
A Comparative Study between Possibilistic and Probabilistic
Approaches for Query Translation Disambiguation
Wiem Ben Romdhane
1
, Bilel Elayeb
1,2
and Narjès Bellamine Ben Saoud
1
1
RIADI Research Laboratory, ENSI, Manouba University, Tunisia
2
Emirates College of Technology, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates
Keywords: Cross-Language Information Retrieval (CLIR), Query Translation, Translation Disambiguation, Probabilistic
Model, Possibilistic Model, Relevance.
Abstract: We propose in this paper a new hybrid possibilistic query translation disambiguation approach combining a
probability-to-possibility transformation-based approach with a discriminative possibilistic one in order to
take advantage of their strengths. The disambiguation process in this approach requires a bilingual lexicon
and a parallel text corpus. Given a source query terms, the first step consists of selecting the existing noun
phrases (NPs) and the remaining single terms which are not included in any NPs. We have translated these
identified NPs as units through the probability-to-possibility transformation-based approach, as a mean to
introduce further tolerance, using a language model and translation patterns. Then, the remaining single source
query terms are translated via the discriminative possibilistic approach. We have modelled in this step the
translation relevance of a given single source query term via two measures: the possible relevance excludes
irrelevant translations, while the necessary relevance reinforces the translations not removed by the
possibility. We have developed a set of experiments using the CLEF-2003 French-English CLIR test
collection and the French-English parallel text corpus Europarl. The reported results highlight some
statistically significant improvements of the hybrid possibilistic approach in the CLIR effectiveness using
diverse evaluation metrics and scenarios for both long and short queries.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, the Internet user requires high-
performance cross-language information retrieval
(CLIR) tools in order to benefit from the huge number
of online non-English documents. The CLIR research
field is mainly focused on query translation (QT)
techniques rather than document translation (DT).
The former is more popular, while the latter is a hard
task because it is time consuming and
computationally expensive (
Zhou et al., 2012). For
example, the availability of machine readable
bilingual lexicons for many languages mainly
supports research efforts in the dictionary-based QT
techniques. However, these approaches are still
suffering from many weaknesses such as: (i) the
challenge of the lexicon coverage since the existing
bilingual dictionaries are still missing several
translations corresponding to new terminologies; and
(ii) the problem of translation disambiguation which
become more and more frequent. To do this, the user
is asked to select the best translation corresponding to
each ambiguous source query term between all
possible translations existing in the lexicon. In fact,
the coverage of some existing lexicons has been
enlarged due to many research efforts (
Zhou et al.,
2012) aiming at collecting automatically or
manually larger lexical resources. Moreover, CLIR
efficiency is mainly sensitive to the translation
ambiguity. To overcome this challenge, a phrase
dictionary has been used in order to select possible
noun phrases from a given source query, and then
translate them as units.
Analogically to the information retrieval task, the
process of QT disambiguation in CLIR requires a
matching model useful to compute a score of
similarity (relevance) between source query
terms/phrases and their possible translations.
However, most of the existing QT techniques in the
literature are based on poor, uncertain and imprecise
data, whereas possibility theory is naturally suitable
for this kind of applications. In fact, it makes it
possible to express ignorance and it takes into account
the imprecision and uncertainty at the same time
932
Ben Romdhane, W., Elayeb, B. and Ben Saoud, N.
A Comparative Study between Possibilistic and Probabilistic Approaches for Query Translation Disambiguation.
DOI: 10.5220/0007697209320943
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2019), pages 932-943
ISBN: 978-989-758-350-6
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

(Dubois and Prade, 1994). Nonetheless, the
translation disambiguation process is based on the
context of source query terms which can be also
ambiguous. Thus, we have considered this case as a
phenomenon of imprecision. For these reasons, we
believe that possibility theory is the best application
to this type of imperfection, while probability theory
is not appropriate to deal with such kind of data.
Consequently, and given that the possibility theory is
the best framework suitable for imprecision
treatment, we have benefited from possibility
distributions in order to overcome the challenge of
translation ambiguity in CLIR task. To the best of our
knowledge, there are some research contributions in
the literature that have taken advantage of the
possibility theory in QT disambiguation such as: (Ben
Romdhane et al., 2017; Ben Khiroun et al., 2018;
Elayeb et al., 2018).
Our goal in this paper is to tackle the problem of
QT disambiguation by overcoming some challenges
of the existing dictionary-based techniques. We
propose, assess and compare in this paper a new
hybrid possibilistic QT disambiguation approach
using both a bilingual dictionary and a parallel text
corpus. In fact, additional terms and their translations
are automatically generated from a parallel bilingual
corpus in order to increase the coverage of the
bilingual lexicon. This approach combines the
probability-to-possibility transformation-based
approach (cf. Section 3.1) with the discriminative
possibilistic one (cf. Section 3.2). Indeed, the former
is promising in the translation of noun phrases (NPs),
while the latter is efficient in the translation of the
remaining single terms. Given a set of source query
terms, the first step consists of selecting noun phrases
(NPs) and translating them as units using translation
patterns and a language model. In this step, we have
benefited from the probability-to-possibility
transformation-based approach as a mean to
introduce further tolerance in the process of NP
translation. In the second step, we focus on the
translation of remaining single source query terms,
which are not included in any selected NPs. We have
benefited from the discriminative possibilistic
approach which models the translation relevance of a
given single source query term via two measures: the
possible relevance allows rejecting irrelevant
translations, while the necessary relevance makes it
possible to reinforce the translations not removed by
the possibility. Moreover, the best translation of every
single source query term or NP has a tendency to co-
occur in the target language documents unlike
unsuitable ones. We have performed our experiments
via the CLEF-2003 French-English CLIR test
collection and the French-English parallel text corpus
Europarl. The hybrid approach has achieved some
statistically significant improvements in CLIR
performance if compared to the probability-to-
possibility transformation-based approach (Elayeb et
al., 2018), to the discriminative possibilistic approach
(Ben Romdhane et al., 2017) and to the known
efficient probabilistic one (Gao et al., 2001), for both
short and long queries and using different assessment
metrics and scenarios.
This paper is structured as follows. Section 2 is
devoted to an overview of possibility theory. The new
hybrid possibilistic QT approach is described in
Section 3. Section 4 details our experimentations and
discusses a comparative study between some QT
disambiguation approaches. In Section 5, we
conclude our work in this paper and we propose some
perspectives for future research.
