
What Kind of Natural Language Inference are NLP Systems Learning:
Is this Enough?
Jean-Philippe Bernardy and Stergios Chatzikyriakidis
CLASP, Department of Philosophy, Linguistics and Theory of Science, University of Gothenburg, Sweden
Keywords:
Natural Language Inference, Textual Entailment, Reasoning in Dialogue, Datasets, SNLI, RTE.
Abstract:
In this paper, we look at Natural Language Inference, arguing that the notion of inference the current NLP
systems are learning is much narrower compared to the range of inference patterns found in human reasoning.
We take a look at the history and the nature of creating datasets for NLI. We discuss the datasets that are
mainly used today for the relevant tasks and show why those are not enough to generalize to other reasoning
tasks, e.g. logical and legal reasoning, or reasoning in dialogue settings. We then proceed to propose ways
in which this can be remedied, effectively producing more realistic datasets for NLI. Lastly, we argue that the
NLP community could have been too hasty to altogether dismiss symbolic approaches in the study of NLI,
given that these might still be relevant for more fine-grained cases of reasoning. As such, we argue for a more
pluralistic take on tackling NLI, favoring hybrid rather than non-hybrid approaches.
1 INTRODUCTION
Reasoning is part of our every day routine: we hear
Natural Language (NL) sentences, we participate in
dialogues, we read books or legal documents. Suc-
cessfully understanding, participating or communi-
cating with others in these situations presupposes
some form of reasoning: about individual sentences,
whole paragraphs of legal documents, small or bigger
pieces of dialogue and so on. The human reasoning
performed in these different situations cannot be ex-
plained by a single rigid system of reasoning, plainly
because reasoning is performed in different ways in
each one of them. Consider the following example:
(1) Three representatives are needed.
If a human reasoner with expert knowledge was to
interpret the above utterance in a legal context, s/he
would most probably judge that a situation where
more than three references are provided could be
compatible with the semantics of the utterance. To
the contrary, if the same reasoner was to interpret
the above as part of a casual, everyday conversation,
then three would most likely be interpreted as exactly
three, making the same situation incompatible with
the utterance. To give another example, consider the
following dialogue interaction between participants A
and B:
(2) A dialogue example
A. Mont Blanc is higher than
B. Mt. Ararat?
A. Yes.
B. No, this is not correct. It is the other way
around.
A. Are you...
B. Sure? Yes, I am.
A. Ok, then.
The listener of this particular piece of dialogue will
have to reason based on utterances that are split be-
tween two participants, thus having to dynamically
keep track of them. Furthermore, the listener must be
able, on the one hand, to compute global inferences,
i.e. inferences that are based on statements/facts that
are shared (agreed upon) by the dialogue participants
and local inferences on the other, i.e. inferences that
are based on facts that are not shared by all dialogue
participants. Generalizing, we could say that the hu-
man ability to reason with Natural Language (NL),
i.e. Natural Language Inference (NLI), cannot be seen
as a single, coherent system of reasoning, but rather as
a collection of reasoning tools, a toolbox to perform
diverse reasoning tasks.
Bernardy, J. and Chatzikyriakidis, S.
What Kind of Natural Language Inference are NLP Systems Learning: Is this Enough?.
DOI: 10.5220/0007683509190931
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2019), pages 919-931
ISBN: 978-989-758-350-6
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
919

Even though current work in NLP can support a
diversity of NLI scenarios, there is still a long way
to go to support the whole range of diversity found
in NLI in general. Despite the usefulness of NLI,
and huge steps made in the recent years, an impor-
tant drawback remains in this line of work: NLI sys-
tems are evaluated against datasets which represent
only a fraction of human reasoning possibilities. Fur-
thermore, these different datasets seem to have arisen
from the need to test specific theoretical architectures,
for example, logical approaches in the case of the
FraCaS test suite (Cooper et al., 1996), Deep Learn-
ing (DL) architectures in the case of Stanford Natura
Language Inference Dataset (SNLI) (Bowman et al.,
2015). What happens in practice is that any NLI sys-
tem performs very poorly on any dataset which was
not specifically intended to test it. As such, the dif-
ferent systems designed to tackle NLI are not only
incomplete, but not even comparable.
This paper investigates the need of creating more
realistic NLI datasets and argues for hybrid ap-
proaches to NLI that maintain a connection to sym-
bolic NLP — contrary to current research trends. The
structure of the paper is as follows: in section 2, the
most prominent datasets used for NLI are presented
and their respective advantages and/or weaknesses are
discussed. In section 3, we ask the question of what
kind of NLI systems trained on the existing datasets
are learning and whether this is enough. Lastly, in
section 4, we propose ways to create a more diverse
and realistic collection of datasets, while we further-
more argue for the use of hybrid systems that retain
connections with the symbolic world. More specifi-
cally, we argue that symbolic systems might still be
relevant for more fine-grained NLI cases, e.g. logi-
cal or legal reasoning, making them useful as part of
hybrid or controlled-domain systems for NLI.
2 NLI DATASETS
In this section, we go through the most prominent
NLI datasets that have been used in NLP throughout
the years. After this is done, we also briefly mention
some datasets that, even though not NLI datasets per
se, are quite useful and have been used for the study
of NLI.
2.1 The FraCaS Test Suite
The FraCaS
1
test suite is an NLI data set consisting of
346 inference problems. Each problem contains one
1
ftp://ftp.cogsci.ed.ac.uk/pub/FRACAS/del16.ps.gz
or more premises followed by one yes/no-question.
There is a three way classification: YES, NO or UNK
(unknown, see (3) for an example from FraCaS). The
FraCaS test suite was later on turned into machine-
readable format by Bill McCartney
2
.
Extensions of FraCaS include: a) MultiFraCaS,
in effect a multilingual FraCaS
3
, and b) JSem, the
Japanese counterpart to FraCaS, which expands the
original FraCaS in a number of ways.
4
Even though the FraCaS test suite contains a
rather small number of examples (346), it covers a lot
of NLI cases and is, at least to some extent, multilin-
gual. On the downside, the suite includes mostly log-
ical inferences. Furthermore, the size of the dataset is
such that it cannot be used to train the Machine Learn-
ing nor Deep Learning (ML, DL) models.
(3) An UNK example from the FraCaS test suite.
P1 A Scandinavian won the Nobel Prize.
P2 Every Swede is Scandinavian.
H. Did a Swede win the Nobel prize?
H. A Swede won the Nobel prize.
Label UNK [FraCaS 065]
2.2 Recognizing Textual Entailment
The Recognizing Textual Entailment (RTE) chal-
lenges first appeared in 2004 as a means to test textual
entailment, i.e. relations between a premise text and
a hypothesis text (4):
(4) An entailment example from RTE1.
P. Budapest again became the focus of national
political drama in the late 1980s, when Hun-
gary led the reform movement in eastern Eu-
rope that broke the communist monopoly on
political power and ushered in the possibility
of multiparty politics.
H. In the late 1980s Budapest became the center
of the reform movement.
Label Entailment [RTE702]
In contrast to the FraCaS test suite, the RTE chal-
lenges use naturally occurring data as premises. The
2
www-nlp.stanford.edu/ wcmac/downloads/fracas.xml.
