
ticAPP – Digital Transformation in the Portuguese Government
Francisco Miguel de Lemos Santos
1
, Andr
´
e Vasconcelos
1,2
, Jos
´
e Tribolet
1
and Pedro Viana
2
1
INESC-ID, Instituto Superior T
´
ecnico, Lisboa, Portugal
2
AMA - Ag
ˆ
encia para a Modernizac¸
˜
ao Administrativa IP, Lisboa, Portugal
Keywords: Enterprise Architecture, Public Administration, Digital Transformation, Center of Excellence, ticAPP,
TOGAF.
Abstract:
IT is fundamental to digital transformation. Digital transformation focuses on driving the organization to a
new level, exposing and extending its processes beyond the organization. Enterprise Architecture provides the
tools and methodologies to manage the complexity of Digital Transformation. A Digital Center of Excellence,
named ticAPP, is going to be assigned to support the Public Administration’s Digital Transformation process.
This paper focuses on building the future state Business Architecture of ticAPP, and how to enable its con-
tinuous evolution. We need to ensure the future state of ticAPP is not confined by the technology used and
that it takes into account both Government’s and ticAPP’s strategic goals. To accomplish that, we follow a
Top-Down Design approach development of ticAPP’s Business architecture, based on TOGAF ADM method-
ology. In the final steps, we will evaluate ticAPP’s maturity level using the Architecture Capability Maturity
Model framework that is included in TOGAF and calculate its maturity rating.
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 Context
The Portuguese ICT Strategy (CTIC, 2017) acknowl-
edges that, IT in the Public Sector has become a
bigger challenge than just going paper free and pro-
cess automation. It must simplify the way citizens
and businesses interact with the Public Administra-
tion. New concepts introduced in the IT environment,
such as Data Science and Artificial Intelligence, en-
able a deep transformation process within the Pub-
lic Administration. One of the key transformations
is designing services, focused around citizens and
businesses (CTIC, 2017). On the one hand, citi-
zens expect public services to be simpler, easy to
use and to access, through mobile devices. Informa-
tion about a subject should be presented at one lo-
cation, to avoid wasted time navigating through nu-
merous portals, which are still in place in the Por-
tuguese Administration. It would also be desirable to
submit information once, and it being updated across
the necessary information systems (CTIC, 2017). On
the other hand, the Public Administration has a ver-
tical structure, that creates information silos. To pre-
vent that situation, the Portuguese ICT Strategy pro-
motes the cooperation across the Public Adminis-
tration, in order to develop cross-functional services
efficiently. A central challenge of this strategy is
the need to account for the reinforcement and shar-
ing of digital skills. Sharing between public bod-
ies avoids redundant platforms and unnecessary por-
tals, cutting back on costs and wasted resources.
One measure of this strategy and stated in the Coun-
cil of Ministers document, a Digital Center of Excel-
lence (Portuguese Council of Ministers, 2018), named
ticAPP will be created.It will operate under the su-
pervision of AMA I.P (Ag
ˆ
encia para a Modernizac¸
˜
ao
da Administrac¸
˜
ao P
´
ublica). It supports public enti-
ties in their digital transformation process, by retain-
ing knowledge and skills within the public adminis-
tration. It supports the solutions design for the pub-
lic services, publishing guidelines and best practices
documents on how to develop web applications for the
government. This increases coherence across public
administration web portals. It will revise the informa-
tion systems architecture currently in place, contribut-
ing to clearly defined and accurate external contracts
and increased efficiency and efficacy.
1.2 Problem Definition
Literature about other Digital Centers of Excellence,
show that they share similar strategic goals and per-
612
Santos, F., Vasconcelos, A., Tribolet, J. and Viana, P.
ticAPP – Digital Transformation in the Portuguese Government.
DOI: 10.5220/0007728606120619
In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2019), pages 612-619
ISBN: 978-989-758-372-8
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

form the same activities. Our problem is how to de-
sign ticAPP business architecture, and how it can act
as a reference architecture for other Centers of Ex-
cellence in Public Administrations. Our goal is to
to develop an artifact for a consistent approach on
how to implement a Digital Center of Excellence.