2 POSSIBILITY THEORY
We focus in this section on the basic elements of
possibility theory: Firstly, we present in Section 2.1
the possibility and necessity measures. Secondly, the
possibilistic networks are briefly summarized in
Section 2.2. Finally, in Section 2.3, we present the
probability-to-possibility transformation. Further
details about possibility theory are discussed in
(Dubois and Prade, 1994).
2.1 Possibility and Necessity Measures
The Possibility (Π) and the Necessity (N) are known
as the two dual measures in which a possibility
distribution
π
on
Ω
enables events to be qualified in
terms of their plausibility and their certainty,
respectively (Dubois and Prade, 1994). Let us
consider a possibility distribution π on the universe of
discourse Ω, the corresponding possibility and
necessity measures of any event A
⊆
2
Ω
are
respectively defined by the Formulas (1) and (2):
)(max)( wA
Aw
π
∈
=∏
(1)
)(1))(1(min)( AwAN
Aw
∏−=−=
∉
π
(2)
The necessity N(A) evaluates at which level the event
A is certainly conditioned by our knowledge
represented by π; because it is a degree of inclusion
of the fuzzy set corresponding to π into the subset A.
Whereas,
the possibility Π(A) computes at which
A Comparative Study between Possibilistic and Probabilistic Approaches for Query Translation Disambiguation
933

level A is consistent with our knowledge represented
by π. It allows an evaluation analogous to a degree of
non-emptiness of the intersection of the fuzzy set
having π as membership function with the classical
subset A (Dubois and Prade, 1994).
2.2 Possibilistic Networks (PN)
We briefly present in the following the directed and
the product-based possibilistic networks.
2.2.1 Directed Possibilistic Networks
Given a variable set V, a directed possibilistic
network is characterized by the graphical and
numerical components (BenFerhat et al., 1999).
Indeed, the graphical component is a directed acyclic
graph (DAG). The
conditional dependency between
independent or dependent variables has been
represented via the DAG. Each node in the graph
represents a domain variable, while each link
represents a dependency between two variables. The
graph structure encodes independence relation sets
between nodes. The numerical component quantifies
the
distinct links in the graph. It represents the
conditional possibility matrix of each node given the
context of its parents. Besides, these possibility
distributions should satisfy the normalization feature.
For each variable V:
If V is not a root node, the conditional distribution of
V in the context of its parents denoted U
V
should
satisfy:
max
v
∈
Dom(V)
Π(v|u
V
) = 1; u
V
∈ Dom(U
V
)
(3)
If V is a root node and Dom(V) the domain of V, the
prior possibility of V should satisfy:
max
v
∈
Dom(V)
Π(v) = 1
(4)
Where: Dom(V): domain of V ; U
V
: value of parents
of V ; Dom(U
V
): domain of parent set of V.
We propose in this paper a new hybrid possibilistic
approach for QT disambiguation. This approach has
benefited from a possibilistic network in the
translation process of single source query terms (cf.
Section 3.2). We link in this network the possible
translations (T
i
) to the single P terms of a source query
SQ = (t
1
, t
2
,…,t
P
), which represents its context. In this
case: v
i
= t
i
; u
V
= T
i
; Dom(V) = {t
1
, t
2
,…,t
P
}; and
Dom(U
V
) = {T
1
, T
2
,…, T
N
}.
2.2.2 Product-based Possibilistic Networks
The product operator is suitable in case of
possibilistic graph associating conditional possibility
distributions. In the numerical setting, the possibility
measures represent numerical values in [0, 1].
Therefore, the product-based possibilistic graph is
generally appropriate in this case. The possibility
distribution of the product-based possibilistic
networks (
π
prod
), achieved by the associated chain
class is computed through Formula (5):
∏
=
Π=
N
i
ViNprod
i
UVVVV
1
21
)(),,,(
π
(5)
2.3 Probability-to-Possibility
Transformation
The probability-to-possibility transformations are
especially useful in case of dealing with
heterogeneous uncertain and imprecise information
(Dubois and Prade, 1985). Many probability-to-
possibility transformations are suggested in the
literature, but we have chosen the following formula
of that satisfy both the preference preservation
principles (i.e. p(ω
i
) > p(ω
j
) π(ω
i
) > π(ω
j
)) and the
probability-to-possibility consistency (i.e. Π(A) ≥
P(A)). Further detailed summary of the existing
transformations is discussed in (Yamada, 2001).
Transformation Formula:
Given a probability distribution p on the universe of
discourse Ω = {ω
1
, ω
2
,…, ω
n
} such that p(ω
1
) ≥ p(ω
2
)
≥ …≥ p(ω
n
), we can transform p into π using the
following formula (Dubois and Prade, 1985):
n1,...,i ,)p(ω)p(ωi)π(ω
n
1ij
jii
=∀+∗=
+=
(6)
Where: ; p(ω
n+1
) = 0 by convention.
Example: Let us consider the universe of discourse
Ω = {ω
1
, ω
2
, ω
3
, ω
4
} and a probability distribution p
on Ω such that:
p(ω
1
) = 0; p(ω
2
) = 0.3; p(ω
3
) = 0.6; p(ω
4
) = 0.1
In formula (6), the factor i means the order of ω
i
in
the descending order: p(ω
3
) > p(ω
2
) > p(ω
4
) > p(ω
1
).
Hence, i = 1 for ω
3
, i = 2 for ω
2
, i = 3 for ω
4
, and i
= 4 for ω
1
.
The corresponding possibility distributions are the
following: π(ω
3
) = (1*0.6) + (0.3 + 0.1) = 1; π(ω
2
) =
1)(
1
=
=
n
j
j
p
ω
NLPinAI 2019 - Special Session on Natural Language Processing in Artificial Intelligence
934

(2*0.3) + 0.1 = 0.7; π(ω
4
) = (3*0.1) + 0 = 0.3; π(ω
1
)
= (4*0) + 0 = 0.
3 THE HYBRID POSSIBILISTIC
QT DISAMBIGUATION
The hybrid possibilistic QT disambiguation approach
is a combination of the following two approaches:
Given a source query terms, we start by identifying
noun phrases (NP) and translating them as a unit
using the probability-to-possibility transformation-
based approach (cf. Section 3.1). However, remaining
single source query terms, which are not included in
any selected NPs, are translated using the
discriminative possibilistic approach (cf. Section
3.2).
3.1 The Probability-to-Possibility
Transformation-based Approach
for NP Translation
Given a French source query to be translated to an
English one, the first step consists of identifying
French noun phrases (NPs) using the Stanford Parser.
