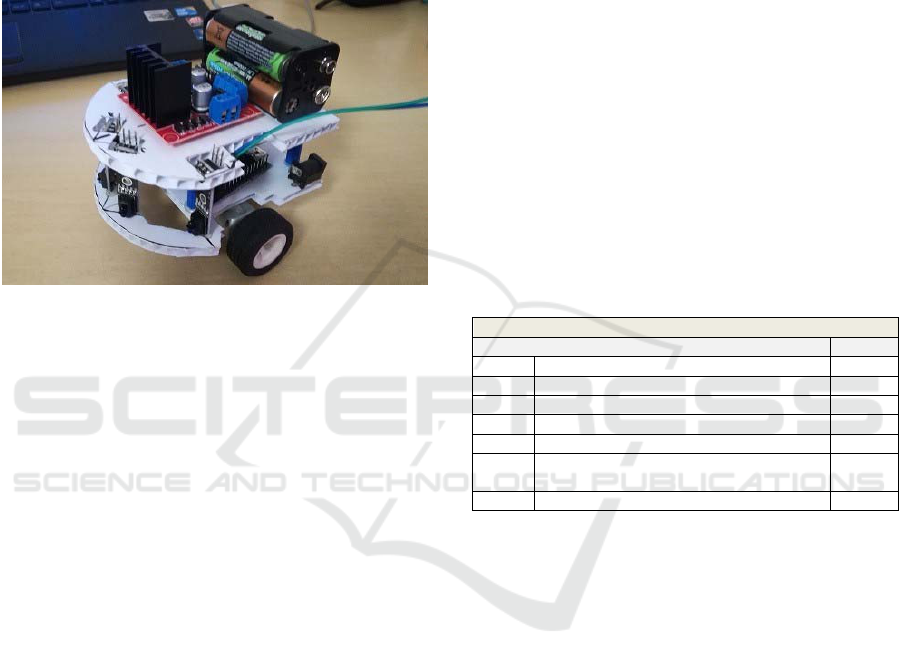
3.2 Design
The results obtained led us to idealise Kid Grígora
(Fig. 2), an educational robot used as a teaching tool
to be integrated into the curriculum. Besides that
primary objective, Kid Grígora was designed to be
small enough to allow children to use it in the
Micromouse Portuguese Contest robotics
Competition.
Figure 2: Alpha version of Kid Grígora.
3.2.1 Heuristic Evaluation of the Alpha
Version
The alpha version of the prototype was tested in a
heuristic evaluation by experts, with the objective of
appraising both usability and potential design
problems. In addition, to gather suggestions from the
experts on how to solve the problems they found,
before performing usability tests with representative
users. To test the prototype, we chose double experts
(Nielsen, 1993) experienced not only in usability but
also with specific expertise in the interface under
evaluation as they potentially find 1.5 times more
problems than simple usability specialists (Nielsen,
1993). We used three experts, with ages from 40 to
48 years old, with a degree in areas related to
computing, electronics and robotics. The average of
teaching experience is 15 years and 9 years of
business experience in developing software and
electronics.
The evaluations were carried out on October 9-12,
2017, with a duration of approximately 90 minutes. It
started with an explanation of the expected use of the
robot by end-users, in particular on its use as an
educational tool, but also on its possible use in a
robotics contest. Then, the evaluators were given the
robot’s parts, a set of tools and assembly instructions
and were asked to assemble the robot.
During the tests, each expert was asked to answer
a heuristic evaluation questionnaire to report possible
problems. To report the problems, they used a 0 to 4
Nielsen’s severity rating scale (Nielsen, 1993) in
which 0 means "I don’t agree that this is a usability
problem at all" and 4 means a "Usability catastrophe:
imperative to fix this before product can be released".
