
Expert Competitive Traffic Light Optimization with Evolutionary
Algorithms
Yann Semet
1
, Benoit Berthelot
2
, Thierry Glais
3
, Christian Isb
´
erie
2
and Aur
´
elien Varest
2
1
Thales Research and Technology, 1 avenue Augustin Fresnel, Palaiseau, France
2
CDVIA, 2 Rue Suchet, Maisons-Alfort, France
3
Thales Communications and Security, Rue de la Mare aux Joncs, Br
´
etigny-sur-Orge, France
Keywords:
Traffic Lights, Optimization, Evolutionary Algorithms, Genetic Algorithms, Artificial Intelligence, Simula-
tion, Calibration, Experts.
Abstract:
We present a complete system to optimize traffic lights green phases and temporal offsets based on a combina-
tion of microscopic simulation and black box, evolutionary algorithms. We also report the outcome of an AI
versus experts comparison workshop conducted with our algorithm and seasoned experts from a specialized
traffic engineering office. Experimental results indicate that the proposed algorithmic scheme significantly
outperforms expert efforts. Our system entails a memetic (genetic+gradient) calibration module to adapt the
Origin/Destination (O/D) matrix to current traffic conditions, an inoculation procedure to incorporate exist-
ing traffic light programs, genetic multi-objective optimization capabilities and sound metrics. Experiments
are conducted over several real world datasets of operational sizes from the Paris outskirts and various other
French urban areas. Our experimental outcome is threefold. First, we report the success of the memetic
calibration module in adjusting the simulator’s O/D matrix to a point with variation levels corresponding to
recorded sensor data. Second, we confirm the ability of the system to obtain significant gains on that sound
basis: gains ranging from 15% to 35% are consistently reached on both traffic jams reduction and pollutant
emissions. Most importantly, we report the outcome of the comparison workshop: a formalized methodology
followed by experts to manually optimize traffic lights, iterative experimental logs tracing the application of
that methodology to two real world cases and comparable results obtained by the algorithm on the same cases.
Results indicate that the AI module performs significantly better than experts in both speed and final solution
quality.
1 INTRODUCTION
Urban planning is a daunting task. Traffic light opti-
mization is one lever to improve the quality of life for
all citizens: less traffic jams means more time, less
stress and cleaner air. But the task is ludicrously diffi-
cult and infrastructure managers or specialized engi-
neering offices need help to reduce the costs and in-
crease the efficiency of traffic light plans design. Ar-
tificial Intelligence can help by providing computa-
tional support in exploring the space of possibilities.
Traffic engineers are usually equipped with so-
phisticated command and control systems that pro-
vide them with substantial data streams and action
possibilities. They are also pressured to pursue var-
ious, varying and sometimes antagonistic objectives
dictated by the needs of the local population, the par-
ticularities of their traffic network and political leader-
ship or sustainable concerns. Making a smart an effi-
cient mapping between complex objectives and com-
plex decision variables with hidden relationships or
correlations is precisely what evolutionary algorithms
can offer. This artificial intelligence technique, com-
ing from the fields of optimization and machine learn-
ing can indeed quickly and reliably figure out the right
elements of solution necessary to achieve what the in-
frastructure engineers want.
In this paper, we present an integrated, global ap-
proach to help experts optimize traffic light settings
on a sound, validated basis. It is organized as fol-
lows: after a brief literature review, we detail the var-
ious components of our system and then present ex-
perimental results on real-world benchmarks. Most
importantly, we conclude with the report of a compet-
itive comparison workshop between actual traffic ex-
perts and our algorithm in order to confirm the ability
Semet, Y., Berthelot, B., Glais, T., Isbérie, C. and Varest, A.
Expert Competitive Traffic Light Optimization with Evolutionary Algorithms.
DOI: 10.5220/0007732701990210
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Vehicle Technology and Intelligent Transport Systems (VEHITS 2019), pages 199-210
ISBN: 978-989-758-374-2
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
199

of this AI-based approach to outperform humans on
this specific mathematical but very complex and sub-
tle task.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Many attempts at optimizing traffic light settings with
various flavors of evolutionary algorithms have been
made, underlining both how promising the approach
is and how important the problem has always been.
Two early examples can be found in (Foy et al., ;
Rouphail et al., 2000). As early as 1992 indeed, Foy,
Benekohal and Goldberg (Foy et al., ) applied bit-
string Genetic Algorithms to the optimization of sig-
nal timing and obtained consistent results in decreas-
ing wait time on variants of a small test case with
four junctions. In 2000, (Rouphail et al., 2000) tried
to minimize queue lengths on a Chicago,IL test case
with 9 signalized intersections using CORSIM and
Transyt.
More recently, (Stevanovic et al., 2008) conducted
a rigorous study with genetic algorithms searching a
sophisticated, complete representation of traffic light
plans tried against a traffic model run by microscopic
simulator VISSIM. Experiments were conducted on
two US benchmarks: Park City, UT and Albany, NY.
One particular focus of the study was to see how op-
timizing parameters in sequence or all at once influ-
enced final solution quality. Optimized plans were fa-
vorably compared to existing plans and to plans pro-
duced by SYNCHRO but with gains limited in ampli-
tude.
(Sanchez-Medina et al., 2008) applied evolution-
ary algorithms to the traffic light optimization prob-
lem with a sophisticated gray-code based encoding
of phases. Plan quality was evaluated with an ad
hoc Cellular Automaton based microscopic simulator
built after the Kraus car following model and run on a
Beowulf cluster. Two rather large test cases and asso-
ciated data were procured from the local councils of
Saragossa and Santa Cruz de Tenerife and significant
gains were obtained with respect to existing traffic
light plans : around 10% on the first benchmark even
though it had little traffic and therefore room for im-
provement and up to 30% on the second one although
with very significant variance between solutions.