3
https://github.com/GU-CLASP/multifracas.
4
More info on the suite and its innovations com-
pared to the original FraCaS can be found here:
http://researchmap.jp/community-inf/JSeM/?lang=english.
NLPinAI 2019 - Special Session on Natural Language Processing in Artificial Intelligence
920

hypothesis text is then constructed based on this
premise text. There is either a binary or a tripar-
tite classification of entailment — depending on the
version of RTE. The first two RTE challenges fol-
low the former scheme and make a binary classifica-
tion of entailment (entailed or not entailed). Tripar-
tite classification (entailment, negation of the hypoth-
esis entailment or no entailment) is added in the later
datasets, retaining two way classification versions as
well. Seven RTE challenges have been created alto-
gether.
The main advantages of the RTE challenges is
their use of examples from natural text and the inclu-
sion of cases that require presupposed information.
Another important characteristic is the inclusion of
non-logical presuppositional inferences.
However, even though the RTE datasets have been
notoriously difficult to tackle for NLI systems (espe-
cially the three-way entailment tasks), most of the ex-
amples do not involve any complex semantic infer-
ence. Rather, they are difficult to handle due to their
use of the full range of natural syntax, and their de-
pendence on world knowledge.
Indeed, the very definition of inference assumed
in a number of the examples is problematic. As Za-
enen et al. (2005) have pointed out, RTE platforms
suffer from cases of inference that should not be cat-
egorised as such. For these cases, a vast amount of
world knowledge needs to be taken into considera-
tion (that most importantly not every linguistic agent
has). The problem is that there is no clear annota-
tion in the data that distinguishes the different kinds
of inference. Furthermore, it is not clear whether
the existence of background/hidden premises will be
used by some speakers in order to classify a case as
entailment, assuming that the presupposed informa-
tion is plausible, or to the contrary render the case as
non-entailment, assuming that the hidden premise is
not plausible. Bernardy and Chatzikyriakidis (2018)
show that validating RTE examples by asking sub-
jects to provide justifications for their answers shows
exactly that: some people may use a hidden assump-
tion to justify an entailment, while some other sub-
jects may use the same hidden premise to the con-
trary, i.e. to justify a non-entailment. Bernardy and
Chatzikyriakidis (2018) asked expert linguists or lo-
gicians to validate a set of 130 examples taken from
the RTE challenges that are marked as “YES”. The
subjects are asked to judge whether the conclusion
follows or not from the premise, noting that in case
extra assumptions need to be made to justify the an-
swer, they should provide them. The results show that
about half of the YES examples receive either a YES,
IF..., a NO, BECAUSE..., or a straight NO answer.
5
Lastly, similarly to the FraCaS, the RTE datasets are
still small (less than 1000 pairs for both the develop-
ment and the test set for all challenges) with regards
to datasets intended to train Deep Learning systems.
2.3 SNLI, MultiNLI and XNLI
SNLI (Bowman et al., 2015) and MultiNLI (Williams
et al., 2017) are two of the standard datasets used to-
day to train and test Deep-Learning-based NLI sys-
tems. Both systems have been created using crowd-
sourcing techniques (Amazon Mechanical Turk). The
process used to create SNLI is as follows: subjects
are given a caption of a picture and then are asked to
provide: a) an alternate true caption, b) an alternate
possibly true caption, and c) an alternate false caption
(figure 1). The dataset constructed out of this process
contains 570k inference pairs, making SNLI two or-
ders of magnitude bigger than datasets like FraCaS or
RTE. MultiNLI was modeled on SNLI but uses data
from a variety of genres. More specifically, ten dif-
ferent genres are represented from both written and
spoken English. The dataset consists of 433k sen-
tence pairs. Lastly, XNLI is a multilingual extension
of MultiNLI (Conneau et al., 2018). It involves 5k
test- and 2,5k dev-set examples from the MultiNLI
translated into 14 languages. The size of SNLI and
MultiNLI is suitable for training DL models, making
them in this respect a very useful resource. Another
defining characteristic is that reasoning in SNLI and
MultiNLI is tied to specific situations (given by the
picture captions).
While situational reasoning can be useful, it can
also be a drawback of these datasets. An issue is
that much reasoning involving quantifiers is not sit-
uational. What would be for example the image de-
scribed by a caption “all men are human”? Simi-
larly to earlier platforms, SNLI and MultiNLI seem
to capture only a fraction of the range of phenomena
associated with NLI. Even though MultiNLI claims
to remedy this issue by introducing data from differ-
ent genres, and indeed it definitely constitutes an im-
provement over SNLI, the definition of inference in-
volved in both SNLI and MultiNLI is the same and
quite narrow. For example, neither stricter/logical (or
in general expert domain) reasoning of the sort found
in the FraCaS test suite, nor the type of inference
using world knowledge found in the RTE challenge,
is found in any of SNLI or MultiNLI. Furthermore,
the dialogue examples in MultiNLI involve clean cut
cases of dialogue where the problematic aspects of
5
https://github.com/GU-CLASP/
PreciseTextualEntailment/blob/master/PilotEmail.txt.
What Kind of Natural Language Inference are NLP Systems Learning: Is this Enough?
921

it do not show up (e.g. split utterances, disfluencies
etc.) and furthermore global vs local inferences are
not checked. What appears to be further problem-
atic in relation to SNLI is the containment of anno-
tation artifacts. Specifically, Gururangan et al. (2018)
show that both SNLI and MultiNLI contain annota-
tion artifacts that help NN models in the classification
task. For example, entailed hypotheses tend to con-
tain generic words like animal, instrument, while con-
tradicting hypotheses tend to involve negative quanti-
fiers like no, nobody etc.
Figure 1: Instructions for the Mechanical Turk Data Collec-
tion.
2.4 SICK Dataset
The Sentences Involving Compositional Knowledge
(Marelli et al., 2014) is a dataset created, at least at its
inception, to test compositional distributional seman-
tics (DS) models. The dataset contains 9,840 exam-
ples of inference patterns (e.g. negation, conjunction,
disjunction, apposition, relative clauses, etc.). How-
ever, it focuses on distributional semantic approaches.
Therefore, it normalises several cases that DS is not
expected to account for. The dataset is constructed by
taking pairs of sentences from a random subset of the
8K ImageFlickr data set (Young et al., 2014) and the
SemEval 2012 STS MSRVideo Description dataset.
2.5 Some Other Datasets Related to NLI
There exist a number of NLI related datasets that have
been used for NLI, which have received less attention
from the community, so far. We mention some briefly
here:
1. The QQP (Quora Question Pairs) dataset (Chen
et al.) is an NLI dataset that contains pairs of
questions from the Quora database and tries to
classify them as semantically equivalent or not.
2. The PPDB (Paraphrase Database) relation extrac-
tion dataset (Ganitkevitch et al., 2015) is primar-
ily a dataset on paraphrase. However, it is further
annotated for entailment (unidirectional, bidirec-
tional etc.), making it useful for entailment tasks
as well.