Talking about the strong points of the heuristic
evaluation, all the experts mentioned that the robot
was very easy to build, mostly because of its small
number of components. They also referred the
physical similarity to professional built Micromouse
robots. Two experts referred that because it has
almost no soldering parts, it should be suitable for all
target users, eventually with the help of an adult. All
experts referred the use of standard components as a
strong point as they are easy to buy, making it easy to
replace damaged parts and due to their low price, they
make this robot an educational tool, potentially for
everyone.
The weakest points in the heuristic evaluation
(ratings 3 and 4) are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1: Related severe and catastrophic errors, according
to Nielsen’s heuristics.
Nielsen’s heuristics
Interface (IN) Degree
IN1 Visibility of system status 4
IN3 User control and freedom 3
IN4 Consistency and standards 4
IN7 Flexibility and efficiency of use 3
IN8 Aesthetic and minimalist design 3
IN9
Help users recognize, diagnose, and
recover from errors
4
IN10 Help and documentation 3
Regarding IN1, two experts mentioned that the
robot had no information on the status. Related with
IN3, all of the experts stated that the robot needed to
have an ON-OFF switch and one of them referred that
as older students may require a little more control
over the robot, it should be useful to have it
equipped with encoders and gyros so that more
elaborated algorithms could be implemented. One of
the experts, referring to IN4, mentioned that the
Traction system would not work at very high speeds
as the motor connected directly to wheel brings speed
but almost no torque. The difficulty on perceiving the
robots movements, when working with youngest
students, was mentioned by one of the experts as
being potentially a problem, related to IN7. All
experts mentioned that the type of battery used could
be lighter, thus reducing the overall weight of the
robot. Still related to IN7, one of the experts
mentioned that the use of IR Sensors might be too
difficult to program and understand by young
students. Regarding the design and IN8, all the
experts mentioned that the battery positioned on the
CSEDU 2019 - 11th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
220

top of the robot would create a very high gravity
center. The fact that the robot has no error messages
led one of the experts to signal a catastrophic error
related to IN9. Referring to IN10, all experts
mentioned the fact that it will be necessary to have
detailed help on the electrical connections assembly
because children may have some difficulty
understanding it.
3.3 Development
3.3.1 Building the Beta Version
Although only Major and Catastrophic problems
(ratings 3 and 4) were described, before building the
beta version, all reported problems and suggestions of
the experts were solved and implemented, as
summarized in Table 2.
Table 2: Solutions for usability problems found.
Heuristic
P
roblem foun
d
Solution
IN1
N
o information on the
status
A
dd a Status LED
IN3
The robot needs an ON-
OFF
switch
Change the electrical
connections
and add a power switch
IN3
E
quip the robot with
encoders
and gyroscope
Create a SemiPro version
w
ith encoders, Gyro and
accelerometer (Figure 3)
IN4
Traction system would
n
ot wor
k
U
se motors with reduction
(Figure 4)
IN7
The type of battery used
could be lighte
r
Change the type of
b
attery from
4
xAA 1.5v to a 9V battery
IN7
The use of IR Sensors
m
ight be too difficult to
p
rogram and understand
b
y young students
U
se simpler Ultrasonic
sensors in Kid Grígora
R
ookie, but keep the
I
R sensors in Kid Grígora
Semi-Pro (Figure 3)
IN7
I
t may be difficulty to
p
erceive the robots
m
ovements, when
w
orking with youngest
students
Create an add-on to the Kid
Grígora Rookie, with a pen,
for the students to visualize
t
he trajectories (Figure 6)
IN8
The battery positioned
on the top of the robot
w
ould create a very
h
igh gravity center.
N
ew battery type allows a
differen
t
p
osition in the chassis,
l
owering the height and
center of gravity
IN9
N
o error messages
U
se a LED to display Error
codes
IN10
M
ore detailed help on
t
he electrical
connections assembly
Created new electrical
schematics
suitable for kids
The results of the heuristics analysis led to the
idealization of two models of our robotic platform,
mainly due to the age difference and academic levels
between our target audiences.