It must be a flexible architecture to allow the inte-
gration of new services and must identify the neces-
sary business elements: organization structure, pro-
cesses, strategies, products, policies, initiatives, and
stakeholders. Enterprise Architecture can help us to
understand the current scenario of an organization,
through as-is views, and what its target state should
be, through to-be views. Typically, when aiming for
a to-be model of the organization, a top-bottom ap-
proach is used. This ensures the future state of the or-
ganization is not confined by the technology used and
that the solution can be traced back to the strategic
drivers placed. TOGAF framework focuses on strate-
gic alignment, between Business and IT, which makes
the Top-Down Design a suitable approach. Focusing
on the layers most important to the problem, Busi-
ness and Information Systems, we asked the follow-
ing questions:
1.3 Document Structure
This paper comprehends 4 parts: the Introduction, al-
ready covered, where we identified the problems that
motivated the development of this paper, and how En-
terprise Architecture can be used to solve them. In
State of the Art, we describe the relationship between
Enterprise Architecture and Digital Transformation.
We introduce three cases of Digital Centers, imple-
mented in different Public Administrations: UK, Italy
and Singapore and analyze the differences and simi-
larities between them. We also provide an overview of
the frameworks and languages associated to the prac-
tice of Enterprise Architecture; In the Proposal sec-
tion, we develop a first draft of TicAPP’s architecture,
focusing on its governance structure. In the Evalua-
tion section we define how we plan to evaluate ticAPP
architecture. We consider its external quality, i.e its
fitness for use, which is perceived by the stakeholders
and internal quality as the quality of the model itself.
2 STATE OF THE ART
2.1 Enterprise Architecture
Enterprise Architecture (EA) provides a coherent set
of principles, methods and models used in the de-
sign and realization of an enterprise’s organizational
structure, business processes, Information Systems
(IS) and infrastructure (Lankhorst, 2005). An effec-
tive EA contributes to a better alignment between the
two domains it concerns: Business and IT (Alonso,
2010). This results in more integrated services that
feel responsive to the citizen. It helps to define bet-
ter business requirements that promote an efficient
and effective IT infrastructure. It facilitates informa-
tion sharing and implementation of best practices and
guidelines across the organization. Within the busi-
ness domain, the business architecture manages the
design, development, implementation and improve-
ment of the company business, adding value to busi-
nesses. The absence of defined standards, running re-
dundant resources to support the business, which can
result in inconsistent data, makes it difficult for a com-
pany to answer business and economic changes. In
the public administration, we also have to account for
political drives. Enterprise Architecture, provides the
tools and methodologies needed to address the com-
plexity of digital transformation working around new
and arising issues systematically (McSweeney, 2016).
In the public sector, Enterprise Architecture aims for
better resource sharing and enable efficient informa-
tion exchange across departments. It improves ser-
vice delivery, enhancing back office processes, adopt-
ing shared platforms. Shared platforms are open plat-
forms that improve sharing of resources and coordi-
nation across departments when delivering citizens, a
service. It must be incrementally extensible, as new
partners gradually desire to join. They derive from
clear political objectives, which leads to the conclu-
sion that, in order to be successful, it is important
for an Enterprise Architecture program to be strongly
backed by the Government. Considering a real case
of Enterprise Architecture, the UK xGEA was cross-
Government Enterprise Architecture. It allowed the
integration between existing architectures and future
ones across the government. The outcome was a
blueprint for the government to have business and IT
aligned.
2.2 Center of Excellence
A Center of Excellence is, usually, a small team that
supports an organization. They are built around a
specific knowledge area, relevant for the organization
and of particular importance for the business (e.g Big
Data, Business Process Management, Software De-
velopment). Their main objectives are to:
• Define best practices to be used across the organi-
zation
• Define standards and promote the use of shared
applications, processes, data and business func-
ticAPP – Digital Transformation in the Portuguese Government
613

tions to increase coherence in the organization
• Identify and reduce points of duplication of effort
across the organization
• Training and education
Implementing a Center of Excellence in an organiza-
tion results in improved consistency and better IT and
business alignment (Accenture, 2013). In the follow-
ing section, we present three examples of Digital Cen-
ters of Excellence. They were chosen due to their im-
pact on transforming their governments, by enhancing
the operation of the public administration services.