Other datasets that are relevant for NLI, but are not
NLI datasets per se include datasets on textual simi-
larity like the Semantic Textual Similarity Benchmark
(STS-B) (Cer et al., 2017), paraphrase datasets, the
Microsoft Research Paraphrase Corpus (MRPC)
6
, as
well as answer sentence selection datasets (selQA)
(Jurczyk et al., 2016). Detailing these datasets cannot
be done here for lack of space: the interested reader is
directed to the relevant papers for more information.
3 CAPABILITIES OF NLI
SYSTEMS
SNLI and/or MultiNLI have been used as the dataset
par excellence to train the latest state-of-the-art NLI
models. This is not an accident, given that all the lat-
est systems involve Neural Network (NN) architec-
tures that require training sets sizes that that datasets
like the FraCaS or RTE do not offer. The first sys-
tem to be tested against SNLI achieved an accuracy of
0.8 using a vanilla Long-Short Term Memory Recur-
rent Neural Network (LSTM RNN) (Bowman et al.,
2015). A number of other variations of LSTMs and
bi-LSTMs improved the performance. For example,
Wang et al. (2017) use a bilateral multi-perspective
matching (BiMPM) model and achieve an accuracy
of 0.888 on the SNLI dataset. This system uses a bi-
LSTM to encode the inference pairs (P and Q), the
pairs are further matched in both directions and then
another bi-LSTM aggregates the results of this match-
ing into a single vector that is used to make the final
scoring decision. Chen et al. (2017a) achieve an accu-
racy of 0.891 on SNLI by enriching existing state-of-
the art NLI models with external knowledge. External
6
https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/
details.aspx?id=52398.
NLPinAI 2019 - Special Session on Natural Language Processing in Artificial Intelligence
922
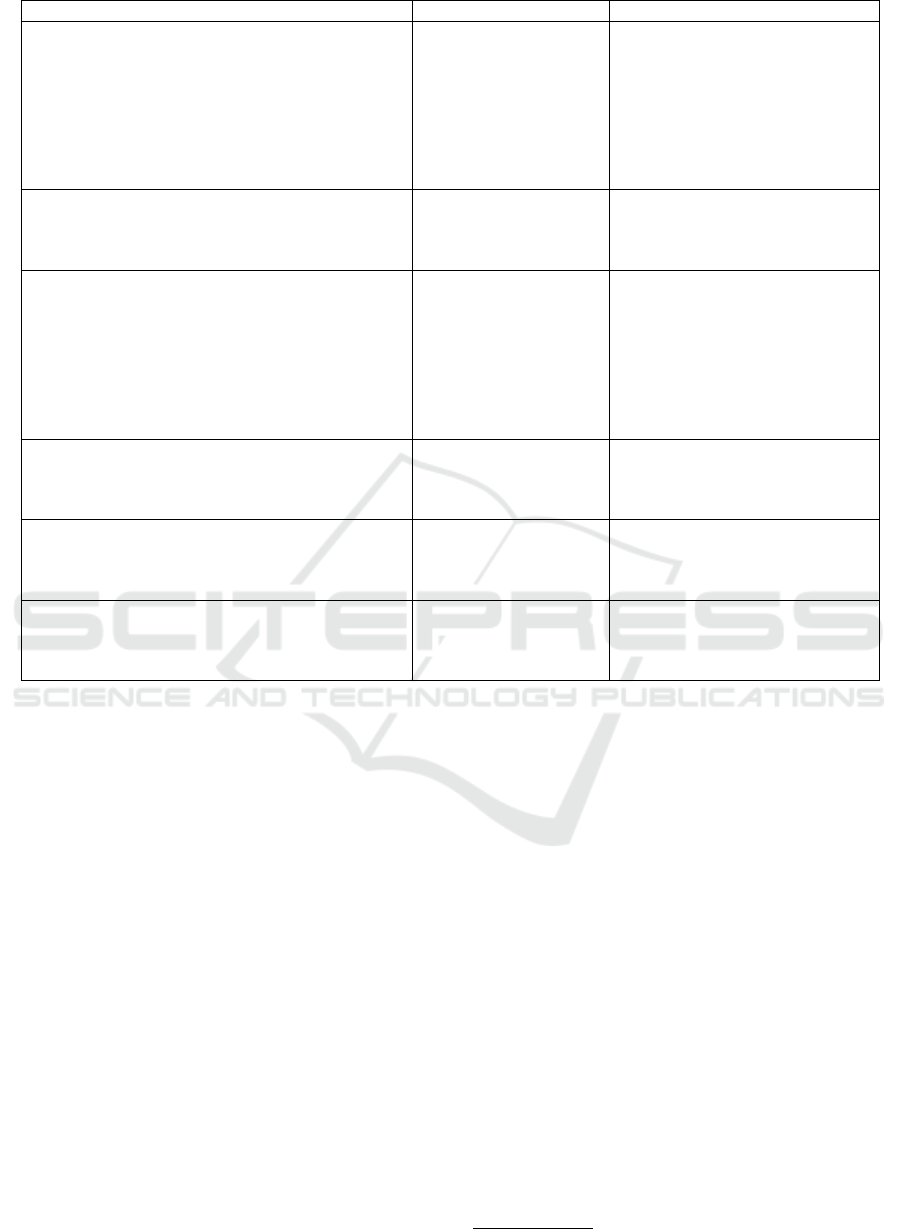
Train Dev Test Test Accuracy Delta Model
SNLI SNLI SNLI 86.1 600D BiLSTM-max
SNLI SNLI SNLI 86.6 600D HBMP Talman et al. (2018)
SNLI SNLI SNLI 88.0 600D ESIM Chen et al. (2017b)
SNLI SNLI SNLI 88.6 300D KIM Kim et al. (2018)
SNLI SNLI MultiNLI-m 55.7
*
-30.4 600D BiLSTM-max
SNLI SNLI MultiNLI-m 56.3
*
-30.3 600D HBMP
SNLI SNLI MultiNLI-m 59.2
*
-28.8 600D ESIM
SNLI SNLI MultiNLI-m 61.7
*
-26.9 300D KIM
SNLI SNLI SICK 54.5 -31.6 600D BiLSTM-max
SNLI SNLI SICK 53.1 -33.5 600D HBMP
SNLI SNLI SICK 54.3 -33.7 600D ESIM
SNLI SNLI SICK 55.8 -32.8 300D KIM
MultiNLI MultiNLI-m MultiNLI-m 73.1
*
600D BiLSTM-max
MultiNLI MultiNLI-m MultiNLI-m 73.2
*
600D HBMP
MultiNLI MultiNLI-m MultiNLI-m 76.8
*
600D ESIM
MultiNLI MultiNLI-m MultiNLI-m 77.3
*
300D KIM
MultiNLI MultiNLI-m SNLI 63.8 -9.3 600D BiLSTM-max
MultiNLI MultiNLI-m SNLI 65.3 -7.9 600D HBMP
MultiNLI MultiNLI-m SNLI 66.4 -10.4 600D ESIM
MultiNLI MultiNLI-m SNLI 68.5 -8.8 300D KIM
MultiNLI MultiNLI-m SICK 54.1 -19.0 600D BiLSTM-max
MultiNLI MultiNLI-m SICK 54.1 -19.1 600D HBMP
MultiNLI MultiNLI-m SICK 47.9 -28.9 600D ESIM
MultiNLI MultiNLI-m SICK 50.9 -26.4 300D KIM
SNLI+MultiNLI SNLI SNLI 86.1 600D BiLSTM-max
SNLI+MultiNLI SNLI SNLI 86.1 600D HBMP
SNLI+MultiNLI SNLI SNLI 87.5 600D ESIM
SNLI+MultiNLI SNLI SNLI 86.2 300D KIM
SNLI+MultiNLI SNLI SICK 54.5 -31.6 600D BiLSTM-max
SNLI+MultiNLI SNLI SICK 55.0 -31.1 600D HBMP
SNLI+MultiNLI SNLI SICK 54.5 -33.0 600D ESIM
SNLI+MultiNLI SNLI SICK 54.6 -31.6 300D KIM
Figure 2: Test accuracies (%). For results highlighted in bold the training data include examples from the same corpus as
the test data. For the other cases, the training and test data involve separate corpora. Delta stands for the difference between
the test accuracy and the baseline accuracy for the same training set. Results marked with
*
are for the development set, as
no annotated test set is openly available. BiLSTM-max is Bidirectional LSTM with max pooling. HBMP is a Hierachical
BiLSTM with max pooling.
