
A Field Research on the Practices of High Performance Software
Engineering Teams
Alessandra C. S. Dutra
1
, Rafael Prikladnicki
1
and Tayana Conte
2
1
School of Technology, Pontifícia Universidade Católica do RS (PUCRS), Porto Alegre, Brazil
2
Department of Computing, Universidade Federal do Amazonas (UFAM), Amazonas, Brazil
Keywords: Software Engineering Education and Training, High Performance Teams, Field Research.
Abstract: This paper presents the results of a field research aiming at identifying the practices adopted by High
Productivity Software Engineering Teams .This field research was developed through interviews with project
managers from several companies with the following objectives: to evaluate the knowledge of the
professionals in relation to the characteristics of the high performance teams found in the literature; understand
and identify which practices companies use to develop each high performance characteristic; identify the
training approaches that are used to improve the professionals in each practice.
1 INTRODUCTION
The software development market operates in a
global environment, with rapid changes, and needs to
respond to these new opportunities and new markets
with agility (Sommerville, 2010). Achieving agility,
competitiveness and results without a qualified
software development team and high performance is
a difficult task and can bring results that are not very
competitive.
A study done in 2015 by Standish Group (Hastie
and Wojewoda, 2015) with a sample of 10,000
projects around the world produced a report called
“Chaos Manifesto 2016”, which revealed that the
Information Technology (IT) industry faces several
challenges; although 29% of the IT projects have
been successful, being delivered before the deadline
and within the estimated cost; 52% of the IT projects
were delivered after the deadline and more expensive
than the original plan; and 19% of the IT projects
were total failures, being cancelled before the
delivered time, or were delivered but never used.
Faraj and Sambamurthy (2006) say that improving
the productivity and quality of projects are important.
Initial approaches were focused on discovering better
methodologies and tools, but there is an increasing
perception that the projects also face several challenges
related to communication, coordination, learning,
negotiation, diversity and on how to form high
performance teams for software development projects.
This context indicates that the qualified education
and training of professionals is more necessary in the
society in which we live. Whether in short courses, or
at the undergraduate or graduate level, training good
professionals it is part of the commitment a Higher
Education Institution (HEI) has in the society
(Dannelly and Steidley, 2001). Beckman (Beckman
et al.,1997) say that, among other factors, the quality
of the professional is directly related to the quality of
the education he/she received.
The quality of SE training can contribute
meaningfully to improvements in the state of the art
of software development and aid in solving some
traditional problems and crises related to software
industry practices (Gibbs, 1994). Training and
capacity-building to prepare a software professional
must include not only basic knowledge of the
Computer Science field, but also the teaching of
concepts, processes and techniques for the definition,
development and maintenance of
software (Saiedian,
1999; ACM/IEEE, 2008).
As a result, the education process in Software
Development has begun to question the methods used
in training activities (Beckman et al., 1997). Recent
studies observe that these methods involve traditional
teaching strategies such as theory presentation,
expositive classes and complementary reading. In this
scenario, students find in the industry a different
scenario than what is taught in academia (Prikladnicki
et al., 2009). At the same time, software development
projects have required high performance team
Dutra, A., Prikladnicki, R. and Conte, T.
A Field Research on the Practices of High Performance Software Engineer ing Teams.
DOI: 10.5220/0007722502450252
In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2019), pages 245-252
ISBN: 978-989-758-372-8
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
245

training, and professionals with strong technical,
behavioural, and business skills which current
educational programs are not able to supply
(Monsalve et al., 2011). One of the reasons is the fact
that such programs concentrate on basic education
focused on the traditional approaches for software
development, instead of preparing the professional to
act as a part of a software development team, which
requires multifunctional competencies and a
multidisciplinary environment.
Thus, the goal of this paper is to develop a
reflection about how the current existing SE training
approaches cover the various high performance teams
characteristics. We first conducted an ad-hoc
literature study about the existing training approaches
in SE and then a systematic literature review (SLR)
about high performance teams characteristics. At the
end, we reflected on how the existing training
approaches help in forming high performance
software development teams.
This paper is divided into six sections. In Section
2 we present the theoretical foundations. In Section 3,
we report on existing training approaches. Section 4
provides a field research on high performance teams
practices. Finally, in Section 5 the conclusions and
future work are addressed.
2 BACKGROUND
2.1 Software Engineering Training
Software Engineering is concerned with theory
application, knowledge and practice for the effective
and efficient software development of systems that
satisfies users requirements (ACM/IEEE, 2008). SE
began to be discussed as a discipline in 1968
(ACM/IEEE, 2004) and currently is part of the
curriculum of several courses such as Computer
Science, Computer Engineering, Information
Systems, Automation Control Engineering and
Software Engineering.