Kid Grígora Rookie is the simpler of the two
models. Aimed to students aged from 8 to 15, this
robot allows younger students to make their first steps
in robotics and programming. The price and the ease
of build have been taken in consideration, to make it
affordable and easy to assemble.
Figure 3: Kid Grígora Rookie and Semi-Pro 3D art, Beta
versions.
Kid Grígora Semi-Pro is the most complex,
having more powerful specifications, allowing
students, from 15 to 18 years old, to apply knowledge
from other areas like Mathematics or Physics. With a
more powerful processor, motors with encoders, a
three-axis gyroscope and accelerometer and four
infrared distance sensors, this model allows a much
more accurate control of movements.
Figure 4: Final design of the Traction System in the Beta
version of Kid Grígora Rookie and Semi-Pro.
3.3.2 Usability Tests with Representative
Users
The usability tests with representative users were
carried out on December 18-22, 2017. Nielsen (2000)
states that "after the fifth user, you are wasting your
time by observing the same findings repeatedly but
not learning much new". Therefore, we chose five
representative users with different age ranges and
robotics knowledge to evaluate our prototype.
Although we developed and built both models of
Kid Grígora, as in our analysis, our target medium
range was 11.3 years old, in this article we will focus
on the tests performed with Kid Grígora Rookie.
The tests were carried by five students, aged from
11 to 17, two boys and three girls, and had an average
duration of 127 minutes, with a 15-minute pause for
Usability Evaluation of an Educational Robot for STEM Areas
221

the users to rest and then regain their focus on the
tasks. As for background on robotics, only two users
were already engaged in extra-curricular robotics
activities at school. The other three had never been in
close contact with robotics.
Figure 5: Representative user performing Usability test.
Starting with a simple explanation on the basics of
the assembly and best practices to do it, the users were
given the robot’s parts, a set of tools and the assembly
instructions in the form of a gallery of pictures and
videos, and were asked to assemble the robot. In all
tests, we used the think-aloud protocol, letting users
verbalize their thoughts as they move through the
interface (Nielsen, 1993), and audio recording to
gather data.
At the end of the tests, the users were asked to fill
a SUS satisfaction questionnaire (Brooke, 1986),
whose average satisfaction results were given a
meaning by using the adjective scale of Bangor et al.,
(2009). The obtained results are summarised in Table
3.
Table 3: Summary of usability tests results by
representative users.
User 1 User 2 User 3 User 4 User 5 Avg
Sex:
F
M M F F
Age 16 13 11 11 17 13.6
Previous
robotics?
N
N N Y Y
Length
(min)
131 134 147 120 103 127
Rating 92.5 85 90 95 100 92.5
Meaning
Best
Imagi
nable
Excell
ent
Excell
ent
Best
Imagi
nable
Best
Imagi
nable
Best
Imagin
able
The mean result of the five tests was 92.5 points,
Best Imaginable, meaning that there were almost no
usability problems detected with the prototype. The
analysis of the results show that the representative
users were unanimous giving the Strongly agree score
to the question "I think that I would like to use this
robotics kit frequently" and the to Strongly disagree
to the question "I found the robotics kit unnecessarily
complex" which shows the good acceptance of this
robotics kit. The analysis of the think-aloud showed
that most of the difficulties lied in the part of the
wiring, particularly in those users who have never had
contact with robotics. This led us to think that perhaps
an introductory session on the concepts of electronics
and wiring will be necessary before end-users start
using the kit.
4 KID GRÍGORA ROOKIE
HARDWARE COMPONENTS
To build Kid Grígora Rookie, we chose to use only
standard electronic components like Arduino Nano,
L298N Motor Controller, two Geared DC Motors,
three HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensors and a 9v battery,
easily available in both local and online electronics
stores.
For the pen add-on, we designed two 3D printed
parts that can be easily fit in a standard 9G servo.
Figure 6: Assembled Kid Grígora Rookie with and without
the pen add-on.