knowledge has been shown to work for earlier mod-
els based on logic or traditional ML techniques, but
had never been used before for DL architectures. Tay
et al. (2017) use a compare-aggregate architecture,
where alignment features are propagated to higher
layers and can thus be used. It provides an accuracy
of 0.893 on the SNLI. The system presented by Kim
et al. (2018), which is at the time of writing the state
of the art on SNLI, uses a densely-connected recur-
rent network, in effect the RNN analogue of Densenet
(Huang and Liu, 2017). Crucially, the recurrent fea-
tures are retained all the way to the uppermost levels
and a concatenation (rather than summation) opera-
tor works along the attention mechanism to preserve
co-attentive information more efficiently. The sys-
tem reports an accuracy of 0.901 on SNLI. Recently,
Google’s BERT system has been proposed, provid-
ing state-of-the-art results for 11 NLP benchmarks,
among them the state-of-the-art result for MultiNLI
at 0.867 accuracy (Devlin et al., 2018).
7
Within this context, and the impressive perfor-
mance of NN systems w.r.t NLI tasks, two questions
come to mind: a) what is the generalization ability
of these systems, and b) what kind of inference are
these systems learning. Both, we believe, are equally
important. With regards to the first question, recent
work on testing various state-of-the-art systems w.r.t
their generalization ability has shown that it is rather
limited. Glockner et al. (2018) have shown that NLI
systems have limited generalization ability outside the
datasets that they are trained and tested on. More
specifically, they show that NLI systems break eas-
ily when, instead of being tested on the original SNLI
test set, they are tested on a test set which contain
sentences that differ by at most one word from sen-
tences in the training set. A significant drop in accu-
7
There are no results reported for SNLI.
What Kind of Natural Language Inference are NLP Systems Learning: Is this Enough?
923

racy, e.g. between 22 and 33 points when trained on
SNLI and tested on the new dataset, is reported for
three out of four state-of-the-art systems tested. The
system less prone to breaking is Kim et al. (2018) (5
points drop when trained on SNLI and tested on the
new dataset), which utilizes external knowledge taken
from WordNet (Miller, 1995). Talman and Chatzikyr-
iakidis (2018) train and test six state-of-the-art NN
models using train and test sets drawn from a different
corpus. For example, the train set is drawn from the
SNLI but the test from the MultiNLI, vice versa and
other similar combinations. The results shows an av-
erage drop of 24.9 points in accuracy for all systems,
including the system by Kim et al. (2018). Results as
reported by Talman and Chatzikyriakidis (2018), are
shown in figure (2). The second question is directly
relevant to the first one. What have these state-of-
the-art models learned? It is obvious that they have
learned something. However, whatever this is, does
not seem to be generalizing well outside one specific
dataset. One plausible explanation is that the system
has learned the very specific patterns of reasoning of
specific datasets and not a generalized notion of infer-
ence per se. Will, then, a system trained on SNLI or
MultiNLI be able to deal with more specialized cases
of reasoning, like legal reasoning or any other kind
of expert reasoning or reasoning in dialogue settings?
The answer is most probably negative. As a hint to
why this is so, consider the following example from
SNLI:
(5) An example from SNLI
Premise: A man selling donuts to a customer
during a world exhibition event held in the city
of Angeles.
Hypothesis: A woman drinks her coffee in a
small cafe.
Label: Contradiction
The above example is labeled as a contradiction. But,
there are a number of non-trivial steps to make in or-
der to get to that conclusion: a) one has to assume that
the two situations described are basically the same sit-
uation and in this sense try to see whether one descrip-
tion contradicts the other, b) the indefinite article in
the premise has to be identified with the indefinite ar-
ticle in the hypothesis, thus man contradicting woman
(a person cannot be a man and a woman at the same
time). Such loose reasoning will not hold in cases
where more precise reasoning might be needed, e.g.
in legal contexts, where indefinites are generally un-
derstood as existential quantification. Thus, training
systems using datasets with such a definition of en-
tailment will most probably not be able to cope with
more other cases of reasoning. To an extent, evidence
of this exists in Talman and Chatzikyriakidis (2018),
where training on SNLI or MultiNLI and testing on
the SICK dataset, the latter involving a more strict
definition of inference than the previous two datasets,
gives a drop in accuracy between 19 and 33.6 points.
To put these results into context, we move from sys-
tems that can be thought of as being useful in deal-
ing with NLI, given that their accuracy is between
0.73 and 0.89, depending on the model and dataset, to
systems that are not useful anymore, given that their
accuracies are getting much closer to chance (.48 to
.55 accuracy). Given these results and, furthermore,
the idiosyncrasies of dialogue data and reasoning with
those, it is safe to assume that state-of-the-art systems
trained on SNLI or MultiNLI will not be able to gen-
eralize over reasoning with pieces of dialogue. On
a more general note, and abstracting away from the
individual datasets, it seems that what these systems
of inference are learning, is a tiny fraction of what
counts as human reasoning. And even in these cases,
i.e. where a tiny fraction of NLI is taken to be NLI,
generalization outside the specific datasets does not
seem to happen.
3.1 Symbolic Systems for NLI: A Lost
Cause?