Software Engineering is related with all software
production aspects, from the initial stage to its
maintenance, involving not only technical
development processes, but also project management
activities and tools, methods and theories that support
its production (Sommerville, 2010). Therefore, SE
goes beyond programming code creation; it tries to
discipline development and brings to software
development principles, techniques and knowledge to
discuss quality questions, deadlines and economic
factors (ACM/IEEE, 2004).
The professionals who conclude their
undergraduate course, according to curricular
recommendations, are able to, among other aspects,
master knowledge and abilities that are part of the SE
area; work individually or as part of a team to develop
software artefacts with quality; design solutions using
appropriate SE approaches that integrate ethical,
social, legal and economic questions; know how to
apply current theories, models and techniques that
provide a baseline for identifying and analyzing
problems, software design, development, implement-
tation, verification and documentation; demonstrate
understanding and appreciation of the importance of
negotiation, efficient work habits, leadership, and
good communication with stakeholders; and learn
new models, techniques and technologies as soon as
them emerge (ACM/IEEE, 2004).
By analyzing the curricular recommendation
listed, we have identified that there are several
required competencies for a SE professional. The SE
curriculum (ACM/IEEE, 2004), (ACM/IEEE, 2008)
points to the necessity of education apart from
expositive class formats, and one of the way to
increase education quality involves innovative
strategies and didactics. According to Beckman
(Beckman et al., 1997), educational quality is one of
the important factors that influence the quality of the
professionals. Thus, some of the challenges for
improving SE education are: to make SE courses
more attractive to students; to focus appropriately on
SE education, understanding its dimensions; to
present industry practices to the students; provide
education to industry professionals; to make
education in SE evidence-based; to ensure that SE
educators have the necessary experience and
knowledge to this assignment; and to increase the
research prestige and quality of the educational SE
(Sommerville, 2010).
According to Conn (Conn, 2002), the SE
professionals are dissatisfied with the lack of training
of the university students that enter the work market,
which means that the industry must complement their
education with training that gives them necessary
knowledge in order to make up this deficiency. This
training can involve professionals or teams, including
high performance teams.
2.2 High Performance Teams
A high performance team is a group that brings
together members committed to the mutual growth
and personal success. According to Chiavenato
(2008), the main high performance teams attributes
are: participation, accountability, clarity, interaction,
ICEIS 2019 - 21st International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
246

flexibility, focalization, creativity and quickness.
According to Cleland and Ireland, the participation in
a team increases the commitment and the fidelity of
the people, resulting in delivery of high quality, work
(Cleland and Ireland, 2000).
According to Moscovici, a high performance
team, besides all the requirements of a team as was
explained in the previous section, must have its
members must be committed to the personal growth
and success of each team member. Such a team will
exceed the performance of all the other teams and
achieve results above expectations (Moscovici,
2003).
Katzenbach and Smith (1993), present some
characteristics of high performance teams: “Deeply
personal commitments of each one to the growth and
the success of the others is what distinguish high
performance teams from the majority of the existing
teams. Energized by this extra sense of commitment,
the high performance team typically reflects a
vigorous amplification of the fundamental teams
characteristics: deeper sense of purpose, more
ambitious performance targets, a more complete
approach, more fullness in mutual accountability,
knowledge interchangeably and complementarity.”
Boyett and Boyett mention some companies that
have achieved great results with high performance
teams. The AT&T Credit Corporation has used high
performance interfunctional teams in order to
improve its efficiency and service to the client
(Boyett and Boyett, 1998).
According to Raj (Raj et al., 2006), it is noticed
that there is a major difficulty for an organization in
disseminating high performance team practices, such
as work reorganization, professional involvement in
decision making processes and improvement in
workers’s skills, despite the evidence that
organizations invest in these s practices to achieve
greater productivity and efficiency. Companies with
significant performance standards, according to
Katzenbach and Smith, stimulate and support high-
performing teams, helping them to establish their own
goals (Katzenbach and Smith, 1993).
3 TRAINING APPROACHES IN
SE
Training in SE should prepare the students in both
theory and effective participation in a collaborative
and interdisciplinary environment. In this regard, it is
important consider the variation in training
techniques.
Traditional approaches in SE training are
considered to be (Anastasiou, 2004):
1. Dialogued expositive classes: This is a content
exposition, with active participation by the
students, whose previous knowledge must be
considered and can be taken as a foundation.