Very recently, (P
´
eres et al., 2018), following sev-
eral studies over preceding years (e.g. see (Garc
´
ıa-
Nieto et al., 2011) or (Garc
´
ıa-Nieto et al., 2013))
tackled real-world cases with evolutionary algorithms
with a particular focus on multiobjective optimiza-
tion and sustainable concerns. Using SUMO, an
open-source traffic simulator, as the objective func-
tion provider, they obtain large and consistent gains
on three real-world benchmarks in Montevideo. They
offer an interesting benchmark comparison of var-
ious classical Multi-Objective Evolutionary Algo-
rithms applied to the problem and shed interesting
light on edge prioritization.
Other studies worth citing (Hu et al., 2015;
Garc
´
ıa-Nieto et al., 2011; Jin et al., 2017; Jin and
Ma, 2014) make use of various computational tech-
niques related to evolutionary algorithms such as Par-
ticle Swarm Optimization in varied operational con-
texts.
There are many ways in which traffic regulation
can be approached with computational support. With
the recent rise of global interest in Machine Learn-
ing, on can note observe an increasing number of at-
tempts at using Reinforcement Learning to approach
the problem with a more dynamic orientation (e.g.
see (Chin et al., 2012; Fakult
¨
at, 2006; Marsetic et al.,
2014; Salkham et al., 2008) and obtain very encourag-
ing results with Q-learning, policy gradients or actor
critic methods.
Most aforementioned approaches make use of
microscopic simulation as the objective function
provider. For any operational application to be con-
sidered or more generally, for any trust to be placed
in the results, care must be taken that simulators and
their models are realistic enough. To that end, cal-
ibration is necessary. Calibration is the problem of
adjusting simulation parameter values so as to maxi-
mize the predictive capability of the simulator. Simu-
lation parameters include physical variables (e.g. ve-
hicle weights and length), behavioral and kinetic vari-
ables and, most importantly, demand modeling with
O/D matrices and dynamic routing parameters. Cal-
ibration is absolutely critical but is often overlooked
in studies that are focused on the main optimization
problem that is difficult enough in itself. There is,
however a significant but rather separate body of work
on that issue. (Paz et al., 2015; Chu et al., 2003) for
example, offer very interesting systematic methodolo-
gies to address all aspects of the calibration problem.
Other approaches, such as (Toledo and Kolechkina,
2013), focus on specific calibration subproblems with
adequate mathematical tooling.
Overall, although many traffic light optimization
studies have been conducted, most of them, while of-
fering interesting insight and convincing results, seem
to be lacking in at least one aspect of this deceptively
complex problem: validation benchmarks, particu-
larly in early studies, are often small and/or unreal-
istic, simulators may have weak or no calibration and
optimization sometimes lack essential aspects such as
multi-objective capabilities or statistical validation of
VEHITS 2019 - 5th International Conference on Vehicle Technology and Intelligent Transport Systems
200

its results. We try to offer a comprehensive algorith-
mic proposal with at least one form of answer for all
key aspects of the problem.
3 SYSTEM OUTLINE AND
ALGORITHMS
3.1 Overview
Our system’s purpose is to try to find optimal or
near optimal values for traffic light plan settings. To
that end, we follow the classical evolutionary black-
box approach which consists in associating a genetic
search engine with a simulator that provides objec-
tive function values. Having a well calibrated simula-
tor is extremely important in such a context because
by providing short term world evolution prediction
for particular individuals to feed the objective func-
tion, the simulator is ultimately and almost entirely
responsible for solution quality. That is the reason
why, as outlined in figure 1, our system is composed
of three main separate boxes whose underlying prin-
ciples and implementation we detail below : simula-
tor, optimizer and calibrator. The input data comes
from the field (sensors providing flow or occupancy
rate measurements and/or existing traffic light plans).
The output is of course, a suggested near optimal traf-
fic light plan for the input traffic model. More detailed
design information, along with experimental valida-
tion of choices can be found in (Damay, 2015).
Figure 1: Global system architecture.
3.2 Genetic Search and Multi-objective
Capabilities
Genetic and Evolutionary Algorithms (Goldberg,
1989; Eiben and Smith, 2003) are mathematical pro-
cedures created in the field of Artificial Intelligence
to solve complex problems by following a biological
metaphor with a few essential aspects : genetic en-
coding, random variations (mutation and crossover)
and survival of the fittest. By using selection pres-
sure to intelligently explore the spaces of possible so-
lutions, engineers have created very powerful algo-
rithms which can favorably solve very difficult real
world problems. Evolutionary algorithms, besides be-
ing mathematically efficient, happen to have several
practical advantages: they provide “anytime” solu-
tions, are highly paralellisable, straightforward to im-
plement, need very little information about the prob-
lem and can be hybridized naturally with specific al-
gorithms or expert knowledge.
Another key advantage of evolutionary algorithms
is that, being population based, they are naturally fit
for multi-objective search in the Pareto sense. By that
we mean the ability to provide the entire set of so-
lutions, or a good approximation of that set, which
are non Pareto-dominated. Practically, it means that
the algorithm is able to identify in a single run all
good solutions which represent interesting compro-
mises for the decision maker facing antagonistic ob-
jectives (e.g. cost vs. engine power when consid-
ering a new car). Very well-known multi-objective
variants of evolutionary algorithms such as NSGA-
II (Deb et al., 2002), SPEA2 (Zitzler et al., 2001),
IBEAx (Zitzler and K
¨
unzli, 2004) or MOEAD (Zhang
and Li, 2007) can indeed provide that service very ef-
ficiently.
Traffic light plan design is a typical optimization
problem : variables are green phases durations and
temporal offsets, constraints are given by law or se-
curity considerations and limit the possible values for
the variables and objective functions are straightfor-
wardly given by traffic fluidity metrics (waiting time,
timeloss, queue length, etc.) or pollutant emissions
measurements (CO, CO2, NOx, PMx, HC, fuel con-
sumption, noise, etc.). Experimenting directly in the
field is of course impossible for obvious security and
public relations reasons so one has to resort to mathe-
matical models or simulators. Vehicular traffic being
a very complex process with significant human and
cognitive components, microscopic simulation is of-
ten the most reasonable option to be sure to take intri-
cate interaction phenomena properly into account.