Symbolic systems for NLI have been criticized as a
means to deal with NLI, and NLP tasks in general,
on the basis of coverage, i.e. the fact that these sys-
tems tend to easily break down once they are moved
to open domains. This, as a general criticism, is of
course to a great extent legit. It is true that sym-
bolic/logical systems can be very precise, but have
very poor recall, i.e. they break easily in the presence
of new data. On the other hand, NN models have of-
fered a hopeful way out of these problems, producing
impressive results in all areas of NLP and most specif-
ically, as already mentioned, in dealing with NLI. At
first sight, these systems do not seem to be suffering
from the brittleness problem just described for sym-
bolic/logical approaches. This is to some extent cor-
rect, but not all the way though. For example, in
the case of NLI, recent studies we have mentioned
in section 2 show that state-of-the-art NLI systems
are rather brittle as well, but brittle in another sense:
they fail to generalize outside individual datasets and
are, furthermore, unable to capture certain NLI pat-
terns, at all. This is a very different kind of brittle-
ness, different to the one found with symbolic/logical
approaches to NLI. For example, it would be highly
unlikely that a symbolic system would break down
NLPinAI 2019 - Special Session on Natural Language Processing in Artificial Intelligence
924

by creating a variation of a test dataset in the sense
of Glockner et al. (2018), a dataset that managed to
break a number of state-of-the-art NN NLI systems.
On the other hand, building a logical system that is
able to parse, in a reasonable way, a huge dataset
like SNLI or MultiNLI, and produce reasonable log-
ical forms is far from trivial. But on the assumption
that this is somehow achieved, such a system will not
be prone to the type of breaking shown by Glockner
et al. (2018). At the same time, going to cases where
a stricter definition of inference is assumed, e.g. log-
ical inference, it is not clear that NN models will be
able to stand up to the task. The difficulty here is that
NN models should be able to somehow closely ap-
proximate or even worse model logics of some sort.
And even though such research exists in the litera-
ture, i.e. using NNs to learn logical inference, the re-
sults are not conclusive. For example, Bowman et al.
(2014) claim that DL systems can learn logic. They
train their system on a task that involves pairs of sim-
ple sentences that have a logical relation to each other
(for example, one simple pair could be “all reptiles
walk” and “all turtles move”). Two recursive neural
networks compute representations for the sentences.
Then, these representations are fed into a simple feed-
forward network that predicts the logical relation be-
tween the sentences. Veldhoen and Zuidema (2018)
show, however, that such a claim is rather strong. NNs
seem to learn local approximations rather than global
solutions, which would be required to learn logical
reasoning. Similar results are reported by Evans et al.
(2018). It is an open question on whether NN mod-
els can actually, at this stage, deal with more strict,
fine-grained cases of inference. Another issue that
makes this task even more difficult are the datasets
that would train NN models for this stricter inference.
Given our discussion so far, it is fairly obvious that
constructing such an expert dataset will have to rely,
at least to a large extent, on expert judgments.
One should also realize that the standard NN mod-
els are limited already at the syntactic level. Indeed,
for the relative simple task of matching agreement,
several authors have found less than ideal accuracy
(Linzen et al., 2016; Bernardy and Lappin, 2018).
Bernardy (2018) also found significant drops in accu-
racy when generalizing to more than two extra nesting
levels, even in the simplest case of a language com-
prised solely of parentheses.
State-of-the-art NN NLI models find limitations
in the semantic level too, as the work of Lake and
Baroni (2017) shows. They even fail to general-
ize between similar data sets. Indeed, Talman and
Chatzikyriakidis (2018) show this when the training
set is changed between datasets especially tailored for
NN NLI models. The most striking cases are those
where the systems are trained on SNLI and tested on
MultiNLI and vice versa, given that these two datasets
involve the same definition of inference (only differ-
ence is that MultiNLI is multi genre
8
). This is a more
complicated problem. Even if a logical model that
can deal with large datasets involving logical reason-
ing is constructed, it is not the case that it will be able
to move to another dataset, where a different defini-
tion for inference is assumed. Asking a logical sys-
tem to perform loose inference, as it is done in SNLI
and MultiNLI, is probably too much to ask from the
logic and even though some tweaking can be made
to recover the hidden assumptions by injecting lexi-
cal knowledge, for datasets like SNLI, this seems to
be a hopeless task. So, how is NLI to be handled?
One way to think about the problem is to revisit ear-
lier approaches to NLI, i.e. logical or vanilla ML ap-
proaches, and understand what individual approaches
do well and what they do not. Given that we are deal-
ing with a phenomenon that looks more like a toolbox
to perform diverse reasoning tasks, rather than a sin-
gle coherent reasoning system, looking at hybrid sys-
tems for NLI might be the optimal way to tackle the
problem more efficiently.
4 TOWARDS MORE REALISTIC
NLI DATASETS
What is a realistic collection of datasets for NLI?
Based on the hypothesis that NLI is a much more
complex phenomenon than NLP practitioners usually
take it to be, one has to strike a balance between the
diversity of reasoning tools found in actual human
reasoning with NL and strive to successfully encode
those in datasets that can be later used for training
NLI systems. To be more precise, we attempt a cate-
gorization of types of reasoning based on five charac-
teristics, shown below:
(6) Types of Reasoning involved in NLI
Types of Reasoning
Situational Non Situational
Precise Loose
Open Genre Genre Specific
External Knowledge-
based
Self-contained
Dialogue Non-Dialogue
8
Note that multi genredness cannot explain why the sys-
tems fail, at least not completely. If this was the case, we
would expect that the systems would fail one way, i.e. when
trained on SNLI (single genre) and tested on MultiNLI
(multi genre). This is however not the case as seen from
the examples in figure 2.
What Kind of Natural Language Inference are NLP Systems Learning: Is this Enough?
925
These different type of reasoning translate to different
features of datasets. Similarly, different systems are
better in some of these types of reasoning, and worse
in others. For example, let us take a state-of-the-art
system like Google’s BERT. What kind of reasoning
has this system learned? BERT is evaluated against
a number of datasets. The ones that are clearly NLI
datasets though are MultiNLI and RTE. BERT does
great on MultiNLI (state-of-the-art results, .867) and
less good on RTE (0.701). Based on this data, the
picture for BERT, as well as similar NN models is as
follows:
9
(7) State-of-the-art NN NLI models
NN NLI models
Situational X Non Situational
Precise Loose X
Open text X Controlled text X
External Knowledge-
based
Self-contained X
Dialogue Non Dialogue X
What are systems based on logic doing? For exam-
ple, let us take the recent system of Bernardy and
Chatzikyriakidis (2017). This is a logical system,
which achieves an accuracy of .83 on approximately
half of the FraCaS test suite. What FraCaS is cap-
turing, and what this system, as well as and similar
systems based on logic are capturing is shown below:
(8) State-of-the-art Logical models of NLI
State-of-the-art Logical Models
Situational Non Situational X
Precise X Loose
Open text Controlled text X
External Knowledge-
based
Self-contained X
Dialogue Non Dialogue X
The two different systems are complementary with re-
spect to the first three points. However, the question
is whether some of these are artifacts of the fact that
these systems are evaluated on different datasets. This
is correct to some extent. For example, SNLI only
has situational reasoning, while the FraCaS non sit-
uational. But you could imagine extensions of both
datasets to include the other options as well. This is
9
MultiNLI involves dialogue data, but reasoning in these
cases is not contingent on the intricacies of dialogue, so at
least with respect to reasoning, there is no dialogue aspect.