We obtain a vector of French NP, and we note FNP =
{f
1
,…,f
n
} of n observed variables F
1
,…,F
n
with its NP
pattern, FPT. Then, we have used the bilingual
dictionary to retrieve all available English
translations e
j
corresponding to each French term f
i
in
FNP. We have also used all available translations
patterns EPT for FPT. The QT disambiguation
process consists of estimating a possibility
distribution on ENP, and of identifying the best
English NP with the highest possibility for the vector
FNP in this quantitative setting:
),,,(
),,,()(
),,,(
21
21
21
n
jnj
nj
fff
efffe
fffe
π
ππ
π
∗
=
(7)
In formula (7), the quantitative component of the
possibilistic QT includes a prior possibility
distribution over the translations and a prior
possibility distribution associated with the input
variables. Besides, the factor
π
(f
1
, f
2
,…,f
n
) is a
normalization factor and it is the same over all
translations terms. In case we suppose that there is no
a priori knowledge about the input vector to translate
and its corresponding translations, we have
π
(e
j
) = 1
and
π
(f
1
, f
2
,…,f
n
) = 1. On the other hand, naïve
possibilistic QT makes an independence hypothesis
about the variables f
i
in the context of their
translations. This assumption is analogously same as
the naïve Bayesian QT (
Ben Amor et al., 2002).
Given the independence hypothesis, the plausibility
of each translation e
j
for a given French source query
terms (f
1
, f
2
,…,f
n
) is computed through formula (8):
),,,(
)()(
),,,(
21
1
21
n
n
i
jij
nj
fff
efe
fffe
π
ππ
π
∏
=
∗
=
(8)
Where the conditional possibilities
)(
ji
ef
π
denote
to which extent f
i
is a possible value for the variable
F
i
in the existence of the English translation e
j
. If we
suppose that there is no a priori knowledge about
translations, the factor
π
(e
j
) can be ignored.
Besides, the operator * (or its extension
Π
) can be
used as the min or the product operator. Indeed, the
min corresponds to complete logical independence,
while the partially possible values are made jointly
less possible due to the use of the product operator.
Using a product-based context, we assign a given
French source query term to the most plausible
English translated phrase, ENP*. Then, the best
English translated phrase, ENP* = {e
1
,…,e
m
}, is the
one that maximizes the formula (9).
(9)
Where:
π
(FNP|ENP) is the translation possibility; and
π
(ENP) is a priori possibility of words of the
translated English NP.
In fact, there is a set-theoretical meaning of
Formula (8): In case when the possibility distributions
have only the values 1 and 0, the Formula (8) means
that a source query term can have a translation in e
j
in
as much as the remaining source query terms are
compatible with this translation. Hence, possibilistic
QT may be considered as an intermediary between a
Bayesian probabilistic QT (Gao et al., 2001) and a
purely set-based QT. Given a source query term, the
possibilistic QT uses the convex hull of the data
values as a possibility distribution to identify the best
translations, mostly leading to many different
translations.
We assume an NP (FNP or ENP) as a set of words (F
or E) gathered by an NP pattern (FPT or EPT).
Supposing that the translation of terms and NP
patterns are independent, we have:
∗=
∗=
=
∏
=
n
i
jij
e
ENP
ENP
efe
ENPENPFNP
FNPENPENP
j
1
*
)()(
maxarg
))()((maxarg
))((maxarg
ππ
ππ
π
A Comparative Study between Possibilistic and Probabilistic Approaches for Query Translation Disambiguation
935

)()(
),(),(
),,()(
EPTFPTEF
EPTEFPTEPTEF
EPTEFPTFENPFNP
ππ
ππ
ππ
∗=
∗=
=
(10)
Substituting Formula (10) in Formula (9), we have:
))()()((maxarg
*
ENPEPTFPTEFENP
ENP
πππ
∗∗=
(11)
Where:
π
(F|E) is the translation possibility from
English terms E in ENP to French terms F in FNP;
and
π
(FPT|EPT) is the possibility of the translation
pattern FPT (i.e. the order of translation terms), given
the English pattern EPT. These possibilities are
determined by applying the probability-to-possibility
transformation formula to the probabilities P(F|E)
and P(FPT|EPT). On the other hand,
π
(ENP) is
calculated using the English trigram language model
as follows:
),(),...,()(
1
121
∏
=
−−
==
n
i
iiin
eeeeeENP
πππ
(12)
We note here that the NP translation process requires
the estimation of the following conditional
possibilities distributions:
π
(F|E),
π
(FPT|EPT) and
π
(e
i
|e
i-2
, e
i-1
). Firstly, we have supposed on our tests a
uniform possibility distribution on a term’s
translation in the estimation of
π
(F|E). Indeed, if an
English term e has n possible translations in the
bilingual lexicon, we assign an equal possibility
distribution, such that:
π
(f |e) = 1/n. This is due to the
lack of our parallel text corpus for its perfect
estimation. Secondly, we have used the Europarl
parallel text corpus for the estimation of
π
(FPT|EPT).
This is requires the automatic generation of the
translation patterns from this corpus before filtering
them by a linguist. Finally, we have benefited from
the probability-to-possibility transformation applied
to the conditional probability distribution P(e
i
|e
i-2
, e
i-
1
) in order to estimate the
π
(e
i
|e
i-2
, e
i-1
).
3.2 The Discriminative Possibilistic
Approach for Single Word
Translation
After the identification and the translation of all
possible NP, a given source query may include some
remaining single terms. The goal is to select the set of
best translations corresponding to the set of single
source query terms t
1
, t
2
,…, t
P
, among the set of all
possible translations T
1
, T
2
,…, T
N
. Each ambiguous
SQ term may have many possible translations in the
bilingual lexicon. We note by DPR(T
j
| SQ) the
Degree of Possibilistic Relevance of a translation T
j
given SQ. Indeed, we evaluate the relevance of a
translation T
j
given a source query SQ using a
possibilistic matching model, analogously to an
information retrieval (IR) context (Elayeb et al.,
2009). We compute, in case of IR, a possibilistic
matching score between the user query and a
document from the collection. However, in case of
QT disambiguation, we model the relevance of a
translation T
j
given SQ via a possibilistic network (cf.
Figure 1) using double measures. The First possible
relevance allows rejecting irrelevant translations,
while the second necessary relevance reinforces the
relevance of the remaining translations, which have
not been rejected by the possibility.
Figure 1: The possibilistic network of single word
translation process.