5 PLANNED SOFTWARE
INTERFACES
5.1 Extensions for mBlock
Currently under development, the two mBlock
(Mblock.cc, 2017) extensions will be one of the core
components of this project (Figure 7).
The Simple KidG extension will have a basic set
of blocks to move the robot, like Move Forward, Turn
Right and Turn Left, and will be used, typically by
students from 8 to 12 years old.
To students from 12 to 15 years old, the KidG
extension provides a greater level of control over the
robot, with different left and right motor speeds and
CSEDU 2019 - 11th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
222
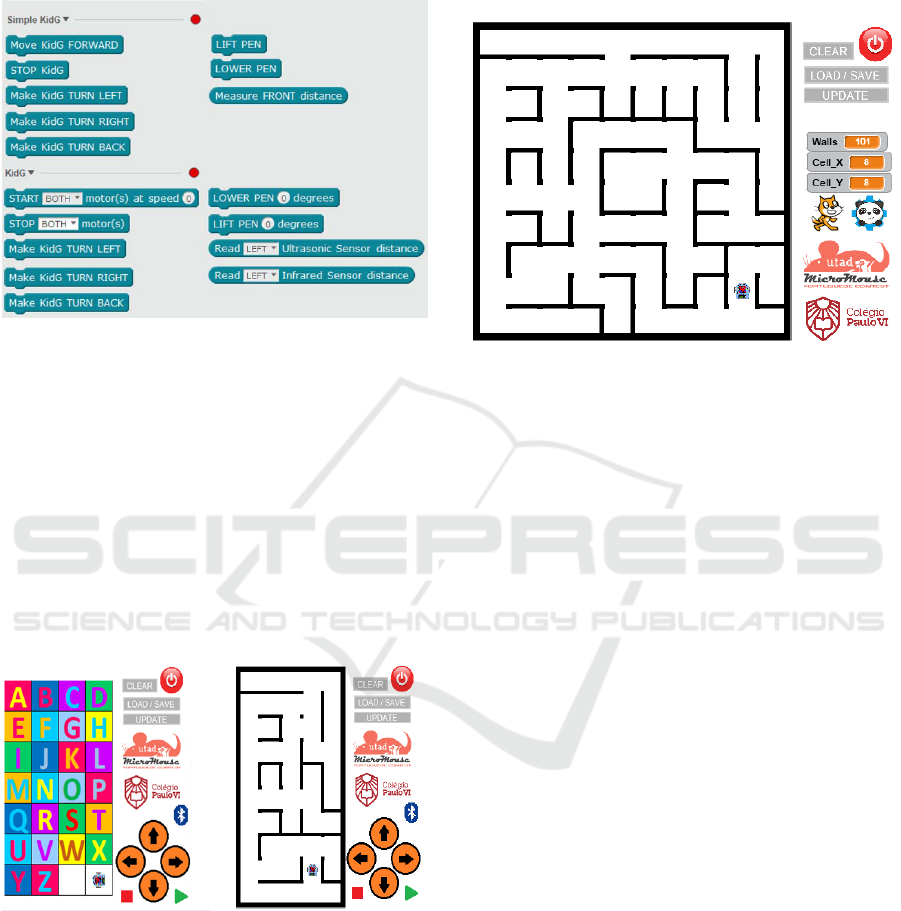
different sensor distance measuring, allowing
students to do different kinds of interactions with the
robot.
Figure 7: Proposed mBlock extensions.
5.2 Android Apps
In order to reach our younger audience, we have
planned the development of two type of Android
Apps, typically to be used by students from 8 to 12
years old.
The KidG Remote Control will allow young
students to remotely control the robot and explore all
its movement possibilities.
The KidG Step by Step will allow students to
create simple algorithms, send them to the robot and
watch it execute them (Figure 8).
Figure 8: Different possibilities of android apps.
5.3 Virtual Maze
Virtual Maze (Figure 9) is a configurable
representation based on a real world maze,
programmed in Scratch. This project was designed to
provide students a first contact with the Micromouse
Contest using it to simulate simple Maze Solving
algorithms.