2. Text Study: This is an exploration of an author’s
idea from the critical study of a text and/or
information research and the author’s ideas
exploration.
3. Directed Study: This is study under guidance
and direction by the professor, aiming to solve
specific difficulties.
4. Use of a Discussion List: This is an opportunity
for group of people be able to debate, at a
distance, a theme in which they are experts or
have done a previous study.
5. Verbalization and Observation Groups
(VG/OG): This is an analysis of theme/problem
under a professor’s coordination that divides the
students in two groups: one for verbalization
(VG) and the other for observation (OG).
6. Seminar: This is a space where a group
discusses or debate themes or problems.
7. Case Study: This is the detailed and objective
analysis of a real situation that needs to be
investigated and that is challenge for the people
that are involved.
8. Workshop: This is the gathering of a small
number of people with common interests, which
aims to study and work for the knowledge and
deepening of a theme, under expert orientation.
These alternative approaches can help students to
learn more effectively. Alternative approaches are
considered to be (Prikladnicki et al., 2009) (Gresse
and Shull, 2009), (Monsalve et al., 2011), (Halma,
2014):
1. Group Activities, distance education and
practice activities: By using this approach,
interaction with the students is emphasized
through icebreakers that explore specific
subjects. The characteristics are: diversification
in the techniques for group activities; practical
classes in laboratories; the planning of the
student work; and part-time classes: 20% of the
discipline is done through distance education.
2. Capstone projects and practices activities: a
Capstone project is an approach where a student
group plans and executes a software project
from the beginning to the end during one whole
semester.
A Field Research on the Practices of High Performance Software Engineering Teams
247

3. Playgroup and games: For this strategy, related
content is first presented to the class. In the end,
in order to consolidate comprehension, a
playgroup is performed using LEGO®. The
game makes it possible to design, from the
defined requirements, a product to be built that
is similar to the software development.
4. Games and educational simulators: Because of
the need for training students in the SE process,
one of the alternatives is the use of games to fill
the gap between theoretical and practical
aspects. From the reports found in the literature
(Monsalve et al., 2011), it was noticed that the
majority of the proposals developed are
associated with simulator games.
The approaches that are more focused on the
students and that promote their further active
participation on the classes, for example with games
and simulators (Monsalve et al., 2011), (Halma,
2009), have the potential to increase the students
interest, motivate them and improve learning at level
of concept application.
4 FIELD RESEARCH ON HPT
PRACTICES
This field research was developed through interviews
with project managers from different companies, with
the following objectives:
• Evaluate the knowledge regarding the
performance of high performance teams in
the literature;
• Understand and activate skills for companies
to become each high performance
characteristic;
• Identify how training approaches are used to
improve the professionals in each practice.
4.1 Field Research Protocol
An exploratory, qualitative, non-experimental,
survey-type field survey was developed for a semi-
structured interview with open and closed questions.
The application of the questionnaire was made
through personal interviews. The following
procedures were developed:
a) Meetings to raise questions and structuring
the interview guide;
b) Review of interview guide;
c) Authorization of participating companies;
d) Validation of face and content;
e) Application of interviews.
The research respondents were project managers,
project leaders, and project coordinators. The
resources used were technological resources
(computer, text and spreadsheet software) and
materials resources (a meeting room in the
organization's own headquarters for half an hour, a
recorder to record interviews, paper and pen).
Data collection was done through semi-structured
interviews with open and closed questions. The
questionnaire will be applied with personal
interviews.
In the analysis of data, a critical analysis of these
results was made through the development of a
comparison of the results obtained with the theories
and related studies (Dutra et al, 2015). The interviews
were recorded and a qualitative analysis of the
collected data was carried out through a mapping of
the respondents' responses.
4.2 Field Research Execution
After we defined the research protocol, the field
research was executed.
In the face-to-face interviews, tape recorders were
used because according to Schraiber (1995), the use
of tape recorders in interviews is indicated to
amplifying the power of recording and capturing
extremely important communication elements,
pauses for reflection, doubts or intonation of the
voice, enhancing the understanding of the narrative.
Authors such as Patton (1990) agree with this
statement because the recorder preserves the original
content and increases the accuracy of the data
collected.
After all the interviews were carried out, each of
them was transcribed. As soon as the transcription of
the information was finalized, the analysis of the data
was started. According to Bardin (2004), the most
used form of treatment is Content Analysis, that
according to Oliveira (Oliveira et. al, 2003), consists
in the detailed reading of all the transcribed material,
in the identification of words and sets of words that
have meaning for the research, as well as in the
classification in categories or themes that have
similarity to the syntactic or semantic criterion. Still,
according to Olabuenaga and Ispizúa (1989), content
analysis is a technique for reading and interpreting the
content of all kinds of documents, which, if it is
properly analyzed, opens the doors to the knowledge
of aspects and phenomena of social life otherwise
inaccessible.