In this network, nodes are the single terms t
1
, t
2
,…, t
P
of a given source query SQ linked to their possible
translations T
1
, T
2
,…, T
N
existing in the bilingual
lexicon. The output of the QT disambiguation process
is to identify the best target query TQ = (T
1
, T
2
,…, T
P
),
including both suitable translations of the NP and of
the single terms, which will be useful to retrieve a set
of relevant documents on the target language.
Let us consider the set of single terms t
1
, t
2
,…,t
P
issued from the source query SQ, the relevance of
each translation T
j
is calculated as the following:
Analogically to the IR matching model, the
possibility Π(T
j
| SQ) is proportional to:
Π
=
∗…∗
=
∗…∗
(13)
Where: nft
ij
= tf
ij
/max(tf
kj
): the normalized frequency
of the source term t
i
in the parallel text of the
translation T
j
. But, tf
ij
is the number of occurrence of
the source term t
i
in the parallel text of the translation
T
j
divided by the number of terms in the parallel text
of the translation T
j
.
We calculate the necessity to restore a relevant
translation T
j
given the source query SQ, denoted
N(T
j
| SQ), as the following:
T
1
t
1
T
i
T
N
t
2
t
3
t
4
t
P
…….
…
NLPinAI 2019 - Special Session on Natural Language Processing in Artificial Intelligence
936

=1−Π¬
(14)
Where:
Π¬
=
Π¬
∗Π(¬
)
Π()
(15)
At the same way Π(¬T
j
| SQ) is proportional to:
Π
¬
=
¬
∗…∗
¬
(16)
This numerator can be expressed as the following:
Π
¬
=1−
∗…∗1−
(17)
Where:
=
∗(
)
(18)
Where: nCT is the number of possible translations in
the bilingual dictionary. But, nT
j
is the number of
parallel texts of the translation T
j
containing the
source term t
i
. This includes all possible translations
existing in the bilingual dictionary.
We compute the Degree of Possibilistic Relevance
(DPR) of each word translation T
j
given a source
query SQ via the following Formula (19):
=Π
+
(19)
Finally, the translations T
j
having the high scores of
DPR(T
j
| SQ) are selected as the best ones to build the
target query TQ = (T
1
, T
2
,…, T
P
).
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
AND COMPARATIVE STUDY
We present in this section the experimental results of
the hybrid possibilistic approach for QT
disambiguation. Indeed, we have conducted several
assessment scenarios and metrics by following the
TREC protocol and using the CLEF-2003 standard
CLIR test collection (54 queries and 56472
documents with 154 MB as size). In addition, we have
used also the Europarl parallel text corpus enclosing
11 language texts issued from the proceedings of the
European Parliament. For the French language, the
number of sentences is 1.023.523 and the number of
words is 32.550.260 after tokenization and sentence-
alignment with English. The 54 test queries enclose
717 French words having 2324 possible English
translations in the bilingual dictionary. We have
firstly generated our bilingual dictionary from the
Europarl parallel corpus using all French words with
their possible translations existing in this corpus in
order to enlarge our lexicon coverage. Then, we have
benefited from the online intelligent speller and
grammar checker Reverso in order to check this
dictionary. Finally, the online Google translate is also
used to enrich and check this bilingual lexicon.
We discuss in Section 4.1 a set of Recall-Precision
curves comparing the hybrid possibilistic approach to
the probabilistic approach (Gao et al., 2001), the
discriminative possibilistic approach (Ben Romdhane
et al., 2017), the probability-to-possibility
transformation-based approach (possibilistic)
(Elayeb et al., 2018) and the monolingual runs using
different scenarios of long and short queries. Indeed,
short queries are limited to the title or the description
or the narrative parts of the source queries, while long
queries involved all possible combinations of these
parts such as: (i) title & desc & narr or (ii) title & desc
or (iii) title & narr or (iv) desc & narr. Our goal here
is to investigate on the sensitivity of these QT
disambiguation approaches to the context provided
by the source query. Besides, we investigate in
Section 4.2 on the precision values at different top
documents P@5, P@10,..., P@1000. For example,
the precision in point 10, namely P@10, is the ratio
of relevant documents between the top 10 retrieved
documents. In Section 4.3, we assessed and compared
our hybrid approach using the MAP and the R-
Precision metrics. Then, we have reinforced our
evaluation using the improvement percentage in
Section 4.4. Finally, the statistical significance of the
improvement of the hybrid possibilistic approach has
been discussed in Section 4.5.
4.1 Evaluation using the
Recall-Precision Curves
Long queries using title & desc & narr provide the
full contextual information, which is suitable to
identify and translate noun phrases (NPs). If we
investigate on the Recall-Precision curves of Fig.
2(a), we remark that the hybrid possibilistic approach
is slightly under the probabilistic, the possibilistic and
the discriminative ones especially in the low-levels
points of recall (0-0.2). Besides, it outperforms the
discriminative approach starting from the point of
recall 0.2 and it is above all these approaches in the
point of recall 0.6. The hybrid approach becomes very
close to the possibilistic run in some high-levels
points of recall (0.7-1.0). It outperforms also the
monolingual run in the point of recall 0.6.
Furthermore, the gaps between the hybrid approach
and the monolingual run are increasingly reduced
starting from the point of recall 0.7.
A Comparative Study between Possibilistic and Probabilistic Approaches for Query Translation Disambiguation
937

On the other hand, and using title & desc, the
hybrid possibilistic approach mainly outperforms the
three other approaches especially in the low-levels
points of recall (0-0.3). Then, it slightly exceeds these
approaches and become very close to the monolingual
run starting from the point of recall 0.3. Besides, the
gaps between these approaches and the monolingual
run are progressively decreased starting from the
point of recall 0.6 (cf. Fig. 2(c)). When we focus on
results using title & narr, the hybrid possibilistic
approach is slightly under the three other approaches
particularly in the low-levels points of recall (0-0.1).
Then it outperforms the probabilistic and the
discriminative runs, but it is still under the
possibilistic in the low-levels points of recall (0.2-
0.3). The gaps between them have been reduced in
some high-levels points of recall (0.7-1.0) (cf. Fig.
2(b)).
Finally, long queries using desc & narr provide
large contextual information and have showed that
the hybrid possibilistic approach is slightly under the
three approaches in some low-levels points of recall
(0-0.2). It outperforms the discriminative run, but it is
still under the possibilistic and the probabilistic ones
in the points of recall between 0.2 and 0.5. In addition,
the hybrid approach outperforms all the three
approaches in some high-levels points of recall (0.6
and 0.8). It achieved also the same performance as the
monolingual run in the point of recall 0.6. The gaps
between all these approaches and the monolingual run
gradually decreases starting from the point of recall
0.7 (cf. Fig. 2(d)).
