
Teaching Design Thinking through Gamified Learning
Hariklia Tsalapatas
1
, Olivier Heidmann
2
, Kai Pata
3
, Carlos Vaz de Carvalho
4
, Merja Bauters
5
,
Spyros Papadopoulos
1
, Costas Katsimendes
1
, Christina Taka
1
and Elias Houstis
1
1
University of Thessaly, Argonafron & Filellinon, 38221 Volos, Greece
2
Centre for Research and Technology Hellas, 6
th
klm Harilaou Thermi Road, 57001 Thessaloniki, Greece
3
Tallinn University, Navra Road 25, 10120 Tallinn, Estonia
4
Porto Polytechnic, Rua Dr. Doberto Frias 712, 4200465 Porto, Portugal
5
Metropolia University, Bulevardi 31 A, 00180 Helsinki, Finland
Keywords: Design Thinking, Higher Education, Active Learning, Creativity, Innovation, Gamification, Engagement.
Abstract: Entrepreneurial capacity has long been considered as a key transversal competency applicable in all subjects
and educational levels. It empowers individuals to explore their talents, to introduce creative ideas, and to
take action towards turning ideas into viable solutions that contribute to business growth and social well-
being. Design thinking is a human-centered, solution-oriented approach to entrepreneurial innovation that
aims at introducing solutions to business as well as social issues by better understanding how a user
experiences a proposed service or product. This paper introduces the design and implementation of active
learning digital services supported by gamification principles in learning contexts that facilitate the
introduction of design thinking to higher education engineering students. The proposed learning intervention
engages students in the design thinking processes of empathizing, ideating, designing, and validating
through an on-line learning platform that promotes collaboration in and across teams, brainstorming, and
peer reviews of designs allowing students to learn from experience through cases inspired by real world
challenges.
1 INTRODUCTION
Innovation is a key driver of economic growth. If
facilitates the implementation of ideas into services,
the delivery of those services to market, and the
support of business operations after launching,
creating jobs throughout this process. By driving
economic growth innovation facilitates higher living
standards and promotes social cohesion. In today's
business environment, where unemployment reaches
high levels at 6.7% in the general population and
14.9% % among youth in EU28. (Eurostat, 2018),
innovation and entrepreneurial thinking can be a
catalyst for growth helping curb unemployment by
facilitating the pursuit of emerging business
opportunities, contributing to the raise of GDP,
making good use of human capital, and promoting
the wellbeing of society.
In order to put ideas into life it is important to
understand the needs and desires of the target group
that will benefit from a product or service and the
design of a product the perspective of consumers in
order to best address those needs. On the other hand,
social entrepreneurship, namely using
entrepreneurial thinking for introducing solutions to
social challenges, is of key importance for today's
youth that will be faced with significant challenges
as a result of global population growth and its
consequences, including shortage of resources,
poverty, need for access to education by all, and
more. Social entrepreneurship often involves finding
solutions where none seems to exist to address
complex issues. Using basic field knowledge in
combination with entrepreneurial capacity and
innovative thinking can lead to social interventions
that powerfully address these challenges.
Building the skills that can shape ideas into
viable solutions is as important in higher education
as developing core knowledge on a specific field.
Without those skills ideas will remain ideas and
never reach the targeted sector. For this reason,
entrepreneurship education is important in higher
education curricula. It typically involves basic
principles such as performing a feasibility analysis
and building a business plan. However,
entrepreneurship higher education often lacks the
278
Tsalapatas, H., Heidmann, O., Pata, K., Vaz de Carvalho, C., Bauters, M., Papadopoulos, S., Katsimendes, C., Taka, C. and Houstis, E.
Teaching Design Thinking through Gamified Learning.
DOI: 10.5220/0007697402780283
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2019), pages 278-283
ISBN: 978-989-758-367-4
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

equally significant social dimension. As a result of
this significant omission, society as a whole misses
the opportunity to put the fresh, open young minds
of students to work towards addressing social
challenges, to build social entrepreneurship
mindsets, and to build related practical skills that
will empower students to be active in the future in
civic matters.
2 DESIGN THINKING
Design thinking is a user centred approach in design
that aims to introduce fitting solutions to business or
social challenges by best understanding how a user
experiences a proposed product or service. In
business, it aims at enhancing customer experiences
helping a company grow. In social entrepreneurship
it aims at introducing economically viable solutions
to challenging social issues.