Future versions will include a Bluetooth
connection to the robot, allowing it to replicate the
robot’s movements on the screen to a real robot, in a
real maze.
Figure 9: VirtualMaze implementation in Scratch/mBlock.
5.4 C++ and the Arduino IDE
Implemented as Firmware and typically used by older
students, the planned Arduino libraries will allow
students to program Kid Grígora with C++ while
providing high levels of abstraction to interact with
the hardware. Planned functions include movement
procedures, like MoveForward, TurnLeft, TurnRight,
TurnBack, and sensing functions, like
ReadDisplacement, isWallLeft and isWallFront. By
using this firmware, students will be able to create
more structured and complex algorithms to control
their robots.
6 EDUCATIONAL USES
6.1 Primary Education
For this range of ages, 8 to 12 years old, our main
objective will be creating activities aimed to develop
Computational Thinking with Kid Grígora Rookie,
the Android Apps and the Simple KidG mBlock
extension. Using real-life problems and scenarios and
interacting with virtual environments, created in
mBlock, children can take their first steps in robotics
and programming.
6.2 Lower Secondary Education
Simulating in the Virtual Maze allows students from
12 to 15 years old, to further develop their Problem-
Solving skills by placing them on the control of a
Usability Evaluation of an Educational Robot for STEM Areas
223

robot that needs to find the center of a maze. By
creating Maze Solving algorithms, students can test
their algorithms on screen and later, with their
assembled robot and the KidG mBlock extension and
bluetooth, they can debug their algorithms in both
Virtual Maze and real life. Later, still using mBlock,
they can develop a program to work autonomously
and enter the Micromouse Portuguese Contest.
6.3 Upper Secondary Education
With the focus on older students and aiming the
participation in a Robotics Competition, the use of the
custom firmware created in the form of Arduino
libraries allows students, mainly from 15 to 18 years
old, to take a step forward and no longer be limited to
making their robot sense their way in the track and
react. Using the libraries and deeper programming
concepts and algorithms, students can create real
autonomous navigation systems and path
optimization algorithms for the robot. They can use
them, for example, to participate in a Micromouse
competition, find all possible ways to the centre of a
maze, return to the starting point, backtrack the
optimal route (Silva et al., 2017) and run to the centre
the fastest it can.
7 CONCLUSIONS
Problem solving and Computational Thinking are two
of the most needed skills for 21st century students.
Following an Instructional System Design (Clark,
2000) we created a prototype of an educational
robotics kit, aimed at children and teens aged from 8
to 18, to be used in scholar activities. In the Analysis
phase, we gathered enough information to idealize the
alpha version of the product, later tested by experts.
All usability issues detected were corrected in the
development phase in which we created the beta
version, tested by representative users. In the
satisfaction test, the prototype obtained 92.5 points,
Best Imaginable, that show a very stable and
satisfactory robotic platform, with almost no usability
problems detected, which serves as an incentive to the
next phases.
8 FUTURE WORK
Future work includes usability tests of Kid Grígora
Semi-Pro and the software interfaces, the
development of other add-ons (see Figure 10) to
increase the flexibility of the platform and the
development of activities adapted to each age range.
Figure 10: Planned add-ons for Kid Grígora.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is partially financed by the ERDF -
European Regional Development Fund through the
Operational Programme for Competitiveness and
Internationalization - COMPETE 2020 Program
within project POCI-01-0145-FEDER-006961, and
by National Funds through the FCT - Fundação para
a Ciência e a Tecnologia (Portuguese Foundation for
Science and Technology) as part of project
UID/EEA/50014/2013.
This work is funded by CIEd – Research Centre
on Education, project UID/CED/01661/2019,
Institute of Education, University of Minho, through
national funds of FCT/MCTES-PT.
This work was partially funded by National Funds
through the FCT - Foundation for Science and
Technology, in the context of the project
UID/CEC/00127/2019.