We therefore have a classical black-box setting,
which we tackle straightforwardly with an evolution-
Expert Competitive Traffic Light Optimization with Evolutionary Algorithms
201

ary algorithm and simulator combination. So as not to
reinvent the wheel and benefit from good implemen-
tation and out of the box parallel computing, we use
the excellent DEAP library (Distributed Evolutionary
Algorithms in Python (Fortin et al., 2012)).
Our particular choice of basis algorithm went to
NSGA-II after an extensive experimental campaign
with statistical significance testing for algorithmic
variants, components and parameter settings. The
fundamental multi-objective mechanism of NSGA-
II uses a combination of crowding distance non-
dominated sorting of its population to ensure diver-
sity preserving and exploration in the Pareto sense.
We use a traditional evolutionary sequence and the
structure of our algorithm follows the NSGA-II ba-
sis, which we use in either mono-objective or multi-
objective mode.
3.3 Problem Representation, Variation
Operators, Metrics
We adopt a very straightforward solution encoding
strategy. As detailed in figure 2, we just use vec-
tors of integer values that represent, junction by junc-
tion successively, green phases durations and tempo-
ral offsets.
Figure 2: Problem representation. The small schematic
zone above contains three junctions (A,B and C) situated
along and aside a main axis of traffic. The corresponding
genome encodes green phase durations for A’s 3 phases and
B and C’s two phases as well as relative temporal offsets for
all 3 junctions.
Variation operators work on that representation di-
rectly. Crossover is a classical two point scheme.
Our mutation is a Gaussian variation whose standard
deviation is controlled dynamically with a sigmoid
swap scheme as introduced in (Semet and Schoe-
nauer, 2006) and used in (Marceau Caron, 2014).
This allows to tune the exploration/exploitation trade-
off by controlling how ”disruptive” the mutation ra-
dius (in our case the standard deviation of the Gaus-
sian variation) shall be over the course of evolution:
σ
mutation
=
(
α if t < t
0
β + 2 × (α − β) ×
1
1+exp
γ(t−t
0
)
if t ≥ t
0
Initialization finally, although not technically a
variation operator, is, as outlined in (Semet and
Schoenauer, 2006), an essential building block of the
overall algorithm. We found that using an “inoc-
ulant”, which means a heuristically built individual
based on the existing traffic light plan was useful to
achieve rapid early search, which is a particularly de-
sirable trait in this fast paced operational context. The
initial population is therefore built as a mix of inoc-
ulants varied with mutation and purely random indi-
viduals.
3.4 Microscopic Simulation and
Calibration
3.4.1 Simulator
To substantiate the objective function, we use the
open-source microscopic traffic simulator SUMO
(Krajzewicz et al., 2012) developed by DLR. In
their own words, taken from SUMO’s homepage
(http://http://sumo.sourceforge.net/) :
”Simulation of Urban MObility”, or ”SUMO”
for short, is an open source, microscopic,
multi-modal traffic simulation. It allows to
simulate how a given traffic demand which
consists of single vehicles moves through a
given road network. The simulation allows
to address a large set of traffic management
topics. It is purely microscopic: each vehicle
is modeled explicitly, has an own route, and
moves individually through the network.
.
SUMO is a very powerful and versatile tool that
provides rigorous traffic representation and easy inte-
gration with computational support algorithms. It is
also very fast, which is particularly precious for pop-
ulation based stochastic search, which requires many
computations of the objective function.
Our SUMO traffic model is an O/D matrix that
is turned into individual routes by shortest path rout-
ing utilities provided with the software (od2trips and
VEHITS 2019 - 5th International Conference on Vehicle Technology and Intelligent Transport Systems
202

duarouter). Some attempts at dynamic equilibrium
finding and routing optimization have also been found
useful and were performed with the duaIterate script
and the Cadyts external utility (Flotterod et al., 2011).
Our GIS based road network was imported and ad-
justed, which is a long, tedious, but absolutely critical
step for any realism to be achieved, with netconvert
and netedit.
3.4.2 Memetic Calibration
One specificity of our algorithmic system is the cal-
ibrator module. Achieving realistic simulation is
extremely important, both for fundamental solution
quality and as a caution of trust for the end-user who
wants guarantees about how well her field is mod-
eled by the computer. To that end, much effort was
spent in trying to procure the best possible O/D ma-
trix. Beyond dynamic routing and calibration outlined
above, specific R&D efforts were conducted to de-
velop an optimization module for that purpose. Ex-
periments, reported in (Damay, 2015) revealed that
the best solution was an hybrid algorithm combining
genetic search and a specific, state-of-the-art gradient
algorithm. Such an hybrid is usually called a Memetic
algorithm and typically tries to combine the benefits
of global stochastic search with local optimization to
refine the solution.
Uncharacteristically, this particular flavor uses
gradient to optimize the starting point (either a zero
or heuristically provided O/D matrix) and produce an
inoculant for the genetic search that will find both lo-
cal and global improvements. The genetic part of the
calibrator is a standard (λ + µ) evolutionary scheme
with Gaussian mutation. The gradient part is an ex-
tended version of the algorithm introduced in (Toledo
and Kolechkina, 2013), which performs steepest de-
scent on matrix coefficients in the error space. For
both parts, error or fitness is measured by comparing
obtained simulated counts with sensor history. Impor-
tantly, considered sensor values can either be averages
or specific values. This allows to serve, at will, two
functional purposes: aiming for robust values with
good generalization ability or being as precisely close
as possible to what is currently happening in the field.
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
4.1 Benchmarks
Validation experiments have been conducted on sev-
eral real-world benchmarks corresponding to regula-
tion zones of medium size, usually a well delimited
neighborhood, portion of the dense center of a city.
Our main test cases were :
• A portion of the downtown area in Rouen, with a
mesh-like network of 10 signalized intersections
• A portion of the downtown area in Strasbourg,
with 9 signalized junctions, one of them being
shared with a tramway line with absolute priority
• A large linear portion of the immediate north-
ern outskirts of Paris with three intersecting high
speed axes of traffic which has 12 to 20 signalized
intersections, depending on the instances.