While user centred design has been applied in
diverse principles for some time, design thinking
innovates by introducing a methodology for more
accurately addressing user needs. Design thinking
differs from traditional analytic user centred design
methods by focusing on “going broad” at the initial
stages of design (Baeck and Gremett, 2011) without
evaluating at that stage potential solutions. The key
idea of design thinking is that by fully understanding
users, accurately defining a problem statement, colla-
borating, and thinking out of the box designers may
be able to introduce solutions to “wicked” problems
to which none appears to exist at first glance.
Varying approaches to design thinking have
been introduced; most have as common activities
empathizing with users, getting inspiration, ideating
for generating a broad range of potential solutions,
creating prototypes that a user can interact with, and
validating solutions with the engagement of users.
3 A GAMIFIED LEARNING
PLATFORM FOR DESIGN
THINKING
This work aims at facilitating design thinking in
higher education by introducing an active,
experiential learning approach that engages students
with design thinking principles towards building
their capacity to act as innovators in business and
civic contents (DesignIT project, 2018). This is
facilitated through a the design and implementation
of a digital platform that allows students to
experiment with design thinking practices by
working on problems inspired by the real world
(DesignIT project, 2017).
3.1 A Problem-based, Active Learning
Methodology for Teaching Design
Thinking
Problem-based learning promotes the development
of knowledge through active approaches that expose
students to problems, often inspired by real life.
Problem based learning is part of wider active
learning models that support the notion that learners
learn better by doing as opposed by being the
passive recipients of information. This links problem
based learning to constructivist learning design that
advocates that knowledge is synthesized rather than
transferred. Various approaches to problem based
learning are used in practice; however the core
principles of identifying a problem, breaking it down
to components, solving those, and synthesizing a final
solution from parts are often part of a problem learn-
ing environment. In additional to core knowledge,
problem based learning supports the development of
transversal learning skills such as analytical thinking,
creativity, ability to collaborate, and others.
This work deploys active and problem-based
learning design by exposing students to real-world
problems that they are asked to solve by applying
design thinking principles (Tsalapatas et. al, 2018).
Students are exposed to a challenge that is based on
the principle of study and has learning objectives
related to curricula work. The challenge is
introduced by the instructor; in some cases, the
challenge may be introduced by an external
company that seeks the innovative mindsets of
young engineers to introduce a potential solution to
actual business challenges within design thinking
practices. Examples of challenges include:
• The design of an e-commerce platform that
allows the marketing of goods and services in
remote areas while at the same time it helps
create sustainable jobs for young individuals.
• The design of a digital learning application
that enriches interactivity and engagement in
high school STEM education.
• The design of a social game for carers.
• The design of a game for raising awareness
on forest fires.
• The design of a user friendly application for
local touristic guides.
Teaching Design Thinking through Gamified Learning
279

• The design of a digital service that supports
pervasive learning, i.e. learning that can take
place interactively anytime, anywhere by
exploiting smart devices, geolocation, and
increasing network bandwidths.
• The enhancement of digital communication
in business.
• The development of innovative search
mechanisms for huge image databases.
• The support of communication among
construction workers speaking multiple
languages.
• The design of smart and sustainable learning
ecosystems in schools.
• The design of digital learning ecosystems that
promote wellbeing and health.
3.2 Gamification in Learning
Serious games are games, in digital application or
other form, which are designed for a purpose other
than entertainment. The broader term of
gamification refers to the deployment of gaming
elements in non-learning contexts, ranging from
business to education and training (Huotari &
Hamari, 2012, Robson et al, 2015). According to
Gartner, gamification elements are deployed in
business process management for engaging workers,
promoting creativity, understanding customer needs,
and meeting objectives (Olding, 2012). In
professional training, serious games, often used as
simulations of the real world, may be deployed for
building skills when training is expensive or
involves training in risky procedures. Examples
include building personnel skills in a simulated
environment for avoiding downtime of production
facilities for training purposes, building piloting
skills in the safe environment of simulators, or
building the skills of medical personnel in emerging
medical processes.
In education, gamification is deployed in broader
blended learning activities as a tool contributing to
the achievement of learning objectives. Gamification
mechanisms may include rewards, a sense of
affiliation, a sense of purpose, access to additional
content upon completion of tasks, assuming roles,
group collaboration, competition, social recognition,
social sharing of achievement, and others.