Short queries using title seem more suitable for
the discriminative approach because they provided
the minimum contextual information, in which we
can find many single terms. Thus, the discriminative
approach mainly outperformed the three other
approaches in many points of recall (from 0.2 to 0.7).
However, and starting from the point 0.6, the hybrid
approach slightly outperformed the probabilistic and
the possibilistic ones. It also achieved a very close
performance to the discriminative run in some high-
levels points of recall (0.7-1.0) (cf. Fig. 2(e)).
However, when we use the description parts of the
source queries, we have further contextual
information suitable to find and translate some NPs.
Consequently, the hybrid approach achieved a slight
outperformance of the three other approaches in some
low- (0.1-0.2) and high-levels (0.5-0.6) points of
recall. Starting from the point of recall 0.6, the gaps
between the monolingual run and the other ones are
considerably reduced especially between the points
0.9 and 1 (cf. Fig. 2(f)).
Finally, if we focus on the narrative parts of the
source queries, the context is larger and therefore
more suitable for the identification and the translation
of NPs. In this case, the hybrid approach is slightly
under both the probabilistic and the possibilistic runs
especially in some low- (0-0.2) and high-levels (0.7-
1.0) points of recall. But, it outperforms the
discriminative run in the most points of recall.
Besides, the hybrid approach seems better than all the
three other approaches in some points of recall such
as (0.2-0.3) and the point 0.6. The gaps between these
approaches are mainly reduced starting from the point
of recall 0.8 (cf. Fig. 2(g)).
Globally, the hybrid possibilistic approach based on
the identification and the translation of NP seems
more efficient using long queries having large
context. On the contrary, the discriminative
possibilistic approach has showed its efficiency in
short queries using title, where the context is more
limited to a small set of terms in which the
identification of the NP is not frequent.
4.2 Evaluation using the Precision
Values at Different Top Documents
Using long queries (cf. Fig.3), the hybrid possibilistic
QT disambiguation approach outperforms both the
probabilistic and the discriminative ones in terms of
precision values at different top returned documents,
except in some rare cases such as:
• The probabilistic is slightly better than the hybrid
in P@1000 using title & narr (cf. Fig. 3(b)).
• The discriminative outperforms the hybrid in
P@10 using title & desc & narr (cf. Fig. 3(a)), in
P@5 using title & narr or desc & narr (cf. Fig.
3(bd)).
• The probability-to-possibility transformation-
based approach (possibilistic) outperforms the
hybrid in P@20 and P@1000 using title & desc &
narr (cf. Fig. 3(a)), in P@100 and P@1000 using
title & desc (cf. Fig. 3(c)), in P@20, P@30, P@50
and P@1000 using title & narr (cf. Fig. 3(b)), and
in P@5, P@10 and P@1000 using desc & narr (cf.
Fig. 3(d)).
If we focus on short queries (cf. Fig. 3(efg)), we remark
that the hybrid seems better than both the probabilistic
and the discriminative using the precision at different
top returned documents, except in some cases such as:
• The probabilistic outperforms the hybrid in P@5
and P@100 using title & desc & narr (cf. Fig. 3(a)),
in P@100 using description (cf. Fig. 3(f)), and in
P@5, P@100 and P@1000 using narrative (cf. Fig.
3(g)).
NLPinAI 2019 - Special Session on Natural Language Processing in Artificial Intelligence
938

• The discriminative seems better than the hybrid in
P@5, P@10, P@15, P@20, P@30 and P@50 using
title (cf. Fig. 3(e)).
The hybrid cannot mainly outperforms the possibilistic
in terms of precision at top returned documents using
title because it has achieved better results only in
P@10, P@15 and P@20 (cf. Fig. 3(e)) in addition to
P@15 and P@100 using narrative (cf. Fig. 3(g)).
However, the possibilistic approach achieved better
results than the hybrid using description only in P@5
and P@100 (cf. Fig. 3(f)). Globally, the precision
values at different top documents confirm that the
hybrid approach is mainly better than the possibilistic,
the probabilistic and the discriminative using long and
short queries with a clear gap for the first values of
recall corresponding to the first selected documents.
However, the discriminative outperforms the hybrid in
case of short queries using title and the possibilistic
achieved better results in case of short queries using
narrative.
4.3 Evaluation using the MAP and the
R-Precision Metrics
We provide in Figure 3 a comparative study using the
MAP and the R-Precision metrics. For long queries, the
hybrid QT outperforms the probabilistic in terms of R-
Precision and in terms of MAP for queries using title
& desc (cf. Fig. 3(c)). Further, the hybrid achieved
better results than the discriminative in terms of both
MAP and R-Precision using all combinations of long
queries, except in case of the MAP using title & narr
(cf. Fig. 3(b)) where the discriminative slightly
outperforms the hybrid. The latter seems better than the
possibilistic in terms of the MAP and R-Precision using
title & desc and in terms of R-Precision using title &
narr.
For short queries, the hybrid outperforms the
probabilistic in terms of MAP using title and in terms
of R-Precision using description or narrative. It is also
better than the discriminative in terms of MAP using
description, and in terms of MAP and R-Precision
using narrative. Finally, the hybrid is better than the
possibilistic in terms of R-Precision using description.
In general, these two metrics confirm again that short
queries using title (where translation of single words is
frequent) are still suitable for the discriminative
approach if compared to all other approaches.
Whereas, the narrative parts of source queries (where
translation of NPs is frequent) are more appropriate for
the possibilistic approach. For these reasons, our new
hybrid possibilistic approach has benefited from their
both strengths at the same time. This has been
confirmed by the achievement of the hybrid approach
in case of long queries using especially title & desc (cf.
Fig. 3(c)) with large gaps in terms of MAP and R-
Precision if compared to its competitors.
4.4 Evaluation using the Improvement
Percentage
We present in Table 1 the improvement percentage of
the hybrid possibilistic approach if compared to the
possibilistic (Poss.), the discriminative (Disc.) and the
probabilistic (Proba.) ones for long and short queries
and using the precision at different top documents, the
MAP and the R-Precision.
Using long queries, the hybrid performs a significant
improvement in terms of precision at different top
documents. For example, if we compare the hybrid to
the probabilistic we have registered an improvement
percentage more than 16% for P@10 and P@15 using
title & desc, and more than 10% for P@30 using title
& desc & narr. Besides, the average improvement is
about 9% if we consider the top returned documents
using title & desc, and the average improvement of the
R-Precision is about 6%. If we compare the hybrid to
the discriminative using title & desc we have achieved
an improvement percentage more than 12% for P@30,
an average improvement about 7.75% for the top
returned documents and the average improvements of
the MAP and R-Precision are about 3% and 5.75%,
respectively. If we compare the hybrid to the
possibilistic using title & desc we have registered an
improvement percentage more than 10% for P@15, an
average improvement about 4% for the top returned
documents and the average improvement of the R-
Precision is about 2.6%.