ICEIS 2019 - 21st International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
248
In this field research, the Thematic Analysis
technique was used, which, according to Bardin
(2004), is inserted in the set of Content Analysis
techniques, whose objective is to highlight the items
of meaning from the description of the "corpus"
constructed based on the coding units or cut-out
categories of the content of interviews and
documents, which are guided by the problem and
objectives of this study (Bardin, 2004).
Bardin (2004), explains that this dialogue -
understood in the light of varied contextual categories
and information - makes interpreting as an intrinsic
element of the research process. Based on these
procedures, the different phases of analysis were
covered: (1) transcription and pre-analysis; (2)
floating reading and exploration of the material with
the establishment of categories; (3) data processing
from logical inference and interpretation; and (4)
confrontation and discussion of the results obtained
with the theories and related studies of the systematic
review of developed literature.
4.3 Field Research Results
Based on the research developed, we analyzed the
demographic data of the professionals interviewed,
according to Table1.
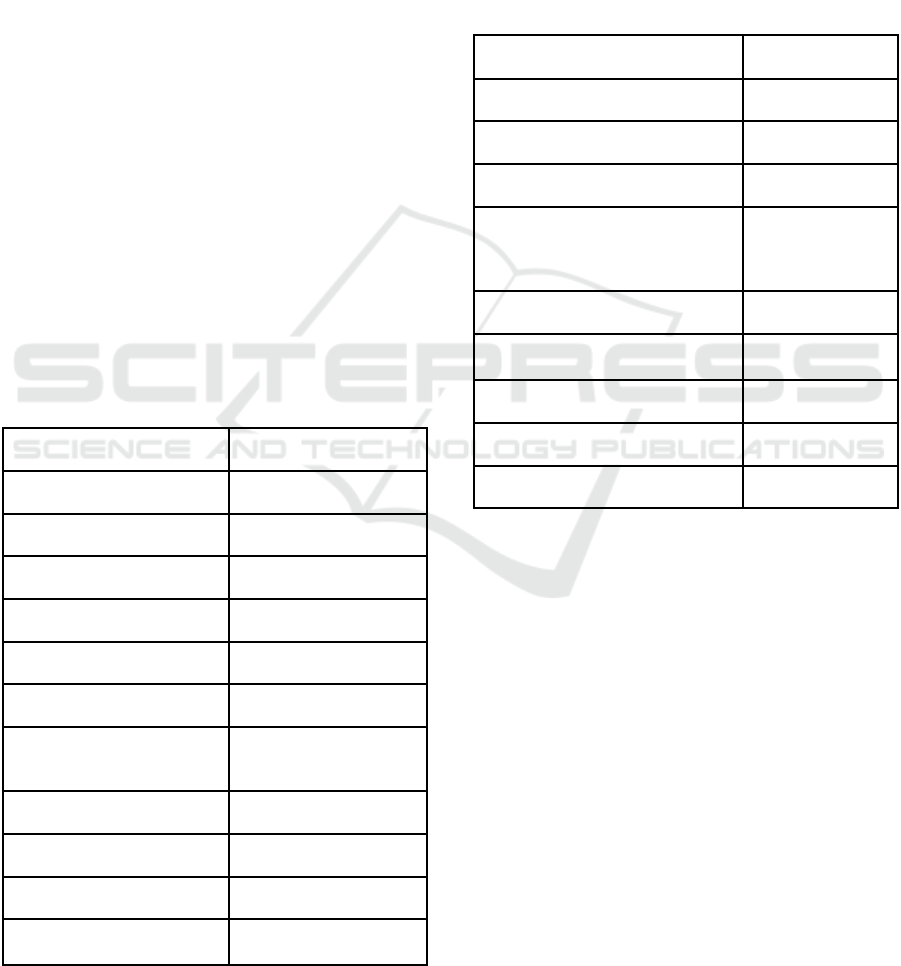
Table 1: Demographics of participants.
Age Respondents
21-30 1
31-40 5
41-50 14
Sex
Female 7
Male 13
Experience in Project
Management
1-5 years 4
6-10 years 3
11-15 years 12
16+ years 1
Most of the interviewees are male, between forty-
one and fifty years old, and work between eleven and
fifteen years in the activity of managing software
projects.