In order to be successful, gamification design
needs to be linked to educational goals. The exact
blend of mechanisms to be deployed depends on the
learning scenario and the target group. To ensure
that gamification is effective as a learning tool, it
must be embedded into wider learning design that
includes debriefing and feedback processes for
assessing behavioural changes related to learning
outcomes (Garris, 2002). The potential that well-
designed games offer for instilling positive
behaviour has led to the emergence of persuasive
games, which aim to provide positive influence in
social issues, e.g. promoting healthy lifestyles,
training educators to act towards suicide prevention,
raising awareness on poverty and homelessness, and
more.
3.3 Platform Design and
Implementation
Design thinking is a process that requires effort and
experience. This work presents a digital platform
that facilitates design thinking in learning contexts.
3.3.1 Learning Objectives
The implemented digital platform targets higher
education engineering students and has the
following high level learning objectives:
• To digitally support broad learning processes
that introduce design thinking in engineering
and wider contexts.
• To allow flexibility to educators on
integrating diverse design thinking practices
in the classroom.
• To promote long-term learner engagement
with educational activities related to design
thinking.
• To enhance collaboration and communication
in an active, digitally enabled classroom by
providing easy to use facilities that foster
ideation, brainstorming, and peer reviews.
• To provide educators with information in
individual and team achievement within
design teams.
3.3.2 Main Functionality
The platform is designed for deployment in blended
learning classroom activities on design (DesignIT
project, 2017).
Each class is assigned a “lobby” accessible by its
members only. Students work in teams, each of
which focuses on a specific challenge. The platform
offers flexibility in terms of the organization of the
CSEDU 2019 - 11th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
280
challenges. Each team may work on a separate
challenge, all teams may work on the same, or
groups of teams may share a challenge. This
flexibility is allowed to support classes in which
diverse challenges may be introduced by the
instructor or other stakeholders, or teams may wish
to define their own challenges.
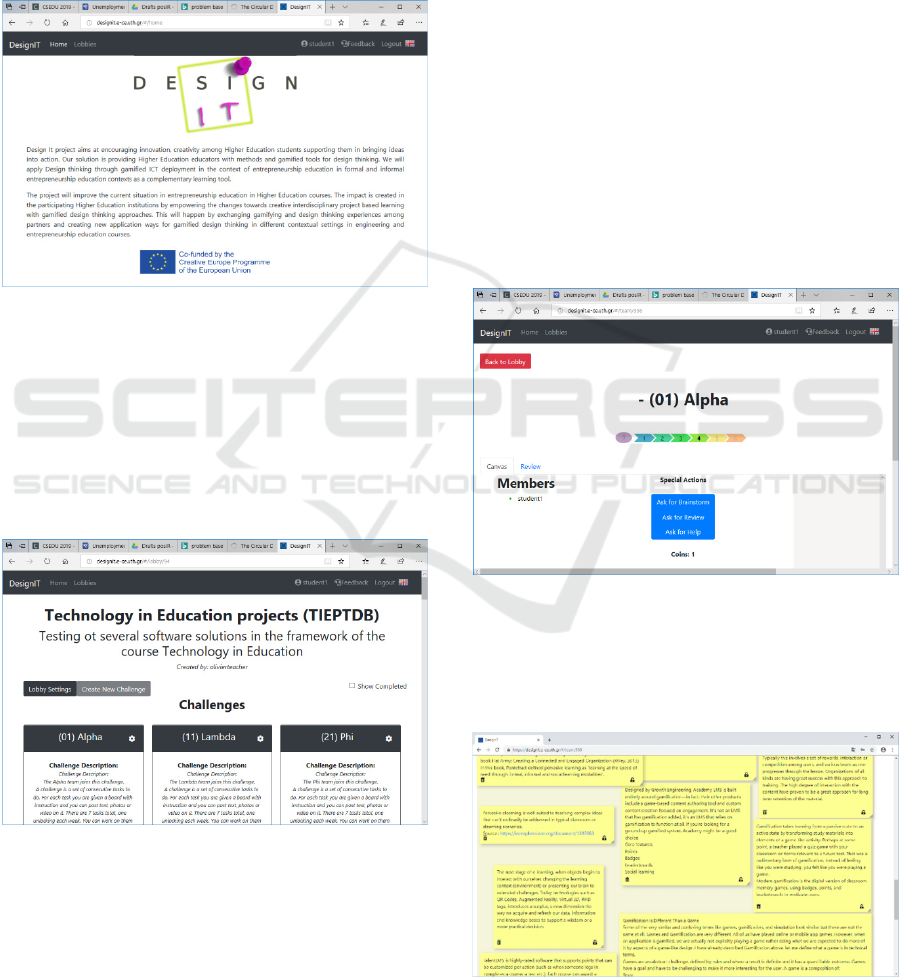
Figure 1 below demonstrates the entry page of
the service.