2.2.1 UK Government Digital Service (GDS)
The GDS aimed to improve citizens’ relationship
with the government by delivering better services
and helped the government to become more efficient
and effective, thus reducing the costs incurred by IT
(GOV.UK, 2018a). On the one hand to improve cit-
izen interaction, GDS created a single point of ac-
cess to the government services to facilitate access
to information, the GOV.UK. On the other hand , it
was necessary to build digital skills and capability
across the Public Administration. The GDS Academy
was created to equip the government with more spe-
cialized people and ready to handle the problems of
the digital future. One driver of this transformation
was Digital Identity, which allows people to prove
their identity online. Working with several partners
across government, they developed the GOV.UK Ver-
ify Platform. Verify is used to protect public ser-
vices against identity fraud and other malicious ac-
tivity. The GOV.UK Verify turned the UK into ref-
erence in digital identity. Other European countries,
like Italy, have incorporated similar systems, sharing
the same guidelines, standards and best practices of
the underlying UK version. The UK also aims to
leverage public data, to enable better data-based de-
cision making. They built and expanded data science
and analytic capabilities across government, and im-
proved data sharing across organizational boundaries.
Government legacy systems made it hard to share in-
formation. There was too much duplication, overlap
and contradiction in the government. They addressed
this issue through the development of a shared Plat-
form as a Service (GOV.UK.PaaS) for government
services. The GDS houses approximately 850 peo-
ple (GOV.UK, 2018a). It is part of the Cabinet Of-
fice and it is governed by the Ministerial Group on
Government Digital Technology (GOV.UK, 2018b).
Their main business activities are simplifying public
services, increase collaboration between departments,
by creating shared platforms based on open standards
and apply Data Science for better decision-making.
2.2.2 Italy Team Digitale
The Digital Transformation Team (Team Digitale)
was organized to create a new, more effective, Italian
Public Administration built on fundamental blocks,
where the services for businesses and citizens and the
Public Administration itself are developed (TeamDig-
itale, 2018). The team is composed of 29 experts with
management and technological skills, namely soft-
ware development, Cybersecurity, UX and Data Sci-
ence. Their strategy was devised in three fronts, each
with its role on Digital Transformation of the Govern-
ment: At a national level, to define the rules, standards
and implement enabling platforms, which are solu-
tions that offer fundamental, crosswise and reusable
functionality in individual projects (TeamDigitale,
2018). These platforms make the methods of delivery
uniform, which enables consistency across the Pub-
lic Administration The Central and Local administra-
tions developed services that best suited their needs
by following the guidelines previously established.
This was accomplished through the use of in-house or
external providers, and collaborating with the private
sector, to explore new solutions that easily integrate
with the national platforms. These actions aimed to
reduce the complexity of the services provided to citi-
zens and businesses, by having secure, scalable and
reliable architectures, supported by clearly defined
APIs. It also supports data driven decision making,
by introducing recent data analysis methods such as
Big Data and Machine Learning As part of their strat-
egy, Team Digitale re-launched 3 existing platforms:
A central payment platform for all administrations
(PagoPA), a digital identity service to facilitate ac-
cess to digital public services (SPID) and a single
national database for Italian Residents(ANPR). Then,
they built new ones on top, such as Developers and
Designers Italia, two open platforms for public ser-
vices’ front and back-end development. The Data &
Analytics Framework, used for sharing and analyzing
public data, to avoid information silos between ad-
ministrations. The API Ecosystem is an API Manage-
ment system, comprising standards and guidelines to
expose and share functionality across the Public Ad-
ministration through APIs. Operation and technolog-
ical principles were defined by Team Digitale, with
Security and Privacy as the most important principles
that cannot be compromised. Every service and pol-
icy should be as simple as possible, to facilitate usage
by the citizens. It should also prioritize a mobile ap-
proach when developing services, and explore exist-
ing open source technologies. Existing assets should
be enhanced, instead of rebuilding what is already in
place. The architectures follow modern design enco-
ICEIS 2019 - 21st International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
614

mpassing reliability, flexibility, security and service-
oriented approaches. Rely on data to solve complex
problems supported by Machine Learning and Artifi-
cial Intelligence and perform analysis to produce use-
ful information and share it publicly, along with other
documents illustrating new developments and bene-
fits associated. The team has a long-term vision for
the Italian administration’s transformation, with con-
tinuous learning and improvement and adding, how-
ever it will also identify intermediate milestones to
add value to the citizen more quickly. It is a cross-
organizational effort where each administration im-
plements its digital transformation such as rationalize
data centers, share data with other organisms, adopt
cloud solutions, the development of a single digital
identity system and include a payment platform in
the services delivered, according to will find in the
strategy defined and several guidelines. The guide-
lines are meant to create a fundamental set of archi-
tectural and design principles, rules of usability and
interoperability as a basis for the operational strategy.