In turn, Table 2 gives us information about the
time and projects developed with a high performance
team. It shows if the interviewee worked on projects
in which a high performance team participated, how
much time worked with this team and how many
projects were developed.
Table 2: Time and projects developed in HPT.
Worked with HPT Number of Votes
Yes 19
No 1’
Time that worked with HPT
0-1 year
2-3 years
13
6
3+ years 0
Projects with HPT
1-5 projects 16
6-10 projects 1
10+ projects 2
4.3.1 Data Analysis
To determine which characteristics of a high
performance team are most relevant to the research,
we used 75% heuristics, that is, three quarters of
respondents should agree that the attribute is a high
performance characteristic, as shown in the following
table. This number is higher than that found in similar
studies in the literature, which suggest that when an
opinion is shared by at least 50% of the respondents,
it should be treated as a relevant impact opinion for
the study in question (Ali-Babar and Niazi, 2008).
Table 3 presents the characteristics of the high
performance teams, the number of votes for each
characteristic and their totals.
A Field Research on the Practices of High Performance Software Engineering Teams
249
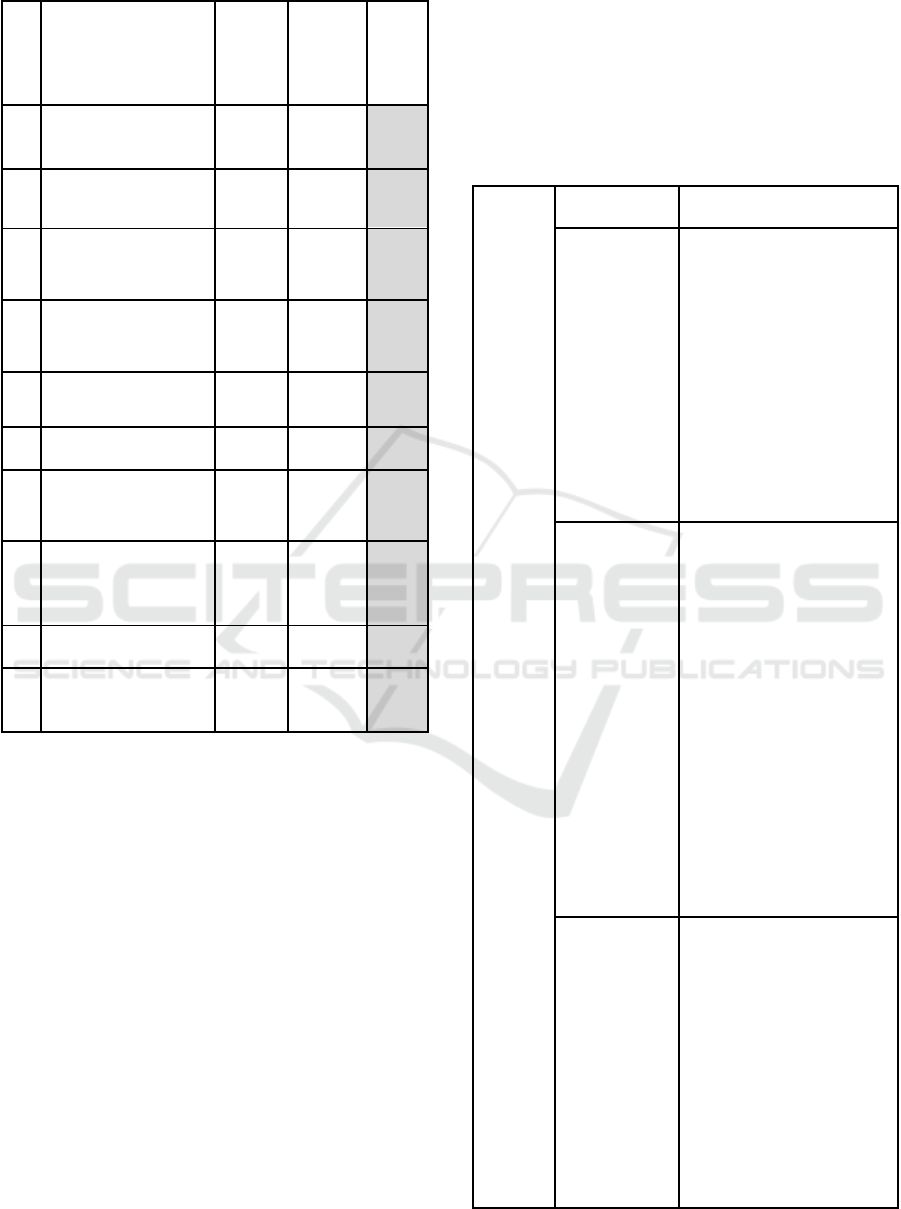
Table 3: Ten most relevant characteristics.