Figure 1: The DesignIT platform entry page.
Figure 2 below demonstrates an example of a
lobby corresponding to the “Technology of
Education” course of the Department of Electrical
and Computer Engineering of the University of
Thessaly. In this example, identical challenges are
allocate to all participating teams. Students may join
the challenges that interest them to collaboratively
work with others on designing a solution.
Figure 2: The lobby of the “Technology in Education”
class at the University of Thessaly, Greece.
By joining a challenge, a student sees in the form
of an arrow at the centre of the screen the list of
design thinking activities defined by the challenge
creator, who often is the instructor.
Notably, design thinking steps are only presented
by numbers as opposed to descriptions. This is a
design choice that allows instructors to apply
different design thinking paradigms without being
restricted to a specific format. The instructor may
define the objectives of each numbered step that the
students are expected to follow in the design
thinking process. For example, step 1 may
correspond to ideation, step 2 to reviewing, step 3 to
brainstorming, step 4 to refining a solution, step 5 to
validating. This is demonstrated below in Figure 3.
Design thinking steps demonstrated as numbers for
flexibility.
On the main working screen, students work on a
canvas on which they introduce “notes”, as
demonstrated on, which corresponds to the main
working page for a student where she may add notes
on ideas towards a potential solution to the
challenge. The main working screen is shared by all
challenge members, who see in real-time additions
and modifications made by team members and
further have the option of processing each other’s
additions.
Figure 3: Design thinking steps demonstrated as numbers
for flexibility.
On the main working screen, students work on a
canvas on which they introduce “notes”, as
demonstrated on Figure 4.
Figure 4: A canvas that supports ideation as a group
activity.
Teaching Design Thinking through Gamified Learning
281
Each note may include plain text, an image, or a
video highlighting concepts related to the challenge
or desired characteristics of a proposed solution. The
canvas represents a board of ideas that support
ideation created by all challenge members. Notes
may be coloured for demonstrating grouping of
functions, implementation priorities, or other desired
characteristics that team wishes to convey. Team
members may also delete notes.
A team may request feedback on a canvas that is
work in progress by other students or by the
instructor. This can be done in one of two ways:
The team may “Ask for Brainstorm”, a function
that opens the canvas to students external to the team
to edit the challenge canvas by adding notes with
ideas. In addition, a team may “Ask for Review”
which calls the instructor and external to the team
students to provide feedback on the canvas.
Feedback may be either in the form of text or
“upvoting” or “downvoting” of ideas, a function
similar to “liking” in social media contexts.
The brainstorming and review processes are
important in design thinking as they promote idea
validation. The facilitate collaboration not only
within a team but also across teams in a class
introducing valuable information towards the design
of a solution that best addresses user needs.
3.3.3 Integrated Gamification Elements
Student engagement is promoted through
gamification elements integrated into the platform.
The elements offer a sense of competition through
rewards and recognition of achievement.
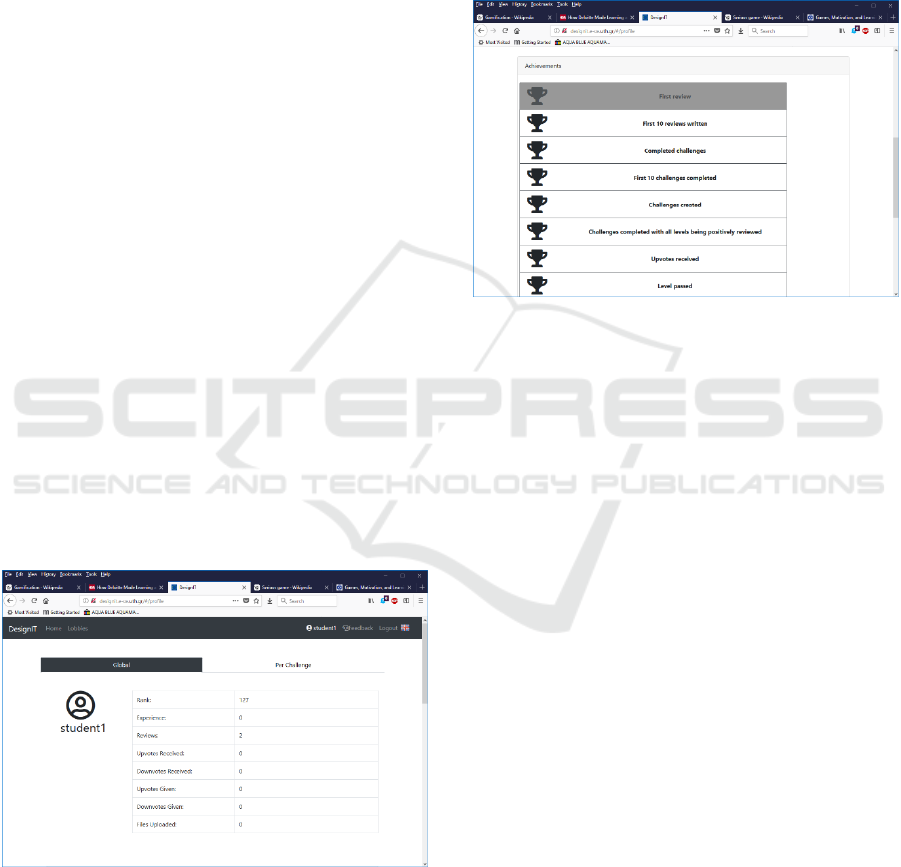
Figure 5: Student rewards: rank, experience, reviews
performed, content uploaded.