Using short queries, and if we focus on the
comparative study between the hybrid and the
probabilistic we have registered the best improvement
percentage in P@15: more than 6% using title, more
than 8.3% using description and more than 4.8% using
narrative. If we consider the precision values at the top
returned documents, the average improvement
percentage is: about 2% using title, about 3.7% using
description and about 0.75% using narrative
A Comparative Study between Possibilistic and Probabilistic Approaches for Query Translation Disambiguation
939

Figure 2: Recall-Precision curves of the five QT runs.
0
0,1
0,2
0,3
0,4
0,5
0,6
0,7
0,8
0,9
0 0,1 0,2 0,3 0,4 0,5 0,6 0,7 0,8 0,9 1
Monolingual_Title+desc+narr Possibilistic_Title+desc+narr
Probabilistic_Title+desc+narr Discriminative_Title+desc+narr
Hybrid_Title+desc+narr
Precision
Recall
(a)
0
0,1
0,2
0,3
0,4
0,5
0,6
0,7
0,8
0,9
0 0,1 0,2 0,3 0,4 0,5 0,6 0,7 0,8 0,9 1
Monolingual_Title Possibilistic_Title
Probabilistic_Title Discriminative_Title
Hybrid_Title
Precision
Recall
0
0,1
0,2
0,3
0,4
0,5
0,6
0,7
0,8
0,9
1
0 0,1 0,2 0,3 0,4 0,5 0,6 0,7 0,8 0,9 1
Monolingual_Title+narr Possibilistic_Title+narr
Probabilistic_Title+narr Discriminative_Title+narr
Hybrid_Title+narr
Precision
Recall
0
0,1
0,2
0,3
0,4
0,5
0,6
0,7
0,8
0,9
1
0 0,1 0,2 0,3 0,4 0,5 0,6 0,7 0,8 0,9 1
Monolingual_Description Possibilistic_Description
Probabilistic_Description Discriminative_Description
Hybrid_Description
Precision
Recall
0
0,1
0,2
0,3
0,4
0,5
0,6
0,7
0,8
0,9
1
0 0,1 0,2 0,3 0,4 0,5 0,6 0,7 0,8 0,9 1
Monolingual_Title+desc Possibilistic_Title+desc
Probabilistic_Title+desc Discriminative_Title+desc
Hybrid_Title+desc
Precision
Recall
0
0,1
0,2
0,3
0,4
0,5
0,6
0,7
0,8
0,9
0 0,1 0,2 0,3 0,4 0,5 0,6 0,7 0,8 0,9 1
Monolingual_Narrative Possibilistic_Narrative
Probabilistic_Narrative Discriminative_Narrative
Hybrid_Narrative
Precision
Recall
0
0,1
0,2
0,3
0,4
0,5
0,6
0,7
0,8
0,9
0 0,1 0,2 0,3 0,4 0,5 0,6 0,7 0,8 0,9 1
Monolingual_desc+narr Possibilistic_desc+narr
Probabilistic_desc+narr Discriminative_desc+narr
Hybrid_desc+narr
Precision
Recall
(e)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(g)
(f)
NLPinAI 2019 - Special Session on Natural Language Processing in Artificial Intelligence
940
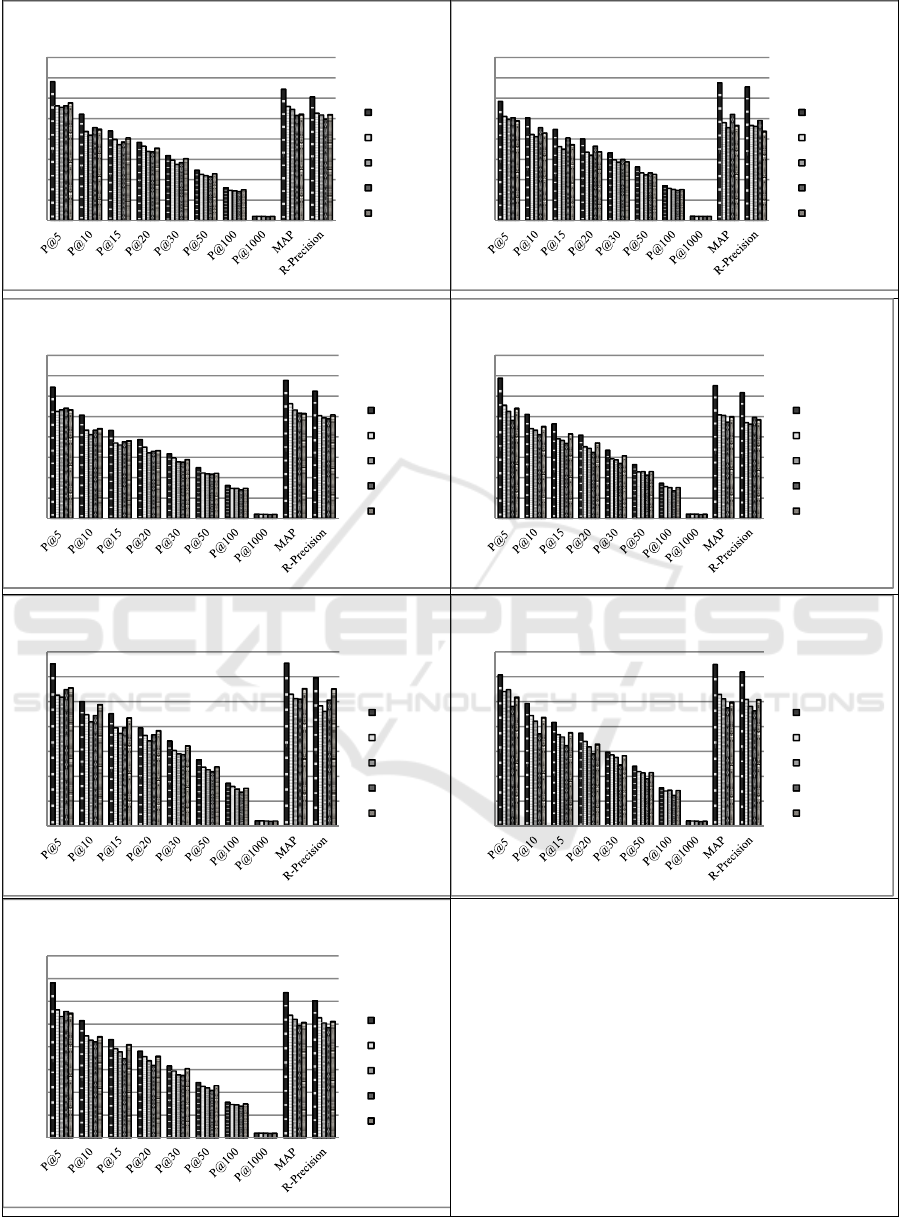
Figure 3: Results using the precision values at different top documents, MAP and R-Precision.