Furthermore, NN systems seem to be tackling some world
knowledge based reasoning, but this is not what they do
very well, so we are reluctant to assume that they are good
at this type of reasoning.
actually the case with MultiNLI, the multi-genre ex-
tension of SNLI, where reasoning there is non situa-
tional. The second aspect, involving precise and loose
reasoning, is more difficult. Datasets actually differ in
their definition of NLI and whether it should be pre-
cise or not. SNLI follows the latter, FraCaS the for-
mer. The problem is that systems capturing one of the
two, will most probably not be able to accommodate
the other. The third aspect relates to inherent difficul-
ties of logical systems and the fact that logical sys-
tems are very brittle, namely they fail on open text.
NN models fare much better in this respect.
10
Both
approaches have difficulties for knowledge based rea-
soning. None of the two can capture aspects of rea-
soning with dialogue in NLI. Actually, at the moment,
no dataset capturing this sort of reasoning in dialogue
exists, so any kind of comparison is not possible. This
also brings up the need for the construction of such
dataset(s).
Having as a starting point this rough break down
of NLI into individual aspects that can take two val-
ues, we argue that general-purpose datasets for NLI
should involve (at least) all these options:
(9) Reasoning cases to be captured by an NLI dataset
Types of Reasoning for better NLI datasets
Situational X Non Situational X
Precise X Loose X
Open Text X Controlled Text X
External Knowledge-
based X
Self-contained X
Dialogue X Non Dialogue X
Conversely, when proposing a new dataset to test NLI
systems, one should attempt to categorize it according
to the above (or be even more precise).
In order to achieve the goal of a full-coverage
dataset, we believe that one has to use a combination
of techniques for data collection and validation, rather
than a single method:
• Expert judgments
• Crowdsourcing using crowdsourcing platforms
like MT or Crowdflower
• Crowdsourcing using Games with a Purpose
(GWAPs)
The aspects situational/non situational and open
text/controlled text are not very difficult to achieve.
Datasets like SNLI involve situational reasoning,
while MultiNLI, which can be seen as the multi genre
extension of SNLI includes non situational reasoning.
They can be both seen as Open text. It is not very hard
10
But can be claimed to be brittle in another sense, as we
have argued in the previous section.
NLPinAI 2019 - Special Session on Natural Language Processing in Artificial Intelligence
926

to assume data collection combining the two, thus the
end result involving both situational and non situa-
tional reasoning.
11
Crowdsourcing platforms like MT
or Crowdflower might be enough in this case.
The criteria of precise/loose and external
knowledge-based/self-contained are trickier. First
of all, it seems that expert judgments will be
necessary when designing datasets for more fine-
grained/precise reasoning. For example, imagine that
you want to train a system to deal with legal text, so
that given a set of legal premises and a conclusion, it
can decide whether the latter follows from the former
or not. Obviously, the dataset used for this purpose
has to be constructed by specialists that know how
to reason within this specialized domain. This might
be a costly task compared to the use of cheap labor
via platforms like Mechanical Turk (MT), but if we
are to get any real sense of the complexity and the
domain specificity of NLI, such tasks need to be
performed and at least to some extent, experts have to
be used. Furthermore, and connected to the external
knowledge-based/self-contained aspect, even every
day reasoning can get more fine-grained depending
on how much time the agent is willing to spend in
thinking about the inference patterns. For example,
look at the following example from RTE3:
(10) RTE3, Problem Number 343
Premise: November 9, 1989, the day the
Berlin Wall fell and the world changed for-
ever. Not even the most astute saw it coming.
As Hungary’s foreign minister in the late sum-
mer of 1989, Gyula Horn gave the order to let
visiting East Germans use his country to do
a 400-mile end run around the Berlin Wall, a
move now seen as the beginning of the end for
hard-line communism in Europe.
Hypothesis: The Berlin Wall was torn down
in 1989.
Label: YES
The problem here is whether the reasoner thinks that
fell can be coerced into implying tear down. Asking 3
expert linguists and one logician to label the example
indeed brought the issue up: two of them labeled it
as Yes, If fell implies tear down and one marked it as
No, because fell does not imply tear down. Here is
another example from Bernardy and Chatzikyriakidis
(2018) that is quite representative of the situation:
11
Actually, it is not very uncommon to train NLI systems
on both SNLI and MultiNLI at the same time. This pretty
much has the effect described.
(11)
P: Philip Morris the US food and tobacco group
that makes Marlboro, the world’s best-selling
cigarette, shrugged off strong anti-smoking sen-
timent in the US.
H: Philip Morris owns the Marlboro brand.
A1: Yes, if making involves owning the brand
A2: Yes, if making something implies owning the
brand
A3: Yes, if a company making a product, owns
the brand of the product
A4: No, because making the product does not im-
ply owning the brand
These examples show that it is very hard to know what
kind of background hidden premises count as more
or less safe to assume and which ones are not. Not
only different people will have different opinions, but,
also, the same people will have different opinions if
you ask them to think more carefully about example
pairs. One way to deal with this problem is to collect
the same external knowledge premises and then count
instances in which they have been used as support-
ing the inference, and instances where the same ones
are used not supporting the inference. For example,
in (11), the premise making the product implies own-
ing the brand is used to justify an entailment by three
annotators, whereas its negation, making the product
does not imply owning the brand, is used by one an-
notator to justify a non-entailment. Having large scale
expert annotation, where at least four expert anno-
tators are involved, can give us a way to construct
knowledge based NLI examples by counting the times
implicit premises are used to justify an entailment,
counting the times the same implicit premises are
used to justify a non-entailment, and then checking
whether the first number is more than half: if it is, then
the example is included as an entailment case along
with its backgrounded world knowledge premise. It is
obvious that using MT, at least in the way it has been
used so far for NLI data collection, will not provide
us with this level of precision
12
So, large scale expert
annotation would be necessary for more fine-grained
or external knowledge-based NLI cases. The current
NLI datasets do not reflect this more fine-grained as-
pect of reasoning.
The last aspect, dialogue/non dialogue, is not cov-
ered at all in NLI datasets. The datasets we have
so far are constructed on the basis of complete sen-
12
Or to put it somewhat more mildly: it will be dif-
ficult to set the task in a way that will capture the fine-
grainedness level intended. Other online crowdsourcing
tools, like semant-o-matic as designed by Dobnik and used
for NLI by Chatzikyriakidis et al. (2017a)) seem to be better
fit for such a task.
What Kind of Natural Language Inference are NLP Systems Learning: Is this Enough?
927

tences/pieces of text pairs. However, language is
rarely that clean cut in everyday linguistic interac-
tion. For example, in conversation, quite often, we
do not speak in complete sentences. What one thinks
as “complete sentences” usually emerge through a se-
quence of subsentential contributions. Each interlocu-
tor potentially adds more structure to an already par-
tial one during turn-taking:
(12) A dialogue example
A. Mont Blanc is higher than
B. Mt. Ararat?
A. Yes.
B. No, this is not correct. It is the other way
around.