One form of rewards is coins, which students for
participation at the global level, which refers to
overall engagement, and at the challenge level,
which refers to engagement in a specific educational
activity. A student receives coins for uploading
content into the platform, reviewing the work of
peers, and receiving reviews.
Students furthermore build experience for
participating in learning, for example for joining a
challenge, reviewing, asking for help, participating
in a brainstorm, and other activities. Students are
ranked by experience, which adds a further element
of competition.
Figure 6: Student achievements for reaching milestones.
Another form of reward is achievement trophies
that student receive upon reaching a milestone such
as creating a challenge, completing a challenge,
completing 10 challenges, completing a challenge
with only positive reviews, reaching the highest
levels of the rank, and more.
4 CONCLUSION
This article presented the design and
implementation of digital services that support
learning processes on design thinking. A flexible
tool has been implemented, aiming to promote
student creativity and collaboration towards
innovative and entrepreneurial thinking. The tool
has been designed for deployment in broad design
thinking activities that empower students to see
opportunities and turn ideas into action. The tool
further promotes the capacity of educators to
introduce innovative learning interventions into the
classroom through emerging technology supported
active learning frameworks. The tool is currently
being evaluated in learning experiments taking
place in higher education institutions in Greece,
Estonia, Portugal, and Finland. Early feedback is
very positive, with students and educators
highlighting the added value of enriched, real-time
collaboration that is facilitated through digital
CSEDU 2019 - 11th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
282

services making design thinking activities more
active, engaging, and participatory.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been funded with the support of the
Erasmus+ Programme of the European Commission,
project ID 2017-1-EE01-KA203-034889.
REFERENCES
Baeck, A., Gremett P., 2011. Design thinking. In UX best
practices – How to achieve more impact with user
experience, eds. H. Degen and X. Yuan. New York:
Mcgraw-Hill Osborne Media.
DesigntIT project, 2017, Design Thinking in Higher
Educatin for Promoting Human-Centered Innovation
in Business and Society, ERASMUS+ project 2017-1-
EE01-KA203-034889.
Djaouti, D., Alvarez, J., Jessel, JP. Classifying Serious
Games: the G/P/S model (PDF), retrieved December
14, 2018.
Garris R., Ahlers R., Driskell J.E., 2002. Games,
motivation, and learning: a research and practice
model, Simulation and Gaming 2002 33(4):441-467.
Huotari, K., & Hamari, J., 2012. Defining gamification – a
service marketing perspective. Proceedings of the 16
th
International Academic MindTrek Conference 2012
Tampere, Finland, October 3-5, 2012.
Olding, A., 2012. Best practices for harnessing
gamification’s potential in the workplace. Gartner
Report ID G00239672, October 18, 2012.
Robson, K., Plangger, K., Kietzmann, J., McCarthy, I. &
Pitt, L., 2015. Is it all a game? Understanding the
principles of gamification. Business Horizons. 58 (4):
411–420.
Tsalapatas, H., Heidmann, O., Pata, K., Bauters, M. Vaz
de Carvalho, C., 2018. Learning needs analysis and
development of methodological learning frameworks
for design thinking in higher education, DesingIT
project report.
Eurostat Statistics Explained, Unemployment Statistics
2018.
Teaching Design Thinking through Gamified Learning
283