The drivers behind these initiatives meant to reduce
expenditure of administrations, improve the quality
of services offered to citizens and businesses and the
tools made available to public administrations. Enter-
prise Architecture is present in Team Digitale strat-
egy. They have a comprehensive description of the
organizational structure, where they identify their IT
areas and their main business arctivities, such as sim-
plify interaction with the Public Administration, en-
hance user experience, promote an architecture based
on interoperability between public services.
2.2.3 Singapore CentEx for ICT
The Singapore Strategy commits to deliver intuitive
digital services that meet citizens’ needs, complete
government transactions in a paperless and presence
less way using any device (mobile, computer) at
any time (SmartNationSG, 2018). They internalized
knowledge and human resources with the specialized
technical skills in an in-house pool of resources, able
to take on innovative projects across the Government.
CentEx embraced areas of expertise, like IoT, Data
Science Application Design, Development and De-
ployment. In order to reduce costs and deliver IT
projects on time, the Singapore Government aims to
streamline platforms where possible and customize
where it is needed, meaning that they wish to en-
hance interoperability between systems and agencies.
They implemented the SGTS (Singapore Government
Technology Stack), a collection of digital services to
build their digital applications and reduce the time re-
quired to deploy new solutions. This allowed agen-
cies to focus on meeting citizens needs and deliver a
seamless, consistent and connected experience across
all government agencies. It adopted a “Once Only”
policy by providing the relevant data and requests
one time and sharing them with right public agencies
to address the situation. This means citizens must
feel confident and assured their data is secured by
the government. The MyInfo Initiative part of The
National Digital Identity, is a “once only” service,
meaning citizens filled their personal details automat-
ically in online forms one time. The Singapore Public
Administration had also developed internal services,
like WOGGA, a platform to monitor all government
digital services and identify gaps in service delivery.
Nectar, a PaaS, designed to host all government dig-
ital services. The APEX, a data sharing platform
that facilitates data-driven decision making and ser-
vice delivery for government agencies by exchanging
data securely through APIs. Enterprise Architecture
is present in Singapore’s CentEx, by having a clear
organizational structure and main business processes:
facilitate data-driven decision across the Public Ad-
ministration, to build shared platforms, integrate ser-
vices around citizens and business and run secure and
robust systems.
2.2.4 Comparative Analysis
The grounds for comparison focus on the objectives
these centers drew while they were operating, the
projects developed and how they were aligned with
the country’s digital strategy. While implemented in
governments with different structures they corrobo-
rate one another. In order to have clearer view of these
cases we summarized the most important information
in the following table.
Figure 1: Summary of the three cases observed (UK, Italy
and Singapore).