# Attribute HPT’s
characte
ristic
(Yes)
HPT’s
characte
ristic
(No)
%
1
Know how to work
in a team 19 1 95%
2 Solid knowledge 18 2 90%
3
Effective
communication 17 3 85%
4
Efficient
coordination 17 3 85%
5 Diversity of skills 16 4 80%
6 Autonomy at work 16 4 80%
7
Organizational
commitment 16 4 80%
8
Unforeseen technical
challenges 16 4 80%
9 Self-manageable 16 4 80%
10
Confidence in their
own abilities 15 5 75%
The most selected characteristic in the field survey
was "know how to work in a team", with 19 votes,
followed by "have a solid knowledge", with 18 votes,
and 17 votes were to "have an efficient coordination"
and "have effective communication.
4.3.2 Categorization
Coding is the process by which raw data is
systematically transformed into categories, allowing
subsequent discussion of the relevant characteristics
of the content (Franco, 1986).
As Olabuenaga and Ispizúa (1989) said, the
process of categorization must be understood, in its
essence, as a process of data reduction. The categories
represent the result of an effort to synthesize a
communication, highlighting in this process its most
important aspects.
First, the data were prepared and, after the
transcriptions, a careful reading was made, in order to
seek the researcher's familiarity with the data before
starting the coding of the categories. In this coding
process, open coding and selective coding were used.
Open coding involves the breaking, analysis,
comparison, conceptualization, and categorization of
data. According to Bandeira-de-Mello and Cunha
Table 4: Practices for the characteristic: know how to work
in a team.
Know
how to
work in a
team
Categories Practices Found
Methodology 1. Develop team-wide
project scope discussions
through pre-planning and
pre-games
2. Develop agile teams,
perform Scrum ceremonies
with the project team
(planning, daily,
retrospectives), sharing
experiences, listening, trying
to help
3. Define a working
methodology
Team Building 1. Encourage and stimulate
teamwork
2. Develop HR integrations
3. Develop self-protection of
the team (the team protects
itself)
4. Use a team mailing list to
exchange messages
5. Make small celebrations
in the deliveries of the
projects
6. Work towards a common
goal by trying to help your
peers
7. Focus much more on the
whole than an individual
focus
Allocation 1. Make the allocation of the
team according to the
project's characteristic and
skills of the members
2. Have people working
physically close
3. Make new allocations
within the same project,
changing the context in the
middle of the project,
forcing a synergy between
the teams and focusing on
the need to work together
ICEIS 2019 - 21st International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
250
(2006), in the initial stages of open coding, the
researcher explores the data by examining in detail
what seems relevant to him due to the intensive
reading of the texts. Table 4 exemplifies the initial
codifications of this research, and in this first stage
170 practices were found.
With the defined categories, it moves to an
intermediate level of abstraction, seeking the relation
between them to form the basis for its theoretical
construction. This process is called "axial coding". In
this stage, the number of practices was 135.
In the table 5, we have: (1) the main characteristic,
(2) the total of categories linked to this characteristic,
and (3) the total of practices extracted from the
interviews for the formation of high performance
teams in Engineering Software.
Selective coding is the final step in data analysis
and coding, and its purpose is to integrate and refine
the constructed categories. Selective coding is being
developed throughout the entire data collection and
analysis process, since integration is a continuous
process.
The final categories found in this field survey, and
this final step was completed with 106 practices.