We want to thank Colégio Paulo VI (Gondomar,
Portugal), and the students of year 6th and 7th, for
their collaboration and the authorisation to perform
this research on their premises.
REFERENCES
Bangor, A., Staff, T., Kortum, P., & Miller, J., 2009.
Determining What Individual SUS Scores Mean:
Adding an Adjective Rating Scale. Journal of Usability
Studies, 4(3), 114-123.
Bazylev, D., Margun, A., Zimenko, K., Kremlev, A., &
Rukujzha, E., 2014. Participation in Robotics
CSEDU 2019 - 11th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
224

Competition as Motivation for Learning. Procedia -
Social and Behavioral Sciences, 152, 835-840.
Brooke, J., 1986. SUS-A quick and dirty usability scale. In
P. W. Jordan, B. Thomas, I. L. McClelland, & B.
Weerdmeester (Eds.), Usability evaluation in industry
(s/d). London: Taylor & Francis. Retrieved from
hell.meiert.org/core/pdf/sus.pdf
Clark, D., 2000. Instructional System Design. Retrieved on
2017-09-11 from http://www.nwlink.com/donclark/
hrd/sat1.html
Jonassen, D., 2011. Learning to solve problems. A
Handbook for Designing Problem-Solving Learning
Environments. New York: Routledge.
Lencastre, J. A., 2012. Educação on-line: análise e
estratégia para criação de um protótipo. In João Batista
Bottentuit Junior & Clara Pereira Coutinho (org.),
Educação on-line: Conceitos, metodologias,
ferramentas e aplicações (pp. 127-136). Maranhão:
Editora CRV.
Mblock.cc. (2017). [online] Available at: http://
www.mblock.cc [Accessed 3 Oct. 2017].
Nielsen, J., 1993. Usability Engineering. San Francisco:
Morgan Kaufmann.
Nielsen, J., 2000. Why You Only Need to Test with 5 Users.
Retrieved on 2017-09-12 from http://www.
nngroup.com/articles/why-you-only-need-to-test-with-
5-users/
Pack, D., Avanzato, R., Ahlgren, D., and Verner, I., 2004.
Fire-fighting mobile robotics and interdisciplinary
design-comparative perspectives, IEEE Transactions
on education, vol. 47, pp. 369-376, 2004.
Partnership for 21st Century Learning, 2016. Framework
for 21st Century Learning. The Partnership for 21st
Century Learning, 37(4), 589.
Resnick, M., Maloney, J., Monroy-Hernandez, A., Rusk,
N., Eastmond, E., Brennan, K., Kafai, Y., 2009.
Scratch: Programming for All. Communications of the
ACM, 52, 60-67.
Resnick, M., 2012. Reviving Papert's Dream. Educational
Technology, vol. 52, no. 4, pp. 42-46.
Silva, S., Soares, S., Valente, A., Barradas, R. Bartolomeu,
P., 2015. Enhancing STEM courses through a robotic
innovative project. Proceedings of the 3rd International
Conference on Technological Ecosystems for
Enhancing Multiculturality - TEEM ’15, Porto,
Portugal. doi: 10.1145/2808580.2808668
Silva, S., Duarte, D., Barradas, R., Soares, S., Valente, A.,
& Reis, M., 2017. Arduino recursive backtracking
implementation for a robotic contest. In Manuel Silva,
G. Virk, M. Tokyo, B. Malheiro, P. Ferreira, & P.
Guedes (EDS.), Proceedings of Clawar 2017: 20th
International Conference on Climbing and Walking
Robots and the Support Technologies for Mobile
Machines (pp. 171-181). Porto, Portugal.
Wing, J. M., 2006. Computational thinking.
Communications of the ACM, 49(3), 33.
Wing, J. M., 2017. Computational thinking’s influence on
research and education for all. Italian Journal of
Educational Technology, 25(2), 7-14. doi: 10.17471/
2499-4324/922
Usability Evaluation of an Educational Robot for STEM Areas
225