A screen capture of the typical Rouen benchmark
is given in figure 3 with sensors and O/D source/sinks.
All benchmarks were complete with digitized road
network, sensor data over several months and/or turn-
ing proportion studies and currently used traffic light
plans.
Figure 3: The downtown Rouen benchmark map. Blue dots
represent O/D entry/exit points, red ones sensors.
4.2 Calibration Results
The first O/D matrix we used for the Rouen bench-
mark was constructed heuristically using a few mea-
sured flow rates and turning proportions studies. In
order to refine it against historical sensor data, we
defined a realism goal by computing statistics on a
carefully chosen subset of sensors. We observed that
within the considered morning peak hours, values for
individual sensors varied within a plus or minus 30
% range over average values. We therefore set as an
objective that the optimized O/D matrix should pro-
duce simulated counts, not only as close as possible
to the average corresponding counts (for each sen-
sor) on average (over all sensors) but that the aver-
age of variances for all sensors should be below the
30% limit as observed in the data. This simple cri-
terion proved difficult to reach and only the memetic
Expert Competitive Traffic Light Optimization with Evolutionary Algorithms
203

hybrid algorithm we proposed was able to reach that
target with a 28% average variance. The heuristic ma-
trix alone yielded
˜
60% variance, gradient alone (as in
(Toledo and Kolechkina, 2013)) yielded 41% and ge-
netic search alone yielded 32%.
Figure 4 illustrates the result obtained by the
memetic algorithm with a star diagram: each branch
of the star shows a specific sensor and the point on
that axis represents the obtained simulated count for
that sensor on a normalized scale valued at 1 if sim-
ulated count exactly equals the average of historical
sensor data. According to our criterion, points should
therefore lie between 0.7 and 1.3 on all axes, which is
represented by the blue and black circles respectively,
the red circle representing the ideal solution. As can
be seen in the figure, while correct on average over all
sensors, our solution has room for improvement on
several underused sensors.
Figure 4: Calibration results star diagram. Each branch rep-
resents a sensor, whose simulated count should reach the
red circle (normalized value of 1) corresponding to the av-
erage measured value. This solution, the best we obtained,
corresponds to an average variance of 28%.
4.3 Optimization Results
4.3.1 Experimental Setup
In order to assess the ability to produce substantial
and reliable gains, we follow the following experi-
mental guidelines:
• All evolutionary algorithm run results are aver-
aged over at least 11 random seeds
• All simulator runs are averaged over 10 random
seeds, a value empirically determined to trigger
sufficiently low variance
• Simulator runs usually have a warm-up time of 5
minutes and metric measuring time window of 20
minutes
• Algorithmic variants, components or parameter
settings are chosen from using the Wilcoxon
signed test for statistical significance
Typical parameter values are as follows: popula-
tion size 12, mutation probability 0.5, crossover prob-
ability 0.25, 100 generations, minimum variable value
1, maximum 120, initial sigma value 10.
4.3.2 Mono-Objective Results
In the following section, we report results obtained on
the Rouen benchmark. Similar results have been ob-
tained on the other test zones. The main objective of
traffic light optimization being to reduce traffic jams,
mono-objective results are related to traffic fluidity
metrics. Many possibilities exist to quantify this, we
chose to use a weighted average of waiting time (total
amount of time spent by vehicles under epsilon speed)
and total number of processed vehicles so as to avoid
solutions where traffic is prevented from entering the
zone by over-saturating entry junctions.
Figure 5 illustrates the typical optimization curve
we obtain on both morning and evening peak hours,
with average and maximum gain (which means min-
imum metric value). Gains of up to 28% in waiting
time are obtained for the morning peak at end of the
run. One notices that variance is limited, making for a
robust result and that, thanks to the anytime property
of evolutionary algorithms, strong gains of 15 to 20
% can be obtained very quickly, as soon as generation
10. As one can see, the evening peak is much more
difficult, maximum gain is only around 12% in that
case.
4.3.3 Multi-objective Results
Thanks to the HBEFA and Harmonoise models pro-
vided with SUMO, one can pursue other objectives
than traffic fluidity: pollutant emissions (CO, CO2,
NOx, PMx, HC, fuel consumption) and noise. Some
of these objectives are correlated, some are antago-
nistic with varying degrees. See (Damay, 2015) for
extensive analysis and experimental results on all ob-
jectives. For the sake of brevity and simplicity, we
report results obtained on the illustrative waiting time
/ CO2 couple. The top-right corner of figure 6 shows
the evolution path followed by the population towards
the Pareto front obtained at the end of the run, one
clearly sees both a strong direction, aiming at the bot-
tom left corner, and a maintained variety of choices
along the front.
VEHITS 2019 - 5th International Conference on Vehicle Technology and Intelligent Transport Systems
204

Figure 5: Mono-Objective (waiting time) results obtained
on morning and evening peak hours.
Zooming in on the obtained Pareto front in fig-
ure 6, one can pick four distinct illustrative solutions
A,B,C and D. A and B are extremal solutions, respec-
tively excellent in waiting time and CO2. C and D
offer two different compromises.
Figure 6: Zoom on the Pareto fronts. 4 representative points
are chosen along it: 2 extremal ones (A and B) and 2 com-
promises (C and D).
Finally, one gives corresponding gain figures : up
to 38% in waiting time (point A) and 24% in CO2
(point B). Point C has 32% gain in waiting time and
13% in CO2. Point D offers 16% and 18% respec-
tively. One notices that optimizing seems to be sig-
nificantly harder and that going from C to D for ex-
ample has a huge cost in waiting time for a limited
CO2 benefit.
4.3.4 Drawing Lessons with Reverse
Engineering
A very interesting characteristic of straightforward
black-box search, where one manipulates decision
variables directly, is that the result can be interpreted
immediately by experts, who can start an analysis pro-
cess to try to understand why the settings proposed
by the algorithm are efficient. This process, based
on the fact that the outcome of the optimization algo-
rithm is interesting in itself, can bring a lot of useful
information by shedding light on the specifics of the
field or by experimentally confirming counterintuitive
ideas. All that can help improve or adjust heuristics
and expert thinking. This reverse engineering process
is not always easy or necessary but it is almost sys-
tematically informative. We give here a simple ex-
ample of solution interpretation to illustrate both the
surprisingly accurate ability of evolutionary search to
detect opportunities in the objective function search
landscape and the type of methodological conclusion
one may draw from observing, a posteriori, building
blocks of the optimized solutions.