A. Are you...
B. Sure? Yes, I am.
A. Ok, then.
Despite the fragmentary nature of dialogue, humans
are able to perform reasoning tasks at each stage of
the interaction and update these inferences if needed
when more information comes in. As far as we know,
there is no entailment dataset for dialogue data, and
thus no dataset that will include reasoning with this
type of data. Given that dialogue data is a core part
of NL, this is something that NLP researchers need
to start thinking about at some point. The question
remains: how is this to be done? One way to do it,
at least as a starting point, is to build such datasets
via extracting dialogue pieces from corpora like the
British National Corpus (BNC) or the newest dia-
logue datasets, most prominently bAbI (Bordes et al.,
2016) and bAbI+ (Shalyminov et al., 2017), use the
pieces as premises and then construct the hypothe-
sis based on those. Given the nature of the task, is-
sues like participants’ individual beliefs will come
into play. For example, here are a number of hypothe-
ses constructed out of the previous artificial dialogue
piece (12):
(13) A formed hypothesis against a fragment of the
dialogue piece
Hypothesis: A and B believe that Mt. Ararat
is higher than Mont Blanc
Label: Entailment
However, note that in case the dialogue piece we use
as a premise is a fragment of the original one, as
shown below, then the entailment does not hold:
(14) Formed hypothesis against the full dialogue
piece
Premise:
A. Mont Blanc is higher than
B. Mt. Ararat?
A. Yes.
B. No, this is not correct. It is the other way
around.
Hypothesis: A and B believe that Mt. Ararat
is higher than Mont Blanc.
Label: Non-entailment
To give a real example, consider the following exam-
ple constructed using a dialogue piece from bAbI+,
an extension of the bAbI dataset, as premise. The lat-
ter contains goal-oriented dialogues in the domain of
restaurant search, and the former expands a subpart
of bAbI, everyday incremental dialogue phenomena
(e.g. hesitations, restarts, and corrections):
(15) An NLI example based on a bAbI+ example
Premise:
sys hello what can I help you with today?
usr Id like to book a uhm yeah Id like to book
a table in a expensive price range
sys Im on it. Any preference on a type of cui-
sine
usr with indian food no sorry with spanish
food please
Hypothesis: The user wants to eat Spanish
food.
Label: Entailment.
4.1 Using Serious Games to
Complement NLI Data Collection
Serious Games or Games With a Purpose (hereafter
GWAP) have been used successfully in collecting lin-
guistic data. A prominent example is the GWAP
JeuxDeMots (JDM, Lafourcade et al. (2015). JDM
is a two-player GWAP, where participants earn and
collect words. The main mechanism to achieve this,
is the provision of lexical and semantic associations
to terms that the system. proposes. The intended
reader is directed to Lafourcade and Joubert (2008);
Chatzikyriakidis et al. (2017b) for more information.
JDM has grown up to include more than 1M terms and
more than 230M lexical relations. The system is very
NLPinAI 2019 - Special Session on Natural Language Processing in Artificial Intelligence
928

Figure 3: Screenshot of an ongoing game with the target
noun fromage (cheese). Several suggestions have been pro-
posed by the user. These are listed on the right hand side.
fine-grained: it is based on 100 pre-defined relation
types.
Using GWAPs might be a solution in order to deal,
at least to some extent, with the problems outlined.
For example, one could envision a GWAP where play-
ers, similarly to proposing lexical relations, are given
a (premise,hypothesis) pair instead and are asked to
provide all the hidden assumptions used in order for
the pair to be labelled as an entailment. In the case of
dialogue data, one can construct a collaborative game
where the players are asked to provide continuations
for fragments of dialogue. Once a database of dia-
logue pieces is constructed, another part of the game
might involve the task of providing inferences based
on the pieces of dialogue just constructed. Of course,
creating such a game is not straightforward, since in
order to be successful, a number of parameters have
to be taken into consideration. As Alain Joubert and
Brun (2018) point out, GWAPs have to:
1. be attractive, fun and interesting.
2. be easy to understand with a simple set of instruc-
tions.
3. be addictive
4. allow filtering of players. This translates to mak-
ing the players feel important when playing and
guilty in case they are not playing for some time.
Serious games can also be used as a means to validate
existing datasets. For example, one way to validate
entailment pairs is to model the task-taking ideas from
the construction of JDM and its “satellite games”.
Satellite games are a number of GWAPs peripheral to
JDM that eventually, besides collecting data on their
right, also feed information and help further develop
JDM. For example, in LikeIt
13
, the players are given
a term and are asked to describe their sentiments to-
wards it (positive, neutral, negative) and in AskIt
14
,
13
http://www.jeuxdemots.org/likeit.php
14
http://www.jeuxdemots.org/askit.php?pass=1
players are given two terms along with a question
about a potential relation between the two and are
asked to mark whether this relation exists, does not
exist or maybe exists (YES, NO, POSSIBLY). What
is important, is that there seems to be a lot of knowl-
edge and experience in the field for how to build sys-
tems that will successfully produce good quality data
for a given task. It remains to be shown in practice by
creating a GWAP that will collect NLI data.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we investigated the type of inference
state-of-the-art NLI systems are learning. Firstly, it
has been argued that current datasets for NLI are far
from reflecting the complexity of NLI and some clear
examples exemplifying why this is so were presented.
Then, we have claimed that a result of this situation is
that state-of-the-art systems will not be able to gen-
eralize across different NLI cases, where a slightly
different definition of inference is involved. This is
partially borne out by the experimental results of Tal-
man and Chatzikyriakidis (2018). Furthermore, and
even worse, state-of-the-art NLI models do not seem
to be able to generalize outside specific datasets, even
when the same definition of NLI is assumed. We then
presented some ideas of how one can build more real-
istic NLI datasets that can be used to better reflect NLI
and potentially help in developing better NLI models.
Lastly, we have discussed the use of symbolic/logical
approaches to NLI and argued that the NLP commu-
nity has been probably too hasty in dismissing them
as a candidate solution for NLI.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors are supported by grant 2014-39 from
the Swedish Research Council, which funds the Cen-
tre for Linguistic Theory and Studies in Probability
(CLASP).
REFERENCES
Alain Joubert, M. L. and Brun, N. L. (2018). The jeuxde-
mots project is 10 years old: what assessments? In
Chamberlain, J., Kruschwitz, U., Fort, K., and Cieri,
C., editors, Proceedings of the Eleventh International
Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation
(LREC 2018), Paris, France. European Language Re-
sources Association (ELRA).
Bernardy, J.-P. (2018). Can rnns learn nested recursion?
Linguistic Issues in Language Technology, 16.
What Kind of Natural Language Inference are NLP Systems Learning: Is this Enough?
929

Bernardy, J.-P. and Chatzikyriakidis, S. (2017). A type-
theoretical system for the fracas test suite: Grammati-
cal framework meets coq. In IWCS 2017-12th Interna-
tional Conference on Computational Semantics-Long
papers.
Bernardy, J.-P. and Chatzikyriakidis, S. (2018). A cor-
pus of precise natural textual entailment problems.
https://arxiv.org/abs/1812.05813.
Bernardy, J.-P. and Lappin, S. (2018). The influence of con-
text on sentence acceptability judgements.
Bordes, A., Boureau, Y.-L., and Weston, J. (2016). Learn-
ing end-to-end goal-oriented dialog. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1605.07683.