These digital centers of excellence are all collab-
orating with the public administration to help them
with their transformation. Acting as an in-house re-
serve of deep technical skills, in areas where inter-
nal capabilities are needed, they deal with highly
complex issues on short notice. They collaborate to
build platforms, standards guidelines and best prac-
tices and digital services Singapore, Italy and the UK
share capabilities such as Data Science, API oriented
ticAPP – Digital Transformation in the Portuguese Government
615

services development, Identity Management and Ap-
plication Development. However, Singapore is also
focusing on Artificial Intelligence, Sensors and IoT,
Cybersecurity, and ICT Infrastructure, and Geospa-
tial plans. The three approaches share two common
goals: On the one hand support the government in
digital transformation by investing on cross organiza-
tional communication and support by enforcing stan-
dards across public bodies; having reliable, fault tol-
erant, resilient and secure systems and motivating the
use of API’s for knowledge sharing across the Pub-
lic Administration. They organize themselves around
the stakeholders instead of the ministries and help
build common digital and data platforms thus increas-
ing the use of shared platforms, components and data
registers across government reducing redundant and
wrong information. All centers are attempting to
leverage data to support the public bodies in mak-
ing the best and most data-driven decisions, adopt-
ing big data and machine learning techniques. On
the other hand collaborate with public services to de-
liver seamless, simpler and secure services to citi-
zens, investing in once-only policies, to minimize the
frequency citizens are requested the same informa-
tion across public bodies, with the help identity ver-
ification platforms(Singapore’s MyInfo, Italy’s SPID
and UK’s gov.uk Verify). Italy goes one step further
by explicitly stating a mobile-first thinking, meaning
government services are designed so citizens can ac-
cess them at any time at their mobile device. So, we
can observe that even with distributed locations (Sin-
gapore - Southeast Asia, Italy- Southern Europe and
the UK - Northern Europe) and different political set-
tings these centers of digital excellence share similar
milestones, such as identity management, once-only
policies common platforms and promote data sharing
across the public administration, by handling complex
projects with tight deadlines. They differ in some of
the departments of digital fields they house but have
Data Science and Analytics and Application Devel-
opment. The following figure represents a quadrant
summarizing the scope and domain of IT and its ap-
plication across the Public Administration or in each
sector:
ticAPP shares the same motivation as the other
centers - to support the digital transformation pro-
cess of government areas by incorporating internal
knowledge and competencies and the development
of cross-government projects (Portuguese Council of
Ministers, 2018). Based on the comparative analy-
sis Italy’s Team Digitale is the closest case. Both are
under a prorogation regime, with the possibility of
being extended for a given time period, which hap-
pened in Italy. They’re both southern Europe coun-
Figure 2: Transversal vs Sector Application of Digital
Transformation in the Public Administration.
tries, meaning they share close political systems and
views, which influence the operation of these cen-
ters. But because the UK GDS inspired Team Digi-
tale, it holds valuable information to be incorporated
at ticAPP.
2.3 Frameworks and Methodologies
2.3.1 TOGAF
The Open Group Architecture Framework is an enter-
prise architecture framework, aiming to provide high-
level design concerning four architecture domains:
Business, Data, Application and Technology. In the
Business layer, we focus defining the business strat-
egy, governance, organization, and key business pro-
cesses of the organization The Architecture Develop-
ment Method, provides a way of working (a method)
for architects (Lankhorst, 2005). It is a cyclic and it-
erative process to build a holistic architecture of the
enterprise. ADM is a comprehensive method, mean-
ing it can be implemented in organizations of any
size and structure. It allows for integrating features
from other frameworks, like the Zachman’s Frame-
work (Schafrik, 2011). Zachman Framework pro-
vides a way to categorize them and TOGAF the means
to create the artifacts. TOGAF is closely related at
the strategic alignment, so it usually followes a Top-
Down Design approach.
2.4 Modelling Languages
2.4.1 Archimate
ArchiMate enables architects to describe, analyze,
and visualize the relationships among business do-
mains by using common language for describing the
design and flow of business processes, organizational
structures, information flows, systems, and infrastruc-
ture. It removes ambiguity brought by different stake-
ICEIS 2019 - 21st International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
616

holders. Its hosted by The Open Group and fully
aligned with TOGAF. It helps stakeholders to assess
the impact of design choices and changes. Archimate
approach on architectural models is based on a lay-
ered, service-oriented perspective, meaning the top
layers consume services delivered by the lower layers.
The concepts are similar between layers at an abstract
level but become finer grained as we reach deeper lay-
ers. Aside from a Motivational Layer, to help describe
the enterprise’s goals and drivers, Archimate distin-
guishes three main layers: Business, Application and
Technology. The Business layer offers products and
services to external customers, which are realized in
the organization by business processes performed by
business actors and roles.