Our example focuses on a specific junction in the
benchmark. It is situated along an important axis
of traffic and has three main successive phases in
its traffic light plan. The first one is for the main
north/south axis, going straight in both directions, the
second phase is for vehicles turning left coming from
that main axis and onto the perpendicular, secondary
axis and the last phase is for the secondary axis, go-
ing straight. The initial, expert provided, traffic light
plan had values, for the respective phases, of [29 12
21]. The optimized plan suggests [20 5 20]. By ob-
serving traffic, one quickly understands why. First
and foremost, there is a significant loss of green time
on the first phase : the light remains green long af-
ter all vehicles have been processed. Secondly, very
few vehicles use the left turn phase. Finally, the flow
of vehicles on the secondary axis is steady and prop-
erly handled. The algorithm has therefore managed
to make the right decisions both by implicitly making
these observations and by adequately sizing the cor-
responding changes.
The methodological conclusion for experts, which
confirms what we have seen on other similar cases is
that one of the most efficient optimization lever, as
opposed to focusing on green splits, consists in re-
ducing unnecessarily long green times to decrease cy-
cle length so as to process more cycles and therefore
more vehicles in a given time window. In our small
example, saving 17 seconds of cycle length procures 3
additional full cycles over the metric measuring time
window.
Expert Competitive Traffic Light Optimization with Evolutionary Algorithms
205

4.4 Additional Results
In order to further substantiate and illustrate the com-
parison between expert and algorithmically computed
settings, we synthetically report below results ob-
tained in other studies we conducted on strongly re-
lated traffic problems.
4.4.1 Traffic Conditions Classification
A critical problem in traffic regulation is to be able to
identify the currently ongoing type of traffic episode
in order to trigger the right plan in a portfolio of pre-
computed options. This is essential in order to avoid
incorrect regulation, which means using a peak hour
plan during off peak hours or vice-versa, and the ensu-
ing consequences on waiting time and pollutant emis-
sions.
As can be seen in figure 7, our algorithm, in that
case a patented combination of optimization and ma-
chine learning, is able to produce a surprisingly com-
pact and accurate decision tree which performs better
than expert provided classification criteria based on
field observation and experience. Estimated gains are
indeed of 264 hours of incorrect regulation over reg-
ular work days in a year, which correspond to more
than 10% of the total regulation time. Through re-
verse engineering analysis, this result also allowed to
correct significant misconceptions about peak hours
starting and end times.
Figure 7: Compact and accurate algorithmically produced
classification tree for traffic episode classification.
4.4.2 Adaptive Traffic Lights
Adaptive traffic lights are based on modern con-
trollers that adjust their plans dynamically according
to on-line sensor feedback. This form of dynamic
regulation is very efficient when allowed by available
equipment but rather difficult to parametrize properly.
In a separate preliminary study, publication pending,
we proposed to genetically optimize such dynamic
controllers based on decision trees. As a preliminary
trial, we only optimized thresholds (on sensor data)
and green phases adjustment values on an otherwise
fixed tree. We intend to apply Genetic Programming
on tree structure exploration in further work.
Experiments were conducted on a benchmark of
three successive intersections with a three hours sim-
ulation time line enriched with three events (simu-
lated accidents obstructing lanes for a certain dura-
tion at distinct timestamps) to assess the adaptive ca-
pacity of the dynamic controller. Comparisons, re-
ported in figure 8 were made between a static plan,
a dynamic plan whose weights and thresholds were
set manually by an expert, and the genetically en-
gineered plan. Results show that the expert tuned
plan performs only slightly better than the static, non-
adaptive plan, while the the decision tree with geneti-
cally optimized thresholds procures a very significant
and promising gain of 34% in waiting time.
Figure 8: Results of the comparative benchmark for dy-
namical control: algorithmically optimized decision trees
largely outperform expert provided trees. The x-axis shows
simulation time steps, the y-axis total accumulated waiting
time. The blue and green curve (top) show the static and
expert plans respectively and the red curve (bottom) shows
the results of the genetically optimized tree.
5 EXPERTS VERSUS
ALGORITHMS
This section details the benchmarking experiment we
conducted to compare the efficiency of traffic light
setting efforts as they are usually performed by ex-
perts to those automatically obtained with our algo-
rithm. We introduce the actual experts who com-
mendably accepted to do this with us, outline their
methodology and report comparative results on two
test zones.
VEHITS 2019 - 5th International Conference on Vehicle Technology and Intelligent Transport Systems
206

5.1 Meet the Experts
This work was conducted with three experts from CD-
VIA, a French traffic engineering office specialized in
mobility, traffic analysis and optimization, measure-
ment and modeling. Created in 1984 by Christian Is-
berie, M. Eng., it now employs a total of 35 engineers
with several offices across the country. CDVIA works
with town councils, cities, local communities or in-
frastructure managers to help them analyze, predict
and design in all mobility related matters. CDVIA is
particularly specialized in traffic flow modeling and
regulation based on macro, micro or mesoscopic sim-
ulation. In constant search of innovative tools and
approaches, CDVIA uses both cutting-edge technol-
ogy and field-honed expertise to tackle large scale
study cases such as the airport platform for Charles
de Gaulle in Paris or the Conakry peninsula project
for the Guinean ministry of transportation.
Christian Isb
´
erie, M. Eng., CDVIA founder and
traffic regulation expert has 35 years of experience in
mobility engineering. After founding the company
as a local, individual consulting business, he gradu-
ally modernized it and steered its growth into a full
fledged engineering company with contracts all over
the country. Besides management duties, he provides
traffic-related expertise and encourages innovation as
well as the adoption of modern technologies particu-
larly in data collection and traffic simulation.