Bowman, S. R., Angeli, G., Potts, C., and Manning, C. D.
(2015). A large annotated corpus for learning natural
language inference. arXiv preprint arXiv:1508.05326.
Bowman, S. R., Potts, C., and Manning, C. D. (2014). Re-
cursive neural networks can learn logical semantics.
arXiv preprint arXiv:1406.1827.
Cer, D., Diab, M., Agirre, E., Lopez-Gazpio, I., and Spe-
cia, L. (2017). Semeval-2017 task 1: Semantic tex-
tual similarity-multilingual and cross-lingual focused
evaluation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1708.00055.
Chatzikyriakidis, S., Cooper, R., Dobnik, S., and Larsson,
S. (2017a). An overview of natural language inference
data collection: The way forward? In Proceedings
of the Computing Natural Language Inference Work-
shop.
Chatzikyriakidis, S., Lafourcade, M., Ramadier, L., and
Zarrouk, M. (2017b). Type theories and lexical net-
works: Using serious games as the basis for multi-
sorted typed systems. Journal of Language Modelling,
5(2):229–272.
Chen, Q., Zhu, X., Ling, Z., Inkpen, D., and Wei, S.
(2017a). Natural language inference with external
knowledge. CoRR, abs/1711.04289.
Chen, Q., Zhu, X., Ling, Z.-H., Wei, S., Jiang, H., and
Inkpen, D. (2017b). Enhanced lstm for natural lan-
guage inference. In Proceedings of the 55th Annual
Meeting of the Association for Computational Lin-
guistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), pages 1657–1668.
Association for Computational Linguistics.
Chen, Z., Zhang, H., Zhang, X., and Zhao, L. Quora ques-
tion pairs.
Conneau, A., Rinott, R., Lample, G., Williams, A., Bow-
man, S. R., Schwenk, H., and Stoyanov, V. (2018).
Xnli: Evaluating cross-lingual sentence representa-
tions. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Em-
pirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. As-
sociation for Computational Linguistics.
Cooper, R., Crouch, D., Van Eijck, J., Fox, C., Van Gen-
abith, J., Jaspars, J., Kamp, H., Milward, D., Pinkal,
M., Poesio, M., et al. (1996). Using the framework.
Technical report.
Devlin, J., Chang, M.-W., Lee, K., and Toutanova, K.
(2018). Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional trans-
formers for language understanding. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1810.04805.
Evans, R., Saxton, D., Amos, D., Kohli, P., and Grefen-
stette, E. (2018). Can neural networks understand log-
ical entailment? arXiv preprint arXiv:1802.08535.
Ganitkevitch, E., Pavlick, P., Rastogi, J., Van Durme, B.,
and Callison-Burch, C. (2015). PPDB 2.0: Better
paraphrase ranking, fine-grained entailment relations,
word embeddings, and style classification. In Pro-
ceedings of the 53rd Annual Meeting of the Associ-
ation for Computational Linguistics and the 7th In-
ternational Joint Conference on Natural Language
Processing (Short Papers), pages 425–430, Beijing,
China. Association for Computational Linguistics.
Glockner, M., Shwartz, V., and Goldberg, Y. (2018). Break-
ing nli systems with sentences that require simple lex-
ical inferences. arXiv preprint arXiv:1805.02266.
Gururangan, S., Swayamdipta, S., Levy, O., Schwartz, R.,
Bowman, S. R., and Smith, N. A. (2018). Annota-
tion artifacts in natural language inference data. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1803.02324.
Huang, G. and Liu, Z. (2017). Densely connected convolu-
tional networks.
Jurczyk, T., Zhai, M., and Choi, J. D. (2016). Selqa: A
new benchmark for selection-based question answer-
ing. In Tools with Artificial Intelligence (ICTAI), 2016
IEEE 28th International Conference on, pages 820–
827. IEEE.
Kim, S., Hong, J.-H., Kang, I., and Kwak, N. (2018). Se-
mantic sentence matching with densely-connected re-
current and co-attentive information. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1805.11360.
Lafourcade, M. and Joubert, A. (2008). Jeuxdemots: un
prototype ludique pour l’
´
emergence de relations en-
tre termes. In JADT’08: Journ
´
ees internationales
d’Analyse statistiques des Donn
´
ees Textuelles, pages
657–666.
Lafourcade, M., Joubert, A., and Le Brun, N. (2015).
Games with a Purpose (GWAPS). John Wiley & Sons.
Lake, B. M. and Baroni, M. (2017). Still not system-
atic after all these years: On the compositional skills
of sequence-to-sequence recurrent networks. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1711.00350.
Linzen, T., Dupoux, E., and Golberg, Y. (2016). Assessing
the ability of LSTMs to learn syntax-sensitive depen-
dencies. Transactions of the Association of Computa-
tional Linguistics, 4:521–535.
Marelli, M., Menini, S., Baroni, M., Bentivogli, L.,
Bernardi, R., and Zamparelli, R. (2014). A SICK cure
for the evaluation of compositional distributional se-
mantic models. In LREC, pages 216–223.
Miller, G. A. (1995). Wordnet: a lexical database for en-
glish. Communications of the ACM, 38(11):39–41.
Shalyminov, I., Eshghi, A., and Lemon, O. (2017). Chal-
lenging neural dialogue models with natural data:
Memory networks fail on incremental phenomena.
arXiv preprint arXiv:1709.07840.
Talman, A. and Chatzikyriakidis, S. (2018). Testing the
generalization power of neural network models across
nli benchmarks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.09774.
Talman, A., Yli-Jyr
¨
a, A., and Tiedemann, J. (2018). Natural
language inference with hierarchical bilstm max pool-
ing architecture. arXiv preprint arXiv:1808.08762.
Tay, Y., Tuan, L. A., and Hui, S. C. (2017). A
compare-propagate architecture with alignment fac-
NLPinAI 2019 - Special Session on Natural Language Processing in Artificial Intelligence
930

torization for natural language inference. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1801.00102.
Veldhoen, S. and Zuidema, W. (2018). Can neural networks
learn logical reasoning? In Proceedings of the Con-
ference on Logic and Machine Learning in Natural
Language.
Wang, Z., Hamza, W., and Florian, R. (2017). Bilateral
multi-perspective matching for natural language sen-
tences. arXiv preprint arXiv:1702.03814.
Williams, A., Nangia, N., and Bowman, S. R. (2017).
A broad-coverage challenge corpus for sentence
understanding through inference. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1704.05426.
Young, P., Lai, A., Hodosh, M., and Hockenmaier, J.
(2014). From image descriptions to visual denota-
tions: New similarity metrics for semantic inference
over event descriptions. Transactions of the Associa-
tion for Computational Linguistics, 2:67–78.
Zaenen, A., Karttunen, L., and Crouch, R. (2005). Lo-
cal textual inference: can it be defined or circum-
scribed? In Proceedings of the ACL workshop on
empirical modeling of semantic equivalence and en-
tailment, pages 31–36. Association for Computational
Linguistics.
What Kind of Natural Language Inference are NLP Systems Learning: Is this Enough?
931