0
0,05
0,1
0,15
0,2
0,25
0,3
0,35
0,4
(a) Title + Desc + Narr
Monolingual
Possibilistic
Probabilistic
Discriminative
Hybrid
0
0,05
0,1
0,15
0,2
0,25
0,3
0,35
0,4
(e) Title
Monolingual
Possibilistic
Probabilistic
Discriminative
Hybrid
0
0,05
0,1
0,15
0,2
0,25
0,3
0,35
0,4
(b) Title + Narr
Monolingual
Possibilistic
Probabilistic
Discriminative
Hybrid
0
0,05
0,1
0,15
0,2
0,25
0,3
0,35
0,4
(f) Description (Desc)
Monolingual
Possibilistic
Probabilistic
Discriminative
Hybrid
0
0,05
0,1
0,15
0,2
0,25
0,3
0,35
(c) Title + Desc
Monolingual
Possibilistic
Probabilistic
Discriminative
Hybrid
0
0,05
0,1
0,15
0,2
0,25
0,3
0,35
(g) Narrative (Narr)
Monolingual
Possibilistic
Probabilistic
Discriminative
Hybrid
0
0,05
0,1
0,15
0,2
0,25
0,3
0,35
0,4
(d) Desc + Narr
Monolingual
Possibilistic
Probabilistic
Discriminative
Hybrid
A Comparative Study between Possibilistic and Probabilistic Approaches for Query Translation Disambiguation
941

The average improvement of the R-Precision is about
1.8%. If we compare hybrid to discriminative we
remark that the best improvement percentage is in
P@100 using title with about 1.9%, while it is more
than 14.3% in P@20 using description and about 18%
in P@10 using narrative. The average improvement
percentage using the precision values at different top
documents is about 11% using description and about
13.4% using narrative. Finally, the hybrid approach is
better than the possibilistic using the description part
of source queries. It exceeds more than 6% as
improvement percentage in P@15, while the average
improvement percentage is about 1.7% for all top
returned documents.
These results confirm again our deduction cited
above about the efficiency of the hybrid approach in
case of both long and short queries.
Table 1: The improvement percentage of the hybrid possibilistic approach.
Long
queries
Precision
metrics
% imp.
Hybrid vs. Poss.
% imp.
Hybrid vs. Disc.
% imp.
Hybrid vs. Proba.
Short
queries
Precision
metrics
% imp.
Hybrid vs. Poss.
% imp.
Hybrid vs. Disc.
% imp.
Hybrid vs.
Proba.
Title
+
desc
+
narr
P@5
2.63 2.63 4
Title
P@5
-4.38 -2.98 -1.49
P@10
2.56 -1.62 7.07
P@10
1.75 -5.71 4.47
P@15
1.86 5.14 8.64
P@15
2.7 -7.95 6.33
P@20
-2.52 5.52 4.96
P@20
0.54 -7.62 5.18
P@30
2.57 6.97 10.31
P@30
-3.36 -4.13 0.42
P@50
0.97 6.12 4
P@50
-3.17 -3.17 0.71
P@100
1.21 5.78 3.02
P@100
-3.81 1.88 -1.05
P@1000
-1.94 6.32 0
P@1000
-1.94 1 1
MAP
-6.85 1.36 -4.36
MAP
-2.71 -10.36 2.55
R-Prec.
-1.21 4.62 0.46
R-Prec.
-5.87 -10.59 -5.1
Title
+
desc
P@5
5.63 1.35 7.13
Desc.
P@5
-2.66 12.34 2.81
P@10
9.06 9.99 16.77
P@10
2.5 9.87 4.25
P@15
10.03 10.03 16.58
P@15
6.3 12.72 8.36
P@20
5.1 4.58 11.91
P@20
5.29 14.32 7.55
P@30
6.06 12.03 11.03
P@30
5.06 13.68 6.88
P@50
0.34 8.78 4.94
P@50
0.61 8 0
P@100
-4.4 11.09 2.01
P@100
-3.46 11.21 -0.26
P@1000
-0.96 4.04 0
P@1000
0 7.22 0
MAP
4.26 8.39 7.93
MAP
-1.85 5.58 -1.38
R-Prec.
14.11 8.84 19.61
R-Prec.
2.97 -2.26 4.76
Title
+
narr
P@5
1.41 -1.37 0
Narr.
P@5
-4.11 7.73 -5.4
P@10
1.71 1.71 7.2
P@10
-1.67 17.98 3.51
P@15
2.65 1.28 5.49
P@15
2.01 16.08 4.86
P@20
-4.74 1.15 3.48
P@20
-3.29 13.34 3.45
P@30
-2.96 4.41 3.96
P@30
-1.26 15.15 2.24
P@50
-0.72 1.65 1.28
P@50
-2.01 12.82 0.37
P@100
0.82 5.56 0.82
P@100
1.27 15.51 -0.97
P@1000
-1.94 5.21 -0.98
P@1000
-2.91 8.7 -1.96
MAP
-8.45 -0.19 -3.16
MAP
-6.01 4.8 -2.74
R-Prec.
0.55 3.97 2.84
R-Prec.
-0.16 9.9 5.78
desc
+
narr
P@5
-2.63 -1.33 2.77
Hybrid: The hybrid possibilistic approach.
Poss.: The probability-to-possibility transformation-
b
ased approach
(Elayeb et al., 2018).
Disc.: The discriminative possibilistic approach (Ben Romdhane et
al., 2017).
Proba.: The Probabilistic approach (Gao et al., 2001).
P@10
-0.85 5.26 3.45
P@15
4.38 17.69 8.47
P@20
0.5 12.74 6.02
P@30
3.4 10.88 9.83
P@50
1.24 9.89 4
P@100
1.5 6.9 2.76
P@1000
-1.94 6.32 0
MAP
-6.04 2.8 -2.72
R-Prec.