Benoit Berthelot, M. Eng., project manager, has
10 years of experience in mobility and traffic regula-
tion related studies and has command over all aspects
of CDVIA’s business areas : field based traffic mea-
surement, mobility modeling tools and urban traffic
simulation.
Aur
´
elien Varest, M. Eng., senior consultant, has
5 years of experience. He graduated with and M. Eng.
from the National School of Geographical Science
Engineers and obtained an additional M. Sc. in Ur-
ban Planning and Information Sciences from the City
of Paris Engineering School. Specialized in traffic en-
gineering and GIS based traffic simulation, he is also
contributing to internal research and development ef-
forts. He has conducted over 70 mobility studies for
CDVIA so far.
5.2 Formalized Expert Methodology
The experts shared their methodology for optimizing
traffic lights in a medium sized urban area with us. It
was formalized through an extensive, procedure ori-
ented discussion to produce this unique set of explicit
steps that is most likely largely followed, more or less
consciously, by numerous other experts. This knowl-
edge is widely transverse but it is usually guarded
or encapsulated by personal field-based expertise or
intuition and oral tradition, leading to pitfalls such
as subjectivity, variability or wishful thinking. The
coarse grained methodology is as follows. Intricate
details, specific principles or tools cannot be shared
for obvious industrial secrecy reasons.
5.2.1 Preamble
We suppose that three aspects of the problem are
kept constant: the infrastructure cannot be modified
to achieve better traffic (e.g. by adding a lane), the
type of ongoing traffic is considered unique and fixed
(e.g. morning peak hours) and traffic light plans are
considered static (no on-line adaptation in relation to
sensors) and fixed in structure, which means that no
changes are allowed besides green phase durations
and relative temporal offsets (phases cannot be added
or removed or see their order changed for example).
The methodology proceeds in four major steps,
usually in the following order, although all steps are
not systematically used and loops can be necessary
: 1) Global Static Analysis, 2) Cycle Length Opti-
mization, 3) Green Split Optimization, 4) Temporal
Offsets and Junction Coordination.
5.2.2 Global Static Analysis
A global analysis is conducted for each individual
flow controlled by a traffic light by comparing theo-
retical demand (vehicle flows pondered by the kind of
movement (straight, turn left, etc.)) and flow capac-
ity, which is a product of current corresponding green
time and number of implicated lanes. The resulting
vector provides a coarse grain analysis of which flows
are in need of more green time and those who have
too much. This step can also be used to provide a first
heuristic traffic light plan based on making, at each
intersection, green splits proportional to relative de-
mands for each flow.
5.2.3 Cycle Length Optimization
If the considered junction is under capacity, shorten-
ing the cycle will help reduce queues and will increase
fluidity. On the contrary, saturated junctions can ben-
efit from longer cycle durations to prevent transmis-
sion of part of the queue from one cycle to the next.
When modifying cycle length, care must be taken
to keep green splits unmodified. In dense urban ar-
eas, shorter cycles are preferred, notably to facilitate
pedestrian traffic.
Expert Competitive Traffic Light Optimization with Evolutionary Algorithms
207

5.2.4 Green Split Optimization
To adjust green split within an intersection, one usu-
ally goes through the following steps:
1. Check all lanes and order them by degree of con-
gestion (queue length, number of unprocessed ve-
hicles in one cycle, etc.)
2. Relate ordered lanes to existing green phases in
the current plan
3. Identify phase couples with one “rich phase” (un-
der capacity) phase and one “poor” phase (satu-
rated) to move green time from the former to the
latter without affecting cycle length.
4. Repeat previous step until no significant couple
can be found
5.2.5 Temporal Offsets and Junction
Coordination
To coordinate junctions with each other, the follow-
ing principles are useful : cycle lengths should be ho-
mogenized, try to ensure that upstream junctions will
not deliver more flow than downstream ones can han-
dle, do not hesitate to limit output flow if necessary to
preserve global fluidity even at the cost of a little local
congestion. Finally, try to create green waves by :
1. Identifying major axes
2. Identifying main direction of traffic for the current
conditions (can be opposite between morning and
evening peak hours)
3. Compute corresponding temporal offsets by ob-
serving actual run times between junctions with
the considered conditions (use simulation or sen-
sor data) as opposed to theoretically calculated
run times.
5.3 Experimental Setup and Results
The experts followed the methodology outlined above
to try to increase traffic fluidity metrics (a combina-
tion of waiting time and total number of processed
vehicles) as given by our simulator. They also used
visual analysis and iterative trial and error to achieve
the best possible result.
5.3.1 First Area
The first optimization session focused on a small trial
zone made of two signalized intersections of medium
complexity. It lasted for two hours and the experts
produced a final gain of 13.68%.
Figure 9 gives, as an illustration of the tedious,
iterative character of the methodology, the last trial
and error steps followed by the experts to get to the
best possible setting they could reach.
Figure 9: Sample of steps followed by experts on the small
test case. The two junctions are named N (North) and S
(South) respectively. Nk means phase number k of junction
N.
In contrast, and as can be seen in figure 10 be-
low, the algorithm managed to reach much better so-
lutions, achieving a final gain of 23.9%. That level
of gain is reached in 37 minutes on a regular laptop
computer without parallel computing and the cross-
ing point with experts in terms of gain amplitude (
˜
13
percent) is reached after 2 minutes only.
Figure 10: Gains obtained by the experts and the algorithm
respectively, on the small test zone.
5.3.2 Second Area
In order to assess whether this result extended to
cases of operational size and complexity, we orga-
nized a second session with a full-fledged zone ex-
tracted from a real world benchmark with 12 signal-
ized intersections in the immediate northern outskirts
of Paris. As can be seen in figure 11, it has one major
north/south axis and two intersecting highways.
Experts tried very hard to manually optimize traf-
fic on this zone under the arbitrage of the simulator.