The final categorization of the characteristics of
HPT found in this survey were:
1. Know how to work in a team: Methodology,
Team Building and Allocation
2. Solid knowledge: Knowledge and Formation
3. Efficient coordination: Team Management,
Methodology, Roles and responsibilities and
Communication
4. Effective communication: Methodology,
Communication, Allocation, Feedback,
Management and Tools
5. Organizational commitment: Commitment,
Strategy, Team Building and Feedbacks
6. Diversity of skills: Knowledge, Feedback, Team
formation, Rotation and Exchange of
experiences
7. Self-manageable: Energy, Autonomy,
Communication and Methodology
8. Autonomy at work: Autonomy, Leadership and
Methodology
9. Unforeseen technical challenges: Knowledge,
Skills and Contingency Analysis
10. Confidence in their own abilities: Roles and
responsibilities, Knowledge and Recognition
From the identification of the categories linked to
the characteristics of the high performance teams, the
data collected were extracted from the interviews,
categorized, and from the identification of the
categories, the practices were listed. This field
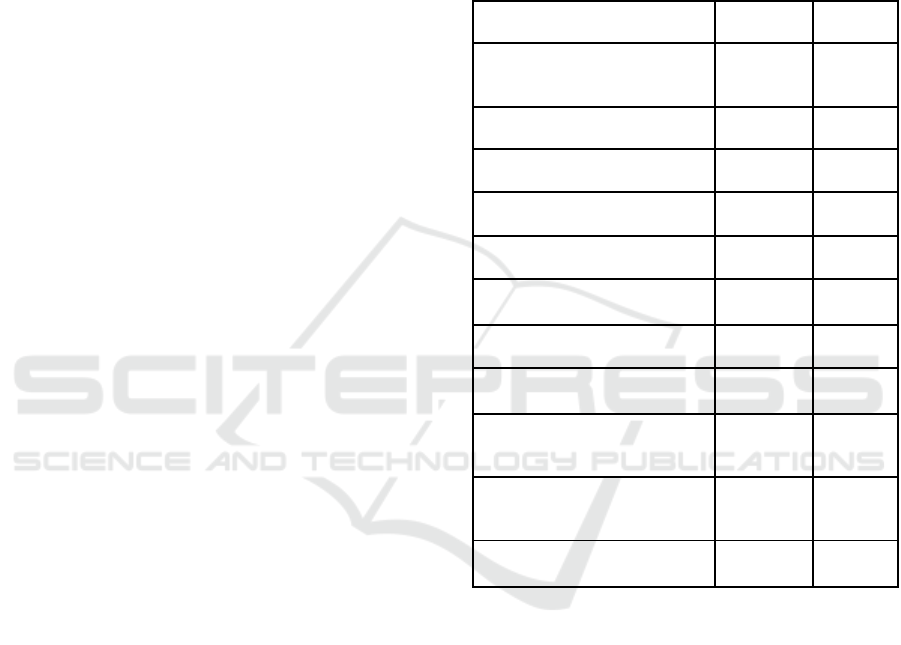
survey, for ten high performance characteristics,
totaled 106 high performance team practices in 37
categories, as shown in Table 5.
Table 5: Number of characteristics x categories x practices.
Characteristics Categories Practices
1. Know how to work in a
team 3 13
2. Solid knowledge 2 7
3. Efficient coordination 4 14
4. Effective communication
6 16
5. Organizational commitment 4 11
6. Diversity of skills
5 10
7. Self-manageable 4 11
8. Autonomy at work
3 5
9. Unforeseen technical
challenges 3 11
10.Confidence in their own
abilities 3 8
Total
37 106
5 CONCLUSIONS
As a conclusion of this field research, we can say that
of the three objectives defined for the research, only
two were successfully completed.
Objective 1, to evaluate the knowledge of the
professionals regarding the characteristics of the high
performance teams found in the literature, was
successfully achieved, since the characteristics of the
high performance teams found in the Systematic
Review of Literature (Dutra et al, 2015), were cited
by the interviewees as characteristics of high
performance teams.
Objective 2, to understand and identify the
practices companies use to develop each high
performance characteristic, has also been
A Field Research on the Practices of High Performance Software Engineering Teams
251

successfully completed. As shown in Table 5, 106
practices of high performance teams were identified
in 37 different categories.
The ultimate goal of this field research was to
identify the training approaches that are used to
enhance people in each identified practice, but this
goal was not successfully completed. That is because,
it was not possible to find such approaches in the data
extracted from the interviews. In most cases, the
interviewees focused on mentioning what training
was made for a particular practice rather than the
training approach that was developed. Considering
this difficulty in extracting the approaches, a new
study was developed with the objective of searching
in the literature the training approaches, the
characteristics of the high performance teams most
cited in field research.
REFERENCES
ACM/IEEE, 2008. Computer Science Curriculum,
Guidelines for Undergraduate Degree Programs in
Software Engineering.
ACM/IEEE, 2004. Software Engineering Curriculum.
Guidelines for Undergraduate Degree Programs in
Software Engineering.
Ali-Babar, M., Niazi, M., 2008. “Implementing Software
Process Improvement Initiatives: An Analysis of
Vietnamese Practitioners’ Views”, In International
Conference on Global Software Engineering, Bangalore,
Índia, p. 67-76.
Anastasiou, L. G. C., Alves, L. P., 2004. "Teaching
Strategies". In: Proceedings of education at the
university. Strategies work in the classroom. 3. ed.