-2.99 5.61 1.43
Table 2: The p-value for the Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-ranks test.
Hybrid
vs.
Possibilistic
P@5 P@10 P@15 P@20 P@30 P@50 P@100 P@1000 MAP R-Prec.
0.479
0.037 0.009
0.723 0.330 0.735 0.479 1.00 0.062 0.865
Long Queries Short Queries
Title + desc + narr Title + desc Title + narr Desc + narr Title desc narr
0.575
0.016
0.798 0.721 0.120 0.213 0.062
Hybrid
vs.
Discriminative
P@5 P@10 P@15 P@20 P@30 P@50 P@100 P@1000 MAP R-Prec.
0.297 0.132 0.062 0.090
0.042 0.042 0.013 0.013
0.310 0.310
Long Queries Short Queries
Title + desc + narr Title + desc Title + narr Desc + narr Title desc narr
0.012 0.005 0.036 0.009 0.012 0.009 0.005
Hybrid
vs.
Probabilistic
P@5 P@10 P@15 P@20 P@30 P@50 P@100 P@1000 MAP R-Prec.
0.345
0.013 0.017 0.017 0.017 0.018
0.310 0.285 0.398 0.128
Long Queries Short Queries
Title + desc + narr Title + desc Title + narr Desc + narr Title desc narr
0.050 0.007
0.085
0.025
0.351
0.035
0.444
NLPinAI 2019 - Special Session on Natural Language Processing in Artificial Intelligence
942

4.5 Statistical Evaluation
It is relevant to confirm that the above improvements
of the hybrid possibilistic approach are statistically
significant. To do this, we use the Wilcoxon Matched-
Pairs Signed-Ranks Test (Hull, 1993). The
improvement is statistically significant if the computed
p-value < 0.05. Results in Table 2 showed that:
• The improvement of the hybrid approach if
compared to the possibilistic is statistically
significant in P@10 (p-value = 0.037< 0.05), in
P@15 (p-value = 0.009) and for long queries using
title & desc (p-value = 0.016).
• The improvement of the hybrid approach if
compared to the discriminative is statistically
significant in P@30 (p-value = 0.042), in P@50 (p-
value = 0.042), in P@100 (p-value = 0.013) and in
P@1000 (p-value = 0.013). It is also statistically
significant for both short queries using description
or narrative and for all combinations of long
queries. Nonetheless, for short queries using title,
the improvement of the discriminative is
statistically significant if compared to the hybrid
(p-value = 0.012).
• The improvement of the hybrid if compared to the
probabilistic is statistically significant in P@10
(p-
value = 0.013), in P@15, in P@20, in P@30
(p-
value = 0.017) and in P@50
(p-value = 0.018). This
improvement is also statistically significant using
all combinations of long queries, except of queries-
based title & narr or title or narr. But, we have
registered a p-value ≅ 0.05 for queries using title &
desc & narr.
Globally, these tests confirm again the performance
of our hybrid possibilistic approach in the
disambiguation of both long and short queries using
different assessment metrics.
5 CONCLUSION
We have proposed, assessed and compared in this
paper a new hybrid QT disambiguation approach
combining a probability-to-possibility transformation-
based approach with a discriminative possibilistic one
in order to take advantage of their strengths. Firstly, we
have taken advantage of the probability-to-possibility
transformation-based approach (possibilistic) in the
translation of the identified NP of a given source query.
Secondly, remaining single source query terms are
translated using the discriminative possibilistic QT
disambiguation approach. The improvements of the
hybrid approach if compared to the probabilistic, the
possibilistic and the discriminative approaches, are
statistically significant in terms of precision values at
different top documents, the MAP and the R-Precision
scores using long and short queries.
In spite of its significant effectiveness, the hybrid
possibilistic approach is still lacked by domain-specific
queries. Besides, the assessment processes of the
hybrid approach should be performed in real contexts
by allowing the users to contribute in its evaluation.
Finally, we plan to compare these QT approaches to
the current neural networks-based approaches (e.g.
word embedding, seq2seq, etc.).
REFERENCES
Ben Amor N., Mellouli K., Benferhat S., Dubois D., Prade
H.: A theoretical framework for possibilistic
independence in a weakly ordered setting. Int. J. Unc.,
Fuz. and Know.-Based Sys. 10: 117–155 (2002).
Ben Khiroun O., Elayeb B., Bellamine Ben Saoud N.:
Towards a Query Translation Disambiguation Approach
using Possibility Theory. In: Proc. ICAART, pp. 606-613
(2018).
Benferhat S., Dubois D., Garcia L., Prade H.: Possibilistic
logic bases and possibilistic graphs. In: Proc. UAI, pp.
57–64 (1999).
Ben Romdhane W., Elayeb B., Bellamine Ben Saoud N.: A
Discriminative Possibilistic Approach for Query
Translation Disambiguation. In: Proc. NLDB, LNCS
10260, pp. 366-379 (2017).
Dubois D., Prade H. (eds): Possibility Theory: An Approach
to computerized Processing of Uncertainty. Plenum
Press, New York, USA, 1994.
Dubois D, Prade H.: Unfair coins and necessity measures:
towards a possibilistic interpretation of histograms.
Fuzzy Sets Systems 10(1): 15–20 (1985).
Elayeb B., Ben Romdhane W., Bellamine Ben Saoud N.:
Towards a New Possibilistic Query Translation Tool for
Cross-Language Information Retrieval. Mult. Tools and
App. 77(2): 2423-2465 (2018).
Elayeb B., Evrard F., Zaghdoud M., Ben Ahmed A.: Towards
an intelligent possibilistic web information retrieval
using multiagent system. Interact. Techn. Smart Edu.
6(1): 40-59 (2009).
Gao J., Nie J. Y., Xun E., Zhang J., Zhou M., Huang C.:
Improving Query Translation for Cross-Language
Information Retrieval using Statistical Models. In: Proc.
ACM SIGIR, pp. 96-104 (2001).
Hull D. A.: Using statistical testing in the evaluation of
retrieval experiments. In: Proc. ACM SIGIR, pp. 329-
338 (1993).
Yamada K.: Probability-possibility transformation based on
evidence theory. In: Proc. IFSA, pp. 70–75 (2001).
Zhou D., Truran M., Brailsford T., Wade V., Ashman, H.:
Translation techniques in cross-language information
retrieval. ACM Comp. Survey 45(1), 1:1-1:44 (2012).
A Comparative Study between Possibilistic and Probabilistic Approaches for Query Translation Disambiguation
943