3 PROPOSAL
Considering the comparative analysis 2 with the sum-
mary table 1 and the quadrant previously made 2, we
found that these centers of digital excellence share
similar objectives and knowledge areas. To answer
our problem, we aim to design ticAPP’s Business Ar-
chitecture. We will be adopting the TOGAF frame-
work and following a Top-Down Design approach.
The result will be a reference architecture, that may
also be considered when implementing other Centers
of Excellence. The solution is based on design sci-
ence research methodology, DSRM (Hevner et al.),
where an innovative solution (an artifact) is developed
in line with the problem domain, hence the artifact
we chose to develop is a Reference Enterprise Archi-
tecture for ticAPP, that can be used in future Digital
Centers of Excellence. This architecture encompasses
a collection of models, based on the ArchiMate to de-
scribe ticAPP in a holistic perspective. Because our
focus is on the Business domain, our target architec-
ture is about the people, processes, products and strat-
egy of ticAPP. We chose TOGAF framework to pro-
vide guidance on what viewpoints need to be mod-
eled. Based on official government documents, pre-
viously mentioned, and other information from Pedro
Viana, we were able to collect business statements for
ticAPP. This will enable us to create a baseline ar-
chitecture. The first architecture element to model is
ticAPP context. We need to understand who are the
stakeholders and how they relate to ticAPP.
Next we modeled an organizational view, depict-
ing an in-depth viewpoint of ticAPP’s internal struc-
ture. TicAPP will house 20 IT specialists, with one
appointed as coordinator/ director, depicted in the fol-
lowing image as the actor “Director X” with the role
of “ticAPP Director”. Resorting to additional infor-
Figure 3: Stakeholders and their relation to ticAPP.
mation, ticAPP should be divided in three depart-
ments: Architecture, Transformation and Data Sci-
ence, each with a team leader directly to the direc-
tor along with a project manager (Actor- “John Doe”
Role - “PMO”).
Figure 4: ticAPP’s Organizational Viewpoint Model.
From the previous diploma (Portuguese Council
of Ministers, 2018), we also collected information
about what activities ticAPP will perform. These are
performed by three departments. We identified five
services ticAPP delivers: Mantaining Information
Systems, Managing Digital Services, Project Man-
agement, Assisting the Public Administration with IT
Soltution (e.g Acquiring software/hardware) and Sup-
porting Data-Driven Decision through Data Science.
To understand what products ticAPP offers, we devel-
oped a Product viewpoint. It groups the services de-
livered by ticAPP by the value they offer to the stake-
holders. Each product must have a contract associ-
ated. Since Data Science deals with potentially sen-
ticAPP – Digital Transformation in the Portuguese Government
617