VEHITS 2019 - 5th International Conference on Vehicle Technology and Intelligent Transport Systems
208
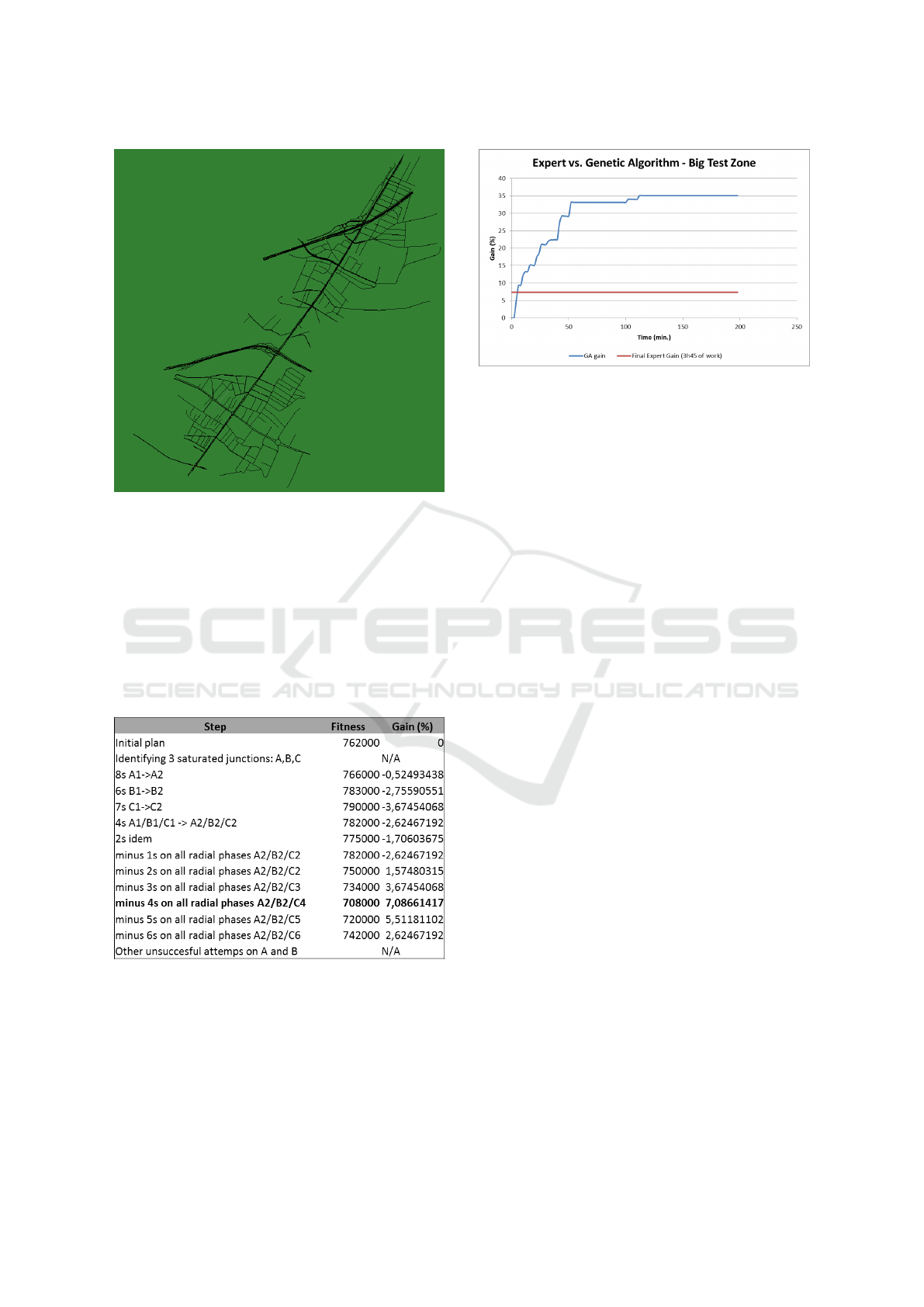
Figure 11: Second testing area: a large portion of a dense
urban area situated along a major traffic north/south axis
with 12 signalized intersections and crossed by two high-
ways.
The experiment lasted for 3 hours and 45 minutes and
while the task proved very hard, the experts managed
to achieve 7.08% gain.
Part of the analysis and of the numerous attempts
they made is traced if figure 12 for illustrative pur-
poses, notably to underline how rigged and counter-
intuitive the search space of this problem can be.
Figure 12: Sample of the steps followed by experts to try to
optimize the large test zone.
Again in striking contrast (see figure 13), the ge-
netic algorithm reached a final gain of 35.06 % in
around 1h42. The crossing point with manual expert
gain was reached in under 6 minutes.
Figure 13: Gains obtained by the experts and the algorithm
respectively, on the large test zone.
6 CONCLUSIONS
We introduced an algorithmic system based on evolu-
tionary algorithms and calibrated microscopic simula-
tion to optimize traffic light green phase durations and
relative temporal offsets in order to reduce traffic jams
and pollutant emissions simultaneously. Our experi-
mental results are threefold. First, we report success
of the calibration module to reach statistically realis-
tic vehicle counts with respect to historical data. Sec-
ondly, we confirm the ability of the introduced sys-
tem to consistently produce significant optimization
gains on real-world benchmarks with respect to expert
provided solutions. Finally, and most importantly, se
report the results of a competitive comparison work-
shop between traffic engineering experts and our algo-
rithm. The results indicate that the evolutionary algo-
rithm performs substantially better in both speed and
final solution quality.
While the results reported here suggest that AI
based optimization modules perform significantly
better than experts at these particular tasks, we firmly
believe that there is much to gain from hybridizing
expert knowledge with stochastic search algorithms.
The former indeed have both precious insights and
heuristics as well as an uncapturable ability to think
globally. The latter, conversely, are uncannily apt at
quickly figuring out the right numerical decisions. We
sincerely think the future belongs to those who will
know how to use both in synergy.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank the LaSDIM project
and BPIFrance for funding part of this work under the
20th FUI call. The authors would also like to thank
Expert Competitive Traffic Light Optimization with Evolutionary Algorithms
209

Nicolas Damay for his remarkable Master’s degree in-
ternship work.