Joinville: Univille, p. 67-100 (in portuguese).
Bandeira-de-Mello, R., Silva, A. B., 2006. “Qualitative
Research in Organizational Studies: Paradigms,
Strategies and Methods”. São Paulo: Saraiva
Bardin, L., 2004. “Content analysis”. Lisboa: Edições 70 (in
portuguese).
Beckman, K., Coulter, N., Khajenouri, S., Mead, N., 1997.
“Collaborations: Closing the industry–academia gap”.
IEEE Software 14 (6), pp. 49–57.
Boyett, J.H., Boyett, J.T., 1998. “The Guru Guide-The Best
Ideas of the Top Management Thinkers”. New York:
Wiley.
Chiavenato, I., 2008. “People management: the new role of
human resources in organizations”. Rio de Janeiro:
Elsevier, 3a ed. (in portuguese).
Cleland, D. I., Ireland R. L., 2000. “Project Manager`s
portable handbook”. New York: McGraw-Hill, 257p.
Conn, R., 2002. “Developing Software Engineers at the C-
130J Software Factory”. IEEE Software, Los Alamitos,
v. 19, n. 5, p. 25-29.
Dannelly R. S., Steidley C. W., 2001. “A student laboratory
environment for real-time software systems
development”, The Journal of Computing in Small
Colleges.
Dutra, A. C. S., Prikladnicki, R., Conte, T., 2015. What are
the Main Characteristics of High Performance Teams for
Software Development In: ICEIS - 17 th Internacional
Conference on Enterprise Information Systems, 2015,
Barcelona, Espanha.
Faraj, S., Sambamurthy, V., 2006. "Leadership of
information systems development projects". In: IEEE
Transactions on Engineering Management.
Franco, M.L.P.B., 1986. “What is Content Analysis”. São
Paulo: PUC, 1986. (in portuguese).
Gibbs, W. 1994 “Software's chronic crisis”. Scientific
American 271 3, pp. 86–95.
Gresse, V. W. C.; Shull, F., 2009. “To Game or Not to
Game?” Software, IEEE, v. 26, n. 2, p. 92-94.
Halma, A., 2009. Robomind.net – Welcome to
Robomind.net, the new way to learn programming.
http://www.robomind.net Access in: set. 2014.
Hastie S., Wojewoda S., 2015. Standish group chaos report,
https://www.infoq.com/ articles/standish-chaos-2015.
Access in: 26 jun. 2017.
Katzenbach, J. R, Smith D. K., 1993. “The Wisom of
Teams”. Summarized by permission of Harvard Business
School Press Copyright by McKinsey & Company, Inc.
275 pages.
Monsalve, E., Werneck V., Leite J., 2011. Teaching Software
Engineering with SimulES-W. Conf. on Software
Engineering Education and Training (CSEE&T).
Moscovici, F., 2003. “Teams work right: Multiplication of
Human Talent ”. Rio de Janeiro: José Olympio, 8a
edition (in portuguese).
Olabuenaga, J. I. R., Ispizua, M. A., 1989. La descodi-
ficacion de la vida cotidiana: metodos de investigacion
cualitativa. Bilbao, Universidad de deusto,
Oliveira, E., Ens, R. T., Andrade, D. B. S. F., Mussis, C. R.,
2003. “Analysis of content and research in the area of
education”. Revista Diálogo Educacional, Curitiba, v. 4,
n. 9, pp. 11-27 (in portuguese).
Patton, M. Q., 1990. “Qualitative Evaluation and Research
Methods”. London: Sage (in portuguese).
Prikladnicki R., Albuquerque A., Wangenheim C., and
Cabral R., 2009. “Teaching Software Engineering:
Challenges, Teaching Strategies and Lessons Learned” in
FEES - Education Forum in Software Engineering (in
portuguese).
Raj, P. P., Baumotte A.C.T., Fonseca D.P.D., Silva,
L.H.C.M., 2006. “Project Human Resource Management
”. Rio de Janeiro: Editora FGV – Fundação Getúlio
Vargas, 180p. (in portuguese).
Saiedian, H., 1999. “Software engineering education and
training for the next millennium, Journal of Systems and
Software”, v. 49, i. 2-3, p. 113-115.
Schraiber, L. B., 1995. “Qualitative research in health:
methodological reflections of the oral report and
production of narratives in study about the medical
profession”. In: Revista de Saúde Pública, São Paulo, pp.
63-74 (in portuguese).
Sommerville, 2010. I. Software Engineering, 9nd edition.
Pearson Prentice Hall.
ICEIS 2019 - 21st International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
252