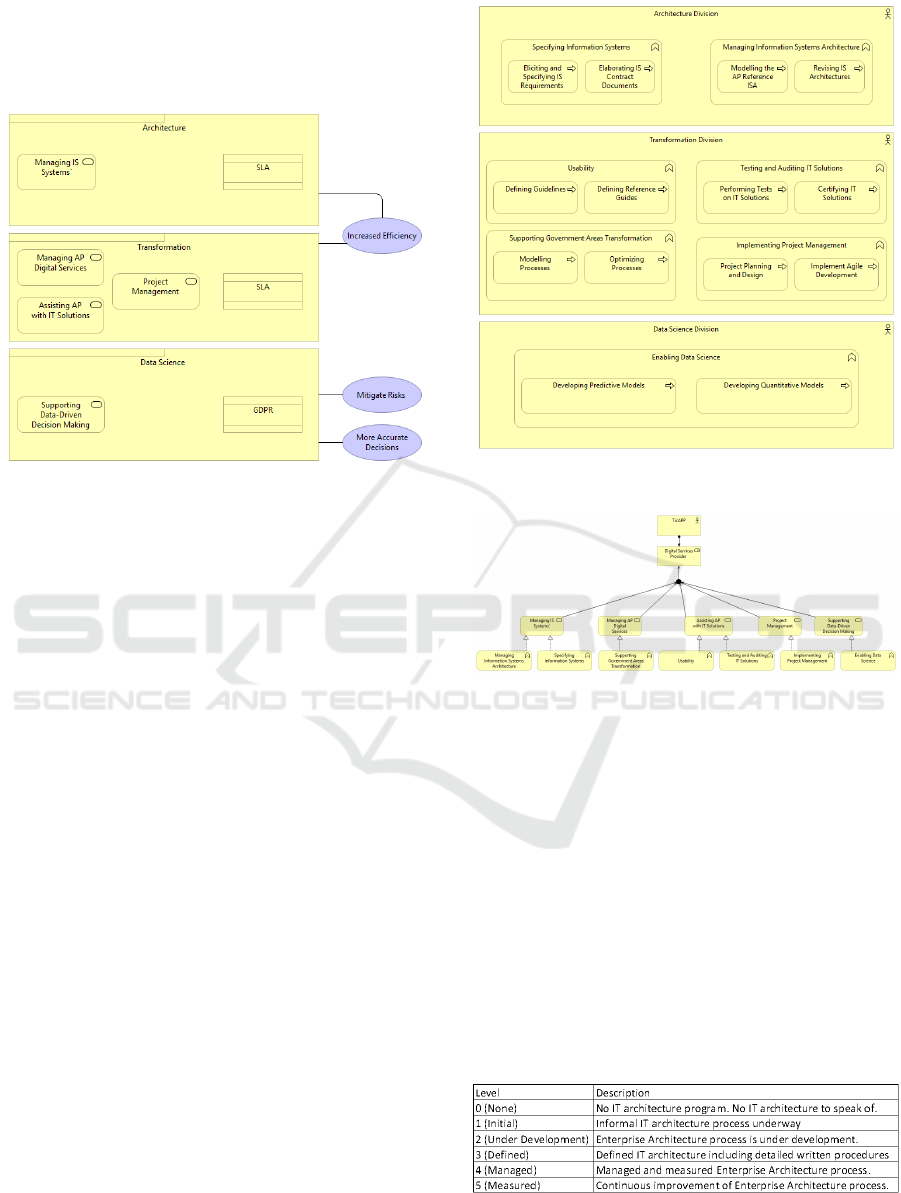
sitive data, we find it relevant to have contract, com-
mitting to GDPR compliance. As for architecture or
transformation projects, a Service Level Agreement
(SLA) should be drawn.
Figure 5: ticAPP’s Products.
Next we developed a model, showing how busi-
ness functions should be distributed across ticAPP.
The Architecture Department, specifies Information
Systems and manages their Architecture. The Trans-
formation department is responsible for publishing
guidelines and reference guides, to be adopted across
public administration, to increase coherence among
government portals and enhance user experience.
It also implements project management initiatives
across the Public Administration, supporting their
transformation by process modelling and optimiza-
tion. These means introducing techniques, such as
Agile development. They’re also in charge of testing
and auditing IT solutions across the Public Admin-
istration. From these activities we identified 3 ser-
vices. Lastly, the Data Science Department, in charge
of producing predictive models, for fraud detection
for example, that realize the service of contributing to
better data-driven decision.
TicAPP’s mission, i.e its role, is to provide digi-
tal services to the Portuguese Public Administration.
We considered relevant to link the business functions
of ticAPP to the services it delivers. This enables us
to observe what every department is in charge of de-
livering. From the services identified in Figure 5, we
developed a model depicting those relations.
4 EVALUATION
We propose a twofold evaluation model. First, we
need to assess its external quality, i.e the fitness for
Figure 6: Business Functions distributed by ticAPP’s struc-
ture.
Figure 7: Business Functions link to Business Services.
use of the architecture. These is necessary to under-
stand whether the architecture is a correct and com-
plete representation of ticAPP. The degree to which
the external quality is high or low is determined by the
stakeholders. Next, we will evaluate ticAPP’s matu-
rity using the ACCM (Architecture Capability Matu-
rity Model) framework, which is included in TOGAF.
ACCM solves the problem of managing change effec-
tively, by structuring the various practices into levels.
Each level represents an increased ability to control
and manage the development environment. The goal
of ACCM assessments is to enhance enterprise ar-
chitectures, identifying quantitatively weak areas and
to follow an improvement path for specific identified
gaps of the assessed architecture (TOGAF, 2018). We
Figure 8: ACCM Maturity Levels - (TOGAF, 2018).
will first calculate the maturity rating by obtaining a
ICEIS 2019 - 21st International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
618

weighted mean IT architecture maturity level. Next
we will calculate the percentage achieved at each ma-
turity level for the nine architecture characteristics
(TOGAF, 2018).