REFERENCES
Chin, Y. K., Kow, W. Y., Khong, W. L., Tan, M. K., and
Teo, K. T. K. (2012). Q-learning traffic signal opti-
mization within multiple intersections traffic network.
In 2012 Sixth UKSim/AMSS European Symposium on
Computer Modeling and Simulation, pages 343–348.
Chu, L., Liu, H. X., Oh, J.-S., and Recker, W. (2003).
A calibration procedure for microscopic traffic sim-
ulation. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE Interna-
tional Conference on Intelligent Transportation Sys-
tems, volume 2, pages 1574–1579 vol.2.
Damay, N. (2015). Multiple-objective optimization of traf-
fic lightsusing a genetic algorithm and a microscopic
traffic simulator. Master’s thesis, KTH, School of
Computer Science and Communication (CSC).
Deb, K., Pratap, A., Agarwal, S., and Meyarivan, T. (2002).
A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm:
Nsga-ii. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Compu-
tation, 6(2):182–197.
Eiben, A. and Smith, J. (2003). Introduction to Evo-
lutionary Computation. Natural Computing Series.
Springer.
Fakult
¨
at, S. R. A. L. U. F. (2006). Learning road traffic
control : Towards practical traffic control using policy
gradients diplomarbeit.
Flotterod, G., Bierlaire, M., and Nagel, K. (2011). Bayesian
demand calibration for dynamic traffic simulations.
Transportation Science, 45(4):541–561.
Fortin, F.-A., De Rainville, F.-M., Gardner, M.-A., Parizeau,
M., and Gagn
´
e, C. (2012). DEAP: Evolutionary algo-
rithms made easy. Journal of Machine Learning Re-
search, 13:2171–2175.
Foy, M. D., F., B. R., and Goldberg, D. E. Signal timing
determination using genetic algorithms.
Garc
´
ıa-Nieto, J., Alba, E., and Olivera, A. C. (2011).
Enhancing the urban road traffic with swarm intel-
ligence: A case study of c
´
ordoba city downtown.
In 2011 11th International Conference on Intelligent
Systems Design and Applications, pages 368–373.
Garc
´
ıa-Nieto, J., Olivera, A. C., and Alba, E. (2013). Opti-
mal cycle program of traffic lights with particle swarm
optimization. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary
Computation, 17(6):823–839.
Goldberg, D. E. (1989). Genetic Algorithms in Search, Op-
timization, and Machine Learning. Addison-Wesley,
New York.
Hu, W., Wang, H., Liping, Y., and Du, B. (2015). A swarm
intelligent method for traffic light scheduling: appli-
cation to real urban traffic networks. Applied Intelli-
gence, 44.
Jin, J. and Ma, X. (2014). Implementation and optimiza-
tion of group-based signal control in traffic simula-
tion. pages 2517–2522.
Jin, J., Ma, X., and Kosonen, I. (2017). A stochastic op-
timization framework for road traffic controls based
on evolutionary algorithms and traffic simulation. Ad-
vances in Engineering Software, 114.
Krajzewicz, D., Erdmann, J., Behrisch, M., and Bieker-
Walz, L. (2012). Recent development and applications
of sumo - simulation of urban mobility. International
Journal On Advances in Systems and Measurements,
3 and 4.
Marceau Caron, G. (2014). Optimization and uncertainty
handling in air traffic management. PhD thesis. Th
`
ese
de doctorat dirig
´
ee par Schoenauer, Marc et Sav
´
eant,
Pierre Informatique Paris 11 2014.
Marsetic, R., Semrov, D., and Zura, M. (2014). Road artery
traffic light optimization with use of the reinforcement
learning. PROMET - Traffic and Transportation, 26.
Paz, A., Molano, V., and Sanchez-Medina, J. (2015). Holis-
tic Calibration of Microscopic Traffic Flow Models:
Methodology and Real World Application Studies,
pages 33–52.
P
´
eres, M., Ruiz, G., Nesmachnow, S., and Olivera, A. C.
(2018). Multiobjective evolutionary optimization of
traffic flow and pollution in montevideo, uruguay. Ap-
plied Soft Computing, 70:472 – 485.
Rouphail, N., Park, B., and Sacks, J. (2000). Direct sig-
nal timing optimization: Strategy development and re-
sults. pages 195 – 206.
Salkham, A., Cunningham, R., Garg, A., and Cahill, V.
(2008). A collaborative reinforcement learning ap-
proach to urban traffic control optimization. In 2008
IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conference on Web In-
telligence and Intelligent Agent Technology, volume 2,
pages 560–566.
Sanchez-Medina, J., J. Gal
´
an Moreno, M., and Rubio, E.
(2008). Evolutionary Computation Applied to Urban
Traffic Optimization.
Semet, Y. and Schoenauer, M. (2006). On the Benefits of
Inoculation, an Example in Train Scheduling. In et al.,
M. C., editor, GECCO-2006, pages 1761–1768, Seat-
tle, United States. ACM Press.
Stevanovic, J., Stevanovic, A., Martin, P. T., and Bauer, T.
(2008). Stochastic optimization of traffic control and
transit priority settings in vissim. Transportation Re-
search Part C: Emerging Technologies, 16(3):332 –
349. Emerging Commercial Technologies.
Toledo, T. and Kolechkina, T. (2013). Estimation of dy-
namic origin–destination matrices using linear assign-
ment matrix approximations. Intelligent Transporta-
tion Systems, IEEE Transactions on, 14:618–626.
Zhang, Q. and Li, H. (2007). Moea/d: A multiob-
jective evolutionary algorithm based on decomposi-
tion. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computa-
tion, 11(6):712–731.
Zitzler, E. and K
¨
unzli, S. (2004). Indicator-based selection
in multiobjective search. In PPSN.
Zitzler, E., Laumanns, M., and Thiele, L. (2001). Spea2:
Improving the strength pareto evolutionary algorithm.
Technical report.
VEHITS 2019 - 5th International Conference on Vehicle Technology and Intelligent Transport Systems
210