5 CONCLUSIONS
We have seen there is a great investment in dig-
ital transformation, to steer Public Administrations
from its silo-based structure to a more citizen ori-
ented one. Enterprise Architecture aims towards bet-
ter resource sharing, to enable efficient information
exchange across departments and to adopt flexible
frameworks. Successful EA programs are generally
strongly backed by the highest level of government.
We have presented Centers of Excellence in Public
Administrations from UK, Italy and Singapore. These
had great political backing and made use of shared
platforms. These house formerly scattered resources,
into single access points. Italy, UK and Singapore,
implemented Digital Centers of Excellence specializ-
ing in recent fields of IT, such as Data Science and
Application Design and Development. They lever-
age digital technologies, are share many similarities.
From the literature reviewed about other Digital Cen-
ters of Excellence, they share similar strategic goals
and perform the same activities. However, we found
no model or reference guide on how to set up one of
these centers. So, we designed ticAPP business archi-
tecture, as a possible reference architecture for other
Centers of Excellence in Public Administrations. Our
goal was to to develop an artifact, i.e a business ar-
chitecture model, for a consistent approach on how to
implement a Digital Center of Excellence. We fol-
lowed a Top-Down Design approach, based on TO-
GAF ADM methodology. We modelled viewpoints,
concerning the structure and core processes that sup-
port the services ticAPP provides. Our models, cover
a great scope and detail of the structure and operation
of ticAPP. Feedback from stakeholders, regarding the
quality of the models was positive and continuous im-
provements to the models will be made. This means
the models are fit for purpose, in a way that they repre-
sent a correct and complete representation of ticAPP.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by national funds through
Fundac¸
˜
ao para a Ci
ˆ
encia e a Tecnologia (FCT) with
reference UID/CEC/50021/2019 and by the European
Commission program H2020 under the grant agree-
ment 822404 (project QualiChain).
REFERENCES
Accenture (2013). Banking on digital: Enabling a dig-
ital first mindset. https://www.accenture.com/ae-
en/
∼
/media/Accenture/Conversion-Assets/DotCom/
Documents/Global/PDF/Technology\
7/Accenture-
Interactive-Banking-Enabler-Digital-Operating-
Model.pdf.
Alonso, I. A. (2010). Enterprise architecture responsibilities
and people roles.
CTIC (2017). ICT Strategy 2020. https://www.tic.gov.pt/
documents/2018/CTIC\ TIC2020\ Estrategia\ TIC\
EN.pdf.
GOV.UK (2018a). About the government digital service.
https://gds.blog.gov.uk/about/.
GOV.UK (2018b). Our governance. https://www.gov.
uk/government/organisations/government-digital-
service/about/our-governance.
Lankhorst, M. (2005). Enterprise Architecture at Work:
Modelling, Communication and Analysis. Springer.
McSweeney, A. (2016). Digital transformation and
enterprise architecture. https://pt.slideshare.
net/alanmcsweeney/digital-transformation-and-
enterprise-architecture.
Portuguese Council of Ministers (2018). Resoluc¸
˜
ao do con-
selho de ministros n.
o
22/2018. Di
´
ario da Rep
´
ublica
n.
o
47/2018, S
´
erie I de 2018-03-07, (22/2018):1185 –
1186.
Schafrik, F. (2011). A practical guide to develop-
ing enterprise architecture. https://www.ibm.
com/developerworks/rational/library/enterprise-
architecture-maximum-value/index.html.
SmartNationSG (2018). https://www.smartnation.
sg/docs/default-source/default-document-
library/dgb\ booklet\ june2018.pdf.
TeamDigitale (2018). Report digital transformation team.
https://teamdigitale.governo.it/assets/pdf/Report\
DigitalTransformationTeam\ 09\ 30\ 2018.pdf.
TOGAF (Retrieved December 2018). Architecture maturity
models.
ticAPP – Digital Transformation in the Portuguese Government
619
